Untermensch on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 ''Untermensch'' (, ;
''Untermensch'' (, ;
 ''Untermensch'' (, ;
''Untermensch'' (, ; plural
The plural (sometimes abbreviated pl., pl, or ), in many languages, is one of the values of the grammatical category of number. The plural of a noun typically denotes a quantity greater than the default quantity represented by that noun. This de ...
: ''Untermenschen'') is a Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
term for non- Aryan "inferior people" who were often referred to as "the masses from the East", that is Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, Roma
Roma or ROMA may refer to:
Places Australia
* Roma, Queensland, a town
** Roma Airport
** Roma Courthouse
** Electoral district of Roma, defunct
** Town of Roma, defunct town, now part of the Maranoa Regional Council
*Roma Street, Brisbane, a ...
, and Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
(mainly ethnic Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
, Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
, and later also Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
). The term was also applied to mixed race
Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-ethn ...
and black people
Black is a racialized classification of people, usually a political and skin color-based category for specific populations with a mid to dark brown complexion. Not all people considered "black" have dark skin; in certain countries, often in s ...
. Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
and Romani people
The Romani (also spelled Romany or Rromani , ), colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group, traditionally nomadic itinerants. They live in Europe and Anatolia, and have diaspora populations located worldwide, with sig ...
, along with the physically and mentally disabled
Developmental disability is a diverse group of chronic conditions, comprising mental or physical impairments that arise before adulthood. Developmental disabilities cause individuals living with them many difficulties in certain areas of life, espe ...
, as well as homosexuals
Homosexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior between members of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions" to pe ...
and political dissidents
Political dissent is a dissatisfaction with or opposition to the policies of a governing body. Expressions of dissent may take forms from vocal disagreement to civil disobedience to the use of violence.exterminated in
 The German word ''Untermensch'' had been used in earlier periods, but it had not been used in a racial sense, for example, it was used in the 1899 novel '' Der Stechlin'' by
The German word ''Untermensch'' had been used in earlier periods, but it had not been used in a racial sense, for example, it was used in the 1899 novel '' Der Stechlin'' by
 The Nazis repeatedly used the term ''Untermensch'' in writings and speeches which they directed against the Jews, the most notorious example of them was a 1942 SS publication with the title ''Der Untermensch'', which contains an
The Nazis repeatedly used the term ''Untermensch'' in writings and speeches which they directed against the Jews, the most notorious example of them was a 1942 SS publication with the title ''Der Untermensch'', which contains an
 While the Nazis were inconsistent in the implementation of their policy – for instance, mostly implementing the
While the Nazis were inconsistent in the implementation of their policy – for instance, mostly implementing the
Rich, Norman (1974). ''Hitler's War Aims: the Establishment of the New Order'', p. 276–277. W. W. Norton & Company Inc., New York. as well as within occupied territories.Norman Davies. '' Europe at War 1939–1945: No Simple Victory''. Pp. 167, 209. The concept of the Slavs in particular being ''Untermenschen'' served the Nazis' political goals; it was used to justify their expansionist policy and especially their aggression against
''Der Untermensch''
"''Die Drohung des Untermenschen''"
This is an example of the term "''Untermensch''" being used in the context of the
''Der Untermensch''
the Nazi pamphlet {{DEFAULTSORT:Untermensch 1920s neologisms American English words Anti-black racism in Germany Anti-Polish sentiment Antiziganism Anti-Russian sentiment Anti-Serbian sentiment Anti-Slavic sentiment Anti-LGBT sentiment Axis powers German words and phrases Historical definitions of race Holocaust terminology Nazi eugenics Ethnic and religious slurs Antisemitism
the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
. According to the ''Generalplan Ost
The ''Generalplan Ost'' (; en, Master Plan for the East), abbreviated GPO, was the Nazi German government's plan for the genocide and ethnic cleansing on a vast scale, and colonization of Central and Eastern Europe by Germans. It was to be un ...
'', the Slavic population of East-Central Europe
East Central Europe is the region between Germanic, West Slavic, and Hungarian-speaking Europe and the East Slavic countries of Belarus, Russia, and Ukraine. Those lands are described as situated "between two": "between two worlds, between tw ...
was to be reduced in part through mass murder in the Holocaust, with a majority expelled to Asia and used as slave labor
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
in the Reich. These concepts were an important part of the Nazi racial policy
The racial policy of Nazi Germany was a set of policies and laws implemented in Nazi Germany under the dictatorship of Adolf Hitler, based on a specific racist doctrine asserting the superiority of the Aryan race, which claimed scientific legi ...
