Etymology
Samuel de Champlain claimed the area around what is now Lake Champlain, giving the name ''Vert Mont'' (Green Mountain) to the region he found, on a 1647 map. Evidence suggests that this name came into use among English settlers, before it morphed to "Vermont", ca. 1760. In 1777, Thomas Young (American revolutionary), Thomas Young introduced the name in writing with a broadside "To the Inhabitants of Vermont, a Free and Independent State".History
Native American
Between 8500 and 7000 BCE, at the time of the Champlain Sea, Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans inhabited and hunted in present-day Vermont. During the Archaic period in the Americas, Archaic period, from the 8th millennium BCE to 1000 BCE, Native Americans migrated year-round. During the Woodland period, from 1000 BCE to 1600 CE, they established villages and trade networks, and developed ceramic and bow (weapon), bow and arrow technology. Their population in 1500 CE was estimated to be around 10,000 people. During colonial times, where encounters and settlement were initiated by French colonists, the territory was occupied mainly by an Abenaki tribe known as the Sokoki, or Missisquois. The eastern part of the state may have also been occupied by the Androscoggin people, Androscoggin and Pennacook peoples. To the west, the Missisquois competed with the Iroquoian Mohawk people, Mohawk, based in the Mohawk valley but with a large territory, and the Algonquin Mohican peoples. Many of the tribes later formed the Wabanaki Confederacy during King Philip's War. The warfare by English colonists defeated and scattered most of the surviving Abenaki tribes.Colonial
 The first European to see Vermont is thought to have been French explorer Jacques Cartier in 1535. On July 30, 1609, French colonization of the Americas, French explorer Samuel de Champlain claimed this territory as part of New France. In 1666, French settlers erected Fort Sainte Anne (Vermont), Fort Sainte Anne on Isle La Motte, the first European settlement in Vermont.
The "violent" 1638 New Hampshire earthquake was centered in the St. Lawrence Valley and reported throughout New England. This was the first seismic event noted in Vermont. In 1690, a group of Dutch-British settlers from Albany, New York, Albany established a settlement and trading post at Chimney Point, Vermont, Chimney Point, west of present-day Addison, Vermont, Addison. During Dummer's War, the first permanent English settlement was established in 1724 with the construction of Fort Dummer. It was intended to protect the nearby settlements of Dummerston, Vermont, Dummerston and Brattleboro (town), Vermont, Brattleboro.
From 1731 to 1734, the French constructed Fort St. Frédéric, which gave them control of the New France–Vermont frontier region in the Lake Champlain Valley. With the outbreak of the French and Indian War in 1754, the North American front of the Seven Years' War between the French and British, the French began construction in 1755 of Fort Ticonderoga, Fort Carillon at present-day Ticonderoga, New York. The British failed to take either fort between 1755 and 1758. In 1759, a combined force of 12,000 British regular and provincial troops under Sir Jeffery Amherst, 1st Baron Amherst, Jeffery Amherst captured Carillon in the Battle of Ticonderoga (1759), Battle of Ticonderoga, after which the French abandoned Fort St. Frédéric. Amherst constructed Fort Crown Point next to the remains of the Fort St. Frédéric, securing British control over the area.
Following France's loss in the French and Indian War, through the Treaty of Paris (1763), 1763 Treaty of Paris, it ceded control of land east of the Mississippi River to the British. The Crown attempted to Royal Proclamation of 1763, limit colonial settlement to lands east of the Appalachians, in order to prohibit encroachment on Native American lands. The territory of Vermont was divided nearly in half in a jagged line running from Fort William Henry in Lake George (lake), New York, Lake George diagonally north-eastward to Lake Memphremagog. With the end of the war, new settlers arrived in Vermont. Ultimately, Massachusetts, New Hampshire and New York all claimed this frontier area.
On July 20, 1764, George III of the United Kingdom, King George III established the boundary between New Hampshire and
The first European to see Vermont is thought to have been French explorer Jacques Cartier in 1535. On July 30, 1609, French colonization of the Americas, French explorer Samuel de Champlain claimed this territory as part of New France. In 1666, French settlers erected Fort Sainte Anne (Vermont), Fort Sainte Anne on Isle La Motte, the first European settlement in Vermont.
The "violent" 1638 New Hampshire earthquake was centered in the St. Lawrence Valley and reported throughout New England. This was the first seismic event noted in Vermont. In 1690, a group of Dutch-British settlers from Albany, New York, Albany established a settlement and trading post at Chimney Point, Vermont, Chimney Point, west of present-day Addison, Vermont, Addison. During Dummer's War, the first permanent English settlement was established in 1724 with the construction of Fort Dummer. It was intended to protect the nearby settlements of Dummerston, Vermont, Dummerston and Brattleboro (town), Vermont, Brattleboro.
From 1731 to 1734, the French constructed Fort St. Frédéric, which gave them control of the New France–Vermont frontier region in the Lake Champlain Valley. With the outbreak of the French and Indian War in 1754, the North American front of the Seven Years' War between the French and British, the French began construction in 1755 of Fort Ticonderoga, Fort Carillon at present-day Ticonderoga, New York. The British failed to take either fort between 1755 and 1758. In 1759, a combined force of 12,000 British regular and provincial troops under Sir Jeffery Amherst, 1st Baron Amherst, Jeffery Amherst captured Carillon in the Battle of Ticonderoga (1759), Battle of Ticonderoga, after which the French abandoned Fort St. Frédéric. Amherst constructed Fort Crown Point next to the remains of the Fort St. Frédéric, securing British control over the area.
Following France's loss in the French and Indian War, through the Treaty of Paris (1763), 1763 Treaty of Paris, it ceded control of land east of the Mississippi River to the British. The Crown attempted to Royal Proclamation of 1763, limit colonial settlement to lands east of the Appalachians, in order to prohibit encroachment on Native American lands. The territory of Vermont was divided nearly in half in a jagged line running from Fort William Henry in Lake George (lake), New York, Lake George diagonally north-eastward to Lake Memphremagog. With the end of the war, new settlers arrived in Vermont. Ultimately, Massachusetts, New Hampshire and New York all claimed this frontier area.
On July 20, 1764, George III of the United Kingdom, King George III established the boundary between New Hampshire and Sovereignty
 On January 15, 1777, representatives of the New Hampshire Grants declared the independence of Vermont Republic, Vermont. For the first six months of its existence, it was called the Republic of New Connecticut.Esther Munroe Swift, ''Vermont Place-Names: Footprints in History'' Picton Press, 1977
On June 2, 1777, a second convention of 72 delegates met and adopted the name "Vermont". This was on the advice of a friendly Pennsylvanian, Dr. Thomas Young (American Revolutionary), Thomas Young, friend and mentor of Ethan Allen. He was advising them on how to achieve admission into the newly independent United States of America as the 14th state. On July 4, they completed the drafting of the Constitution of the Vermont Republic, Constitution of Vermont at the Old Constitution House, Windsor Tavern, and adopted it on July 8. This was the first written constitution in North America to ban adult slavery, saying slavery in Vermont, male slaves become free at the age of 21 and females at 18. It provided for universal adult male suffrage and required support of public schools. It was in effect from 1777 to 1786.
On January 15, 1777, representatives of the New Hampshire Grants declared the independence of Vermont Republic, Vermont. For the first six months of its existence, it was called the Republic of New Connecticut.Esther Munroe Swift, ''Vermont Place-Names: Footprints in History'' Picton Press, 1977
On June 2, 1777, a second convention of 72 delegates met and adopted the name "Vermont". This was on the advice of a friendly Pennsylvanian, Dr. Thomas Young (American Revolutionary), Thomas Young, friend and mentor of Ethan Allen. He was advising them on how to achieve admission into the newly independent United States of America as the 14th state. On July 4, they completed the drafting of the Constitution of the Vermont Republic, Constitution of Vermont at the Old Constitution House, Windsor Tavern, and adopted it on July 8. This was the first written constitution in North America to ban adult slavery, saying slavery in Vermont, male slaves become free at the age of 21 and females at 18. It provided for universal adult male suffrage and required support of public schools. It was in effect from 1777 to 1786.
Revolutionary War
The Battle of Bennington, fought on August 16, 1777, was a seminal event in the history of the state of Vermont and the United States. A combined American force, under General John Stark's command, attacked the Hessian (soldier), Hessian column at Hoosick, New York, just across the border from Bennington. It killed or captured virtually the entire Hessian detachment. General John Burgoyne, Burgoyne never recovered from this loss and eventually surrendered the remainder of his 6,000-man force at Saratoga, New York, on October 17 that year. The battles of Battle of Bennington, Bennington and Battle of Saratoga, Saratoga together are recognized as the turning point in the Revolutionary War because they were the first major defeat of a British army. The anniversary of the battle is still celebrated in Vermont as a legal holiday. The Battle of Hubbardton (July 7, 1777) was the only Revolutionary Military history of Vermont, battle within the present boundaries of Vermont. Although the Continental forces were technically defeated, the British forces were damaged to the point that they did not pursue the Americans (retreating from Fort Ticonderoga) any further.Admission to the Union
Vermont continued to govern itself as a sovereign entity based in the eastern town of Windsor for 14 years. The independent state of Vermont issued its own coinage from 1785 to 1788 and operated a national postal service. Thomas Chittenden was the Governor in 1778–89 and in 1790–91. Because the state of New York continued to assert a disputed claim that Vermont was a part of New York, Vermont could not be admission to the Union, admitted to the Union under Article IV, Section3 of the Constitution until the legislature of New York consented. On March 6, 1790, the legislature made its consent contingent upon a negotiated agreement on the precise boundary between the two states. When commissioners from New York and Vermont met to decide on the boundary, Vermont's negotiators insisted on also settling the property ownership disputes with New Yorkers, rather than leaving that to be decided later in a federal court. The negotiations were successfully concluded in October 1790 with an agreement that Vermont would pay $30,000 to New York to be distributed among New Yorkers who claimed land in Vermont under New York land patents. In January 1791, a convention in Vermont voted 105–4 to petition Congress to become a state in the federal union. Congress acted on February 18, 1791, to admit Vermont to the Union as the 14th state as of March 4, 1791. Vermont became the first state to enter the Union after the original 13 states. The revised constitution of 1786, which established a greater separation of powers, continued in effect until 1793, two years after Vermont's admission to the Union. Under the Act "To Secure Freedom to All Persons Within This State," slavery was officially banned by state law on November 25, 1858, less than three years before the American Civil War. Vermonters provided refuge in several sites for escaped slaves, fleeing to Canada, as part of what was called the Underground Railroad.Civil War
 From the mid-1850s on, some Vermonters became activists opposing slavery, which they had previously worked to contain in the South. Abolitionism in the United States, Abolitionist Thaddeus Stevens was born in Vermont and later represented a district in Pennsylvania in Congress. He developed as a national leader and later promoted Radical Republicans, Radical Republican goals after the American Civil War. While the Whig Party shriveled, and the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party emerged, Vermont supported Republican candidates. In 1860, it voted for Abraham Lincoln, giving him the largest margin of victory of any state.
During the American Civil War, Vermont sent 33,288 men into United States service. 5,224 Vermonters (more than 15 percent) were killed.
The northernmost land action of the war was the St. Albans Raid—the robbery of three St. Albans banks, perpetrated in October 1864 by 21 Confederate agents. A posse pursued the Confederate raiders into Canada and captured several of them. They had to turn their captives over to Canadian officials. Canada reimbursed the banks, released, and later re-arrested some of the perpetrators.
From the mid-1850s on, some Vermonters became activists opposing slavery, which they had previously worked to contain in the South. Abolitionism in the United States, Abolitionist Thaddeus Stevens was born in Vermont and later represented a district in Pennsylvania in Congress. He developed as a national leader and later promoted Radical Republicans, Radical Republican goals after the American Civil War. While the Whig Party shriveled, and the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party emerged, Vermont supported Republican candidates. In 1860, it voted for Abraham Lincoln, giving him the largest margin of victory of any state.
During the American Civil War, Vermont sent 33,288 men into United States service. 5,224 Vermonters (more than 15 percent) were killed.
The northernmost land action of the war was the St. Albans Raid—the robbery of three St. Albans banks, perpetrated in October 1864 by 21 Confederate agents. A posse pursued the Confederate raiders into Canada and captured several of them. They had to turn their captives over to Canadian officials. Canada reimbursed the banks, released, and later re-arrested some of the perpetrators.
