University of Oslo Faculty of Law on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
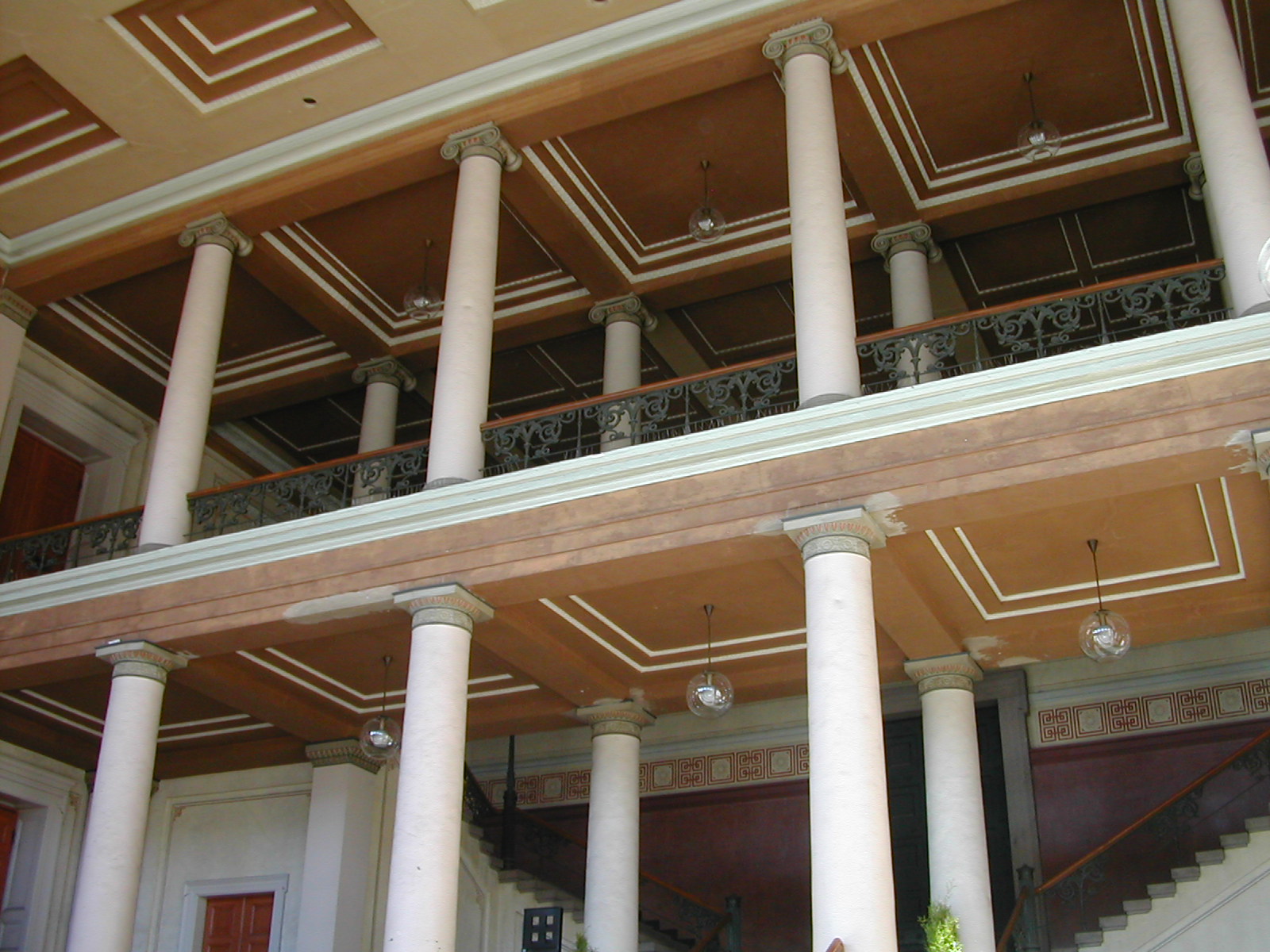






 The Faculty of Law ( no, Det juridiske fakultet) of the
The Faculty of Law ( no, Det juridiske fakultet) of the
 Historically, the rector of the university, elected among all the professors, was '' ex officio'' also dean of his own faculty. Otherwise the dean was elected among the professors at the faculty.
Readers became eligible to vote in 1939 and other academics and students in 1955. From 1975, even the administrative staff were granted the right to vote.
* Torkel Halvorsen Aschehoug ca. 1879
*
Historically, the rector of the university, elected among all the professors, was '' ex officio'' also dean of his own faculty. Otherwise the dean was elected among the professors at the faculty.
Readers became eligible to vote in 1939 and other academics and students in 1955. From 1975, even the administrative staff were granted the right to vote.
* Torkel Halvorsen Aschehoug ca. 1879
*
 Prior to 1990, all professors (i.e. full professors, the only ones who are called "professors" in Norway) were appointed by the King-in-Council to their
Prior to 1990, all professors (i.e. full professors, the only ones who are called "professors" in Norway) were appointed by the King-in-Council to their
Official website
{{Coord, 59.9158, 10.7356, type:edu:NO-30, display=title Law schools in Norway University of Oslo Neoclassical architecture in Norway Educational institutions established in 1811 1811 establishments in Norway University and college campuses in Norway




University of Oslo
The University of Oslo ( no, Universitetet i Oslo; la, Universitas Osloensis) is a public research university located in Oslo, Norway. It is the highest ranked and oldest university in Norway. It is consistently ranked among the top univers ...
is Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
's oldest law faculty
Faculty may refer to:
* Faculty (academic staff), the academic staff of a university (North American usage)
* Faculty (division), a division within a university (usage outside of the United States)
* Faculty (instrument)
A faculty is a legal in ...
