V-22 Osprey Tiltrotor Aircraft on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
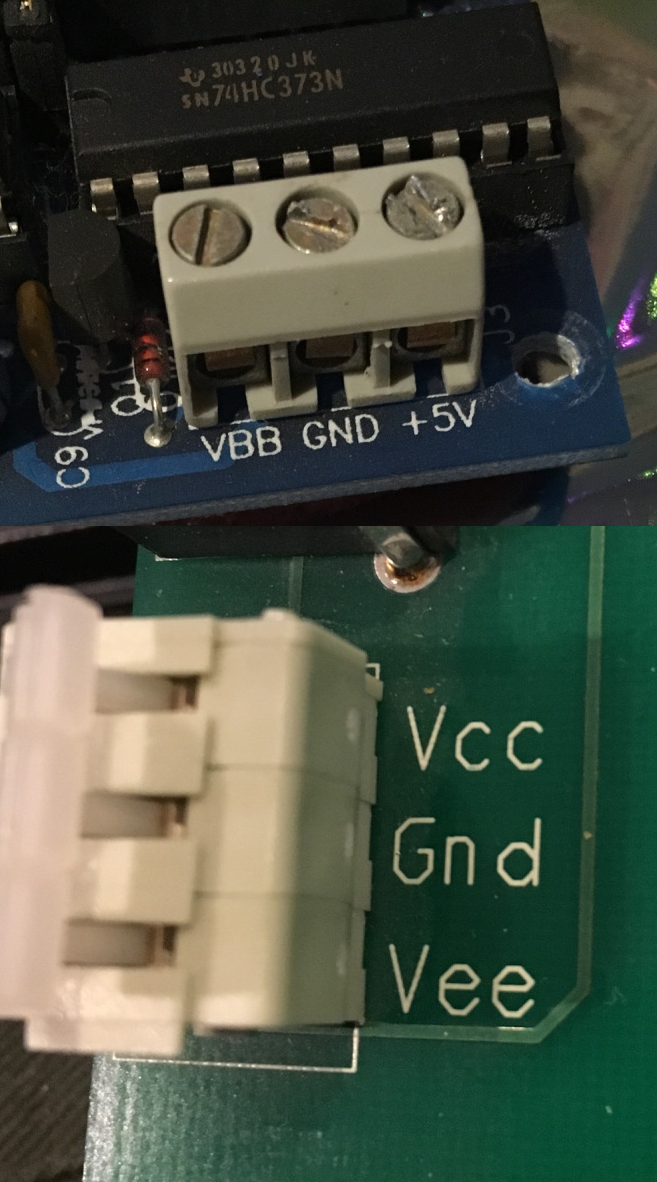 IC power-supply pins denote a voltage and current supply terminals in electric,
IC power-supply pins denote a voltage and current supply terminals in electric, Op-amps: Some Standard Conconfigurations and Applications, Fall 2012
Washington and Lee University, Lexington, VA.
 IC power-supply pins denote a voltage and current supply terminals in electric,
IC power-supply pins denote a voltage and current supply terminals in electric, electronics engineering
Electronics engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering which emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current f ...
, and in Integrated circuit design. Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
s (ICs) have at least two pins that connect to the power rails of the circuit in which they are installed. These are known as the power-supply pins. However, the labeling of the pins varies by IC family and manufacturer. The double subscript notation usually corresponds to a first letter in a given IC family (transistors) notation of the terminals (e.g. VDD supply for a drain terminal in FETs etc.).
The simplest labels are V+ and V−, but internal design and historical traditions have led to a variety of other labels being used. V+ and V− may also refer to the non-inverting (+) and inverting (−) voltage inputs of ICs like op amp
An operational amplifier (often op amp or opamp) is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op amp produces an output potential (relative to ...
s.
For power supplies, sometimes one of the supply rails is referred to as ground
Ground may refer to:
Geology
* Land, the surface of the Earth not covered by water
* Soil, a mixture of clay, sand and organic matter present on the surface of the Earth
Electricity
* Ground (electricity), the reference point in an electrical c ...
(abbreviated "GND") positive and negative voltages are relative to the ground. In digital electronics, negative voltages are seldom present, and the ground nearly always is the most negative voltage level. In analog electronics (e.g. an audio power amplifier) the ground can be a voltage level between the most positive and most negative voltage level.
While double subscript notation, where subscripted letters denote the difference between two points, uses similar-looking placeholders with subscripts, the double-letter supply voltage subscript notation is not directly linked (though it may have been an influencing factor).Washington and Lee University, Lexington, VA.
BJTs
ICs using bipolar transistors have ''VCC'' (+, positive) and ''VEE'' (-, negative) power-supply pins though ''VCC'' is also often used for CMOS devices as well. In circuit diagrams and circuit analysis, there are long-standing conventions regarding the naming of voltages, currents, and some components. In the analysis of a bipolar junction transistor, for example, in a common-emitter configuration, theDC voltage
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow throug ...
at the collector, emitter, and base (with respect to ground) may be written as ''V''C, ''V''E, and ''V''B respectively.
