very-high-frequency on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Very high frequency (VHF) is the
Very high frequency (VHF) is the
 VHF transmission range is a function of transmitter power, receiver sensitivity, and distance to the horizon, since VHF signals propagate under normal conditions as a near line-of-sight phenomenon. The distance to the
VHF transmission range is a function of transmitter power, receiver sensitivity, and distance to the horizon, since VHF signals propagate under normal conditions as a near line-of-sight phenomenon. The distance to the
 VHF is the first band at which wavelengths are small enough that efficient transmitting antennas are short enough to mount on vehicles and handheld devices, a quarter wave whip antenna at VHF frequencies is 25 cm to 2.5 meter (10 inches to 8 feet) long. So the VHF and UHF wavelengths are used for
VHF is the first band at which wavelengths are small enough that efficient transmitting antennas are short enough to mount on vehicles and handheld devices, a quarter wave whip antenna at VHF frequencies is 25 cm to 2.5 meter (10 inches to 8 feet) long. So the VHF and UHF wavelengths are used for

 Very high frequency (VHF) is the
Very high frequency (VHF) is the ITU
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
designation for the range of radio frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the upp ...
electromagnetic wave
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visib ...
s (radio wave
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies of 300 gigahertz (GHz) and below. At 300 GHz, the corresponding wavelength is 1 mm (short ...
s) from 30 to 300 megahertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or Cycle per second, cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, me ...
(MHz), with corresponding wavelengths of ten meters to one meter.
Frequencies immediately below VHF are denoted high frequency
High frequency (HF) is the ITU designation for the range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves (radio waves) between 3 and 30 megahertz (MHz). It is also known as the decameter band or decameter wave as its wavelengths range from one to ten ...
(HF), and the next higher frequencies are known as ultra high frequency
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequency, radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one ten ...
(UHF).
VHF radio waves propagate mainly by line-of-sight, so they are blocked by hills and mountains, although due to refraction they can travel somewhat beyond the visual horizon out to about 160 km (100 miles). Common uses for radio waves in the VHF band are Digital Audio Broadcasting
Digital radio is the use of digital technology to transmit or receive across the radio spectrum. Digital transmission by radio waves includes digital broadcasting, and especially digital audio radio services.
Types
In digital broadcasting syst ...
(DAB) and FM radio
FM broadcasting is a method of radio broadcasting using frequency modulation (FM). Invented in 1933 by American engineer Edwin Armstrong, wide-band FM is used worldwide to provide high fidelity sound over broadcast radio. FM broadcasting is cap ...
broadcasting, television broadcasting
A television network or television broadcaster is a telecommunications network for distribution of television program content, where a central operation provides programming to many television stations or pay television providers. Until the mid-1 ...
, two-way
Two-way or Two Way may refer to:
* " 2-Way", single by rapper Lil' Romeo
* Two-way, Cincinnati chili
Cincinnati chili (or Cincinnati-style chili) is a Mediterranean-spiced meat sauce used as a topping for spaghetti or hot dogs ("coneys"); b ...
land mobile radio system
A land mobile radio system (LMRS) is a person-to-person voice communication system consisting of two-way radio transceivers (an audio transmitter and receiver in one unit) which can be stationary ( base station units), mobile (installed in vehicl ...
s (emergency, business, private use and military), long range data communication up to several tens of kilometers with radio modem
Radio modems are modems that transfer data wirelessly across a range of up to tens of kilometres.
Using radio modems is a modern way to create Private Radio Networks (PRN). Private radio networks are used in critical industrial applications, when r ...
s, amateur radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communic ...
, and marine communications. Air traffic control
Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airs ...
communications and air navigation systems (e.g. VOR
VOR or vor may refer to:
Organizations
* Vale of Rheidol Railway in Wales
* Voice of Russia, a radio broadcaster
* Volvo Ocean Race, a yacht race
Science, technology and medicine
* VHF omnidirectional range, a radio navigation aid used in a ...
and ILS) work at distances of or more to aircraft at cruising altitude.
In the Americas and many other parts of the world, VHF Band I
Band I is a range of radio frequencies within the very high frequency (VHF) part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The first time there was defined "for simplicity" in Annex 1 of "Final acts of the European Broadcasting Conference in the VHF and U ...
was used for the transmission of analog television
Analog television is the original television technology that uses analog signals to transmit video and audio. In an analog television broadcast, the brightness, colors and sound are represented by amplitude, instantaneous phase and frequency, ...
. As part of the worldwide transition to digital terrestrial television most countries require broadcasters to air television in the VHF range using digital, rather than analog encoding.
Propagation characteristics
Radio waves in the VHF band propagate mainly by line-of-sight and ground-bounce paths; unlike in the HF band there is only some reflection at lower frequencies from theionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an ...