.
Etymology
It is widely believed that the term "under man" was coined by the Nazis, but this belief is incorrect because the term "under man" was first used by the American author andKu Klux Klan
The Ku Klux Klan (), commonly shortened to the KKK or the Klan, is an American white supremacist, right-wing terrorist, and hate group whose primary targets are African Americans, Jews, Latinos, Asian Americans, Native Americans, and ...
member Lothrop Stoddard
Theodore Lothrop Stoddard (June 29, 1883 – May 1, 1950) was an American historian, journalist, political scientist, conspiracy theorist, white supremacist, and white nationalist. Stoddard wrote several books which advocated eugenics and sci ...
in the title of his 1922 book ''The Revolt Against Civilization: The Menace of the Under-man''. Stoddard applies the term to those who he considers unable to function in civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
Ci ...
, which he generally (but not entirely) attributes to race
Race, RACE or "The Race" may refer to:
* Race (biology), an informal taxonomic classification within a species, generally within a sub-species
* Race (human categorization), classification of humans into groups based on physical traits, and/or s ...
. The Nazis later adopted it from the title of the book's German edition ''Der Kulturumsturz: Die Drohung des Untermenschen'' (1925).
 The German word ''Untermensch'' had been used in earlier periods, but it had not been used in a racial sense, for example, it was used in the 1899 novel '' Der Stechlin'' by
The German word ''Untermensch'' had been used in earlier periods, but it had not been used in a racial sense, for example, it was used in the 1899 novel '' Der Stechlin'' by Theodor Fontane
Theodor Fontane (; 30 December 1819 – 20 September 1898) was a German novelist and poet, regarded by many as the most important 19th-century German-language realist author. He published the first of his novels, for which he is best known toda ...
. Since most writers who employed the term did not address the question of when and how the word entered the German language, into English, ''Untermensch'' is usually translated as "subhuman". The leading Nazi who attributed the concept of the East-European "under man" to Stoddard was Alfred Rosenberg
Alfred Ernst Rosenberg ( – 16 October 1946) was a Baltic German Nazi theorist and ideologue. Rosenberg was first introduced to Adolf Hitler by Dietrich Eckart and he held several important posts in the Nazi government. He was the head of ...
who, referring to Russian communists, wrote in his '' Der Mythus des zwanzigsten Jahrhunderts'' (1930) that "this is the kind of human being that Lothrop Stoddard has called the 'under man.'" ...den Lothrop Stoddard als 'Untermenschen' bezeichnete."ref name="Rosenberg"> Quoting Stoddard: "The Under-Man – the man who measures under the standards of capacity and adaptability which is imposed by the social order in which he lives".
It is possible that Stoddard constructed his "under man" as an opposite of Friedrich Nietzsche
Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche (; or ; 15 October 1844 – 25 August 1900) was a German philosopher, prose poet, cultural critic, philologist, and composer whose work has exerted a profound influence on contemporary philosophy. He began his ...
's ''Übermensch
The (; "Overhuman") is a concept in the philosophy of Friedrich Nietzsche. In his 1883 book ''Thus Spoke Zarathustra'' (german: Also sprach Zarathustra), Nietzsche has his character Zarathustra posit the as a goal for humanity to set for itse ...
'' (superman) concept. Stoddard does not explicitly say this, but he critically refers to the "superman" idea at the end of his book (p. 262). Wordplays with Nietzsche's term seem to have been used repeatedly as early as the 19th century and, due to the German linguistic trait of being able to combine prefixes
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the Word stem, stem of a word. Adding it to the beginning of one word changes it into another word. For example, when the prefix ''un-'' is added to the word ''happy'', it creates the word ''unhappy'' ...
and root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the sur ...
s almost at will in order to create new words, this development can be considered logical. For instance, German author Theodor Fontane
Theodor Fontane (; 30 December 1819 – 20 September 1898) was a German novelist and poet, regarded by many as the most important 19th-century German-language realist author. He published the first of his novels, for which he is best known toda ...
contrasts the ''Übermensch/Untermensch'' word pair in chapter 33 of his novel ''Der Stechlin''. Nietzsche used ''Untermensch'' at least once in contrast to ''Übermensch'' in ''Die fröhliche Wissenschaft
''The Gay Science'' (german: Die fröhliche Wissenschaft), sometimes translated as ''The Joyful Wisdom'' or ''The Joyous Science'', is a book by Friedrich Nietzsche published in 1882, and followed by a second edition in 1887 after the completio ...
