Venkateswara Temple, Tirumala on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sri Venkateswara Swami Vaari Temple is a
 After the end of
After the end of

 ;Dwarams and Prakarams
There are three Dwarams (entrances) which lead to ''
;Dwarams and Prakarams
There are three Dwarams (entrances) which lead to ''
 The world-famous "''
The world-famous "''
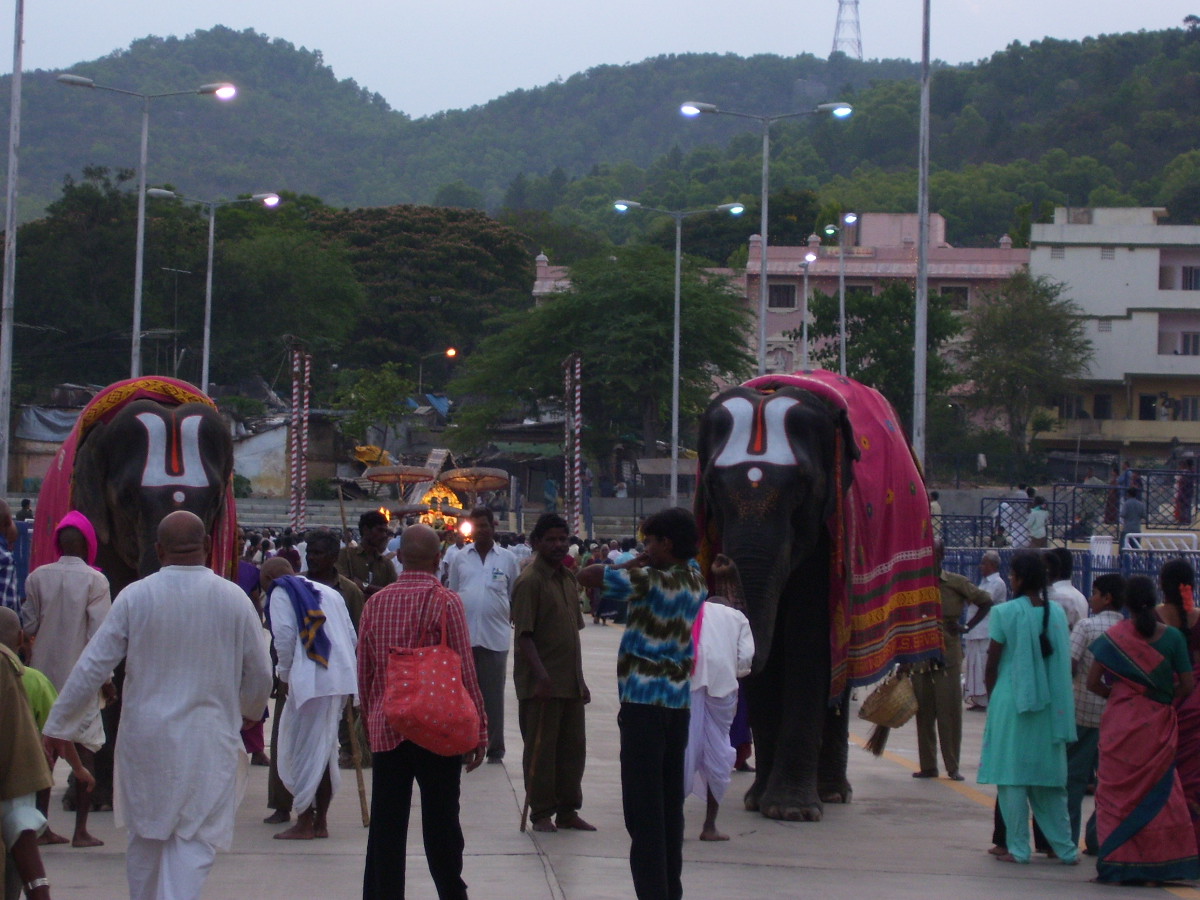 In the Venkateswara Temple over 433 festivals are being observed in 365 days of a year suiting the title "Nitya Kalyanam Paccha Toranam" where every day is a festival.
Sri Venkateswara Brahmotsavams, a nine-day event, which is celebrated every year during month of October, is the major event of Venkateswara Temple. During brahmotsavams the processional deity Malayappa along with his consorts SriDevi and BhuDevi, is taken in a procession in four mada streets around the temple on different vahanams. Vahanams include Dwajarohanam, Pedda Sesha Vahanam, Chinna Sesha Vahanam, Hamsa Vahanam, Simha Vahanam, Muthaypu pandiri Vahanam, Kalpavriksha Vahanam, Sarva Bhoopala Vahanam, Mohini Avataram, Garuda Vahanam, Hanumantha Vahanam, Swarna Rathotsavam (Golden Chariot), Gajavahanam, Rathotsavam (Chariot), Ashwa Vahanam, and Chakra Snanam. During Brahmotsavams, the temple will witness lakhs of devotees particularly on Garuda vahanam.
In the Venkateswara Temple over 433 festivals are being observed in 365 days of a year suiting the title "Nitya Kalyanam Paccha Toranam" where every day is a festival.
Sri Venkateswara Brahmotsavams, a nine-day event, which is celebrated every year during month of October, is the major event of Venkateswara Temple. During brahmotsavams the processional deity Malayappa along with his consorts SriDevi and BhuDevi, is taken in a procession in four mada streets around the temple on different vahanams. Vahanams include Dwajarohanam, Pedda Sesha Vahanam, Chinna Sesha Vahanam, Hamsa Vahanam, Simha Vahanam, Muthaypu pandiri Vahanam, Kalpavriksha Vahanam, Sarva Bhoopala Vahanam, Mohini Avataram, Garuda Vahanam, Hanumantha Vahanam, Swarna Rathotsavam (Golden Chariot), Gajavahanam, Rathotsavam (Chariot), Ashwa Vahanam, and Chakra Snanam. During Brahmotsavams, the temple will witness lakhs of devotees particularly on Garuda vahanam.
 *Vrushabhadri—Hill of Vrishabasura, who was killed by Srinivasa
*Anjanadri—Hill of
*Vrushabhadri—Hill of Vrishabasura, who was killed by Srinivasa
*Anjanadri—Hill of
 Sri Tallapaka Annamacharya (or Annamayya) (22 May 1408 – 4 April 1503) was the official songmaster of the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, and a
Sri Tallapaka Annamacharya (or Annamayya) (22 May 1408 – 4 April 1503) was the official songmaster of the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, and a
Hindu temple
A Hindu temple, or ''mandir'' or ''koil'' in Indian languages, is a house, seat and body of divinity for Hindus. It is a structure designed to bring human beings and gods together through worship, sacrifice, and devotion.; Quote: "The Hin ...
situated in the hill town of Tirumala
Tirumala is a spiritual town in Tirupati district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is one of the suburbs of the Tirupati urban agglomeration. The town is a part of Tirupati Urban Development Authority and located in Tirupati (rura ...
at Tirupati
Tirupati () is a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of the Tirupati district. The city is home to the important Hindu shrine of Tirumala Venkateswara Temple and other historic temples and is re ...
in Tirupati district
Tirupati district () is one of the twenty-six districts in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and one of the eight districts in the Rayalaseema region of the Andhra Pradesh state. The district headquarters is located at Tirupati city. Tirupati ...
of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
, India. The Temple is dedicated to Venkateswara
Venkateswara, also known by various other names, is a form of the Hindu god Vishnu. Venkateswara is the presiding deity of the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, located in Tirupati, Sri Balaji District, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Etymology
Venkat ...
, a form of Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" withi ...
, who is believed to have appeared on the earth to save mankind from trials and troubles of ''Kali Yuga
''Kali Yuga'', in Hinduism, is the fourth and worst of the four ''yugas'' (world ages) in a '' Yuga Cycle'', preceded by '' Dvapara Yuga'' and followed by the next cycle's '' Krita (Satya) Yuga''. It is believed to be the present age, which i ...
''. Hence the place has also got the name Kaliyuga Vaikuntha
Vaikuntha ( sa, वैकुण्ठ, lit=without anxiety, translit=Vaikuṇṭha), also called Vishnuloka (), and Tirunatu (Tirunāṭu) in Tamil, is the abode of Vishnu, the supreme deity in the Vaishnava tradition of Hinduism,Gavin Flood, ...
and the Lord here is referred to as Kaliyuga Prathyaksha Daivam. The temple is also known by other names like Tirumala Temple, Tirupati Temple and Tirupati Balaji Temple. Venkateswara is known by many other names: Balaji, Govinda, and Srinivasa. The temple is run by Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams
Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams (TTD) is an independent trust which manages the temples including the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple in Andhra Pradesh. The trust oversees the operations and finances of the richest and the most visited religious cen ...
(TTD), which is under control of Andhra Pradesh Government. The head of TTD is appointed by Andhra Pradesh Government. The revenue from this shrine is used by Andhra Pradesh government.
Tirumala Hills are part of Seshachalam Hills
Seshachalam Hills are hilly ranges part of the Eastern Ghats in southern Andhra Pradesh state, in southeastern India. The Seshachalam hill ranges are predominantly present in Tirupati district of the Rayalaseema region in Andhra Pradesh, India.
...
range. The hills are above sea level and comprise seven peaks, representing the seven heads of Adisesha
Shesha ( Sanskrit: शेष; ) , also known as Sheshanaga ( Sanskrit: शेषनाग; ) or Adishesha (), is a serpentine demigod (Naga) and Nagaraja (King of all serpents), as well as a primordial being of creation in Hinduism. In the Pu ...
. The temple lies on the seventh peak—Venkatadri
The Venkata hill (853 m) is part of the Seshachalam Hills, located in the Tirupati district of Andhra Pradesh, India. Also known as Venkatadri or Venkatachalam, it is one of the seven peaks of the Tirumala Hill located in the temple town of Tirum ...
, on the southern banks of Sri Swami Pushkarini, a holy water tank. Hence the temple is also referred to as "Temple of Seven Hills". Tirumala town covers an area of about .
The Temple is constructed in South Indian architecture and is believed to be constructed over a period of time starting from 300 CE. The Garbhagruha (Sanctum Sanctorum) is called Ananda Nilayam. The presiding deity, Venkateswara, is in standing posture and faces east in Garbha Gruha. The temple follows Vaikhanasa Agama tradition of worship. The temple is one of the eight Vishnu Swayambhu Kshetras and is listed as the 75th Divya Desam. The Temple premises have two modern Queue complex buildings to manage the pilgrim crowd, Tarigonda Vengamamba Annaprasadam complex for free meals to Pilgrims, hair tonsure buildings and a number of pilgrim lodging sites.
