The Vicksburg campaign was a series of maneuvers and battles in the
Western Theater of the American Civil War directed against
Vicksburg, Mississippi
Vicksburg is a historic city in Warren County, Mississippi, United States. It is the county seat, and the population at the 2010 census was 23,856.
Located on a high bluff on the east bank of the Mississippi River across from Louisiana, Vi ...
, a fortress city that dominated the last
Confederate-controlled section of the
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem), second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest Drainage system (geomorphology), drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson B ...
. The
Union Army of the Tennessee
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
under
Major General
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of ...
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union A ...
gained control of the river by capturing this stronghold and defeating
Lieutenant General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on th ...
John C. Pemberton
John Clifford Pemberton (August 10, 1814 – July 13, 1881) was a career United States Army officer who fought in the Seminole Wars and with distinction during the Mexican–American War. He resigned his commission to serve as a Confederate ...
's forces stationed there.
The campaign consisted of many important naval operations, troop maneuvers, failed initiatives, and eleven distinct battles from December 26, 1862, to July 4, 1863. Military historians divide the campaign into two formal phases: operations against Vicksburg (December 1862 – January 1863) and Grant's operations against Vicksburg (March–July 1863).
Grant initially planned a two-pronged approach in which half of his army, under Maj. Gen.
William Tecumseh Sherman
William Tecumseh Sherman ( ; February 8, 1820February 14, 1891) was an American soldier, businessman, educator, and author. He served as a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War (1861–1865), achieving recognition for his com ...
, would advance to the
Yazoo River
The Yazoo River is a river in the U.S. states of Louisiana and Mississippi. It is considered by some to mark the southern boundary of what is called the Mississippi Delta, a broad floodplain that was cultivated for cotton plantations before th ...
and attempt to reach Vicksburg from the northeast, while Grant took the remainder of the army down the Mississippi Central Railroad. Both of these initiatives failed. Grant conducted a number of "experiments" or expeditions—Grant's bayou operations—that attempted to enable waterborne access to the Mississippi south of Vicksburg's artillery batteries. All five of these initiatives failed as well. Finally, Union gunboats and troop transport boats ran the batteries at Vicksburg and met up with Grant's men who had marched overland in
Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bord ...
. On April 29 and April 30, 1863, Grant's army crossed the Mississippi and landed at
Bruinsburg, Mississippi. An elaborate series of demonstrations and diversions fooled the Confederates and the landings occurred without opposition. Over the next 17 days, Grant maneuvered his army inland and won five battles, captured the state capital of
Jackson, Mississippi
Jackson, officially the City of Jackson, is the capital of and the most populous city in the U.S. state of Mississippi. The city is also one of two county seats of Hinds County, along with Raymond. The city had a population of 153,701 at t ...
, and assaulted and laid siege to Vicksburg.
After Pemberton's army surrendered on July 4 (one day after the Confederate defeat at
Gettysburg), and when
Port Hudson surrendered to Maj. Gen.
Nathaniel P. Banks
Nathaniel Prentice (or Prentiss) Banks (January 30, 1816 – September 1, 1894) was an American politician from Massachusetts and a Union general during the Civil War. A millworker by background, Banks was prominent in local debating societies, ...
on July 9, Texas and Arkansas were effectively cut off from the Confederacy, and the Mississippi River was once again open for northern commerce to reach the Gulf of Mexico, and as a supply line for the Union Army. Grant's Vicksburg campaign is studied as a masterpiece of military operations and a major
turning point of the war.
Background
Military situation
Vicksburg was strategically vital to the Confederates.
Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the United States Senate and the House of Representatives as ...
said, "Vicksburg is the nail head that holds the South's two halves together." While in their hands, it blocked Union navigation down the Mississippi; together with control of the mouth of the
Red River and of
Port Hudson to the south, it allowed communication with the states west of the river, upon which the Confederates depended extensively for horses, cattle and reinforcements. The natural defenses of the city were ideal, earning it the nickname "The Gibraltar of the Confederacy". It was located on a high bluff overlooking a horseshoe-shaped bend in the river, De Soto Peninsula, making it almost impossible to approach by ship. North and east of Vicksburg was the
Mississippi Delta
The Mississippi Delta, also known as the Yazoo–Mississippi Delta, or simply the Delta, is the distinctive northwest section of the U.S. state of Mississippi (and portions of Arkansas and Louisiana) that lies between the Mississippi and Yaz ...
(sometimes known as the Yazoo Delta), an area 200 miles (320 km) north to south and up to 50 miles (80 km) across, which has been described by geographer Warren E. Grabau as an "astonishingly complex network of intersecting waterways", some of which were navigable by small steamboats. The regions between modern rivers and bayous formed closed basins called backswamps, of which Grabau judged, "Whether permanently flooded or not, the backswamps were, for all practical purposes, untamed wildernesses, utterly impassable by a man on horseback or by any form of wheeled vehicle, and very difficult even for a man on foot." About twelve miles (19 km) up the
Yazoo River
The Yazoo River is a river in the U.S. states of Louisiana and Mississippi. It is considered by some to mark the southern boundary of what is called the Mississippi Delta, a broad floodplain that was cultivated for cotton plantations before th ...
were Confederate batteries and entrenchments at Haynes Bluff. The
Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bord ...
land west of Vicksburg was also difficult, with many streams and poor country roads, widespread winter flooding, and it was on the opposite side of the river from the fortress.
The city had been under Union naval attack before. Admiral
David Farragut
David Glasgow Farragut (; also spelled Glascoe; July 5, 1801 – August 14, 1870) was a flag officer of the United States Navy during the American Civil War. He was the first rear admiral, vice admiral, and admiral in the United States Navy. F ...
moved up the river after his
capture of New Orleans
The capture of New Orleans (April 25 – May 1, 1862) during the American Civil War was a turning point in the war, which precipitated the capture of the Mississippi River. Having fought past Forts Jackson and St. Philip, the Union was ...
and on May 18, 1862, demanded the surrender of Vicksburg. Farragut had insufficient troops to force the issue, and he moved back to New Orleans. He returned with a flotilla in June 1862, but their attempts (June 26–28) to bombard the fortress into surrender failed. They shelled Vicksburg throughout July and fought some minor battles with a few Confederate vessels in the area, but their forces were insufficient to attempt a landing, and they abandoned attempts to force the surrender of the city. Farragut investigated the possibility of bypassing the fortified cliffs by digging a canal across the neck of the river's bend, the De Soto Peninsula. On June 28,
Brig. Gen. Thomas Williams, attached to Farragut's command, began digging work on the canal by employing local laborers and some soldiers. Many of the men fell victim to tropical diseases and heat exhaustion, and the work was abandoned by July 24. (Williams was killed two weeks later in the
Battle of Baton Rouge).
In the fall of 1862, Maj. Gen.
Henry W. Halleck was promoted from command of the Western Theater to General-in-Chief of all Union armies. On November 23, he indicated to Grant his preference for a major move down the Mississippi to Vicksburg; in Halleck's style, he left considerable initiative to design a campaign, an opportunity that the pugnacious Grant seized. Halleck has received criticism for not moving promptly overland from
Memphis, Tennessee
Memphis is a city in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the seat of Shelby County in the southwest part of the state; it is situated along the Mississippi River. With a population of 633,104 at the 2020 U.S. census, Memphis is the second-mo ...
, to seize Vicksburg during the summer when he was in command on the scene. He believed that the Navy could capture the fortress on its own, not knowing that the naval force was insufficiently manned with ground troops to finish the job. What might have achieved success in the summer of 1862 was no longer possible by November because the Confederates had amply reinforced the garrison by that time. Also, reliable navigation on the river was seasonal, and the natural fall in the level of the river during the fall and winter months limited the utility of shipping, the usable draft of riverboats, and the quantity of men, supplies, and equipment, they could transport.
Grant's army marched south down the
Mississippi Central Railroad, making a forward base at
Holly Springs. He planned a two-pronged assault in the direction of Vicksburg. His principal subordinate, Maj. Gen.