'' (1882). Earlier examples of ''Untermensch'' include Romanticist Jean Paul
Jean Paul (; born Johann Paul Friedrich Richter, 21 March 1763 – 14 November 1825) was a German Romantic writer, best known for his humorous novels and stories.
Life and work
Jean Paul was born at Wunsiedel, in the Fichtelgebirge mountain ...
using the term in his novel ''Hesperus'' (1795) in reference to an Orangutan
Orangutans are great apes native to the rainforests of Indonesia and Malaysia. They are now found only in parts of Borneo and Sumatra, but during the Pleistocene they ranged throughout Southeast Asia and South China. Classified in the genu ...
(Chapter "8. Hundposttag").
Nazi propaganda and policy
In a speech which he delivered to the Bavarian regional parliament in 1927, the Nazi propagandistJulius Streicher
Julius Streicher (12 February 1885 – 16 October 1946) was a member of the Nazi Party, the ''Gauleiter'' (regional leader) of Franconia and a member of the '' Reichstag'', the national legislature. He was the founder and publisher of the virul ...
, publisher of ''Der Stürmer
''Der Stürmer'' (, literally "The Stormer / Attacker / Striker") was a weekly German tabloid-format newspaper published from 1923 to the end of the Second World War by Julius Streicher, the ''Gauleiter'' of Franconia, with brief suspensions ...
,'' used the term ''Untermensch'' referring to the communists of the German Bavarian Soviet Republic
The Bavarian Soviet Republic, or Munich Soviet Republic (german: Räterepublik Baiern, Münchner Räterepublik),Hollander, Neil (2013) ''Elusive Dove: The Search for Peace During World War I''. McFarland. p.283, note 269. was a short-lived unre ...
:
 The Nazis repeatedly used the term ''Untermensch'' in writings and speeches which they directed against the Jews, the most notorious example of them was a 1942 SS publication with the title ''Der Untermensch'', which contains an
The Nazis repeatedly used the term ''Untermensch'' in writings and speeches which they directed against the Jews, the most notorious example of them was a 1942 SS publication with the title ''Der Untermensch'', which contains an anti-semitic
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
tirade sometimes considered to be an extract from a speech by Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was of the (Protection Squadron; SS), and a leading member of the Nazi Party of Germany. Himmler was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and a main architect of th ...
. In the pamphlet "The SS as an Anti-Bolshevist Fighting Organization", published in 1936, Himmler wrote:
In his speech "''Weltgefahr des Bolschewismus''" ("World danger of Bolshevism") in 1936, Joseph Goebbels
Paul Joseph Goebbels (; 29 October 1897 – 1 May 1945) was a German Nazi politician who was the ''Gauleiter'' (district leader) of Berlin, chief propagandist for the Nazi Party, and then Reich Minister of Propaganda from 1933 to 19 ...
said that "subhumans exist in every people as a leavening agent
In cooking, a leavening agent () or raising agent, also called a leaven () or leavener, is any one of a number of substances used in doughs and batters that cause a foaming action (gas bubbles) that lightens and softens the mixture. An altern ...
". At the 1935 Nazi party congress rally at Nuremberg, Goebbels also declared that "Bolshevism is the declaration of war by Jewish-led international subhumans against culture itself."
Another example of the use of the term ''Untermensch'', this time in connection with anti-Soviet propaganda, is a brochure entitled "''Der Untermensch''", edited by Himmler and distributed by the Race and Settlement Head Office. SS-Obersturmführer Ludwig Pröscholdt, Jupp Daehler and SS-Hauptamt-Schulungsamt Koenig are associated with its production. Published in 1942 after the start of Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after ...