It is one of the richest temples in the world in terms of donations received and wealth.
There are several legends associated with the manifestation of the Lord in Tirumala. According to one legend, the temple has a murti
In the Hindu tradition, a ''murti'' ( sa, मूर्ति, mūrti, ) is a devotional image such as a statue, or "idol" (a common and non-pejorative term in Indian English), of a deity or saint. In Hindu temples, it is a symbolic icon. T ...
of Venkateswara, it is believed, which shall remain here for the entire duration of the present ''Kali Yuga
''Kali Yuga'', in Hinduism, is the fourth and worst of the four ''yugas'' (world ages) in a '' Yuga Cycle'', preceded by '' Dvapara Yuga'' and followed by the next cycle's '' Krita (Satya) Yuga''. It is believed to be the present age, which i ...
''.
Temple legend
During ''Dvapara Yuga
''Dvapara Yuga'' ( Dwapara Yuga), in Hinduism, is the third and third best of the four ''yugas'' (world ages) in a '' Yuga Cycle'', preceded by ''Treta Yuga'' and followed by ''Kali Yuga''. ''Dvapara Yuga'' lasts for 864,000 years (2,400 divine ...
'', Adisesha
Shesha ( Sanskrit: शेष; ) , also known as Sheshanaga ( Sanskrit: शेषनाग; ) or Adishesha (), is a serpentine demigod (Naga) and Nagaraja (King of all serpents), as well as a primordial being of creation in Hinduism. In the Pu ...
resided on earth as Seshachalam Hills
Seshachalam Hills are hilly ranges part of the Eastern Ghats in southern Andhra Pradesh state, in southeastern India. The Seshachalam hill ranges are predominantly present in Tirupati district of the Rayalaseema region in Andhra Pradesh, India.
...
after losing a contest with Vayu
Vayu (, sa, वायु, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
. According to Puranas
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends an ...
, Tirumala
Tirumala is a spiritual town in Tirupati district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is one of the suburbs of the Tirupati urban agglomeration. The town is a part of Tirupati Urban Development Authority and located in Tirupati (rura ...
is regarded as Adivaraha Kshetra. After killing Hiranyaksha
__NOTOC__
Hiranyaksha ( sa, हिरण्याक्ष, "golden-eyed"), also known as Hiranyanetra ( sa, हिरण्यनेत्र) was an oppressive Asura who attacked the heavens and thereafter kidnapped and attempted to destroy th ...
, Adivaraha resided on this hill. Venkatachala Mahatyam is the widely accepted legend over Tirumala Temple.
During ''Kali Yuga
''Kali Yuga'', in Hinduism, is the fourth and worst of the four ''yugas'' (world ages) in a '' Yuga Cycle'', preceded by '' Dvapara Yuga'' and followed by the next cycle's '' Krita (Satya) Yuga''. It is believed to be the present age, which i ...
'', Narada
Narada ( sa, नारद, ), or Narada Muni, is a sage divinity, famous in Hindu traditions as a travelling musician and storyteller, who carries news and enlightening wisdom. He is one of mind-created children of Brahma, the creator god. He ...
advised some sages who were performing yagna
Yajna ( sa, यज्ञ, yajña, translit-std=IAST, sacrifice, devotion, worship, offering) refers in Hinduism to any ritual done in front of a sacred fire, often with mantras.SG Nigal (1986), Axiological Approach to the Vedas, Northern Book ...
to decide who could be given the fruits of yagna among Trimurti
The Trimūrti (; Sanskrit: त्रिमूर्ति ', "three forms" or "trinity") are the trinity of supreme divinity in Hinduism, in which the cosmic functions of creation, maintenance, and destruction are personified as a triad of ...
s (Brahma
Brahma ( sa, ब्रह्मा, Brahmā) is a Hindu god, referred to as "the Creator" within the Trimurti, the trinity of supreme divinity that includes Vishnu, and Shiva.Jan Gonda (1969)The Hindu Trinity Anthropos, Bd 63/64, H 1/2, pp ...
, Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" withi ...
and Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one o ...
). Bhrigu
Bhrigu ( sa, भृगु, ) was a rishi in Hinduism. He was one of the seven great sages, the Saptarshis, one of the many Prajapatis (the facilitators of Creation) created by Brahma. The first compiler of predictive astrology, and also the ...
was sent to test the Trinity. The sage who had an extra eye in the sole of his foot visited Brahma
Brahma ( sa, ब्रह्मा, Brahmā) is a Hindu god, referred to as "the Creator" within the Trimurti, the trinity of supreme divinity that includes Vishnu, and Shiva.Jan Gonda (1969)The Hindu Trinity Anthropos, Bd 63/64, H 1/2, pp ...
and Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one o ...
and went unnoticed in both these locations. He cursed Brahma to be not worshipped and Shiva to be worshipped as a lingam
A lingam ( sa, लिङ्ग , lit. "sign, symbol or mark"), sometimes referred to as linga or Shiva linga, is an abstract or aniconic representation of the Hindu god Shiva in Shaivism. It is typically the primary '' murti'' or devoti ...
. At last he visited Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" withi ...
and the lord acts as if he had not noticed Bhrigu. Getting angered by this act, sage Bhrigu kicked Vishnu in the chest, to which Vishnu did not react and instead apologised to the Sage by massaging his feet. During this act, he squashed the extra eye that was present in the sole of Bhrigu's foot. However Lakshmi
Lakshmi (; , sometimes spelled Laxmi, ), also known as Shri (, ), is one of the principal goddesses in Hinduism. She is the goddess of wealth, fortune, power, beauty, fertility and prosperity, and associated with '' Maya'' ("Illusion"). A ...
finds it as an insult since Vishnu's chest was considered as Lakshmi's residence (''vakshasthala'') and Bhrigu kicked it which indirectly insulted Lakshmi. She then left Vaikuntha
Vaikuntha ( sa, वैकुण्ठ, lit=without anxiety, translit=Vaikuṇṭha), also called Vishnuloka (), and Tirunatu (Tirunāṭu) in Tamil, is the abode of Vishnu, the supreme deity in the Vaishnava tradition of Hinduism,Gavin Flood, ...
and came to Earth to Kolhapur
Kolhapur () is a city on the banks of the Panchganga River in the southern part of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the administrative headquarter of the Kolhapur district. In, around 2 C.E. Kolapur's name was 'Kuntal'.
Kolhapur is ...
and started meditating.
Vishnu bore human form as Srinivasa
Venkateswara, also known by various other names, is a form of the Hindu god Vishnu. Venkateswara is the presiding deity of the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, located in Tirupati, Sri Balaji District, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Etymology
Venkatesw ...
, left Vaikuntha, in search of Lakshmi, reached the ''Seshachalam'' hills in Tirumala and started meditating. Lakshmi learned of the condition of Srinivasa and called Shiva and Brahma. Shiva and Brahma then converted themselves into Cow and Calf and Lakshmi had handed over the cow and calf to Chola
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil thalassocratic empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BCE d ...
king ruling over Tirumala Hills at that time. The Cow would provide milk to Srinivasa daily while it was taken for grazing. One day, a cowherd saw this and tried to beat the Cow with his staff but Srinivasa had borne the injury. Getting angered by this Srinivasa had cursed the Chola king to become a Demon
A demon is a malevolent supernatural entity. Historically, belief in demons, or stories about demons, occurs in religion, occultism, literature, fiction, mythology, and folklore; as well as in Media (communication), media such as comics, video ...
as dharma says sins committed by servants (''shudras'') should be borne by Kings. The king prayed for mercy after which Srinivasa said to him, that the King should take next birth as Akasharaja and should perform marriage of his daughter Padmavati with Srinivasa.
Srinivasa went to his foster-mother Vakula Devi
Vakula Devi is the foster mother of Lord Venkateswara. Vakula Matha Temple is situated in Peruru(patakaluva) located in Tirupati city, Andhra Pradesh. As per the legend of Tirumala, it dates back to Dvapara Yuga when Yasoda, the foster mother o ...
on Tirumala hills and stayed there for a while. After curse, Chola
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil thalassocratic empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BCE d ...
king took rebirth as Akasharaja and he had a daughter named Padmavati, who was born in the Padmapushkarini situated at present day Tiruchanur in Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
. Srinivasa married Padmavati at present day Narayanavanam in Andhra Pradesh and returned to Tirumala Hills. After few months, Goddess Lakshmi had discovered the marriage of Srinivasa with Padamavati and went to Tirumala hills to question Srinivasa. Srinivasa, unable to bear the quarrel between Lakshmi and Padmavati, turned into stone right when he was encountered by Lakshmi and Padmavathi. Brahma and Shiva appeared before the confused queens and explain the main purpose behind all this - The Lord's desire to be on the seven hills for the emancipation of mankind from the perpetual troubles of ''Kali Yuga''. Goddesses Lakshmi and Padmavathi also turn into stone deities expressing their wish to be always there. Lakshmi stays with Him on His Chest on the left side while Padmavathi rests on His Chest's right side.
History of the temple
Medieval history
The first recorded endowment was made by Pallava queen Samavai in the year 966 CE. She donated many jewels and two parcels of land (one 10 acres and other 13 acres) and ordered to use the revenues generated from that land for the celebration of major festivals in the temple. ThePallava dynasty
The Pallava dynasty existed from 275 CE to 897 CE, ruling a significant portion of the Deccan, also known as Tondaimandalam. The dynasty rose to prominence after the downfall of the Satavahana dynasty, with whom they had formerly served as f ...
(9th century), the Chola dynasty
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil thalassocratic empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BC ...
(10th century), and Vijayanagara pradhans (14th and 15th centuries) were committed devotees of Venkateswara. The temple gained most of its current wealth and size under the Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also called the Karnata Kingdom, was a Hindu empire based in the region of South India, which consisted the modern states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Goa and some parts of Telangana and Mahar ...
, present-day Karnataka state
Karnataka (; ISO 15919, ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reor ...
, with the donation of diamonds and gold. In 16th century, Vijayanagara Emperor Krishnadevaraya
Krishnadevaraya (17 January 1471 – 17 October 1529) was an emperor of the Vijayanagara Empire, also known as the Karnata Empire, reigning from 1509 to 1529. He was the third monarch of the Tuluva dynasty, and is considered to be one of the ...
was a frequent donor and visitor to the temple. His donations of gold and jewels enabled the Ananda Nilayam (inner shrine) roofing to be gilded. On 2 January 1517, Krishnadevaraya installed his own statue in the temple.
