Van Buren Street Tunnel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Between 1892 and 1906, Chicago had three
Between 1892 and 1906, Chicago had three
Engineering and Contracting
Vol. XXXIII, No. 16 (April 20, 1910); page 356. Note: Illustrated.
NCSR at Chicagology.comWCSR at Chicagology.com
Streetcars in Illinois Railroad tunnels in Illinois
 Between 1892 and 1906, Chicago had three
Between 1892 and 1906, Chicago had three cable car Cable car most commonly refers to the following cable transportation systems:
* Aerial lift, such as aerial tramways and gondola lifts, in which the vehicle is suspended in the air from a cable
** Aerial tramway
** Chairlift
** Gondola lift
*** Bi ...
tunnels under the Chicago River
The Chicago River is a system of rivers and canals with a combined length of that runs through the city of Chicago, including its center (the Chicago Loop). Though not especially long, the river is notable because it is one of the reasons for ...
. Two were built for pedestrian and horse traffic and later converted, the third was built specially for cable-cars. After cable service ended they would be used by electric streetcars.
By 1900, Chicago had a cable-based transit system that carried 80 million passengers a year, but all cable routes leaving downtown
''Downtown'' is a term primarily used in North America by English speakers to refer to a city's sometimes commercial, cultural and often the historical, political and geographic heart. It is often synonymous with its central business distric ...
to the North or West had to cross the navigable Chicago River. Heavy shipping traffic required movable bridges, which cable lines couldn't cross. Two existing public tunnels were converted for cable use, and a third was built as a private venture.
In 1906, all Chicago cable lines were converted to electricity and the tunnels were closed. All would reopen for streetcar service, but with the change to electricity streetcars could cross bridges and the tunnels were less important. One ended regular service in 1924, one was closed in 1939, and one remained in regular service until 1952. In 2010 all approaches had been covered but two tunnels still existed.
These tunnels should not be confused with a network of small freight tunnels under the downtown area.
History
Background
In 1882, the Chicago City Railway opened the first of two cable car lines south from the downtown business district. Used as the backbone of a system of local horse and electric lines, the cable lines were immediately successful and greatly improved public transit in the South Side. But the Chicago River, with its two branches, separated the North andWest
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sunset, Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic languages, German ...
Sides from the downtown and South Side. To enter downtown cable cars would have to cross the river.
