United States Strategic Command on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
United States Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM) is one of the eleven
 *J1 – Human Capital: Develops and administers command manpower and personnel policies, human resources, and personnel assignment programs.
*J2 – Intelligence: Responsible for delivering all-source intelligence while enabling the execution of assigned strategic deterrence, space and cyberspace operations. Directs all intelligence-related support for the commander and ensures unity of intelligence effort across the Command.
*J3 – Global Operations: Coordinates the planning, employment and operation of DoD strategic assets and combines all current operations, intelligence, and global command and control operations. Subdivisions within J3 include Combat and Information Operations, Current Operations, Logistics, and Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Operations (JEMSO).
*J4 – Logistics: The Logistics Directorate plans, coordinates and executes joint logistics functions, and provides capability-based readiness assessments and facilities management in support of U.S. Strategic Command's global mission.
*J5 – Plans and Policy: Responsible for coordinating the development and implementation of national security policy as it applies to the command and the execution of its mission. Develops future plans, policy and strategy across all mission areas as outlined in the Unified Command Plan.
*J6 – C4 Systems: Coordinates, facilitates, monitors and assesses systems, networks and communications requirements.
*J7 – Joint Exercises, Training and Assessments: Manages the USSTRATCOM commander's Joint Exercises, Training, and Assessments programs in order to ensure readiness to perform the Command missions. Provides modeling and simulation support for exercises and training events to the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS), Combatant Commands, and other Major Commands (MAJCOM). Manages the Joint Lessons Learned Program. Augments the battle staff during a crisis.
*J8 – Capability and Resource Integration: Conducts force management and analysis to include integrating, coordinating, prioritizing, and advocating USSTRATCOM future concepts, mission capability needs, weapons system development, support for emerging technologies, and command and control architecture across the mission areas. Responsible for all command requirement processes, and ensures appropriate decision support tools and assessment processes are in place to enhance operational capabilities.
*J1 – Human Capital: Develops and administers command manpower and personnel policies, human resources, and personnel assignment programs.
*J2 – Intelligence: Responsible for delivering all-source intelligence while enabling the execution of assigned strategic deterrence, space and cyberspace operations. Directs all intelligence-related support for the commander and ensures unity of intelligence effort across the Command.
*J3 – Global Operations: Coordinates the planning, employment and operation of DoD strategic assets and combines all current operations, intelligence, and global command and control operations. Subdivisions within J3 include Combat and Information Operations, Current Operations, Logistics, and Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Operations (JEMSO).
*J4 – Logistics: The Logistics Directorate plans, coordinates and executes joint logistics functions, and provides capability-based readiness assessments and facilities management in support of U.S. Strategic Command's global mission.
*J5 – Plans and Policy: Responsible for coordinating the development and implementation of national security policy as it applies to the command and the execution of its mission. Develops future plans, policy and strategy across all mission areas as outlined in the Unified Command Plan.
*J6 – C4 Systems: Coordinates, facilitates, monitors and assesses systems, networks and communications requirements.
*J7 – Joint Exercises, Training and Assessments: Manages the USSTRATCOM commander's Joint Exercises, Training, and Assessments programs in order to ensure readiness to perform the Command missions. Provides modeling and simulation support for exercises and training events to the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS), Combatant Commands, and other Major Commands (MAJCOM). Manages the Joint Lessons Learned Program. Augments the battle staff during a crisis.
*J8 – Capability and Resource Integration: Conducts force management and analysis to include integrating, coordinating, prioritizing, and advocating USSTRATCOM future concepts, mission capability needs, weapons system development, support for emerging technologies, and command and control architecture across the mission areas. Responsible for all command requirement processes, and ensures appropriate decision support tools and assessment processes are in place to enhance operational capabilities.
 The Alternate Processing and Correlation Center in the USSTRATCOM Underground Command Complex at Offutt AFB provides an alternate missile warning correlation center to the Cheyenne Mountain Missile Warning Center. It is the prime source of missile warning data for USSTRATCOM for force survival and force management. The facility consists of the integration of the SCIS, CSSR, and CCPDS-R systems and also upgrade equipment and communications links.
The Alternate Processing and Correlation Center in the USSTRATCOM Underground Command Complex at Offutt AFB provides an alternate missile warning correlation center to the Cheyenne Mountain Missile Warning Center. It is the prime source of missile warning data for USSTRATCOM for force survival and force management. The facility consists of the integration of the SCIS, CSSR, and CCPDS-R systems and also upgrade equipment and communications links.
