Voisin IX on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
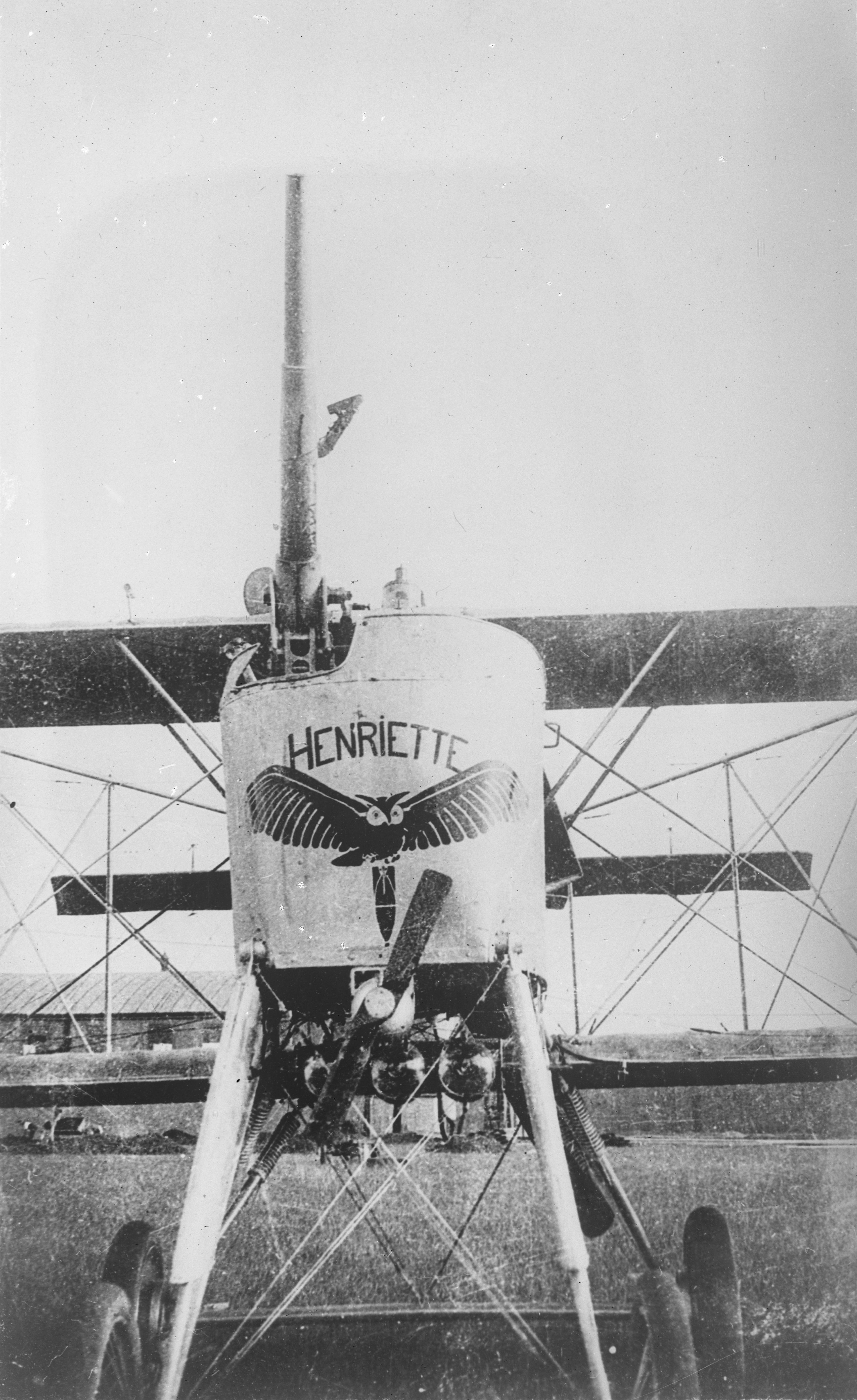 The Voisin VIII was a French two-seat biplane pusher which was built in two versions, one fitted with a 37mm Hotchkiss cannon (the LBP or Ca.2), and the other as a conventional bomber (the LAP or Bn.2).Davilla, p.559 Problems with the Peugeot engine led to a short operational career with front line units before being superseded by the Voisin X, which aside from the installation of a new Renault engine, was nearly identical to the VIII.