William Tecumseh Sherman
William Tecumseh Sherman ( ; February 8, 1820February 14, 1891) was an American soldier, businessman, educator, and author. He served as a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War (1861–1865), achieving recognition for his com ...
, was to advance down the river with four divisions (about 32,000 men) and Grant would continue with the remaining forces (about 40,000) down the railroad line to
Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
, where he would wait for developments, hoping to lure the Confederate army out of the city to attack him in the vicinity of
Grenada, Mississippi
Grenada is a city in Grenada County, Mississippi, United States. The population was 13,092 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Grenada County.
History
Grenada was formed in 1836, after federal removal of the Choctaw people who ha ...
.
On the Confederate side, forces in Mississippi were under the command of Lt. Gen.
John C. Pemberton
John Clifford Pemberton (August 10, 1814 – July 13, 1881) was a career United States Army officer who fought in the Seminole Wars and with distinction during the Mexican–American War. He resigned his commission to serve as a Confederate ...
, an officer from
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
who chose to fight for the
South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
. Pemberton had approximately 12,000 men in Vicksburg and
Jackson, Mississippi
Jackson, officially the City of Jackson, is the capital of and the most populous city in the U.S. state of Mississippi. The city is also one of two county seats of Hinds County, along with Raymond. The city had a population of 153,701 at t ...
, and Maj. Gen.
Earl Van Dorn
Earl Van Dorn (September 17, 1820May 7, 1863) started his military career as a United States Army officer but joined Confederate forces in 1861 after the Civil War broke out. He was a major general when he was killed in a private conflict.
A g ...
had approximately 24,000 at Grenada.
Meanwhile, political forces were at work.
President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation throu ...
had long recognized the importance of Vicksburg; he wrote "Vicksburg is the key. ...The war can never be brought to a close until that key is in our pocket." Lincoln also envisioned a two-pronged offensive, but one up and down the river. Maj. Gen.
John A. McClernand
John Alexander McClernand (May 30, 1812 – September 20, 1900) was an American lawyer and politician, and a Union Army general in the American Civil War. He was a prominent Democratic politician in Illinois and a member of the United States H ...
, a
War Democrat politician, had convinced Lincoln that he could lead an army down the river and take Vicksburg. Lincoln approved his proposal and wanted Maj. Gen.
Nathaniel P. Banks
Nathaniel Prentice (or Prentiss) Banks (January 30, 1816 – September 1, 1894) was an American politician from Massachusetts and a Union general during the Civil War. A millworker by background, Banks was prominent in local debating societies, ...
to advance up river from New Orleans at the same time. McClernand began organizing regiments, sending them to Memphis. Back in
Washington, D.C., Halleck was nervous about McClernand and gave Grant control of all troops in his own department. McClernand's troops were split into two corps, one under McClernand, the other under Sherman. McClernand complained but to no avail. Grant appropriated his troops, one of several maneuvers in a private dispute within the Union Army between Grant and McClernand that continued throughout the campaign.
Battles in the operations against Vicksburg, December 1862 – January 1863
The "operations against Vicksburg" phase of the Vicksburg campaign comprises the following battles:
Chickasaw Bayou (December 26–29, 1862)
Sherman disembarked with three divisions at Johnson's Plantation on the Yazoo River to approach the Vicksburg defenses from the northeast. On December 27, the Federals pushed their lines forward through the swamps toward the Walnut Hills, which were strongly defended. On December 28, several futile attempts were made to get around these defenses. On December 29, Sherman ordered a frontal assault, which was repulsed with heavy casualties, and then withdrew.
During this period, the overland half of Grant's offensive was failing. His lines of communication were disrupted by raids by Van Dorn and
Brig. Gen. Nathan Bedford Forrest
Nathan Bedford Forrest (July 13, 1821October 29, 1877) was a prominent Confederate Army general during the American Civil War and the first Grand Wizard of the Ku Klux Klan from 1867 to 1869. Before the war, Forrest amassed substantial wealt ...
, who destroyed his large supply depot at Holly Springs. Unable to subsist his army without these supplies, Grant abandoned his overland advance.
In early January, McClernand arrived at Memphis with the corps he had recruited (the
XIII Corps under Brig. Gen.
George W. Morgan
George Washington Morgan (September 20, 1820 – July 26, 1893) was an American soldier, lawyer, politician, and diplomat. He fought in the Texas Revolution and the Mexican–American War, and was a general in the Union Army during the Americ ...
) and commenced his operation down the Mississippi. On January 4, he ordered Sherman to attach his
XV Corps 15th Corps, Fifteenth Corps, or XV Corps may refer to:
* XV Corps (British India)
*XV Corps (German Empire), a unit of the Imperial German Army prior to and during World War I
*15th Army Corps (Russian Empire), a unit in World War I
* XV Royal Bav ...
to the expedition, calling his combined 32,000-man force the
Army of the Mississippi. This was a direct provocation against Grant, but Sherman acceded to the senior officer. Sherman suggested beginning with a combined land and naval movement against Fort Hindman, on the
Arkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in the western United ...
at
Arkansas Post
The Arkansas Post (french: Poste de Arkansea) ( Spanish: ''Puesto de Arkansas''), formally the Arkansas Post National Memorial, was the first European settlement in the Mississippi Alluvial Plain and present-day U.S. state of Arkansas. In ...
, 50 miles up the Arkansas from its confluence with the Mississippi, a base from which Confederate gunboats were attacking Union shipping on the river. The expedition started without notifying Grant.
Arkansas Post (January 9–11, 1863)
Union boats under
Rear Adm. David Dixon Porter
David Dixon Porter (June 8, 1813 – February 13, 1891) was a United States Navy admiral and a member of one of the most distinguished families in the history of the U.S. Navy. Promoted as the second U.S. Navy officer ever to attain the rank of ...
began landing troops near Arkansas Post in the evening of January 9. The troops started up river towards Fort Hindman. Sherman's corps overran Confederate trenches, and the defenders retreated to the protection of the fort and adjacent rifle-pits. Porter, on January 10, moved his fleet towards Fort Hindman and bombarded it, withdrawing at dusk. Union artillery fired on the fort from positions across the river on January 11, and the infantry moved into position for an attack. Union ironclads commenced shelling the fort and Porter's fleet passed it to cut off any retreat. As a result of this envelopment, and the attack by Morgan's troops, the Confederate command surrendered in the afternoon. Although Union losses were high and the victory did not contribute to the capture of Vicksburg, it did eliminate one more impediment to Union shipping on the Mississippi.
Grant was not happy to learn that McClernand had conducted the operation without his approval, considering it a distraction from his main objective of Vicksburg, but since it had been successful and his ally Sherman had suggested it, he took no punitive action. However, he ordered McClernand back to the Mississippi and assumed personal command of the campaign on January 13 at Milliken's Bend, 15 miles northwest of Vicksburg.
Grant's bayou operations, January–March 1863
That winter, Grant conducted a series of initiatives to approach and capture Vicksburg, termed "Grant's bayou operations". Their general theme was to use or construct alternative waterways so that troops could be positioned within striking distance of Vicksburg, without requiring a direct approach on the Mississippi under the Confederate guns.
Grant's Canal
The Williams Canal across De Soto Peninsula had been abandoned by Adm. Farragut and Brig. Gen. Williams in July 1862, but it had the potential to offer a route downriver that bypassed Vicksburg's guns. In late January 1863, Sherman's men, at the urging of Grant—who was advised by the navy that President Lincoln liked the idea—resumed digging. Sherman derisively called the work "Butler's Ditch" (since it was Maj. Gen.
Benjamin Butler who had sent Williams upriver to do the work), which was barely 6 feet wide by 6 feet deep. Grant, undoubtedly influenced by Lincoln's continuous inquiries as to the status of the canal, ordered Sherman to expand the canal to 60 feet wide and 7 feet deep and the effort became known as Grant's Canal. It was not properly engineered based upon the hydrology of the Mississippi River, however, and a sudden rise in the river broke through the dam at the head of the canal and flooded the area. The canal began to fill up with back water and sediment. In a desperate effort to rescue the project, two huge steam-driven dipper dredges, ''Hercules'' and ''Sampson'', attempted to clear the channel, but the dredges were exposed to Confederate artillery fire from the bluffs at Vicksburg and driven away. By late March, work on the canal was abandoned. (Remnants of about 200 yards of Grant's Canal are maintained by the Vicksburg National Military Park in Louisiana).