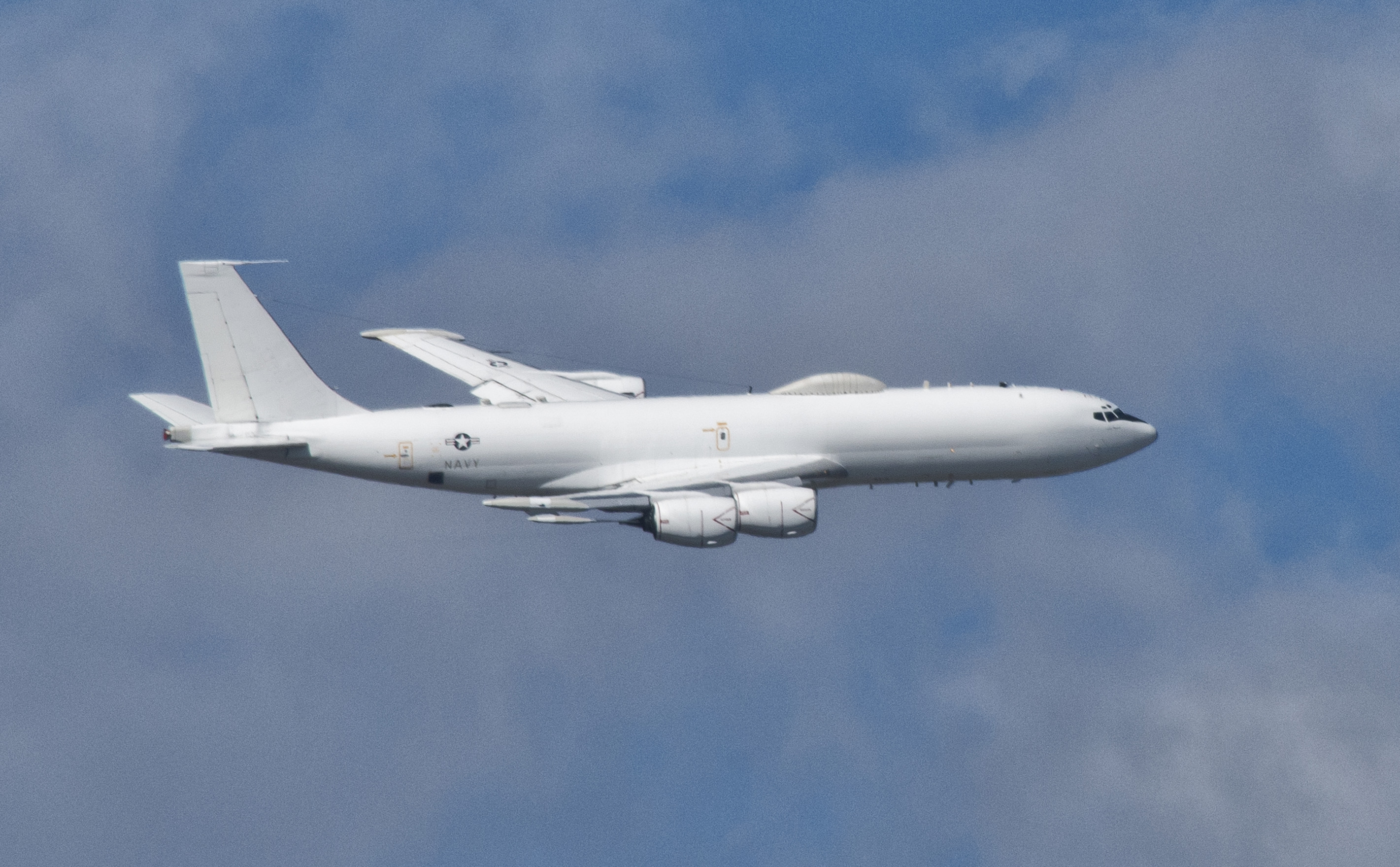
 U.S. Strategic Command's Airborne Command Post (ABNCP), also called " Looking Glass", allows USSTRATCOM the ability to command, control, and communicate with its nuclear forces should ground-based command centers become inoperable.
U.S. Strategic Command's Airborne Command Post (ABNCP), also called " Looking Glass", allows USSTRATCOM the ability to command, control, and communicate with its nuclear forces should ground-based command centers become inoperable.
United States Strategic Command Official Website
US Strategic Command Airborne Command Post Fact Sheet
Air Force Magazine
Journal of the Air Force Assoc., August 2008.
GAO Report: Additional Actions Needed by U.S. Strategic Command to Strengthen Implementation of Its Many Missions and New Organization
{{Strategic forces Strategic Command Military units and formations established in 1992 1992 establishments in the United States Military units and formations in Nebraska Organizations based in Omaha, Nebraska United States nuclear command and control Strategic forces
unified combatant command
A unified combatant command (CCMD), also referred to as a combatant command, is a joint command (military formation), military command of the United States Department of Defense that is composed of units from two or more service branches of the ...
s in the United States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD or DOD) is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national secur ...
