Undernutrition In Children on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Undernutrition in children, occurs when children do not consume enough calories, protein, or
Safer water, better health вАУ Costs, benefits and sustainability of interventions to protect and promote health
World Health Organization (WHO), Geneva, Switzerland The main causes of malnutrition are often related to
 Linked to of all child deaths,
Linked to of all child deaths,
 Inadequate food intake such as a lack of proteins can lead to Kwashiorkor, Marasmus and other forms of
Inadequate food intake such as a lack of proteins can lead to Kwashiorkor, Marasmus and other forms of
 The
The
micronutrients
Micronutrients are nutrient, essential dietary elements required by organisms in varying quantities throughout life to orchestrate a range of physiological functions to maintain health. Micronutrient requirements differ between organisms; for exam ...
to maintain good health. It is common globally and may result in both short and long term irreversible adverse health outcomes. Undernutrition is sometimes used synonymously with malnutrition, however, malnutrition could mean both undernutrition or overnutrition (causing childhood obesity). The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
(WHO) estimates that malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
accounts for 54 percent of child mortality worldwide, which is about 1 million children. Another estimate, also by WHO, states that childhood underweight is the cause for about 35% of all deaths of children under the age of five worldwide.Pr√Љss-√Ьst√Љn, A., Bos, R., Gore, F., Bartram, J. (2008)Safer water, better health вАУ Costs, benefits and sustainability of interventions to protect and promote health
World Health Organization (WHO), Geneva, Switzerland The main causes of malnutrition are often related to
poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in ...
: unsafe water, inadequate sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
or insufficient hygiene
Hygiene is a series of practices performed to preserve health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refer ...
, factors related to society, diseases, maternal factors, gender
Gender is the range of characteristics pertaining to femininity and masculinity and differentiating between them. Depending on the context, this may include sex-based social structures (i.e. gender roles) and gender identity. Most cultures u ...
issues as well as other factors.
Background
 Linked to of all child deaths,
Linked to of all child deaths, malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
is especially dangerous for women and children. Malnourished women will usually have malnourished fetuses while they are pregnant, which can lead to physically and mentally stunted children, creating a cycle of malnutrition and underdevelopment. One of the most severe at risk populations are children under 5. Malnutrition during the early stages of development can have negative and severe effects on growth and intellectual development. This effect on a child's intellectual quotient makes it harder for them later in life to achieve their true potential abilities. Breaking the cycle of malnutrition during early childhood development can break the cycle of intergenerational poverty among poor communities.
There are a variety of ways in which malnutrition can affect the body. Globally, 162 million children show symptoms of malnutrition such as stunting, which is an indicator of malnourishment. The WHO reported that two out of five children that are stunted live in Southern Asia, however Africa is the only region where there is an increasing number of stunted children. Common micronutrient deficiencies are iron, zinc, iodine, and vitamin A. Micronutrient deficiencies can cause an increase of illness due to a compromised immune systems or abnormal physiology and development.
Protein-Energy Malnutrition (PEM) is another form of malnutrition that affects children. PEM can appear as conditions called marasmus, kwashiorkor, and an intermediate state of marasmus-kwashiorkor. Although malnutrition can have severe and lasting health effects on women and children, they are still susceptible to other water-related dangers.
