Ukrainian People's Republic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Ukrainian People's Republic (UPR), or Ukrainian National Republic (UNR), was a country in
 On 10 June 1917, the
On 10 June 1917, the 
 * 14–15 December – the Petty Council adopted the Law about the General Court, the highest judicial institution of the Ukrainian People's Republic. International diplomatic missions transferred their offices from Mohyliv-Podilsky to
* 14–15 December – the Petty Council adopted the Law about the General Court, the highest judicial institution of the Ukrainian People's Republic. International diplomatic missions transferred their offices from Mohyliv-Podilsky to
 Due to the aggression from Soviet Russia, on 22 January 1918, the Tsentralna Rada issued its Fourth Universal (dated 22 January 1918), breaking ties with Bolshevik Russia and proclaiming a sovereign Ukrainian state. Less than a month later, on 9 February 1918, the Red Army seized Kyiv.
Besieged by the Bolsheviks and having lost much territory, the Rada was forced to seek foreign aid, and signed the
Due to the aggression from Soviet Russia, on 22 January 1918, the Tsentralna Rada issued its Fourth Universal (dated 22 January 1918), breaking ties with Bolshevik Russia and proclaiming a sovereign Ukrainian state. Less than a month later, on 9 February 1918, the Red Army seized Kyiv.
Besieged by the Bolsheviks and having lost much territory, the Rada was forced to seek foreign aid, and signed the
'' New York Herald'' (18 May 1918)War Without Fronts: Atamans and Commissars in Ukraine, 1917–1919
by Mikhail Akulov,
 After the coup, the Rada was replaced by the conservative government of
After the coup, the Rada was replaced by the conservative government of



 The Directorate gained massive popularity, and the support of some of Skoropadsky's military units including the Serdiuk Division. Their insurgent army encircled Kyiv on 21 November. After a three-week-long stalemate Skoropadsky abdicated in favor of the Council of Ministers who surrendered to the Revolutionary forces. On 19 December 1918, the Directorate took control of Kyiv.
The Bolsheviks invaded Ukraine from Kursk in late December 1918 where the new Ukrainian Soviet government was reestablished earlier in November of the same year. On 16 January 1919 Ukraine officially declared a war on Russia while the Russian Soviet government continued to deny all claims of invasion. On 22 January 1919, the Directorate was officially united with the West Ukrainian People's Republic, although the latter entity ''
The Directorate gained massive popularity, and the support of some of Skoropadsky's military units including the Serdiuk Division. Their insurgent army encircled Kyiv on 21 November. After a three-week-long stalemate Skoropadsky abdicated in favor of the Council of Ministers who surrendered to the Revolutionary forces. On 19 December 1918, the Directorate took control of Kyiv.
The Bolsheviks invaded Ukraine from Kursk in late December 1918 where the new Ukrainian Soviet government was reestablished earlier in November of the same year. On 16 January 1919 Ukraine officially declared a war on Russia while the Russian Soviet government continued to deny all claims of invasion. On 22 January 1919, the Directorate was officially united with the West Ukrainian People's Republic, although the latter entity ''
 The government of Ukrainian People's Republic operated in
The government of Ukrainian People's Republic operated in
Державний центр УНР на еміграції (ДЦ УНР)
(''tr. "UKR State Center for Emigration (UKR State Center)"'')
TERMS OF PEACE MADE BY UKRAINE; New Republic Gets Increased Territory at Expense of Rest of Russia
''

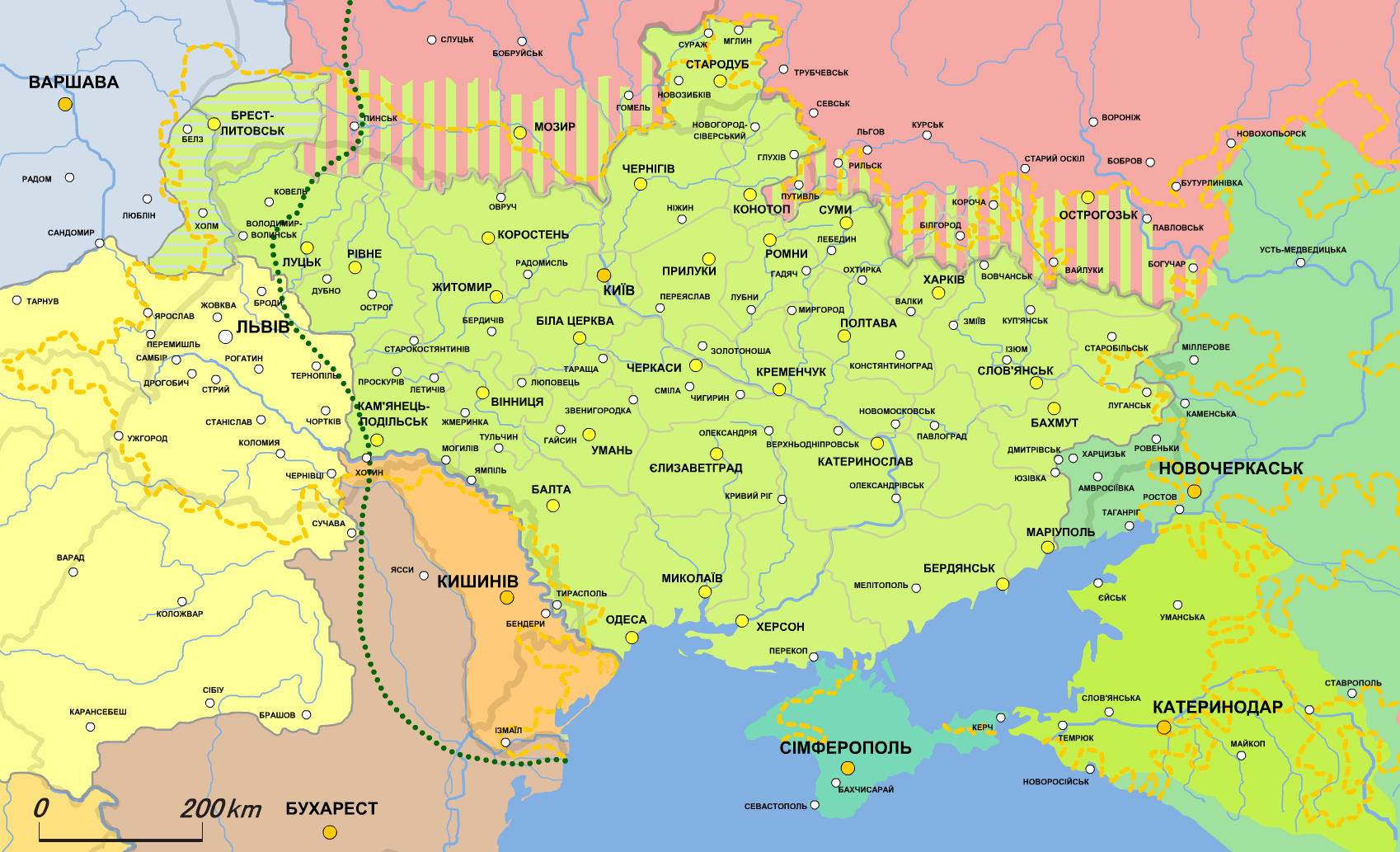
Image:Ukraine map provisional borders 1919.jpg, Provisional borders of Ukraine in 1919
People's war 1917–1932 by Kyiv city organization "Memorial"
UNIVERSAL of the Ukrainian Central Rada addressed to the Ukrainian people living in and outside of Ukraine.