After the decline of Vijayanagara Empire, rulers from states such as the Kingdom of Mysore
The Kingdom of Mysore was a realm in South India, southern India, traditionally believed to have been founded in 1399 in the vicinity of the modern city of Mysore. From 1799 until 1950, it was a princely state, until 1947 in a subsidiary allia ...
and the Gadwal Samsthanam worshipped as pilgrims and donated ornaments and valuables to the temple. Maratha general Raghoji I Bhonsle
Raghoji Bhonsle or Raghoji I Bhonsale or Raghuji the Great (1695 – February 1755) of the Bhonsale dynasty, was a Maratha general who took control of the Nagpur Kingdom in east-central India during the reign of Shahu I. His successors rul ...
(died 1755) visited the temple and set up a permanent administration for the conduct of worship in the temple. Between 1320 CE and 1369 CE, idols of Ranganatha temple of Srirangapatnam were brought to this temple for safe keeping.
Ramanujacharya's visits
In the 11th and 12th centuries, Ramanujacharya visited Tirupati thrice. On the first occasion, he spent a year with his uncle, Tirumalai Nambi, learning the esoteric meaning ofRamayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th to 4th centuries BCE, and later stages ...
. His second visit was for settling a dispute that arose between the Saivites
Shaivism (; sa, शैवसम्प्रदायः, Śaivasampradāyaḥ) is one of the major Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Supreme Being. One of the largest Hindu denominations, it incorporates many sub-traditions rangin ...
and Vaishnavites
Vaishnavism ( sa, वैष्णवसम्प्रदायः, Vaiṣṇavasampradāyaḥ) is one of the major Hindu denominations along with Shaivism, Shaktism, and Smartism. It is also called Vishnuism since it considers Vishnu as the ...
regarding the nature of the image set up in the Tirumala temple. During the last visit, which was at an advanced old age of 102 years, the acharya installed the image of Govindaraja and laid the foundations of the present town of Tirupati. Ramanuja streamlined the rituals at Tirumala temple according to Vaikanasa Agama tradition and introduced the recitation of Naalayira Divya Prabandham
The Naalayira Divya Prabandham ( ta, நாலாயிரத் திவ்வியப் பிரபந்தம், lit=Four Thousand Divine Hymns, translit=Nālāyira Divya Prabandham) is a collection of 4,000 Tamil verses composed by ...
. He also set up Tirupati Jeeyar Mutt in 1119 AD in consultation with Tirumalai Ananthalwan to institutionalize service to the Lord and supervise the temple rituals. The Jeeyars to this day ensures that the rituals ordained by Ramanuja are observed.
Modern history
Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also called the Karnata Kingdom, was a Hindu empire based in the region of South India, which consisted the modern states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Goa and some parts of Telangana and Mahar ...
, the temple went into the hands of Golconda
Fort (Telugu: గోల్కొండ, romanized: ''Gōlkōnḍa'') is a historic fortress and ruined city located in Hyderabad, Telangana, India. It was originally called Mankal. The fort was originally built by Kakatiya ruler Pratāparu ...
in July 1656 and then it was under the
French for a short period of time and under Nawab of Carnatic
The Carnatic Sultanate was a kingdom in South India between about 1690 and 1855, and was under the legal purview of the Nizam of Hyderabad, until their demise. They initially had their capital at Arcot in the present-day Indian state of Tamil N ...
till 1801 CE. With the advent of British during the early 19th century, the management of the temple passed to hands of East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sou ...
, who accorded special status to temple and avoided interference in temple activities. Madras government passed Regulation seven of 1817, which passed the temple to Board of Revenue through collector of North Arcot District. In 1821, Mr. Bruce, the then East India company commissioner for Chittoor district, had drawn rules for the management of Temple which is referred to as '' Bruce's Code''.
The 7th Nizam
The Nizams were the rulers of Hyderabad from the 18th through the 20th century. Nizam of Hyderabad (Niẓām ul-Mulk, also known as Asaf Jah) was the title of the monarch of the Hyderabad State ( divided between the state of Telangana, Mar ...
of Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River, in the northern part of Southern Indi ...
, Mir Osman Ali Khan
Mir Osman Ali Khan, Asaf Jah VII (5 or 6 April 1886 — 24 February 1967), was the last Nizam (ruler) of the Princely State of Hyderabad, the largest princely state in British India. He ascended the throne on 29 August 1911, at the age o ...
donated 8,000 to the temple.
In 1843, the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sou ...
transferred the Administration of Temple along with other Temples in Tirupati to Mahant
Mahant () is a religious superior, in particular the chief of a temple or the head of a monastery in Indian religions.
James Mallinson, one of the few westerners to be named as a mahant, describes the position of a mahant as a combination of a ...
s of Hathiramji Muth, who acted as Vicaranakartas. It was under the rule of Mahants for six generations until 1933 when Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams
Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams (TTD) is an independent trust which manages the temples including the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple in Andhra Pradesh. The trust oversees the operations and finances of the richest and the most visited religious cen ...
was formed as a result of the TTD Act in 1933. The Act of 1933 was superseded by Madras Hindu Religious and Charitable Endowment Act of 1951. Again in 1966, the temple was placed under direct control of Andhra pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
State Endowments Department, with Andhra Pradesh Charitable and Hindu Religious Institutions and Endowments act. In 1979, act of 1966 was rolled back with new Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams act, where temple administration was vested to a committee consisting of Executive officer, Chairman and two other members nominated by Government of Andhra Pradesh
Government of Andhra Pradesh, abbreviated as, GOAP, or, Andhra Government, is the subnational government for the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is an elected government with 175 MLAs elected to the Legislative Assembly of Andhra Pradesh fo ...
.
The temple is run by body Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams
Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams (TTD) is an independent trust which manages the temples including the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple in Andhra Pradesh. The trust oversees the operations and finances of the richest and the most visited religious cen ...
(TTD) which is under control of Andhra Pradesh Government. The head of TTD is appointed by Andhra Pradesh Government. The revenue from this shrine is used by Andhra Pradesh government.
The temple bears as many as 640 inscriptions in Kannada
Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native s ...
, Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
, Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
** Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, na ...
, Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of India
*Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Telugu language
** Telugu (Unicode block), a block of Telugu characters in Unicode
...
languages. There is a unique collection of about 3000 copper plates on which the Telugu Sankirtanas of Tallapaka Annamacharya and his descendants are inscribed. This collection forms a valuable source of material for a historical linguist in Telugu apart from its importance to musicologists.
Temple administration
Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams
Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams (TTD) is an independent trust which manages the temples including the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple in Andhra Pradesh. The trust oversees the operations and finances of the richest and the most visited religious cen ...
(TTD) is the trust board which oversees and manages the operations of Tirumala Venkateswara Temple. It is operated by a Board of Trustees that has increased in size from five (1951) to eighteen (2015) through the adoption of Acts. The daily operation and management of TTD is the responsibility of an executive officer, who is appointed by the Government of Andhra Pradesh
Government of Andhra Pradesh, abbreviated as, GOAP, or, Andhra Government, is the subnational government for the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is an elected government with 175 MLAs elected to the Legislative Assembly of Andhra Pradesh fo ...
.
The temple attracts approximately 75,000 pilgrims every day. The annual budget, estimated at INR 2530.10 crores for the financial year 2015–16, runs charitable trusts whose funds are derived from the budget and donations from the devotees. The annual income is estimated at INR 10 billion in 2008. Most of its income is derived from the donations in SriVari Hundi. Devotees donate to the TTD, which runs into millions of rupees. TTD, the organisation running the welfare of the temple, runs various charitable trusts, whose funds are derived from the budget and donations from the devotees.
Architecture
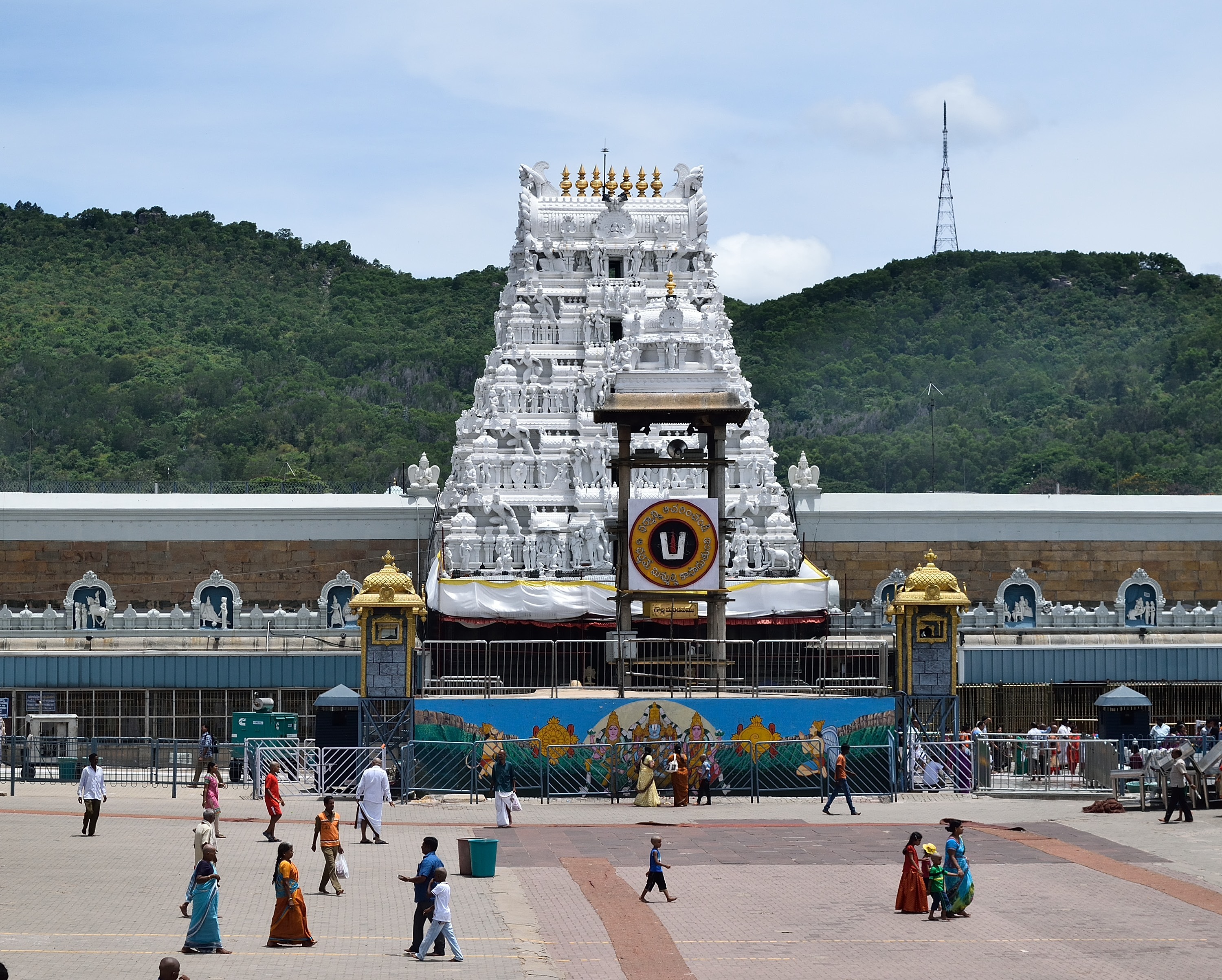
 ;Dwarams and Prakarams
There are three Dwarams (entrances) which lead to ''
;Dwarams and Prakarams
There are three Dwarams (entrances) which lead to ''Garbhagriha
A ''garbhagriha'' or ''sannidhanam'' is the ''sanctum sanctorum'', the innermost sanctuary of a Hindu and Jain temples where resides the '' murti'' (idol or icon) of the primary deity of the temple. In Jainism, the main deity is known as the ' ...
