Vocal cord dysfunction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Vocal cord dysfunction (VCD) is a pathology affecting the
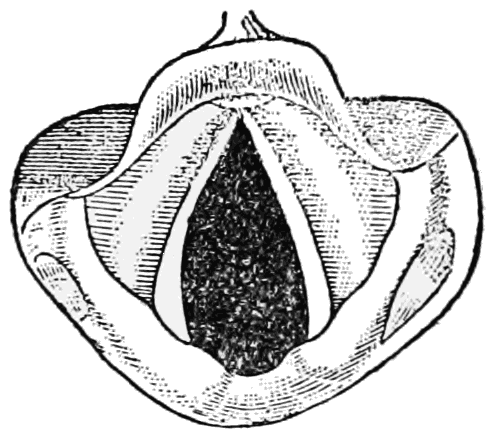
 VCD can mimic asthma,
VCD can mimic asthma,
In individuals who experience a persistent difficulty with inhaling, consideration should be given to a neurological cause such as brain stem compression, cerebral palsy, etc. The main difference between VCD and asthma is the audible stridor or wheezing that occurs at different stages of the breath cycle: VCD usually causes stridor on the inhalation, while asthma results in wheezing during exhalation. Patients with asthma usually respond to the usual medication and see their symptoms resolve. Clinical measures that can be done to differentiate VCD from asthma include: * rhino
vocal folds
In humans, vocal cords, also known as vocal folds or voice reeds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through vocalization. The size of vocal cords affects the pitch of voice. Open when breathing and vibrating for speech ...
(commonly referred to as the vocal cords) characterized by full or partial vocal fold closure causing difficulty and distress during respiration, especially during inhalation.
Due to the similarity in symptoms, VCD attack are often mistaken for asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, cou ...
attacks or laryngospasm
Laryngospasm is an uncontrolled or involuntary muscular contraction (spasm) of the vocal folds. The condition typically lasts less than 60 seconds, but in cases partial blocking it may last 20 to 30 minutes and hinder inspiration, while exhala ...
s. Symptoms of VCD are not always present. Rather, they often occur episodically, often defined as "attacks," where the patient will be symptomatic for a short period of time. Although several contributing factors have been identified, the exact cause of VCD is unknown.
Diagnosis of VCD may include a series of evaluations including pulmonary function tests, medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
, and the evaluation or visualization of the vocal folds during an episode through the use of videolaryngoscopy. Such evaluations can also help to rule out other conditions that can affect the upper and lower airway. Treatment of VCD often combines behavioural, medical and psychological approaches, most often including an otolaryngologist
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical a ...
, a psychologist, and a speech-language pathologist. Although information on the incidence and prevalence of VCD is limited, it is known to occur most frequently in young women.
Signs and symptoms
Many of the symptoms are not limited to the disorder, as they may resemble a number of conditions that affect the upper and lower airway. Such conditions includeasthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, cou ...
, angioedema
Angioedema is an area of swelling ( edema) of the lower layer of skin and tissue just under the skin or mucous membranes. The swelling may occur in the face, tongue, larynx, abdomen, or arms and legs. Often it is associated with hives, which ...
, vocal cord tumors, and vocal cord paralysis.
People with vocal cord dysfunction often complain of "difficulty in breathing in" or "fighting for breath", which can lead to subjective respiratory distress, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness. They may report tightness in the throat or chest, choking, stridor on inhalation and wheezing, which can resemble the symptoms of asthma. These episodes of dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathing, breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of brea ...
can be recurrent and symptoms can range from mild to severe and prolonged in some cases. Agitation and a sense of panic are not uncommon and can result in hospitalization.
Different subtypes of vocal cord dysfunction are characterized by additional symptoms. For instance, momentary aphonia can be caused by laryngospasm, an involuntary spasm of the vocal cords and a strained or hoarse voice may be perceived when the vocal cord dysfunction occurs during speech.
Many of the symptoms are not specific to vocal cord dysfunction and can resemble a number of conditions that affect the upper and lower airway.
Presentation

 VCD can mimic asthma,
VCD can mimic asthma, anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of use of emergency medication on site. It typically causes more than one of the follow ...