, the German invasion of the Soviet Union, it is around 50 pages long and consists for the most part of photos portraying the enemy in an extremely negative way (see link below for the title page). 3,860,995 copies were printed in the German language. It was translated into Greek, French, Dutch, Danish, Bulgarian, Hungarian, Czech and seven other languages. The pamphlet says the following:
Sub-human types
The Nazis divided the people who they considered the sub-humans into different types; they placed priority on the extermination of the Jews, and the exploitation of others as slaves. HistorianRobert Jan van Pelt
Robert Jan van Pelt (born 15 August 1955) is a Dutch author, architectural historian, professor at the University of Waterloo and a Holocaust scholar. One of the world's leading experts on Auschwitz, he regularly speaks on Holocaust related topic ...
writes that for the Nazis, "it was only a small step to a rhetoric pitting the European Mensch against the Soviet ''Untermensch'', which had come to mean a Russian in the clutches of Judeo-Bolshevism
Jewish Bolshevism, also Judeo–Bolshevism, is an anti-communist and antisemitic canard, which alleges that the Jews were the originators of the Russian Revolution in 1917, and that they held primary power among the Bolsheviks who led the r ...
."
The ''Untermensch'' concept included Jews, Roma and Sinti (Gypsies), and Slavic peoples such as Poles, Serbs and Russians. Slavs were regarded as ''Untermenschen'', barely fit for exploitation as slaves. Hitler and Goebbels compared them to the "rabbit family" or to "stolid animals" that were "idle" and "disorganized" and spread like a "wave of filth". However, some among the Slavs who happened to have Nordic racial features were deemed to have distant Germanic descent which meant partially "Aryan" origin, and if under 10 years old, they were to be Germanized
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In ling ...
(see: kidnapping of children by Nazi Germany
During World War II, around 200,000 ethnic Polish children as well as an unspecified number of children of other ethnicities were abducted from their homes and forcibly transported to Nazi Germany for purposes of forced labour, medical experimenta ...
).
The Nazis were utterly contemptuous of the Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
, as even prior to World War II, Slavs – particularly the Poles – were deemed to be inferior to Germans and other Aryans. After Adolf Hitler gained political power in Germany, the concept of non-Aryan "sub-human slave-material" was developed and started to be used also towards other Slavic peoples.Timm, Annette F. (2010) ''The Politics of Fertility in Twentieth-Century Berlin''. London: Cambridge University Press. p.188 Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
and Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
were at the bottom of the Slavic "racial hierarchy" established by the Nazis. Soon after the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
, long_name = Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
, image = Bundesarchiv Bild 183-H27337, Moskau, Stalin und Ribbentrop im Kreml.jpg
, image_width = 200
, caption = Stalin and Ribbentrop shaking ...
expired, Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
also started to be seen as "subhumans". Similarly, Belarusians
, native_name_lang = be
, pop = 9.5–10 million
, image =
, caption =
, popplace = 7.99 million
, region1 =
, pop1 = 600,000–768,000
, region2 =
, pop2 ...
, Czechs
The Czechs ( cs, Češi, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common ancestry, c ...
, Slovaks
The Slovaks ( sk, Slováci, singular: ''Slovák'', feminine: ''Slovenka'', plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovak.
In Slovakia, 4.4 mi ...
, and Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian. The majority ...
were considered to be inferior. Nonetheless, there were Slavs such as Bosniaks
The Bosniaks ( bs, Bošnjaci, Cyrillic: Бошњаци, ; , ) are a South Slavic ethnic group native to the Southeast European historical region of Bosnia, which is today part of Bosnia and Herzegovina, who share a common Bosnian ancestry ...
, Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe.
Etymology
Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not completely understo ...
, and Croats
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic, G ...
who collaborated with Nazi Germany that were still being perceived as not racially "pure" enough to reach the status of Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
, yet they were eventually considered ethnically better than other Slavs, mostly due to theories about these nations having a minimal amount of Slavic genes and considerable admixtures of Germanic and Turkic blood.
In order to forge a strategic alliance with the Independent State of Croatia
The Independent State of Croatia ( sh, Nezavisna Država Hrvatska, NDH; german: Unabhängiger Staat Kroatien; it, Stato indipendente di Croazia) was a World War II-era puppet state of Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. It was established in p ...
– a puppet state
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government, is a State (polity), state that is ''de jure'' independent but ''de facto'' completely dependent upon an outside Power (international relations), power and subject to its o ...
created after the invasion of Yugoslavia
The invasion of Yugoslavia, also known as the April War or Operation 25, or ''Projekt 25'' was a German-led attack on the Kingdom of Yugoslavia by the Axis powers which began on 6 April 1941 during World War II. The order for the invasion was p ...
and the Kingdom of Bulgaria
The Tsardom of Bulgaria ( bg, Царство България, translit=Tsarstvo Balgariya), also referred to as the Third Bulgarian Tsardom ( bg, Трето Българско Царство, translit=Treto Balgarsko Tsarstvo, links=no), someti ...
