Urushiol on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Urushiol is an oily mixture of
Poison Oak
at ''Wayne's Word''
* ttp://www.cattail.nu/ivy/ivy_index.html The Poison Ivy Tutorial {{authority control Catechols Resins Contact dermatitis
organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The ...
s with allergenic
An allergen is a type of antigen that produces an abnormally vigorous immune response in which the immune system fights off a perceived threat that would otherwise be harmless to the body. Such reactions are called allergies.
In technical terms ...
properties found in plants
Plants are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all curr ...
of the family
Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its ...
Anacardiaceae
The Anacardiaceae, commonly known as the cashew family or sumac family, are a family of flowering plants, including about 83 genera with about 860 known species. Members of the Anacardiaceae bear fruits that are drupes and in some cases produce ...
, especially ''Toxicodendron
''Toxicodendron'' is a genus of flowering plants in the sumac family, Anacardiaceae. It contains trees, shrubs and woody vines, including poison ivy, poison oak, and the lacquer tree. All members of the genus produce the skin-irritating oi ...
'' ''spp.'' (e.g., poison oak Poison oak refers to two plant species in the genus ''Toxicodendron,'' both of which can cause skin irritation:
*''Toxicodendron diversilobum'' or Western poison oak, found in western North America
*''Toxicodendron pubescens
''Toxicodendron pub ...
, Chinese lacquer tree, poison ivy, poison sumac
''Toxicodendron vernix'', commonly known as poison sumac, or swamp-sumach, is a woody shrub or small tree growing to 9 metres (30 feet) tall. It was previously known as ''Rhus vernix''. This plant is also known as thunderwood, particul ...
), ''Comocladia spp.'' (maidenplums), ''Metopium spp''. (poisonwood), and also in parts of the mango
A mango is an edible stone fruit produced by the tropical tree ''Mangifera indica''. It is believed to have originated in the region between northwestern Myanmar, Bangladesh, and northeastern India. ''M. indica'' has been cultivated in South a ...
tree as well as the fruit of the cashew
The cashew tree (''Anacardium occidentale'') is a tropical evergreen tree native to South America in the genus ''Anacardium'' that produces the cashew seed and the cashew apple accessory fruit. The tree can grow as tall as , but the dwarf cult ...
tree. In most individuals, urushiol causes an allergic skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have diffe ...
rash on contact, known as urushiol-induced contact dermatitis
Urushiol-induced contact dermatitis (also called Toxicodendron dermatitis or Rhus dermatitis) is a type of allergic contact dermatitis caused by the oil urushiol found in various plants, most notably species of the genus ''Toxicodendron'': poison ...
.
The name urushiol is derived from the Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
word for the lacquer tree, . The oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
and polymerization of urushiol in the tree's sap in the presence of moisture allows it to form a hard lacquer
Lacquer is a type of hard and usually shiny coating or finish applied to materials such as wood or metal. It is most often made from resin extracted from trees and waxes and has been in use since antiquity.
Asian lacquerware, which may be ca ...
, which is used to produce traditional Chinese, Korean and Japanese lacquerware
Lacquerware are objects decoratively covered with lacquer. Lacquerware includes small or large containers, tableware, a variety of small objects carried by people, and larger objects such as furniture and even coffins painted with lacquer. Befor ...
.
History
Although urushiol-containinglacquer
Lacquer is a type of hard and usually shiny coating or finish applied to materials such as wood or metal. It is most often made from resin extracted from trees and waxes and has been in use since antiquity.
Asian lacquerware, which may be ca ...
s and their skin-irritating properties were well known in East Asia for several millennia, its first recorded Western texts were in 1624 by John Smith and he initially likened poison ivy to English Ivy
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national id ...