. Headquartered at Offutt Air Force Base, Nebraska, USSTRATCOM is responsible for strategic nuclear deterrence, global strike, and operating the Defense Department's Global Information Grid. It also provides a host of capabilities to support the other combatant commands, including integrated missile defense; and global command, control, communications, computers, intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (C4ISR). This command exists to give "national leadership a unified resource for greater understanding of specific threats around the world and the means to respond to those threats rapidly".
Mission statement
USSTRATCOM employs nuclear, cyber, global strike, joint electronic warfare, missile defense, and intelligence capabilities to deter aggression, decisively and accurately respond if deterrence fails, assure allies, shape adversary behavior, defeat terror, and define the force of the future.Priorities
*Strategic Deterrence *Decisive Response *A Combat-Ready ForceCommander's intent
*Embrace strategic deterrence, consisting of innovative joint fighting forces integrated and synchronized in multiple domains to ensure national security. *Ensure a decisive response to aggression, against any threat, when called upon by civilian national leadership. *Anticipate and meet tactical, theater, and strategic demands through operational plans and capability development. *Develop the next generation of people and capabilities in order to prevail in future conflicts.Headquarters organizational structure
 *J1 – Human Capital: Develops and administers command manpower and personnel policies, human resources, and personnel assignment programs.
*J2 – Intelligence: Responsible for delivering all-source intelligence while enabling the execution of assigned strategic deterrence, space and cyberspace operations. Directs all intelligence-related support for the commander and ensures unity of intelligence effort across the Command.
*J3 – Global Operations: Coordinates the planning, employment and operation of DoD strategic assets and combines all current operations, intelligence, and global command and control operations. Subdivisions within J3 include Combat and Information Operations, Current Operations, Logistics, and Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Operations (JEMSO).
*J4 – Logistics: The Logistics Directorate plans, coordinates and executes joint logistics functions, and provides capability-based readiness assessments and facilities management in support of U.S. Strategic Command's global mission.
*J5 – Plans and Policy: Responsible for coordinating the development and implementation of national security policy as it applies to the command and the execution of its mission. Develops future plans, policy and strategy across all mission areas as outlined in the Unified Command Plan.
*J6 – C4 Systems: Coordinates, facilitates, monitors and assesses systems, networks and communications requirements.
*J7 – Joint Exercises, Training and Assessments: Manages the USSTRATCOM commander's Joint Exercises, Training, and Assessments programs in order to ensure readiness to perform the Command missions. Provides modeling and simulation support for exercises and training events to the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS), Combatant Commands, and other Major Commands (MAJCOM). Manages the Joint Lessons Learned Program. Augments the battle staff during a crisis.
*J8 – Capability and Resource Integration: Conducts force management and analysis to include integrating, coordinating, prioritizing, and advocating USSTRATCOM future concepts, mission capability needs, weapons system development, support for emerging technologies, and command and control architecture across the mission areas. Responsible for all command requirement processes, and ensures appropriate decision support tools and assessment processes are in place to enhance operational capabilities.
*J1 – Human Capital: Develops and administers command manpower and personnel policies, human resources, and personnel assignment programs.
*J2 – Intelligence: Responsible for delivering all-source intelligence while enabling the execution of assigned strategic deterrence, space and cyberspace operations. Directs all intelligence-related support for the commander and ensures unity of intelligence effort across the Command.
*J3 – Global Operations: Coordinates the planning, employment and operation of DoD strategic assets and combines all current operations, intelligence, and global command and control operations. Subdivisions within J3 include Combat and Information Operations, Current Operations, Logistics, and Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Operations (JEMSO).
*J4 – Logistics: The Logistics Directorate plans, coordinates and executes joint logistics functions, and provides capability-based readiness assessments and facilities management in support of U.S. Strategic Command's global mission.
*J5 – Plans and Policy: Responsible for coordinating the development and implementation of national security policy as it applies to the command and the execution of its mission. Develops future plans, policy and strategy across all mission areas as outlined in the Unified Command Plan.
*J6 – C4 Systems: Coordinates, facilitates, monitors and assesses systems, networks and communications requirements.
*J7 – Joint Exercises, Training and Assessments: Manages the USSTRATCOM commander's Joint Exercises, Training, and Assessments programs in order to ensure readiness to perform the Command missions. Provides modeling and simulation support for exercises and training events to the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS), Combatant Commands, and other Major Commands (MAJCOM). Manages the Joint Lessons Learned Program. Augments the battle staff during a crisis.