Signs and symptoms

Measures
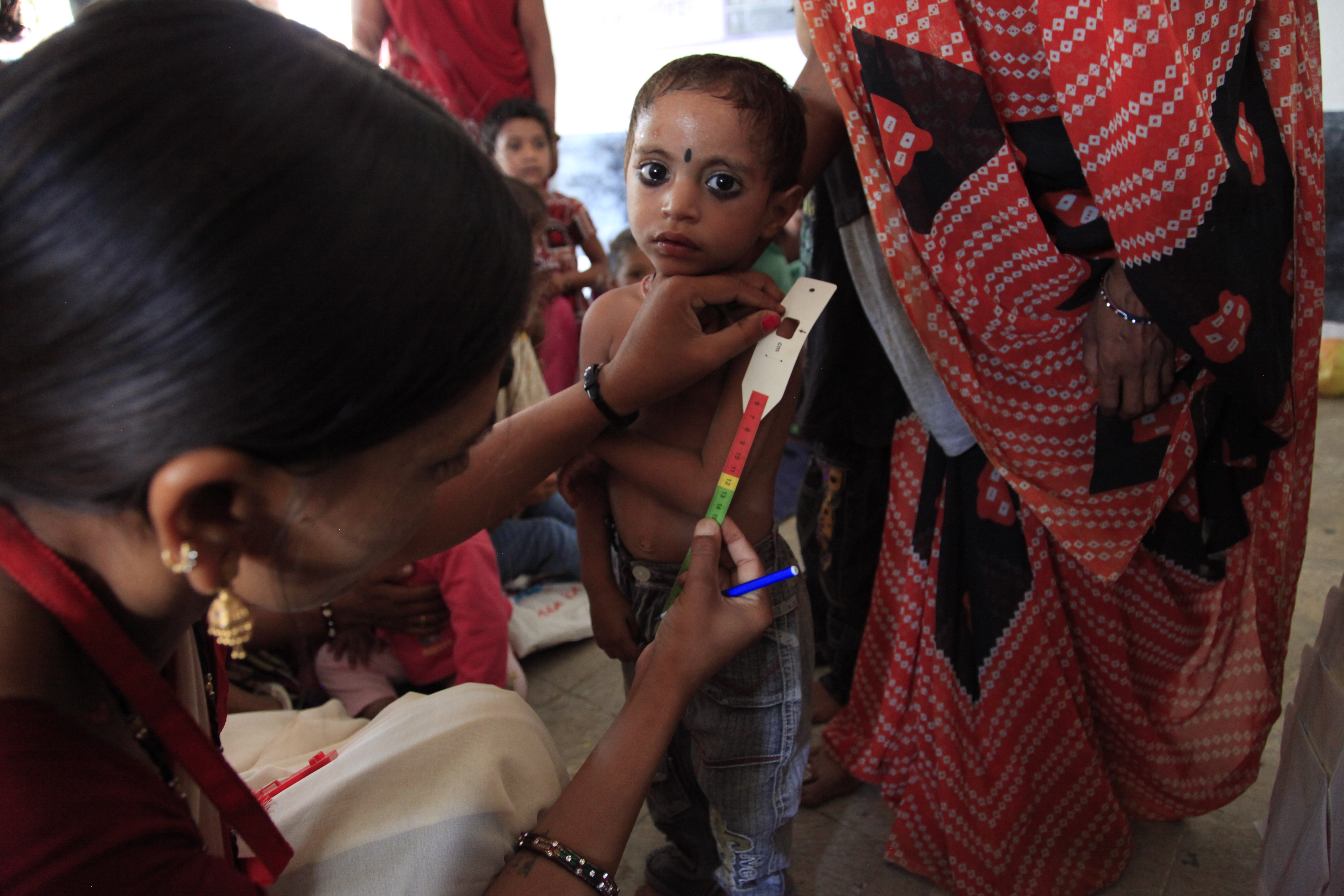
There are three commonly used measures for detectingmalnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
in children:
* stunting (extremely low height for age),
* underweight (extremely low weight for age), and
* wasting (extremely low weight for height).
These measures of malnutrition are interrelated, but studies for the World Bank found that only 9 percent of children exhibit stunting, underweight, and wasting.
Children with severe acute malnutrition are very thin, but they often also have swollen hands and feet, making the internal problems more evident to health workers.
Children with severe malnutrition are very susceptible to infection.
Effects later in life
Undernutrition in children causes direct structural damage to the brain and impairs infant motor development and exploratory behavior. Children who are undernourished before age two and gain weight quickly later in childhood and in adolescence are at high risk of chronic diseases related to nutrition. Studies have found a strong association between undernutrition and child mortality. Once malnutrition is treated, adequate growth is an indication of health and recovery. Even after recovering from severe malnutrition, children often remainstunted
Stunted growth is a reduced growth rate in human development. It is a primary manifestation of malnutrition (or more precisely undernutrition) and recurrent infections, such as diarrhea and helminthiasis, in early childhood and even before birth, ...
for the rest of their lives.
Even mild degrees of malnutrition double the risk of mortality for respiratory and diarrheal disease mortality and malaria. This risk is greatly increased in more severe cases of malnutrition.
Undernourished girls tend to grow into short adults and are more likely to have small children.
Prenatal malnutrition and early life growth patterns can alter metabolism and physiological patterns and have lifelong effects on the risk of cardiovascular disease. Children who are undernourished are more likely to be short in adulthood, have lower educational achievement and economic status, and give birth to smaller infants. Children often face malnutrition during the age of rapid development, which can have long-lasting impacts on health.