Lake Providence expedition
Grant ordered Brig. Gen.
James B. McPherson to construct a canal of several hundred yards from the Mississippi to
Lake Providence
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
, northwest of the city. This would allow passage to the Red River, through Bayous Baxter and Macon, and the Tensas and Black Rivers. Reaching the Red River, Grant's force could join with Banks at Port Hudson. McPherson reported that the connection was navigable on March 18, but the few "ordinary Ohio River boats" that had been sent to Grant for navigation of the bayous could only transport 8,500 men. The boats through Lake Providence increased the Union soldiers to a force of 30,000 and provided the field commander the flexibility of a 4:1 advantage, potentially more than enough to ensure a successful siege of Port Hudson. Although this was the only one of the bayou expeditions to successfully bypass the Vicksburg defenses, historian
Ed Bearss diminishes this exploit as the "Lake Providence Boondoggle".
Yazoo Pass expedition
The next attempt was to get to the high ground of the
loess
Loess (, ; from german: Löss ) is a clastic, predominantly silt-sized sediment that is formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. Ten percent of Earth's land area is covered by loess or similar deposits.
Loess is a periglacial or aeoli ...
bluffs above Hayne's Bluff and below Yazoo City by blowing up the Mississippi River levee near
Moon Lake, some 150 miles (240 km) above Vicksburg, near
Helena, Arkansas
Helena is the eastern portion of Helena–West Helena, Arkansas, a city in Phillips County, Arkansas. It was founded in 1833 by Nicholas Rightor and is named after the daughter of Sylvanus Phillips, an early settler of Phillips County and the n ...
, and following the Yazoo Pass (an old route from Yazoo City to Memphis, which was curtailed by the 1856 levee construction that sealed off the Pass from the Mississippi River to Moon Lake) into the Coldwater River, then to the
Tallahatchie River, and finally into the Yazoo River at
Greenwood, Mississippi
Greenwood is a city in and the county seat of Leflore County, Mississippi, United States, located at the eastern edge of the Mississippi Delta region, approximately 96 miles north of the state capital, Jackson, and 130 miles south of the riverp ...
. The dikes were blown up on February 3, beginning what was called the Yazoo Pass Expedition. Ten Union boats, under the command of Lt. Cmdr. Watson Smith, with army troops under the command of Brig. Gen.
Benjamin Prentiss
Benjamin Mayberry Prentiss (November 23, 1819 – February 8, 1901) was an American soldier and politician. He fought in the Mexican–American War and on the Union side of the American Civil War, rising to the rank of major general. He commande ...
, began moving through the pass on February 7. But low-hanging trees destroyed anything on the gunboats above deck and Confederates felled more trees to block the way. These delays allowed the Confederates time to quickly construct a "Fort Pemberton" near the confluence of the Tallahatchie and
Yalobusha River
The Yalobusha River is a river, long, in north-central Mississippi in the United States. It is a principal tributary of the Yazoo River, via which it is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River.
The name "Yalobusha" comes from the Choctaw ...
s near
Greenwood, Mississippi
Greenwood is a city in and the county seat of Leflore County, Mississippi, United States, located at the eastern edge of the Mississippi Delta region, approximately 96 miles north of the state capital, Jackson, and 130 miles south of the riverp ...
, which repulsed the naval force on March 11, March 14, and March 16. The Union effort collapsed in early April.
Steele's Bayou expedition
Admiral Porter started an effort on March 14 to go up the Yazoo Delta via Steele's Bayou, just north of Vicksburg, to
Deer Creek. This would
outflank Fort Pemberton and allow landing troops between Vicksburg and
Yazoo City
Yazoo City is a U.S. city in Yazoo County, Mississippi. It was named after the Yazoo River, which, in turn was named by the French explorer Robert La Salle in 1682 as "Rivière des Yazous" in reference to the Yazoo tribe living near the river's ...
. Confederates once again felled trees in their path, and willow reeds fouled the boats' paddlewheels. This time the Union boats became immobilized, and Confederate cavalry and infantry threatened to capture them. Sherman sent infantry assistance to repel the Confederates bedeviling Porter, but Porter's approach was abandoned as too difficult.
Duckport Canal
Grant's final attempt was to dig another canal from Duckport Landing to Walnut Bayou, aimed at getting lighter boats past Vicksburg. By the time the canal was almost finished, on April 6, water levels were declining, and none but the lightest of flatboats could get through. Grant abandoned this canal and started planning anew.
From December through March, including Chickasaw Bayou and the Mississippi Central advance, seven initiatives, or "experiments", by Grant had failed. Grant claimed in his memoirs that he had undertaken these experiments primarily to keep his troops busy during the flooded and disease-laden winter months and that he had had no expectation of success. This claim is contradicted by correspondence from Grant at the time.
Plan for the 1863 campaign and initial movements
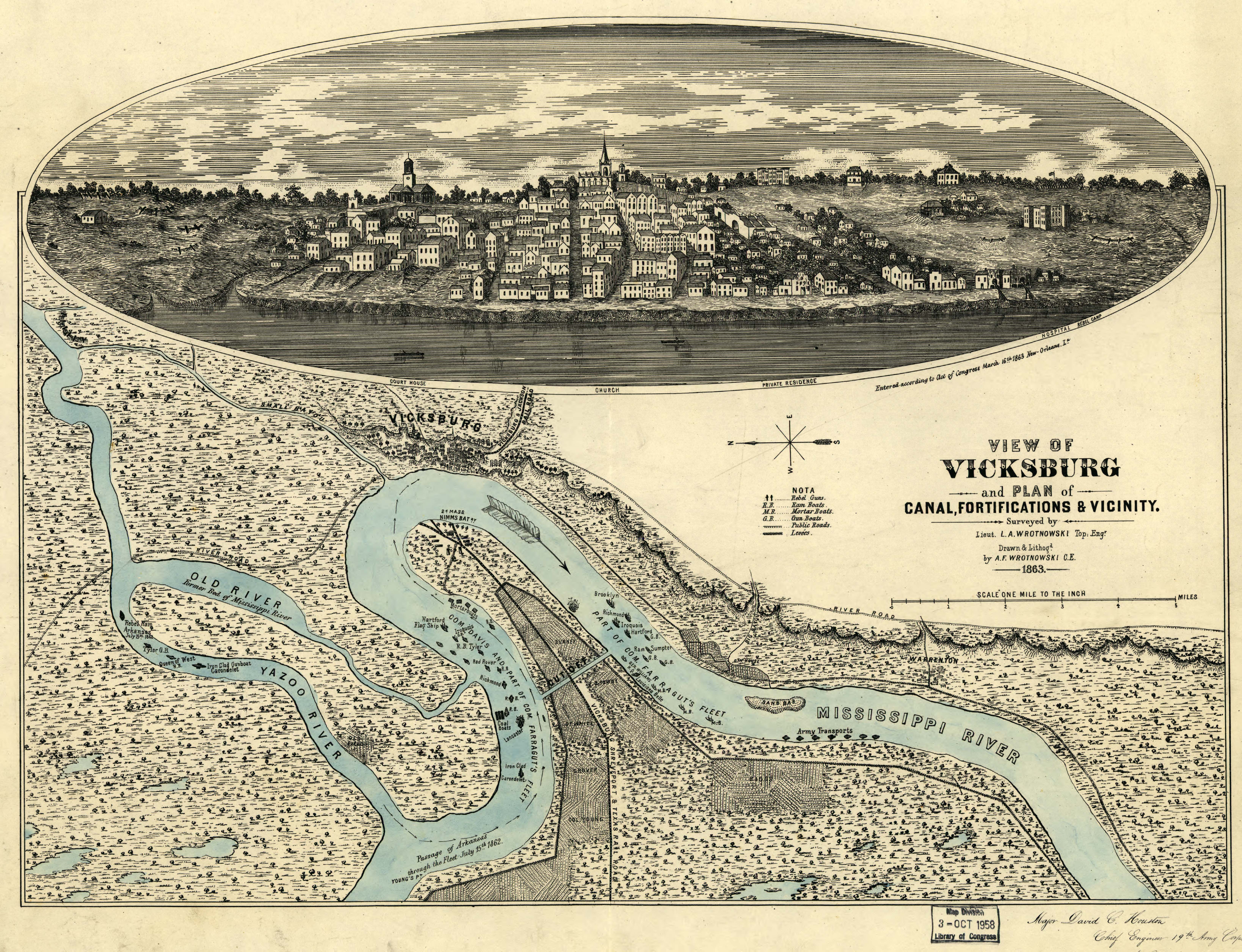
All of the bayou operations were failures, but Grant was known for his stubborn determination and would not quit. His final option was bold but risky: March the army down the west side of the Mississippi, cross the river south of Vicksburg, and either attack Vicksburg from the south and the east or join forces with Banks, capture Port Hudson, and then together reduce Vicksburg. Porter would have to sneak past the guns to get sufficient gunboats and transport ships south of the city. Once they had completed the downstream passage, they would not be able to return past Vicksburg's guns because the river current would slow them too much.