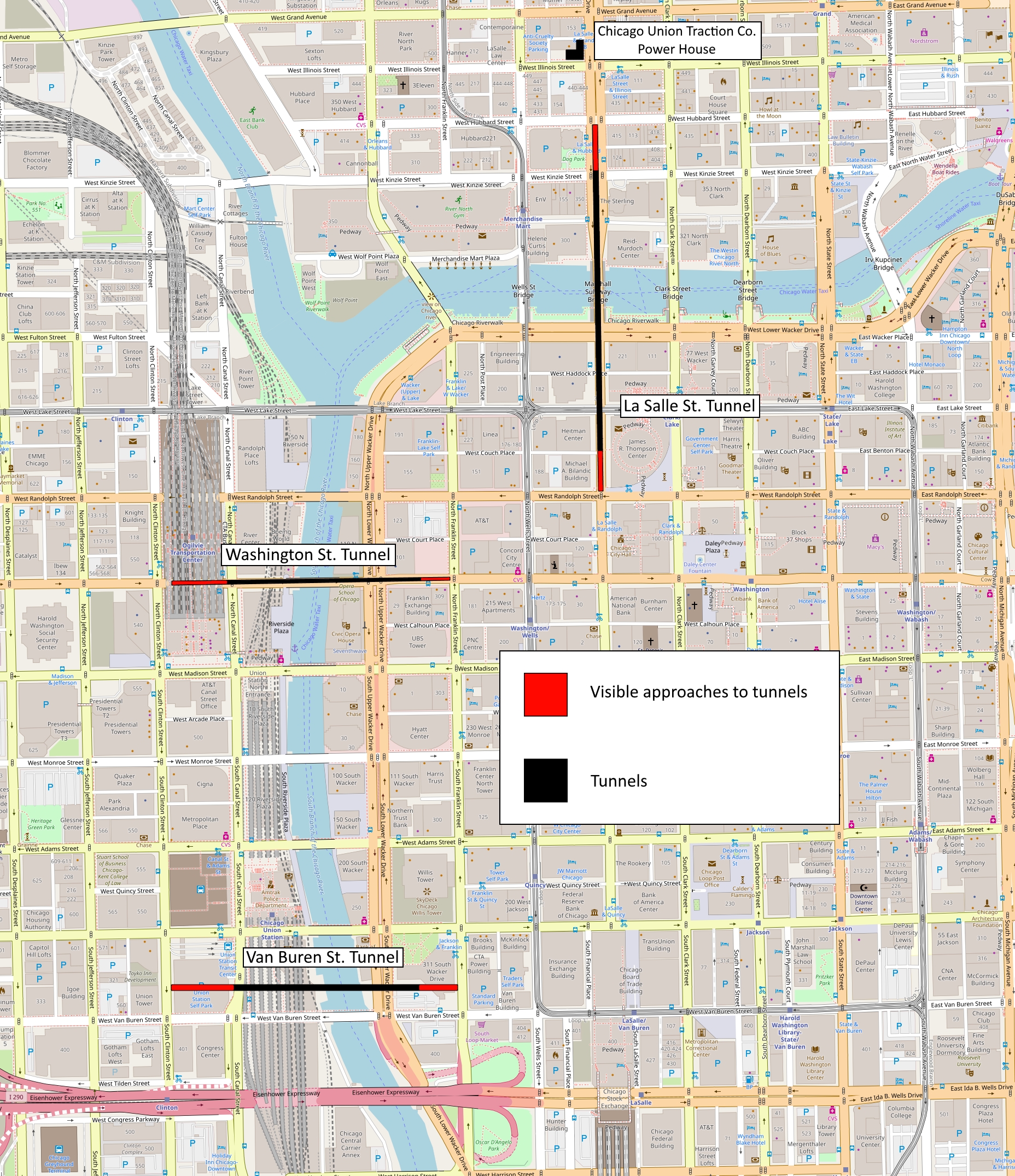
The Chicago River was the city's port, and shipping had priority over land transport. Heavy river traffic and flat terrain required movable bridges, causing long traffic delays, and which could not have cables on them. But the city had previously built two horse and pedestrian tunnels under the river, both were in poor condition and neither was being used. One under LaSalle St. connected the North Side and one under Washington St. the West Side. A third tunnel next to Van Buren St., also connecting the West Side, was built later.
Cable service
An 1886 ordinance allowed the North Chicago Street Railroad to use the LaSalle St. tunnel in exchange for payment, moving a bridge, rehabilitating, and maintaining the tunnel. Cable service began on March 26, 1888 and ended October 21, 1906. In 1888, The West Chicago Street Railway (WCSRy) made a similar arrangement with the city over the Washington St. tunnel. Cable service began August 12, 1890 and ended August 19, 1906. The last tunnel was built privately by the WCSRy next to Van Buren St. Construction began in 1890 but went slow and the tunnel didn't enter service until July 27, 1893. It was closed for cable July 22, 1906. When built all three tunnels were 18 feet under the riverbed, but in 1900 the direction of the Chicago River was reversed by deepening it. The lower bottom level exposed all three tunnels and ships ran aground on the Washington St. tunnel. In 1904, the Federal government declared that all three tunnels were hazards to navigation and had to be removed. In 1906 all cables, which had become obsolete, were replaced by electric service that could cross the bridges and all three tunnels were closed.After cable service ended
After the end of cable service all three tunnels were lowered, converted to electricity, and reopened. The LaSalle and Washington St. tunnels were owned by the city, but the privately owned Van Buren St. tunnel would have to be lowered or removed at the owner's cost. The WCSR filed a suit that went to the US Supreme Court, but they lost and had to pay for lowering the tunnel. The Van Buren St. tunnel was reopened in 1910, the Washington in 1911, and the LaSalle in 1912. The Van Buren St. tunnel was closed again in 1915-1916 during construction of the newChicago Union Station
Chicago Union Station is an intercity and commuter rail terminal located in the Near West Side neighborhood of Chicago, Illinois. The station is Amtrak's flagship station in the Midwest. While serving long-distance passenger trains, it is also ...
.
With the change to electricity cars could cross bridges and the tunnels were less important. The Van Buren St. tunnel ended regular service on September 14, 1924, after that it was sometimes used as a bypass when bridges were open. The LaSalle St. tunnel was closed in 1939 for construction of the State St. subway. The Washington St. remained in regular service until 1952.