(skywave
In radio communication, skywave or skip refers to the propagation of radio waves reflected or refracted back toward Earth from the ionosphere, an electrically charged layer of the upper atmosphere. Since it is not limited by the curvature of ...
propagation). They do not follow the contour of the Earth as ground wave
Ground waves are radio waves propagating parallel to and adjacent to the surface of the Earth, following the curvature of the Earth. This radiation is known as Norton surface wave, or more properly Norton ground wave, because ground waves in rad ...
s and so are blocked by hills and mountains, although because they are weakly refracted (bent) by the atmosphere they can travel somewhat beyond the visual horizon out to about 160 km (100 miles). They can penetrate building walls and be received indoors, although in urban areas reflections from buildings cause multipath propagation
In radio communication, multipath is the propagation phenomenon that results in radio signals reaching the receiving antenna by two or more paths. Causes of multipath include atmospheric ducting, ionospheric reflection and refraction, and reflec ...
, which can interfere with television reception. Atmospheric radio noise
In radio reception, radio noise is unwanted random radio frequency electrical signals, fluctuating voltages, always present in a radio receiver in addition to the desired radio signal. Radio noise near in frequency to the radio signal being receive ...
and interference ( RFI) from electrical equipment is less of a problem in this and higher frequency bands than at lower frequencies. The VHF band is the first band at which efficient transmitting antennas are small enough that they can be mounted on vehicles and portable devices, so the band is used for two-way
Two-way or Two Way may refer to:
* " 2-Way", single by rapper Lil' Romeo
* Two-way, Cincinnati chili
Cincinnati chili (or Cincinnati-style chili) is a Mediterranean-spiced meat sauce used as a topping for spaghetti or hot dogs ("coneys"); b ...
land mobile radio system
A land mobile radio system (LMRS) is a person-to-person voice communication system consisting of two-way radio transceivers (an audio transmitter and receiver in one unit) which can be stationary ( base station units), mobile (installed in vehicl ...
s, such as walkie-talkie
A walkie-talkie, more formally known as a handheld transceiver (HT), is a hand-held, portable, two-way radio transceiver. Its development during the Second World War has been variously credited to Donald Hings, radio engineer Alfred J. Gross, ...
s, and two way radio
A two-way radio is a radio that can both transmit and receive radio waves (a transceiver), unlike a broadcast receiver which only receives content. It is an audio (sound) transceiver, a transmitter and receiver in one unit, used for bidirection ...
communication with aircraft (Airband
Airband or aircraft band is the name for a group of frequencies in the VHF radio spectrum allocated to radio communication in civil aviation, sometimes also referred to as ''VHF'', or phonetically as ''"Victor"''. Different sections of the ban ...
) and ships (marine radio
Marine VHF radio is a worldwide system of two way radio transceivers on ships and watercraft used for bidirectional voice communication from ship-to-ship, ship-to-shore (for example with harbormasters), and in certain circumstances ship-to-a ...
). Occasionally, when conditions are right, VHF waves can travel long distances by tropospheric ducting
Tropospheric propagation describes electromagnetic propagation in relation to the troposphere.
The service area from a VHF or UHF radio transmitter extends to just beyond the horizon, optical horizon, at which point signals start to rapidly reduc ...
due to refraction by temperature gradients in the atmosphere.
Line-of-sight calculation
 VHF transmission range is a function of transmitter power, receiver sensitivity, and distance to the horizon, since VHF signals propagate under normal conditions as a near line-of-sight phenomenon. The distance to the
VHF transmission range is a function of transmitter power, receiver sensitivity, and distance to the horizon, since VHF signals propagate under normal conditions as a near line-of-sight phenomenon. The distance to the radio horizon
Line-of-sight propagation is a characteristic of electromagnetic radiation or acoustic wave propagation which means waves travel in a direct path from the source to the receiver. Electromagnetic transmission includes light emissions traveling ...
is slightly extended over the geometric line of sight to the horizon, as radio waves are weakly bent back toward the Earth by the atmosphere.
An approximation to calculate the line-of-sight horizon distance (on Earth) is:
*distance in nautical miles = where is the height of the antenna in feet
*distance in kilometers = where is the height of the antenna in meters.
These approximations are only valid for antennas at heights that are small compared to the radius of the Earth. They may not necessarily be accurate in mountainous areas, since the landscape may not be transparent enough for radio waves.
In engineered communications systems, more complex calculations are required to assess the probable coverage area of a proposed transmitter station.
Antennas
two-way radio
A two-way radio is a radio that can both transmit and receive radio waves (a transceiver), unlike a broadcast receiver which only receives content. It is an audio (sound) transceiver, a transmitter and receiver in one unit, used for bidirecti ...
s in vehicles, aircraft, and handheld transceiver
In radio communication, a transceiver is an electronic device which is a combination of a radio ''trans''mitter and a re''ceiver'', hence the name. It can both transmit and receive radio waves using an antenna, for communication purposes. The ...
s and walkie-talkie
A walkie-talkie, more formally known as a handheld transceiver (HT), is a hand-held, portable, two-way radio transceiver. Its development during the Second World War has been variously credited to Donald Hings, radio engineer Alfred J. Gross, ...
s. Portable radios usually use whips
A whip is a tool or weapon designed to strike humans or other animals to exert control through pain compliance or fear of pain. They can also be used without inflicting pain, for audiovisual cues, such as in equestrianism. They are generally e ...
or rubber ducky antenna
The rubber ducky antenna (or rubber duck aerial) is an electrically short monopole antenna that functions somewhat like a base-loaded whip antenna. It consists of a springy wire in the shape of a narrow helix, sealed in a rubber or plastic jac ...
s, while base stations usually use larger fiberglass whips or collinear arrays of vertical dipoles.