On March 29, McClernand set his troops to work building bridges and
corduroy road
A corduroy road or log road is a type of road or timber trackway made by placing logs, perpendicular to the direction of the road over a low or swampy area. The result is an improvement over impassable mud or dirt roads, yet rough in the bes ...
s. They filled in the swamps in their way as well, and by April 17 they had a rough, tortuous 70-mile (110 km) road from Milliken's Bend to the proposed river crossing at
Hard Times, Louisiana, below Vicksburg.

On April 16, a clear night with no moon, Porter sent seven gunboats and three empty troop transports loaded with stores to run the bluff, taking care to minimize noise and lights. But the preparations were ineffective. Confederate sentries sighted the boats, and the bluff exploded with massive artillery fire. Fires were set along the banks to improve visibility. The Union gunboats answered back. Porter observed that the Confederates mainly hit the high parts of his boats, reasoned that they could not depress their guns, and had them hug the east shore, right under Confederate cannon, so close he could hear their commanders giving orders, shells flying overhead. The fleet survived with little damage; thirteen men were wounded and none killed. The ''Henry Clay'' was disabled and burned at the water's edge. On April 22, six more boats loaded with supplies made the run; one boat did not make it, though no one was killed. The crew floated downstream on the boat's remnants.
The final piece of Grant's strategy was to divert Pemberton's attention from the river crossing site that the Union troops would use. Grant chose two operations: a feint by Sherman against
Snyder's Bluff, Mississippi, north of Vicksburg (see the
Battle of Snyder's Bluff below), and a daring cavalry raid through central Mississippi by
Col. Benjamin Grierson
Benjamin Henry Grierson (July 8, 1826 – August 31, 1911) was a music teacher, then a career officer in the United States Army. He was a cavalry general in the volunteer Union Army during the Civil War and later led troops in the American O ...
, known as
Grierson's Raid
Grierson's Raid was a Union cavalry raid during the Vicksburg Campaign of the American Civil War. It ran from April 17 to May 2, 1863, as a diversion from Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant's main attack plan on Vicksburg, Mississippi.
Background
Ea ...
. Both were eminently successful. Of Sherman's feint, Grant writes:
"My object was to compel Pemberton to keep as much force about Vicksburg as I could, until I could secure a good footing on high land east of the river. The move was eminently successful and, as we afterwards learned, created great confusion about Vicksburg and doubts about our real design."
Grierson was able to draw out significant Confederate forces to chase him, and Pemberton's defenses were dispersed too far around the state. (Pemberton was also wary of Nathaniel Banks's impending advance up the river from
Baton Rouge
Baton Rouge ( ; ) is a city in and the capital of the U.S. state of Louisiana. Located the eastern bank of the Mississippi River, it is the parish seat of East Baton Rouge Parish, Louisiana's most populous parish—the equivalent of counti ...
to threaten Port Hudson.). Of Grierson's raid, Grant writes:
"It was at Port Gibson I first heard through a Southern paper of the complete success of Colonel Grierson, who was making a raid through central Mississippi...This raid was of great importance, for Grierson had attracted the attention of the enemy from the main movement against Vicksburg."
Opposing forces
Union
Maj. Gen.
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union A ...
's Union
Army of the Tennessee
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
started the campaign with about 44,000 men, which grew by July to 75,000. The army was composed of five corps: the
XIII Corps, under Maj. Gen.
John A. McClernand
John Alexander McClernand (May 30, 1812 – September 20, 1900) was an American lawyer and politician, and a Union Army general in the American Civil War. He was a prominent Democratic politician in Illinois and a member of the United States H ...
; the
XV Corps 15th Corps, Fifteenth Corps, or XV Corps may refer to:
* XV Corps (British India)
*XV Corps (German Empire), a unit of the Imperial German Army prior to and during World War I
*15th Army Corps (Russian Empire), a unit in World War I
* XV Royal Bav ...
, under Maj. Gen.
William T. Sherman; the
XVII Corps, under Maj. Gen.
James B. McPherson; a three-division detachment of the
XVI Corps, under Maj. Gen.
Cadwallader C. Washburn; and a detachment from the District of Northeast Louisiana, under Brig. Gen.
Elias S. Dennis. The
IX Corps 9 Corps, 9th Corps, Ninth Corps, or IX Corps may refer to:
France
* 9th Army Corps (France)
* IX Corps (Grande Armée), a unit of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
Germany
* IX Corps (German Empire), a unit of the Imperial German ...
, commanded by Maj. Gen.
John G. Parke
John Grubb Parke (September 22, 1827 – December 16, 1900) was a United States Army engineer and a Union general in the American Civil War. Parke's Civil War service was closely associated with Ambrose E. Burnside, often serving him as chi ...
, joined the army in mid-June.
Confederate
Lt. Gen.
John C. Pemberton
John Clifford Pemberton (August 10, 1814 – July 13, 1881) was a career United States Army officer who fought in the Seminole Wars and with distinction during the Mexican–American War. He resigned his commission to serve as a Confederate ...
's Confederate
Army of Mississippi, approximately 30,000 men, consisted of five divisions, under Maj. Gens.
William W. Loring
William Wing Loring (December 4, 1818 – December 30, 1886) was an American soldier who served in the armies of the United States, the Confederacy, and Egypt.
Biography
Early life
William was born in Wilmington, North Carolina, to Reuben a ...
,
Carter L. Stevenson
Carter Littlepage Stevenson, Jr. (September 21, 1817 – August 15, 1888) was a career military officer, serving in the United States Army in several antebellum wars and then in the Confederate States Army as a general in the Western Theater ...
,
John H. Forney,
Martin L. Smith, and
John S. Bowen
John Stevens Bowen (October 30, 1830 – July 13, 1863) was a career United States Army officer who later became a general in the Confederate Army and a commander in the Western Theater of the American Civil War. He fought at the battles ...
.
General
Joseph E. Johnston's forces in
Raymond and
Jackson, Mississippi
Jackson, officially the City of Jackson, is the capital of and the most populous city in the U.S. state of Mississippi. The city is also one of two county seats of Hinds County, along with Raymond. The city had a population of 153,701 at t ...
, about 6,000 men, were elements of his Department of the West, including the brigades of Brig. Gen.
John Gregg, and Col.
Peyton H. Colquitt. Loring's division had joined Johnston on May 17 after the retreat from Champion Hill and Johnston was further reinforced by Brig. Gen.
William H.T. Walker's division, and the cavalry division of Brig. Gen.
William Hicks Jackson in late May, followed by the divisions of Maj. Gens.
John C. Breckinridge and
Samuel G. French in June, bringing his total strength to about 36,000 when Vicksburg surrendered.
