V603 Aquilae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 V603 Aquilae (or Nova Aquilae 1918) was a bright
V603 Aquilae (or Nova Aquilae 1918) was a bright
Image V603 Aquilae
HIC 92316
HIP 92316
{{DEFAULTSORT:V603 Aquilae 174107 Novae Aquila (constellation) 19180608 Aquilae, V603 092316
 V603 Aquilae (or Nova Aquilae 1918) was a bright
V603 Aquilae (or Nova Aquilae 1918) was a bright nova
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramati ...
first observed (from Earth) in the constellation Aquila in 1918. It was the brightest "new star" to appear in the sky since Kepler's Supernova
SN 1604, also known as Kepler's Supernova, Kepler's Nova or Kepler's Star, was a Type Ia supernova that occurred in the Milky Way, in the constellation Ophiuchus. Appearing in 1604, it is the most recent supernova in the Milky Way galaxy to have ...
in 1604. Like all novae, it is a binary system, comprising a white dwarf and donor low-mass star in close orbit to the point of being only semidetached. The white dwarf sucks matter off its companion, which has filled its Roche lobe
In astronomy, the Roche lobe is the region around a star in a binary system within which orbiting material is gravitationally bound to that star. It is an approximately teardrop-shaped region bounded by a critical gravitational equipotential, wit ...
, onto its accretion disk
An accretion disk is a structure (often a circumstellar disk) formed by diffuse material in orbital motion around a massive central body. The central body is typically a star. Friction, uneven irradiance, magnetohydrodynamic effects, and other fo ...
and surface until the excess material is blown off in a thermonuclear event. This material then forms an expanding shell, which eventually thins out and disappears.
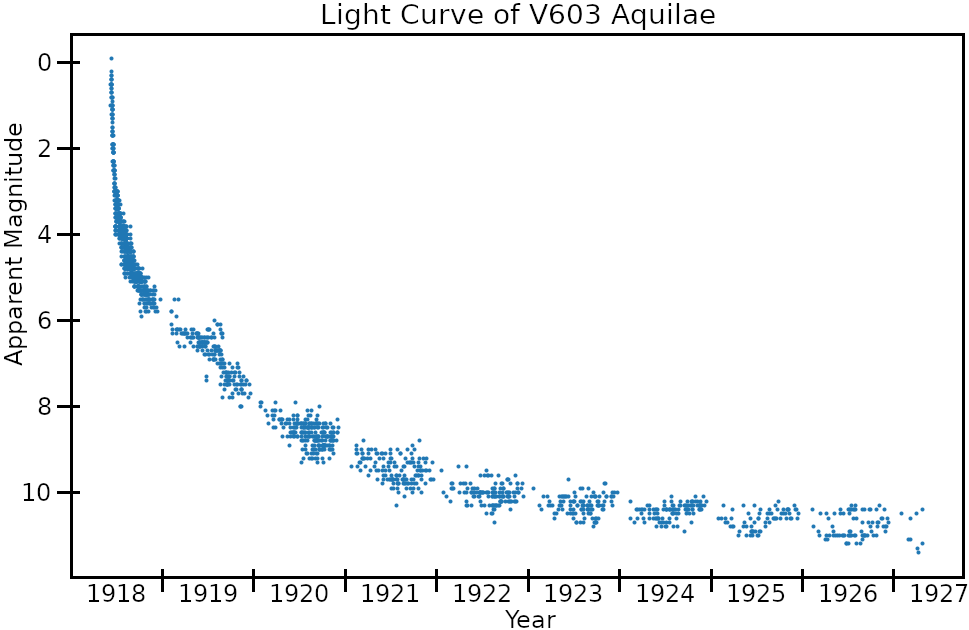
First seen by Zygmunt Laskowski, a medical professor and amateur astronomer, and then confirmed on the night of 8 June 1918 by the UK amateur astronomer Grace Cook, Nova Aquilae reached a peak magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
of −0.5; it was the brightest nova recorded in the era of the telescope. It was brighter than all stars but Sirius
Sirius is the list of brightest stars, brightest star in the night sky. Its name is derived from the Ancient Greek language, Greek word , or , meaning 'glowing' or 'scorching'. The star is designated α Canis Majoris, Latinisation ...
and Canopus
Canopus is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Carina (constellation), Carina and the list of brightest stars, second-brightest star in the night sky. It is also Bayer designation, designated α Carinae, which is Lat ...
. Tycho's and Kepler's supernovae were brighter, but both occurred before the invention of the telescope. Originally a star system with a magnitude of 11.43, it took twelve days to fade three magnitudes and then 18.6 years to fade to quiescence. In 1964 Robert P. Kraft ascertained that it was a binary system, recently determined to be true for several other novae at the time.
The star system has settled to an average apparent magnitude of 11.4 since the 1940s, fading by around 1/100 of a magnitude per decade. The nova's parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby objects ...
, 3.191±0.069 milliarcseconds, was measured by the Gaia spacecraft
''Gaia'' is a space observatory of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 2013 and expected to operate until 2025. The spacecraft is designed for astrometry: measuring the positions, distances and motions of stars with unprecedented preci ...
which implies a distance of 1020±23 light years. Spectroscopic analysis conducted by Arenas and colleagues indicated the system consisted of a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes fro ...
of about 1.2 times as massive as the sun, with an accretion disk, and a companion star with about 20% of the Sun's mass. This second star is most likely a red dwarf
''Red Dwarf'' is a British science fiction comedy franchise created by Rob Grant and Doug Naylor, which primarily consists of a television sitcom that aired on BBC Two between 1988 and 1999, and on Dave since 2009, gaining a cult following. T ...
. The two stars orbit each other approximately every 3 hours 20 minutes.
In 1983 VLA VLA or vla may refer to:
Organizations
* Vermont Library Association, professional organization for librarians from Vermont
* Veterinary Laboratories Agency, a UK government agency for researching animal and public health
* Victoria Legal Aid, an ...
observations detected radio emission from this nova at 5 GHz. The upgraded JVLA detected 8.9 GHz emission in 2013, and MeerKAT
MeerKAT, originally the Karoo Array Telescope, is a radio telescope consisting of 64 antennas in the Meerkat National Park, in the Northern Cape of South Africa. In 2003, South Africa submitted an expression of interest to host the Square Kilom ...
detected 1.3 GHz emission in 2019. The radio emission is consistent with gyrosynchrotron, cyclotron maser and optically thick synchrotron emission.
References
*Image V603 Aquilae
External links
HIC 92316
HIP 92316
{{DEFAULTSORT:V603 Aquilae 174107 Novae Aquila (constellation) 19180608 Aquilae, V603 092316