Translationreport. {{coord, 50, 27, N, 30, 30, E, type:country_source:kolossus-ptwiki, display=title Modern history of Ukraine Russian Revolution in Ukraine Ukrainian independence movement History of Ukraine (1795–1918) History of Ukraine (1918–1991) Post–Russian Empire states Former Slavic countries 1910s in Ukraine 1920s in Ukraine States and territories established in 1917 States and territories established in 1918 States and territories disestablished in 1918 States and territories disestablished in 1920 States and territories disestablished in 1921 1917 establishments in Ukraine 1918 establishments in Ukraine 1918 disestablishments in Ukraine 1920 disestablishments in Ukraine 1921 disestablishments in Ukraine Russia–Ukraine relations Russian-speaking countries and territories Former countries of the interwar period Former socialist republics Former countries
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whi ...
that existed between 1917 and 1920. It was declared following the February Revolution in Russia by the First Universal. In March 1917, the National Congress in Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
elected the Central Council composed of socialist parties on the same principles as throughout the rest of the Russian Republic
The Russian Republic,. referred to as the Russian Democratic Federal Republic. in the 1918 Constitution, was a short-lived state which controlled, ''de jure'', the territory of the former Russian Empire after its proclamation by the Rus ...
. The republic's autonomy was recognized by the Russian Provisional Government. Following the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mom ...
, it proclaimed its independence from the Russian Republic on 22 January 1918 by the Fourth Universal.
During its short existence, the republic went through several political transformations – from the socialist-leaning republic headed by the Central Council of Ukraine
The Central Council of Ukraine ( uk, Українська Центральна Рада, ) (also called the Tsentralna Rada or the Central Rada) was the All-Ukrainian council (soviet) that united deputies of soldiers, workers, and peasants deputie ...
with its general secretariat to the socialist republic led by the Directorate and by Symon Petliura. Between April and December 1918, the socialist authority of the Ukrainian People's Republic was suspended, having been overthrown by the pro-German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
Ukrainian State of Pavlo Skoropadskyi, who was elected as a Hetman
( uk, гетьман, translit=het'man) is a political title from Central and Eastern Europe, historically assigned to military commanders.
Used by the Czechs in Bohemia since the 15th century. It was the title of the second-highest military ...
by a congress of peasants. From late 1919, the UNR operated as an ally of the Second Polish Republic. On 10 November 1920, the state lost the remainder of its territory to the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
. The 18 March 1921 Peace of Riga
The Peace of Riga, also known as the Treaty of Riga ( pl, Traktat Ryski), was signed in Riga on 18 March 1921, among Poland, Soviet Russia (acting also on behalf of Soviet Belarus) and Soviet Ukraine. The treaty ended the Polish–Soviet Wa ...
between the Second Polish Republic, Soviet Russia (acting also on behalf of Soviet Belarus
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR, or Byelorussian SSR; be, Беларуская Савецкая Сацыялістычная Рэспубліка, Bielaruskaja Savieckaja Sacyjalistyčnaja Respublika; russian: Белор� ...
), and Soviet Ukraine
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic ( uk, Украї́нська Радя́нська Соціалісти́чна Респу́бліка, ; russian: Украи́нская Сове́тская Социалисти́ческая Респ ...
sealed the fate of the Ukrainian People's Republic.
After the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mom ...
, many governments formed in Ukraine, most notably the Ukrainian People's Republic of Soviets
The Ukrainian People's Republic of Soviets (russian: Украинская Народная Республика Советов, translit=Ukrainskaya Narodnaya Respublika Sovjetov) was a short-lived (1917–1918) Soviet republic of the Russian S ...
(1917–1918) based in Kharkiv
Kharkiv ( uk, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest city and municipality in Ukraine.
, and its Soviet successors. This force, along with the Ukrainian Republic (based in Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
), plus the White Movement, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, Green armies, and the Anarchists, fought constantly with each other, which resulted in many casualties among Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Ort ...
fighting in a 1917–21 Ukrainian Civil War as part of the wider Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
of 1917–23. The Russian SFSR would (after the 1921 Treaty of Riga) extend control over what would ultimately become the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic ( uk, Украї́нська Радя́нська Соціалісти́чна Респу́бліка, ; russian: Украи́нская Сове́тская Социалисти́ческая Респ ...
and (in 1922) a founding member of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
.
History
Revolutionary wave
 On 10 June 1917, the
On 10 June 1917, the Central Council of Ukraine
The Central Council of Ukraine ( uk, Українська Центральна Рада, ) (also called the Tsentralna Rada or the Central Rada) was the All-Ukrainian council (soviet) that united deputies of soldiers, workers, and peasants deputie ...
declared its autonomy as part of the Russian Republic
The Russian Republic,. referred to as the Russian Democratic Federal Republic. in the 1918 Constitution, was a short-lived state which controlled, ''de jure'', the territory of the former Russian Empire after its proclamation by the Rus ...
by its First Universal at the All-Ukrainian Military Congress. The highest governing body of the Ukrainian People's Republic became the General Secretariat headed by Volodymyr Vynnychenko. The Prime Minister of Russia Alexander Kerensky
Alexander Fyodorovich Kerensky, ; original spelling: ( – 11 June 1970) was a Russian lawyer and revolutionary who led the Russian Provisional Government and the short-lived Russian Republic for three months from late July to early Novem ...
recognized the Secretariat, appointing it as the representative governing body of the Russian Provisional Government and limiting its powers to five governorates: Volyn, Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
, Podolia
Podolia or Podilia ( uk, Поділля, Podillia, ; russian: Подолье, Podolye; ro, Podolia; pl, Podole; german: Podolien; be, Падолле, Padollie; lt, Podolė), is a historic region in Eastern Europe, located in the west-centra ...
, Chernigov, and Poltava. At first Vynnychenko protested and left his post as Secretariat leader, but eventually returned to reassemble the Secretariat after the Tsentralna Rada accepted the ''Kerensky Instruktsiya'' and issued the Second Universal.
After the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mom ...
the Kyivan faction of the Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
Party instigated the uprising in Kyiv on 8 November 1917 in order to establish Soviet power in the city. Kyiv Military District
The Kiev Military District (; , abbreviated ) was a military district of the Imperial Russian Army and subsequently of the Red Army and Soviet Armed Forces. It was first formed in 1862, and was headquartered in Kiev (Kyiv) for most of its exi ...
forces attempted to stop it, but after the Tsentralna Rada threw its support behind the Bolsheviks, the Russian forces were eliminated from Kyiv. After expelling the government forces, the Rada announced a wider autonomy for the Ukrainian Republic, still maintaining ties to Russia, on 22 November 1917. The territory of the republic was proclaimed by the Third Universal 20 November 1917 (7 November by Old Style) of the Tsentralna Rada encompassing the governorates: Volyn, Kyiv, Podolie, Chernigov, Poltava, Kharkov
Kharkiv ( uk, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest city and municipality in Ukraine.
, Yekaterinoslav
Dnipro, previously called Dnipropetrovsk from 1926 until May 2016, is Ukraine's fourth-largest city, with about one million inhabitants. It is located in the eastern part of Ukraine, southeast of the Ukrainian capital Kyiv on the Dnieper Rive ...
, Kherson, Taurida (not including Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
). It also stated that the people of the governorates: Voronezh, Kholm, and Kursk were welcome to join the republic through a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a Representative democr ...
. Further the Tsentralna Rada in its Universal stated that because there was no Government in the Russian Republic after the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mom ...
it proclaimed itself the Supreme governing body of the territory of Ukraine until order in the Russian republic could be restored. The Central Council of Ukraine
The Central Council of Ukraine ( uk, Українська Центральна Рада, ) (also called the Tsentralna Rada or the Central Rada) was the All-Ukrainian council (soviet) that united deputies of soldiers, workers, and peasants deputie ...
called all revolutionary activities such as the October Revolution a civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polici ...
and expressed its hopes for the resolution of the chaos.