[
]
Battles in Grant's operations against Vicksburg, April – July 1863
The "Grant's operations against Vicksburg" phase of the Vicksburg campaign comprises the following battles:
Grand Gulf (April 29, 1863)
Admiral Porter led seven ironclads in an attack on the fortifications and batteries at Grand Gulf, Mississippi
Grand Gulf is a ghost town in Claiborne County, Mississippi, United States.
History
Grand Gulf was named for the large whirlpool, (or gulf), formed by the Mississippi River flowing against a large rocky bluff. La Salle and Zadok Cramer commented ...
, with the intention of silencing the Confederate guns and then securing the area with troops of McClernand's XIII Corps who were on the accompanying transports and barges. The attack by the seven ironclads began at 8 a.m. and continued until about 1:30 p.m. During the fight, the ironclads moved within 100 yards of the Confederate guns and silenced the lower batteries of Fort Wade. The Confederate upper batteries at Fort Cobun remained out of reach and continued to fire. Due to the strong Confederate resistance, Grant and Porter decided it was not feasible to make an amphibious landing
Amphibious warfare is a type of offensive military operation that today uses naval ships to project ground and air power onto a hostile or potentially hostile shore at a designated landing beach. Through history the operations were conducte ...
at Grand Gulf, but later landed at Bruinsburg, Mississippi, instead. The Union ironclads (one of which, the ''Tuscumbia'', had been put out of action) and the transports drew off. After dark, however, the ironclads engaged the Confederate guns again while the steamboats and barges ran the gauntlet. Grant marched his men overland across Coffee Point to below the Gulf. After the transports had passed Grand Gulf, they embarked the troops at Disharoon's plantation and disembarked them on the Mississippi shore at Bruinsburg, below Grand Gulf. Grant landed 17,000 soldiers there, the largest amphibious operation in American military history until the Invasion of Normandy
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 (D-Day) with the Norm ...
. The men immediately began marching overland towards Port Gibson, Mississippi, where, on May 1, they fought the Battle of Port Gibson
The Battle of Port Gibson was fought near Port Gibson, Mississippi, on May 1, 1863, between Union and Confederate forces during the Vicksburg Campaign of the American Civil War. The Union Army was led by Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant, and was v ...
with Bowen's Confederates. Bowen's right flank was driven in, and Bowen's men conducted a fighting withdrawal from the field. On May 3, the Confederates abandoned the fortifications at Grand Gulf. The Confederates had won a hollow victory, since the loss at Grand Gulf caused just a slight change in Grant's offensive.
Snyder's Bluff (April 29 – May 1)
To ensure that troops would not be withdrawn to Grand Gulf to assist Confederates there, a combined Union army-navy force feigned an attack on Snyder's Bluff. After noon on April 29, Lt. Cdr. K. Randolph Breese, with his eight gunboats and ten transports carrying Maj. Gen. Francis P. Blair
Francis Preston Blair Sr. (April 12, 1791 – October 18, 1876) was an American journalist, newspaper editor, and influential figure in national politics advising several U.S. presidents across party lines.
Blair was an early member of the De ...
's division, inched up the Yazoo River to the mouth of Chickasaw Bayou where they spent the night. At 9 a.m., the next morning, the force, minus one gunboat, continued upriver to Drumgould's Bluff and engaged the enemy batteries. During the fighting, ''Choctaw'' suffered more than fifty hits, but no casualties occurred. Around 6 p.m., the troops disembarked and marched along Blake's Levee toward the guns. As they neared Drumgould's Bluff, a battery opened on them, creating havoc and casualties. The Union advance halted and, after dark, the men reembarked on the transports. The next morning, transports disembarked other troops. The swampy terrain and enemy heavy artillery fire forced them to retire. The gunboats opened fire again, about 3 p.m. on May 1, causing some damage. Later, the boats' fire slackened and stopped altogether after dark. Sherman had received orders to land his troops at Milliken's Bend, so the gunboats returned to their anchorages at the mouth of the Yazoo.
Port Gibson (May 1)
Grant's army began marching inland from Bruinsburg. Advancing on the Rodney Road towards Port Gibson, they ran into Confederate outposts after midnight and skirmished with them for around three hours. After 3 a.m., the fighting stopped. Union forces advanced on the Rodney Road and a plantation road at dawn. At 5:30 a.m., the Confederates engaged the Union advance and the battle ensued. Federals forced the Confederates to fall back. The Confederates established new defensive positions at different times during the day but they could not stop the Union onslaught and left the field in the early evening. This defeat demonstrated that the Confederates were unable to defend the Mississippi River line, and the Federals had secured their beachhead.
At this point, Grant faced a decision. His original orders were to capture Grand Gulf and then proceed south to link up with Banks and reduce Port Hudson, after which their combined armies would return and capture Vicksburg. Unfortunately for Grant, such a course would put him under the command of the more senior major general and the credit for any success in the theater would go to Banks. Since Banks was occupied with operations on the Red River and had informed Grant that he was not ready to begin operations against Port Hudson within the next few days, Grant decided to move on his own against Vicksburg. He sent a message to Halleck about his intentions, knowing that it would take as many as eight days for Washington to receive the message and respond.
After the Union army seized the crossing at Grindstone Ford, any Confederate forces between the Big Bayou Pierre and the Big Black River were compromised. Realizing this, Bowen evacuated Grand Gulf and proceeded with all speed to Hankinson's Ford across the Big Black, barely escaping the Union trap. Grant's intention at this time was to move north over this same route and advance directly on Vicksburg. However, scouting parties that he sent out found that Pemberton had good defensive positions to the south of the city. Instead, he decided to break the city's supply line by seizing the railroad from Jackson to Vicksburg. He gave orders for his three corps (Sherman having arrived across the river) to advance over three separate routes to attack the railroad at Edwards Station (the westernmost objective, with McClernand's corps), Clinton (easternmost, with McPherson's) and Midway Station (center, with Sherman's).
Raymond (May 12)
On May 10, Pemberton ordered all reinforcements arriving at Jackson to march to Raymond, 20 miles (32 km) to the southwest. Brig. Gen. John Gregg's overstrength brigade, having endured a grueling march from Port Hudson, Louisiana, began marching to Raymond the next morning, arriving late in the afternoon of May 11. On May 12, Gregg's brigade moved to ambush a Union raiding party at Fourteen Mile Creek. The raiding party turned out to be Maj. Gen. John A. Logan's Division of the XVII Corps. Gregg decided to dispute the crossing of Fourteen Mile Creek and arrayed his men and artillery accordingly. As Logan's men approached, the Confederates opened fire, initially causing heavy casualties. Some Union troops broke, but Logan rallied a force to hold the line. Confederate troops attacked the line but were forced to retire. Additional Union troops arrived and counterattacked. Heavy fighting ensued that continued for six hours, but the overwhelming Union force prevailed. Gregg's men left the field. Although they lost the battle, they had held up a much superior Union force for a day. General Gregg, under orders to withdraw to Jackson in the face of a superior force, withdrew five miles (8 km) in the direction of Jackson to Mississippi Springs, Mississippi. This retrograde movement exposed the Southern Railroad of Mississippi to Union forces, thus severing the lifeline of Vicksburg.
Despite McPherson's victory, the presence of Confederate forces attacking Grant's right flank caused him to reconsider his plan. He learned that Gen. Joseph E. Johnston was due in Jackson with reinforcements within the next couple of days, and there was a rumor that Gen. P.G.T. Beauregard would also arrive on the scene. In this situation, the Union army would be between enemy forces on each flank. Therefore, he chose to deal with the threat from the east first and ordered Sherman and McPherson to seize Jackson.
Jackson (May 14)
On May 9, Gen. Johnston received a dispatch from the Confederate Secretary of War directing him to "proceed at once to Mississippi and take chief command of the forces in the field". When he arrived in Jackson on May 13 from Middle Tennessee
Middle Tennessee is one of the three Grand Divisions of the U.S. state of Tennessee that composes roughly the central portion of the state. It is delineated according to state law as 41 of the state's 95 counties. Middle Tennessee contains the ...