Postbellum era to present
Demographic changes and rise of eugenics in 20th century
As English speakers came to dominate the population in Vermont, they anglicized the names of many ethnic French residents and often discriminated against them. In the mid-20th century, descendants began to reclaim their French names, especially surnames. Beginning in the mid-19th century, Vermont industries attracted numerous Irish Americans, Irish, Scotch-Irish Americans, Scots-Irish and Italian Americans, Italian immigrants, adding to its residents of mostly English Americans, English and some Quebec diaspora#United States, French-Canadian ancestry. Many of the immigrants migrated to Barre (city), Vermont, Barre, where the men worked as stonecutters of granite, for which there was a national market. Vermont granite was used in major public buildings in many states. In this period, many Italian and Scottish women operated boarding houses to support their families. Such facilities also helped absorb new residents and help them learn the new culture; European immigrants peaked in number between 1890 and 1900. Typically immigrants boarded with people of their own language and ethnicity, but sometimes they boarded with others. Gradually the new immigrants were absorbed into the state. Times of tension aroused divisions. In the early 20th century, some people in Vermont became alarmed about what they considered to be a decline in rural areas; people left farming to move to cities and others seemed unable to fit within society. In addition, there was a wave of immigration by French Canadians, and Protestant Anglo-Americans feared being overtaken by the new immigrants, who added to the Catholic population of Irish and Italians. Based on the colonial past, some Yankee residents considered the French Canadians to have intermarried too frequently with Native Americans. In an era influenced by ideas of Social Darwinism, some Vermont leaders promoted eugenics, an idea that the population could be managed and improved by limiting marriage and reproduction by certain members classified as unfit or defective. It passed a marriage law, to limit marriage by people considered unfit. In 1915, the Brandon State School opened, the beginning of a related effort to segregate and control those judged unfit to reproduce. The state followed efforts to improve children's welfare by establishing other institutions to house the mentally ill or disabled. From 1925 to 1928 the Eugenics Survey of Vermont conducted research and recorded the histories of families it determined were degenerate or dependent. It also attempted to educate the public about why restrictive measures, including voluntary sterilization, were desirable. Review by current historians reveals the results were socially prejudiced, as the surveys tended to target the poor and disenfranchised minorities, including French Canadians, Abenaki, and disabled. In 1931, Vermont was the 29th state to pass a eugenics law. Vermont like other states, sterilized some patients in institutions and persons it had identified through surveys as degenerate or unfit. It nominally had permission from the patients or their guardians, but abuses have been documented. Two-thirds of the sterilizations were done on women, and poor, unwed mothers were targeted, among others. The surgery was performed at institutions and hospitals in the state supposedly devoted to care of people in need. There is disagreement about how many sterilizations were performed; most were completed from 1931 to 1941, but such procedures were recorded as late as 1970.Political changes
Vermont approved women's suffrage decades before it became part of the national constitution. Women were first allowed to vote in the elections of December 18, 1880, when women were granted limited suffrage. They were first allowed to vote in town elections, and later in state legislative races. In 1964, the Supreme Court of the United States, U.S. Supreme Court decision in ''Reynolds v. Sims'' required "one man, one vote" redistricting in all states. It had found that many state legislatures had not redistricted and were unjustly dominated by rural interests, years after the development of densely populated and industrial urban areas. In addition, it found that many states had an upper house based on geographical jurisdictions, such as counties. This gave disproportionate power to rural and lightly populated counties. The court ruled there was no basis for such a structure. Major changes in political apportionment took place in Vermont and other affected states. This ruling required districts to be reassessed after every census and to be based on roughly equal population, rather than geography (such as counties). Under redistricting, residents in urban areas were to gain an equitable share of apportionment in both houses in every state. Vermont and some other northern states had long been dominated by rural districts, as were several Southern states in those years, who had not redistricted since the turn of the century. Until that time, apportionment of upper houses was often based on county jurisdictions, which had given more power to rural counties and failed to acknowledge the increased population in urban areas. This arrangement had meant that urban areas did not have proportionate political power and often suffered from underinvestment in needed infrastructure; other urban issues were also neglected by rural-dominated legislatures. In July 2000, Vermont became the first state to introduce civil unions. In 2009, Vermont became the first state to legalize same-sex marriage, unforced by court challenge or ruling. In 2002, the State of Vermont reported that the Abenaki people had migrated north to Quebec by the end of the 17th century; however, in 2011, the State of Vermont designated the Elnu Abenaki Tribe and the Nulhegan Band of the Coosuk Abenaki Nation as state-recognized tribes; in 2012 it recognized the Abenaki Nation of Missisquoi and the Koasek Traditional Band of the Koos Abenaki Nation. In 2016, the state governor proclaimed Columbus Day as Indigenous Peoples Day. Vermont has no federally recognized tribes. On January 22, 2018, Vermont became the first of the United States to legalize cannabis for recreational use by legislative action, and the ninth state in the United States to legalize marijuana for medical purposes. This law was signed by Republican Governor Phil Scott.Geography
 Vermont is located in the New England region of the northeastern United States and comprises , making it the 45th-largest state. It is the only state that List of tallest buildings in Vermont, does not have any buildings taller than . Land comprises and water comprises , making it the 43rd-largest in land area and the 47th in water area. In total area, it is larger than El Salvador and smaller than Haiti. It is the only landlocked state in New England, and it is the easternmost and the smallest in area of all landlocked states.
The Green Mountains in Vermont form a north–south spine running most of the length of the state, slightly west of its center. In the southwest portion of the state are located the Taconic Mountains. In the northwest, near Lake Champlain, is the fertile Champlain Valley. In the south of the valley is Bomoseen Lake, Lake Bomoseen.
The west bank of the Connecticut River marks the state's eastern border with New Hampshire, though much of the river flows within New Hampshire's territory. 41% of Vermont's land area is part of the Connecticut River's watershed.
Lake Champlain, the sixth-largest body of fresh water in the United States, separates Vermont from New York in the northwest portion of the state. From north to south, Vermont is long. Its greatest width, from east to west, is at the Canada–U.S. border; the narrowest width is near the Massachusetts border. The width averages . The state's Centroid, geographic center is approximately three miles (5 km) east of Roxbury, Vermont, Roxbury, in Washington County, Vermont, Washington County. There are List of Canada–United States border crossings, fifteen U.S. federal border crossings between Vermont and Canada.
Several mountains have timberlines with delicate year-round alpine ecosystems, including Mount Mansfield, the highest mountain in the state; Killington Peak, the second-highest; Camel's Hump (Vermont), Camel's Hump, the state's third-highest; and Mount Abraham (Vermont), Mount Abraham, the fifth-highest peak. Areas in Vermont administered by the National Park Service include the Marsh-Billings-Rockefeller National Historical Park (in Woodstock, Vermont, Woodstock) and the Appalachian Trail by state#Vermont, Appalachian National Scenic Trail.
The topography and climate make sections of Vermont subject to large-scale flooding. Incidents include the Great Vermont Flood of 1927, which killed 84 and damaged much of the state's infrastructure, the flood of 1973, which covered many of the state's roads in the southeast, and Hurricane Irene, Tropical Storm Irene in 2011, which caused substantial damage throughout the state. In response to the 1927 flood, the Federal government funded construction of six flood control dams in the state, run by the Army Corps of Engineers. These extreme rain and flooding events are expected to Climate change in Vermont, get worse with climate change.
Vermont is located in the New England region of the northeastern United States and comprises , making it the 45th-largest state. It is the only state that List of tallest buildings in Vermont, does not have any buildings taller than . Land comprises and water comprises , making it the 43rd-largest in land area and the 47th in water area. In total area, it is larger than El Salvador and smaller than Haiti. It is the only landlocked state in New England, and it is the easternmost and the smallest in area of all landlocked states.
The Green Mountains in Vermont form a north–south spine running most of the length of the state, slightly west of its center. In the southwest portion of the state are located the Taconic Mountains. In the northwest, near Lake Champlain, is the fertile Champlain Valley. In the south of the valley is Bomoseen Lake, Lake Bomoseen.
The west bank of the Connecticut River marks the state's eastern border with New Hampshire, though much of the river flows within New Hampshire's territory. 41% of Vermont's land area is part of the Connecticut River's watershed.
Lake Champlain, the sixth-largest body of fresh water in the United States, separates Vermont from New York in the northwest portion of the state. From north to south, Vermont is long. Its greatest width, from east to west, is at the Canada–U.S. border; the narrowest width is near the Massachusetts border. The width averages . The state's Centroid, geographic center is approximately three miles (5 km) east of Roxbury, Vermont, Roxbury, in Washington County, Vermont, Washington County. There are List of Canada–United States border crossings, fifteen U.S. federal border crossings between Vermont and Canada.
Several mountains have timberlines with delicate year-round alpine ecosystems, including Mount Mansfield, the highest mountain in the state; Killington Peak, the second-highest; Camel's Hump (Vermont), Camel's Hump, the state's third-highest; and Mount Abraham (Vermont), Mount Abraham, the fifth-highest peak. Areas in Vermont administered by the National Park Service include the Marsh-Billings-Rockefeller National Historical Park (in Woodstock, Vermont, Woodstock) and the Appalachian Trail by state#Vermont, Appalachian National Scenic Trail.
The topography and climate make sections of Vermont subject to large-scale flooding. Incidents include the Great Vermont Flood of 1927, which killed 84 and damaged much of the state's infrastructure, the flood of 1973, which covered many of the state's roads in the southeast, and Hurricane Irene, Tropical Storm Irene in 2011, which caused substantial damage throughout the state. In response to the 1927 flood, the Federal government funded construction of six flood control dams in the state, run by the Army Corps of Engineers. These extreme rain and flooding events are expected to Climate change in Vermont, get worse with climate change.
Cities
Vermont has ten incorporated cities. The most populous city in Vermont is Burlington, Vermont, Burlington. Its metropolitan area is also the most populous in the state, with an estimate of 225,562 as of 2020.Largest towns
Although these New England town, towns are large enough to be considered cities, they are not incorporated as such.Climate
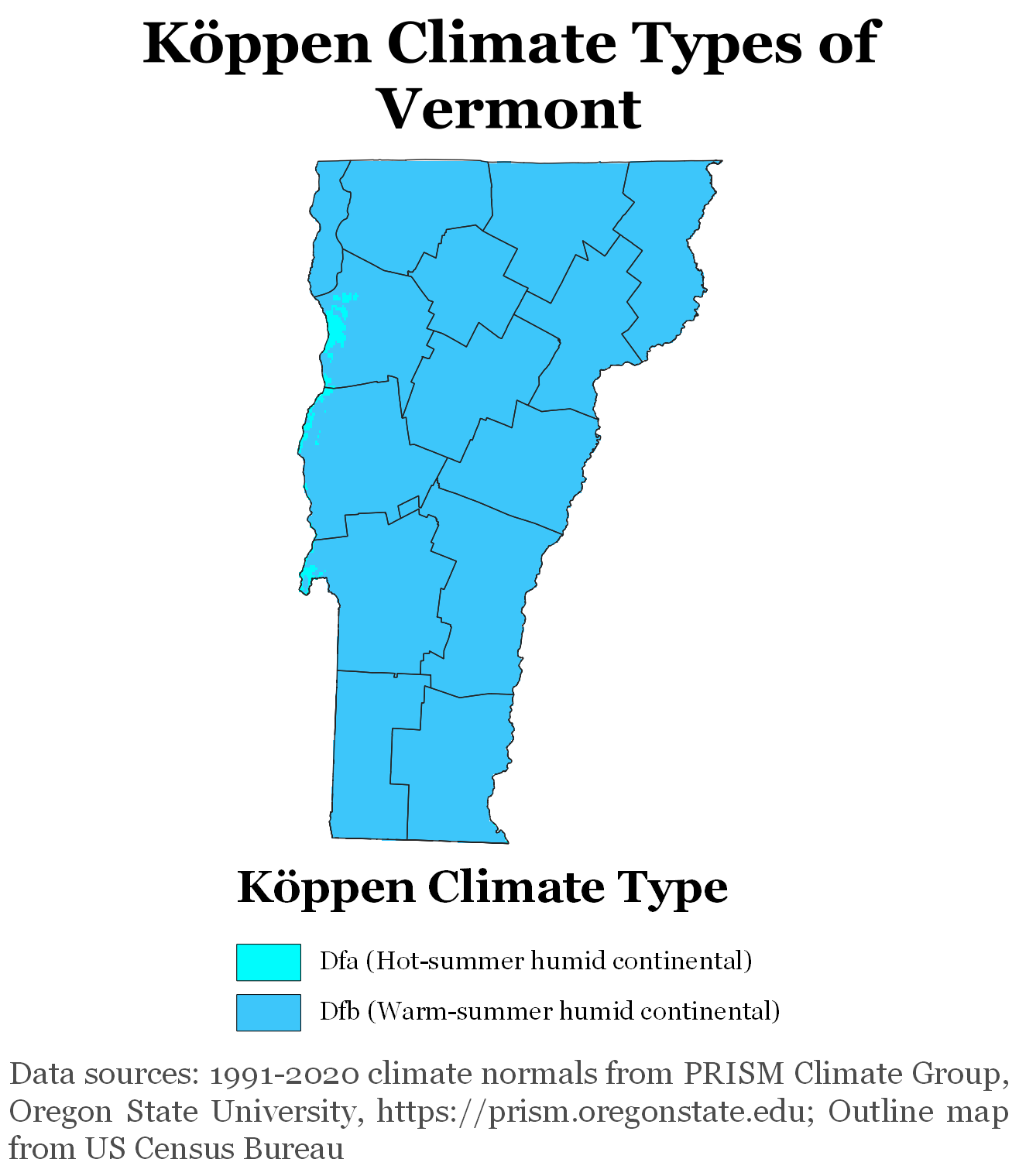 The annual mean temperature for the state is . Vermont has a humid continental climate, with mud season, muddy springs, in general a mild early summer, hot Augusts; it has autumn in New England, colorful autumns: Vermont's hills reveal red, orange, and (on sugar maples) gold foliage as cold weather approaches. Winters are colder at higher elevations. It has a Köppen climate classification of Dfb, a temperate continental climate.