After a brief truce, the Bolsheviks realized that the Rada had no intention of supporting the Bolshevik Revolution. They re-organized into an All-Ukrainian Council of Soviets in December 1917 in an attempt to seize power. When that failed due to the Bolsheviks' relative lack of popularity in Kyiv, they moved to Kharkiv
Kharkiv ( uk, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest city and municipality in Ukraine.
. The Bolsheviks of Ukraine declared the government of the Ukrainian People's Republic outlawed and proclaimed the Ukrainian People's Republic of Soviets
The Ukrainian People's Republic of Soviets (russian: Украинская Народная Республика Советов, translit=Ukrainskaya Narodnaya Respublika Sovjetov) was a short-lived (1917–1918) Soviet republic of the Russian S ...
with capital in Kyiv, claiming that the government of the People's Secretaries of Ukraine was the only government in the country. The Bolshevik Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
entered Ukraine from the Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
in support of the local Soviet government. As the relationships between members within the Tsentralna Rada soured, a series of regional Soviet republics on the territory of Ukraine proclaimed their independence and allegiance to the Petrograd sovnarkom ( Odessa Soviet Republic (southern Ukraine), Donetsk-Krivoi Rog Soviet Republic (eastern Ukraine)). The Donetsk-Kryvoi Rog Republic was created by a direct decree of Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1 ...
as part of the Russian SFSR with its capital in Kharkiv. That decree was successfully implemented by Fyodor Sergeyev
Fyodor Andreyevich Sergeyev (, ; March 19, 1883 – July 24, 1921), better known as Comrade Artyom (), was a Russian Bolshevik revolutionary, Soviet politician, agitator, and journalist. He was a close friend of Sergei Kirov and Joseph Sta ...
who became the chairman of the local government as well as joining the Soviet government of Ukraine, simultaneously. Unlike ''Fyodor Sergeyev's'' Republic, the Odessa Republic was not recognized by any other Bolshevik governments and on its own initiative had entered a military conflict with Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
for control over the Moldavian Democratic Republic, whose territory it was contesting.

Timeline
The following information is based on the exposition of the Museum of Soviet occupation in Kyiv ( Memorial in Kyiv).Spring 1917
* 8–12 March – February Revolution in theRussian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
, victory of the democratic forces
* 17 March – establishment of the Ukrainian Central Council
* 4 April – recreation of Prosvita, establishment of the Ukrainian Cooperative Committee, and the Temporary Military Council, liberation of the people of Galicia, particularly Andrey Sheptytsky
Andrey Sheptytsky, OSBM (; uk, Митрополит Андрей Шептицький; 29 July 1865 – 1 November 1944) was the Metropolitan Archbishop of the Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church from 1901 until his death in 1944. His tenure sp ...
* 9 April – Mykhailo Hrushevsky
Mykhailo Serhiiovych Hrushevsky ( uk, Михайло Сергійович Грушевський, Chełm, – Kislovodsk, 24 November 1934) was a Ukrainian academician, politician, historian and statesman who was one of the most important figure ...
returns from exile to head the Ukrainian Central Council
* 10 April – the Ukrainian Central Council supported the convocation of the Ukrainian National Congress
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
* 11 April – establishment of the Ukrainian Military Society of Hetman Polubotok headed by Mykola Mikhnovsky
Mykola Ivanovych Mikhnovsky ( uk, Мико́ла Іва́нович Міхно́вський; – 3 May 1924) was a Ukrainian independence activist, lawyer and journalist who was one of the early leaders of the Ukrainian nationalist movement ...
, organization of the 1st Ukrainian Volunteer Regiment of Bohdan Khmelnytsky
* 13 April – a big demonstration took place in Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
with over 100,000 people, establishment of the Ukrainian National Council in Petrograd
* 2–4 May – the Ukrainian National Congress took place in Kyiv, involving about 900 delegates, the Congress confirmed the composition of the Ukrainian Central Council of 150 members headed by Mykhailo Hrushevsky
Mykhailo Serhiiovych Hrushevsky ( uk, Михайло Сергійович Грушевський, Chełm, – Kislovodsk, 24 November 1934) was a Ukrainian academician, politician, historian and statesman who was one of the most important figure ...
* 17 May – the commander of the Southwestern Front General Brusilov permitted the organization of the Bohdan Khmelnytsky Regiment which drafted 3,574 volunteers
* 18 – 1 May Ukrainian Military Congress took place in Kyiv attended by over 700 delegates. The Congress elected the Ukrainian General Military Committee Ukrainian General Military Committee ( uk, Український генеральний військовий комітет; ''Ukrayinskyi heneralnyi viyskovyi komitet'') was the highest military institution in Ukrainian People's Republic establish ...
of 18 members headed by Symon Petliura
Summer 1917
* 10–15 June – the 1st All-Ukrainian Peasant Congress took place in Kyiv in which 2,200 delegates participated * 11 June – extraordinary congress of the council of Ukrainian Military Society of Doroshenko inSimferopol
Simferopol () is the second-largest city in the Crimean Peninsula. The city, along with the rest of Crimea, is internationally recognised as part of Ukraine, and is considered the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea. However, it is ...
decided to create a separate Ukrainian Regiment
* 18–24 June – ignoring the prohibition of the Russian Provisional Government, the 2nd Ukrainian Military Congress took place in Kyiv. The congress accepted the declaration of a detailed plan of Ukrainization of the Russian Army, leaving Symon Petlyura as the head of the Ukrainian General Military Committee. The congress showed its support to the Ukrainian Central Council. The council of Kharkiv Governorate
Kharkiv Governorate ( uk, Харківська губернія, translit=Kharkivska huberniia) was a governorate of Ukraine from 1918 to 1925.
The region was re-established in 1918 as the Kharkov Governorate plus southern regions of Kursk Gove ...
recognized the Ukrainian Central Council as a government authority in Ukraine
* 24 June – announcement of the 1st Universal (Declaration) of the Ukrainian Central Council at Sofiyivska Ploshcha (Sofia Square)
* 28 June – the Ukrainian Central Council elects the General Secretariat of Ukraine as an authority of state power
* 11 July – a delegation of the Russian Provisional Government (Kerenskyi, Tereshchenko, and Tsereteli) arrived in Kyiv
* 14 July – the Ukrainian Central Council adopted that ''Petty Council'' consisting of 40 representatives from Ukrainian and 18 from national minorities
* 16 July – the Petty Council adopted the 2nd Universal (Declaration) of the Ukrainian Central Council
* 29 July – the Petty Council adopted the Statute of the Highest Government of Ukraine
* 8 August – a terrorist attack took place at the railroad station "Post-Volynsky" (Kyiv) where the newly formed Bohdan Khmelnytsky Regiment was attacked by the Moscow cuirassiers and Don Cossacks
* 17 August – the Russian Provisional Government issued a temporary instruction (Instruktsia) for the General Secretariat of Provisional Government in Ukraine where it recognized the competency of the General Secretariat over five Governorates (Gubernias): Kyiv, Volyn, Poltava, Chernihiv, and Podillia
Autumn 1917
* 22 September – the Petty Council adopted the declaration about the Ukrainian Constituent Assembly. The representatives of national minorities in the Petty Council condemned the intentions of Ukraine to separate from Russia * 27 September – start of the State Democratic Convention in Petrograd * 13 October – by the petition of the Kyiv Court Chamber the Russian Provisional Government initiates investigation against the General Secretariat for the intention to convene the Ukrainian Constituent Assembly * 7 November –October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mom ...
in Petrograd. Petty Council created of the Regional Committee in Protection of Revolution in Ukraine. The committee announced the extension of its powers over the nine Ukrainian governorates
* 8 November – the Ukrainian Central Council adopted a resolution which condemned the revolution. In protest, the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
left the Regional Committee and the Ukrainian Central Council
* 9 November – the commander of the Kyiv Military District
The Kiev Military District (; , abbreviated ) was a military district of the Imperial Russian Army and subsequently of the Red Army and Soviet Armed Forces. It was first formed in 1862, and was headquartered in Kiev (Kyiv) for most of its exi ...