, the Nazis deviated from a strict interpretation of their racial ideology, and Croats were officially described as "more Germanic than Slav", a notion supported by Croatia's fascist ( Ustashe) dictator Ante Pavelić
Ante Pavelić (; 14 July 1889 – 28 December 1959) was a Croatian politician who founded and headed the fascist ultranationalist organization known as the Ustaše in 1929 and served as dictator of the Independent State of Croatia ( hr, l ...
who maintained that the "Croatians were descendants of the ancient Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
" and "had the Panslav idea forced upon them as something artificial". Hitler, Adolf and Weinberg, Gerhard (2007) ''Hitler's Table Talk, 1941-1944: His Private Conversations''. Enigma Books. p.356. Quoting Hitler: "For example to label the Bulgarians as Slavs is pure nonsense; originally they were Turkomans." However the Nazis continued to classify Croats as a "subhuman" in spite of the alliance.Norman Davies. '' Europe at War 1939–1945: No Simple Victory''. Pan Macmillan, 2008. Pp. 167, 209. Hitler also deemed the Bulgarians to be " Turkoman" in origin.
 While the Nazis were inconsistent in the implementation of their policy – for instance, mostly implementing the
While the Nazis were inconsistent in the implementation of their policy – for instance, mostly implementing the Final Solution
The Final Solution (german: die Endlösung, ) or the Final Solution to the Jewish Question (german: Endlösung der Judenfrage, ) was a Nazi plan for the genocide of individuals they defined as Jews during World War II. The "Final Solution to th ...
while also implementing Generalplan Ost
The ''Generalplan Ost'' (; en, Master Plan for the East), abbreviated GPO, was the Nazi German government's plan for the genocide and ethnic cleansing on a vast scale, and colonization of Central and Eastern Europe by Germans. It was to be un ...
– the democidal
Democide is a term coined by American political scientist Rudolph Rummel to describe "the intentional killing of an unarmed or disarmed person by government agents acting in their authoritative capacity and pursuant to government policy or high ...
death toll was in the range of tens of millions of victims. It is related to the concept of "life unworthy of life
The phrase "life unworthy of life" (german: Lebensunwertes Leben) was a Nazi designation for the segments of the populace which according to the Nazi regime had no right to live. Those individuals were targeted to be murdered by the state (" ...
", a more specific term which originally referred to the severely disabled who were involuntarily euthanised in Aktion T4
(German, ) was a campaign of mass murder by involuntary euthanasia in Nazi Germany. The term was first used in post-war trials against doctors who had been involved in the killings. The name T4 is an abbreviation of 4, a street address of ...
, and was eventually applied to the extermination of the Jews. That policy of euthanasia started officially on 1 September 1939 when Hitler signed an edict to the effect, and carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simple ...
was first used to murder disabled patients. The same gas was used in the death camps
Nazi Germany used six extermination camps (german: Vernichtungslager), also called death camps (), or killing centers (), in Central Europe during World War II to systematically murder over 2.7 million peoplemostly Jewsin the Holocaust. The v ...
such as Treblinka
Treblinka () was an extermination camp, built and operated by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland during World War II. It was in a forest north-east of Warsaw, south of the village of Treblinka in what is now the Masovian Voivodeship. The cam ...
, although they used engine exhaust gases to achieve the same end. In directive No. 1306 by Reich Ministry of Public Enlightenment and Propaganda
The Reich Ministry for Public Enlightenment and Propaganda (; RMVP), also known simply as the Ministry of Propaganda (), controlled the content of the press, literature, visual arts, film, theater, music and radio in Nazi Germany.
The ministry ...
from 24 October 1939, the term "Untermensch" is used in reference to Polish ethnicity and culture, as follows:
Biology classes in Nazi Germany schools taught about differences between the race of Nordic German "''Übermenschen''" and "ignoble" Jewish and Slavic "subhumans". The view that Slavs were subhuman was widespread among the German masses, and chiefly applied to the Poles. It continued to find support after the war.