, established in 1811 as one of the four original faculties of The Royal Frederick University (renamed the University of Oslo in 1939). Alongside the law faculties in Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan ar ...
, Lund and Uppsala
Uppsala (, or all ending in , ; archaically spelled ''Upsala'') is the county seat of Uppsala County and the List of urban areas in Sweden by population, fourth-largest city in Sweden, after Stockholm, Gothenburg, and Malmö. It had 177,074 inha ...
, it is one of Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
's leading institutions of legal education and research. The faculty is the highest-ranked institution of legal education in Norway and is responsible for the professional law degree, one of the most competitive programmes at any Norwegian university.
Prior to 1811, the University of Copenhagen
The University of Copenhagen ( da, Københavns Universitet, KU) is a prestigious public university, public research university in Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark. Founded in 1479, the University of Copenhagen is the second-oldest university in ...
was the only university of Denmark-Norway, and the curriculum of the new law faculty in Christiania (renamed Oslo in 1925) was based on that of the University of Copenhagen Faculty of Law and long retained strong similarities, even after the dissolution of the Dano-Norwegian union in 1814. As the only faculty of law in Norway until 1980, it traditionally educated all lawyers of Norway and remains the country's most important law faculty, educating around 75% of all new legal candidates in Norway. Its law programme is one of the most competitive programmes to get into at any Norwegian university, with an acceptance rate of 12%. The faculty offers education and conducts research in both law and in related areas such as criminology and sociology of law
The sociology of law (legal sociology, or law and society) is often described as a sub-discipline of sociology or an interdisciplinary approach within legal studies. Some see sociology of law as belonging "necessarily" to the field of sociology ...
, and historically also in economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analy ...
(its former Dean, Ragnar Frisch
Ragnar Anton Kittil Frisch (3 March 1895 – 31 January 1973) was an influential Norwegian economist known for being one of the major contributors to establishing economics as a quantitative and statistically informed science in the early 20th c ...
, was awarded the first Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences
The Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, officially the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel ( sv, Sveriges riksbanks pris i ekonomisk vetenskap till Alfred Nobels minne), is an economics award administered ...
).
The faculty occupies the old university campus in the centre of Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of ...
, near the National Theatre, the Royal Palace
This is a list of royal palaces, sorted by continent.
Africa
* Abdin Palace, Cairo
* Al-Gawhara Palace, Cairo
* Koubbeh Palace, Cairo
* Tahra Palace, Cairo
* Menelik Palace
* Jubilee Palace
* Guenete Leul Palace
* Imperial Palace- Mass ...
, and the Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. ...
, constructed 1841–1851 by Christian Heinrich Grosch with the assistance of world-famous Prussian architect Karl Friedrich Schinkel
Karl Friedrich Schinkel (13 March 1781 – 9 October 1841) was a Prussian architect, city planner
An urban planner (also known as town planner) is a professional who practices in the field of town planning, urban planning or city planning.
...
in Schinkel's neoclassical style, with strong similarities to Schinkel's famous museums on the Museum Island
The Museum Island (german: Museumsinsel) is a museum complex on the northern part of the Spree Island in the historic heart of Berlin. It is one of the most visited sights of Germany's capital and one of the most important museum sites in Euro ...
in Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European U ...
. The old campus includes three main buildings, called ''Domus Academica'', ''Domus Media'' and ''Domus Bibliotheca'', centered on the University Square and facing Karl Johans gate
Karl Johans gate is the main street of the city of Oslo, Norway. The street was named in honor of King Charles III John, who was also King of Sweden as Charles XIV John.
Karl Johans gate is a composite of several older streets that used to be ...
. It is complemented by the new building ''Domus Juridica'' in the opposite direction, located between the Old National Gallery and the Museum of Cultural History, facing the old campus.
The Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor and armaments (military weapons and equipment) manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Chemistry, Physics, Physiolog ...
was awarded in the atrium of the central building of the old campus, ''Domus Media'', 1947–1989 and in 2020. The Parliament of Norway
The Storting ( no, Stortinget ) (lit. the Great Thing) is the supreme legislature of Norway, established in 1814 by the Constitution of Norway. It is located in Oslo. The unicameral parliament has 169 members and is elected every four years bas ...
convened in the Old Ceremonial Hall in ''Domus Academica'' 1854–1866. The faculty publishes several academic journals, including the English-language journal ''Oslo Law Review''.
History
TheUniversity of Copenhagen
The University of Copenhagen ( da, Københavns Universitet, KU) is a prestigious public university, public research university in Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark. Founded in 1479, the University of Copenhagen is the second-oldest university in ...
was founded in 1479. As there was no university in Norway itself, the University of Copenhagen served both Denmark and Norway during the countries' personal union, and the University of Copenhagen had both Norwegian students and teachers. With the rise of absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy (or Absolutism as a doctrine) is a form of monarchy in which the monarch rules in their own right or power. In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen is by no means limited and has absolute power, though a limited constituti ...
and a more professional civil service, legal education became of central importance by the early 18th century. During the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, and after years of discussion, The Royal Frederick University in Norway was established in 1811 and named in honour of Frederick VI of Denmark and Norway, and the Faculty of Law was one of the four original faculties, ranking second after the Faculty of Theology and before the Faculty of Medicine and the Faculty of Arts. In 1816, its first lecturers were appointed by the government: Lorents Lange
Lorentz Lange (23 December 1783 – 8 March 1860) was a Norwegian judge and politician.
He was born in Vang, Hedmark.
He was appointed by the government as the first Professor of Law at the University of Oslo
The University of Oslo ( no, ...
(born 1781) was appointed Professor of Jurisprudence, and Henrik Lauritz Nicolai Steenbuch (born 1774) was appointed Lecturer in Jurisprudence.