General Kvetsinsky refused to recognize the Regional Committee which in turn was dissolved transferring all its powers to the General Secretariat
* 11 November – arrested Bolsheviks of a revolutionary committee. The Ukrainian Central Council adopted a bill about elections to the Ukrainian Constituent Assembly handing to the Petty Council to finalize the law and conduct the elections
* 14 November – the Ukrainian Central Council and the General Secretary are recognized as state authorities. The General Secretary of Military Affairs Symon Petliura subordinates the Kyiv militia (law enforcement) to the Ukrainian government
* 20 November – after the announcement of the 3rd Universal (Declaration) the deputies of Russian Cadets V. Krupkov and Polish Kolo V. Rudnytsky surrendered their mandates of the Ukrainian Central Council
* 21 November – the General Secretary of Military Affairs Symon Petliura appoints General Pavlo Skoropadsky a commander of the Right-bank Ukraine
Right-bank Ukraine ( uk , Правобережна Україна, ''Pravoberezhna Ukrayina''; russian: Правобережная Украина, ''Pravoberezhnaya Ukraina''; pl, Prawobrzeżna Ukraina, sk, Pravobrežná Ukrajina, hu, Jobb p ...
armed forces
* 22 November – in the presence of the French, Italian, and Romanian diplomatic missions, the 3rd Universal (Declaration) was announced at Sofiyivska Ploshcha (Sofia Square)
* 27 November – the Ukrainian Central Council adopted a resolution regarding the Kholm Governorate protesting its annexation by Poland
* 30 November – General Secretariat announced that Sovnarkom is not a legal authority of Russia. The Petty Council adopted the Law "About the Ukrainian Constituent Assembly" where it was established its composition of 301 members:
** Kyiv Governorate – 45
** Volyn Governorate – 30
** Podillya Governorate – 30
** Yekaterinoslav Governorate – 36
** Poltava Governorate – 30
** Kherson Governorate – 34
** Kharkiv Governorate – 35
** Tavria Governorate – 9
** Chernihiv Governorate – 27
** Ostrohozh district – 15
(Each deputy represents 100,000 of population, a right of vote have citizens of 20 years and older; established the Central Election Commission to the Ukrainian Constituent Assembly)
Winter 1917–18
 * 14–15 December – the Petty Council adopted the Law about the General Court, the highest judicial institution of the Ukrainian People's Republic. International diplomatic missions transferred their offices from Mohyliv-Podilsky to
* 14–15 December – the Petty Council adopted the Law about the General Court, the highest judicial institution of the Ukrainian People's Republic. International diplomatic missions transferred their offices from Mohyliv-Podilsky to Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
. The government of France on 18 December announced its intention to have a diplomatic relationship with Ukraine. England declared a similar intention
* 19 – 1 December Congress of Soviets of Workers', Soldiers', and Peasants' deputies of Ukraine expressed its complete trust to the Ukrainian Central Council and General Secretariat and condemned the Ultimatum of Lenin-Trotsky
* 22 December – the Petty Council adopted the Law on taxes and collections, with which all taxes and collections belonged to the State Treasury of Ukraine
* 23 December – the General Secretariat determined the composition of the Ukrainian delegation to the peace talks in Brest-Litovsk
* 25 December – the Peace Conference in Brest-Litovsk sent in a telegram for Ukraine to join the negotiations
* 3 January – General Georges Tabouis was appointed the Commissar of French Republic to the Government of Ukrainian People's Republic
* 6 January – start of the peace negotiations in Brest. The head of Ukrainian delegation Vsevolod Holubovych requests recognition of Ukraine as a sovereign state, adding of the Kholm Governorate, and conducting a plebiscite
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
on the territory of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
where dominated the Ukrainian population to add that territory to Ukraine
* 9 January – 171 delegates were elected to the Ukrainian Constituent Assembly
* 10–12 January – the Central powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in W ...
recognized the Ukrainian delegation at the talks in Brest as a separate and plenipotentiary to conduct negotiations on the behalf of Ukrainian People's Republic
* 16 January – the Petty Council adopted the law about creation of the Ukrainian National Army and its composition based on a militia principle
* 22 January – the Petty Council adopted the law about the National-Individual Autonomy. For the last text of the 4th Universal (Declaration) voted: "for" – 39 voices, "against" – 4 voices, "abstained" – 6
* 29 January – Battle of Kruty
The Battle of Kruty ( uk, Бій під Крутами, ) took place on January 29 or 30, 1918 , near Kruty railway station (today the village of Pamiatne, Nizhyn Raion, Chernihiv Oblast), about northeast of Kyiv, Ukraine, which at the time ...
* 9 February – the Brest peace treaty was signed with Germany, Austria-Hungary, Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
, and Bulgaria
* 10 February – Due to advance of the Russian Bolshevik forces the government of Ukraine was evacuated to Zhytomyr from Kyiv
* 21 February – the Ukrainian delegation issued a declaration about reasons for the arrival of German forces in Ukraine
* 27 February – the Ukrainian Central Council adopted the law about the introduction in Ukraine a new style of calendar according which a time moves 13 days ahead. The Petty Council adopted the law about the new monetary system. The monetary unit became hryvnia that had 8.712 units of pure gold. Adoption of the law about the coat of arms of the Ukrainian People's Republic – Trident ( Tryzub)
Spring 1918
In April 1918 troops loyal to the Ukrainian People's Republic take control of several cities in the Donbass region. * 2 March – the Petty Council adopted the law about citizenship of Ukraine, the law about new administrative system. The Russian established gubernias were to be replaced by new administrative unit – zemlia (land) * 18 March – several perished student-veterans of Kruty were reburied in Kyiv * 11 April – 12 May 1918 was designated as the first convocation of the Ukrainian Constituent Assembly * 13 April – Adoption of the Ukrainian Central Council resolution condemning the annexation of Bessarabia by Romania * 23 April – an economic treaty is signed between Ukraine and Germany with Austria-Hungary * 25 April – Adoption of the law about the Central Economic Council of Ukraine * 29 April – Adopted a bill on the Constitution of Ukraine. The All-Ukrainian Agrarian Congress elects Pavlo Skoropadsky the Hetman of UkraineIndependence
 Due to the aggression from Soviet Russia, on 22 January 1918, the Tsentralna Rada issued its Fourth Universal (dated 22 January 1918), breaking ties with Bolshevik Russia and proclaiming a sovereign Ukrainian state. Less than a month later, on 9 February 1918, the Red Army seized Kyiv.
Besieged by the Bolsheviks and having lost much territory, the Rada was forced to seek foreign aid, and signed the
Due to the aggression from Soviet Russia, on 22 January 1918, the Tsentralna Rada issued its Fourth Universal (dated 22 January 1918), breaking ties with Bolshevik Russia and proclaiming a sovereign Ukrainian state. Less than a month later, on 9 February 1918, the Red Army seized Kyiv.
Besieged by the Bolsheviks and having lost much territory, the Rada was forced to seek foreign aid, and signed the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers ( Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russi ...
on 9 February 1918 to obtain military help from the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
and Austro-Hungarian Empires. Germany helped the Ukrainian Army force the Bolsheviks out of Ukraine. On 20 February 1918 the council of the Kuban People's Republic accepted the resolution for a federal union of Kuban with Ukraine as Bolshevik forces pushed towards Yekaterinodar. It was agreed to forward the resolution for ratification to the Ukrainian government.