The rural northeastern section known as the "Northeast Kingdom" often averages colder than the southern areas of the state during winter. The annual snowfall averages between depending on elevation. Vermont is the seventh coldest state in the country.
The highest recorded temperature was , at Vernon, Vermont, Vernon, on July 4, 1911. The lowest recorded temperature was , at Bloomfield, Vermont, Bloomfield, on December 30, 1933; this is the lowest temperature recorded in New England alongside Big Black River (Saint John River tributary), Big Black River, which recorded a verified in 2009. The agricultural growing season ranges from 120 to 180 days. The United States Department of Agriculture plant hardiness zones for the state range between zone 3b, no colder than , in the Northeast Kingdom and northern part of the state and zone 5b, no colder than , in the southern part of the state. The state receives between 2,200 and 2,400 hours of sunshine annually. New England as a whole receives a range of less than 2,000 hours of sunshine in part of New Hampshire to as much as 2,600 hours of sunshine per year in Connecticut and Rhode Island.
The annual mean temperature for the state is . Vermont has a humid continental climate, with mud season, muddy springs, in general a mild early summer, hot Augusts; it has autumn in New England, colorful autumns: Vermont's hills reveal red, orange, and (on sugar maples) gold foliage as cold weather approaches. Winters are colder at higher elevations. It has a Köppen climate classification of Dfb, a temperate continental climate.
The rural northeastern section known as the "Northeast Kingdom" often averages colder than the southern areas of the state during winter. The annual snowfall averages between depending on elevation. Vermont is the seventh coldest state in the country.
The highest recorded temperature was , at Vernon, Vermont, Vernon, on July 4, 1911. The lowest recorded temperature was , at Bloomfield, Vermont, Bloomfield, on December 30, 1933; this is the lowest temperature recorded in New England alongside Big Black River (Saint John River tributary), Big Black River, which recorded a verified in 2009. The agricultural growing season ranges from 120 to 180 days. The United States Department of Agriculture plant hardiness zones for the state range between zone 3b, no colder than , in the Northeast Kingdom and northern part of the state and zone 5b, no colder than , in the southern part of the state. The state receives between 2,200 and 2,400 hours of sunshine annually. New England as a whole receives a range of less than 2,000 hours of sunshine in part of New Hampshire to as much as 2,600 hours of sunshine per year in Connecticut and Rhode Island.
Climate change
Climate change in Vermont encompasses the effects of climate change, attributed to man-made increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide, in the U.S. state of Vermont. The state is already seeing effects of climate change that affect its ecosystems, economy and public health. According to the Vermont state government, rainfall has significantly increased in the last 50 years, storms and flooding have increased, and winters have become warmer and shorter. These changes have led to significant impacts on both the winter tourism industry, and a decline in critical agricultural and woodland industries like maple sugaring. The state openly acknowledges and is developing programs that respond to global warming. Vermont was one of the first states in the United States to adopt greenhouse gas emissions goals in 2006.Geology
 There are five distinct physiographic regions of Vermont. Categorized by geological and physical attributes, they are the Northeastern Highlands, the Green Mountains, the Taconic Mountains, the Champlain Lowlands, and the Vermont Piedmont.
About 500 million years ago, Vermont was part of Laurentia and located in the tropics. The central and southern Green Mountain range include the oldest rocks in Vermont, formed about one billion years ago during the first mountain building period (or orogeny). Subsequently, about years ago, the second mountain building period created Green Mountain peaks that were tall, three to four times their current height and comparable to the Himalayas. The geological pressures that created those peaks remain evident as the Champlain Thrust, running north–south to the west of the mountains (now the eastern shore of Lake Champlain). It is an example of geological fault thrusting where bedrock is pushed over the newer rock formation.
As a result of tectonic formation, Vermont east of the Green Mountains tends to be formed from rocks produced in the Silurian and Devonian periods, and western Vermont mainly from the older Pre-Cambrian and Cambrian material. Several large deposits within the state contain granite. The remains of the Chazy Formation can be observed in Isle La Motte, Vermont, Isle La Motte. It was one of the first tropical reefs. It is the site of the limestone Fisk Quarry, which contains a collection of ancient marine fossils, such as Stromatoporoidea, stromatoporoids, that date to years ago. At one point, Vermont is believed to have been connected to Africa (Pangaea); the fossils found and the rock formations found on the coasts in both Africa and America are evidence affirming the Pangaea theory.
In the past four centuries, Vermont has experienced a few earthquakes, rarely centered under the state. The highest ranked, in 1952, had a Richter magnitude scale 6.0 and was based in Canada.
There are five distinct physiographic regions of Vermont. Categorized by geological and physical attributes, they are the Northeastern Highlands, the Green Mountains, the Taconic Mountains, the Champlain Lowlands, and the Vermont Piedmont.
About 500 million years ago, Vermont was part of Laurentia and located in the tropics. The central and southern Green Mountain range include the oldest rocks in Vermont, formed about one billion years ago during the first mountain building period (or orogeny). Subsequently, about years ago, the second mountain building period created Green Mountain peaks that were tall, three to four times their current height and comparable to the Himalayas. The geological pressures that created those peaks remain evident as the Champlain Thrust, running north–south to the west of the mountains (now the eastern shore of Lake Champlain). It is an example of geological fault thrusting where bedrock is pushed over the newer rock formation.
As a result of tectonic formation, Vermont east of the Green Mountains tends to be formed from rocks produced in the Silurian and Devonian periods, and western Vermont mainly from the older Pre-Cambrian and Cambrian material. Several large deposits within the state contain granite. The remains of the Chazy Formation can be observed in Isle La Motte, Vermont, Isle La Motte. It was one of the first tropical reefs. It is the site of the limestone Fisk Quarry, which contains a collection of ancient marine fossils, such as Stromatoporoidea, stromatoporoids, that date to years ago. At one point, Vermont is believed to have been connected to Africa (Pangaea); the fossils found and the rock formations found on the coasts in both Africa and America are evidence affirming the Pangaea theory.
In the past four centuries, Vermont has experienced a few earthquakes, rarely centered under the state. The highest ranked, in 1952, had a Richter magnitude scale 6.0 and was based in Canada.
Fauna
 The state contains 41 species of reptiles and amphibians (including the spring peeper), 89 species of fish, of which 12 are non native; 193 species of breeding birds, 58 species of mammals (including American black bear, black bears, eastern chipmunks, coyotes, Fisher (animal), fishers, Red fox, red and gray foxes, porcupines, and Groundhog, woodchucks), more than 15,000 insect species (including luna moths), and 2,000 higher plant species, plus fungi, algae, and 75 different types of natural communities. Vermont contains one species of venomous snake, the timber rattlesnake, which is confined to a few acres in western Rutland County, Vermont, Rutland County.
Wildlife has suffered because of human development of the state. By the mid-19th century, wild turkeys were exterminated in the state through overhunting and destruction of habitat. Sixteen were re-introduced in 1969, and had grown to a flock estimated to number 45,000 in 2009. In 2013, hunters killed 6,968 of these. Since 1970, reduction of farmland has resulted in reduced environment for, and resulted in a decline in numbers of various shrubland birds, including the American woodcock, brown thrasher, eastern towhee, willow flycatcher, golden-winged warbler, blue-winged warbler, field sparrow, and Baltimore oriole. Ospreys, whose eggs were previously damaged by DDT, began to reappear in 1998 and by 2010 were no longer endangered in the state.
Several species have declined or disappeared from the state, including bats, many of which have been killed by white-nose syndrome, the New England cottontail, out-competed by the eastern cottontail rabbit, and the Bombus terricola, yellow-banded bumblebee, gone as one of 19 species of bee in decline.
Invasive species and organisms include the Asian Drosophila suzukii, spotted-wing drosophila, a destroyer of crops, and eastern equine encephalitis virus whose antibodies were found in moose or deer in each of Vermont's counties.
The state contains 41 species of reptiles and amphibians (including the spring peeper), 89 species of fish, of which 12 are non native; 193 species of breeding birds, 58 species of mammals (including American black bear, black bears, eastern chipmunks, coyotes, Fisher (animal), fishers, Red fox, red and gray foxes, porcupines, and Groundhog, woodchucks), more than 15,000 insect species (including luna moths), and 2,000 higher plant species, plus fungi, algae, and 75 different types of natural communities. Vermont contains one species of venomous snake, the timber rattlesnake, which is confined to a few acres in western Rutland County, Vermont, Rutland County.
Wildlife has suffered because of human development of the state. By the mid-19th century, wild turkeys were exterminated in the state through overhunting and destruction of habitat. Sixteen were re-introduced in 1969, and had grown to a flock estimated to number 45,000 in 2009. In 2013, hunters killed 6,968 of these. Since 1970, reduction of farmland has resulted in reduced environment for, and resulted in a decline in numbers of various shrubland birds, including the American woodcock, brown thrasher, eastern towhee, willow flycatcher, golden-winged warbler, blue-winged warbler, field sparrow, and Baltimore oriole. Ospreys, whose eggs were previously damaged by DDT, began to reappear in 1998 and by 2010 were no longer endangered in the state.
Several species have declined or disappeared from the state, including bats, many of which have been killed by white-nose syndrome, the New England cottontail, out-competed by the eastern cottontail rabbit, and the Bombus terricola, yellow-banded bumblebee, gone as one of 19 species of bee in decline.
Invasive species and organisms include the Asian Drosophila suzukii, spotted-wing drosophila, a destroyer of crops, and eastern equine encephalitis virus whose antibodies were found in moose or deer in each of Vermont's counties.