. He did not classify it as a poison at first due to the speed with which its rash disappeared and Smith hypothesized that there may actually be medicinal uses for the plant. In the 18th and 19th centuries, many experiments were done in this area to determine whether or not this theory was true. Because that era's medicinal culture was dominated by plant-based treatments, physicians were hopeful that the strong effect this chemical produced on the body could be effective in some way. André-Ignace-Joseph Dufresnoy was one of the first to come up with a medicinal use for this chemical in 1780 when he boiled poison ivy to produce an infusion for internal use. This led to a distilled extract of poison ivy which he prescribed to many people suffering from skin problems and even paralysis. He claimed this treatment to have yielded several positive results.
For many years, poison ivy was thought to fall into the Rhus genus; however, in the 1900s, it was reclassified into a more appropriate genus, Toxicodendron
''Toxicodendron'' is a genus of flowering plants in the sumac family, Anacardiaceae. It contains trees, shrubs and woody vines, including poison ivy, poison oak, and the lacquer tree. All members of the genus produce the skin-irritating oi ...
, meaning ''poison tree''. There were many documented cases of irritations and allergic reactions from the plant, and its prevalence in medicinal use quickly dwindled. After this new categorization, scientists began attempts to determine what it was that rendered plants of this genus noxious, starting with a hypothesis of a volatile oil present in the plants. While this proved incorrect, Rikou Majima from Japan was able to determine that the chemical urushiol was the irritant. Further, he determined that the substance was a type of alkyl catechol, and due to its structure it was able to penetrate the skin and survive on surfaces for months to years. Urushiol's ability to polymerise into a hard glossy coating is the chemical basis for traditional lacquerware in many Asian countries. After urushiol comes in contact with oxygen, under certain conditions it becomes a black lacquer and has been named urushi lacquer.
Characteristics
Urushiol in its pure form is a pale-yellowliquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, a ...
with a specific gravity
Relative density, or specific gravity, is the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water (molecule), wa ...
of 0.968 and a boiling point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor.
The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding envir ...
of . It is soluble in diethyl ether
Diethyl ether, or simply ether, is an organic compound in the ether class with the formula , sometimes abbreviated as (see Pseudoelement symbols). It is a colourless, highly volatile, sweet-smelling ("ethereal odour"), extremely flammable liq ...
, acetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone), is an organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour.
Acetone is miscib ...
, ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl ...
, carbon tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names (such as tetrachloromethane, also IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry, recognised by the IUPAC, carbon tet in the cleaning industry, Halon-104 in firefighting, and Refrigerant-10 in HVAC ...
, and benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, ...
.
Urushiol is a mixture of several closely related organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The ...
s. Each consists of a catechol
Catechol ( or ), also known as pyrocatechol or 1,2-dihydroxybenzene, is a toxic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is the ''ortho'' isomer of the three isomeric benzenediols. This colorless compound occurs naturally in trace amoun ...
substituted in the 3 position with a hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ex ...
chain that has 15 or 17 carbon atoms. The hydrocarbon group may be saturated
Saturation, saturated, unsaturation or unsaturated may refer to:
Chemistry
* Saturation, a property of organic compounds referring to carbon-carbon bonds
** Saturated and unsaturated compounds
**Degree of unsaturation
** Saturated fat or fatty ac ...
or unsaturated. The exact composition of the mixture varies, depending on the plant source. Whereas western poison oak
''Toxicodendron diversilobum'' (syn. ''Rhus diversiloba''), commonly named Pacific poison oak or western poison oak, is a woody vine or shrub in the sumac family, Anacardiaceae. It is widely distributed in western North America, inhabiting coni ...
urushiol contains chiefly catechols with C17 side-chains, poison ivy and poison sumac contain mostly catechols with C15 sidechains.
The likelihood and severity of allergic reaction to urushiol is dependent on the degree of unsaturation of the hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ex ...
chain. Less than half of the general population experience a reaction with the saturated urushiol alone, but over 90% do so with urushiol that contains at least two degrees of unsaturation
In the analysis of the molecular formula of organic molecules, the degree of unsaturation (also known as the index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD), double bond equivalents, or unsaturation index) is a calculation that determines the total number of r ...