Construction
Washington St.
Originally built for pedestrians and horse-drawn traffic, this was the first tunnel under the river. Construction began in 1867 and it opened January 1, 1869, but it wasn't successful. The approach grades were steep for horses, it leaked, and it was dark and uncomfortable for pedestrians, by 1884 it had been closed as unsafe. In 1888 the West Chicago Street Railroad Co. began to rehabilitate it. On August 12, 1890, cable car service began and continued until August 19, 1906. The east approach began in the middle of the street just west of Franklin St. The track descended and was covered. Under the river the tunnel had two horse and one pedestrian lanes. West of the river the approach climbed and the track came to street level just east of Clinton. The tunnel, including the approaches, was long. After closing in 1906, a wider and deeper replacement was built under the original and the approaches were deepened to the new lower level. The grades were aligned for the cars to enter a shallow subway just below street level but the subway was never built, concrete ramps raised the tracks up to street grade. It opened to electric streetcar service on January 29, 1911. The tunnel was in regular use until 1953. By 2013 the tunnel was closed and both approaches had been covered.LaSalle St.
Originally built for pedestrians and horse-drawn traffic construction started right after the Washington St. tunnel was finished, but was built to a different design. Like the Washington St. tunnel, approach grades were steep for horses, it leaked, and it was dark and uncomfortable for pedestrians. In 1888 the North Chicago Street Railroad leased the tunnel and began to rehabilitate it. On March 23, 1888 cable service began and continued until October 21, 1906, when it was closed for lowering. The north approach began in the middle of the street just north of Hubbard St. (Michigan St. in 1871). The track descended and the approach was covered. Under the river the tunnel had two horse and one pedestrian masonry arch lanes. South of the river the approach climbed and the track came to street level just north of Randolph St. The tunnel, including the approaches, was long. A replacement tunnel was built in adrydock
A dry dock (sometimes drydock or dry-dock) is a narrow basin or vessel that can be flooded to allow a load to be floated in, then drained to allow that load to come to rest on a dry platform. Dry docks are used for the construction, maintenance, ...
on Goose Island from steel plate. When the tunnel closed the replacement was lowered into a trench in the riverbed and the approaches were deepened to a new lower level. Like the Washington St. tunnel the grades were aligned for the cars to enter a shallow subway just below street level. The subway was never built, concrete ramps raised the tracks up to street grade.
The deepened tunnel was opened to electric streetcar service on July 21, 1912. It was in regular service until November 27, 1939, when it was closed during the construction of the Milwaukee-Lake-Dearborn-Congress subway, the Lake & LaSalle (now Clark & Lake) station of which intersected the tunnel's south ramp under Lake Street. As of 1954, the north tunnel portal was still extant, but both approaches are now filled in, although the tunnel itself still exists under the river. A ramp in the middle of LaSalle St. south of Kinzie St., an access down to Carroll Ave., is sometimes mistaken for the north portal, which was a block north and aligned below the current ramp.
Van Buren St.
The Van Buren St. tunnel was the last of the three built, and the only one built privately specifically for cable cars. Construction began in 1890 but progress was slow. Cable service started on March 24, 1894 and ended on July 22, 1906. The east approach began at Franklin St. Unlike the city-owned tunnels, it didn't go under the street itself, but 150 feet north of and parallel to it. This meant the cars had to slow down, turn north on Franklin, then immediately turn west into a driveway to the approach. It was a stone walled wide ramp which descended at 12% for before being covered under an alley. As the shortest tunnel it had the steepest grade. Under the river the tunnel had a single two-lane arched roof. West of the river the approach climbed to Clinton St. where the line had to turn south. Because of the entrances and steep approaches the tunnel always had operating problems. The tunnel, including the approaches, was long as built. A deeper replacement was built thru the original tunnel and opened to electric streetcar service in 1910. Closed again in 1915 to construct the approaches to the new Union Station, it was reopened in 1916. Closed to regular service in 1924, the tunnel was sometimes used until 1952, when all service ended.Plans for subways
In 1937, Chicago petitioned thePublic Works Administration
The Public Works Administration (PWA), part of the New Deal of 1933, was a large-scale public works construction agency in the United States headed by Secretary of the Interior Harold L. Ickes. It was created by the National Industrial Recove ...
