Valence Isomer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In organic chemistry, two molecules are valence isomers when they are
Image:Benzene-2D-flat.png,
Image:Cyclooctatetraen.svg,
Image:Naphthalene-2D-Skeletal.svg,
constitutional isomer
In chemistry, a structural isomer (or constitutional isomer in the IUPAC nomenclature) of a compound is another compound whose molecule has the same number of atoms of each element, but with logically distinct bonds between them. The term meta ...
s that can interconvert through pericyclic reaction
In organic chemistry, a pericyclic reaction is the type of organic reaction wherein the transition state of the molecule has a cyclic geometry, the reaction progresses in a concerted fashion, and the bond orbitals involved in the reaction over ...
s.
Benzene
There are many valence isomers one can draw for the C6H6 formulabenzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms ...
. Some were originally proposed for benzene itself before the actual structure of benzene was known. Others were later synthesized in lab. Some have been observed to isomerize to benzene, whereas others tend to undergo other reactions instead, or isomerize by ways other than pericyclic reactions.
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms ...
Image:Historic Benzene Formulae Dewar(1867) V.1.svg, Dewar benzene
Dewar benzene (also spelled ''dewarbenzene'') or bicyclo .2.0exa-2,5-diene is a bicyclic isomer of benzene with the molecular formula C6H6. The compound is named after James Dewar who included this structure in a list of possible C6H6 structures ...
Image:Prisman2.svg, Prismane
Image:Benzvalene.png, Benzvalene
Image:Bicycloprop-2-enyl.svg, Bicyclopropenyl
Cyclooctatetraene
The valence isomers are not restricted to isomers of benzene. Valence isomers are also seen in the series (CH)8. Due to the larger number of units, the number of possible valence isomers is also greater and at least 21:Cyclooctatetraene
1,3,5,7-Cyclooctatetraene (COT) is an unsaturated derivative of cyclooctane, with the formula C8H8. It is also known as nnulene. This polyunsaturated hydrocarbon is a colorless to light yellow flammable liquid at room temperature. Because of ...
(COT)
Image:Barrelene structure.png, Barrelene
Barrelene is a bicyclic organic compound with chemical formula C8H8 and systematic name bicyclo .2.2cta-2,5,7-triene. First synthesized and described by Howard Zimmerman in 1960, the name derives from the resemblance to a barrel, with the staves ...
Image:Cuban.svg, Cubane
Cubane () is a synthetic hydrocarbon compound that consists of eight carbon atoms arranged at the corners of a cube, with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom. A solid crystalline substance, cubane is one of the Platonic hydrocarbons an ...
Image:Cuneane.png, Cuneane
Cuneane (C8H8, pentacyclo .3.0.02,4.03,7.06,8ctane) is a saturated hydrocarbon. Its name is derived from the Latin ''cuneus'', meaning a wedge. Cuneane may be produced from cubane by metal-ion-catalyzed σ-bond rearrangement. Similar reactions ar ...
Image:Semibullvalene.svg, Semibullvalene
Bullvalene is a hydrocarbon with the chemical formula . The molecule has a cage-like structure formed by the fusion of one cyclopropane and three cyclohepta-1,4-diene rings. Bullvalene is unusual as an organic molecule due to the and bonds fo ...
Image:1,5-dihydropentalene.png, 1,5-dihydropentalene
Image:2a,2b,4a,4b-tetrahydrocyclopropa cd pentalene.png, 2a,2b,4a,4b-Tetrahydrocyclopropa dentalene
Image:Bicyclo420octa247triene.svg, Bicyclo .2.0cta-2,4,7-triene. Tautomer
Tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert.
The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hy ...
with COT by thermal 6e process or photochemical 4e process
Image:Tricyclo33006octa38diene.svg, Tricyclo ,3,0,02,6cta-3,8-diene. Isomerises to semibullvalene at room temperature, stable at −60 °C
Image:Cyclobutadiene dimer cis trans.svg, Tricyclo ,2,0,02,5cta-3,7-diene. The dimer of cyclobutadiene
Cyclobutadiene is an organic compound with the formula . It is very reactive owing to its tendency to dimerize. Although the parent compound has not been isolated, some substituted derivatives are robust and a single molecule of cyclobutadiene is ...
occurs as a cis isomer
Cis or cis- may refer to:
Places
* Cis, Trentino, in Italy
* In Poland:
** Cis, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, south-central
** Cis, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, north
Math, science and biology
* cis (mathematics) (cis(''θ'')), a trigonom ...
and a trans isomer. Both isomers convert to COT (symmetry forbidden hence stable) with a half-life of 20 minutes at 140 °C
Image:Tetracyclooctaene.svg, Tetracyclo ,3,0,02,4,03,6octa-7-ene is only known as its 4-carbomethoxy derivative.
Image:Tetracyclooct-7-ene.svg, Tetracyclo ,2,0,02,4,03,5octa-7-ene has been prepared from benzvalene and isomerises to COT
Image:Octabisvalene.svg, Pentacyclo .1.0.02,4. 03,5.06,8ctane (octabisvalene) is the third saturated valence isomer. The (Z)-3,7-phenylsulfonyl derivative is stable up to 200 °C.
Image:Octavalene.svg, Tricyclo .1.0.02,8cta-3,5-diene (octavalene) was reported synthesised from homobenzvalene and converts to COT at 50 °C ''Electronic structure of octavalene. Photoelectron spectroscopic investigations'' Rolf Gleiter, Peter Bischof, Manfred Christl J. Org. Chem., 1986, 51 (15), pp 2895–2898
Naphthalene and azulene
Perhaps no pair of valence isomers differ more strongly in appearance than colourless naphthalene and the intensely violet azulene.Naphthalene
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromat ...
Image:Azulene-numbers.png, Azulene
Azulene is an organic compound and an isomer of naphthalene. Naphthalene is colourless, whereas azulene is dark blue. Two terpenoids, vetivazulene (4,8-dimethyl-2-isopropylazulene) and guaiazulene (1,4-dimethyl-7-isopropylazulene), that featur ...
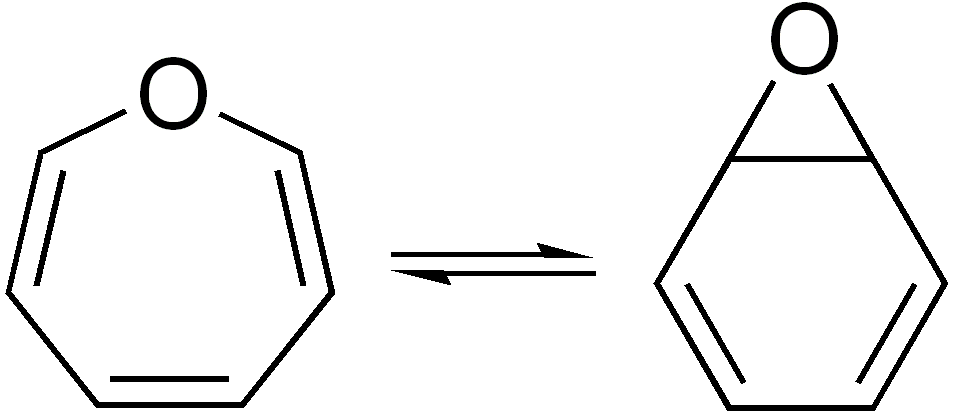
Benzene oxide and oxepin

References
External links
*{{Commonscatinline Isomerism