(double bonds). Longer side chains tend to produce a stronger reaction.
Urushiol is an oleoresin Oleoresins are semi-solid extracts composed of resin and essential or fatty oil, obtained by evaporation of the solvents used for their production. The oleoresin of conifers is known as crude turpentine or gum turpentine, which consists of oil of ...
contained within the sap of poison ivy and related plants, and after injury to the plant, or late in the fall, the sap leaks to the surface of the plant, where under certain temperature and humidity conditions the urushiol becomes a blackish lacquer
Lacquer is a type of hard and usually shiny coating or finish applied to materials such as wood or metal. It is most often made from resin extracted from trees and waxes and has been in use since antiquity.
Asian lacquerware, which may be ca ...
after being in contact with oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
. Urushi lacquer is very stable. It is able to withstand disturbances from alkali, acid, and alcohol, while also being able to resist temperatures of over 300 °C. However, the lacquer can be degraded by UV rays from the sun and other sources.
Within the United States, urushiol-containing plants are distributed throughout. Poison ivy can be found in all states except California, Alaska, and Hawaii. Poison Oak can be found on the west coast or some states in the southeast, while poison sumac can be found only in the eastern half of the country.
These plants all have distinguishing features that will help in identification. Poison ivy always grows with three shiny, pointy leaves. Poison oak has a similar look, but with larger and more rounded leaves that are hairy and grow in groups of 3, 5, or 7. Poison sumac grows in groups of 7 to 13 leaves, but always in an odd number. The leaves are feather-shaped and shiny.
Allergic response and treatment
Before the urushiol has been absorbed by the skin, it can be removed with soap and water. Substantial amounts of urushiol may be absorbed within minutes. Once urushiol has penetrated the skin, attempting to remove it with water is ineffective. After being absorbed by the skin, it is recognized by theimmune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
's dendritic cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. ...
s, otherwise called Langerhans cell
A Langerhans cell (LC) is a tissue-resident macrophage of the skin. These cells contain organelles called Birbeck granules. They are present in all layers of the epidermis and are most prominent in the stratum spinosum. They also occur in the ...
s. These cells then migrate to the lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
, where they present the urushiol to T-lymphocytes
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
and thus recruit them to the skin, and the T-lymphocytes cause pathology through the production of cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
s and cytotoxic
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are an immune cell or some types of venom, e.g. from the puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') or brown recluse spider (''Loxosceles reclusa'').
Cell physiology
Treating cells ...
damage to the skin. This causes the painful rash, blisters, and itching.
Once this response starts, only a few treatments, such as cortisone
Cortisone is a pregnene (21-carbon) steroid hormone. It is a naturally-occurring corticosteroid metabolite that is also used as a pharmaceutical prodrug; it is not synthesized in the adrenal glands. Cortisol is converted by the action of the enz ...
or prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to immunosuppressive drug, suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium ...
, are effective. Medications that can reduce the irritation include antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides re ...
s (diphenhydramine
Diphenhydramine (DPH) is an antihistamine and sedative mainly used to treat allergies, insomnia, and symptoms of the common cold. It is also less commonly used for tremor in parkinsonism, and nausea. It is taken by mouth, injected into a vein ...
(Benadryl) or cetirizine
Cetirizine, sold under the brand name Zyrtec among others, is a second-generation antihistamine used to treat allergic rhinitis (hay fever), dermatitis, and urticaria (hives). It is taken by mouth. Effects generally begin within thirty minutes a ...
(Zyrtec)). Other treatments include applying cold water or calamine lotion to soothe the pain and stop the itching.
Mechanism of action
To cause anallergic dermatitis
Dermatitis is inflammation of the Human skin, skin, typically characterized by itchiness, erythema, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become lichenification, thick ...