'' from outside. ''Mahadwaram,'' also known as ''padikavali'', is the first entrance which is provided through ''Mahaprakaram'' (outer compound wall). A 50 feet, five storied Gopuram
A ''gopuram'' or ''gopura'' ( Tamil: கோபுரம், Malayalam: ഗോപുരം, Kannada: ಗೋಪುರ, Telugu: గోపురం) is a monumental entrance tower, usually ornate, at the entrance of a Hindu temple, in the Sout ...
(Temple tower) is constructed over this Mahadwaram with seven Kalasam
A kalasam is a finial typically placed atop the towers of Hindu temples. These kalasams, in the form of an inverted pot with a point facing the sky, are prominent elements of temple architecture. Periodic renewal of the temple is called ''samprok ...
s at its apex. ''Vendivakili'' (Silver Entrance), also known as ''Nadimipadikavali'', is the second entrance and is provided through ''SampangiPrakaram'' (Inner compound wall). A three storied Gopuram is constructed over Vendivakili with seven Kalasams at its apex. ''Bangaruvakili'' (Golden Entrance) is the third entrance which leads into ''Garbhagriha
A ''garbhagriha'' or ''sannidhanam'' is the ''sanctum sanctorum'', the innermost sanctuary of a Hindu and Jain temples where resides the '' murti'' (idol or icon) of the primary deity of the temple. In Jainism, the main deity is known as the ' ...
''. There are two tall copper images of the Dvarapala
A Dvarapala or Dvarapalaka (Sanskrit, "door guard"; IAST: ' ) is a door or gate guardian often portrayed as a warrior or fearsome giant, usually armed with a weapon - the most common being the ''gada'' (mace). The dvarapala statue is a wide ...
kas Jaya-Vijaya
In Hinduism, Jaya and Vijaya are the two '' dvarapalakas'' (gatekeepers) of the abode of Vishnu, known as Vaikuntha (meaning ''place of eternal bliss''). Due to a curse by the four Kumaras, they were forced to undergo multiple births as mortals ...
on either side of this door. The thick wooden door is covered with gold gilt plates depicting the Dasavathaaram
''Dasavathaaram'' () is a 2008 Indian Tamil-language science fiction action film directed by K. S. Ravikumar. It stars Kamal Haasan, who also wrote the script, in ten distinct roles. Asin appears in two roles and Mallika Sherawat plays a subs ...
of Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" withi ...
.
;Pradakshinams
Circumambulation around Sanctum sanctorum
The Latin phrase ''sanctum sanctorum'' is a translation of the Hebrew term ''קֹדֶשׁ הַקֳּדָשִׁים'' (Qṓḏeš HaQŏḏāšîm), literally meaning Holy of Holies, which generally refers in Latin texts to the holiest place of t ...
in the temple or deities is called Pradakshinam. There are two circumbulation paths in the temple. The first one is area between ''Mahaprakaram'' and ''sampangiprakaram''. This path known as ''Sampangipradakshinam'' has many Mandapa
A mandapa or mantapa () is a pillared hall or pavilion for public rituals in Indian architecture, especially featured in Hindu temple architecture.
Mandapas are described as "open" or "closed" depending on whether they have walls. In temples ...
s, Dwajasthambam
The dhvajastambha (ध्वजस्तम्भ) refers to the flagstaff erected in front of the ''mukhamaṇḍapa'' (front pavilion) of a Hindu temple. The ''dhvajastambha'' is usually built within the temple walls (''prākāra''). They are ...
, Balipeetam, Kshetrapalika sila, prasadam distribution area etc. The ''Vimanapradakhinam'' is the second ''pradakshinam'', which circumbulates '' Ananda Nilayam Vimanam''. This path has sub-shrines dedicted to Varadaraja and Yoga Narasimha, Potu (main kitchen), Bangaru Bavi (golden well), Ankurarpana Mandapam, Yagasala, Nanala (coins and Notla (Paper notes) Parkamani, Almyrah of Sandal paste (Chandanapu ara), cell of records, Sannidhi Bhashyakarulu, Lords's hundi and the seat of Vishvaksena
Vishvaksena ()Nayar p. 103 or Vishwaksena, is the commander-in-chief of the army of the Hindu deity Vishnu, additionally serving as a gatekeeper and chamberlain of his celestial abode of Vaikuntha. As the embodiment of the tantras, Vishvaksena ...
.
;Anandanilayam vimanam and Garbhagriha
''Garbhagriha
A ''garbhagriha'' or ''sannidhanam'' is the ''sanctum sanctorum'', the innermost sanctuary of a Hindu and Jain temples where resides the '' murti'' (idol or icon) of the primary deity of the temple. In Jainism, the main deity is known as the ' ...
'' is the Sanctum sanctorum
The Latin phrase ''sanctum sanctorum'' is a translation of the Hebrew term ''קֹדֶשׁ הַקֳּדָשִׁים'' (Qṓḏeš HaQŏḏāšîm), literally meaning Holy of Holies, which generally refers in Latin texts to the holiest place of t ...
where the presiding deity Venkateswara
Venkateswara, also known by various other names, is a form of the Hindu god Vishnu. Venkateswara is the presiding deity of the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, located in Tirupati, Sri Balaji District, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Etymology
Venkat ...
resides along with other small deities. Golden Entrance leads to ''Garbhagriha''. There are two more doors in between ''Bangaruvakili'' and ''Garbhagriha''. The deity is in a standing posture with four hands in different postures - one in ''varada'' posture, one placed over thigh and other two holding '' Shanka'' and ''Sudarshana Chakra
Sudarshana Chakra (Sanskrit: सुदर्शन चक्र, lit. "disc of auspicious vision", IAST: Sudarśana Chakra) is a spinning, celestial discus with 108 serrated edges, attributed to Vishnu and Krishna in the Hindu scriptures. The Su ...
''. The deity is decorated with precious ornaments. The deity bears Goddess Lakshmi
Lakshmi (; , sometimes spelled Laxmi, ), also known as Shri (, ), is one of the principal goddesses in Hinduism. She is the goddess of wealth, fortune, power, beauty, fertility and prosperity, and associated with '' Maya'' ("Illusion"). A ...
on the right chest and Goddess Padmavathi on the left. Pilgrims are not allowed to enter the ''Garbhagriha'' (beyond ''Kulasekharapadi'' (path).
'' Ananda Nilayam Vimanam'' is the main Gopuram constructed over ''Garbhagriha''. This is a three storied Gopuram and has single Kalasam
A kalasam is a finial typically placed atop the towers of Hindu temples. These kalasams, in the form of an inverted pot with a point facing the sky, are prominent elements of temple architecture. Periodic renewal of the temple is called ''samprok ...
at its apex. It is covered with gilt copper plates and covered with a golden vase. There are many deities of gods carved over this Gopuram. On this Gopuram, there is a deity of Venkateswara known as ''"Vimana Venkateswara"'' which is believed to be exact replica of deity inside ''Garbhagriha''.
Deities in the temple
Venkateswara
Venkateswara, also known by various other names, is a form of the Hindu god Vishnu. Venkateswara is the presiding deity of the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, located in Tirupati, Sri Balaji District, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Etymology
Venkat ...
, an avatar
Avatar (, ; ), is a concept within Hinduism that in Sanskrit literally means "descent". It signifies the material appearance or incarnation of a powerful deity, goddess or spirit on Earth. The relative verb to "alight, to make one's appear ...
of Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" withi ...
is the presiding deity of the temple. It is believed that the Moolavirat is Swayambhu (self manifested).

Pancha berams
As per Vaikhanasa Agamas, Venkateswara is represented by fivedeities
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greater ...
(berams) including the Moolavirat which are together referred to as Pancha beramulu (Pancha means five; Beram means Deity). The five deities are Dhruva Beram (Moolavar), Kautuka Beram, Snapana Beram, Utsava Beram, Bali Beram. All the pancha berams are placed in the Garbha griha under Ananda Nilayam Vimanam.
#Moolavirat or Dhruva Beram- In the centre of Garbha griha
A ''garbhagriha'' or ''sannidhanam'' is the ''sanctum sanctorum'', the innermost sanctuary of a Hindu and Jain temples where resides the ''murti'' (idol or icon) of the primary deity of the temple. In Jainism, the main deity is known as the ''M ...
, under the Ananda Nilayam Vimana, the Moolavirat of Venkateswara is seen in standing posture on lotus base, with four arms, two holding Shanka and Chakra and one in Varada posture and other in Kati posture. This deity is considered the main source of energy for the temple and adorns with the Vaishnavite nama and jewels including vajra kiritam (diamond crown), Makarakundalas, Nagabharana, Makara Kanti, Saligrama haram, Lakshmi haram. Venkateswara's consort, Lakshmi
Lakshmi (; , sometimes spelled Laxmi, ), also known as Shri (, ), is one of the principal goddesses in Hinduism. She is the goddess of wealth, fortune, power, beauty, fertility and prosperity, and associated with '' Maya'' ("Illusion"). A ...
stays on the chest of the Moolavirat as Vyuha Lakshmi.