After the treaty of Brest-Litovsk, Ukraine became a virtual protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its in ...
of the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
which at that time seemed more favorable than being overrun by the Soviet forces that were spreading havoc in the country. Germany was anxious about losing the war and was trying to speed up the process of food extraction from Ukraine, so it decided to install its own administration in the person of Generalfeldmarschall von Eichhorn who replaced the Colonel General Alexander von Linsingen
Alexander Adolf August Karl von Linsingen (10 February 1850 – 5 June 1935) was a German general during World War I.
Military service
Linsingen joined the Prussian Army in 1868 and rose to Corps Commander ( II Corps) in 1909. He was one of th ...
. On 6 April the commander of the Army group ''Kijew'' issued an order in which he explained his intentions to execute the conditions of the treaty. That, of course, conflicted with the laws of the Ukrainian government, which annulled his order. By April 1918 the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
-Austrian
Austrian may refer to:
* Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent
** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen, see Austrian nationality law
* Austrian German dialect
* Something associated with the country Austria, for example: ...
Operation Faustschlag offensive had completely removed the Bolsheviks from Ukraine.100 years ago Bakhmut and the rest of Donbass liberatedUkrayinska Pravda
''Ukrainska Pravda'' ( uk, Українська правда, lit=Ukrainian Truth) is a Ukrainian online newspaper founded by Georgiy Gongadze on 16 April 2000 (the day of the Ukrainian constitutional referendum). Published mainly in Ukrai ...
(18 April 2018)Germany Takes Control of Crimea'' New York Herald'' (18 May 1918)War Without Fronts: Atamans and Commissars in Ukraine, 1917–1919
by Mikhail Akulov,
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of highe ...
, August 2013 (pp. 102 and 103) The German/Austro-Hungarian victories in Ukraine were due to the apathy of the locals and the inferior fighting skills of Bolsheviks troops compared to their Austro-Hungarian and German counterparts.
The Germans arrested and disbanded the Tsentralna Rada on 29 April 1918 to stop the social reforms that were taking place and restarted the process of food supply transfer to Germany and Austria-Hungary. The German authorities also arrested the Ukrainian Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
, Vsevolod Holubovych, on terrorist charges, and thus disbanded the Council of People's Ministers. Prior to this, the Rada had approved the Constitution of the Ukrainian People's Republic
The Constitution of Ukrainian People's Republic ( uk, Конституція Української Народної Республіки, translit=Konstytutsiia Ukrainskoi Narodnoi Respubliky) is a constitutional document approved by the Central ...
. Concurrently with all these events and a few days prior to the change of powers in the country on 24 April 1918 the government of Belarus confirmed the Belarusian Chamber of Commerce in Kyiv headed by Mitrofan Dovnar-Zapolsky
Mitrofan Viktorovich Dovnar-Zapol'skiy ( be, Мітрафан Віктаравіч Доўнар-Запольскі, russian: link=no, Митрофан Викторович Довнар-Запольский; , Rechytsa, Minsk Governorate – 30 Sep ...
on the initiative of the Belarusian secretary of finance Pyotr Krechevsky.
Hetmanate
 After the coup, the Rada was replaced by the conservative government of
After the coup, the Rada was replaced by the conservative government of Hetman
( uk, гетьман, translit=het'man) is a political title from Central and Eastern Europe, historically assigned to military commanders.
Used by the Czechs in Bohemia since the 15th century. It was the title of the second-highest military ...
Pavlo Skoropadsky, the Hetmanate, and the Ukrainian People's Republic by a "Ukrainian State" (''Ukrayinska derzhava''). Skoropadsky, a former officer of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
, established a regime favoring large landowners and concentrating power at the top. The government had little support from Ukrainian activists, but unlike the socialist Rada, it was able to establish an effective administrative organization, established diplomatic ties with many countries, and concluded a peace treaty with Soviet Russia. In a few months, the Hetmanate also printed millions of Ukrainian language
Ukrainian ( uk, украї́нська мо́ва, translit=ukrainska mova, label=native name, ) is an East Slavic language of the Indo-European language family. It is the native language of about 40 million people and the official state lan ...
textbooks, established many Ukrainian schools, two universities, and the Ukrainian Academy of Sciences.
The Hetmanate government also supported the confiscation of previously-nationalized peasant lands by wealthy estate owners, often with the help of German troops. This led to unrest, the rise of a peasant partisan ( guerrilla) movement, and a series of large-scale popular armed revolts. Negotiations were held to garner support from previous Rada members Petliura
Symon Vasylyovych Petliura ( uk, Си́мон Васи́льович Петлю́ра; – May 25, 1926) was a Ukrainian politician and journalist. He became the Supreme Commander of the Ukrainian Army and the President of the Ukrainian People' ...
and Vynnychenko, but these activists worked to overthrow Skoropadsky. On 30 July, a Russian Left Socialist-Revolutionary
The Party of Left Socialist-Revolutionaries (russian: Партия левых социалистов-революционеров-интернационалистов) was a revolutionary socialist political party formed during the Russian Revol ...
, Boris Mikhailovich Donskoy, with help from the local USRP
Universal Software Radio Peripheral (USRP) is a range of software-defined radios designed and sold by Ettus Research and its parent company, National Instruments. Developed by a team led by Matt Ettus, the USRP product family is commonly used ...
succeeded in assassinating von Eichhorn, blowing him up in downtown Kyiv at a broadlight.
Due to the impending loss of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
by Germany and Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, Skoropadsky's sponsors, the Hetman formed a new cabinet of Russian Monarchists and committed to federation with a possible future non-Bolshevik Russia. In response, the Ukrainian socialists announced a new revolutionary government, the Directorate, on 14 November 1918.
Timeline
Spring 1918
* 29 April – All-Ukrainian Agrarian Congress elects Pavlo Skoropadsky as the Hetman of Ukraine * 30 April – Mykola Vasylenko was appointed the Chairman of Council of Ministers and tasked with the formation of government * 7 May – the Council of Ministers confirmed its intentions to add Crimea to the Ukrainian State * 15 May – Signing of a treaty between governments of Ukraine from one side and Germany and Austria-Hungary from another to provide a loan in amount of 400 million karbovanets for acquiring the Ukrainian food * 18 May – the Council of Ministers adopted the law about a creation of the State Guard * 23 May – startedpeace negotiations
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an agreement to stop hostilities; a surr ...
between representatives of Ukraine and Russia
* 28 May – to Kyiv arrived the plenipotentiary delegation of the Regional Council of Kuban headed by Mykola Ryabovol with proposition of unification of Kuban with Ukraine
* 30 May – the Minister of Foreign Affairs Dmytro Doroshenko petitioned with a special letter to the Ambassador of Germany in Ukraine, baron Alfons Mumm von Schwarzenstein, to include Crimea to Ukraine
Summer 1918
* 12 June – the Congress of Landowners and Agrarians of Tavria Governorate that took place inSimferopol
Simferopol () is the second-largest city in the Crimean Peninsula. The city, along with the rest of Crimea, is internationally recognised as part of Ukraine, and is considered the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea. However, it is ...
supported the proposition to include Tavria to Ukraine
* 20 June – the All-Ukrainian Church Council took place in Kyiv
* 1 July – adopted the decision about a creation of the Ukrainian university in Kamianets-Podilsky
Kamianets-Podilskyi ( uk, Ка́м'яне́ць-Поді́льський, russian: Каменец-Подольский, Kamenets-Podolskiy, pl, Kamieniec Podolski, ro, Camenița, yi, קאַמענעץ־פּאָדאָלסק / קאַמעניץ, ...