The Voisin VIII was a French two-seat biplane pusher which was built in two versions, one fitted with a 37mm Hotchkiss cannon (the LBP or Ca.2), and the other as a conventional bomber (the LAP or Bn.2).Davilla, p.559 Problems with the Peugeot engine led to a short operational career with front line units before being superseded by the Voisin X, which aside from the installation of a new Renault engine, was nearly identical to the VIII.

 The Voisin VIII was a French two-seat biplane pusher which was built in two versions, one fitted with a 37mm Hotchkiss cannon (the LBP or Ca.2), and the other as a conventional bomber (the LAP or Bn.2).Davilla, p.559 Problems with the Peugeot engine led to a short operational career with front line units before being superseded by the Voisin X, which aside from the installation of a new Renault engine, was nearly identical to the VIII.
The Voisin VIII was a French two-seat biplane pusher which was built in two versions, one fitted with a 37mm Hotchkiss cannon (the LBP or Ca.2), and the other as a conventional bomber (the LAP or Bn.2).Davilla, p.559 Problems with the Peugeot engine led to a short operational career with front line units before being superseded by the Voisin X, which aside from the installation of a new Renault engine, was nearly identical to the VIII.
Development
With the failure of the 1915 and 1916 bomber contests to produce any usable types to replace the Voisin V, Voisin was asked to produce an interim type pending the development of the next generation of bombers. This was based partly on the preceding Voisin VII which was itself an enlarged V, but was to be powered by a larger engine as the VII was found to be underpowered,Davilla, p.557 and would dispense with the nose radiator, reverting to drag-inducing side radiators. Two versions were to be built, a conventionalbomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped ...
, and an aircraft armed with a large single shot 37mm Hotchkiss cannon
A cannon is a large- caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder ...
as was used on the Voisin IV. Initially it was thought the cannon would be used for air-air attacks and was officially designated a cannon fighter (Ca.2) however this was found to be unworkable as both bomber and fighter types were vulnerable to fighters as they were too slow and unmaneuverable but at least one enemy aircraft was destroyed — with a single shot. As a result, a variety of other roles were attempted with it. Flying artillery, using indirect shots were impossible to aim accurately, balloon busting highlighted the type's vulnerability to anti-aircraft artillery
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes surface based, ...
fire, but some success was found with used in the ground attack firing directly at the target. Many had their cannons removed while in operational service but at least one was armed with additional machine guns. The LBP with the cannon had the pilot in the rear seat, while in the LAP, the pilot sat in the front seat, while the rear occupant could be equipped with a light machine gun such as a Lewis. On some aircraft, the observer's gun was mounted on a ring that was tilted to make movement forward easier against the wind. Unlike with the Voisin IV, installation of the cannon did not require that the top wing be staggered forward to maintain fore-aft balance.
Like the previous Voisins going back to the Voisin III
The Voisin III was a French World War I two-seat pusher biplane multi-purpose aircraft developed by Voisin in 1914 as a more powerful version of the 1912 Voisin I. It is notable for being the aircraft used for the first successful shooting down ...
, the Voisin VIII had a steel tube structure to provide adequate strength. Unusually for the period, and because it had no skid to drag it to a stop, it was equipped with drum brakes. These were fitted to the rear wheels. Like the Voisin VII, the VIII was fitted with two large strut mounted teardrop fuel tanks that could be jettisoned in the event of a fire. Due to problems with exhaust ventilation on the VII, the VIII and later types were fitted with tall individual exhaust stacks projecting above the top wing.
Operational history
French service
By the start of 1917, the Voisin VIII made up the bulk of the Aviation Militaire's night bombing force having gradually replaced the precedingVoisin V
The Voisin V was a French pusher-type bomber aircraft of World War I.
Development history
The Voisin III had proved a successful bomber, but its payload was limited by the Salmson M9 engine, which produced only 120-hp. With an already identif ...