During the war, Nazi propaganda instructed Wehrmacht officers to tell their soldiers to target people who it considered "Jewish Bolshevik subhumans" and it also stated that the war in the Soviet Union was being waged between the Germans and the Jewish, Gypsies and Slavic ''Untermenschen''.
During the Warsaw Uprising
The Warsaw Uprising ( pl, powstanie warszawskie; german: Warschauer Aufstand) was a major World War II operation by the Polish resistance movement in World War II, Polish underground resistance to liberate Warsaw from German occupation. It occ ...
, Himmler ordered the destruction of the Warsaw ghetto
The Warsaw Ghetto (german: Warschauer Ghetto, officially , "Jewish Residential District in Warsaw"; pl, getto warszawskie) was the largest of the Nazi ghettos during World War II and the Holocaust. It was established in November 1940 by the G ...
because according to him it allowed the "living space" of 500,000 subhumans.
As a pragmatic way to solve military manpower shortages, the Nazis used soldiers from some Slavic countries, firstly from the Reich's allies Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
and Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
According to Nazi policy, the Croats were considered more "Germanic than Slavic"; this claim was supported by Croatia's fascist dictator Ante Pavelić
Ante Pavelić (; 14 July 1889 – 28 December 1959) was a Croatian politician who founded and headed the fascist ultranationalist organization known as the Ustaše in 1929 and served as dictator of the Independent State of Croatia ( hr, l ...
, who maintained the view that the Croatians were the descendants of the ancient Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
along with the view that they "had the Pan-Slav idea forced upon them as something artificial".Rich, Norman (1974). ''Hitler's War Aims: the Establishment of the New Order'', p. 276–277. W. W. Norton & Company Inc., New York. as well as within occupied territories.Norman Davies. '' Europe at War 1939–1945: No Simple Victory''. Pp. 167, 209. The concept of the Slavs in particular being ''Untermenschen'' served the Nazis' political goals; it was used to justify their expansionist policy and especially their aggression against
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
in order to achieve ''Lebensraum
(, ''living space'') is a German concept of settler colonialism, the philosophy and policies of which were common to German politics from the 1890s to the 1940s. First popularized around 1901, '' lso in:' became a geopolitical goal of Imperi ...
'', particularly in Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
. Early plans of the German Reich (summarized as ''Generalplan Ost'') envisioned the ethnic cleansing and elimination of no fewer than 50 million people, who were not considered fit for Germanization
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In ling ...
, from territories it wanted to conquer in Europe; Ukraine's chernozem
Chernozem (from rus, чернозём, p=tɕɪrnɐˈzʲɵm, r=chernozyom; "black ground"), also called black soil, is a black-colored soil containing a high percentage of humus (4% to 16%) and high percentages of phosphorus and ammonia compoun ...
("black earth") soil was considered a particularly desirable zone for colonization by the ''Herrenvolk
The master race (german: Herrenrasse) is a pseudoscientific concept in Nazi ideology in which the putative "Aryan race" is deemed the pinnacle of human racial hierarchy. Members were referred to as "''Herrenmenschen''" ("master humans").
Th ...
''.
See also
*Afrophobia
Afrophobia, Afroscepticism, or Anti-African sentiment is a perceived or actual prejudice, hostility, discrimination, or racism towards people and cultures of Africa and the African diaspora.
Prejudice against Africans and people of African desce ...
* Antisemitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
* Anti-Slavic sentiment
Anti-Slavic sentiment, also known as Slavophobia, a form of racism or xenophobia, refers to various negative attitudes towards Slavic peoples, the most common manifestation is the claim that the inhabitants of Slavic nations are inferior to oth ...
* Antiziganism
Anti-Romani sentiment (also antigypsyism, anti-Romanyism, Romaphobia, or Antiziganism) is hostility, prejudice, discrimination or racism which is specifically directed at Romani people (Roma, Sinti, Iberian Kale, Welsh Kale, Finnish Kale, H ...
* Aryan certificate
In Nazi Germany, the Aryan certificate/passport (german: Ariernachweis) was a document which certified that a person was a member of the presumed Aryan race. Beginning in April 1933, it was required from all employees and officials in the publ ...
* Caste
Caste is a form of social stratification characterised by endogamy, hereditary transmission of a style of life which often includes an occupation, ritual status in a hierarchy, and customary social interaction and exclusion based on cultura ...
* Class discrimination
Class discrimination, also known as classism, is prejudice or discrimination on the basis of social class. It includes individual attitudes, behaviors, systems of policies and practices that are set up to benefit the upper class at the expense of ...