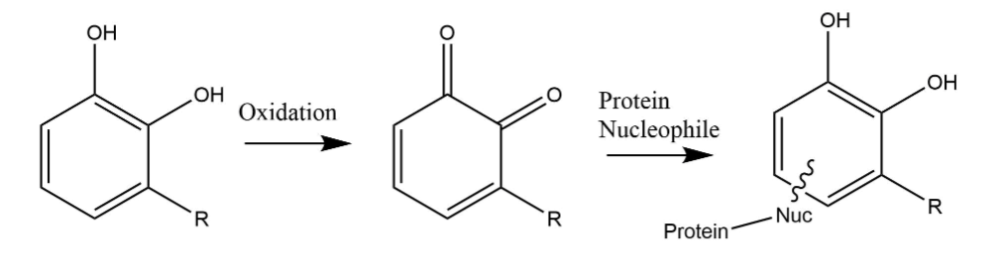
reaction, the urushiol is first oxidized to create two double-bonded oxygens on the chemical. It then reacts with a protein nucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are ...
to trigger a reaction within the skin. Dermatitis
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved can v ...
is mediated by an induced immune response. Urushiol is too small a molecule to directly activate an immune response. Instead, it attaches to certain proteins of the skin, where it acts as a hapten
In immunology, haptens are small molecules that elicit an immune response only when attached to a large carrier such as a protein; the carrier may be one that also does not elicit an immune response by itself (in general, only large molecules, i ...
, leading to a type IV hypersensitive reaction.
Hydrocortisone
Hydrocortisone is the name for the hormone cortisol when supplied as a medication. Uses include conditions such as adrenocortical insufficiency, adrenogenital syndrome, high blood calcium, thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, dermatitis, asthma, ...
, the active ingredient in cortisone, works to alleviate this condition by stopping the release of chemicals that cause the dermatitis reaction. Hydrocortisone itself does not react with urushiol in any way.

See also
*Anti-itch drug
Antipruritics, abirritants, or anti-itch drugs, are medications that inhibit the itching (Latin: ''pruritus'') often associated with sunburns, allergic reactions, eczema, psoriasis, chickenpox, fungal infections, insect bites and stings like those ...
s, for treating the toxin.
* Bentoquatam, a barrier cream
A barrier cream is a topical formulation used in industrial applications and as a cosmetic to place a physical barrier between the skin and contaminants that may irritate the skin (contact dermatitis or occupational dermatitis). There are many o ...
applied before exposure.
* Burow's solution
Burow's solution is an aqueous solution of aluminium triacetate. It is available in the U.S. as an over-the-counter drug for topical administration, with brand names including Domeboro (Moberg Pharma), Domeboro Otic (ear drops), Star-Otic, and Bor ...
which can treat the symptoms of the rash caused by urushiol.
* ''Ginkgo biloba
''Ginkgo biloba'', commonly known as ginkgo or gingko ( ), also known as the maidenhair tree, is a species of tree native to China. It is the last living species in the order Ginkgoales, which first appeared over 290 million years ago. Fossils ...
'' and cashew
The cashew tree (''Anacardium occidentale'') is a tropical evergreen tree native to South America in the genus ''Anacardium'' that produces the cashew seed and the cashew apple accessory fruit. The tree can grow as tall as , but the dwarf cult ...
, plants containing chemicals closely related to urushiol.
* Hapten
In immunology, haptens are small molecules that elicit an immune response only when attached to a large carrier such as a protein; the carrier may be one that also does not elicit an immune response by itself (in general, only large molecules, i ...
, small molecules that can elicit an immune response under certain conditions.
* Mango tree
''Mangifera indica'', commonly known as mango, is a species of flowering plant in the family Anacardiaceae. It is a large fruit tree, capable of growing to a height of . There are two distinct genetic populations in modern mangoesthe "Indian t ...
s, which may cause cross-reaction allergies with urushiol.
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * *External links
Poison Oak
at ''Wayne's Word''
* ttp://www.cattail.nu/ivy/ivy_index.html The Poison Ivy Tutorial {{authority control Catechols Resins Contact dermatitis