, collapsed lungs, pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain p ...
, or fat embolism, which can lead to an inaccurate diagnosis and inappropriate, potentially harmful, treatment. Some incidences of VCD are misdiagnosed as asthma, but are unresponsive to asthma therapy, including bronchodilators and steroids. Among adult patients, women tend to be diagnosed more often. Among children and teenage patients, VCD has been linked with high participation in competitive sports and family orientation towards high achievement.
Vocal cord dysfunction co-occurs with asthma approximately 40% of the time. This frequently results in a misdiagnosis of asthma alone. Even young children can tell the difference between an asthma attack (primarily difficulty exhaling) and a VCD attack (primarily difficulty inhaling). Knowing the difference between the two will help those who have both know when to use the rescue inhaler prescribed or when to use the breathing recovery exercises trained by a speech-language pathologist.
Episodes can be triggered suddenly or develop gradually and triggers are numerous. Primary causes are believed to be gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the upper gastrointestinal chronic diseases where stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/ ...
(GERD), extra-esophageal reflux (EERD), exposure to inhaled allergens, post-nasal drip
Post-nasal drip (PND), also known as upper airway cough syndrome (UACS), occurs when excessive mucus is produced by the nasal mucosa. The excess mucus accumulates in the back of the nose, and eventually in the throat once it drips down the back of ...
, exercise, or neurological conditions that can cause difficulty inhaling only during waking. Published studies emphasize anxiety or stress as a primary cause while more recent literature indicates a likely physical etiology. This disorder has been observed from infancy through old age, with the observation of its occurrence in infants leading some to believe that a physiological cause such as reflux or allergy is likely. Certain medications, such as antihistamines for allergies, cause drying of the mucous membranes, which can cause further irritation or hypersensitivity of the vocal cords.
Potential comorbidities
VCD has long been strongly associated with a variety of psychological or psychogenic factors, includingconversion disorder
Conversion disorder (CD), or functional neurologic symptom disorder, is a diagnostic category used in some psychiatric classification systems. It is sometimes applied to patients who present with neurological symptoms, such as numbness, blindness ...
, major depression
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Introdu ...
, obsessive-compulsive disorder, anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
(especially in adolescents), stress (particularly stress relating to competitive sports), physical and sexual abuse, post-traumatic stress disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental and behavioral disorder that can develop because of exposure to a traumatic event, such as sexual assault, warfare, traffic collisions, child abuse, domestic violence, or other threats on ...
, panic attack
Panic attacks are sudden periods of intense fear and discomfort that may include palpitations, sweating, chest pain or chest discomfort, shortness of breath, trembling, dizziness, numbness, confusion, or a feeling of impending doom or of losing ...
s, factitious disorder
A factitious disorder is a condition in which a person, ''without'' a malingering motive, acts as if they have an illness by deliberately producing, feigning, or exaggerating symptoms, purely to attain (for themselves or for another) a patient' ...
and adjustment disorder
Adjustment disorder is a maladaptive response to a psychosocial stressor. It is classified as a mental disorder. The maladaptive response usually involves otherwise normal emotional and behavioral reactions that manifest more intensely than usual ...
. It is important to note that anxiety and depression may occur in certain patients as a ''result'' of having VCD, rather than being the cause of it. Psychological factors are important precipitating factors for many patients with VCD; although exercise is also a major trigger for episodes of VCD, some patients experience VCD co-occurring with anxiety regardless of whether or not they are physically active at the time of the VCD/anxiety episode. Experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event related to breathing (such as a near-drowning or life-threatening asthma attack, for example), has also been identified as a risk factor for VCD.
VCD has also been associated with certain neurologic
Neurology (from el, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal c ...
diseases including Arnold-Chiari malformation, cerebral aqueduct stenosis
A stenosis (from Ancient Greek στενός, "narrow") is an abnormal narrowing in a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture).
''Stricture'' ...