* Enemy of the people
The term enemy of the people or enemy of the nation, is a designation for the political or class opponents of the subgroup in power within a larger group. The term implies that by opposing the ruling subgroup, the "enemies" in question are ac ...
* Extremism
Extremism is "the quality or state of being extreme" or "the advocacy of extreme measures or views". The term is primarily used in a political or religious sense to refer to an ideology that is considered (by the speaker or by some implied share ...
* The Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
* Incitement to genocide
Incitement to genocide is a crime under international law which prohibits inciting (encouraging) the commission of genocide. An extreme form of hate speech, incitement to genocide is considered an inchoate offense and is theoretically subject t ...
* ''Mischling
(; " mix-ling"; plural: ) was a pejorative legal term used in Nazi Germany to denote persons of mixed "Aryan" and non-Aryan, such as Jewish, ancestry as codified in the Nuremberg racial laws of 1935. In German, the word has the general denota ...
''
* Nazi eugenics
Nazi eugenics refers to the social policies of eugenics in Nazi Germany, composed of various pseudoscientific ideas about genetics. The racial ideology of Nazism placed the biological improvement of the German people by selective breeding of ...
* Nazi racial theories
The Nazi Party adopted and developed several pseudoscientific racial classifications as part of its ideology (Nazism) in order to justify the genocide of groups of people which it deemed racially inferior. The Nazis considered the putative " ...
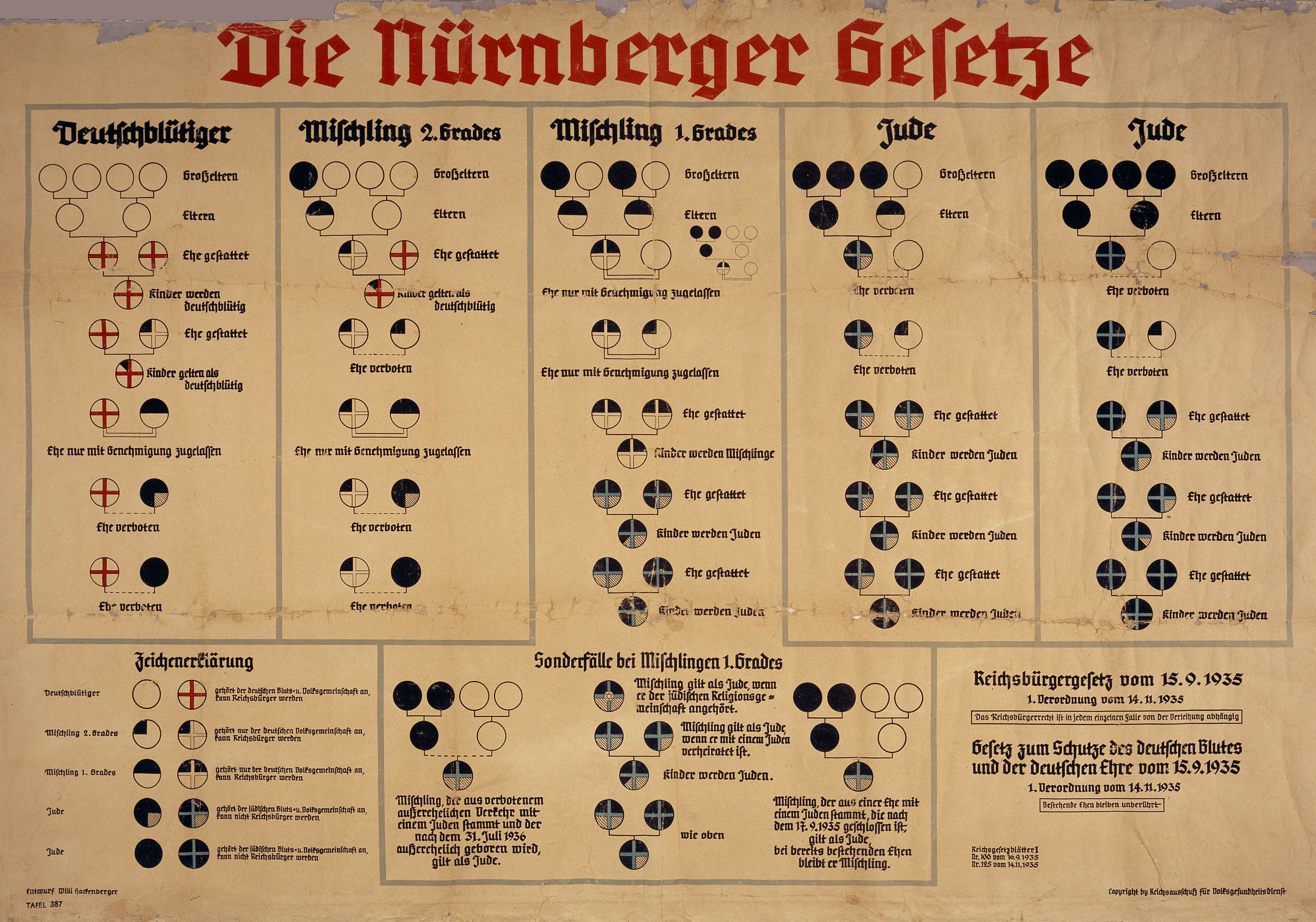
* Nuremberg Laws
The Nuremberg Laws (german: link=no, Nürnberger Gesetze, ) were antisemitic and racist laws that were enacted in Nazi Germany on 15 September 1935, at a special meeting of the Reichstag convened during the annual Nuremberg Rally of ...