(PWA) for funding for the State Street subway
The State Street subway is an underground section of the Chicago "L" system in The Loop which serves as the center of the Red Line. It is long and has a boarding average of 53,601 passengers every weekday as of February 2013. It owes its name t ...
. Originally included in the proposal was a plan for two more streetcar tunnels. Harold L. Ickes
Harold LeClair Ickes ( ; March 15, 1874 – February 3, 1952) was an American administrator, politician and lawyer. He served as United States Secretary of the Interior for nearly 13 years from 1933 to 1946, the longest tenure of anyone to hold th ...
vetoed this plan in favor of a Milwaukee-Dearborn subway, which was eventually enacted.
Plans were made to incorporate the tunnel into a high-level subway to run under Washington Street between Clinton Street and Grant Park. The plans were expanded after the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
to add an additional high-level subway running parallel to the Washington Street line under Jackson Street, similarly using the tunnel located between Jackson and Van Buren Streets. Both would be tied into another subway tunnel to be dug under Clinton Street, proposed in the interim. The only construction accomplished in advance of these plans were the pair of portals in the Eisenhower Expressway
Interstate 290 (I-290) is an auxiliary Interstate Highway that runs westward from the Chicago Loop. The portion of I-290 from I-294 to its east end is officially called the Dwight D. Eisenhower Expressway. In short form, it is known as "the ...
median, 200 feet east of Halsted Street
Halsted Street is a major north-south street in the U.S. city of Chicago, Illinois.
Location
In Chicago's grid system, Halsted Street marks 800 West, west of State Street, from Grace Street (3800 N) in Lakeview south to the city limits at t ...
, constructed in 1952 simultaneously with the pair of portals for the Blue Line, and the double-wide station built at Peoria Street in 1964 to accommodate the anticipated platform north of the UIC-Halsted platform for the Blue Line. In 1951-1952, the plans were modified to use the Washington Street subway as a busway rather than as a train tunnel, while Clinton and Jackson tunnels were merged and remained a rail plan. The plan was cancelled in April 1962, although the design and placement of the Peoria Street station house went unchanged.
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Chicago Department of Subways and Traction, ''A Comprehensive Plan for the Extension of the Subway System of the City of Chicago Including Provision for the Widening of E. and W. Congress Street'' (Chicago: City of Chicago, October 30, 1939), 2-3, III; and City of Chicago, Department of Subways and Superhighways, ''Second'' ''Annual Report of the Department of Subways and Superhighways, City of Chicago, for the Year Ending December 31, 1940'' (Chicago: City of Chicago, December 31, 1940), 1. * Chicago Transit Authority, ''Chicago Transit Authority's Proposed $315,000,000 Transit Expansion and Improvement Program'' (Chicago: Chicago Transit Authority, 1957), ''New Horizons for Chicago Metropolitan Area'' (Chicago: Chicago Transit Authority, 1958), and ''T.E.D. 8-320'' (map) (Chicago, Chicago Transit Authority, September 30, 1958). * Chicago Transit Board, ''Plan for Expanding Rapid Transit Service in the Central Area of Chicago'' (Chicago: Chicago Transit Board, April 20, 1962), 1, 6-7, 10-11. * City of Chicago, Department of Development and Planning, Chicago Plan Commission, ''1963 Annual Report'' (Chicago: City of Chicago, 1963), 22. * City of Chicago, Department of Streets and Superhighways, ''Sixth Annual Report of the Department of Subways and Superhighways, City of Chicago, for the Year Ending December 31, 1944.'' * City of Chicago, Department of Streets and Superhighways, ''Eighth Annual Report of the Department of Subways and Superhighways, City of Chicago, for the Year Ending December 31, 1946.'' * City of Chicago, Department of Streets and Superhighways, ''Fourteenth Annual Report of the Department of Subways and Superhighways, City of Chicago, for the Year Ending December 31, 1952,'' 36-37. * {{cite book, last=Hilton, first=George W., title=The Cable Car in America, year=1997, publisher=Stanford University, isbn=0-8047-3051-2 * Method of Reconstructing the Washington Street Tunnel of the Chicago Railways Company; a New and Economical Method of Constructing TunnelsEngineering and Contracting
Vol. XXXIII, No. 16 (April 20, 1910); page 356. Note: Illustrated.
External links
Streetcars in Illinois Railroad tunnels in Illinois
Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
Rail technologies
Railways by type
Transportation buildings and structures in Chicago