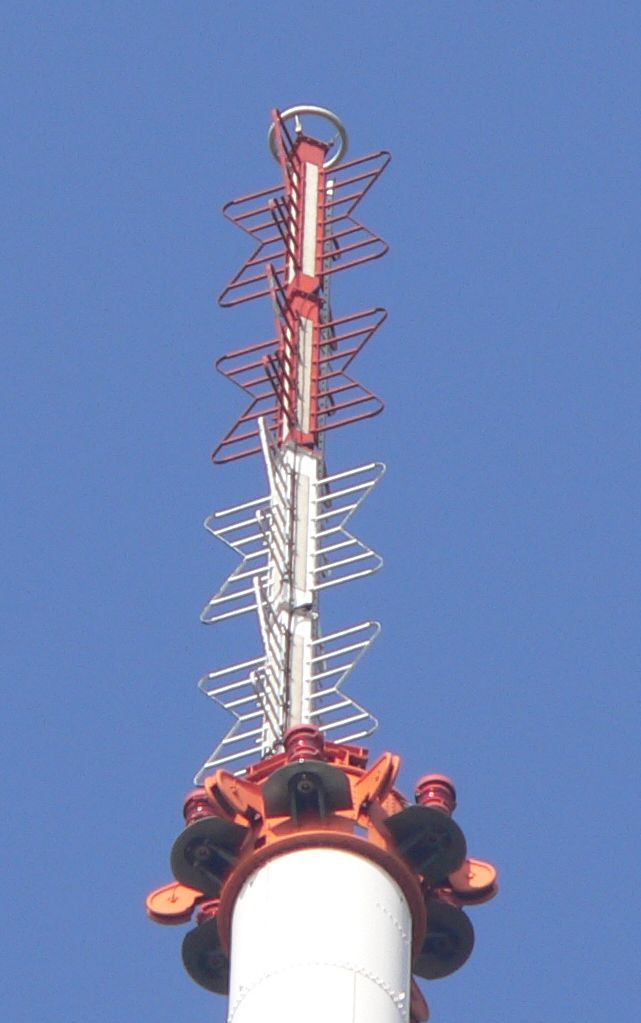
For directional antennas, the Yagi antenna Yagi may refer to:
Places
*Yagi, Kyoto, in Japan
*Yagi (Kashihara), in Nara Prefecture, Japan
*Yagi-nishiguchi Station, in Kashihara, Nara, Japan
*Kami-Yagi Station, a JR-West Kabe Line station located in 3-chōme, Yagi, Asaminami-ku, Hiroshima, Hi ...
is the most widely used as a high gain or "beam" antenna. For television reception, the Yagi is used, as well as the log-periodic antenna due to its wider bandwidth. Helical
Helical may refer to:
* Helix, the mathematical concept for the shape
* Helical engine, a proposed spacecraft propulsion drive
* Helical spring, a coilspring
* Helical plc, a British property company, once a maker of steel bar stock
* Helicoil
A t ...
and turnstile antenna
A turnstile antenna, or crossed-dipole antenna, is a radio antenna consisting of a set of two identical dipole antennas mounted at right angles to each other and fed in phase quadrature; the two currents applied to the dipoles are 90° out of pha ...
s are used for satellite communication
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. C ...
since they employ circular polarization
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to t ...
. For even higher gain, multiple Yagis or helicals can be mounted together to make array antennas
An antenna array (or array antenna) is a set of multiple connected antennas which work together as a single antenna, to transmit or receive radio waves. The individual antennas (called ''elements'') are usually connected to a single receiver ...
. Vertical collinear arrays of dipoles can be used to make high gain omnidirectional antenna
In radio communication, an omnidirectional antenna is a class of antenna which radiates equal radio power in all directions perpendicular to an axis (azimuthal directions), with power varying with angle to the axis (elevation angle), declining t ...
s, in which more of the antenna's power is radiated in horizontal directions. Television and FM broadcasting stations use collinear arrays of specialized dipole antennas such as batwing antenna
A batwing or super turnstile antenna is a type of broadcasting antenna used at VHF and UHF frequencies, named for its distinctive shape which resembles a bat wing or bow tie. Stacked arrays of batwing antennas are used as television broadcas ...
s.
Universal use
Certain subparts of the VHF band have the same use around the world. Some national uses are detailed below. *50–54 MHz:Amateur Radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communic ...
6-meter band
The 6-meter band is the lowest portion of the very high frequency (VHF) radio spectrum internationally allocated to amateur radio use. The term refers to the average signal wavelength of 6 meters.