As a sovereign kingdom, Norway always had its own laws, but in 1687, Norway received its Norwegian Code, which was nearly identical to the Danish Code
Danske Lov (''English'': Danish Code) is the title of a Danish statute book from 1683 that previously formed the basis for the Danish legislation. Even though it was mainly a compilation of older, regional laws, it took seven different commissions ...
, and parts of which remain in effect until this day. Norway and Denmark hence shared a common legal tradition and in fact many of the same laws. The curriculum of the Faculty of Law in Christiania was hence to a large degree a direct continuation of the curriculum and traditions of the University of Copenhagen. Similarities exist until this day, although they have gradually been weakened.
The field of economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analy ...
as an academic discipline in Norway evolved at the Faculty of Law. In 1840, a chair in "Jurisprudence, Economics, and Statistics" was created by the King; it was first held by Anton Martin Schweigaard
Anton Martin Schweigaard (11 April 1808 – 1 February 1870) was a Norwegian educator, jurist, economist and member of the Norwegian Parliament.
Background
Schweigaard was born at Kragerø in Telemark, Norway. He was one of three children of J ...
.
Programmes and degrees
Principal law programme
The most important programme of the Faculty of Law is the 5-year legal education leading to aMaster of Laws
A Master of Laws (M.L. or LL.M.; Latin: ' or ') is an advanced postgraduate academic degree, pursued by those either holding an undergraduate academic law degree, a professional law degree, or an undergraduate degree in a related subject. In mos ...
(LL.M.) degree, known in Norwegian as ''master i rettsvitenskap'' (literally, "master of jurisprudence"), which is a protected title under Norwegian law. The programme replaced (2004–2007) the former six-year programme leading to a Candidate of Law
Candidate of Law (Latin: ''candidatus/candidata juris/iuris'') is both a graduate law degree awarded to law students in the Nordic region as well as an academic status designation for advanced Law School students in German-speaking countries.
N ...
(cand.jur.) degree, which was created in 1736 at the University of Copenhagen
The University of Copenhagen ( da, Københavns Universitet, KU) is a prestigious public university, public research university in Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark. Founded in 1479, the University of Copenhagen is the second-oldest university in ...
and retained at the Royal Frederick University from 1811 (the degree is still awarded in Copenhagen).
The Master or Laws or the former Candidate of Law are the only degrees qualifying for legal work in Norway. The graduates have a monopoly on a number of occupations, such as advocate (barrister), judge and, traditionally, all the high ranks of the Norwegian Police Service
The Norwegian Police Service ( no, Politi- og lensmannsetaten) is the Norwegian national civilian police agency. The service dates to the 13th century when the first sheriffs were appointed, and the current structure established in 2003. It ...
and a number of senior civil servant positions. Norway has a united legal profession and all persons working in legal occupations have the same education. Alongside the programme in medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, and Health promotion ...
, the programme in law in Oslo is one of the most competitive to get into at any Norwegian university with an acceptance rate of 12%.
Although students do not receive a formal degree before they have completed the five-year programme, the first four years correspond to an American J.D. degree. In the fifth year, students usually write a thesis corresponding to one semester and take advanced courses of their choice also corresponding to one semester. Alternatively, they may choose to write a longer thesis, corresponding to a full year. Parts of the fifth year, or even the full year, may also be taken abroad. The fifth year leads to the Master of Laws degree.
Other degrees
From 1840 to 1966, the field ofeconomics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analy ...
was part of the Faculty of Law, and most of the professors of economics until the mid 20th century had a background in law. Prior to 1966, the Faculty of Law conferred the degree cand.oecon., created in 1905, which was originally a 2-year supplementary degree in economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analy ...
intended for those already holding a cand.jur. degree, and which in 1934 evolved into an independent five-year degree in economics.
The Faculty of Law also offers degrees at all levels in criminology and a master's degree in sociology of law
The sociology of law (legal sociology, or law and society) is often described as a sub-discipline of sociology or an interdisciplinary approach within legal studies. Some see sociology of law as belonging "necessarily" to the field of sociology ...
.
In recent years, a number of specialized master's degree programmes in law, so-called LL.M. degrees, have been established. The Faculty of Law offers 1,5-year master's degrees in international public law, international criminal and humanitarian law, international economic law, international environmental and energy law and human rights. These degrees are intended for those already holding a law degree, whether foreign or Norwegian. They do not qualify for legal work in Norway, however, and very few Norwegian students obtain such degrees, as the basic legal education in Norway already leads to a degree at the LL.M. level. These programmes are hence mostly attracting foreign students.
Doctoral, licentiate and PhD degrees
The former doctorate in law, ''doctor juris'' (dr. jur.), created with the establishment of the University of Copenhagen in 1479 and retained by The Royal Frederick University from 1811, was gradually replaced (2004–2008) by the new degree ''philosophiae doctor'' (ph.d.), created in 2003. The faculty also confers the doctoral degree ''doctor philosophiae'' (dr.philos.), created in 1824, traditionally to doctoral candidates who are not legal professionals (for example to those with degrees in humanities or social sciences) or to scholars with a background in law who write a dissertation in a different field than law, and today to doctoral candidates who are not enrolled in the structured doctoral programme, but hand in their dissertation following independent research only (as was the case also for the dr.jur. degree until the 1990s). Traditionally, a doctoral degree was not a prerequisite for employment as a researcher, and was usually obtained after many years of research (ten or more), often by researchers at the associate professor level. The Faculty of Law confers doctorates in law and in other relevant disciplines such as criminology, sociology of law, philosophy of law, and formerly in economics. Prior to 1845, the licentiate degree also existed at The Royal Frederick University, as a degree below the doctorate but above the professional degrees. The licentiate degree was reintroduced in 1955 at the Faculty of Law (lic.jur.) and was awarded until 2003. It corresponds to a PhD degree. Prior to the Bologna Process, the degree system at the University of Oslo Faculty of Law mirrored that of theUniversity of Copenhagen
The University of Copenhagen ( da, Københavns Universitet, KU) is a prestigious public university, public research university in Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark. Founded in 1479, the University of Copenhagen is the second-oldest university in ...
