Video Random-access Memory on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
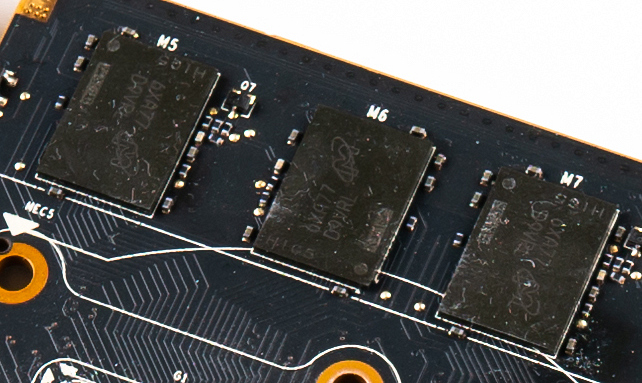 Video random-access memory (VRAM) is dedicated computer memory used to store the
Video random-access memory (VRAM) is dedicated computer memory used to store the
 Video random-access memory (VRAM) is dedicated computer memory used to store the
Video random-access memory (VRAM) is dedicated computer memory used to store the pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the s ...
s and other graphics data as a framebuffer
A framebuffer (frame buffer, or sometimes framestore) is a portion of random-access memory (RAM) containing a bitmap that drives a video display. It is a memory buffer containing data representing all the pixels in a complete video frame. Moder ...
to be rendered on a computer monitor. This is often different technology than other computer memory, to facilitate being read rapidly to draw the image.
Relation to GPUs
Many modern GPUs rely on VRAM. In contrast, a GPU that does ''not'' use VRAM, and relies instead on system RAM, is said to have aunified memory architecture
Unified may refer to:
* The Unified, a wine symposium held in Sacramento, California, USA
* ''Unified'', the official student newspaper of Canterbury Christ Church University
, mottoeng = The truth shall set you free
, estab ...
, or shared graphics memory
In computer architecture, shared graphics memory refers to a design where the graphics chip does not have its own dedicated memory, and instead shares the main system RAM with the CPU and other components.
This design is used with many integra ...
.
System RAM and VRAM have been segregated due to the bandwidth requirements of GPUs, and to achieve lower latency, since VRAM is physically closer to the GPU die.
Modern VRAM is typically found in a BGA package soldered onto a graphics card. The VRAM is cooled along with the GPU by the GPU heatsink.
Technologies
*Dual-ported video RAM
Dual-ported video RAM, or VRAM, is a dual-ported variant of dynamic RAM (DRAM), which was once commonly used to store the framebuffer in graphics adapters. Note that most computers and game consoles do not use this form of memory, and dual-porte ...
, used in the 1990s and at the time often called "VRAM"
* SGRAM
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal.
DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the e ...
* GDDR SDRAM
Graphics DDR SDRAM (GDDR SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) specifically designed for applications requiring high bandwidth, e.g. graphics processing units (GPUs). GDDR SDRAM is distinct from the more widely kno ...
* High Bandwidth Memory
High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) is a high-speed computer memory interface for 3D-stacked synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) initially from Samsung, AMD and SK Hynix. It is used in conjunction with high-performance graphics accelerator ...
(HBM)
See also
*Graphics processing unit
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed to manipulate and alter memory to accelerate the creation of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display device. GPUs are used in embedded systems, mo ...
* Tiled rendering Tiled rendering is the process of subdividing a computer graphics image by a regular grid in optical space and rendering each section of the grid, or ''tile'', separately. The advantage to this design is that the amount of memory and bandwidth is ...
, a method to reduce VRAM bandwidth requirements
References
{{reflist Types of RAM