Flora
Vermont is in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome. Much of the state, in particular the Green Mountains, is covered by the conifers and northern hardwood forest, northern hardwoods of the New England-Acadian forests. The western border with New York and the area around Lake Champlain lies within the Eastern Great Lakes lowland forests. The southwest corner of the state and parts of the Connecticut River are covered by northeastern coastal forests of mixed Quercus, oak. Invasive Lonicera japonica, wild honeysuckle has been deemed a threat to the state's forests, native species of plants, and wildlife. Many of Vermont's rivers, including the Winooski River, have been subjected to man-made barriers to prevent flooding. Climate change appears to be affecting the maple sugar industry. Sugar maples have been subject to stress by acid rain, asian longhorn beetles, and Thripidae, pear thrips. In 2011, the deer herd had grown too large for habitat, and many resorted to eating bark to survive the winter, destroying trees in the process. In addition, the sugar maples need a certain period of cold to produce sap for maple syrup. The time to tap these trees has shrunk to one week in some years. The tree may be replaced by the more aggressive Norway maples, in effect forcing the sugar maples to "migrate" north to Canada.Demographics
Population
According to the United States Census Bureau, the state of Vermont had a population of 643,503 in the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. census. At the July 1, 2019 Population Estimates Program, Vermont had an estimated population of 623,989. This included a natural increase of 3,178 (31,716 births minus 28,538 deaths) and a decrease due to net migration of 2,432 people out of the state. In 2006, it had the second lowest birthrate in the nation, 42/1000 women. The center of population of Vermont is located in Washington County, Vermont, Washington County, in the town of Warren, Vermont, Warren. As of 2014, 51.3% of Vermont's population was born in the state (compared with 58.7% for the United States). The changing demographics between those with multi-generational ties to the state and those who are newcomers, bringing different values with them, has resulted in a degree of tension between the two perspectives. This tension is expressed in the terms, "Woodchuck", being applied to those established in the state, and "Flatlander", applied to the newcomers. Vermont is the least populous New England state. As of 2012, Vermont was one of only two states in the U.S. with fewer people than the District of Columbia (Wyoming was the other). From 2010 to 2013, 16 out of Vermont's 251 towns experienced an increase in population. All towns in Chittenden increased with the exception of Burlington. More than 180 towns experienced a decrease, which had not happened since the mid-19th century. As of 2010, Vermont was the second most rural state in the country, following Maine, with 61% of the population living in rural areas.Birth data
''Note: Births in table do not add up, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.'' * Since 2016, data for births of White Hispanic and Latino Americans, White Hispanic origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race. Of the population, 94.3% of the state identified as Non-Hispanic whites, white not of Hispanic or Latino origin in a 2013 U.S. census estimate. As of the 2010 census, Vermont was the second-whitest state in the U.S. after Maine. It has the List of U.S. states by Hispanic and Latino population, smallest number of Hispanics of any state in the country but not the lowest percentage of Hispanics, which is found in West Virginia. In 2009, 12.6% of people over 15 were divorced. This was the fifth highest percentage in the nation. As of 2008, the median age of Vermonters was 40.6 and that of the work force was 43.7, compared with the national average of 41.1 years. Vermont leads U.S. states with the highest rates of LGBT identification, at 5.3%. Its LGBT population density is second in the U.S. only to the District of Columbia. Following national trends for opioid use, people seeking treatment for opioid addiction in Vermont increased from 650 in 2011 to 7,500 in 2016.Dialect
Linguists have identified speech patterns found among Vermonters as belonging to Western New England English, a dialect of New England English, which features Rhoticity in English, full pronunciation of all ''r'' sounds, horse–hoarse merger, pronouncing ''horse'' and ''hoarse'' the same, and father–bother merger, pronouncing vowels in ''father'' and ''bother'' the same, none of which are features traditionally shared in neighboring Eastern New England English. Some rural speakers realize the ''t'' as a glottal stop (''mitten'' sounds like "mi'in" and ''Vermont'' like "Vermon' "). A dwindling segment of the Vermont population, generally both rural and male, pronounces certain vowels in a distinctive manner (e.g. ''cows'' with a raised vowel as and ''ride'' with a backed, somewhat rounded vowel as ). Eastern New England English—also found in New Hampshire, Maine and eastern Massachusetts—was common in eastern Vermont in the mid-twentieth century and before, but has become rare.Stanford, James N.; Leddy-Cecere, Thomas A.; Baclawski Jr., Kenneth P. "Farewell To The Founders: Major Dialect Changes Along The East–West New England Border." ''American Speech'' 87.2 (2012): pp. 126–169. Communication & Mass Media Complete. Web. November 2, 2015. This accent rhoticity in English, drops the ''r'' sound in words ending in ''r'' (''farmer'' sounds like "farm-uh") and Linking and intrusive R#Intrusive R, adds an ''r'' sound to some words ending in a vowel (''idea'' sounds like "idee-er") was common. Those characteristics in eastern Vermont appear to have been inherited from West Country and Ulster Scots people, Scots-Irish ancestors.Religion
According to the Pew Research Center in 2014, 37% reported no religion, the highest rate of irreligion of all U.S. states. The Pew Research Center also determined the largest religion was Christianity; Catholic Church, Catholics made 22% of the population and Protestantism, Protestants were 30%. In contrast with Southern United States, Southern U.S. trends, the majority of Protestants are Mainline Protestant dominated by Methodism. The United Methodist Church was the largest Mainline Protestant denomination in Vermont, followed by the American Baptist Churches USA and United Church of Christ. Evangelical Protestants were dominated by Independent Baptist, independent Baptist churches. Major non-Christian religions were Judaism, Islam, Buddhism, Hinduism, and other faiths. The largest non-Christian religious group outside of irreligion were Unitarianism, Unitarians. An estimated 3.1% of the irreligious were Atheism, atheist. With the publication of a study by the Public Religion Research Institute in 2020, Christianity spread among Protestantism, Catholicism, and non-mainstream Christians including Mormonism and the Jehovah's Witnesses were approximately 64% of the adult population. The religiously unaffiliated were determined to be an estimated 30% of the total adult population according to the Public Religion Research Institute. Additionally, the Association of Religion Data Archives reported that the single largest denominations were the following: the Catholic Church (124,208); United Church of Christ (11,882); and the United Methodist Church (9,652). Non-denominational Protestants numbered 29,830.Economy
Personal income
In 2019, the state had a median household income of $61,973. Approximately 10.2% of the population lived at or below the poverty line. The median household income from 2002 to 2004 was $45,692. This was 15th nationally. The median wage in the state in 2008 was $15.31 hourly or $31,845 annually. In 2007, about 80% of the 68,000 Vermonters who qualify for food stamps received them. 40% of seniors 75 years or older live on annual incomes of $21,660 or less. In 2011, 15.2% of Vermonters received Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, food stamps. This compares to 14.8% nationally. In 2011, 91,000 seniors received an annual average of $14,000 from Social Security (United States), Social Security. This was 59% of the average senior's income. This contributed $1.7 billion to the state's economy.Agriculture
Dairy farming
Dairy farming is the primary source of agricultural income. In the second half of the 20th century, developers had plans to build Condominium (housing), condos and houses on what was relatively inexpensive, open land. Vermont's government responded with a series of laws Growth management, controlling development and with some pioneering initiatives to prevent the loss of Vermont's dairy industry. Still, the number of Vermont dairy farms has declined more than 85% from the 11,206 dairy farms operating in 1947. In 2003, there were fewer than 1,500 dairy farms in the state; in 2006 there were 1,138; in 2019 there were 658. The number of dairy farms has been diminishing by 10% annually. 80% of open land is controlled by dairy farms. The number of cattle in Vermont had declined by 40%; however, milk production has doubled in the same period due to tripling the production per cow. While milk production rose, Vermont's market share declined. Within a group of states supplying the Greater Boston, Boston and New York metropolitan area, New York City markets (called "Federal order Class I"), Vermont was third in market share, with 10.6%; New York has 44.9% and Pennsylvania has 32.9%. In 2007, dairy farmers received a record $23.60 for (11.63 gallons at $2.03/gallon) of milk. This dropped in 2008 to $17 ($1.46/gallon). The average dairy farm produced pounds of milk annually in 2008. The dairy barn remains an iconic image of Vermont, but the 87% decrease in active dairy farms between 1947 and 2003 means that preservation of the dairy barns has increasingly become dependent upon a commitment to maintaining a legacy rather than basic need in the agricultural economy. The Vermont Barn Census, organized by a collaboration of educational and nonprofit state and local historic preservation programs, has developed educational and administrative systems for recording the number, condition, and features of barns throughout Vermont. In 2009, there were 543 organic farming, organic farms. Twenty percent of the dairy farms were organic and 23% (128) vegetable farms were organic. Organic farming increased in 2006–07, but leveled off in 2008–09. A significant amount of milk is shipped into the Boston market. Therefore the Commonwealth of Massachusetts certifies that Vermont farms meet Massachusetts sanitary standards. Without this certification, a farmer may not sell milk for distribution into the bulk market. In 2019, two-thirds of all milk in New England was produced by Vermont dairies.Forestry
Forest products have always been a staple to the economy, comprising 1% of the total gross state output and 9% of total manufacturing as of 2013. In 2007, Windham County, Vermont, Windham County contained the largest concentration of kilns for drying lumber east of the Mississippi River. The decline of farms has resulted in a regrowth of Vermont's forests due to ecological succession. Today, most of Vermont's forests are Secondary forest, secondary. The state and non-profit organizations are actively encouraging regrowth and careful forest management. Over 78% of the land area of the state is forested compared to only 37% in the 1880s, when sheep farming was at its peak and large amounts of acreage were cleared for grazing. Over 85% of that area is non-industrial, private forestland owned by individuals or families. In 2013, of wood was harvested in Vermont. A large amount of Vermont forest products are exports with being shipped overseas plus an additional to Canada. Most of it was processed within the state. In this century the manufacture of wood products has fallen by almost half. The annual net growth has been estimated at . The United States Department of Agriculture, USDA estimates that remain in the state. Forest products also add to carbon sequestration since lumber and timber used in houses and furniture hold carbon for long periods of time while the trees that were removed are replaced overtime with new growing stock. In 2017, the price of wood products had either plummeted or remained the same when compared to previous decades, which meant there was cause for concern with jobs in the industry. For example, in 1994, the price of a thousand board feet was $300, the same as it was in 2017. The price of wood chips has halved in the same time frame. In 1980, the price for a cord of wood was $50; in 2017, $25. For lack of demand, Vermont's forests are growing twice as fast as they are being cut.Other
An important and growing part of Vermont's economy is the manufacture and sale of artisan foods, fancy foods, and novelty items trading in part upon the Vermont "brand," which the state manages and defends. Examples of these specialty exports include Cabot Cheese, the Vermont Teddy Bear Company, Fine Paints of Europe, Vermont Butter and Cheese Company, several Brewing in Vermont, microbreweries, ginseng growers, Burton Snowboards, King Arthur Flour, and Ben & Jerry's, Ben and Jerry's Ice Cream. As of 2019, Vermont was the leading producer of maple syrup in the United States. There were about 2,000 maple products producers in 2010. Production rose to in 2009. The state's share of the nation's production rose to 42% in 2013. It had the second lowest price at $33.40/gallon. The Vermont wine, wine industry in Vermont started in 1985. As of 2007, there were 14 wineries.Manufacturing
As of 2015, GlobalFoundries was the largest private employer in the state and provides jobs to 3,000 employees at its plant in the village of Essex Junction, Vermont, Essex Junction within Chittenden County, Vermont, Chittenden County. A 2010 University of Connecticut study reported that Vermont, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire tied as the most costly states in the U.S. for manufacturers.Energy
Vermont has no fossil-fuel reserves, however its forest products industry provides fuel for electricity generation and home heating. Electricity consumption per capita ranks it among the lowest 20% of states, and total electricity consumption was the lowest in the United States. Vermont consumed three times more electricity than it generated in-state in 2019, and imported its largest share of electricity from Canada. Vermont's 99.9% share of in-state electricity generation from renewable sources was the highest among all 50 states.Health
An increasingly aging population is expected to improve the position of aging services and health care in the state economy. The University of Vermont Medical Center, with approximately 6,400 employees, is the largest employer in the state. In 2010, all of Vermont's hospitals billed patients $3.76 billion, and collected $2 billion. 92,000 people are enrolled in Medicare. In 2011, Medicare spent $740 million on health care in the state.Labor
In 2009, the state attained a high of 361,290 workers. As of 2006, there were 305,000 workers in Vermont. Eleven percent of these are unionized. Out of a workforce of 299,200 workers, 52,000 were government jobs, federal, state, and local. A modern high unemployment rate of 9% was reached in June 1976. A modern low of 2.4% was measured in February 2000. As of October 2019, the unemployment rate was 2.2%. Employment grew 7.5% from 2000 to 2006. From 1980 to 2000, employment grew by 3.4%; nationally it was up 4.6%. Real wages were $33,385 in 2006 constant dollars and remained there in 2010; the nation, $36,871.Insurance
Captive insurance plays an increasingly large role in Vermont's economy. With this form of alternative insurance, large corporations or industry associations form standalone insurance companies to insure their own risks, thereby substantially reducing their insurance premiums and gaining a significant measure of control over types of risks to be covered. There are also significant tax advantages to be gained from the formation and operation of captive insurance companies. According to the Insurance Information Institute, Vermont in 2009 was the world's third-largest domicile for captive insurance companies, following Bermuda and the Cayman Islands. In 2009, there were 560 such companies. In 2010, the state had 900 such companies.Recreation
 Summer camps such as Camp Abenaki, Camp Billings, Camp Dudley, YMCA, Camp Dudley, and Camp Hochelaga contribute to Vermont's tourist economy.
In 2005, visitors made an estimated trips to the state, spending .
In 2012, fall accounted for $460 million of income, about one-quarter of all tourism.
In 2011, the state government earned $274 million in taxes and fees from tourism. 89% of the money came from out-of-state visitors. Tourism supported over 26,000 jobs, 7.2% of total employment.
According to the 2000 Census, almost 15% of all housing units in Vermont were vacant and classified "for seasonal, recreational, or occasional use". This was the second highest percentage nationwide, after Maine. In some Vermont cities, vacation homes owned by wealthy residents of New England and
Summer camps such as Camp Abenaki, Camp Billings, Camp Dudley, YMCA, Camp Dudley, and Camp Hochelaga contribute to Vermont's tourist economy.
In 2005, visitors made an estimated trips to the state, spending .
In 2012, fall accounted for $460 million of income, about one-quarter of all tourism.
In 2011, the state government earned $274 million in taxes and fees from tourism. 89% of the money came from out-of-state visitors. Tourism supported over 26,000 jobs, 7.2% of total employment.