#Bhoga Srinivasa
Bhoga Srinivasa is a silver deity that is a near-replica of the main deity (''Dhruva Bera'') of the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple in Tirumala, Andhra Pradesh, India. The deity is also known as ''Manavalapperumal'' or ''Kautuka Bera''. The deity ...
or Kautuka Beram -- This is a small one-foot (0.3 m) silver deity which was given to the temple in 614 AD by the Pallava
The Pallava dynasty existed from 275 CE to 897 CE, ruling a significant portion of the Deccan, also known as Tondaimandalam. The dynasty rose to prominence after the downfall of the Satavahana dynasty, with whom they had formerly served as f ...
Queen Samavai for conducting festivals. Bhoga Srinivasa is always placed near the left foot of Moolavirat and is always connected to the main deity by a holy ''Sambandha Kroocha''.This deity receives many daily sevas(pleasures) on behalf of Moolavar and hence known as Bhoga Srinivasa(Telugu: Bhoga means Pleasure). This deity receives Ekanthaseva daily and SahasraKalasabhisheka on Wednesdays.
# Ugra Srinivasa or Snapana Beram - This deity represents the fearsome (Telugu: Ugra means angry) aspect of Lord Venkateswara. This deity was the main processional deity until 1330 CE when it was replaced by the Malayappa Swami deity. Ugra Srinivasa remains inside the sanctum sanctorum and comes out on a procession only one day in a year: on ''Kaishika Dwadasi,'' before the sunrise. This deity receives daily ''abhishekam
Abhisheka () means "bathing of the divinity to whom worship is offered." It is a religious rite or method of prayer in which a devotee pours a liquid offering on an image or murti of a God or Goddess. Abhisheka is common to Indian religions s ...
'' on behalf of Moolavirat, giving the name Snapana Beram(Sanskrit: Snapana means cleansing)
#Malayappa Swami
Malayappa Swami is the current ''utsava murti'' (procession deity) in the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, Tirumala. Malayappa Swami is worshipped during religious ceremonies and processions wherein it would be inappropriate to use the main deity (f ...
or Utsava Beram - Malayappa is the processional deity (Utsava beram) of the Temple and is always flanked by the deities of his consorts Sridevi
Shree Amma Yanger Ayyappan (13 August 1963 – 24 February 2018), professionally credited with her stage name Sridevi, was an Indian actress who worked in Telugu, Tamil, Hindi, Malayalam, and Kannada language films. Cited as the "First Fem ...
and Bhudevi
Bhumi ( sa, भूमि, Bhūmi), also known as Bhudevi and Vasundhara, is a Hindu goddess who is the personification of the Earth. She is a consort of the god Vishnu. According to Vaishnava tradition, she is the second aspect of Vishnu's cons ...
. This deity receives all festivals like Brahmotsavams, Kalyanotsavam, Dolotsavam, Vasanthotsavam, Sahasra deepalankarana seva, Padmavati parinyotsavams, pushpapallaki, Anivara asthanam, Ugadi asthanam etc.
#Koluvu Srinivasa
Koluvu Srinivasa is an idol of Lord Venkateswara in the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, Andhra Pradesh. This silver idol that resembles the Tirumala Dhruva Bera, main deity represents the presiding officer for all activities and rituals in the temp ...
or Bali Beram- Koluvu Srinivasa represents Bali Beram. Koluvu Srinivasa is regarded as the guardian deity of the temple that presides over its financial and economic affairs. Daily Koluvu seva(Telugu: Koluvu means engaged in) is held in the morning, during which, the previous day's offerings, income, expenditures are notified to this deity, with a presentation of accounts. Panchanga sravanam also is held at the same time during which that particular days Tithi
In Vedic timekeeping, a ''tithi'' is a uration of two faces of moon that is observed from earth known as ''milа̄lyа̄'' (𑐩𑐶𑐮𑐵𑐮𑑂𑐫𑐵𑑅, मिलाल्याः) in Nepal Bhasa, or the time it takes for the longi ...
, sunrise and sunset time, nakshatra are notified to the Venkateswara.
Other Murtis
Along with Pancha berams, the garbha griha also hosts thepanchaloha
''Panchaloha'' ( sa, पञ्चलोह), also called ''Pañcadhātu'' ( sa, पञ्चधातु, lit=five metals), is a term for traditional five-metal alloys of sacred significance, used for making Hindu temple ''murti'' and jewelry.
...
deities of Sita
Sita (; ) also called as Janaki and Vaidehi is a Hindu goddess and the female protagonist of the Hindu epic, ''Ramayana''. She is the consort of Rama, the avatar of the god Vishnu, and is regarded as a form of Vishnu's consort, Lakshmi. She ...
, Rama
Rama (; ), Ram, Raman or Ramar, also known as Ramachandra (; , ), is a major deity in Hinduism. He is the seventh and one of the most popular '' avatars'' of Vishnu. In Rama-centric traditions of Hinduism, he is considered the Supreme Bei ...
, Lakshmana
Lakshmana ( sa, लक्ष्मण, lit=the fortunate one, translit=Lakṣmaṇa), also spelled as Laxmana, is the younger brother of Rama and his loyalist in the Hindu epic '' Ramayana''. He bears the epithets of Saumitra () and Ramanuja ( ...
, Rukmini
Rukmini ( sa, रुक्मिणी, , ) is a Hindu goddess and the first queen and chief wife of Krishna. In Vaishnava tradition, she is described as Krishna's principal queen in Dvaraka, as well as the chief of his wives. She is an in ...
, Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is on ...
, Chakratalvar. The temple hosts the deities of Garuda
Garuda ( Sanskrit: ; Pāli: ; Vedic Sanskrit: गरुळ Garuḷa) is a Hindu demigod and divine creature mentioned in the Hindu, Buddhist and Jain faiths. He is primarily depicted as the mount (''vahana'') of the Hindu god Vishnu. Garu ...
(Vishnu's vehicle), Narasimha
Narasimha ( sa, नरसिंह, lit=man-lion, ), sometimes rendered Narasingha, is the fourth avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. He is regarded to have incarnated in the form of a part-lion, part-man being to slay Hiranyakashipu, to end rel ...
, Varadaraja, Kubera
Kubera ( sa, कुबेर, translit=Kuberā) also known as Kuvera, Kuber and Kuberan, is the god of wealth, and the god-king of the semi-divine yakshas in Hinduism. He is regarded as the regent of the north (''Dikpala''), and a protecto ...
, Hanuman
Hanuman (; sa, हनुमान, ), also called Anjaneya (), is a Hindu god and a divine '' vanara'' companion of the god Rama. Hanuman is one of the central characters of the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. He is an ardent devotee of Rama and on ...
in their respective sub-shrines. The temple also host the deities of Shesha
Shesha ( Sanskrit: शेष; ) , also known as Sheshanaga ( Sanskrit: शेषनाग; ) or Adishesha (), is a serpentine demigod (Naga) and Nagaraja (King of all serpents), as well as a primordial being of creation in Hinduism. In the ...
(Vishnu's serpent), Viswaksena, Sugriva
''This character is about the vanara, in the Ramayana.''
Sugriva ( sa, सुग्रीव, , ) is a character In the ancient Indian epic Ramayana. He is the younger brother of Vali, whom he succeeded as ruler of the vanara kingdom of Kis ...
, Ramanuja
Ramanuja (Middle Tamil: Rāmāṉujam; Classical Sanskrit: Rāmanuja; 1017 CE – 1137 CE; ; ), also known as Ramanujacharya, was an Indian Hindu philosopher, guru and a social reformer. He is noted to be one of the most important exponents ...
. Vimana Venkateswara is the exact replica icon of Venkateswara carved on the Ananda Nilayam Viamana's second tier north west corner.
Worship
Puja
The temple follows ''" Vaikhanasa Agama"'' tradition of worship, which is believed to be revealed by Sage Vikhanasa and is propagated by his disciplesAtri
Atri ( sa, अत्रि) or Attri is a Vedic sage, who is credited with composing numerous hymns to Agni, Indra, and other Vedic deities of Hinduism. Atri is one of the Saptarishi (seven great Vedic sages) in the Hindu tradition, and the on ...
, Bhrigu
Bhrigu ( sa, भृगु, ) was a rishi in Hinduism. He was one of the seven great sages, the Saptarshis, one of the many Prajapatis (the facilitators of Creation) created by Brahma. The first compiler of predictive astrology, and also the ...
, Marichi
Marichi ( sa, मरीचि, Marīci, lit=ray of light) or Mareechi or Marishi is the mind-born son of Brahma, and one of the Saptarishi in Hindu mythology. He is also the father of Kashyapa, and the grandfather of the ''devas'' and the ...
, Kasyapa
Kashyapa ( sa, कश्यप}, ) is a revered Vedic sage of Hinduism., Quote: "Kasyapa (Rudra),(Vedic Seer)..." He is one of the Saptarishis, the seven ancient sages of the ''Rigveda''. Kashyapa is the most ancient and venerated rishi, al ...
. Vaikhanasa is one of the principal traditions of Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
and primarily worships Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" withi ...
(and his associated Avatars) as the Supreme God. This ancient texts recommends six times a day puja (worship) for Vishnu, of which minimum one puja is mandatory. Rituals are classified as daily, weekly and periodical. The daily sevas in Temple (in order of occurrence) include Suprabhata Seva, Thomala Seva, Archana, Kalyanotsavam, Dolotsavam (Unjal Seva), Arjita Brahmotsavam, Arjita Vasantotsavam, Sahasra Dipalankarana Seva, Ekanta Seva. Weekly sevas of the Temple include Vishesha Pooja on Monday, Ashtadala Pada Padmaradhana on Tuesday, Sahasra Kalasabhishekam on Wednesday, Tiruppavada Seva on Thursday, Abhishekam and Nijapada Darshanam on Friday. There are no weekly sevas on Saturday and Sunday. Periodical rituals include Jyesthabhishekam, Aaniwara Asthanam, Pavithrotsavam, Koil Alwar Tirumanjanam.