, cortical or upper motor neuron
Upper motor neurons (UMNs) is a term introduced by William Gowers in 1886. They are found in the cerebral cortex and brainstem and carry information down to activate interneurons and lower motor neurons, which in turn directly signal muscles t ...
injury (such as that resulting from stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or Lou Gehrig's disease, is a neurodegenerative disease that results in the progressive loss of motor neurons that control voluntary muscles. ALS is the most comm ...
(ALS), parkinsonism
Parkinsonism is a clinical syndrome characterized by tremor, bradykinesia (slowed movements), rigidity, and postural instability. These are the four motor symptoms found in Parkinson's disease (PD), after which it is named, dementia with Lewy bo ...
syndromes and other movement disorders. However, this association occurs only rarely. In addition, it has been associated with Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes, a group of connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
disorders.
Causes
The exact cause of VCD is not known, and it is unlikely that a single underlying cause exists. Several contributing factors have been identified, which vary widely among VCD patients with different medical histories. Physical exercise (including, but not limited to, competitive athletics) is one of the major triggers for VCD episodes, leading to its frequent misdiagnosis as exercise-induced asthma. Other triggers include airborne pollutants and irritants such as smoke, dust, gases, soldering fumes, cleaning chemicals such as ammonia, perfumes, and other odours.Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the upper gastrointestinal chronic diseases where stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/ ...
(GERD) and rhinosinusitis
Rhinosinusitis is a simultaneous infection of the nasal mucosa (rhinitis) and an infection of the mucosa of the paranasal sinuses (sinusitis). A distinction is made between acute rhinosinusitis and chronic rhinosinusitis.
Background
Because sinu ...
(inflammation of the paranasal sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoid ...
and nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal c ...
) may also play a role in inflaming the airway
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to th ...
and leading to symptoms of VCD as discussed below.
Laryngeal hyperresponsiveness is considered the most likely physiologic cause of VCD, brought on by a range of different triggers that cause inflammation and/or irritation of the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about ...
(voice box). The glottic closure reflex
In biology, a reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary, unplanned sequence or action and nearly instantaneous response to a stimulus.
Reflexes are found with varying levels of complexity in organisms with a nervous system. A reflex occurs ...
(or laryngeal adductor reflex) serves to protect the airway, and it is possible that this reflex becomes hyperactive in some individuals, resulting in the paradoxical vocal fold closure seen in VCD. Two major causes of laryngeal inflammation and hyperresponsiveness are gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and postnasal drip (associated with rhinosinusitis
Rhinosinusitis is a simultaneous infection of the nasal mucosa (rhinitis) and an infection of the mucosa of the paranasal sinuses (sinusitis). A distinction is made between acute rhinosinusitis and chronic rhinosinusitis.
Background
Because sinu ...
, allergic or nonallergic rhinitis
Rhinitis, also known as coryza, is irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane inside the nose. Common symptoms are a stuffy nose, runny nose, sneezing, and post-nasal drip.
The inflammation is caused by viruses, bacteria, irritants o ...
, or a viral upper respiratory tract infection
An upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) is an illness caused by an acute infection, which involves the upper respiratory tract, including the nose, sinuses, pharynx, larynx or trachea. This commonly includes nasal obstruction, sore throat, t ...
(URI)). Rhinosinusitis is very common among patients with VCD and for many patients, VCD symptoms are ameliorated when the rhinosinusitis is treated. GERD is also common among VCD patients, but only some experience an improvement in VCD symptoms when GERD is treated. Other causes of laryngeal hyperresponsiveness include inhalation of toxins and irritants, cold and dry air, episodic croup
Croup, also known as laryngotracheobronchitis, is a type of respiratory infection that is usually caused by a virus. The infection leads to swelling inside the trachea, which interferes with normal breathing and produces the classic symptoms o ...
and laryngopharyngeal reflux
Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) is the retrograde flow of gastric contents into the larynx, oropharynx and/or the nasopharynx. LPR causes respiratory symptoms such as cough and wheezing and is often associated with head and neck complaints such as ...
(LPR).
Risk factors
The following increase an individual's chances for acquiring VCD: * Upper airway inflammation ( allergic or non-allergic rhinitis,chronic sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, heada ...