Although located in the lower portion of t ...
.
*108–118 MHz: Air navigation beacons VOR
VOR or vor may refer to:
Organizations
* Vale of Rheidol Railway in Wales
* Voice of Russia, a radio broadcaster
* Volvo Ocean Race, a yacht race
Science, technology and medicine
* VHF omnidirectional range, a radio navigation aid used in a ...
and Instrument Landing System
In aviation, the instrument landing system (ILS) is a precision radio navigation system that provides short-range guidance to aircraft to allow them to approach a runway at night or in bad weather. In its original form, it allows an aircraft to ...
localizer.
*118–137 MHz: Airband
Airband or aircraft band is the name for a group of frequencies in the VHF radio spectrum allocated to radio communication in civil aviation, sometimes also referred to as ''VHF'', or phonetically as ''"Victor"''. Different sections of the ban ...
for air traffic control
Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airs ...
, AM, 121.5 MHz is emergency frequency
*144–146 MHz: Amateur Radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communic ...
2-meter band
The 2-meter amateur radio band is a portion of the VHF radio spectrum that comprises frequencies stretching from 144 MHz to 148 MHz in International Telecommunication Union region (ITU) Regions 2 (North and South America plus Hawaii) ...
(Extends up to 148 MHz in some Regions).
*156–174 MHz: VHF maritime mobile band for maritime two-way radio on ships.
By country
Australia
The VHF TV band in Australia was originally allocated channels 1 to 10-with channels 2, 7 and 9 assigned for the initial services in Sydney and Melbourne, and later the same channels were assigned in Brisbane, Adelaide and Perth. Other capital cities and regional areas used a combination of these and other frequencies as available. The initial commercial services in Hobart and Darwin were respectively allocated channels 6 and 8 rather than 7 or 9. By the early 1960s it became apparent that the 10 VHF channels were insufficient to support the growth of television services. This was rectified by the addition of three additional frequencies-channels 0, 5A and 11. Older television sets using rotary dial tuners required adjustment to receive these new channels. Most TVs of that era were not equipped to receive these broadcasts, and so were modified at the owners' expense to be able to tune into these bands; otherwise the owner had to buy a new TV. Several TV stations were allocated to VHF channels 3, 4 and 5, which were within the FM radio bands although not yet used for that purpose. A couple of notable examples were NBN-3Newcastle Newcastle usually refers to:
*Newcastle upon Tyne, a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England
*Newcastle-under-Lyme, a town in Staffordshire, England
*Newcastle, New South Wales, a metropolitan area in Australia, named after Newcastle ...
, WIN-4
WIN is a television station serving southern New South Wales and the Australian Capital Territory. It is the flagship station of the WIN Television network.
History
Programming
WIN Television broadcasts its programming from Nine Network, incl ...
Wollongong
Wollongong ( ), colloquially referred to as The Gong, is a city located in the Illawarra region of New South Wales, Australia. The name is believed to originate from the Dharawal language, meaning either 'five islands/clouds', 'ground near wate ...
and ABC
ABC are the first three letters of the Latin script known as the alphabet.
ABC or abc may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Broadcasting
* American Broadcasting Company, a commercial U.S. TV broadcaster
** Disney–ABC Television ...
Newcastle Newcastle usually refers to:
*Newcastle upon Tyne, a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England
*Newcastle-under-Lyme, a town in Staffordshire, England
*Newcastle, New South Wales, a metropolitan area in Australia, named after Newcastle ...
on channel 5. While some Channel 5 stations were moved to 5A in the 1970s and 80s, beginning in the 1990s, the Australian Broadcasting Authority began a process to move these stations to UHF
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter (on ...
bands to free up valuable VHF spectrum for its original purpose of FM radio. In addition, by 1985 the federal government decided new TV stations are to be broadcast on the UHF band.
Two new VHF channels, 9A and 12, have since been made available and are being used primarily for digital services (e.g. ABC
ABC are the first three letters of the Latin script known as the alphabet.
ABC or abc may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Broadcasting
* American Broadcasting Company, a commercial U.S. TV broadcaster
** Disney–ABC Television ...
in capital cities) but also for some new analogue services in regional areas. Because channel 9A is not used for television services in or near Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Adelaide or Perth, digital radio
Digital radio is the use of digital technology to transmit or receive across the radio spectrum. Digital transmission by radio waves includes digital broadcasting, and especially digital audio radio services.
Types
In digital broadcasting syst ...
in those cities are broadcast on DAB frequencies blocks 9A, 9B and 9C.
VHF radio is also used for marine Radio as per its long-distance reachability comparing UHF frequencies.
Example allocation of VHF–UHF frequencies:
* Radionavigation 60: 84–86 MHz
* Fixed Maritime Mobile: 130–135.7 MHz
* Fixed Aeronautical radio navigation: 160–190 MHz
* Broadcasting Aeronautical Radionavigation: 255–283.5 MHz
* Aeronautical Radionavigation AUS 49 / Maritime Radionavigation (radiobeacons) 73: 315–325 MHz
New Zealand
*44–51, 54–68 MHz:Band I
Band I is a range of radio frequencies within the very high frequency (VHF) part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The first time there was defined "for simplicity" in Annex 1 of "Final acts of the European Broadcasting Conference in the VHF and U ...