According to the 2000 Census, almost 15% of all housing units in Vermont were vacant and classified "for seasonal, recreational, or occasional use". This was the second highest percentage nationwide, after Maine. In some Vermont cities, vacation homes owned by wealthy residents of New England and Hunting
 Hunting is controlled for American black bear, black bear, wild turkeys, deer, and moose. There are 5,500 bears in the state. The goal is to keep the numbers between 4,500 and 6,000.
In 2010, there were about 141,000 deer in the state, which is in range of government goals. However, these are distributed unevenly and when in excess of , negatively impact timber growth.
In 2012, hunting of migratory birds was limited to October 13 to December 16. Waterfowl hunting is also controlled by federal law.
Hunting is controlled for American black bear, black bear, wild turkeys, deer, and moose. There are 5,500 bears in the state. The goal is to keep the numbers between 4,500 and 6,000.
In 2010, there were about 141,000 deer in the state, which is in range of government goals. However, these are distributed unevenly and when in excess of , negatively impact timber growth.
In 2012, hunting of migratory birds was limited to October 13 to December 16. Waterfowl hunting is also controlled by federal law.
Skiing and snowmobiling
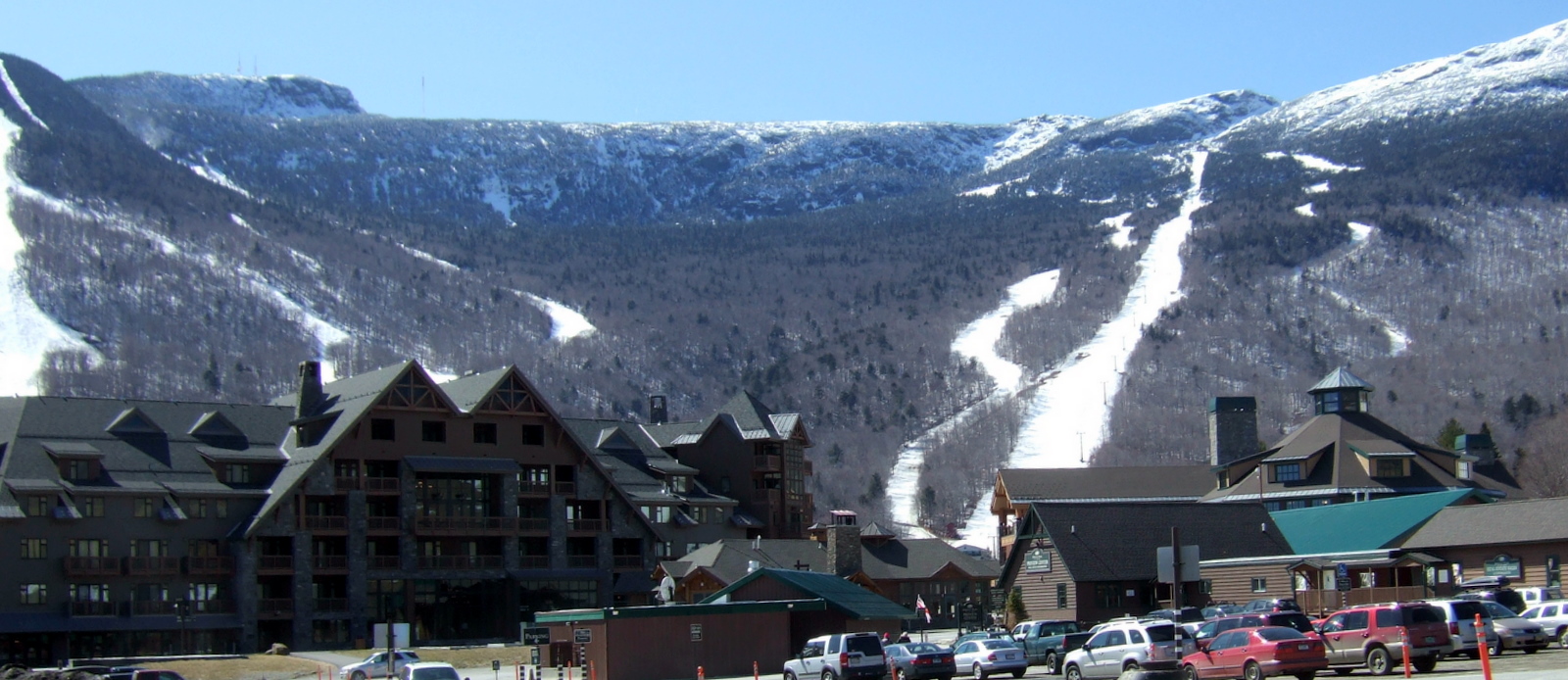 Some of the List of New England ski areas by vertical drop, largest ski areas in New England are located in Vermont. Skiers and snowboarders visit Burke Mountain Ski Area, Bolton Valley, Smugglers' Notch, Killington Ski Resort, Mad River Glen, Stowe Mountain Resort, Cochrans Ski Area, Sugarbush Resort, Sugarbush, Stratton, Vermont, Stratton, Jay Peak Resort, Jay Peak, Okemo Mountain, Okemo, Saskadena Six, Mount Snow, Bromley Mountain, Bromley, and Magic Mountain Ski Area. Summer visitors tour resort towns like Stowe, Vermont, Stowe, Manchester, Vermont, Manchester, Quechee, Vermont, Quechee, Wilmington, Vermont, Wilmington and Woodstock, Vermont, Woodstock. The effects of global warming have been predicted to shorten the length of the ski season across Vermont, which would continue the contraction and consolidation of the Ski Resorts in Vermont, ski industry in Vermont and threaten individual ski businesses and communities that rely on ski tourism.
In winter, Nordic and backcountry skiers visit to travel the length of the state on the Catamount Trail. Several horse shows are annual events. Vermont's state parks, historic sites, museums, golf courses, and new boutique hotels with spas were designed to attract tourists.
In 2000–01, there were 4,579,719 skier and snowboarder visits to the state. There were 4,125,082 visits in 2009–2010, a rise from recent years.
In 2008, there were 35,000 members of 138 snowmobiling clubs in Vermont. The combined association of clubs maintains of trail often over private lands. The industry is said to generate "hundreds of millions of dollars worth of business."
Some of the List of New England ski areas by vertical drop, largest ski areas in New England are located in Vermont. Skiers and snowboarders visit Burke Mountain Ski Area, Bolton Valley, Smugglers' Notch, Killington Ski Resort, Mad River Glen, Stowe Mountain Resort, Cochrans Ski Area, Sugarbush Resort, Sugarbush, Stratton, Vermont, Stratton, Jay Peak Resort, Jay Peak, Okemo Mountain, Okemo, Saskadena Six, Mount Snow, Bromley Mountain, Bromley, and Magic Mountain Ski Area. Summer visitors tour resort towns like Stowe, Vermont, Stowe, Manchester, Vermont, Manchester, Quechee, Vermont, Quechee, Wilmington, Vermont, Wilmington and Woodstock, Vermont, Woodstock. The effects of global warming have been predicted to shorten the length of the ski season across Vermont, which would continue the contraction and consolidation of the Ski Resorts in Vermont, ski industry in Vermont and threaten individual ski businesses and communities that rely on ski tourism.
In winter, Nordic and backcountry skiers visit to travel the length of the state on the Catamount Trail. Several horse shows are annual events. Vermont's state parks, historic sites, museums, golf courses, and new boutique hotels with spas were designed to attract tourists.
In 2000–01, there were 4,579,719 skier and snowboarder visits to the state. There were 4,125,082 visits in 2009–2010, a rise from recent years.
In 2008, there were 35,000 members of 138 snowmobiling clubs in Vermont. The combined association of clubs maintains of trail often over private lands. The industry is said to generate "hundreds of millions of dollars worth of business."
Quarrying
The towns of Rutland (town), Vermont, Rutland and Barre (town), Vermont, Barre are the traditional centers of marble and granite quarrying and carving in the U.S. For many years Vermont was also the headquarters of the smallest union in the U.S., the Journeymen Stonecutters' Association of North America, of about 500 members. The first marble quarry in America was on Mount Aeolus (Vermont), Mount Aeolus overlooking East Dorset, Vermont, East Dorset. The granite industry attracted numerous skilled stonecutters in the late 19th century from Italy, Scotland, and Ireland. Barre is the location of the Rock of Ages Corporation, Rock of Ages quarry, the largest dimension stone granite quarry in the United States. Vermont is the largest producer of slate in the country. The highest quarrying revenues result from the production of dimension stone. The Rock of Ages quarry in Barre (town), Vermont, Barre is one of the leading exporters of granite in the country. The work of the sculptors of this corporation can be seen down the road at the Hope Cemetery, where there are gravestones and mausoleums.Non-profits and volunteerism
There were 2,682 non-profit organizations in Vermont in 2008, with in revenue. The state ranked ninth in the country for volunteerism for the period 2005–08. 35.6% of the population volunteered during this period. The national average was 26.4%.Education
 Vermont was named the nation's smartest state in 2005 and 2006. In 2006, there was a gap between state testing standards and national, which is biased in favor of the state standards by 30%, on average. This puts Vermont 11th-best in the nation. Most states have a higher bias. However, when allowance for race is considered, a 2007 U.S. Government list of test scores shows Vermont white fourth graders performed 25th in the nation for reading (229) and 26th for math (247). White eighth graders scored 18th for math (292) and 12th for reading (273). The first three scores were not considered statistically different from average. White eighth graders scored significantly above average in reading. Statistics for black students were not reliable because of their small representation in the testing.
In 2017, spending $1.6 billion on education for 76,000 public school children, represents more than $21,000 per student.
''Education Week'' ranked the state second in high school graduation rates for 2007.
In 2011, 91% of the population had graduated from high school compared with 85% nationally. Almost 34% have at least an undergraduate degree compared with 28% nationally.
In 2013, the ratio of pupils to teachers was the lowest in the country.
Vermont was named the nation's smartest state in 2005 and 2006. In 2006, there was a gap between state testing standards and national, which is biased in favor of the state standards by 30%, on average. This puts Vermont 11th-best in the nation. Most states have a higher bias. However, when allowance for race is considered, a 2007 U.S. Government list of test scores shows Vermont white fourth graders performed 25th in the nation for reading (229) and 26th for math (247). White eighth graders scored 18th for math (292) and 12th for reading (273). The first three scores were not considered statistically different from average. White eighth graders scored significantly above average in reading. Statistics for black students were not reliable because of their small representation in the testing.
In 2017, spending $1.6 billion on education for 76,000 public school children, represents more than $21,000 per student.
''Education Week'' ranked the state second in high school graduation rates for 2007.
In 2011, 91% of the population had graduated from high school compared with 85% nationally. Almost 34% have at least an undergraduate degree compared with 28% nationally.
In 2013, the ratio of pupils to teachers was the lowest in the country.
Higher education
 Experimentation at the University of Vermont by George Perkins Marsh, and later the influence of Vermont-born philosopher and educator John Dewey brought about the concepts of electives and learning by doing.
Vermont has five colleges within the Vermont State Colleges system, University of Vermont, University of Vermont (UVM), and several other private, degree-granting colleges, including Bennington College, Champlain College, Goddard College, Middlebury College, Saint Michael's College, the Vermont Law School, and Norwich University.
Experimentation at the University of Vermont by George Perkins Marsh, and later the influence of Vermont-born philosopher and educator John Dewey brought about the concepts of electives and learning by doing.
Vermont has five colleges within the Vermont State Colleges system, University of Vermont, University of Vermont (UVM), and several other private, degree-granting colleges, including Bennington College, Champlain College, Goddard College, Middlebury College, Saint Michael's College, the Vermont Law School, and Norwich University.
Transportation
The Vermont Agency of Transportation (VTrans) is responsible for Vermont's transport infrastructure. The principal mode of travel in Vermont is via motor vehicle, with 94.3% of Vermont households owning a car in 2008. Four car ferry routes operate across Lake Champlain. Passenger rail is provided by Amtrak, Amtrak's daily Vermonter (train), ''Vermonter'' and ''Ethan Allen Express'' trains. Intercity bus operators include Vermont Translines, Greyhound Lines, and Megabus (North America), Megabus. A number of public transit agencies operate bus service at the local, county, and regional levels. Burlington International Airport is the state's primary airport.Road
 In 2012, there were 605,000 motor vehicles registered, nearly one car for every person in the state. This is similar to average car ownership nationwide.
In 2012, about half the carbon emissions in the state resulted from vehicles.
In 2010, Vermont owned of highway. This was the third smallest quantity among the 50 states. 2.5% of the highways were listed as "congested," the fifth lowest in the country. The highway fatality rate was one per , tenth lowest in the nation. The highways cost to maintain, the 17th highest in the states. 34.4% of its 2,691 bridges were rated deficient or obsolete, the eighth worst in the nation. A 2005–06 study ranked Vermont 37th out of the states for "cost-effective road maintenance", a decline of thirteen places since 2004–05.
