Urine Cytology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
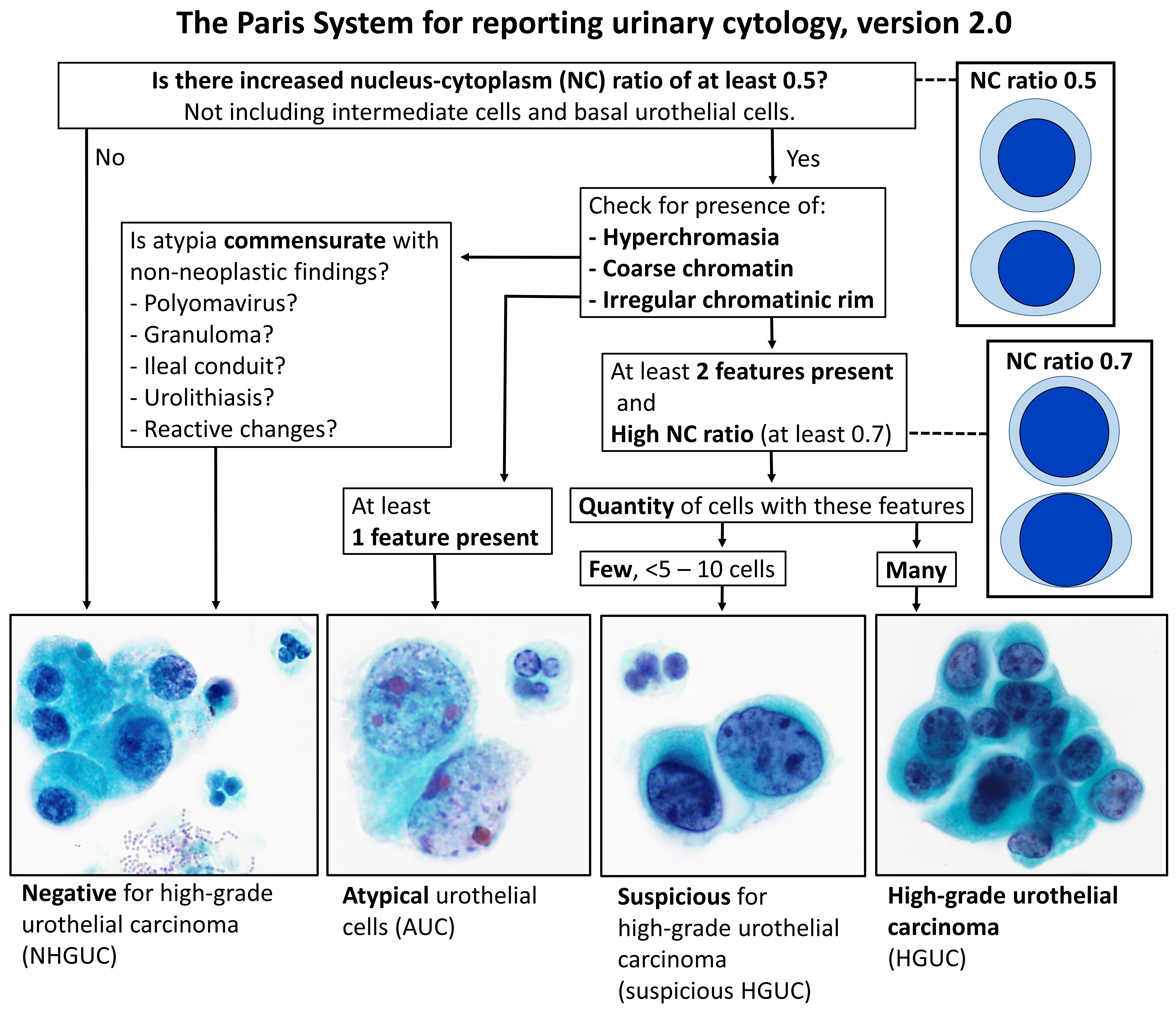 Urine cytology is a test that looks for abnormal cells in
Urine cytology is a test that looks for abnormal cells in
 Urine cytology is a test that looks for abnormal cells in
Urine cytology is a test that looks for abnormal cells in urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excretion, excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cel ...
under a microscope. The test commonly checks for infection, inflammatory disease of the urinary tract
The urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, con ...
, cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
, or precancerous conditions. It can be part of a broader urinalysis
Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words ''urine'' and ''analysis'', is a panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and microscopic examination. Macroscopic e ...
. If a cancerous condition is detected, other tests and procedures are usually recommended to diagnose cancers, including bladder cancer
Bladder cancer is any of several types of cancer arising from the tissues of the urinary bladder. Symptoms include blood in the urine, pain with urination, and low back pain. It is caused when epithelial cells that line the bladder become mali ...
, ureteral cancer
Ureteral cancer is cancer of the ureters, muscular tubes that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. It is also known as ureter cancer,cancer of the urethra. It is especially recommended when blood in the urine (
File:Cytology of normal urothelial cells, Pap stain.jpg, Normal urothelial intermediate cells,
hematuria
Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. “Gross hematuria” occurs when urine appears red, brown, or tea-colored due to the presence of blood. Hematuria may also be subtle and only detectable w ...
) has been detected.
Urine typically contains epithelial cell
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellula ...
s shed from the urinary tract, and urine cytology evaluates this urinary sediment for the presence of cancerous cells from the lining of the urinary tract, and it is a convenient noninvasive technique for follow-up analysis of patients treated for urinary tract cancers.
For this process, urine must be collected in a reliable fashion, and if urine samples are inadequate, the urinary tract can be assessed via instrumentation
Instrumentation a collective term for measuring instruments that are used for indicating, measuring and recording physical quantities. The term has its origins in the art and science of scientific instrument-making.
Instrumentation can refer to ...
, such as a catheter
In medicine, a catheter (/ˈkæθətər/) is a thin tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Cath ...
. In urine cytology, collected urine is examined microscopically.
One limitation, however, is the inability to definitively identify low-grade cancer cells and urine cytology is used mostly to identify high-grade tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s.
If the test detects atypical or cancerous cells, further tests may be recommended, such as cystoscopy
Cystoscopy is endoscopy of the urinary bladder via the urethra. It is carried out with a cystoscope.
The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
The cystoscope has lenses like a telescope or microscope ...
and a CT scan.
Pap stain
Papanicolaou stain (also Papanicolaou's stain and Pap stain) is a multichromatic (multicolored) Cytopathology, cytological staining technique developed by Georgios_Papanikolaou, George Papanicolaou in 1942. The Papanicolaou stain is one of the mos ...
File:HIgh-Grade Urothelial Carcinoma (28263697589).jpg, High-grade urothelial carcinoma
Transitional epithelium also known as urothelium is a type of stratified epithelium. Transitional epithelium is a type of tissue that changes shape in response to stretching (stretchable epithelium). The transitional epithelium usually appears ...
. A cytologic diagnosis of high-grade urothelial carcinoma requires > 10 cells with high N/C ratio, irregular chromatin pattern and hyperchromatic nuclei (Pap stain).
File:Decoy cell cytology.png, Decoy cells
Decoy cells are virally infected epithelial cells that can be found in the urine. Decoy cells owe their name to their strong resemblance to cancer cells, and may as such confuse the diagnosis of either viral infection or urothelial malignancy. ...
, which are virally infected epithelial cells that may look like carcinoma (Pap stain).
File:Urine cytology with red blood cells.jpg, Red blood cells
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek language, Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''k ...
, indicating hematuria
Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. “Gross hematuria” occurs when urine appears red, brown, or tea-colored due to the presence of blood. Hematuria may also be subtle and only detectable w ...
.
See also
*Urinalysis
Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words ''urine'' and ''analysis'', is a panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and microscopic examination. Macroscopic e ...
References
Urine tests {{oncology-stub