Television (channels 1–3)
*87.5–108 MHz: Band II
Band II is the range of radio frequencies within the very high frequency (VHF) part of the electromagnetic spectrum from 87.5 to 108.0 megahertz (MHz).
Radio
Band II is primarily used worldwide for FM radio broadcasting.
Broadcast telev ...
Radio
*174–230 MHz: Band III
Band III is the name of the range of radio frequencies within the very high frequency (VHF) part of the electromagnetic spectrum from 174 to 240 megahertz (MHz). It is primarily used for radio and television broadcasting. It is also called high-b ...
Television (channels 4–11)
Until 2013, the four main free-to-air TV stations in New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
used the VHF television bands (Band I
Band I is a range of radio frequencies within the very high frequency (VHF) part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The first time there was defined "for simplicity" in Annex 1 of "Final acts of the European Broadcasting Conference in the VHF and U ...
and Band III
Band III is the name of the range of radio frequencies within the very high frequency (VHF) part of the electromagnetic spectrum from 174 to 240 megahertz (MHz). It is primarily used for radio and television broadcasting. It is also called high-b ...
) to transmit to New Zealand households. Other stations, including a variety of pay and regional free-to-air stations, were forced to broadcast in the UHF
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter (on ...
band, since the VHF band had been very overloaded with four stations sharing a very small frequency band, which was so overcrowded that one or more channels would not be available in some smaller towns.
However, at the end of 2013, all television channels stopped broadcasting on the VHF bands, as New Zealand moved to digital television broadcasting, requiring all stations to either broadcast on UHF or satellite (where UHF was unavailable) utilising the Freeview Freeview may refer to:
*Freeview (Australia), the marketing name for the digital terrestrial television platform in Australia
*Freeview (New Zealand), a digital satellite and digital terrestrial television platform in New Zealand
*Freeview (UK), a ...
service.
Refer to Australasian television frequencies
Television frequency allocation has evolved since the start of television in Australia in 1956, and later in New Zealand in 1960. There was no coordination between the national spectrum management authorities in either country to establish the f ...
for more information.
United Kingdom
British television originally used VHFband I
Band I is a range of radio frequencies within the very high frequency (VHF) part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The first time there was defined "for simplicity" in Annex 1 of "Final acts of the European Broadcasting Conference in the VHF and U ...
and band III
Band III is the name of the range of radio frequencies within the very high frequency (VHF) part of the electromagnetic spectrum from 174 to 240 megahertz (MHz). It is primarily used for radio and television broadcasting. It is also called high-b ...
. Television on VHF was in black and white with 405-line
The 405-line monochrome analogue television broadcasting system was the first fully electronic television system to be used in regular broadcasting. The number of television lines influences the image resolution, or quality of the picture.
It was ...
format (although there were experiments with all three colour systems-NTSC
The first American standard for analog television broadcast was developed by National Television System Committee (NTSC)National Television System Committee (1951–1953), Report and Reports of Panel No. 11, 11-A, 12–19, with Some supplement ...
, PAL
Phase Alternating Line (PAL) is a colour encoding system for analogue television. It was one of three major analogue colour television standards, the others being NTSC and SECAM. In most countries it was broadcast at 625 lines, 50 fields (25 ...
, and SECAM
SECAM, also written SÉCAM (, ''Séquentiel de couleur à mémoire'', French for ''color sequential with memory''), is an analog color television system that was used in France, some parts of Europe and Africa, and Russia. It was one of th ...
-adapted for the 405-line system in the late 1950s and early 60s).
British colour television was broadcast on UHF
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter (on ...
(channels 21–69), beginning in the late 1960s. From then on, TV was broadcast on both VHF and UHF (VHF being a monochromatic downconversion from the 625-line colour signal), with the exception of BBC2
BBC Two is a British free-to-air public broadcast television network owned and operated by the BBC. It covers a wide range of subject matter, with a remit "to broadcast programmes of depth and substance" in contrast to the more mainstream an ...
(which had always broadcast solely on UHF). The last British VHF TV transmitters closed down on January 3, 1985. VHF band III
Band III is the name of the range of radio frequencies within the very high frequency (VHF) part of the electromagnetic spectrum from 174 to 240 megahertz (MHz). It is primarily used for radio and television broadcasting. It is also called high-b ...
is now used in the UK for digital audio broadcasting
Digital radio is the use of digital technology to transmit or receive across the radio spectrum. Digital transmission by radio waves includes digital broadcasting, and especially digital audio radio services.
Types
In digital broadcasting syst ...
, and VHF band II
Band II is the range of radio frequencies within the very high frequency (VHF) part of the electromagnetic spectrum from 87.5 to 108.0 megahertz (MHz).
Radio
Band II is primarily used worldwide for FM radio broadcasting.