, he learned that two army corps—Sherman's and McPherson's—were advancing on Jackson and that Gregg had only about 6,000 troops available to defend the city. Johnston ordered the evacuation of Jackson, but Gregg was to defend Jackson until the evacuation was completed. By 10 a.m., both Union army corps were near Jackson and had engaged the enemy. Rain, Confederate resistance, and poor defenses prevented heavy fighting until around 11 a.m., when Union forces attacked in numbers and slowly but surely pushed the enemy back. In mid-afternoon, Johnston informed Gregg that the evacuation was complete and that he should disengage and follow. Soon after, the Union troops entered Jackson and had a celebration hosted by Grant, who had been traveling with Sherman's corps, in the Bowman House. They then burned part of the town, destroyed numerous factories, and cut the railroad connections with Vicksburg. Johnston's evacuation is seen as a mistake because he could, by late on May 14, have had 11,000 troops at his disposal and by the morning of May 15, another 4,000. The fall of the Mississippi state capital was a blow to Confederate morale. Having broken the rail links, Grant temporarily abandoned the city to allow his troops to concentrate on Vicksburg.
Johnston retreated with most of his army up the Canton Road, but he ordered Pemberton to leave Edwards Station and attack the Federals at Clinton. Pemberton and his generals felt that Johnston's plan was dangerous and decided instead to attack the Union supply trains moving from Grand Gulf to Raymond. On May 16, however, Pemberton received another order from Johnston repeating his former directions. Pemberton had already started after the supply trains and was on the Raymond-Edwards Road with his rear at the crossroads one-third mile south of the crest of Champion Hill. Thus, when he ordered a countermarch, his rear, including his many supply wagons, became the vanguard of his force.
Champion Hill (May 16)
On May 16, about 7 a.m., the Union forces engaged the Confederates and the Battle of Champion Hill began. Pemberton's force drew up into a defensive line along a crest of a ridge overlooking Jackson Creek. Pemberton was unaware that one Union column was moving along the Jackson Road against his unprotected left flank. For protection, Pemberton posted Brig. Gen. Stephen D. Lee's men atop Champion Hill where they could watch for the reported Union column moving to the crossroads. Lee spotted the Union troops and they soon saw him. If this force was not stopped, it would cut the Confederates off from their Vicksburg base. Pemberton received warning of the Union movement and sent troops to his left flank. Union forces at the Champion House moved into action and emplaced artillery to begin firing. When Grant arrived at Champion Hill, around 10 a.m., he ordered the attack to begin. By 11:30 a.m., Union forces had reached the Confederate main line and about 1 p.m., they took the crest while the Confederates retreated in disorder. The Federals swept forward, capturing the crossroads and closing the Jackson Road escape route. One of Pemberton's divisions (Bowen's) then counterattacked, pushing the Federals back beyond the Champion Hill crest before their surge came to a halt. Grant then counterattacked, committing forces that had just arrived from Clinton by way of Bolton. Pemberton's men could not stand up to this assault, so he ordered his men from the field to the one escape route still open: the Raymond Road crossing of Bakers Creek. Brig. Gen. Lloyd Tilghman
Lloyd Tilghman (January 26, 1816 – May 16, 1863) was a Confederate general in the American Civil War.
A railroad construction engineer by background, he was selected by the Confederate government to build two forts to defend the Tennesse ...
's brigade formed the rearguard, and they held at all costs, including the loss of Tilghman. In the late afternoon, Union troops seized the Bakers Creek Bridge, and by midnight, they occupied Edwards. The Confederates were in full retreat towards Vicksburg.
Big Black River Bridge (May 17)
The Confederate retreat reached Big Black River Bridge the night of May 16–17. Pemberton ordered Brig. Gen. Bowen, with three brigades, to man the fortifications on the east bank of the river and impede any Union pursuit. Three divisions of McClernand's corps moved out from Edwards Station on the morning of May 17. The corps encountered the Confederates behind breastworks and took cover as enemy artillery began firing. Union Brig. Gen. Michael K. Lawler formed his 2nd Brigade, Brig. Gen. Eugene A. Carr
Eugene Asa Niel Carr (March 20, 1830 – December 2, 1910) was a soldier in the United States Army and a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War. He was awarded the Medal of Honor for his actions at the Battle of Pea Ridge.
Ea ...
's Division, which surged out of a river meander scar, across the front of the Confederate forces, and into the enemy's breastworks, held by Brig. Gen. John C. Vaughn's inexperienced East Tennessee Brigade. Confused and panicked, the Confederates began to withdraw across the Big Black on two bridges: the railroad bridge and the steamboat dock moored athwart the river. As soon as they had crossed, the Confederates set fire to the bridges, preventing close Union pursuit. The fleeing Confederates who arrived in Vicksburg later that day were disorganized. The Union forces captured approximately 1,800 troops at Big Black, a loss that the Confederates could ill afford.
Siege of Vicksburg (May 18 – July 4)
The Union army converged on Vicksburg, trapping Pemberton's force. Grant attempted two assaults to break through the strong Confederate fieldworks: May 19 and May 22. The latter assault initially achieved some success in McClernand's sector, but it was repulsed with 3,200 casualties. Johnston ordered Pemberton to evacuate the city and save his army, but Pemberton thought it impossible to withdraw safely. Johnston planned to attack Grant and relieve Pemberton but was unable to arrange it in time. Grant besieged the Confederate army. On July 4, after six weeks in which the soldiers and civilians of Vicksburg had no food supplies and were bombarded constantly, Pemberton surrendered the city and his army.
In addition to Pemberton at his front, Grant had to be concerned with Confederate forces in his rear. He stationed one division in the vicinity of the Big Black River bridge and another reconnoitered as far north as Mechanicsburg, both to act as a covering force. By June 10, the IX Corps 9 Corps, 9th Corps, Ninth Corps, or IX Corps may refer to:
France
* 9th Army Corps (France)
* IX Corps (Grande Armée), a unit of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
Germany
* IX Corps (German Empire), a unit of the Imperial German ...
, under Maj. Gen. John G. Parke
John Grubb Parke (September 22, 1827 – December 16, 1900) was a United States Army engineer and a Union general in the American Civil War. Parke's Civil War service was closely associated with Ambrose E. Burnside, often serving him as chi ...
, was transferred to Grant's command. This corps became the nucleus of a special task force whose mission was to prevent Johnston, gathering his forces at Canton
Canton may refer to:
Administrative division terminology
* Canton (administrative division), territorial/administrative division in some countries, notably Switzerland
* Township (Canada), known as ''canton'' in Canadian French
Arts and ente ...
, from interfering with the siege. Sherman was given command of this task force and Brig. Gen. Frederick Steele replaced him at the XV Corps on June 22. Johnston eventually began moving to relieve Pemberton and reached the Big Black River on July 1, but he delayed a potentially difficult encounter with Sherman until it was too late for the Vicksburg garrison, and then fell back to Jackson.
Louisiana operations
During the siege of Vicksburg, three other battles took place in the vicinity:
Milliken's Bend (June 7)
In an effort to cut Grant's supply line during the siege, the Confederates attacked the Milliken's Bend supply area up the Mississippi. This was mainly defended by untrained black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ha ...
troops, who fought with inferior weaponry and finally repelled the Confederates with help from gunboats, although at significant cost; the defenders lost 652 to the Confederate 185.
Goodrich's Landing (June 29–30)
After Union forces began occupying the Louisiana river parishes, thousands of escaped slaves flocked to them. The Federals, therefore, leased some plantations and put the freedmen to work growing cotton or other crops; the proceeds from the sale of the crops helped defray expenses for food, clothing, etc. African-American troops were assigned to protect these plantations, releasing other troops to fight. Confederates, determined to recapture some of these freedmen and destroy the crops, undertook an expedition from Gaines's Landing, Arkansas, to Lake Providence. Although the Confederates disrupted these operations, destroyed much property, and captured many supplies and weapons, the raid was only a minor setback for the Union. The Confederates could cause momentary disturbances, but they were unable to effect any lasting changes.