, and Denmark in general. In Denmark, both the dr.jur. degree and the ph.d. degree exist today. The ph.d. degree, conferred following a 3-year programme by those already holding a (5-year) cand.jur. degree, is considered equivalent to and a direct continuation of the licentiate degree, whereas the dr.jur. degree is considered a doctorate in the proper sense, also referred to as a higher doctorate
A doctorate (from Latin ''docere'', "to teach"), doctor's degree (from Latin ''doctor'', "teacher"), or doctoral degree is an academic degree awarded by universities and some other educational institutions, derived from the ancient formalism '' ...
. Often the dr.jur. degree is obtained by those already holding a cand.jur. and a ph.d. degree.
Research
The faculty's two departments of Sociology of Law and Criminology, which are now merged to form a single department, are famous internationally for their contributions to the fields ofsociology of law
The sociology of law (legal sociology, or law and society) is often described as a sub-discipline of sociology or an interdisciplinary approach within legal studies. Some see sociology of law as belonging "necessarily" to the field of sociology ...
and criminology since the 1950s. Eminent academics in this field include Nils Christie, Vilhelm Aubert
Johan Vilhelm Aubert (7 June 1922 – 19 July 1988) was an influential Norwegian sociologist. He was a professor at the Faculty of Law, University of Oslo from 1963 to 1971 and at the Department of Sociology from 1971 to 1988. He co-founded t ...
, and Thomas Mathiesen
Thomas Mathiesen (5 October 1933 – 29 May 2021) was a Norwegian sociologist.
Background
Mathiesen grew up in the Norwegian county of Akershus, as the only child of Einar Mathiesen (1903–1983) and Birgit Mathiesen (1908–1990).Mathiesen, ...
.
Ragnar Frisch
Ragnar Anton Kittil Frisch (3 March 1895 – 31 January 1973) was an influential Norwegian economist known for being one of the major contributors to establishing economics as a quantitative and statistically informed science in the early 20th c ...
, who was professor of economics and statistics at the Faculty of Law from 1931 and also served as its dean, founded the discipline of econometrics
Econometrics is the application of statistical methods to economic data in order to give empirical content to economic relationships.M. Hashem Pesaran (1987). "Econometrics," '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', v. 2, p. 8 p. 8� ...
and coined the terms macroeconomics/ microeconomics, and was awarded the first Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences
The Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, officially the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel ( sv, Sveriges riksbanks pris i ekonomisk vetenskap till Alfred Nobels minne), is an economics award administered ...
in 1969.
The faculty is also recognized internationally for its research on maritime law, petroleum and energy law
Energy laws govern the use and taxation of energy, both renewable and non-renewable. These laws are the primary authorities (such as caselaw, statutes, rules, regulations and edicts) related to energy. In contrast, energy policy refers t ...
, human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
, feminist jurisprudence, and the emerging field of information/communication technology law. The Norwegian Research Center for Computers and Law is the second-oldest institution in the world in this field. Feminist jurisprudence became a recognised discipline at the faculty in 1975, and the faculty established a department of feminist jurisprudence, headed by Tove Stang Dahl, in 1978.
A number of academic journals are published by or edited at the Faculty of Law, including the ''Nordic Journal of Human Rights
The ''Nordic Journal of Human Rights'' is a Peer review, peer-reviewed academic journal published by the Norwegian Centre for Human Rights (part of the Faculty of Law at the University of Oslo) in collaboration with Universitetsforlaget. The journa ...
'' and '' Tidsskrift for Rettsvitenskap'' (Scandinavia's leading law journal, established in 1888).
Buildings
The faculty's main,neoclassicist
Neoclassicism (also spelled Neo-classicism) was a Western cultural movement in the decorative and visual arts, literature, theatre, music, and architecture that drew inspiration from the art and culture of classical antiquity. Neoclassicism w ...
buildings, centered on the University Square and facing Karl Johans gate
Karl Johans gate is the main street of the city of Oslo, Norway. The street was named in honor of King Charles III John, who was also King of Sweden as Charles XIV John.
Karl Johans gate is a composite of several older streets that used to be ...
, constructed by Christian Heinrich Grosch and Karl Friedrich Schinkel
Karl Friedrich Schinkel (13 March 1781 – 9 October 1841) was a Prussian architect, city planner
An urban planner (also known as town planner) is a professional who practices in the field of town planning, urban planning or city planning.
...
1841–1851, are
*Domus Bibliotheca (to the left, seen from Karl Johans gate), which includes the Law Library, IT rooms, lecture halls and offices for professors
*Domus Media (in the centre), which includes reading rooms, lecture halls, offices for professors, and in the centre, the Atrium
*Domus Academica (to the right, seen from Karl Johans gate), which includes the Old Ceremonial Hall, lecture halls, offices for the administration, and IT rooms
These buildings are strongly influenced by Schinkel's monumental buildings in Berlin, in particular the Museumsinsel. The impressive stair hall of Domus Media is closely inspired by the stair hall of Altes Museum
The Altes Museum (English: ''Old Museum'') is a listed building on the Museum Island in the historic centre of Berlin. Built from 1825 to 1830 by order of King Frederick William III of Prussia according to plans by Karl Friedrich Schinkel, it is ...
in Berlin (completed in 1830).