Broadcast telev ...
is used for FM radio
FM broadcasting is a method of radio broadcasting using frequency modulation (FM). Invented in 1933 by American engineer Edwin Armstrong, wide-band FM is used worldwide to provide high fidelity sound over broadcast radio. FM broadcasting is cap ...
, as it is in most of the world.
Unusually, the UK has an amateur radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communic ...
allocation at 4 metres
The 4-metre (70 MHz) band is an amateur radio band within the lower part of the very high frequency (VHF) band.
As only a few countries within and outside of Europe have allocated the band for amateur radio access, the availability of dedica ...
, 70–70.5 MHz.
United States and Canada
Frequency assignments between US and Canadian users are closely coordinated since much of the Canadian population is within VHF radio range of the US border. Certain discrete frequencies are reserved forradio astronomy
Radio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies celestial objects at radio frequencies. The first detection of radio waves from an astronomical object was in 1933, when Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories reported radiation coming f ...
.
The general services in the VHF band are:
*30–49.6 MHz: Licensed 2-way land mobile communication, with various sub-bands.The 42 MHz Segment is still in current use by the California Highway Patrol
The California Highway Patrol (CHP) is a state law enforcement agency of the U.S. state of California. The CHP has primary patrol jurisdiction over all California highways and roads and streets outside city limits, and can exercise law enfor ...
, New Jersey State Police
The New Jersey State Police (NJSP) is the official state police force of the U.S. state of New Jersey. It is a general-powers police agency with statewide jurisdiction, designated by troop sectors.
History
As with other state police organization ...
, Tennessee Highway Patrol, and other state law enforcement agencies.
*30–88 MHz: Military VHF FM, including SINCGARS
Single Channel Ground and Airborne Radio System (SINCGARS) is a Combat-net radio (CNR) used by U.S. and allied military forces. The CNR network is designed around three systems: SINCGARS, the high frequency (HF) radio, and the SC tactical satel ...
*43–50 MHz: Cordless telephone
A cordless telephone or portable telephone has a portable telephone handset that connects by radio to a base station connected to the public telephone network. The operational range is limited, usually to the same building or within some short ...
s, 49 MHz FM walkie-talkies and radio controlled toys, and mixed 2-way mobile communication. The FM broadcast band originally operated here (42–50 MHz) before it was moved to 88–108 MHz.
*50–54 MHz: Amateur radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communic ...
6-meter band
The 6-meter band is the lowest portion of the very high frequency (VHF) radio spectrum internationally allocated to amateur radio use. The term refers to the average signal wavelength of 6 meters.
Although located in the lower portion of t ...
**50.8–51 MHz: Radio-controlled aircraft
A radio-controlled aircraft (often called RC aircraft or RC plane) is a small flying machine that is controlled remotely by an operator on the ground using a hand-held radio transmitter. The transmitter continuously communicates with a receiver ( ...
(on ten fixed frequencies at 20 kHz spacing) with an FCC Amateur Radio Service license, flown under FCC Part 97, rule 97.215.
*54–88 MHz, known as " Band I" internationally; some DTV stations will appear here. See Pan-American television frequencies
The Pan-American television frequencies are different for terrestrial and cable television systems. Terrestrial television channels are divided into two bands: the VHF band which comprises channels 2 through 13 and occupies frequencies between 54 a ...
.
**54–72 MHz TV channels 2–4 (VHF-Lo)
**72–76 MHz: Radio controlled models, industrial remote control, and other devices. Model aircraft
A model aircraft is a small unmanned aircraft. Many are replicas of real aircraft. Model aircraft are divided into two basic groups: flying and non-flying. Non-flying models are also termed static, display, or shelf models.
Aircraft manufactur ...
operate on 72 MHz while surface models operate on 75 MHz in the US and Canada, air navigation beacons 74.8–75.2 MHz.
**76–88 MHz TV channels 5–6 (VHF-Lo)
*87.5–108 MHz: FM radio
FM broadcasting is a method of radio broadcasting using frequency modulation (FM). Invented in 1933 by American engineer Edwin Armstrong, wide-band FM is used worldwide to provide high fidelity sound over broadcast radio. FM broadcasting is cap ...
broadcasting (87.9–91.9 non-commercial, 92–108 commercial in the United States) (known as " Band II" internationally)
*108–118 MHz: Air navigation beacons VOR
VOR or vor may refer to:
Organizations
* Vale of Rheidol Railway in Wales
* Voice of Russia, a radio broadcaster
* Volvo Ocean Race, a yacht race
Science, technology and medicine
* VHF omnidirectional range, a radio navigation aid used in a ...
*118–137 MHz: Airband
Airband or aircraft band is the name for a group of frequencies in the VHF radio spectrum allocated to radio communication in civil aviation, sometimes also referred to as ''VHF'', or phonetically as ''"Victor"''. Different sections of the ban ...
for air traffic control
Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airs ...