's and fully equipped two Groupes de Bombardment (GB 1 & GB 3) before the unreliability of their engines resulted in them being gradually replaced by French-built Sopwith 1½ Strutter
The Sopwith Strutter was a British single- or two-seat multi-role biplane aircraft of the First World War.Lake 2002, p. 40. It was the first British two-seat tractor fighter and the first British aircraft to enter service with a synchronised ...
s and the higher powered Voisin Xs, and withdrawn to secondary units, which continued to operate them until the end of the war. The ''l'Aéronavale''/''Aviation Maritime'' operated 20 Voisin VIIIs.Davilla, p.561
American service
Based on the experiences of some Americans serving with these aircraft, the United States'American Expeditionary Force
The American Expeditionary Forces (A. E. F.) was a formation of the United States Army on the Western Front of World War I. The A. E. F. was established on July 5, 1917, in France under the command of General John J. Pershing. It fought alon ...
planned to field a single night bomber unit equipped with the Voisin VIII, however only a training unit was formed before the war ended.
British service
TheRoyal Naval Air Service
The Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) was the air arm of the Royal Navy, under the direction of the Admiralty's Air Department, and existed formally from 1 July 1914 to 1 April 1918, when it was merged with the British Army's Royal Flying Corps t ...
purchased two examples for trials work, one fitted with the cannon, and one of the bomber types, however no further examples were purchased.
Variants
;Voisin VIII * Peugeot 8Aa **Voisin LAP - factory designation for VIII night bomber **Voisin LBP - factory designation for VIII armed with cannon ;Voisin IX *lightened one-off prototype withRenault 8G
The Renault 8G was a family of French liquid-cooled V-8 aero engines of the World War I era that produced from to .
Design and development
Construction used separate cast iron blocks for each pair of cylinders, mounted on a light-alloy crankc ...
b for reconnaissance, with radiator in rounded nose
**Voisin LC - factory designation for IX
; Voisin X
*re-engined VIII with Renault 12Fe
Groupe Renault ( , , , also known as the Renault Group in English; legally Renault S.A.) is a French multinational automobile manufacturer established in 1899. The company produces a range of cars and vans, and in the past has manufactured ...
**Voisin LAR - factory designation for X night bomber
**Voisin LBR - factory designation for X armed with cannon
;Voisin XI
*Variant of X with Panhard 12B
Panhard was a French motor vehicle manufacturer that began as one of the first makers of automobiles. It was a manufacturer of light tactical and military vehicles. Its final incarnation, now owned by Renault Trucks Defense, was formed ...
c and minor changes to proportions but only around 10 built
Operators
; * ''Aéronautique Militaire'' **Ecole Militaire d'Avord **VB.101 **V.481/551 operated alongside Letord 4 & 5 **G.482 operated alongsideCaudron G.6
The Caudron G.6 was a French reconnaissance aircraft of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the ...
aircraft
**VB.483
**V.484
**Let.485 operated alongside Letord 4 aircraft
**V.486
**V.487 operated alongside Letord 4 & 5 aircraft
**V.491 operated alongside Letord 4 aircraft
** 1
***VB.110
***VB.114 first unit to receive type
** 3
***VB.107
***VB.108
***VB.109
***VB.113
* ''l'Aéronavale''/''Aviation Maritime''
** de Dunkerque
;
*Royal Naval Air Service
The Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) was the air arm of the Royal Navy, under the direction of the Admiralty's Air Department, and existed formally from 1 July 1914 to 1 April 1918, when it was merged with the British Army's Royal Flying Corps t ...
;
*American Expeditionary Force
The American Expeditionary Forces (A. E. F.) was a formation of the United States Army on the Western Front of World War I. The A. E. F. was established on July 5, 1917, in France under the command of General John J. Pershing. It fought alon ...
Survivors/Aircraft on display
*National Air and Space Museum
The National Air and Space Museum of the Smithsonian Institution, also called the Air and Space Museum, is a museum in Washington, D.C., in the United States.
Established in 1946 as the National Air Museum, it opened its main building on the Nat ...
has a Voisin VIII/LAP bomber on display
* Musée de l'air et de l'espace has a fuselage of a Voisin X/LBR equipped with a cannon.
Specifications

See also
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * *Further reading
* {{Voisin aircraft 08 1910s French bomber aircraft Single-engined pusher aircraft Biplanes Military aircraft of World War I Aircraft first flown in 1916