* 2 July – adoption of the law about citizenship of the Ukrainian State
* 8 July – creation of the State Senate of the Ukrainian State as the supreme judicial institution
* 9 July – creation of the commission in development of project of the Ukrainian Academy of Sciences
* 10 July – Kyiv Orthodox clergy lifted the anathema on Hetman Mazepa
* 24 July – Ukraine and Germany ratified the Brest Peace Treaty, adoption of laws about the general military obligation, criminal responsibility for exceeding the maximum established prices and speculation, appointments to government service
* 27 July – due to the anti-Ukrainian policies of the Crimean government of Sulkevich the Ukrainian State established an economical blockade of the peninsula
* 1 August – adoption of laws about supreme government and political position of military servicemen
* 2 August – adoption of the law about the creation of fund of the National Library of Ukrainian State
* 6 August – the All-Ukrainian Church Council called for the autocephaly of the Ukrainian Church
* 10 August – confirmed the statute of the Ukrainian State Bank and its base and reserve capitals
* 17 August – adopted the law about a restriction on import of the Russian monetary units
* 22 August – in Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
Turkey and Ukraine exchanged documents that ratified the Brest Peace Treaty
* 10 September – signing of an economic agreement between Ukraine, Germany, Austria-Hungary for the 1918–1919 fiscal years
* 18 September – temporary stop of custom war with Crimea on the petition of the Sulkevich governmentAutumn 1918
* 5 October – in Kyiv started negotiations between Ukraine and Crimea about the conditions of Crimea inclusion to Ukraine * 6 October – Kyiv State Ukrainian University is opened * 16 October – Hetman of Ukraine issued declaration on the revival of cossackdom * 17 October – adopted a declaration about organization of volunteer militia on upholding the order of law * 21 October – Hetman of Ukraine met with the extraordinary mission of the Kuban regional government headed by Colonel V. Tkachov * 6 November – the German authorities transferred the ships of the Black Sea fleet to the Ukrainian State * 13 November – the Soviets annulled the Brest Peace Treaty and refused to recognize the independence of the Ukrainian State * 13–16 November – signing of agreement about trade, consulate, and sea relationships, railway and financial treaties between the government of Ukraine and the extraordinary mission of the Kuban regional government * 14 November – anti-Hetman Uprising * 26 November – the Ukrainian Academy of Sciences is created chaired by Vladimir VernadskyWinter 1918
* 5 December – signing of agreement of cooperation between Ukraine and Georgia * 14 December – Hetman of Ukraine surrender his powers and emigrated to GermanyDirectorate



 The Directorate gained massive popularity, and the support of some of Skoropadsky's military units including the Serdiuk Division. Their insurgent army encircled Kyiv on 21 November. After a three-week-long stalemate Skoropadsky abdicated in favor of the Council of Ministers who surrendered to the Revolutionary forces. On 19 December 1918, the Directorate took control of Kyiv.
The Bolsheviks invaded Ukraine from Kursk in late December 1918 where the new Ukrainian Soviet government was reestablished earlier in November of the same year. On 16 January 1919 Ukraine officially declared a war on Russia while the Russian Soviet government continued to deny all claims of invasion. On 22 January 1919, the Directorate was officially united with the West Ukrainian People's Republic, although the latter entity ''
The Directorate gained massive popularity, and the support of some of Skoropadsky's military units including the Serdiuk Division. Their insurgent army encircled Kyiv on 21 November. After a three-week-long stalemate Skoropadsky abdicated in favor of the Council of Ministers who surrendered to the Revolutionary forces. On 19 December 1918, the Directorate took control of Kyiv.
The Bolsheviks invaded Ukraine from Kursk in late December 1918 where the new Ukrainian Soviet government was reestablished earlier in November of the same year. On 16 January 1919 Ukraine officially declared a war on Russia while the Russian Soviet government continued to deny all claims of invasion. On 22 January 1919, the Directorate was officially united with the West Ukrainian People's Republic, although the latter entity ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with '' de jure'' ("by l ...
'' maintained its own army and government. On 5 February, the Bolsheviks captured Kyiv.
Throughout 1919, Ukraine experienced chaos as the armies of the Ukrainian Republic, the Bolsheviks, the Whites, the foreign powers of the Entente, and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, as well as anarchist forces such as that of Nestor Makhno
Nestor Ivanovych Makhno, The surname "Makhno" ( uk, Махно́) was itself a corruption of Nestor's father's surname "Mikhnenko" ( uk, Міхненко). ( 1888 – 25 July 1934), also known as Bat'ko Makhno ("Father Makhno"),; According to ...
tried to prevail. The subsequent Kyiv Offensive, staged by the Polish army and allied Ukrainian forces, was unable to change the situation. On 10 November 1920, the Directorate lost the remainder of its territory to the Bolsheviks in Volhynia as it crossed into Poland to accept internment. In March 1921, the Peace of Riga
The Peace of Riga, also known as the Treaty of Riga ( pl, Traktat Ryski), was signed in Riga on 18 March 1921, among Poland, Soviet Russia (acting also on behalf of Soviet Belarus) and Soviet Ukraine. The treaty ended the Polish–Soviet Wa ...
sealed a shared control of the territory by Poland, the Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
, and the Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic ( uk, Украї́нська Радя́нська Соціалісти́чна Респу́бліка, ; russian: Украи́нская Сове́тская Социалисти́ческая Респ ...
.
As the result, the lands of Galicia (''Halychyna'') as well as a large part of the Volhynian territory were incorporated into Poland, while the areas to the east and south became part of Soviet Ukraine.
After its military and political defeat, the Directorate continued to maintain control over some of its military forces. Preempting a planned invasion by its rival Archduke Wilhelm of Austria
Archduke Wilhelm Franz of Austria, later Wilhelm Franz von Habsburg-Lothringen (10 February 1895 – 18 August 1948), also known as Vasyl Vyshyvanyi ( uk, Василь Вишиваний }), was an Austrian archduke, a colonel of the Ukra ...
, in October 1921 the Ukrainian National Republic's government-in-exile launched a series of guerrilla raids into central Ukraine that reached as far east as Kyiv Oblast
Kyiv Oblast ( uk, Ки́ївська о́бласть, translit=Kyïvska oblast), also called Kyivshchyna ( uk, Ки́ївщина), is an oblast (province) in central and northern Ukraine. It surrounds, but does not include, the city of Kyiv, ...
. On 4 November, the Directorate's guerrillas captured Korosten and seized much military supplies. But on 17 November 1921, this force was surrounded by Bolshevik cavalry and destroyed.