Causes
Inadequate food intake, infections, psychosocial deprivation, the environment (lack of sanitation and hygiene),social inequality
Social inequality occurs when resources in a given society are distributed unevenly, typically through norms of allocation, that engender specific patterns along lines of socially defined categories of persons. It posses and creates gender c ...
and perhaps genetics contribute to childhood malnutrition.
Inadequate food intake
 Inadequate food intake such as a lack of proteins can lead to Kwashiorkor, Marasmus and other forms of
Inadequate food intake such as a lack of proteins can lead to Kwashiorkor, Marasmus and other forms of ProteinвАУenergy malnutrition
ProteinвАУenergy malnutrition (PEM), sometimes called protein-energy undernutrition (PEU), is a form of malnutrition that is defined as a range of conditions arising from coincident lack of dietary protein and/or energy (calories) in varying propo ...
.
Sanitation
 The
The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
estimated in 2008 that globally, half of all cases of undernutrition in children under five were caused by unsafe water, inadequate sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
, or insufficient hygiene. This link is often due to repeated diarrhea and intestinal worm infections as a result of inadequate sanitation. However, the relative contribution of diarrhea to undernutrition and, in turn, stunting remains controversial.
Social inequality
In almost all countries, the poorest quintile of children has the highest rate of malnutrition. However, inequalities in malnutrition between children of poor and rich families vary from country to country, with studies finding large gaps in Peru and very small gaps in Egypt. In 2000, rates of child malnutrition were much higher in low- income countries (36 percent) compared to middle-income countries (12 percent) and the United States (1 percent). Studies in Bangladesh in 2009 found that the mother's illiteracy, low household income, higher number of siblings, less access to mass media, less supplementation of diets, unhygienic water andsanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
are associated with chronic and severe malnutrition in children.
Diseases
Diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin wi ...
and other infections can cause malnutrition through decreased nutrient absorption, decreased intake of food, increased metabolic requirements, and direct nutrient loss. Parasite infections, in particular intestinal worm infections (helminthiasis), can also lead to malnutrition. A leading cause of diarrhea and intestinal worm infections in children in developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
is a lack of sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
and hygiene
Hygiene is a series of practices performed to preserve health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refer ...
. Other diseases that cause chronic intestinal inflammation may lead to malnutrition, such as some cases of untreated celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barle ...
and inflammatory bowel disease.
Children with chronic diseases like HIV have a higher risk of malnutrition, since their bodies cannot absorb nutrients as well. Diseases such as measles are a major cause of malnutrition in children; thus, immunizations present a way to relieve the burden.
Maternal factors
The nutrition of children 5 years and younger depends strongly on the nutrition level of their mothers during pregnancy andbreastfeeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that br ...
.
Infants born to young mothers who are not fully developed are found to have low birth weights. The level of maternal nutrition during pregnancy can affect a newborn baby's body size and composition. Iodine deficiency in mothers usually causes brain damage in their offspring, and some cases cause extreme physical and intellectual disability. This affects the children's ability to achieve their full potential. In 2011 UNICEF reported that 30 percent of households in the developing world were not consuming iodized salt, which accounted for 41 million infants and newborns in whom iodine deficiency could still be prevented. Maternal body size is strongly associated with the size of newborn children.
Short stature of the mother and poor maternal nutrition stores increase the risk of intrauterine growth retardation
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), or fetal growth restriction, refers to poor growth of a fetus while in the womb during pregnancy. IUGR is defined by clinical features of malnutrition and evidence of reduced growth regardless of an infant's ...
(IUGR). However, environmental factors can weaken the effect of IUGR on cognitive performance.
Gender
A study in Bangladesh in 2008 reported that rates of malnutrition were higher in female children than male children. Other studies show that, at the national level, differences between undernutrition prevalence rates between young boys and girls are generally small. Girls often have a lower nutritional status in South and Southeastern Asia compared to boys. In other developing regions, the nutritional status of girls is slightly higher.Diagnosis
Measurements of a child's growth provide the key information for the presence of malnutrition. However, weight and height measurements alone can lead to failure to recognize kwashiorkor and an underestimation of the severity of malnutrition in children. Since undernourished children are also more likely to die from preventable infections, there is some research into developing a rapid diagnostic tool to detect malnourishment and common infections from a drop of blood. This research was spearheaded by Evelyn Gitau.Prevention
Measures have been taken to reduce child malnutrition. Studies for the World Bank found that, from 1970 to 2000, the number of malnourished children decreased by 20 percent indeveloping countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
. Iodine supplement trials in pregnant women have been shown to reduce offspring deaths during infancy and early childhood by 29 percent. However, universal salt iodization has largely replaced this intervention.