, recurrent upper respiratory infections)
* Gastroesophageal reflux disease
* Past traumatic event that involved breathing (e.g. near-drowning, suffocation)
* Severe emotional trauma or distress
* Female gender
* Playing a wind instrument
A wind instrument is a musical instrument that contains some type of resonator (usually a tube) in which a column of air is set into vibration by the player blowing into (or over) a mouthpiece set at or near the end of the resonator. The pitc ...
* Playing a competitive or elite sport
Diagnosis
The most effective diagnostic strategy is to performlaryngoscopy
Laryngoscopy () is endoscopy of the larynx, a part of the throat. It is a medical procedure that is used to obtain a view, for example, of the vocal folds and the glottis. Laryngoscopy may be performed to facilitate tracheal intubation during ...
during an episode, at which time abnormal movement of the cords, if present, can be observed. If the endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
is not performed during an episode, it is likely that the vocal folds will be moving normally, a 'false negative
A false positive is an error in binary classification in which a test result incorrectly indicates the presence of a condition (such as a disease when the disease is not present), while a false negative is the opposite error, where the test result ...
' finding.
Spirometry may also be useful to establish the diagnosis of VCD when performed during a crisis or after a nasal provocation test. With spirometry, just as the expiratory loop may show flattening or concavity when expiration is affected in asthma, so may the Inspiratory loop show truncation or flattening in VCD. Of course, testing may well be negative when symptoms are absent.
Differential diagnosis
The symptoms of VCD are often inaccurately attributed to asthma, which in turn results in the unnecessary and futile intake ofcorticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involv ...
s, bronchodilator
A bronchodilator or broncholytic (although the latter occasionally includes secretory inhibition as well) is a substance that dilates the bronchi and bronchioles, decreasing resistance in the respiratory airway and increasing airflow to the lung ...
s and leukotriene modifiers
An antileukotriene, also known as leukotriene modifier and leukotriene receptor antagonist, is a medication which functions as a leukotriene-related enzyme inhibitor (arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase) or leukotriene receptor antagonist (cysteinyl leuko ...
, although there are instances of comorbidity of asthma and VCD.
The differential diagnosis
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (abbreviated DDx) is a method of analysis of a patient's history and physical examination to arrive at the correct diagnosis. It involves distinguishing a particular disease or condition from others that p ...
for vocal cord dysfunction includes vocal fold swelling from allergy, asthma, or some obstruction of the vocal folds or throat. Anyone suspected of this condition should be evaluated and the vocal folds (voice box) visualized. In individuals who experience a persistent difficulty with inhaling, consideration should be given to a neurological cause such as brain stem compression, cerebral palsy, etc. The main difference between VCD and asthma is the audible stridor or wheezing that occurs at different stages of the breath cycle: VCD usually causes stridor on the inhalation, while asthma results in wheezing during exhalation. Patients with asthma usually respond to the usual medication and see their symptoms resolve. Clinical measures that can be done to differentiate VCD from asthma include: * rhino
laryngoscopy
Laryngoscopy () is endoscopy of the larynx, a part of the throat. It is a medical procedure that is used to obtain a view, for example, of the vocal folds and the glottis. Laryngoscopy may be performed to facilitate tracheal intubation during ...
: A patient with asthma will have normal vocal cord movement, while one with VCD will display vocal cord abduction during inhalation
* spirometry: A change in the measure following the administration of a bronchodilator is suggestive of asthma rather than VCD
* chest radiograph
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
y: The presence of hyperinflation and peribronchial thickening are indicative of asthma, as patients with VCD will show normal results
Treatments
Once a diagnosis of VCD has been confirmed by a medical professional, a specific treatment plan can be implemented. If vocal cord dysfunction is secondary to an underlying condition, such as asthma, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), or postnasal drip, it is important to treat the primary condition as this will help control VCD symptoms. Conventional treatments for VCD are often multidisciplinary and include speech-language pathology,psychotherapy
Psychotherapy (also psychological therapy, talk therapy, or talking therapy) is the use of psychological methods, particularly when based on regular personal interaction, to help a person change behavior, increase happiness, and overcome pro ...