The Atrium of Domus Media was built as an extension of Domus Media on the occasion of the 100th anniversary of the founding of the university in 1911. It was decorated by Edvard Munch
Edvard Munch ( , ; 12 December 1863 – 23 January 1944) was a Norwegian painter. His best known work, '' The Scream'' (1893), has become one of Western art's most iconic images.
His childhood was overshadowed by illness, bereavement and the d ...
1909–16. In front of Domus Media, statues of Peter Andreas Munch
Peter Andreas Munch (15 December 1810 – 25 May 1863), usually known as P. A. Munch, was a Norwegian historian, known for his work on the medieval history of Norway. Munch's scholarship included Norwegian archaeology, geography, ethnograph ...
and Anton Martin Schweigaard
Anton Martin Schweigaard (11 April 1808 – 1 February 1870) was a Norwegian educator, jurist, economist and member of the Norwegian Parliament.
Background
Schweigaard was born at Kragerø in Telemark, Norway. He was one of three children of J ...
are displayed.
The Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor and armaments (military weapons and equipment) manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Chemistry, Physics, Physiolog ...
was awarded in the Atrium of Domus Media 1947–1989. Among those who received the prize in Domus Media are Martin Luther King Jr. (1964), Mother Teresa
Mary Teresa Bojaxhiu, MC (; 26 August 1910 – 5 September 1997), better known as Mother Teresa ( sq, Nënë Tereza), was an Indian-Albanian Catholic nun who, in 1950, founded the Missionaries of Charity. Anjezë Gonxhe Bojaxhiu () was ...
(1979), Desmond Tutu
Desmond Mpilo Tutu (7 October 193126 December 2021) was a South African Anglican bishop and theologian, known for his work as an anti-apartheid and human rights activist. He was Bishop of Johannesburg from 1985 to 1986 and then Archbish ...
(1984), and the 14th Dalai Lama
The 14th Dalai Lama (spiritual name Jetsun Jamphel Ngawang Lobsang Yeshe Tenzin Gyatso, known as Tenzin Gyatso (Tibetan: བསྟན་འཛིན་རྒྱ་མཚོ་, Wylie: ''bsTan-'dzin rgya-mtsho''); né Lhamo Thondup), known as ...
(1989). Before 1947, the prize was awarded in the Norwegian Nobel Institute
The Norwegian Nobel Institute ( no, Det Norske Nobelinstitutt) is located in Oslo, Norway. The institute is located at Henrik Ibsen Street 51 in the center of the city. It is situated just by the side of the Royal Palace.
History
The institute ...
, and since 1990, it has been awarded in Oslo City Hall
Oslo City Hall ( no, Oslo rådhus) is a municipal building in Oslo, the capital of Norway. It houses the city council, the city's administration and various other municipal organisations. The building as it stands today was constructed between ...
two minutes walk from the Faculty of Law. Since 2003, the Abel Prize
The Abel Prize ( ; no, Abelprisen ) is awarded annually by the King of Norway to one or more outstanding mathematicians. It is named after the Norwegian mathematician Niels Henrik Abel (1802–1829) and directly modeled after the Nobel Pri ...
has been awarded in the Atrium. The Atrium is also used for concerts and cultural events, and for the Faculty of Law's own events.
The Parliament of Norway
The Storting ( no, Stortinget ) (lit. the Great Thing) is the supreme legislature of Norway, established in 1814 by the Constitution of Norway. It is located in Oslo. The unicameral parliament has 169 members and is elected every four years bas ...
convened in the Old Ceremonial Hall of Domus Academica from 1854 to 1866, when the Parliament of Norway Building was completed.
In addition to the three main buildings of the old campus, the faculty uses several other newer buildings in the immediate vicinity of the old campus in central Oslo.
The Faculty of Law has occupied the old campus continuously since 1851. Until the mid-1980s, the Faculty of Law shared the old campus with the Faculty of Medicine, which was also partially based at the university hospitals in the Oslo area. The Faculty of Medicine has since completely relocated to the university hospitals (mainly Rikshospitalet
Oslo University Hospital, Rikshospitalet is one of the four main campuses of Oslo University Hospital in Oslo, Norway. It was an independent hospital, ''Rigshospitalet'', later spelled ''Rikshospitalet'' ("The National Hospital"), from 1826 to 200 ...
), leaving the Faculty of Law as the only faculty occupying the old campus. The Atrium in Domus Media and the Old Ceremonial Hall in Domus Academica are still used for ceremonial purposes by other parts of the university. The faculties of theology, humanities and mathematics-natural sciences relocated to Blindern
Blindern is the main campus of the University of Oslo, located in Nordre Aker in Oslo, Norway.
Campus
Most of the departments of the University of Oslo are located at Blindern; other, smaller campuses include Sentrum (law), Gaustad (medicine ...
in the suburban West End
West End most commonly refers to:
* West End of London, an area of central London, England
* West End theatre, a popular term for mainstream professional theatre staged in the large theatres of London, England
West End may also refer to:
Pl ...
in the 1930s, where the newer faculties of social sciences and education are also found.
Departments
For the first one and a half century of its existence, the Faculty of Law was not organised into departments, but rather centered on eachchair
A chair is a type of seat, typically designed for one person and consisting of one or more legs, a flat or slightly angled seat and a back-rest. They may be made of wood, metal, or synthetic materials, and may be padded or upholstered in vari ...
. From the 1950s, a number of departments have been established. All academics are now affiliated with one of the departments. The establishment of the departments was supported by generous grants from shipping magnate (and lawyer) Anders Jahre
Anders August Jahre (28 May 1891 – 26 February 1982) was a Norwegian shipping magnate. Jahre was educated in law, and worked as a lawyer in Sandefjord from 1916 until 1928. Meanwhile, he was also involved in the whaling industry, and he founded ...