Timeline
Winter 1918–19
* 14 December – the Directorate of Ukraine received the state powers in Ukraine after the Hetman of Ukraine emigrated to Germany * 16 December – the Directorate renewed the law about National-Individual Autonomy * 19 December – the grand entry of Directorate to the capital of Ukraine. Military parade at Sofiyivska Ploshcha. Note of protest to the countries of Entente due to occupation of ports of the Southern Ukraine ( Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War) * 26 December – Directorate published a basis of its economic-social policies and political system * 31 December – Directorate issued a note of protest to the Soviet Russia due to its invasion of Ukraine * 1 January – Directorate adopted the law about the Supreme body of the Ukrainian Autocephalous Orthodox Cathedral Church * 2 January – order of the Chief Otaman Symon Petlyura to exile all enemies of Ukraine * 3–4 January – repeated notes of protest to the Soviet Russia due to its intervention * 4 January – Directorate adopted the law about Ukrainian monetary unit, hryvnia * 8 January – the government of Ukraine adopted the Land Law, based on the principles of socialism * 16 January – declaration of war withMoscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
due to no results of peace negotiations
* 22 January – declaration of Unification between Ukraine and West Ukraine at Sofiyivska Ploshcha
* 23 January – session of Labor Congress initiated by Directorate was opened in Kyiv. The congress attended over 400 delegates, out which 65 represented the West Ukraine. It expressed its trust in Directorate and adopted the law about the form of government in Ukraine
* 2 February – due to the advance of Bolsheviks Directorate moved from Kyiv to Vinnytsia
* 13 February – Directorate changed the composition of the Council of National Ministers
* 17 February – Directorate petitioned to the governments of Entente and the US for help in fight with Bolsheviks
* 27 February – Chief Otaman met with Entente Commission in Khodoriv
Spring 1919
* 15 March – the delegation of West Ukraine headed by Yevhen Petrushevych met with Directory in Proskuriv to further discuss development of joint operations * 4 April – plenipotentiary representative of Ukraine at the Versailles Peace Conference H.Sydorenko expressed his protest to the Polish military attack onto the Ukrainian territory and its political and material support by Entente * 9 April – Directory adopted the declaration on resignation of the Ostapenko government and appointing the new composition of the Council of National Ministers headed byBorys Martos
Borys Mykolayovych Martos ( Ukrainian: Борис Миколайович Мартос) (May 20, 1879 – September 19, 1977) was a Ukrainian politician, pedagogue, and economist.
Biography
Martos was born in Hradyzk, Poltava Governorate, R ...
* 15 April – the government of Ukraine appointed General Oleksandr Osetsky as the Otaman of the Army
* 29 April – Volodymyr Oskilko Affairs
* 9 May – Symon Petlyura was elected the head of Directory in Radyvyliv
* 20 May – the peace negotiations of the diplomatic mission of Ukraine with the command of the Polish Army of Haller in Lublin showed no results
Summer 1919
* 12 June – the government ofFinland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bot ...
reestablished its diplomatic relationships with Ukraine
* 16 June – the Cardinal Secretary of State Pietro Gasparri
Pietro Gasparri, GCTE (5 May 1852 – 18 November 1934) was a Roman Catholic cardinal, diplomat and politician in the Roman Curia and the signatory of the Lateran Pacts. He served also as Cardinal Secretary of State under Popes Benedict XV a ...
informed the Chairman of Directorate S. Petliura on the approval of Count Mykhailo Tyshkevych as the Ambassador of Ukraine to the Holy See
* 18 June – the delegation of Ukraine at the Versailles Peace Conference together with the representatives of Estonia, Latvia, Belarus, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Northern Caucasus expressed its protest against recognition of the Supreme Council of the Paris Peace conference the government of Admiral Kolchak as the Supreme government of Russia
* 20–21 June – signing of a temporary agreement of Ukraine with Poland in Lviv
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in Western Ukraine, western Ukraine, and the List of cities in Ukraine, seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is o ...
and establishment of demarcation line (Delwig line)
Anti-Bolshevik and other uprisings
The following is the list of numerous uprisings that took place during the formation of the Ukrainian People's Republic. Some of them were in opposition to the Petlyura's government (such as the Oskilko's Affair), some were against the establishment of the Soviet regime, some took place to eliminate the Entente forces. According to Cheka documentation, in Ukraine took place 268 uprisings from 1917 through 1932, where in over 100 raions the mutinied peasants were killing chekists, communists, and prodotryads that were requisitioning food by force which more resembledexpropriation
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to p ...
.
* Makhnovshchina
The Makhnovshchina () was an attempt to form a stateless anarchist society in parts of Ukraine during the Russian Revolution of 1917–1923. It existed from 1918 to 1921, during which time free soviets and libertarian communes operated un ...
(Nestor Makhno
Nestor Ivanovych Makhno, The surname "Makhno" ( uk, Махно́) was itself a corruption of Nestor's father's surname "Mikhnenko" ( uk, Міхненко). ( 1888 – 25 July 1934), also known as Bat'ko Makhno ("Father Makhno"),; According to ...
)
* Otaman Grigoriev
* Otaman Oskilko Affair ( Volodymyr Oskilko)
* Otaman Zelenyi Uprising
* Kholodnyi Yar (Cold Ravine)
* Otaman Kamenyuka
* Free Cossacks
Free Cossacks ( uk, Вільне козацтво) were Ukrainian Cossacks that were organized as volunteer militia units in the spring of 1917 in the Ukrainian People's Republic. The Free Cossacks are seen as precursors of the modern Ukrainian ...
( Semen Hryzlo)
* Zazymia Uprising ( Troyeshchyna) - Otaman Romashka and Otaman Anhel against Kyiv and Chernihiv Cheka and Bashkir Cavalry Brigade Bashkir may refer to:
* Bashkirs, an ethnic group in Russia
*Bashkir language, a Turkic language spoken by the Bashkirs
*A citizen of Bashkortostan
*The (American) Bashkir Curly or Curly Horse, a curly-coated American horse breed
*The Bashkir horse ...
* Anti-Red Army ambush near Uman
Uman ( uk, Умань, ; pl, Humań; yi, אומאַן) is a city located in Cherkasy Oblast in central Ukraine, to the east of Vinnytsia. Located in the historical region of the eastern Podolia, the city rests on the banks of the Umanka River ...
in 1920
Exile
 The government of Ukrainian People's Republic operated in
The government of Ukrainian People's Republic operated in Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officiall ...
, Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
, Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in Central Germany between Erfurt in the west and Jena in the east, approximately southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together with the neighbouri ...
, Kissingen
Bad Kissingen is a German spa town in the Bavarian region of Lower Franconia and seat of the district Bad Kissingen. Situated to the south of the Rhön Mountains on the Franconian Saale river, it is one of the health resorts, which beca ...
, Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and ...
, and Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since ...
.
After the beginning of the World War II Taras Bulba-Borovets, with the support of the President of the Ukrainian People's Republic in exile Andrii Livytskyi, crossed the German-Soviet border and started organizing UPA military units subordinate to the UPR Government.
The 10th Emergency Session of the Ukrainian National Council recognized the state of Ukraine as the successor of the Ukrainian People's Republic in exile and agreed to transfer the powers and attributes of state power to the newly elected President of Ukraine
The president of Ukraine ( uk, Президент України, Prezydent Ukrainy) is the head of state of Ukraine. The president represents the nation in international relations, administers the foreign political activity of the state, condu ...
in 1991.''Плав'юк М.'Державний центр УНР на еміграції (ДЦ УНР)
(''tr. "UKR State Center for Emigration (UKR State Center)"'')
International recognition
The Ukrainian People's Republic was recognized ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legall ...
'' in February 1918 by the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in W ...
of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
(Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
and Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
)''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'', 12 February 1918 ( PDF) and by Bolshevik Russia, the Baltic States (Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, an ...
, Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
and Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
), Georgia, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
, Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
, and the Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of R ...
. ''De facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with '' de jure'' ("by l ...
'' recognition was granted by Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
, Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
, and Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. Partial de facto recognition was received from the Belarusian Democratic Republic (see Belarus–Ukraine relations).
Later in 1918 Russia chose to withdraw its recognition of independent Ukraine, representing the protocols of the Versailles Treaty as justification for its action. In 1920 Symon Petliura and Józef Piłsudski signed the Warsaw Treaty in which both countries established their borders along the Zbruch River. The states that previously recognized the Ukrainian People's Republic ceased any relationships with its Government-in-exile
A government in exile (abbreviated as GiE) is a political group that claims to be a country or semi-sovereign state's legitimate government, but is unable to exercise legal power and instead resides in a foreign country. Governments in exile ...
after they recognized the Soviet Government in Kyiv.
Important diplomatic missions and results
* Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, 9 February 1918 (Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in W ...