Naivedhyam
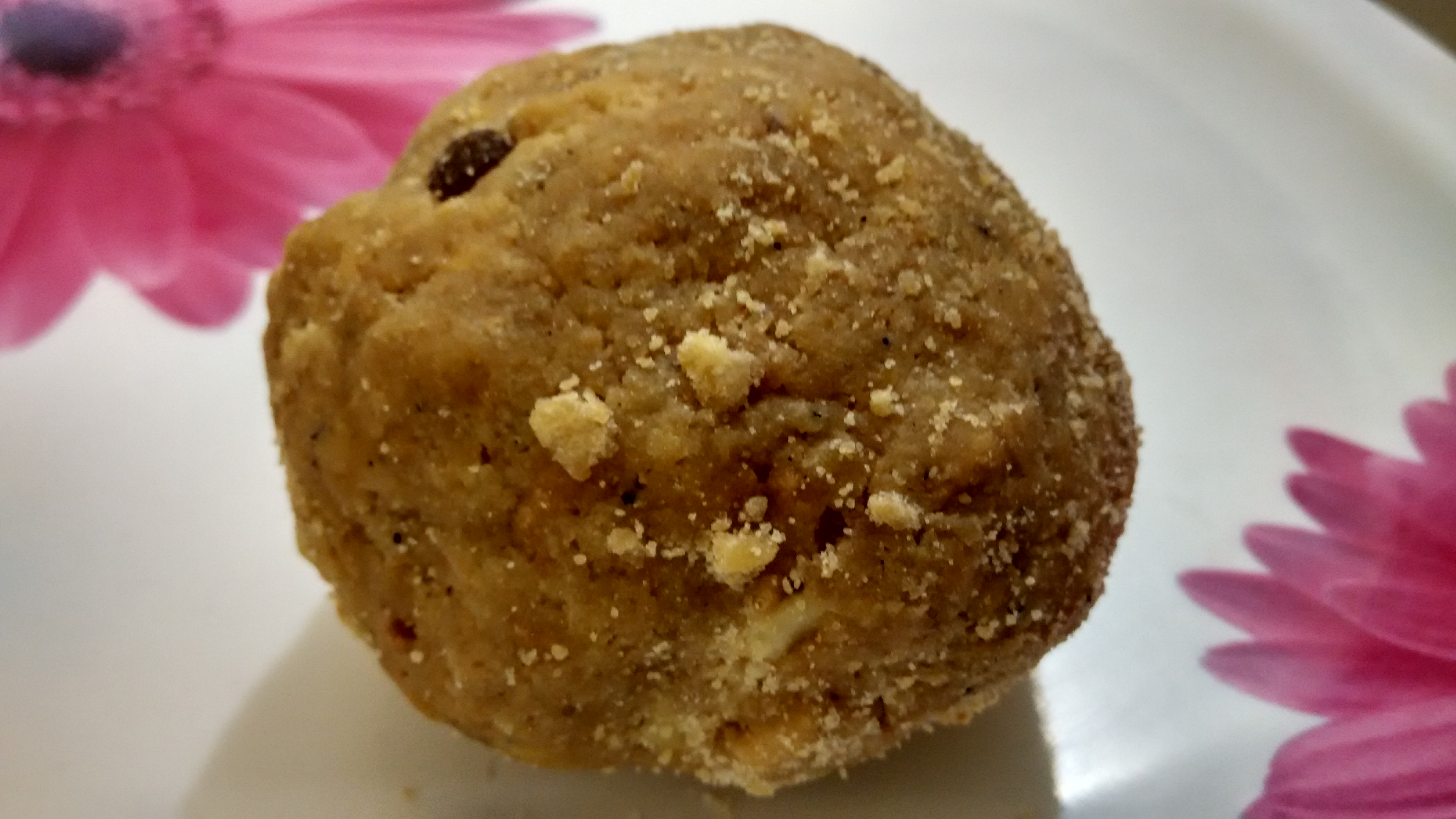
 The world-famous "''
The world-famous "''Tirupati Laddu
Tirupati Laddu or SriVari Laddu is the laddu sweet offered as Naivedhyam to Venkateswara at Tirumala Venkateswara Temple in Tirupati, Tirupati district, Andhra Pradesh, India. The laddu is given as prasadam to devotees after having the darshan i ...
''" is given at Tirumala Temple as prasadam. Tirupati Laddu had got Geographical indication
A geographical indication (GI) is a name or sign used on products which corresponds to a specific geographical location or origin (e.g., a town, region, or country). The use of a geographical indication, as an indication of the product's source, ...
tag which entitles only Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams
Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams (TTD) is an independent trust which manages the temples including the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple in Andhra Pradesh. The trust oversees the operations and finances of the richest and the most visited religious cen ...
to make or sell it. Many other prasadams are also offered to Venkateswara and they are classified as Anna-prasadams and Panyarams. Annaprasadams include chakerapongal (sweet), Pulihora (tamarind rice), miryala pongal, kadambham, daddojanam (curd rice). Panyarams include laddu, vada, Dosa
Dosa may refer to:
People
* Bogoljub Mitić Đoša, Serbian actor
* Csaba Dosa (born 1951), Romanian athlete
* Dosa ben Harkinas
* Dosa ben Saadia (935 - 1018), Talmudic scholar and philosopher
* Dosa or Dossa Júnior
* Edward Dosa-Wea Neufv ...
, Appam
Appam is a type of thin pancake originating from South India. It is made with fermented rice batter and coconut milk, traditionally cooked in an ''appachatti'', a deep pan similar in shape to a wok. It is common in the cusine of Kerala and Tam ...
, jilebi, muruku
Murukku (Malayalam – മുറുക്ക്, Tamil – முறுக்கு) is a savoury, crunchy snack originating from the Indian subcontinent. The name ''murukku'' derives from the Tamil word for "twisted", which refers to its shape. ...
, poli, payasam
Kheer, also known as payasam, is a sweet dish and a type of wet pudding popular in the Indian subcontinent, usually made by boiling milk, sugar or jaggery, and rice, although rice may be substituted with one of the following: daals, bulgur w ...
. Free meals are given daily to the pilgrims. On Thursdays, the Tiruppavada seva is conducted, where huge quantity of pulihora is offered to Venkateswara by heaping up into a pyramidal shape in Tirummani mandapam (ghanta mandapam).
Darshan
To manage the huge number of Devotees visiting the temple, Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanam constructed two Vaikuntam Queue Complexes: one in the year 1983 and the other in the year 2000. Vaikuntam Queue complexes have rooms where Devotees can sit and wait until their turn for Darshan. According to tradition, it is important for a devotee to have darshan of Bhuvaraha swamy temple lying on the northern banks of Swami Pushkarini before having Darshan of Venkateswara in the main temple. Recently, the administration introduced a separate queue for pedestrian pilgrims. Free but limited number of biometric tokens are issued for the pilgrims to access this special queue. Tokens are provided on a first-come, first-served basis. The pilgrims can worshipVenkateswara
Venkateswara, also known by various other names, is a form of the Hindu god Vishnu. Venkateswara is the presiding deity of the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, located in Tirupati, Sri Balaji District, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Etymology
Venkat ...
on the allotted time slots issued in the token. There are two entry points for the foot-path pilgrims: Alipiri Mettu and Srivari Mettu. Alipiri Mettu is open round the clock, whereas Srivari Mettu is open from 6am - 6pm.
Hair tonsuring
Many devotees have their head tonsured as "Mokku", an offering to God. The daily amount of hair collected is over a ton. The hair is collected and is sold internationally creating a substantial profit for the temple. As per legend, when Venkateswara was hit on his head by a cowherd, a small portion of his scalp became bald. This was noticed by Neela Devi, aGandharva
A gandharva () is a member of a class of celestial beings in Dharmic religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism, whose males are divine performers such as musicians and singers, and the females are divine dancers. In Hinduism, they are ...
princess. Immediately, she cut a portion of her hair and, with her magic, implanted it on his scalp. Venkateswara noticed her sacrifice. As hair is a beautiful asset of the female form, he promised her that all his devotees who come to his abode would offer their hair to him, and she would be the recipient of all the hair received. Hence, it is believed that hair offered by the devotees is accepted by Neela Devi. The hill, Neeladri, one of the seven hills, is named after her. Traditionally the barbers employed to do the tonsuring were male and from the Nayee caste and this caused some discrimination and failed to resolve the requests from women that they would like a female barber. A protest led by Kagganapalli Radha Devi overturned the objections and temple agreed to appoint women barbers. Devi was recognised by Andhra Pradesh in 2017 and with an award of the Nari Shakti Puraskar
The Nari Shakti Puraskar is an annual award given by the Ministry of Women and Child Development of the Government of India to individual women or to institutions that work towards the cause of women empowerment. It is the highest civilian hon ...
by the President of India in 2019.
Hundi (donation pot)
In remembrance of this, devotees go to Tirupati to donate money in Venkateswara's hundi (donation pot) so that he can pay it back to Kubera. The hundi collections go as high as 22.5 million INR a day.Thulabaram
In the Thulabaram ritual, a devotee sits on a pan of a weighing balance and the other pan is filled with materials greater than the weight of the devotee. Devotees usually offer sugar, jaggery, tulsi leaves, banana, gold, coins. This is mostly performed with newborn babies or children.Festivals
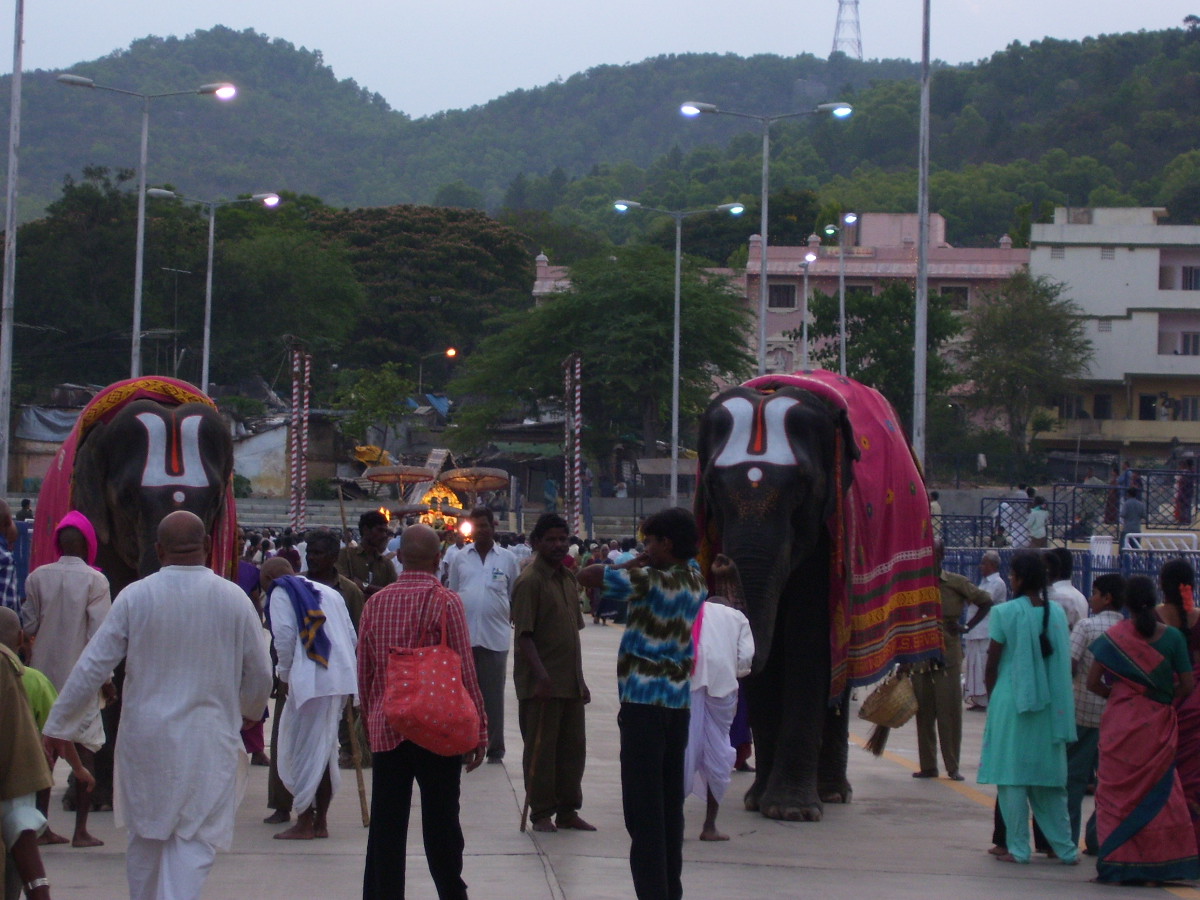 In the Venkateswara Temple over 433 festivals are being observed in 365 days of a year suiting the title "Nitya Kalyanam Paccha Toranam" where every day is a festival.