. For the first decades, the departments had a fairly weak position organisationally. The boundaries between departments in the three traditional higher faculties, i.e. the faculties of theology, law and medicine, are significantly weaker than in the other faculties, and the faculty identity stronger, due to the fact that most employees share the same profession. Historically, all Professors of Law at the Faculty of Law were expected to teach all areas of law.
Law students (i.e. students enrolled in the Master of Laws programme) are not affiliated with any specific department, only with the faculty. Students of criminology, sociology of law or some specialized fields are affiliated with a department, however.
Department of Criminology and Sociology of Law
The Department of Criminology and Sociology of Law is the largest academic institution in the fields of criminology andsociology of law
The sociology of law (legal sociology, or law and society) is often described as a sub-discipline of sociology or an interdisciplinary approach within legal studies. Some see sociology of law as belonging "necessarily" to the field of sociology ...
in the Nordic countries. The department was established in 2000 by the merger of the Department of Criminology (established in 1954 as the Department of Criminology and Criminal Law) and the Department of Sociology of Law (established in 1961). Criminology and criminal law split in the early 1990s, when criminal law became part of the Department of Public and International Law.
Department of Public and International Law
The Department of Public and International Law was established in 1957. It covers a number of fields inpublic
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociological concept of the ''Öffentlichk ...
and international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
, including constitutional law
Constitutional law is a body of law which defines the role, powers, and structure of different entities within a state, namely, the executive, the parliament or legislature, and the judiciary; as well as the basic rights of citizens and, in fed ...
, administrative law
Administrative law is the division of law that governs the activities of executive branch agencies of government. Administrative law concerns executive branch rule making (executive branch rules are generally referred to as " regulations"), ...
, public international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
, criminal law and criminal procedure
Criminal procedure is the adjudication process of the criminal law. While criminal procedure differs dramatically by jurisdiction, the process generally begins with a formal criminal charge with the person on trial either being free on bail o ...
, civil procedure
Civil procedure is the body of law that sets out the rules and standards that courts follow when adjudicating civil lawsuits (as opposed to procedures in criminal law matters). These rules govern how a lawsuit or case may be commenced; what ki ...
, environmental law
Environmental law is a collective term encompassing aspects of the law that provide protection to the environment. A related but distinct set of regulatory regimes, now strongly influenced by environmental legal principles, focus on the managem ...
, labour law, legal history
Legal history or the history of law is the study of how law has Sociocultural evolution, evolved and why it has changed. Legal history is closely connected to the development of civilisations and operates in the wider context of social history. C ...
, legal theory
Jurisprudence, or legal theory, is the theoretical study of the propriety of law. Scholars of jurisprudence seek to explain the nature of law in its most general form and they also seek to achieve a deeper understanding of legal reasoning ...
, refugee and asylum law, social law, tax law
Tax law or revenue law is an area of legal study in which public or sanctioned authorities, such as federal, state and municipal governments (as in the case of the US) use a body of rules and procedures (laws) to assess and collect taxes in a ...
and women's law.
Department of Private Law
The Department of Private Law was established in 1955.Scandinavian Institute of Maritime Law
The Scandinavian Institute of Maritime Law was established in 1955, as the Department of Maritime Law. It includes the Department of Maritime Law and the Department of Petroleum and Energy Law.Norwegian Centre for Human Rights
The Norwegian Centre for Human Rights has the status ofnational human rights institution
A national human rights institution (NHRI) is an independent state-based institution with the responsibility to broadly protect and promote human rights in a given country. The growth of such bodies has been encouraged by the Office of the United ...
in Norway, and is internationally recognised as a leading research institution in the field of human rights. The centre is cross-disciplinary, and its staff includes lawyers, social scientists, and philosophers. The centre was established in 1987, and was originally an independent research institution that arose from a cooperation between the University of Oslo and the Peace Research Institute Oslo
The Peace Research Institute Oslo (PRIO; no, Institutt for fredsforskning) is a private research institution in peace and conflict studies, based in Oslo, Norway, with around 100 employees. It was founded in 1959 by a group of Norwegian researcher ...
. It was completely integrated into the University of Oslo Faculty of Law in 2003.
Centre of European Law
The Centre of European Law is a research centre focusing onEuropean Union law
European Union law is a system of rules operating within the member states of the European Union (EU). Since the founding of the European Coal and Steel Community following World War II, the EU has developed the aim to "promote peace, its valu ...
and EEA law. It was established in 1989.
Norwegian Research Center for Computers and Law
The Norwegian Research Center for Computers and Law is the second oldest institution in this field in the world. It includes the Section for eGovernment Studies.Former departments
The faculty formerly had a Department of Economics, which became part of the new Faculty of Social Sciences in 1966.Cooperation
The Faculty of Law cooperates with other entities of the University of Oslo which are not formally part of the Faculty of Law, for example the Norwegian Centre for Violence and Traumatic Stress Studies.Deans
 Historically, the rector of the university, elected among all the professors, was '' ex officio'' also dean of his own faculty. Otherwise the dean was elected among the professors at the faculty.
Readers became eligible to vote in 1939 and other academics and students in 1955. From 1975, even the administrative staff were granted the right to vote.
* Torkel Halvorsen Aschehoug ca. 1879
*
Historically, the rector of the university, elected among all the professors, was '' ex officio'' also dean of his own faculty. Otherwise the dean was elected among the professors at the faculty.
Readers became eligible to vote in 1939 and other academics and students in 1955. From 1975, even the administrative staff were granted the right to vote.
* Torkel Halvorsen Aschehoug ca. 1879
*Frederik Peter Brandt
Frederik Peter Brandt (24 July 1825 – 2 May 1891) was a Norwegian jurist, legal historian and professor at the Faculty of Law of the Royal Frederick University (1866–1890).