, AM
**121.5 MHz is an emergency frequency
*137–138 MHz Space research, space operations, meteorological satellite
*138–144 MHz: Land mobile, auxiliary civil services, satellite, space research, and other miscellaneous services
*144–148 MHz: Amateur radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communic ...
2-meter band
The 2-meter amateur radio band is a portion of the VHF radio spectrum that comprises frequencies stretching from 144 MHz to 148 MHz in International Telecommunication Union region (ITU) Regions 2 (North and South America plus Hawaii) ...
*148–150 MHz: Land mobile, fixed, satellite
*150–156 MHz: "VHF business band
In the United States, the business band is the colloquial name used by radio users who utilize, and scanner hobbyists who listen to, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Industrial/Business pool frequencies. The regulations listing frequen ...
," public safety, the unlicensed Multi-Use Radio Service
In the United States, the Multi-Use Radio Service (MURS) is a licensed by rule (i.e. under part 95, subpart J, of title 47, Code of Federal Regulations) two-way radio service similar to the Citizens band (CB). Established by the U.S. Federal Comm ...
(MURS), and other 2-way land mobile, FM
*156–158 MHz VHF Marine Radio
**156.8 MHz (Channel 16) is the maritime emergency and contact frequency.
* 159.81-161.565 MHz railways The 160 and 161 areas are Association of American Railroads (AAR) 99 channel railroad
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
radios, issued to the railroad. For example, AAR 21 is 160.425 MHz and that is issued to Tennessee Valley Railroad Museum
The Tennessee Valley Railroad Museum is a railroad museum and heritage railroad in Chattanooga, Tennessee.
The Tennessee Valley Railroad Museum was founded as a chapter of the National Railway Historical Society in 1960 by Paul H. Merriman an ...
, as well as other railroads that want AAR Channel 21.
**159.81–160.2 are railroads in Canada only and is used by trucking companies in the U.S.
*160.6–162 Wireless microphones and TV/FM broadcast remote pickup
*162.4–162.55: NOAA Weather Stations, narrowband FM, Weatheradio Canada Stations
*174–240 MHz, known as " Band III" internationally. A number of DTV channels have begun broadcasting here, especially many of the stations which were assigned to these channels for previous analog operation.
**174–216 MHz television channels 7–13 (VHF-Hi)
**174–216 MHz: professional wireless microphones (low power, certain exact frequencies only)
**216–222 MHz: land mobile, fixed, maritime mobile,
**222–225 MHz: 1.25 meters (US) (Canada 219–220, 222–225 MHz) amateur radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communic ...
*225 MHz and above (UHF): Military aircraft radio, 243 MHz is an emergency frequency (225–400 MHz) AM, including HAVE QUICK, dGPS RTCM-104
Cable television
Cable television is a system of delivering television programming to consumers via radio frequency (RF) signals transmitted through coaxial cables, or in more recent systems, light pulses through fibre-optic cables. This contrasts with broa ...
, though not transmitted aerially, uses a spectrum of frequencies overlapping VHF.
VHF television
The U.S.FCC
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government that regulates communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable across the United States. The FCC maintains jurisdiction ...
allocated television broadcasting to a channelized roster as early as 1938 with 19 channels. That changed three more times: in 1940 when Channel 19 was deleted and several channels changed frequencies, then in 1946 with television going from 18 channels to 13 channels, again with different frequencies, and finally in 1948 with the removal of Channel 1 (analog channels 2–13 remain as they were, even on cable television
Cable television is a system of delivering television programming to consumers via radio frequency (RF) signals transmitted through coaxial cables, or in more recent systems, light pulses through fibre-optic cables. This contrasts with broa ...
). Channels 14–19 later appeared on the UHF band, while channel 1 remains unused.
87.5–87.9 MHz
87.5–87.9 MHz is a radio frequency which, in most of the world, is used forFM broadcasting
FM broadcasting is a method of radio broadcasting using frequency modulation (FM). Invented in 1933 by American engineer Edwin Armstrong, wide-band FM is used worldwide to provide high fidelity sound over broadcast radio. FM broadcasting is cap ...
. In North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, however, this bandwidth is allocated to VHF television channel 6 (82–88 MHz). The analog audio for TV channel 6 is broadcast at 87.75 MHz (adjustable down to 87.74). Several stations, known as Frankenstation
This is a list of low-power television stations (LPTV) in the United States, transmitting on VHF channel 6, which operate as radio stations capable of being picked up by standard FM receivers. These stations are colloquially known as "Franken FMs" ...
s, most notably those joining the Pulse 87
Pulse 87 is an online radio station with an EDM music format. It started out as the audio feed of a channel-6 “Franken-FM” television station in New York City, audible on traditional FM radios at 87.7, before moving solely to streaming online ...
franchise, have operated on this frequency as radio stations, though they use television licenses. As a result, FM radio receivers such as those found in automobiles which are designed to tune into this frequency range could receive the audio for analog-mode programming on the local TV channel 6 while in North America. The practice largely ended with the DTV transition
The digital television transition, also called the digital switchover (DSO), the analogue switch/sign-off (ASO), the digital migration, or the analogue shutdown, is the process in which older analogue television broadcasting technology is conv ...
in 2009, although some still exist.