Sri Venkateswara Brahmotsavams, a nine-day event, which is celebrated every year during month of October, is the major event of Venkateswara Temple. During brahmotsavams the processional deity Malayappa along with his consorts SriDevi and BhuDevi, is taken in a procession in four mada streets around the temple on different vahanams. Vahanams include Dwajarohanam, Pedda Sesha Vahanam, Chinna Sesha Vahanam, Hamsa Vahanam, Simha Vahanam, Muthaypu pandiri Vahanam, Kalpavriksha Vahanam, Sarva Bhoopala Vahanam, Mohini Avataram, Garuda Vahanam, Hanumantha Vahanam, Swarna Rathotsavam (Golden Chariot), Gajavahanam, Rathotsavam (Chariot), Ashwa Vahanam, and Chakra Snanam. During Brahmotsavams, the temple will witness lakhs of devotees particularly on Garuda vahanam.
In the Venkateswara Temple over 433 festivals are being observed in 365 days of a year suiting the title "Nitya Kalyanam Paccha Toranam" where every day is a festival.
Sri Venkateswara Brahmotsavams, a nine-day event, which is celebrated every year during month of October, is the major event of Venkateswara Temple. During brahmotsavams the processional deity Malayappa along with his consorts SriDevi and BhuDevi, is taken in a procession in four mada streets around the temple on different vahanams. Vahanams include Dwajarohanam, Pedda Sesha Vahanam, Chinna Sesha Vahanam, Hamsa Vahanam, Simha Vahanam, Muthaypu pandiri Vahanam, Kalpavriksha Vahanam, Sarva Bhoopala Vahanam, Mohini Avataram, Garuda Vahanam, Hanumantha Vahanam, Swarna Rathotsavam (Golden Chariot), Gajavahanam, Rathotsavam (Chariot), Ashwa Vahanam, and Chakra Snanam. During Brahmotsavams, the temple will witness lakhs of devotees particularly on Garuda vahanam. Vaikunta Ekadasi
Vaikuntha Ekadashi () is a Hindu occasion and festival. It is primarily observed by Vaishnavas, who regard it to be a special Ekādaśī. It coincides with '' Mokṣadā Ekādaśī'' or Putrada Ekādaśī. It is observed on the 11th lunar da ...
, the day on which it is believed that Vaikunta Dwarams will be opened and the most important Vasihnavite festival, is celebrated with grandeur in Tirumala. The Tirumala Venkateswara Temple will be flooded with devotees on a single day with numbers reaching up to 150,000, to have a darshan of Venkateswara
Venkateswara, also known by various other names, is a form of the Hindu god Vishnu. Venkateswara is the presiding deity of the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, located in Tirupati, Sri Balaji District, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Etymology
Venkat ...
through special entrance which encircles inner sanctum called "Vaikunta Dwaram". Rathasapthami is another festival, celebrated during February, when Venkateswara's processional deity ( Malayappa) is taken in a procession around the temple on seven different vahana
''Vahana'' ( sa, वाहन, or animal vehicle, literally "that which carries, that which pulls") denotes the being, typically an animal or mythical, a particular Hindu God is said to use as a vehicle. In this capacity, the vahana is often ...
ms starting from early morning to late night. The other annual festivals include Rama Navami
Rama Navami () is a Hindu festival that celebrates the birthday of Rama, the seventh avatar of the deity Vishnu. people from different parts of Jharkhand attended the world famous international Hazaribagh procession organized in the city every ...
, Janmashtami
Krishna Janmashtami , also known simply as Krishnashtami, Janmashtami, or Gokulashtami, is an annual Hindu festival that celebrates the birth of Krishna, the eighth avatar of Vishnu. According to the Hindu lunisolar calendar, it is observed ...
, Ugadi
Ugadi or Yugadi, also known as Samvatsarādi (), is New Year's Day according to the Hindu calendar and is celebrated in the states of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Karnataka in India. It is festively observed in these regions on the first ...
, Teppotsavam (Float Festival), Sri Padmavati Parinayotsavams, Pushpa yagam, Pushpa pallaki, Vasanthotsavam (spring festival) conducted in March–April, were celebrated with great splendor.
Songs and hymns
Venkateswara Suprabhatam is the first and pre-dawn seva performed toVenkateswara
Venkateswara, also known by various other names, is a form of the Hindu god Vishnu. Venkateswara is the presiding deity of the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, located in Tirupati, Sri Balaji District, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Etymology
Venkat ...
at Sayana Mandapam inside sanctum sanctorum of Tirumala Temple. 'Suprabhatam' is a Sanskrit term which literally means 'Good Morning' and is meant to wake up the Lord from His celestial sleep. Venkateswara Suprabhatam hymns were composed by Prathivadhi Bhayankaram Annangaracharya
Prathivadhi Bhayankaram Aṇṇan was a Sri Vaishnava acharya, Tamil and Sanskrit scholar, and the composer of the popular Venkateswara Suprabhatam.
Born Hasthigirinathar Aṇṇan in the year 1361, he was one of the prominent disciples o ...
during 13th century and consists of 70 slokas in four parts including Suprabhatam(29), Stotram(11), Prapatti(14) and Mangalasasanam(16). The thirteenth sloka of Venkateswara Suprabhatam is as follows:
Tallapaka Annamacharya (Annamayya), the poet saint of 14th century, one of the greatest Telugu poets and a great devotee of Venkateswara, had sung 32000 songs in praise of Venkateswara. All his songs which are in Telugu and Sanskrit, are referred to as Sankirtanas and are classified as Sringara Sankirtanalu and Adhyatma Sankirtanalu.Devanagari Devanagari ( ; , , Sanskrit pronunciation: ), also called Nagari (),Kathleen Kuiper (2010), The Culture of India, New York: The Rosen Publishing Group, , page 83 is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental writing system), based on the ...
श्रीमन्नभीष्ट-वरदाखिललोक-बन्धो
श्रीश्रीनिवास-जगदेकदयैकसिन्धो ।
श्रीदेवतागृहभुजान्तर-दिव्यमूर्ते
श्रीवेङ्कटाचलपते तव सुप्रभातम् ॥
Telugu script
శ్రీమన్నాభీష్ట -వరదఖిలలోక -బంధో
శ్రీ శ్రీనివాస-జగదేకదయైకసింధో ,
శ్రీదేవతాగృహభుజాన్తర-దివ్యమూర్తే
శ్రీవెంకటాచలపతే తవ సుప్రభాతం, ,
IAST The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that emerged during ...
śrīmannabhīṣṭavaradākhilalokabandho
śrīśrīnivāsajagadekadayaikasindho ।
śrīdevatāgṛhabhujāntaradivyamūrte
śrīveṅkaṭācalapate tava suprabhātam ॥
The Seven Hills
The temple is located on seven hills. The presiding deity is also referred to as Sapthagirisha or Lord of Seven hills. It is believed that seven hills, also referred to as Saptagiri, represent the seven hoods of Adisesha. The seven hills are as follows: *Vrushabhadri—Hill of Vrishabasura, who was killed by Srinivasa
*Anjanadri—Hill of
*Vrushabhadri—Hill of Vrishabasura, who was killed by Srinivasa
*Anjanadri—Hill of Hanuman
Hanuman (; sa, हनुमान, ), also called Anjaneya (), is a Hindu god and a divine '' vanara'' companion of the god Rama. Hanuman is one of the central characters of the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. He is an ardent devotee of Rama and on ...
.
*Neeladri—Hill of Neela Devi
*Garudadri or Garudachalam—Hill of Garuda
Garuda ( Sanskrit: ; Pāli: ; Vedic Sanskrit: गरुळ Garuḷa) is a Hindu demigod and divine creature mentioned in the Hindu, Buddhist and Jain faiths. He is primarily depicted as the mount (''vahana'') of the Hindu god Vishnu. Garu ...
, the vahana of Vishnu
*Seshadri or Seshachalam—Hill of Sesha
Shesha (Sanskrit: शेष; ) , also known as Sheshanaga (Sanskrit: शेषनाग; ) or Adishesha (), is a serpentine demigod (Naga) and Nagaraja (King of all serpents), as well as a primordial being of creation in Hinduism. In the Pura ...
, the dasa
''Dasa'' ( sa, दास, Dāsa) is a Sanskrit word found in ancient Indian texts such as the ''Rigveda'' and '' Arthasastra''. It usually means "enemy" or "servant" but ''dasa'', or ''das'', also means a " servant of God", "devotee," " votary" or ...
of Vishnu
*Narayanadri—Hill of Narayana. Srivari Padalu (footprints of Venkateswara) are located here
*Venkatadri
The Venkata hill (853 m) is part of the Seshachalam Hills, located in the Tirupati district of Andhra Pradesh, India. Also known as Venkatadri or Venkatachalam, it is one of the seven peaks of the Tirumala Hill located in the temple town of Tirum ...