Biography
Frederik Peter Brandt was born at Åmli in Aust-Agder, No ...
* Marcus Pløen Ingstad
*Oskar Jæger
Oskar Gustav Jæger (16 June 1864 – 19 August 1933) was a Norwegian economist and politician. He obtained the cand.jur. degree in 1897 and was appointed research fellow in national economics in 1898. He was Professor of Economics (1902–1930) ...
1909–1911
*Absalon Taranger
Absalon (21 March 1201) was a Danish statesman and prelate of the Catholic Church who served as the bishop of Roskilde from 1158 to 1192 and archbishop of Lund from 1178 until his death. He was the foremost politician and church father of Denm ...
* Bredo Henrik von Munthe af Morgenstierne 1912–1918 (''ex officio'')
* Fredrik Stang 1921–1927 (''ex officio'')
* Ingvar Wedervang 1933–1935
* Frede Castberg ca. 1940
*Theodor Grundt
Theodor is a masculine given name. It is a German form of Theodore. It is also a variant of Teodor.
List of people with the given name Theodor
* Theodor Adorno, (1903–1969), German philosopher
* Theodor Aman, Romanian painter
* Theodor Blueg ...
1940
*Ragnar Frisch
Ragnar Anton Kittil Frisch (3 March 1895 – 31 January 1973) was an influential Norwegian economist known for being one of the major contributors to establishing economics as a quantitative and statistically informed science in the early 20th c ...
1942–1943
* Carl Jacob Arnholm 1945–1951
* Johannes Andenæs 1959–1960
*Johan Einarsen
Johan Einarsen (30 August 1903 – 1980) was a Norwegian jurist and economist.
He was born in Bergen as a son of jurist and economist Einar Einarsen (1868–1913) and Emilie Wiborg (1868–1953). He examen artium, finished his secondary degree in ...
–1963
*Sjur Brækhus
Sjur Brækhus (19 June 1918 – 19 May 2009) was a Norwegian legal scholar and judge.
He was born in Bergen as a son of captain and ship-owner Sigurd Alfred Brækhus (1879–1952) and Hilda Sverresdatter Klingenberg (1884–1957). He finished his ...
1963–1967
* Johannes Andenæs 1968–1969
* Anders Bratholm 1974–1976
* Carsten Smith 1977–1979
*Peter Lødrup Peter Lødrup (29 August 1932 – 16 June 2010) was a Norwegian legal scholar and judge.
He was born in Bærum and grew up in Oslo as a son of district stipendiary magistrate Mentz Darre Lødrup (1901–1968) and writer Evi Bøgenæs Lødrup (1906 ...
1980–1985
*Erling Selvig
Erling Christian Øverland Selvig (born 23 August 1931) is a Norwegian legal scholar and judge.
He was born in Egge as a son of manager Sverre Arthur Birger Selvig (1892–1968) and Sigfrid Øverland (1900–1984). He finished his secondary educa ...
1989–1994
*Frederik Zimmer
Frederik Zimmer (born 1944) is a Norwegian legal scholar.
He graduated with the cand.jur. degree in 1970. He worked as a deputy judge from 1970 to 1971, then as a lecturer and research fellow at the University of Oslo from 1971. He took his dr.jur ...
1995–2000
* Knut Kaasen 2001–2003
*Jon T. Johnsen
Jon Thorvald Johnsen (born 25 October 1942) is a Norwegian legal scholar.
He graduated with the cand.jur. degree in 1969. In his early career he worked as a research assistant at the University of Oslo, deputy judge, research fellow at the Univ ...
2004–2008
* Hans Petter Graver 2008–2015
*Dag Michalsen 2015–present
Notable academics
 Prior to 1990, all professors (i.e. full professors, the only ones who are called "professors" in Norway) were appointed by the King-in-Council to their
Prior to 1990, all professors (i.e. full professors, the only ones who are called "professors" in Norway) were appointed by the King-in-Council to their chairs
A chair is a type of seat, typically designed for one person and consisting of one or more legs, a flat or slightly angled seat and a back-rest. They may be made of wood, metal, or synthetic materials, and may be padded or upholstered in vari ...
, but today, new Professors are appointed directly by the Faculty of Law. The positions below that of professor are called ''dosent'' ( reader, abolished in 1985), '' førsteamanuensis'' (associate professor), and ''universitetslektor'' or ''amanuensis'' (lecturer or assistant professor). Temporary, qualifying positions are ''postdoktor'' (senior research fellow) and ''stipendiat'' (a research fellow enrolled in a doctoral programme). A small number of employees hold the title ''forsker'' (researcher) and usually have no teaching obligations; their formal qualifications may vary from the assistant professor level to the full professor level. Full professors with part-time positions (20% or less) are called ''professor II'', but otherwise hold the same status as other professors; usually such professors hold a chair or main position at a different university or research institution.
Academics of note include
;Law
* Claus Winter Hjelm
* Bredo Henrik von Munthe af Morgenstierne
*Francis Hagerup
George Francis Hagerup (22 January 1853 – 8 February 1921) was a Norwegian law professor, diplomat, politician for the Conservative Party and women's rights advocate. He was the 7th prime minister of Norway from 1895 to 1898 and from 1903 ...
*Frederik Stang
Frederik Stang (4 March 1808 – 8 June 1884) was a Norwegian lawyer, public servant, and politician who served as Norway's 1st prime minister in Christiana.
Stang was born on the Nordre Rostad farm at Stokke in Vestfold, Norway. He was the so ...
* Fredrik Stang
* Frede Castberg
* Johannes Andenæs
* Torstein Eckhoff
*Carl August Fleischer
Carl August Fleischer (born 26 August 1936) is a Norwegian jurist, born in Oslo. He was professor of jurisprudence at the University of Oslo from 1970. He has been a long-term consultant for the Ministry of Foreign Affairs In many countries, the M ...