, behavioral therapy
Behaviour therapy or behavioural psychotherapy is a broad term referring to clinical psychotherapy that uses techniques derived from behaviourism and/or cognitive psychology. It looks at specific, learned behaviours and how the environment, or o ...
, use of anti-anxiety and anti-depressant medications, medical interventions, and hypnotherapy. There is no uniform approach.
The information from randomized, blinded studies is limited.
Behavioral approaches
Speech-language pathologists provide behavioral treatment of VCD. Speech therapy usually involves educating the client on the nature of the problem, what happens when symptoms are present, and then comparing this to what happens during normal breathing andphonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defini ...
. Intervention goals target teaching a client breathing and relaxation exercises so that they can control their throat muscles and keep the airway open, allowing air to flow in and out.
Breathing techniques can be taught to reduce tension in the throat, neck, and upper body and bring attention to the flow of air during respiration. Diaphragm support during breathing decreases muscle tension in the larynx. These techniques are meant to move awareness away from the act of breathing in and focus on the auditory feedback
Auditory feedback (AF) is an aid used by humans to control speech production and singing by helping the individual verify whether the current production of speech or singing is in accordance with his acoustic-auditory intention. This process is po ...
provided by the air moving in and out.
Other techniques can involve breathing through a straw and panting, which widens the opening of the throat by activating the Posterior cricoarytenoid
The posterior cricoarytenoid muscles are small, paired intrinsic muscles of the larynx that extend between cricoid cartilage to the arytenoid cartilages in the larynx.
Structure Origin and insertion
The posterior cricoarytenoid originates fro ...
(PCA) muscle. Endoscopic feedback can also be used to show a patient what is happening when they are doing simple tasks such as taking a deep breath or speaking on an inspiration. This provides the client with visual information so that they can actually see what behaviours help to open the throat and what behaviors constrict the throat. Respiratory muscle strength training, a form of increased resistance training using a hand-held breathing device has also been reported to alleviate symptoms.
Speech therapy has been found to eliminate up to 90% of ER visits in patients with VCD.
Medical approaches
Medical often works in conjunction with behavioral approaches. A pulmonary or ENT (otolaryngologist
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical a ...
) specialist will screen for and address any potential underlying pathology that may be associated with VCD. Managing GERD has also been found to relieve laryngospasm, a spasm of the vocal cords that makes breathing and speaking difficult.
Non-invasive positive pressure ventilation can be used if a patient's vocal cords adduct (close) during exhalation. Mild sedatives have also been employed to reduce anxiety as well as reduce acute symptoms of VCD. Benzodiazepines are an example of one such treatment, though they have been linked to a risk of suppression of the respiratory drive. While Ketamine, a dissociative anesthetic, does not suppress respiratory drive, it has been thought to be associated with laryngospasms.
For more severe VCD cases, physicians may inject botulinum toxin
Botulinum toxin, or botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT), is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium ''Clostridium botulinum'' and related species. It prevents the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from axon endings at the neuromusc ...
into the vocal ( thyroarytenoid) muscles to weaken or decrease muscle tension. Nebulized Lignocaine can also been used in acute cases and helium-oxygen inhalation given by face mask has been used in cases of respiratory distress.
Psychological approaches
Psychological interventions including psychotherapy,cognitive behavioural therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a psycho-social intervention that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression and anxiety disorders. CBT focuses on challenging and changing cognitive distortions (su ...
(CBT), Biofeedback, and teaching self-hypnosis are also suggested to treat VCD. Intervention is generally targeted at making the client aware of stressors that may trigger VCD symptoms, to implement strategies to reduce stress and anxiety, and to teach techniques for coping with their symptoms.
CBT can focus on bringing awareness to negative thought patterns and help reframe them by focusing on problem solving strategies. Psychologists may also use relaxation to reduce distress when a patient is experiencing symptoms. Biofeedback
Biofeedback is the process of gaining greater awareness of many physiology, physiological functions of one's own body by using Electronics, electronic or other instruments, and with a goal of being able to Manipulation (psychology), manipulate t ...
can be a helpful addition to psychotherapy. The aim of Biofeedback is to educate the client on what happens to the vocal cords during breathing and to help them learn to control their symptoms.