*J8 – Capability and Resource Integration: Conducts force management and analysis to include integrating, coordinating, prioritizing, and advocating USSTRATCOM future concepts, mission capability needs, weapons system development, support for emerging technologies, and command and control architecture across the mission areas. Responsible for all command requirement processes, and ensures appropriate decision support tools and assessment processes are in place to enhance operational capabilities.
Organizational structure
Component Commands
Command posts
TheGlobal Operations Center
Global means of or referring to a globe and may also refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Global'' (Paul van Dyk album), 2003
* ''Global'' (Bunji Garlin album), 2007
* ''Global'' (Humanoid album), 1989
* ''Global'' (Todd Rundgren album), 2015
* Bruno ...
, or GOC, is the nerve center for USSTRATCOM. The GOC is responsible for the global situational awareness of the commander, USSTRATCOM, and is the mechanism by which he exercises operational command and control of the Nation's global strategic forces.

 U.S. Strategic Command's Airborne Command Post (ABNCP), also called " Looking Glass", allows USSTRATCOM the ability to command, control, and communicate with its nuclear forces should ground-based command centers become inoperable.
U.S. Strategic Command's Airborne Command Post (ABNCP), also called " Looking Glass", allows USSTRATCOM the ability to command, control, and communicate with its nuclear forces should ground-based command centers become inoperable.
History
USSTRATCOM was originally formed in 1992, as a successor toStrategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was both a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile c ...
in response to the end of the Cold War and a new vision of nuclear warfare in U.S. defense policy. Department of Defense changes in command structure due to the " Goldwater-Nichols Act" of 1986, led to a single command responsible for all strategic nuclear weapons. As a result, USSTRATCOM's principal mission was to deter military attack, and if deterrence failed, to counter with nuclear weapons.
Throughout its history, it has drawn from important contributions from many different organizations stretching back to World War II. Providing national leadership with a single command responsible for all strategic nuclear forces, General George Butler, in establishing the new command, borrowed from the work of General Curtis LeMay
Curtis Emerson LeMay (November 15, 1906 – October 1, 1990) was an American Air Force general who implemented a controversial strategic bombing campaign in the Pacific theater of World War II. He later served as Chief of Staff of the U.S. A ...
, an early commander of Strategic Air Command. LeMay was a very vocal advocate for a strong national defense, particularly as regards nuclear weapons.
Being a Unified Command, another major concern for Gen. Butler was interservice rivalry, having soldiers, sailors, airmen and marines in one command. There had been decades of rivalry between the branches of the U.S. military regarding control of nuclear weapons. Even though a compromise had established the Joint Strategic Target Planning Staff, there were systemic and institutional problems that could not be overcome.
USSTRATCOM was re-structured 1 October 2002 by Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld. It was now to merge with the United States Space Command and assume all duties for full-spectrum global strike, operational space support, integrated missile defense, and global Command, Control, Communications, Computers, Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (C4ISR) and specialized planning. Its duties now include intelligence and cyber support as well as monitoring orbiting satellites and space debris.
In February 2008, USSTRATCOM succeeded in destroying a satellite, USA193, about to re-enter the earth's atmosphere.
USSTRATCOM also supported United States Africa Command's 2011 military intervention in Libya in a variety of ways, including long-range conventional strikes and intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR).
An intention by the U.S. Air Force to create a 'cyber command' was announced in October 2006. On 21 May 2010, part of USSTRATCOM's responsibility regarding cyber-warfare operations was spun off into a 10th Unified Command, the United States Cyber Command. As a result, USSTRATCOM's Joint Task Force-Global Network Operations
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGra ...
(JTF-GNO) and Joint Functional Component Command – Network Warfare
The Joint Functional Component Command – Network Warfare (JFCC-NW) at Fort Meade, Maryland was a subordinate component command of United States Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM) active from 2005 to 2010. It was responsible for coordinating offensiv ...
(JFCC-NW) were disestablished.
List of combatant commanders
See also
*Nuclear weapons and the United States
The United States was the first country to manufacture nuclear weapons and is the only country to have used them in combat, with the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in World War II. Before and during the Cold War, it conducted 1,054 nucl ...
References
External links
United States Strategic Command Official Website
US Strategic Command Airborne Command Post Fact Sheet
Air Force Magazine
Journal of the Air Force Assoc., August 2008.
GAO Report: Additional Actions Needed by U.S. Strategic Command to Strengthen Implementation of Its Many Missions and New Organization
{{Strategic forces Strategic Command Military units and formations established in 1992 1992 establishments in the United States Military units and formations in Nebraska Organizations based in Omaha, Nebraska United States nuclear command and control Strategic forces