*Mads H. Andenæs
Mads Henry Andenæs (22 April 1940 – 12 May 2019) was a Norwegian legal academic.
He was born in Oslo as a son of Johs. Andenæs. He took the dr.juris degree in 1978 on the thesis ''Sameier og selskaper'', and was appointed as a professor ...
* Tove Stang Dahl
*Jon Bing
Jon Bing (30 April 1944 – 14 January 2014) was a Norwegian writer and law professor at the Norwegian Research Center for Computers and Law (NRCCL), and the Faculty of Law at the University of Oslo. Bing was considered a pioneer in internationa ...
*Peter Lødrup Peter Lødrup (29 August 1932 – 16 June 2010) was a Norwegian legal scholar and judge.
He was born in Bærum and grew up in Oslo as a son of district stipendiary magistrate Mentz Darre Lødrup (1901–1968) and writer Evi Bøgenæs Lødrup (1906 ...
*Frederik Zimmer
Frederik Zimmer (born 1944) is a Norwegian legal scholar.
He graduated with the cand.jur. degree in 1970. He worked as a deputy judge from 1970 to 1971, then as a lecturer and research fellow at the University of Oslo from 1971. He took his dr.jur ...
* Tone Sverdrup
* Lucy Smith
* Carsten Smith
*Eivind Smith
Eivind Smith (born 4 December 1949) is a Norwegian jurist and professor of law.
He was born in Bærum, and took the dr.juris degree in 1979. Since 1986, he has been Professor of Law at the Faculty of Law, University of Oslo. He is a member of t ...
* Knut Selmer
*Sjur Brækhus
Sjur Brækhus (19 June 1918 – 19 May 2009) was a Norwegian legal scholar and judge.
He was born in Bergen as a son of captain and ship-owner Sigurd Alfred Brækhus (1879–1952) and Hilda Sverresdatter Klingenberg (1884–1957). He finished his ...
* Thor Falkanger
*Kirsti Strøm Bull
Kirsti Strøm Bull (born 27 April 1945) is a Norwegian professor of law.
She took the cand.jur. degree in 1969 and the dr.juris degree in 1993. Having worked at the University of Oslo since 1971, she was promoted to associate professor
Asso ...
* Anders Bratholm
* Birger Stuevold Lassen
* Viggo Hagstrøm
*Henning Jakhelln
Henning (Tønsberg) Jakhelln (born 22 March 1939) is a Norwegian legal academic, and Professor Emeritus of Law (labour law) at the University of Oslo.
He was born in Bodø, and obtained the cand.jur. degree in 1963 and the lic.jur. degree in 1967 ...
*Anne Hellum Anne Hellum (born 1952) is a Norwegian jurist. She is Professor of Public Law at the Department of Public and International Law at the University of Oslo Faculty of Law. Her main areas of expertise are anti-discrimination and equality law, women's ...
;Economics
*Anton Martin Schweigaard
Anton Martin Schweigaard (11 April 1808 – 1 February 1870) was a Norwegian educator, jurist, economist and member of the Norwegian Parliament.
Background
Schweigaard was born at Kragerø in Telemark, Norway. He was one of three children of J ...
(Professor of Jurisprudence, Economics, and Statistics)
* Torkel Halvorsen Aschehoug (Professor of Jurisprudence, Economics, and Statistics)
*Oskar Jæger
Oskar Gustav Jæger (16 June 1864 – 19 August 1933) was a Norwegian economist and politician. He obtained the cand.jur. degree in 1897 and was appointed research fellow in national economics in 1898. He was Professor of Economics (1902–1930) ...
*Ragnar Frisch
Ragnar Anton Kittil Frisch (3 March 1895 – 31 January 1973) was an influential Norwegian economist known for being one of the major contributors to establishing economics as a quantitative and statistically informed science in the early 20th c ...
* Ingvar Wedervang
*Johan Einarsen
Johan Einarsen (30 August 1903 – 1980) was a Norwegian jurist and economist.
He was born in Bergen as a son of jurist and economist Einar Einarsen (1868–1913) and Emilie Wiborg (1868–1953). He examen artium, finished his secondary degree in ...
;Criminology and Sociology of Law
* Nils Christie
*Thomas Mathiesen
Thomas Mathiesen (5 October 1933 – 29 May 2021) was a Norwegian sociologist.
Background
Mathiesen grew up in the Norwegian county of Akershus, as the only child of Einar Mathiesen (1903–1983) and Birgit Mathiesen (1908–1990).Mathiesen, ...
*Vilhelm Aubert
Johan Vilhelm Aubert (7 June 1922 – 19 July 1988) was an influential Norwegian sociologist. He was a professor at the Faculty of Law, University of Oslo from 1963 to 1971 and at the Department of Sociology from 1971 to 1988. He co-founded t ...
*Kjersti Ericsson
Kjersti Ericsson (born 18 January 1944 in Oslo, Norway) is a Norwegian psychologist, criminologist, writer, poet and former politician. She is Professor of Criminology at the Faculty of Law of the University of Oslo.
Ericsson obtained her cand.ps ...
Notable alumni
From 1811 to 1980, the faculty educated all lawyers of Norway, and still educates around 75% of new legal candidates. Its alumni hence includes the vast majority of the country's preeminent legal professionals, including academics, supreme court justices, senior civil servants, and a large number of politicians, among them 11 Prime Ministers and many cabinet ministers.References
External links
Official website
{{Coord, 59.9158, 10.7356, type:edu:NO-30, display=title Law schools in Norway University of Oslo Neoclassical architecture in Norway Educational institutions established in 1811 1811 establishments in Norway University and college campuses in Norway