Helena (July 4)
Confederate Lt. Gen. Theophilus H. Holmes's troops attacked Helena, Arkansas
Helena is the eastern portion of Helena–West Helena, Arkansas, a city in Phillips County, Arkansas. It was founded in 1833 by Nicholas Rightor and is named after the daughter of Sylvanus Phillips, an early settler of Phillips County and the n ...
, in an attempt to relieve pressure on Vicksburg. Although the Confederates had more troops and did initially capture some of the fortifications, the Union forces repelled them.
Aftermath
Although the Confederate killed and wounded in the battle and siege of Vicksburg were a relatively small 2,872, and Union 4,910, Grant captured his second Confederate army in its entirety (the first being at Fort Donelson
Fort Donelson was a fortress built early in 1862 by the Confederacy during the American Civil War to control the Cumberland River, which led to the heart of Tennessee, and thereby the Confederacy. The fort was named after Confederate general Da ...
): 29,495 surrendered. Most of the Confederates were paroled. The Union also captured significant quantities of artillery, small arms, and ammunition. The full campaign, since March 29, claimed 10,142 Union and 9,091 Confederate killed and wounded.
This was the second major blow to the Confederacy in the summer of 1863. On July 3, Gen. Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, towards the end of which he was appointed the overall commander of the Confederate States Army. He led the Army of Nor ...
's invasion of the North collapsed at Gettysburg. On July 4, the Stars and Stripes rose over Vicksburg. To the Confederates, surrendering on Independence Day
An independence day is an annual event commemorating the anniversary of a nation's independence or statehood, usually after ceasing to be a group or part of another nation or state, or more rarely after the end of a military occupation. Many ...
was a bitter defeat. Union troops behaved well, mixing with Confederates and giving rations to starving soldiers. Speculators who had been hoarding food for higher prices saw their stores broken open and the contents thrown on the streets for the starving rebels. In his ''Personal Memoirs'', Grant observed, "The men of the two armies fraternized as if they had been fighting for the same cause." But resentments lingered: allegedly tradition holds that the Fourth of July
Independence Day (colloquially the Fourth of July) is a federal holiday in the United States commemorating the Declaration of Independence, which was ratified by the Second Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, establishing the United States ...
holiday was not celebrated by Vicksburg until World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. This claim has been challenged because large Fourth of July celebrations were being held by 1907.
The most significant result of the campaign was control of the Mississippi River, which the Union obtained completely after Port Hudson, which had been besieged by Banks since May 27, heard news of Vicksburg's fall and surrendered on July 9. The Confederacy was now cut in two; one week later, an unarmed ship arrived in Union-held New Orleans from St. Louis after an uneventful trip down the river. President Lincoln announced, "The Father of Waters again goes unvexed to the sea."
Grant deployed Sherman and 50,000 troops against Johnston's 31,000 in Jackson. Johnston tried to lure Sherman into a frontal assault, but Sherman had seen the results of such at Vicksburg. He demurred and began surrounding the city. Johnston escaped with his army, which was more than Pemberton had achieved, but all of central Mississippi was now under Sherman's control. He used a subsequent operation against Meridian, Mississippi
Meridian is the seventh largest city in the U.S. state of Mississippi, with a population of 41,148 at the 2010 census and an estimated population in 2018 of 36,347. It is the county seat of Lauderdale County and the principal city of the Merid ...
, as a harbinger of the scorched earth
A scorched-earth policy is a military strategy that aims to destroy anything that might be useful to the enemy. Any assets that could be used by the enemy may be targeted, which usually includes obvious weapons, transport vehicles, commun ...
tactics he later employed in his March to the Sea through Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, and then South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
.
One of Grant's actions during the siege was to settle a lingering rivalry. On May 30, General McClernand wrote a self-adulatory note to his troops, claiming much of the credit for the soon-to-be victory. Grant had been waiting six months for him to slip, ever since they clashed early in the campaign, around the Battle of Arkansas Post
The Battle of Arkansas Post, also known as Battle of Fort Hindman, was fought from January 9 to 11, 1863, near the mouth of the Arkansas River at Arkansas Post, Arkansas, as part of the Vicksburg Campaign of the American Civil War. Confederat ...
. Grant finally relieved McClernand on June 18. McClernand's XIII Corps was turned over to Maj. Gen. Edward Ord
Edward Otho Cresap Ord (October 18, 1818 – July 22, 1883) was an American engineer and United States Army officer who saw action in the Seminole War, the Indian Wars, and the American Civil War. He commanded an army during the final days of ...
. In May 1864, McClernand was restored to a command in remote Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
.
Grant was the undisputed victor of the Vicksburg campaign. He was rewarded for his victory with a promotion to major general in the regular army
A regular army is the official army of a state or country (the official armed forces), contrasting with irregular forces, such as volunteer irregular militias, private armies, mercenaries, etc. A regular army usually has the following:
* a standin ...
, effective on July 4, 1863. He also received an unusual letter:
Grant went on to rescue Union forces besieged at Chattanooga
Chattanooga ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Hamilton County, Tennessee, United States. Located along the Tennessee River bordering Georgia, it also extends into Marion County on its western end. With a population of 181,099 in 2020, ...
and then replaced Halleck as general in chief of all Union armies, with the recently re-activated rank of lieutenant general
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on th ...
. Despite his ultimate success in winning the war, historians have often considered Vicksburg his finest campaign—imaginative, audacious, relentless, and a masterpiece of maneuver warfare. James M. McPherson
James Munro McPherson (born October 11, 1936) is an American Civil War historian, and is the George Henry Davis '86 Professor Emeritus of United States History at Princeton University. He received the 1989 Pulitzer Prize for '' Battle Cry ...
called Vicksburg "the most brilliant and innovative campaign of the Civil War"; T. Harry Williams
Thomas Harry Williams (May 19, 1909 — July 8, 1979) was an American academic and author. For the majority of his academic career between the 1930s to 1970s, Williams taught history at Louisiana State University. While at LSU, Williams was a Boyd ...
described it as "one of the classic campaigns of the Civil War and, indeed, of military history"; and the U.S. Army '' Field Manual 100–5'' (May 1986) called it "the most brilliant campaign ever fought on American soil".
Historian Steven E. Woodworth
Steven E. Woodworth (born January 28, 1961) is an American historian specializing in studies of the American Civil War. He has written numerous books concerning the Civil War, and as a professor has taught classes on the Civil War, the Reconstructi ...
wrote that Pemberton "had a strong claim to the title of the most hated man in the South, certainly the most hated to wear a Confederate uniform". There were accusations that adequate supplies had been on hand and that it was only his treachery that caused the surrender. Even his friend, Confederate general Richard Taylor, wrote after the war that a large part of the population believed "He had joined the South for the express purpose of betraying it, and this was clearly proven by the fact that he surrendered on the 4th of July, a day sacred to the Yankees."
The blame for losing Vicksburg fell not only on John Pemberton, but on the overcautious Joseph E. Johnston. Jefferson Davis said of the defeat, "Yes, from a want of provisions inside and a General outside who wouldn't fight."[McPherson, p. 637.] Anguished soldiers and civilians starving in the siege held hopes that he would come to their aid, but he never did. Accusations of cowardice that had dogged him since the 1862 Peninsula Campaign continued to follow him in the 1864 Atlanta Campaign against Sherman. However, Johnston was far outnumbered. While he was one of few Confederate generals whom Grant respected, he was outgeneraled.
Memorials

See also
* Troop engagements of the American Civil War, 1863
The following engagements took place in the year 1863 during the American Civil War. During the year, Union forces captured the Confederate cities of Vicksburg and Port Hudson, giving them complete control over the Mississippi River, while forci ...
* List of costliest American Civil War land battles
* Armies in the American Civil War This article is designed to give background into the organization and tactics of Civil War armies. This brief survey is by no means exhaustive, but it should give enough material to have a better understanding of the capabilities of the forces that ...
* Commemoration of the American Civil War
The commemoration of the American Civil War is based on the memories of the Civil War that Americans have shaped according to their political, social and cultural circumstances and needs, starting with the Gettysburg Address and the dedication of ...
* Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps
The Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps concerns both the actual stamps and covers used during the American Civil War, and the later postage celebrations. The latter include commemorative stamp issues devoted to the actua ...