: ratification of Germany and Turkey)
* Preliminary peace treaty with the Soviet Russia, 12 June 1918 (renouncement of Brest-Litovsk treaty on 13 November 1918)
* Peace treaty with Don Republic, 8 August 1918
* Unification Act, 20 January 1919 (unification of two semi-recognized entities), Hutsul Republic (Eastern Zakarpattia) announced their will to join as well
* Loss of Kyiv to Soviets on 2 February 1919 and political crisis within the national government of Ukraine
* Resignation of Serhiy Ostapenko and his government due to failure on series of negotiations with representatives of Entente
* Participation at the Paris Peace Conference, 1919
* The Eastern Galician mandate of the Jules Cambon Commission was approved by the Entente leaders to hand it over the Poland, 21 November 1919
* Treaty of Warsaw (1920)
, uk, Варшавський договір
, image =
, image_width = 234px
, caption =
, type = Bilateral political treaty (Military alliance)
, date_drafted =
, date_signed ...
(Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
)
Demographics
According to the latest census that was taken 1897, the republic was accounted for over 20 million population in seven former Russian guberniyas, plus three uyezds of theTaurida Governorate
The Taurida Governorate (russian: Тавріическая губернія, modern spelling , ; crh, script=Latn, Tavrida guberniyası, ) or the Government of Taurida, was a historical governorate of the Russian Empire. It included the Crime ...
that were located on the mainland.
; National composition (thousands)
* Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Ort ...
– 14,931.5 (73%)
* Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
– 2,146.1 (11%)
* Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
– 1,871.8 (9%)
* Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
– 451.3 (2%)
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in ...
– 375.9 (2%)
* Belarusians – 208.5 (1%)
* Romanians
The Romanians ( ro, români, ; dated exonym '' Vlachs'') are a Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Romanian culture and ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language, they live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The 2011 Romania ...
– 185.7 (1%)
* Other – 1%
Administrative division
On 4 March 1918 the Ukrainian government accepted the law about the administrative-territorial division of Ukraine. The law stated that Ukraine is divided into 32 zemlia (''land'') which are administrated by their respective zemstvo. This law was not fully implemented as on 29 April 1918 there was the anti-socialist coup in Kyiv, after which Hetman Pavlo Skoropadsky reverted the reform back to the guberniya-type administration.Armed forces
The headquarters of the republic's armed forces was called the General Bulawa and was considered to be located in Kyiv. Of course, due to constant intervention from the Petrograd sovnarkom and theGerman Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
the physical location of it was changing (Kamyanets-Podilsky
Kamianets-Podilskyi ( uk, Ка́м'яне́ць-Поді́льський, russian: Каменец-Подольский, Kamenets-Podolskiy, pl, Kamieniec Podolski, ro, Camenița, yi, קאַמענעץ־פּאָדאָלסק / קאַמעניץ, ...
, Bila Tserkva
Bila Tserkva ( uk, Бі́ла Це́рква ; ) is a city in the center of Ukraine, the largest city in Kyiv Oblast (after Kyiv, which is the administrative center, but not part of the oblast), and part of the Right Bank. It serves as the adm ...
, others).
Main military formations (UPR)
*Sich Riflemen
The Sich Riflemen Halych-Bukovyna Kurin ( uk, Січові Cтрільці з Галичини та Буковини) were one of the first regular military units of the Ukrainian People's Army. The unit operated from 1917 to 1919 and was for ...
** Ukrainian Sich Riflemen
Legion of Ukrainian Sich Riflemen (german: Ukrainische Sitschower Schützen; uk, Українські cічові стрільці (УСС), translit=Ukraïnski sichovi stril’tsi (USS)) was a Ukrainian unit within the Austro-Hungarian Army d ...
were a similar unit, however, that unit wasn't part of Ukrainian military
* Free Cossacks
Free Cossacks ( uk, Вільне козацтво) were Ukrainian Cossacks that were organized as volunteer militia units in the spring of 1917 in the Ukrainian People's Republic. The Free Cossacks are seen as precursors of the modern Ukrainian ...
The following three Zaporizhian infantry regiments and the 3 Haidamaka Regiment of the biggest Ukrainian military formation, the Zaporizhian Corps, later were reorganized into the 1 Zaporizhian Division.
* Zaporizhian Corps
* Ukrainian Steppe Division (Anti-Bolshevik revolutionary-military unit)
* Ukrainian Marines
* 1 Riflemen-Cavalry Division (Gray-Coats)
* Blue-Coats
* Sloboda Ukraine Haidamaka Kosh
* 3 Iron Riflemen Division
* Ukrainian People's Republic Air Fleet
* Navy of the Ukrainian People's Republic
Main military formations (WUPR)
*Ukrainian Galician Army
Ukrainian Galician Army ( uk, Українська Галицька Армія, translit=Ukrayins’ka Halyts’ka Armiya, UHA), was the Ukrainian military of the West Ukrainian National Republic during and after the Polish-Ukrainian War. It w ...
, was a military formation of the West Ukrainian People's Republic
Money and banking
In December 1918 a temporary law about the issue of state banknotes by the UPR was adopted. According to this law: "Bank-notes must be issued in karbovanets" (Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
: Карбованець). Each karbovanets contains 17.424 parts of pure gold and is divided into two ''hrivnas'' (Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
: Гривня) or 200 ''shahs
Shah (; fa, شاه, , ) is a royal title that was historically used by the leading figures of Iranian monarchies.Yarshater, EhsaPersia or Iran, Persian or Farsi, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII no. 1 (1989) It was also used by a variety of ...
'' (Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
: Шаг).
There were numerous banks in the republic among the most popular ones were the ''Ukrainabank'' and the ''Soyuzbank'' that were created by Khrystofor Baranovsky
Khrystofor Antonovich Baranovsky (; ; — 1941) was a financial expert and a leader of cooperative movement in the Russian Empire, Ukrainian People's Republic, Ukraine, and Brazil.
He was born in the village of Nemirintsy, Nemyryntsi, Berdychiv ...
, the leader of a cooperative movement.

Maps
Green indicates UPR-controlled territory, red indicates the Red Army control, light yellow for the White Army control, dark yellow for Germany, blue for Poland, and brown for Romania. Bold black line indicates the borders of modern Ukraine.See also
* General Secretariat of Ukraine * West Ukrainian People's Republic * Ukraine after the Russian Revolution * History of the Jews in Ukraine#Ukrainian People's Republic * Ukrainian karbovanets – first Ukrainian official currency * Belarusian People's Republic * Universal (act) * Orange Revolution * February 2014 Euromaidan clashes * 2014 Russian military intervention in Ukraine * 2014 Crimean crisis * Ukrainian Death Triangle * Government of the Ukrainian People's Republic in exileNotes
References
Sources
* * * * * *Further reading
External links
*People's war 1917–1932 by Kyiv city organization "Memorial"
UNIVERSAL of the Ukrainian Central Rada addressed to the Ukrainian people living in and outside of Ukraine.
Translationreport. {{coord, 50, 27, N, 30, 30, E, type:country_source:kolossus-ptwiki, display=title Modern history of Ukraine Russian Revolution in Ukraine Ukrainian independence movement History of Ukraine (1795–1918) History of Ukraine (1918–1991) Post–Russian Empire states Former Slavic countries 1910s in Ukraine 1920s in Ukraine States and territories established in 1917 States and territories established in 1918 States and territories disestablished in 1918 States and territories disestablished in 1920 States and territories disestablished in 1921 1917 establishments in Ukraine 1918 establishments in Ukraine 1918 disestablishments in Ukraine 1920 disestablishments in Ukraine 1921 disestablishments in Ukraine Russia–Ukraine relations Russian-speaking countries and territories Former countries of the interwar period Former socialist republics Former countries