—Hill of Venkateswara
Subshrines
Varadaraja Temple There is a small shrine dedicated to Varadaraja located in Vimana-pradakshinam, towards left of Vendivakili (silver entrance) while entering temple. It is not known when this deity was installed. The stone deity is sitting posture facing west. Yoga Narasimha Temple A shrine is dedicated to Narasimha in North-east corner of the Vimana-Pradakshina. The Yoga-Narasimha is seen sitting in cross-legged posture bound by yoga patta and holding Shankha and chakra in upper two hands and two lower hands in yoga mudra. Garuthmantha Temple A small shrine dedicated to Garuda the vehicle of Venkateswara is situated exactly opposite to the Bangaruvakili (Golden Entrance) ofJaya-Vijaya
In Hinduism, Jaya and Vijaya are the two '' dvarapalakas'' (gatekeepers) of the abode of Vishnu, known as Vaikuntha (meaning ''place of eternal bliss''). Due to a curse by the four Kumaras, they were forced to undergo multiple births as mortals ...
. This sub-shrine is part of Garudamandapam. The Garuthmantha deity is six feet tall and faces west looking towards Venkateswara inside Garbhagriha.
Bhuvaraha Swamy Temple
Bhuvaraha Swamy Temple is the temple dedicated to Varaha an incarnation of Vishnu. This temple is believed to be older than Venkateswara Temple. The temple lies on the Northern Banks of Swami Pushkarini. As per tradition, at first Naivedyam will be offered to Bhuvaraha Swamy before offering it to Venkateswara in main Temple. And also as per tradition, devotees should have the darshan of Bhuvaraha swamy before Venkateswara.
Bedi-Anjaneya Temple
Bedi-Anjaneya Temple is the sub-shrine dedicated to Hanuman
Hanuman (; sa, हनुमान, ), also called Anjaneya (), is a Hindu god and a divine '' vanara'' companion of the god Rama. Hanuman is one of the central characters of the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. He is an ardent devotee of Rama and on ...
. The temple lies exactly opposite to the Mahadwaram near Akhilandam (place where coconuts are offered). The deity in this temple has both of his hands handcuffed (Telugu Language
Telugu (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken by Telugu people predominantly living in the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, where it is also the official language. It is the most widely spoken ...
:Bedilu).
Vakulamatha Sannidhi
Vakulamatha is the mother of Venkateswara. There is statue dedicated to her in the main temple just ahead of Varadaraja shrine. The deity is in sitting posture. As per legend, she supervises the preparation of food that is to be offered to her son. For this reason a hole is made to the wall which separates Vakulamatha sannidhi and Srivari potu(Kitchen).
Kubera Sannidi
There is a sub-shrine dedicated to Kubera within the Vimanapradakshina. The deity lies to the right side of Garbhagriha and faces south towards preciding deity.
Ramanuja Shrine
The Shrine of Sri Ramanuja is located adjacent to the northern corridor of the Vimana Pradakshinam. It is also known as the Bhashyakara Sannidhi. The shrine was built around in the 13th century A.D.
Notable devotees
Ramanuja
Ramanuja (Middle Tamil: Rāmāṉujam; Classical Sanskrit: Rāmanuja; 1017 CE – 1137 CE; ; ), also known as Ramanujacharya, was an Indian Hindu philosopher, guru and a social reformer. He is noted to be one of the most important exponents ...
(1017–1137) the most important Acharya
In Indian religions and society, an ''acharya'' ( Sanskrit: आचार्य, IAST: ; Pali: ''ācariya'') is a preceptor and expert instructor in matters such as religion, or any other subject. An acharya is a highly learned person with a ...
of Sri Vaishnavism
Sri Vaishnavism, or the Sri Vaishnava Sampradaya, is a denomination within the Vaishnavism tradition of Hinduism. The name refers to goddess Lakshmi (also known as Sri), as well as a prefix that means "sacred, revered", and the god Vishnu, who ...
. was responsible for managing the worshipping procedures and other affairs of the Venkateswara temple. He is credited for gifting the holy conch and the discus, the weapons of Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" withi ...
during his visit. So he is considered as 'Acharya'(Guru or teacher) to the himself. He established the Pedda Jeeyar Matam. He has a sannidhi(shrine) inside the temple which was built by Sri AnanthALwAn.
 Sri Tallapaka Annamacharya (or Annamayya) (22 May 1408 – 4 April 1503) was the official songmaster of the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, and a
Sri Tallapaka Annamacharya (or Annamayya) (22 May 1408 – 4 April 1503) was the official songmaster of the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, and a Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of India
*Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Telugu language
** Telugu (Unicode block), a block of Telugu characters in Unicode
...
composer who composed around 36000 keertanas, many of which were in praise of Venkateswara, the presiding deity of the temple.
Hathiram Bhavaji was a saint from Ayodhya
Ayodhya (; ) is a city situated on the banks of holy river Saryu in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh.
Ayodhya, also known as Saketa, is an ancient city of India, the birthplace of Rama and setting of the great epic Ramayana. Ayodhy ...
who visited Tirumala
Tirumala is a spiritual town in Tirupati district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is one of the suburbs of the Tirupati urban agglomeration. The town is a part of Tirupati Urban Development Authority and located in Tirupati (rura ...
around 1500 CE on a pilgrimage and became a devotee of Venkateswara
Venkateswara, also known by various other names, is a form of the Hindu god Vishnu. Venkateswara is the presiding deity of the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, located in Tirupati, Sri Balaji District, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Etymology
Venkat ...
.
Religious significance
The temple is considered one of the eight ''Swayambhu Kshetras'' of Vishnu where presiding deity is believed to have manifested on its own. Seven other temples in the line areSrirangam Ranganathaswamy temple
Sri Ranganathaswamy Temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to Ranganatha (a form of Vishnu), located in Srirangam, Tiruchirapalli, Tamil Nadu, India. Constructed in the Hindu architectural style, the temple is glorified by Alvars in their Na ...
, Bhu Varaha Swamy temple
Bhu Varaha Swamy temple is a Hindu temple, located at Srimushnam, in the South Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Constructed in the South Indian architecture, the temple is dedicated to Varaha (Bhu Varaha Swamy), the boar-avatar of the god Vishnu and ...
, and Vanamamalai Perumal Temple in South India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union terr ...
and Saligrama in Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
, Naimisaranya
Naimisaranyam, also known as Neemsar, Nimsar or Nimkhar, and the Naimishnath Devaraja temple, is a Hindu temple dedicated to Vishnu located in the north Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is one of the ''Divya Desams'', the 108 temples of Vishnu r ...
, Pushkar
Pushkar is a city and headquarters of Pushkar tehsil in the Ajmer district in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It is situated about northwest of Ajmer and about southwest of Jaipur.Badrinath Temple in
Veṅkaṭācala-māhātmya, Skanda Purana
* {{Authority control 3rd-century establishments 3rd-century establishments in India Tirupati * Hindu pilgrimage sites in India Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams Vaishnavism Vishnu temples Buildings and structures in Tirupati
North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Cen ...
.
The temple is revered by Alvars
The Alvars ( ta, ஆழ்வார், Āḻvār, translit-std=ISO, lit=The Immersed) were the Tamil poet-saints of South India who espoused '' bhakti'' (devotion) to the Hindu preserver deity Vishnu, in their songs of longing, ecstasy, an ...
in '' Divya Prabandham''. The temple is classified as a ''Divyadesam
A Divya Desam or Vaishnava Divya Desam is one of the 108 Vishnu and Lakshmi temples that is mentioned in the works of the Alvars, the poet-saints of the Sri Vaishnava tradition.
Of the 108 temples, 105 are in India, one is in Nepal, and the las ...
'', one of the 108 Vishnu temples that are mentioned in these books. The benefits acquired by a pilgrimage to Venkatachala are mentioned in the Rig Veda and Asthadasa Puranas. In these epics, Venkateswara is described as the great bestower of boons. There are several legends associated with the manifestation of the at Tirumala.
Nearby temples
There are many ancient temples nearbyTirumala
Tirumala is a spiritual town in Tirupati district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is one of the suburbs of the Tirupati urban agglomeration. The town is a part of Tirupati Urban Development Authority and located in Tirupati (rura ...
. Sri Padamavathi Temple is temple dedicated to Padmavathi, the wife of Venkateswara
Venkateswara, also known by various other names, is a form of the Hindu god Vishnu. Venkateswara is the presiding deity of the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, located in Tirupati, Sri Balaji District, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Etymology
Venkat ...
, situated at Tiruchanur which is 5 km from Tirupati
Tirupati () is a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of the Tirupati district. The city is home to the important Hindu shrine of Tirumala Venkateswara Temple and other historic temples and is re ...
. Srikalahasteeswara Temple is the temple dedicated to Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one o ...
which represents "''Vayu''"(air) form of elements of Nature, is situated at Srikalahasti
Srikalahasti is a holy town in Tirupati district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is a municipality and the revenue division of Srikalahasti mandal & Srikalahasti revenue division. It is a part of Tirupati Urban Development Authority, ...
which is 38 km from Tirupati. Sri Varasiddhi Vinayaka Temple, situated at Kanipakam town, is a 10th-century Temple dedicated to Vinayaka
Ganesha ( sa, गणेश, ), also known as Ganapati, Vinayaka, and Pillaiyar, is one of the best-known and most worshipped deities in the Hindu pantheon and is the Supreme God in Ganapatya sect. His image is found throughout India. Hindu de ...
at 75 km from Tirupati. Other than these, temples like Govindaraja Temple, Kalyana Venkateswara Temple(Srinivasa Mangapuram), Kodandarama Temple, Kapila Theertham
Kapila Theertham is a famous Saivite Temple and Theertham, located at Tirupati in the Tirupati District of Andhra Pradesh, India. The idol is believed to be installed by Kapila Muni and hence Lord Siva here is referred to as Kapileswara. ...
are situated within the Tirupati city.
See also
*Balaji Temple, Ketkawla
Balaji Temple of Ketkawle, is copy of the real Tirumala Venkateswara Temple
Sri Venkateswara Swami Vaari Temple is a Hindu temple situated in the hill town of Tirumala at Tirupati in Tirupati district of Andhra Pradesh, India. The Temple is ...
* Sri Lakshmi Narasimha Swamy Temple, Yadadri
* Bruce's Code
* Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams
Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams (TTD) is an independent trust which manages the temples including the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple in Andhra Pradesh. The trust oversees the operations and finances of the richest and the most visited religious cen ...
Notes
References
* * * * * *External links
Veṅkaṭācala-māhātmya, Skanda Purana
* {{Authority control 3rd-century establishments 3rd-century establishments in India Tirupati * Hindu pilgrimage sites in India Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams Vaishnavism Vishnu temples Buildings and structures in Tirupati