Choosing an intervention strategy needs to be assessed by a multidisciplinary team and individualized therapy planned carefully, keeping the characteristics of each patient in mind.
Prognosis
The natural prognosis of VCD in both children and adults is not well described in the literature. Additionally, there is currently no research that has studied whether the underlying cause of VCD makes a difference in the resolution of symptoms or in the long-term prognosis of the impairment. Information on the prognosis of VCD after acute therapies is also limited. Minimal response has been documented with the continued treatment of asthma in people with VCD using inhaled bronchodilators,corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involve ...
and other asthma medications. While using Botox
Botulinum toxin, or botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT), is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium '' Clostridium botulinum'' and related species. It prevents the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from axon endings at the neuromus ...
in VCD has limited reports, those that are available report successful resolution of exercise-induced VCD symptoms for up to 2 months.
Outcomes of chronic VCD treatment are similarly limited. When pediatric patients undergoing hypnosis therapy were studied, more than half saw either a reduction or resolution of VCD. Even though it is widely used, no long-term studies have been done to study the prognosis of VCD after psychotherapy.
Speech therapy
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are th ...
is the main course of treatment for long-term management of VCD and includes a variety of techniques such as relaxed-throat breathing, respiratory retraining therapy, and vocal hygiene counselling. Most studies agree that symptoms of VCD improve in patients and few continue to require asthma medications six months post speech therapy intervention. Significant improvements were reported for respiratory retraining therapy, including fewer episodes of dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathing, breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of brea ...
per month and decreased respiratory stress severity.
For those adolescent patients who recovered from VCD, the average time before the symptoms were resolved was 4–5 months. However, some adolescents had VCD symptoms even 5 years post VCD onset, regardless of intervention. It has been noted that some patients do not respond to standard VCD therapies and continue to express recurrent symptoms.
Epidemiology
There is currently a limited amount of information available on the incidence andprevalence
In epidemiology, prevalence is the proportion of a particular population found to be affected by a medical condition (typically a disease or a risk factor such as smoking or seatbelt use) at a specific time. It is derived by comparing the number o ...
of VCD, and the various rates reported in the literature are most likely an underestimate. Although VCD is thought to be rare overall, its prevalence among the population at large is not known.
However, numerous studies have been conducted on its incidence and prevalence among patients presenting with asthma and exertional dyspnea. A VCD incidence rate of 2% has been reported among patients whose primary complaint was either asthma or dyspnea; the same incidence rate has also been reported among patients with acute asthma exacerbation. Meanwhile, much higher VCD incidence rates have also been reported in asthmatic populations, ranging from 14% in children with refractory asthma to 40% in adults with the same complaint. It has also been reported that the VCD incidence rate is as high as 27% in non-asthmatic teenagers and young adults.
Data on the prevalence of VCD is also limited. An overall prevalence of 2.5% has been reported in patients presenting with asthma. Among adults with asthma considered "difficult to control", 10% were found to have VCD while 30% were found to have both VCD and asthma. Among children with severe asthma, a VCD prevalence rate of 14% has been reported. However, higher rates have also been reported; among one group of schoolchildren thought to have exercise-induced asthma, it was found that 26.9% actually had VCD and not asthma. Among intercollegiate athletes with exercise-induced asthma, the VCD rate has been estimated at 3%.
In patients presenting with symptoms of dyspnea, prevalence rates ranging from 2.8% to 22% have been reported in various studies. It has been reported that two to three times more females than males have VCD. VCD is especially common in females who have psychological conditions. There is an increased risk associated with being young and female. Among patients with VCD, 71% are over the age of 18. In addition, 73% of those with VCD have a previous psychiatric diagnosis. VCD has also been reported in newborns with gastroesophageal reflux disorder (GERD).
See also
*Puberphonia Puberphonia (also known as mutational falsetto, functional falsetto, incomplete mutation, adolescent falsetto, or pubescent falsetto) is a functional voice disorder that is characterized by the habitual use of a high-pitched voice after puberty, he ...
References
External links
{{Respiratory pathology Otorhinolaryngology Vocal fold disorders