* Vicksburg National Military Park
Vicksburg National Military Park preserves the site of the American Civil War Battle of Vicksburg, waged from March 29 to July 4, 1863. The park, located in Vicksburg, Mississippi (flanking the Mississippi River), also commemorates the greater ...
Notes
References
* Ballard, Michael B. ''Vicksburg, The Campaign that Opened the Mississippi''. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2004. .
* Bearss, Edwin C. ''The Campaign for Vicksburg''. Vol. 1, ''Vicksburg is the Key''. Dayton, OH: Morningside House, 1985. .
* Bearss, Edwin C. ''The Campaign for Vicksburg''. Vol. 2, ''Grant Strikes a Fatal Blow''. Dayton, OH: Morningside House, 1986. .
* Bearss, Edwin C. ''The Campaign for Vicksburg''. Vol. 3, ''Unvexed to the Sea''. Dayton, OH: Morningside House, 1986. .
* Bonekemper, Edward H. ''A Victor, Not a Butcher: Ulysses S. Grant's Overlooked Military Genius''. Washington, D.C.: Regnery Publishing, 2004. .
* Catton, Bruce. ''The Centennial History of the Civil War''. Vol. 3, ''Never Call Retreat''. Garden City, NY: Doubleday, 1965. .
* Eicher, David J. ''The Longest Night: A Military History of the Civil War''. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2001. .
* Esposito, Vincent J. ''West Point Atlas of American Wars''. New York: Frederick A. Praeger, 1959. . The collection of maps (without explanatory text) is available online at th
West Point website
* Foote, Shelby. '' The Civil War: A Narrative''. Vol. 2, ''Fredericksburg to Meridian''. New York: Random House, 1958. .
* Gabel, Christopher R.
''Staff ride handbook for the Vicksburg Campaign, December 1862 – July 1863''
Fort Leavenworth, Kan.: Combat Studies Institute Press, 2001. .
* Grabau, Warren E. ''Ninety-Eighty Days: A Geographer's View of the Vicksburg Campaign''. Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2000. .
* Kennedy, Frances H., ed. ''The Civil War Battlefield Guide''. 2nd ed. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Co., 1998. .
* Korn, Jerry, and the Editors of Time-Life Books. ''War on the Mississippi: Grant's Vicksburg Campaign''. Alexandria, VA: Time-Life Books, 1985. .
* McPherson, James M. '' Battle Cry of Freedom: The Civil War Era''. Oxford History of the United States. New York: Oxford University Press, 1988. .
* Smith, Jean Edward. ''Grant''. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2001. .
*
* Winschel, Terrence J. ''Vicksburg: Fall of the Confederate Gibraltar''. Abilene, TX: McWhiney Foundation Press, 1999. .
* Woodworth, Steven E. ''Jefferson Davis and His Generals: The Failure of Confederate Command in the West''. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, 1990. .
National Park Service battle descriptions
Memoirs and primary sources
* Grant, Ulysses S.br>''Personal Memoirs of U. S. Grant''
2 vols. Charles L. Webster & Company, 1885–86. .
* U.S. War Department
''a Compilation of the Official Records of the Union and Confederate Armies''. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1880–1901.
''Organization of the Department of the Tennessee, Major General Ulysses S. Grant, U. S. Army, commanding, April 30, 1863'': Official Records, Series I, Volume XXIV, Part 3, pages 250–259.
Further reading
* Bearss, Edwin C. ''Receding Tide: Vicksburg and Gettysburg: The Campaigns That Changed the Civil War''. Washington, DC: National Geographic Society, 2010. .
* Groom, Winston. ''Vicksburg, 1863''. New York: Knopf, 2009. .
* Huffstodt, James. ''Hard Dying Men: The Story of General W. H. L. Wallace, General Thomas E. G. Ransom, and the "Old Eleventh" Illinois Infantry in the American Civil War (1861–1865)''. Bowie, MD: Heritage Press. .
* Smith, Timothy B. ''Champion Hill: Decisive Battle for Vicksburg''. El Dorado Hills, CA: Savas Beatie, 2004. .
* Winschel, Terrence J. ''Triumph & Defeat: The Vicksburg Campaign''. Campbell, CA: Savas Publishing Company, 1999. .
* Woodworth, Steven E., ed. ''Grant's Lieutenants: From Cairo to Vicksburg''. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, 2001. .
* Woodworth, Steven E. ''Nothing but Victory: The Army of the Tennessee, 1861–1865''. New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 2005. .
External links
National Park Service, Vicksburg
photos, history articles, and battlefield news ( Civil War Trust)
Animated map of the Vicksburg Campaign
( Civil War Trust)
First Vicksburg Campaign
{{Authority control
Military operations of the American Civil War in Mississippi
Campaigns of the Western Theater of the American Civil War
Battles commanded by Ulysses S. Grant
 All of the bayou operations were failures, but Grant was known for his stubborn determination and would not quit. His final option was bold but risky: March the army down the west side of the Mississippi, cross the river south of Vicksburg, and either attack Vicksburg from the south and the east or join forces with Banks, capture Port Hudson, and then together reduce Vicksburg. Porter would have to sneak past the guns to get sufficient gunboats and transport ships south of the city. Once they had completed the downstream passage, they would not be able to return past Vicksburg's guns because the river current would slow them too much.
On March 29, McClernand set his troops to work building bridges and
All of the bayou operations were failures, but Grant was known for his stubborn determination and would not quit. His final option was bold but risky: March the army down the west side of the Mississippi, cross the river south of Vicksburg, and either attack Vicksburg from the south and the east or join forces with Banks, capture Port Hudson, and then together reduce Vicksburg. Porter would have to sneak past the guns to get sufficient gunboats and transport ships south of the city. Once they had completed the downstream passage, they would not be able to return past Vicksburg's guns because the river current would slow them too much.
On March 29, McClernand set his troops to work building bridges and  On April 16, a clear night with no moon, Porter sent seven gunboats and three empty troop transports loaded with stores to run the bluff, taking care to minimize noise and lights. But the preparations were ineffective. Confederate sentries sighted the boats, and the bluff exploded with massive artillery fire. Fires were set along the banks to improve visibility. The Union gunboats answered back. Porter observed that the Confederates mainly hit the high parts of his boats, reasoned that they could not depress their guns, and had them hug the east shore, right under Confederate cannon, so close he could hear their commanders giving orders, shells flying overhead. The fleet survived with little damage; thirteen men were wounded and none killed. The ''Henry Clay'' was disabled and burned at the water's edge. On April 22, six more boats loaded with supplies made the run; one boat did not make it, though no one was killed. The crew floated downstream on the boat's remnants.
The final piece of Grant's strategy was to divert Pemberton's attention from the river crossing site that the Union troops would use. Grant chose two operations: a feint by Sherman against Snyder's Bluff, Mississippi, north of Vicksburg (see the Battle of Snyder's Bluff below), and a daring cavalry raid through central Mississippi by Col.
On April 16, a clear night with no moon, Porter sent seven gunboats and three empty troop transports loaded with stores to run the bluff, taking care to minimize noise and lights. But the preparations were ineffective. Confederate sentries sighted the boats, and the bluff exploded with massive artillery fire. Fires were set along the banks to improve visibility. The Union gunboats answered back. Porter observed that the Confederates mainly hit the high parts of his boats, reasoned that they could not depress their guns, and had them hug the east shore, right under Confederate cannon, so close he could hear their commanders giving orders, shells flying overhead. The fleet survived with little damage; thirteen men were wounded and none killed. The ''Henry Clay'' was disabled and burned at the water's edge. On April 22, six more boats loaded with supplies made the run; one boat did not make it, though no one was killed. The crew floated downstream on the boat's remnants.
The final piece of Grant's strategy was to divert Pemberton's attention from the river crossing site that the Union troops would use. Grant chose two operations: a feint by Sherman against Snyder's Bluff, Mississippi, north of Vicksburg (see the Battle of Snyder's Bluff below), and a daring cavalry raid through central Mississippi by Col. 