The FM broadcast channel at 87.9 MHz is normally off-limits for FM audio broadcasting; it is reserved for displaced class D stations which have no other frequencies in the normal 88.1–107.9 MHz subband to move to. So far, only two stations have qualified to operate on 87.9 MHz: 10–watt KSFH
KSFH was an American non-commercial educational FM radio station licensed to operate on 87.9 MHz with an effective radiated power of 10 watts. KSFH started as the radio station of Saint Francis High School at Mountain View, California. It ...
in Mountain View, California
Mountain View is a city in Santa Clara County, California, United States. Named for its views of the Santa Cruz Mountains, it has a population of 82,376.
Mountain View was integral to the early history and growth of Silicon Valley, and is the ...
and 34–watt translator K200AA
K, or k, is the eleventh Letter (alphabet), letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet#Le ...
in Sun Valley, Nevada
Sun Valley is a census-designated place (CDP) in Washoe County, Nevada, United States. The population was 19,299 at the 2010 census. It is north of Reno and is part of the Reno– Sparks Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Geography
The community ...
.
Unlicensed operation
In some countries, particularly the United States and Canada, limited low-power license-free operation is available in the FM broadcast band for purposes such asmicro-broadcasting
Microbroadcasting is the process of broadcasting a message to a relatively small audience. This is not to be confused with low-power broadcasting.
Microbroadcasting, in radio terms, is the use of low-power transmitters (often Title 47 CFR Part 1 ...
and sending output from CD or digital media players to radios without auxiliary-in jacks, though this is illegal in some other countries. This practice was legalised in the United Kingdom on 8 December 2006.
See also
*Marine VHF radio
Marine VHF radio is a worldwide system of two way radio transceivers on ships and watercraft used for bidirectional voice communication from ship-to-ship, ship-to-shore (for example with harbormasters), and in certain circumstances ship-to-ai ...
*TV radio
TV radio, TV band radio, and TV audio radio are common names for a type of radio receiver that can play the audio portion of a TV channel. The actual name of the device may comprise a list of all frequency bands the device can receive (e.g. A ...
*List of oldest radio stations
It is generally recognised that the first radio transmission was made from a temporary station set up by Guglielmo Marconi in 1895. This followed on from pioneering work in the field by a number of people including Alessandro Volta, André-Mari ...
*Apex (radio band)
Apex radio stations (also known as skyscraper and pinnacle) was the name commonly given to a short-lived group of United States broadcasting stations, which were used to evaluate transmitting on frequencies that were much higher than the ones used ...
*FM broadcast band
The FM broadcast band is a range of radio frequencies used for FM broadcasting by radio stations. The range of frequencies used differs between different parts of the world. In Europe and Africa (defined as International Telecommunication Union (I ...
*Moving image formats
This article discusses moving image capture, transmission and presentation from today's technical and creative points of view; concentrating on aspects of frame rates.
Essential parameters
The essential parameters of any moving image sequence a ...
*Polar mesosphere summer echoes
Polar mesospheric summer echoes (PMSE) is the phenomenon of anomalous radar echoes found between 80 and 90 km in altitude from May through early August in the Arctic, and from November through to February in the Antarctic. These strong radar ...
*Television channel frequencies
The following tables show the frequencies assigned to broadcast television channels in various regions of the world, along with the ITU letter designator for the system used. The frequencies shown are for the analogue video and audio carriers. ...
*Knife-edge effect
Diffraction is defined as the interference or bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle/aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a s ...
*Instrument Landing System
In aviation, the instrument landing system (ILS) is a precision radio navigation system that provides short-range guidance to aircraft to allow them to approach a runway at night or in bad weather. In its original form, it allows an aircraft to ...
*VHF omnidirectional range
Very high frequency omnirange station (VOR) is a type of short-range radio navigation system for aircraft, enabling aircraft with a receiving unit to determine its position and stay on course by receiving radio signals transmitted by a network ...
* High frequency
High frequency (HF) is the ITU designation for the range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves (radio waves) between 3 and 30 megahertz (MHz). It is also known as the decameter band or decameter wave as its wavelengths range from one to ten ...
* Low frequency
Low frequency (LF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 30–300 kHz. Since its wavelengths range from 10–1 km, respectively, it is also known as the kilometre band or kilometre wave.
LF radio waves exh ...
* Extremely low frequency
Extremely low frequency (ELF) is the ITU designation for electromagnetic radiation ( radio waves) with frequencies from 3 to 30 Hz, and corresponding wavelengths of 100,000 to 10,000 kilometers, respectively. In atmospheric sc ...
* Ultra low frequency
Ultra low frequency (ULF) is the ITU designation for the frequency range of electromagnetic waves between 300 hertz and 3 kilohertz, corresponding to wavelengths between 1,000 to 100 km. In magnetosphere science and seismology, alternative defin ...
Notes
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Very High Frequency Radio spectrum Television terminology