In 2007, Vermont was ranked the third safest state for highway fatalities. One third of these fatal crashes involved a drunken driver. On average, 20–25 people die each year from drunk driving incidents, and 70–80 people are in fatal car crashes in the state. Collisions with moose constitute a traffic threat, particularly in northern Vermont, and cause several deaths per year. In 2009, 93% of Vermont motorists were insured, tying the state with Pennsylvania for the highest percentage. In 2008, Vermont was the fifth best state for fewest uninsured motorists—6%.
Trucks weighing less than can use Vermont's interstate highways. The limit for state roads is . This means that vehicles too heavy for the interstates can legally use only secondary roads.
In 1968, Vermont outlawed the use of billboards for advertisement along its roads. It is one of four states in the U.S. to have done this, along with Hawaii, Maine, and Alaska.
In 2012, there were 605,000 motor vehicles registered, nearly one car for every person in the state. This is similar to average car ownership nationwide.
In 2012, about half the carbon emissions in the state resulted from vehicles.
In 2010, Vermont owned of highway. This was the third smallest quantity among the 50 states. 2.5% of the highways were listed as "congested," the fifth lowest in the country. The highway fatality rate was one per , tenth lowest in the nation. The highways cost to maintain, the 17th highest in the states. 34.4% of its 2,691 bridges were rated deficient or obsolete, the eighth worst in the nation. A 2005–06 study ranked Vermont 37th out of the states for "cost-effective road maintenance", a decline of thirteen places since 2004–05.
In 2007, Vermont was ranked the third safest state for highway fatalities. One third of these fatal crashes involved a drunken driver. On average, 20–25 people die each year from drunk driving incidents, and 70–80 people are in fatal car crashes in the state. Collisions with moose constitute a traffic threat, particularly in northern Vermont, and cause several deaths per year. In 2009, 93% of Vermont motorists were insured, tying the state with Pennsylvania for the highest percentage. In 2008, Vermont was the fifth best state for fewest uninsured motorists—6%.
Trucks weighing less than can use Vermont's interstate highways. The limit for state roads is . This means that vehicles too heavy for the interstates can legally use only secondary roads.
In 1968, Vermont outlawed the use of billboards for advertisement along its roads. It is one of four states in the U.S. to have done this, along with Hawaii, Maine, and Alaska.
Major north–south routes
*Major east–west routes
*Ferry
 There is a year-round ferry service to and from New York State across Lake Champlain from Burlington, Charlotte, Grand Isle, Vermont, Grand Isle, and Shoreham, Vermont, Shoreham. All but the Shoreham ferry are operated by the Lake Champlain Transportation Company (LCTC).
There is a year-round ferry service to and from New York State across Lake Champlain from Burlington, Charlotte, Grand Isle, Vermont, Grand Isle, and Shoreham, Vermont, Shoreham. All but the Shoreham ferry are operated by the Lake Champlain Transportation Company (LCTC).
Rail
 The state is served by Amtrak's ''Vermonter (train), Vermonter'' and ''Ethan Allen Express'', the New England Central Railroad, the Vermont Railway, and the Green Mountain Railroad.
The ''Ethan Allen Express'' serves Burlington Union Station, , , , and , while the ''Vermonter'' serves St. Albans station (Vermont), St. Albans, Essex Junction station, Essex Junction, Waterbury station (Vermont), Waterbury, Montpelier station (Vermont), Montpelier, Randolph station, Randolph, White River Junction station, White River Junction, Windsor-Mt. Ascutney station, Windsor, Bellows Falls station, Bellows Falls, and Union Station (Brattleboro, Vermont), Brattleboro.
The state is served by Amtrak's ''Vermonter (train), Vermonter'' and ''Ethan Allen Express'', the New England Central Railroad, the Vermont Railway, and the Green Mountain Railroad.
The ''Ethan Allen Express'' serves Burlington Union Station, , , , and , while the ''Vermonter'' serves St. Albans station (Vermont), St. Albans, Essex Junction station, Essex Junction, Waterbury station (Vermont), Waterbury, Montpelier station (Vermont), Montpelier, Randolph station, Randolph, White River Junction station, White River Junction, Windsor-Mt. Ascutney station, Windsor, Bellows Falls station, Bellows Falls, and Union Station (Brattleboro, Vermont), Brattleboro.
Intercity bus
Greyhound Lines stops at Bellows Falls, Brattleboro, Burlington, Montpelier, and White River Junction. Megabus (North America), Megabus, as of November 2014, stops in Burlington and Montpelier. Vermont Translines, an intercity bus company started by Premier Coach in 2013 partnering with Greyhound and starting service on June 9, 2014, serves Milton, Colchester, Burlington, Middlebury, Brandon, Rutland, Wallingford, Manchester and Bennington on its Burlington to Albany, New York, Albany line, and Rutland, Killington, Bridgewater, Woodstock, Queechee and White River Junction along the U.S. Route 4, U.S. Route4 corridor. The town of Bennington, Vermont, Bennington also has the weekday-operating Albany, New York, Albany-Bennington Shuttle, an intercity bus operated by Yankee Trails World Travel.Local bus
 A patchwork of transit providers operate local Public transport bus service, bus service in every Vermont county, though route frequency and coverage are often limited outside major cities. Many operators also provide paratransit and regional express bus service, express bus services. Green Mountain Transit is the largest operator in the state, with weekday ridership of as of . Other major systems are Marble Valley Regional Transit District (The Bus), Southeast Vermont Transit (MOOver), Tri-Valley Transit, Rural Community Transportation, Advance Transit, and Green Mountain Community Network.
A patchwork of transit providers operate local Public transport bus service, bus service in every Vermont county, though route frequency and coverage are often limited outside major cities. Many operators also provide paratransit and regional express bus service, express bus services. Green Mountain Transit is the largest operator in the state, with weekday ridership of as of . Other major systems are Marble Valley Regional Transit District (The Bus), Southeast Vermont Transit (MOOver), Tri-Valley Transit, Rural Community Transportation, Advance Transit, and Green Mountain Community Network.
Air
 Burlington International Airport is the largest in the state, with regular flights to Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport, Atlanta, Charlotte Douglas International Airport, Charlotte, Chicago O'Hare, Chicago, Denver International Airport, Denver, Detroit Metropolitan Airport, Detroit, Washington Dulles Airport, Washington Dulles, JFK Airport, JFK, LaGuardia Airport, LaGuardia, Newark Liberty International Airport, Newark, Orlando Sanford International Airport, Orlando, and Philadelphia International Airport, Philadelphia. Airlines serving the airport include: American Airlines, American, Delta Air Lines, Delta, Frontier Airlines, Frontier, JetBlue, and United Airlines, United. This is also the airport where the 134th fighter squadron of the 158th fighter wing is located. Known as the "Green Mountain Boys," this squadron is armed with the General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon, Block 30 F-16C/D Fighting Falcon and is tasked with protecting the Northeastern United States from the air.
Rutland Southern Vermont Regional Airport has regular flights to Boston via Cape Air.
Burlington International Airport is the largest in the state, with regular flights to Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport, Atlanta, Charlotte Douglas International Airport, Charlotte, Chicago O'Hare, Chicago, Denver International Airport, Denver, Detroit Metropolitan Airport, Detroit, Washington Dulles Airport, Washington Dulles, JFK Airport, JFK, LaGuardia Airport, LaGuardia, Newark Liberty International Airport, Newark, Orlando Sanford International Airport, Orlando, and Philadelphia International Airport, Philadelphia. Airlines serving the airport include: American Airlines, American, Delta Air Lines, Delta, Frontier Airlines, Frontier, JetBlue, and United Airlines, United. This is also the airport where the 134th fighter squadron of the 158th fighter wing is located. Known as the "Green Mountain Boys," this squadron is armed with the General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon, Block 30 F-16C/D Fighting Falcon and is tasked with protecting the Northeastern United States from the air.
Rutland Southern Vermont Regional Airport has regular flights to Boston via Cape Air.
Media
Newspapers of record
Vermont statute requires the Vermont Secretary of State to designate newspapers that provide general coverage across the state as the "Newspapers of Record." This is the list, as of 2019: * ''Addison County Independent, Addison Independent'' * ''Bennington Banner'' * ''Brattleboro Reformer'' * ''Burlington Free Press'' * ''Caledonian Record'' * ''The Chronicle (Barton, Vermont), The Chronicle'' * ''Islander'' * ''Newport Daily Express'' * ''News & Citizen'' / ''The Transcript'' * ''Rutland Herald'' * ''Seven Days (newspaper), Seven Days'' * ''St. Albans Messenger'' * ''Barre Montpelier Times Argus, Times Argus'' * ''Valley News'' * ''Vermont Lawyer'' * ''White River Valley Herald'' (a.k.a. ''Herald of Randolph'')Broadcast media
Vermont hosts 93 radio broadcast stations. The top categories are talk/information (11), country (9) and classic rock (9). The top owner of radio broadcast stations is Vermont Public Radio (11 broadcast frequencies and 13 low-power, local transmitters). Other companies had five or fewer stations. The state has 15 online radio stations. Vermont hosts 10 high-power television broadcast stations, three of which are satellites of a primary station. Represented are the following networks and number of high-power transmitters, American Broadcasting Company, ABC (1), CBS (1), Fox Broadcasting Company, Fox (1), NBC (2), Public Broadcasting Service, PBS (4), and Retro Television Network, RTV (1). In addition, it has 17 low-power television broadcast stations, which in several cases are satellites of the high-power stations.Electrical utilities
 Vermont electric power needs are served by over twenty utilities. The largest is Green Mountain Power, a subsidiary of Énergir which recently also took over Central Vermont Public Service. Together this single company represents 70% of the retail customers in Vermont. The state is a small electricity consumer compared with other states. Therefore, its electricity sector has the lowest carbon footprint in the country. As of 2010, the state had the lowest wholesale electricity costs in New England.
Vermont electric power needs are served by over twenty utilities. The largest is Green Mountain Power, a subsidiary of Énergir which recently also took over Central Vermont Public Service. Together this single company represents 70% of the retail customers in Vermont. The state is a small electricity consumer compared with other states. Therefore, its electricity sector has the lowest carbon footprint in the country. As of 2010, the state had the lowest wholesale electricity costs in New England.