The Progresa program in Mexico combined conditional cash transfers with nutritional education and micronutrient-fortified food supplement
A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement one's diet by taking a pill, capsule, tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients either extracted from food sources or that are synthetic in order ...
s; this resulted in a 10 percent reduction in the prevalence of stunting in children 12вАУ36 months old. Milk fortified with zinc and iron reduced the incidence of diarrhea by 18 percent in a study in India.
In Nigeria, the use of imported Ready to Use Therapeutic Food (RUTF) has been used to combat malnutrition in the North. However, research has shown that ''Soy Kunu'', a locally sourced and prepared blend consisting of peanut, millet, and soya beans, contains the components of the Ready to Use Therapeutic Food (RUTF) and this has been used massively to reduce malnutrition in the north.
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding can reduce rates of malnutrition and dehydration caused by diarrhea, but mothers are sometimes wrongly advised not to breastfeed their children. Breastfeeding has been shown to reduce mortality in infants and young children. Since only 38 percent of children worldwide under 6 months are exclusively breastfed, education programs could have large impacts on children's malnutrition rates. However, breastfeeding cannot fully prevent PEM if not enough nutrients are consumed.Treatment
Treatment withantibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
s such as amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is an antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infection, strep throat, pneumonia, skin infections, and urinary tract infections among others. It is taken by mouth, or less c ...
or cefdinir improves the response and survival rate of severely malnourished children to an outpatient treatment plan which provided therapeutic food
Therapeutic foods are foods designed for specific, usually nutritional, therapeutic purposes as a form of dietary supplement. The primary examples of therapeutic foods are used for emergency feeding of malnourished children or to supplement th ...
. This confirms the recommendation, "In addition to the provision of RUTF eady-to-use therapeutic food children need to receive a short course of basic oral medication to treat infections." contained in "Community-based management of severe acute malnutrition, A Joint Statement by the World Health Organization, the World Food Programme
The World Food Programme; it, Programma alimentare mondiale; es, Programa Mundial de Alimentos; ar, Ў®Ў±ўЖЎІўЕЎђ ЎІўДЎ£ЎЇЎ∞ўКЎ© ЎІўДЎєЎІўДўЕўК, translit=barnamaj al'aghdhiat alealami; russian: –Т—Б–µ–Љ–Є—А–љ–∞—П –њ—А–Њ–і–Њ–≤–Њ–ї—М—Б—В–≤–µ–љ– ...
, the United Nations System Standing Committee on Nutrition and the United Nations Children's Fund."
Epidemiology
The World Health Organization estimates that malnutrition accounts for 54 percent of child mortality worldwide, about 1 million children. Another estimate also by WHO states that childhood underweight is the cause for about 35% of all deaths of children under the age of five years worldwide. According to a 2008 review, an estimated 178 million children under age 5 arestunted
Stunted growth is a reduced growth rate in human development. It is a primary manifestation of malnutrition (or more precisely undernutrition) and recurrent infections, such as diarrhea and helminthiasis, in early childhood and even before birth, ...
, most of whom live in sub-Saharan Africa. A 2008 review of malnutrition found that about 55 million children are wasted, including 19 million who have severe wasting or severe acute malnutrition. In 2020, a research paper that mapped stunting, wasting, and underweight among children across 105 low- and middle-income countries found that only five countries were expected to meet global nutrition targets in all second administrative subdivisions.
As underweight children are more vulnerable to almost all infectious diseases, the ''indirect'' disease burden of malnutrition is estimated to be an order of magnitude higher than the disease burden of the ''direct'' effects of malnutrition. The combination of direct and indirect deaths from malnutrition caused by unsafe water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH
WASH (or Watsan, WaSH) is an acronym that stands for "water, sanitation and hygiene". It is used widely by non-governmental organizations and aid agencies in developing countries. The purposes of providing access to WASH services include achievin ...
) practices is estimated to lead to 860,000 deaths per year in children under five years of age.
See also
* Child nutrition in AustraliaReferences
Further reading
* {{Authority control Malnutrition Pediatrics