Resistors associated with these transistor terminals may be designated ''RC'', ''RE'', and ''RB''. In order to create the DC voltages, the furthest voltage, beyond these resistors or other components if present, was often referred to as ''VCC'', ''VEE'', and ''VBB''. In practice ''VCC'' and ''VEE'' then refer to the positive and negative supply lines respectively in common
Common may refer to:
Places
* Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland
* Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts
* Cambridge Common, common land area in Cambridge, Massachusetts
* Clapham Common, originally com ...
NPN circuits. Note that ''VCC'' would be negative, and ''VEE'' would be positive in equivalent PNP circuits.
The ''VBB'' specifies reference bias supply voltage in TTL logic.
FETs
Exactly analogous conventions were applied to field-effect transistors with their drain, source and gate terminals. This led to ''VD'' and ''VS'' being created by supply voltages designated ''VDD'' and ''VSS'' in the more common circuit configurations. In equivalence to the difference between NPN and PNP bipolars, ''VDD'' is positive with regard to ''VSS'' in the case of ''n''-channel FETs andMOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
s and negative for circuits based on ''p''-channel FETs and MOSFETs.
CMOS
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFE ...
ICs have generally borrowed the NMOS convention of ''VDD'' for positive and ''VSS'' for negative, even though both positive and negative supply rails connect to source terminals (the positive supply goes to PMOS sources, the negative supply to NMOS sources).
In many single-supply digital and analog circuits the negative power supply is also called "GND". In "split-rail" supply systems there are multiple supply voltages. Examples of such systems include modern cell phones, with GND and voltages such as 1.2 V, 1.8 V, 2.4 V, 3.3 V, and PCs, with GND and voltages such as −5 V, 3.3 V, 5 V, 12 V. Power-sensitive designs often have multiple power rails at a given voltage, using them to conserve energy by switching off supplies to components that are not in active use.
More advanced circuits often have pins carrying voltage levels for more specialized functions, and these are generally labeled with some abbreviation of their purpose. For example, VUSB for the supply delivered to a USB device (nominally 5 V), VBAT for a battery, or Vref for the reference voltage for an analog-to-digital converter. Systems combining both digital and analog circuits often distinguish digital and analog grounds (GND and AGND), helping isolate digital noise from sensitive analog circuits. High-security cryptographic devices and other secure systems sometimes require separate power supplies for their unencrypted and encrypted ( red/black) subsystems to prevent leakage of sensitive plaintext.
BJTs and FETs Mixed
Although still in relatively common use, there is limited relevance of these device-specific power-supply designations in circuits that use a mixture of bipolar and FET elements, or in those that employ either both NPN and PNP transistors or both ''n''- and ''p''-channel FETs. This latter case is very common in modern chips, which are often based onCMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFE ...
technology, where the ''C'' stands for ''complementary'', meaning that complementary pairs of ''n''- and ''p''-channel devices are common throughout.
These naming conventions were part of a bigger picture, where, to continue with bipolar-transistor examples, although the FET remains entirely analogous, DC or bias currents into or out of each terminal may be written ''IC'', ''IE'', and ''IB''. Apart from DC or bias conditions, many transistor circuits also process a smaller audio-, video-, or radio-frequency signal that is superimposed on the bias at the terminals. Lower-case letters and subscripts are used to refer to these signal levels at the terminals, either peak-to-peak or RMS as required. So we see ''vc'', ''ve'', and ''vb'', as well as ''ic'', ''ie'', and ''ib''. Using these conventions, in a common-emitter amplifier, the ratio ''vc''/''vb'' represents the small-signal voltage gain at the transistor, and ''vc''/''ib'' the small-signal ''trans-resistance'', from which the name ''transistor'' is derived by contraction. In this convention, ''vi'' and ''vo'' usually refer to the external input and output voltages of the circuit or stage.
Similar conventions were applied to circuits involving vacuum tubes, or ''thermionic valves'', as they were known outside of the U.S. Therefore, we see ''VP'', ''VK'', and ''VG'' referring to plate (or ''anode'' outside of the U.S.), cathode (note ''K'', not ''C'') and grid voltages in analyses of vacuum triode, tetrode, and pentode
A pentode is an electronic device having five electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a three-grid amplifying vacuum tube or thermionic valve that was invented by Gilles Holst and Bernhard D.H. Tellegen in 1926. The pentode (called a ''tripl ...
circuits.
See also
*4000 series
The 4000 series is a CMOS logic family of integrated circuits (ICs) first introduced in 1968 by RCA. It had a supply voltage range of 5V to 20V, which is much wider than any contemporary logic family.
Almost all IC manufacturers active during thi ...
* 7400 series
* Bob Widlar
* Differential amplifier
* List of 4000 series integrated circuits
* List of 7400 series integrated circuits
* Logic family
*Logic gate
A logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function, a logical operation performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, ...
* Open collector
*Operational amplifier applications
This article illustrates some typical operational amplifier applications. A non-ideal operational amplifier's equivalent circuit has a finite input impedance, a non-zero output impedance, and a finite gain. A real op-amp has a number of non-ideal f ...
* Pin-compatibility
Notes
References
{{reflist, colwidth=30em Integrated circuits fr:Boîtier de circuit intégré#Broches d'alimentation d'un circuit intégré