Public health
In 2010, Vermont was the sixth highest ranked state for Well-Being in a study by Gallup and Healthways. In 2010, the state stood third in physical well-being of children. In 2010, Vermont was ranked the highest in the country for health outcomes. In 2000, the state implemented the Vermont Child Health Improvement Program to improve preventive services and management of chronic conditions. In 2011, the state ranked third in the nation in child health system performance. In 2011, the March of Dimes gave Vermont an "A," ranking it number one in the country on its Prematurity Report Card. In 2008, Vermont was ranked number one in the nation as the healthiest place to live for the seventh time in eight years. Criteria included low teenage birth rate, strong health coverage, the lowest AIDS rate in the country, and 18 other factors. The state scored well in cessation of smoking, obesity, fewer occupational fatalities, prevalence of health insurance, and low infant mortality. A problem area was a high prevalence of binge drinking. While ranking sixth from best for adults in obesity in 2009, the state still had 22% obese with a rate of 27% for children 10–17. The ranking for children was ninth best in the nation. In 1993, the obesity rate for adults was 12%. Vermonters spend annually in medical costs related to obesity. The combined figures for overweight and obese adults rose from 40.7% in 1990 to 58.4% in 2010. This is better than most other states. In 2011, Vermont led the nation in the rate of young people who had consumed alcohol in the past month; one-third of people aged 11 through 20. One-fifth of that group had binged during that time. The state was second for the use of marijuana by young people; 30% of adults 18 to 25 in the past month. In 2009, Vermont was ranked second in the nation for safety. Crime statistics on violence were used for the criteria. In 2007, Vermont was ranked among the best five states in the country for preventing "premature death" in people under 75 years of age. The rate of survival was twice that of the five lowest performing states. Parts of the state have been declared federal disaster areas on 28 occasions from 1963 to 2008. In 2007, the Environmental Protection Agency cited Chittenden and Bennington as counties with 70 parts per billion of smog which is undesirable. In 2008, about 100,000 Vermonters got their health care through the federal government, Medicare (United States), Medicare, TRICARE, Tri-Care, and the Veteran's Administration. An additional 10,000 Vermonters work for employers who provide insurance under federal law under ERISA#Health benefit plans, ERISA. About 20% of Vermonters receive health care outside of Vermont; 20% of the care provided within the state is to non-Vermonters. In 2008, the state had an estimated 7.6% with no medical insurance, down from 9.8% in 2005. In 2008, the Vermont Health Access Program for low-income, uninsured adults cost from $7 to $49 per month. A "Catamount Health" premium assistance program was available for Vermonters who do not qualify for other programs. Total monthly premiums ranged from $60 to $393 for an individual. There was a $250 deductible. Insured paid $10 toward each generic prescription. 16.9% of residents 18 to 35 were uninsured, the highest group. Health care spending increased from in 2000 to in 2009. In 2009, adult day care services cost more in Vermont than any other state—$150 daily. The state started air drops of rabies vaccine, rabies bait for raccoons in 1997. Known rabies cases in raccoons peaked in 2007 at 165. The program is in cooperation with neighboring states and Canada.Law and government
Finances and taxation
Vermont is the only state in the union not to have a balanced-budget requirement, yet it has had a balanced budget every year since 1991. In 2007, Moody's Investors Service, Moody's gave its top bond credit rating (Aaa) to the state. The state uses enterprise funds for operations that are similar to private business enterprises. The Vermont Lottery Commission, the Liquor Control Fund, and the Unemployment Compensation Trust Fund, are the largest of the State's enterprise funds. Also in 2007, Vermont was the 14th highest out of 50 states and the District of Columbia for state and local taxation, with a per capita load of $3,681. The national average was $3,447. However, CNNMoney ranked Vermont highest in the nation based on the percentage of per capita income. The rankings showed Vermont had a per capita tax load of $5,387, 14.1% of the per capita income of $38,306. Vermont collects a State income tax, state personal income tax in a Progressive tax, progressive structure of five different income brackets, with marginal tax rates ranging from 3.6% to 9.5%. In 2008, the top 1% of Vermont residents provided 30% of the income tax revenue; around 2,000 people had sufficient income to be taxed at the highest marginal rate of 9.5%. Vermont's general Sales taxes in the United States, state sales tax rate is 6%, which is imposed on sales of tangible personal property, amusement charges, fabrication charges, some public utility charges and some service contracts. Some towns and cities impose an additional 1% Local Option Tax. There are 46 Tax exemption, exemptions from the sales tax, including exemptions for food, medical items, manufacturing machinery, equipment and fuel, residential fuel and electricity, clothing, and shoes. A use tax is imposed on the buyer at the same rate as the sales tax. The buyer pays the use tax when the seller fails to collect the sales tax or the items are purchased from a source where no tax is collected. The use tax applies to items taxable under the sales tax. Vermont does not collect inheritance taxes, but does impose a Estate tax in the United States, state estate tax; a Vermont estate Tax return (United States), tax return must be filed if the Estate (law), estate must file a federal estate tax return (the requirement for which depends on federal law).Major Vermont TaxesVermont Department of Taxes. Vermont does not collect a state gift tax. Property taxes are levied by municipalities for the support of education and municipal services. Vermont does not assess tax on personal property.Property Valuation and Review
Vermont Department of Taxes. Retrieved March 10, 2009. Property taxes are based on appraisal of the fair market value of real property. Rates vary from 0.97% on homesteaded property in Ferdinand, Essex County, to 2.72% on nonresidents' property in Barre City. Statewide, towns average 1.77% to 1.82% tax rate. In 2007, Vermont counties were among the highest in the country for property taxes. Chittenden ($3,809 median), Windham ($3,412), Addison ($3,352), and Windsor ($3,327) ranked in the top 100, out of 1,817 counties in the nation with populations greater than 20,000. Twelve of the state's 14 counties stood in the top 20%. Median annual property taxes as a percentage of median homeowners income, 5.4%, was rated as the third highest in the nation in 2011. To equitably support education, some towns are required by Act 60 (Vermont law), Act 60 to send some of their collected taxes to be redistributed to school districts lacking adequate support.
Politics
Vermont is one of four states that were once Republic of Vermont, independent nations (Texas, California, and Hawaii are the others). Notably, Vermont is the only state to have voted for a presidential candidate from the Anti-Masonic Party, and Vermont was one of only two states to vote against Franklin D. Roosevelt in all four of his presidential campaigns (the other was Maine). Vermont's history of independent political thought has led to movements for the establishment of the Second Vermont Republic and other plans advocating secession. Vermont is the only state in the United States that requires voters to be sworn in, having established the voter's oath or affirmation in 1777. All white men were granted universal suffrage in 1777.State politics
 Republican Party (United States), Republicans dominated local Vermont politics from the party's founding in 1854 until the mid-1970s, and at the presidential level until the 1990s. Before the 1960s, rural interests dominated the legislature. As a result, cities, particularly the older sections of Burlington and Winooski, were neglected and fell into decay, and people began to move out to newer suburbs.
A series of one man, one vote decisions made by the United States Supreme Court in the 1960s required states to redraw their legislative districts to accurately reflect population. As a result, urban areas in Vermont gained political power.
The legislature was redistricted under one-person, one-vote in the 1960s. It passed the Land Use and Development Law (Act 250 (Vermont law), Act 250) in 1970, to discourage suburban sprawl and to limit major growth to already developed areas. The law, the first of its kind in the nation, created nine District Environmental Commissions appointed by the Governor, who judged land development and subdivision plans that would have a significant impact on the state's environment and many small communities. As a result of Act 250, Vermont was the last state to get a Wal-Mart (there are now six Wal-Marts in the state, as of November 2017, but only three — in Williston, St. Albans, and Derby — were newly built from the ground up). Because of the successful attempts to dilute what is perceived as the original intent of Act 250, and other development pressures, Vermont has been designated one of America's most "endangered historic places" by the National Trust for Historic Preservation.
From 1856 United States presidential election in Vermont, 1856 (the first presidential election after the Republican Party's founding) to 1988 United States presidential election in Vermont, 1988, Vermont voted Republican in every presidential election except 1964 United States presidential election in Vermont, 1964, when Democratic Party (United States), Democrat Lyndon B. Johnson became the first of his party to carry the state amidst a national landslide. Since 1992 United States presidential election in Vermont, 1992, Vermont has voted Democratic in every presidential election, marking a massive shift in the state's politics.
In 1995, the state banned the spreading of manure from December 15 to April 1, to prevent run-off and protect the water. Therefore, farms must have environmentally approved facilities to store manure during this time frame.
While the state voted largely Democratic, Republican Governor Douglas won all counties but Windham County, Vermont, Windham in the 2006 election.
A controversy dating from 1999 has been over the adoption of civil unions, an institution which grants same-sex couples nearly all the rights and privileges of marriage at the state, but not federal, level. In ''Baker v. Vermont'' (1999), the Vermont Supreme Court ruled that, under the Constitution of Vermont, the state must either allow same-sex marriage or provide a "separate but equal, separate, but equal" status for them. The state legislature chose the second option, by creating the institution of civil union; the bill was passed by the legislature and signed into law by Governor Howard Dean.
In April 2009, the state legislature overrode governor Jim Douglas's veto to allow same-sex marriage, becoming the first state in the nation to legalize same-sex marriage through legislation. In September 2009, Vermont became the fourth state in which same-sex couples could marry. The previous three were Same-sex marriage in Massachusetts, Massachusetts, Same-sex marriage in Connecticut, Connecticut, and Same-sex marriage in Iowa, Iowa.
In 2007, the state's House of Representatives rejected a measure which would have legalized Assisted suicide in the United States, assisted suicide for the terminally ill, by a vote of (82–63). With the governor's signature on May 20, 2013, Vermont became the fourth state to pass a "death with dignity" law — the first to be passed through legislation, rather than by ballot initiative.
Minor parties and independents flourish. Rules which eliminate smaller parties from the ballot in most states do not exist in Vermont. As a result, voters often have extensive choices for general elections. Among others, this more open policy enabled independents like Bernie Sanders to win election as mayor of Burlington, Vermont, Burlington, as a U.S. Congressman, and as a U.S. Senator.
A political issue has been Act 60 (Vermont law), Act 60, which balances taxation for education funding. This has resulted in the town of Killington, Vermont secession movement, Killington trying to secede from Vermont and join New Hampshire, due to what the locals say is an unfair tax burden.
The Vermont constitution and the courts supports the right of a person to walk (fish and hunt) on any unposted, unfenced land. That is, trespass must be proven by the owner; it is not automatically assumed.
Vermont has some of the Gun laws in Vermont, least restrictive gun control laws in the country. A permit or license is not required for purchasing or carrying firearms. Concealed carry in the United States, Concealed carry and Open carry in the United States, open carry of a firearm is legal over the age of 16, with those below 16 requiring parental permission.
Vermont has a pro-sanctuary city law.
The state is an alcoholic beverage control state. In 2007, through the Vermont Department of Liquor Control, it took in over $14 million from the sale and distribution of liquor.
In 2013, Vermont became the 17th state to decriminalize marijuana. The statute makes possession of less than an ounce of the drug punishable by a small fine, rather than arrest and possible jail time.
In 2014, Vermont became the first state to call for a Second Constitutional Convention of the United States, constitutional convention to overturn the Supreme Court's decision in ''Citizens United v. FEC''.
In 2014, Vermont became the first state to mandate labeling of genetically modified organisms in the retail food supply.
In January 2018, Governor Phil Scott opted to sign H.511, the Vermont marijuana legalization bill, which allows adults 21 and older to possess up to one ounce of marijuana and grow up to two mature plants starting July 1, 2018.
Republican Party (United States), Republicans dominated local Vermont politics from the party's founding in 1854 until the mid-1970s, and at the presidential level until the 1990s. Before the 1960s, rural interests dominated the legislature. As a result, cities, particularly the older sections of Burlington and Winooski, were neglected and fell into decay, and people began to move out to newer suburbs.
A series of one man, one vote decisions made by the United States Supreme Court in the 1960s required states to redraw their legislative districts to accurately reflect population. As a result, urban areas in Vermont gained political power.
The legislature was redistricted under one-person, one-vote in the 1960s. It passed the Land Use and Development Law (Act 250 (Vermont law), Act 250) in 1970, to discourage suburban sprawl and to limit major growth to already developed areas. The law, the first of its kind in the nation, created nine District Environmental Commissions appointed by the Governor, who judged land development and subdivision plans that would have a significant impact on the state's environment and many small communities. As a result of Act 250, Vermont was the last state to get a Wal-Mart (there are now six Wal-Marts in the state, as of November 2017, but only three — in Williston, St. Albans, and Derby — were newly built from the ground up). Because of the successful attempts to dilute what is perceived as the original intent of Act 250, and other development pressures, Vermont has been designated one of America's most "endangered historic places" by the National Trust for Historic Preservation.
From 1856 United States presidential election in Vermont, 1856 (the first presidential election after the Republican Party's founding) to 1988 United States presidential election in Vermont, 1988, Vermont voted Republican in every presidential election except 1964 United States presidential election in Vermont, 1964, when Democratic Party (United States), Democrat Lyndon B. Johnson became the first of his party to carry the state amidst a national landslide. Since 1992 United States presidential election in Vermont, 1992, Vermont has voted Democratic in every presidential election, marking a massive shift in the state's politics.
In 1995, the state banned the spreading of manure from December 15 to April 1, to prevent run-off and protect the water. Therefore, farms must have environmentally approved facilities to store manure during this time frame.
While the state voted largely Democratic, Republican Governor Douglas won all counties but Windham County, Vermont, Windham in the 2006 election.
A controversy dating from 1999 has been over the adoption of civil unions, an institution which grants same-sex couples nearly all the rights and privileges of marriage at the state, but not federal, level. In ''Baker v. Vermont'' (1999), the Vermont Supreme Court ruled that, under the Constitution of Vermont, the state must either allow same-sex marriage or provide a "separate but equal, separate, but equal" status for them. The state legislature chose the second option, by creating the institution of civil union; the bill was passed by the legislature and signed into law by Governor Howard Dean.
In April 2009, the state legislature overrode governor Jim Douglas's veto to allow same-sex marriage, becoming the first state in the nation to legalize same-sex marriage through legislation. In September 2009, Vermont became the fourth state in which same-sex couples could marry. The previous three were Same-sex marriage in Massachusetts, Massachusetts, Same-sex marriage in Connecticut, Connecticut, and Same-sex marriage in Iowa, Iowa.
In 2007, the state's House of Representatives rejected a measure which would have legalized Assisted suicide in the United States, assisted suicide for the terminally ill, by a vote of (82–63). With the governor's signature on May 20, 2013, Vermont became the fourth state to pass a "death with dignity" law — the first to be passed through legislation, rather than by ballot initiative.
Minor parties and independents flourish. Rules which eliminate smaller parties from the ballot in most states do not exist in Vermont. As a result, voters often have extensive choices for general elections. Among others, this more open policy enabled independents like Bernie Sanders to win election as mayor of Burlington, Vermont, Burlington, as a U.S. Congressman, and as a U.S. Senator.
A political issue has been Act 60 (Vermont law), Act 60, which balances taxation for education funding. This has resulted in the town of Killington, Vermont secession movement, Killington trying to secede from Vermont and join New Hampshire, due to what the locals say is an unfair tax burden.