* ''Rassenschande
''Rassenschande'' (, "racial shame") or ''Blutschande'' ( "blood disgrace") was an anti-miscegenation concept in Nazi German racial policy, pertaining to sexual relations between Aryans and non-Aryans. It was put into practice by policies like ...
''
* Racial hierarchy
A racial hierarchy is a system of stratification that is based on the belief that some racial groups are superior to other racial groups. At various points of history, racial hierarchies have featured in societies, often being formally institut ...
* Racial hygiene
The term racial hygiene was used to describe an approach to eugenics in the early 20th century, which found its most extensive implementation in Nazi Germany (Nazi eugenics). It was marked by efforts to avoid miscegenation, analogous to an animal ...
* Racial policy of Nazi Germany
The racial policy of Nazi Germany was a set of policies and laws implemented in Nazi Germany under the dictatorship of Adolf Hitler, based on a specific racist doctrine asserting the superiority of the Aryan race, which claimed scientific legi ...
* Racism
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagonism ...
* ''Übermensch
The (; "Overhuman") is a concept in the philosophy of Friedrich Nietzsche. In his 1883 book ''Thus Spoke Zarathustra'' (german: Also sprach Zarathustra), Nietzsche has his character Zarathustra posit the as a goal for humanity to set for itse ...
''
* White nationalism
White nationalism is a type of racial nationalism or pan-nationalism which espouses the belief that white people are a raceHeidi Beirich and Kevin Hicks. "Chapter 7: White nationalism in America". In Perry, Barbara. ''Hate Crimes''. Greenwo ...
* White supremacy
White supremacy or white supremacism is the belief that white people are superior to those of other races and thus should dominate them. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any power and privilege held by white people. White su ...
References
Notes Further reading *External links
''Der Untermensch''
propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded ...
poster published by the SS.
*
"''Die Drohung des Untermenschen''"
This is an example of the term "''Untermensch''" being used in the context of the
Nazi eugenics
Nazi eugenics refers to the social policies of eugenics in Nazi Germany, composed of various pseudoscientific ideas about genetics. The racial ideology of Nazism placed the biological improvement of the German people by selective breeding of ...
programme. The table suggests that "inferior" people (unmarried and married criminals, parents whose children have learning disabilities) have more children than "superior" people (ordinary Germans, academics). Note that the heading is the subtitle of the German version of Lothrop Stoddard
Theodore Lothrop Stoddard (June 29, 1883 – May 1, 1950) was an American historian, journalist, political scientist, conspiracy theorist, white supremacist, and white nationalist. Stoddard wrote several books which advocated eugenics and sci ...
's book.
''Der Untermensch''
the Nazi pamphlet {{DEFAULTSORT:Untermensch 1920s neologisms American English words Anti-black racism in Germany Anti-Polish sentiment Antiziganism Anti-Russian sentiment Anti-Serbian sentiment Anti-Slavic sentiment Anti-LGBT sentiment Axis powers German words and phrases Historical definitions of race Holocaust terminology Nazi eugenics Ethnic and religious slurs Antisemitism