The Vermont constitution and the courts supports the right of a person to walk (fish and hunt) on any unposted, unfenced land. That is, trespass must be proven by the owner; it is not automatically assumed.
Vermont has some of the Gun laws in Vermont, least restrictive gun control laws in the country. A permit or license is not required for purchasing or carrying firearms. Concealed carry in the United States, Concealed carry and Open carry in the United States, open carry of a firearm is legal over the age of 16, with those below 16 requiring parental permission.
Vermont has a pro-sanctuary city law.
The state is an alcoholic beverage control state. In 2007, through the Vermont Department of Liquor Control, it took in over $14 million from the sale and distribution of liquor.
In 2013, Vermont became the 17th state to decriminalize marijuana. The statute makes possession of less than an ounce of the drug punishable by a small fine, rather than arrest and possible jail time.
In 2014, Vermont became the first state to call for a Second Constitutional Convention of the United States, constitutional convention to overturn the Supreme Court's decision in ''Citizens United v. FEC''.
In 2014, Vermont became the first state to mandate labeling of genetically modified organisms in the retail food supply.
In January 2018, Governor Phil Scott opted to sign H.511, the Vermont marijuana legalization bill, which allows adults 21 and older to possess up to one ounce of marijuana and grow up to two mature plants starting July 1, 2018.
Federal politics
 Historically, Vermont was considered one of the most reliably Republican Party (United States), Republican states in the country in terms of national elections. From 1856 United States presidential election in Vermont, 1856 to 1988 United States presidential election in Vermont, 1988, Vermont voted Democratic Party (United States), Democratic only once, in Lyndon B. Johnson's 1964 United States presidential election in Vermont, landslide victory of 1964 against Barry M. Goldwater. It was also one of only two states—As Maine goes, so goes Vermont, Maine is the other—where Franklin D. Roosevelt was completely shut out in all four of his presidential bids. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Republican presidential candidates frequently won the state with over 70% of the vote.
In the 1980s and 1990s, many people moved in from out of state. Much of this immigration included the arrival of more liberal political influences of the urban areas of
Historically, Vermont was considered one of the most reliably Republican Party (United States), Republican states in the country in terms of national elections. From 1856 United States presidential election in Vermont, 1856 to 1988 United States presidential election in Vermont, 1988, Vermont voted Democratic Party (United States), Democratic only once, in Lyndon B. Johnson's 1964 United States presidential election in Vermont, landslide victory of 1964 against Barry M. Goldwater. It was also one of only two states—As Maine goes, so goes Vermont, Maine is the other—where Franklin D. Roosevelt was completely shut out in all four of his presidential bids. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Republican presidential candidates frequently won the state with over 70% of the vote.
In the 1980s and 1990s, many people moved in from out of state. Much of this immigration included the arrival of more liberal political influences of the urban areas of Culture
 Vermont festivals include the Vermont Maple Festival, Festival on the Green, The Vermont Dairy Festival in Enosburg Falls, the Apple Festival (held each Columbus Day Weekend), the Marlboro Music School and Festival, Marlboro Music Festival, and the Vermont Brewers Festival. The Vermont Symphony Orchestra is supported by the state and performs throughout the area.
Since 1973 the Sage City Symphony, formed by composer Louis Calabro, has performed in the Bennington area. In 1988, a number of Vermont-based composers including Gwyneth Walker formed the Vermont Composers Consortium, which was recognized by the governor proclaiming 2011 as ''The Year of the Composer''.
Burlington, Vermont's largest city, hosts the annual Vermont International Film Festival, which presents ten days in October of independent films. The Brattleboro, Vermont, Brattleboro-based Vermont Theatre Company presents an annual summer Shakespeare festival. Brattleboro also hosts the summertime Strolling of the Heifers parade which celebrates Vermont's dairy culture. The annual Green Mountain Film Festival is held in Montpelier.
In the Northeast Kingdom, the Bread and Puppet Theatre holds weekly shows in Glover in a natural outdoor amphitheater.
One of Vermont's best known musical acts is the rock band Phish, whose members met while attending school in Vermont and spent much of their early years playing at venues across the state.
The Vermont-based House of LeMay performs several shows a year, hosts the annual "Winter is a Drag Ball," and performs for fundraisers.
Examples of folk art found in Vermont include the Vermontasaurus in Thetford, Vermont, Post Mills, a community in Thetford.
The rate of volunteerism in Vermont was eighth in the nation with 37% in 2007. The state stood first in New England. In 2011, Vermont residents were ranked as the healthiest in the country. Also in 2011, Vermont was ranked as the fourth most peaceful state in the United States. In 2011, Vermont residents were ranked as the sixth most fit/leanest in the country. Vermonters were the second most active citizens of state with 55.9% meeting the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's physical activity requirements. Vermont was ranked as the 12th happiest state in the country.
Vermont festivals include the Vermont Maple Festival, Festival on the Green, The Vermont Dairy Festival in Enosburg Falls, the Apple Festival (held each Columbus Day Weekend), the Marlboro Music School and Festival, Marlboro Music Festival, and the Vermont Brewers Festival. The Vermont Symphony Orchestra is supported by the state and performs throughout the area.
Since 1973 the Sage City Symphony, formed by composer Louis Calabro, has performed in the Bennington area. In 1988, a number of Vermont-based composers including Gwyneth Walker formed the Vermont Composers Consortium, which was recognized by the governor proclaiming 2011 as ''The Year of the Composer''.
Burlington, Vermont's largest city, hosts the annual Vermont International Film Festival, which presents ten days in October of independent films. The Brattleboro, Vermont, Brattleboro-based Vermont Theatre Company presents an annual summer Shakespeare festival. Brattleboro also hosts the summertime Strolling of the Heifers parade which celebrates Vermont's dairy culture. The annual Green Mountain Film Festival is held in Montpelier.
In the Northeast Kingdom, the Bread and Puppet Theatre holds weekly shows in Glover in a natural outdoor amphitheater.
One of Vermont's best known musical acts is the rock band Phish, whose members met while attending school in Vermont and spent much of their early years playing at venues across the state.
The Vermont-based House of LeMay performs several shows a year, hosts the annual "Winter is a Drag Ball," and performs for fundraisers.
Examples of folk art found in Vermont include the Vermontasaurus in Thetford, Vermont, Post Mills, a community in Thetford.
The rate of volunteerism in Vermont was eighth in the nation with 37% in 2007. The state stood first in New England. In 2011, Vermont residents were ranked as the healthiest in the country. Also in 2011, Vermont was ranked as the fourth most peaceful state in the United States. In 2011, Vermont residents were ranked as the sixth most fit/leanest in the country. Vermonters were the second most active citizens of state with 55.9% meeting the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's physical activity requirements. Vermont was ranked as the 12th happiest state in the country.
Sports
Winter sports
Winter sports are popular in New England, and Vermont's winter sports attractions are a big part of Vermont tourism. Some well known attractions include Burke Mountain (Vermont), Burke Mountain ski area, Jay Peak Resort, Killington Ski Resort, Stowe Mountain Resort, the Quechee Club Ski Area, and Smugglers' Notch Resort. Vermont natives in the snowboarding profession include Kevin Pearce (snowboarder), Kevin Pearce, Ross Powers, Hannah Teter, and Kelly Clark. Others learned snowboarding in the state, such as Louie Vito and Ellery Hollingsworth (snowboarder), Ellery Hollingsworth. Vermont Olympic gold medalists include Barbara Cochran, Hannah Kearney, Kelly Clark, Ross Powers, and Hannah Teter.Baseball
The largest professional franchise is the Vermont Lake Monsters of the Futures Collegiate Baseball League, based in Burlington, Vermont, Burlington. They were named the Vermont Expos before 2006. Up until the 2011 season, they were the affiliate of the Washington Nationals (formerly the Montreal Expos). Up until 2020 in baseball, 2020, they played in the New York-Penn League of Single-A and were the Single-A affiliate of the Oakland AthleticsBasketball
Currently the highest-ranked teams in basketball representing Vermont are the NCAA's Vermont Catamounts—male and female. The Vermont Frost Heaves, the 2007 and 2008 American Basketball Association national champions, were a franchise of the Premier Basketball League, and were based in Barre (city), Vermont, Barre and Burlington, Vermont, Burlington from the fall of 2006 through the winter of 2011.Football
The Vermont Bucks, an Indoor American football, indoor football team, were based in Burlington, Vermont, Burlington and began play in 2017 as the founding team in the Can-Am Indoor Football League. For 2018, the Bucks joined the American Arena League, but folded prior to playing in the new league.Hockey
Vermont is home to the University of Vermont Vermont Catamounts men's ice hockey, Men's and Vermont Catamounts women's ice hockey, Women's hockey teams. Vermont's only professional hockey team was the Vermont Wild who played in the Federal Hockey League during the 2011–12 season, but the team folded before the season ended.Soccer
The Vermont Voltage were a USL Premier Development League soccer club that played in St. Albans (city), Vermont, St. Albans. Vermont Green FC are a USL League 2 club that will play at University of Vermont's Virtue Field in Burlington. Annually since 2002, high school statewide all stars compete against New Hampshire in ten sports during "Twin State" playoffs.Motorsport
Vermont also has a few auto racing venues. The most popular of them is Thunder Road International Speedbowl in Barre (town), Vermont, Barre, Vermont. It is well known for its tight racing and has become well known in short track stock car racing. Other racing circuits include the United States Auto Club, USC sanctioned Bear Ridge Speedway, and the NASCAR sanctioned Devil's Bowl Speedway. Some NASCAR Cup drivers have come to Vermont circuits to compete against local weekly drivers such as Tony Stewart, Clint Bowyer, Kyle Busch, Kenny Wallace, Ken Schrader, and Christopher Bell (racing driver), Christopher Bell. Kevin Lepage from Shelburne, Vermont is one of a few professional drivers from Vermont. Racing series in Vermont include NASCAR Whelen All-American Series, American Canadian Tour, and Vermont's own Tiger Sportsman Series.Residents
The following were either born in Vermont or resided there for a substantial period during their lives and whose names are widely known. * Chester A. Arthur, 21st President of the United States * Pearl S. Buck, author * Jake Burton Carpenter, inventor of the snowboard * Calvin Coolidge, 30th President of the United States * John Deere (inventor), John Deere, founder of Deere & Company * George Dewey, the only Admiral of the Navy in U.S. history * John Dewey, philosopher, psychologist, and educator * Stephen Douglas, 19th-century politician * Carlton Fisk, Baseball Hall of Fame catcher * James Fisk (financier), James Fisk, financier * Robert Frost, poet * Richard Morris Hunt, architect * Rudyard Kipling, author * Bill McKibben, environmentalist * Samuel Morey, inventor of the steam-powered paddle wheel boat * Norman Rockwell, painter, author, and illustrator * Bernie Sanders, politician and legislator * Joseph Smith, founder of the Latter Day Saint movement * Alexander Solzhenitsyn, Russian author and Soviet dissident * Rudy Vallée, singer and actor * Brigham Young, 2nd President of the Church (LDS Church), President of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day SaintsIn fiction
* Vermont was also the home of Dick Loudon, Bob Newhart's character on the 1980s sitcom ''Newhart''. All action supposedly took place in Vermont. * Vermont was the home of Pollyanna and her Aunt Polly in the novel ''Pollyanna'', later made into the 1960 Walt Disney, Disney Pollyanna (1960 film), film starring Hayley Mills and Jane Wyman.Retrieved September 12, 2008.
See also
* Outline of Vermont * Index of Vermont-related articles * French language in the United StatesNotes
References
Bibliography
Sources
* . * * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * . *External links
General
*Government
*Energy Data and Statistics for Vermont
Vermont Agriculture
Vermont League of Cities and Towns
USDA Vermont State Facts
Roads compared to other states
Geology
Rodinia to Pangea: The Lithotectonic Record of the Appalachian Region
Laurentia-Gondwana connections before Pangea
Bedrock Geologic Map of Vermont
United States Geological Survey
Maps and demographics
Earthquake History of Vermont
USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Vermont
*
Tourism and recreation
Vermont Department of Tourism and Marketing
Business
Vermont Chamber of Commerce
Culture and history
Conservation Corps
Center for Digital Initiatives, University of Vermont Libraries
Central Vermont: Explore History in the Heart of the Green Mountains, a National Park Service ''Discover Our Shared Heritage'' Travel Itinerary
Vermont Arts Council
Vermont Historical Society
Vermont International Film Foundation
Vermont Native American Museum & Cultural Center
{{coord, 44.0, N, 72.7, W, type:adm1st_region:US-VT, name=State of Vermont, display=title Vermont, 1791 establishments in the United States New England states Northeastern United States States and territories established in 1791 States of the United States Contiguous United States