Umayyad Conquest Of Spain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
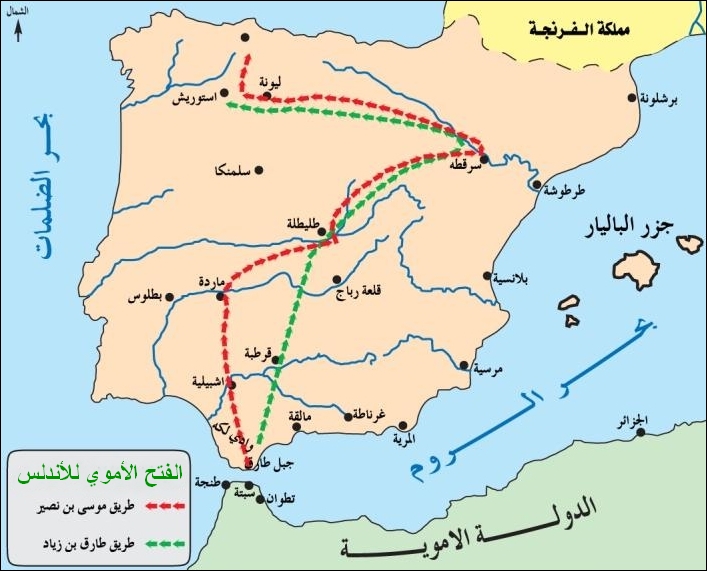 The Umayyad conquest of Hispania, also known as the Umayyad conquest of the Visigothic Kingdom, was the initial expansion of the Umayyad Caliphate over Hispania (in the Iberian Peninsula) from 711 to 718. The conquest resulted in the decline of the Visigothic Kingdom and the establishment of the Umayyad Wilayah of Al-Andalus.
During the caliphate of the sixth Umayyad caliph
The Umayyad conquest of Hispania, also known as the Umayyad conquest of the Visigothic Kingdom, was the initial expansion of the Umayyad Caliphate over Hispania (in the Iberian Peninsula) from 711 to 718. The conquest resulted in the decline of the Visigothic Kingdom and the establishment of the Umayyad Wilayah of Al-Andalus.
During the caliphate of the sixth Umayyad caliph
 The Chronicle of 754 stated that "the entire army of the Goths, which had come with him odericfraudulently and in rivalry out of hopes of the Kingship, fled". This is the only contemporary account of the battle and the paucity of detail led many later historians to invent their own. The location of the battle, though not clear, was probably the
The Chronicle of 754 stated that "the entire army of the Goths, which had come with him odericfraudulently and in rivalry out of hopes of the Kingship, fled". This is the only contemporary account of the battle and the paucity of detail led many later historians to invent their own. The location of the battle, though not clear, was probably the  In 714, Musa ibn Nusayr headed north-west up the Ebro river to overrun the western Basque regions and the Cantabrian mountains all the way to Gallaecia, with no relevant or attested opposition. During the period of the second (or first, depending on the sources) Arab governor Abd al-Aziz ibn Musa (714–716), the principal urban centres of Catalonia surrendered. In 714, his father, Musa ibn Nusayr, advanced and overran Soria, the western Basque regions, Palencia, and as far west as Gijón or León, where a Berber governor was appointed with no recorded opposition. The northern areas of Iberia drew little attention from the conquerors and were hard to defend when taken. The high western and central sub-Pyrenean valleys remained unconquered.
At this time, Umayyad troops reached Pamplona, and the Basque town submitted after a compromise was brokered with Arab commanders to respect the town and its inhabitants, a practice that was common in many towns of the Iberian Peninsula. The Umayyad troops met little resistance. Considering that era's communication capabilities, three years was a reasonable time spent almost reaching the Pyrenees, after making the necessary arrangements for the towns' submissions and their future governance.
In 714, Musa ibn Nusayr headed north-west up the Ebro river to overrun the western Basque regions and the Cantabrian mountains all the way to Gallaecia, with no relevant or attested opposition. During the period of the second (or first, depending on the sources) Arab governor Abd al-Aziz ibn Musa (714–716), the principal urban centres of Catalonia surrendered. In 714, his father, Musa ibn Nusayr, advanced and overran Soria, the western Basque regions, Palencia, and as far west as Gijón or León, where a Berber governor was appointed with no recorded opposition. The northern areas of Iberia drew little attention from the conquerors and were hard to defend when taken. The high western and central sub-Pyrenean valleys remained unconquered.
At this time, Umayyad troops reached Pamplona, and the Basque town submitted after a compromise was brokered with Arab commanders to respect the town and its inhabitants, a practice that was common in many towns of the Iberian Peninsula. The Umayyad troops met little resistance. Considering that era's communication capabilities, three years was a reasonable time spent almost reaching the Pyrenees, after making the necessary arrangements for the towns' submissions and their future governance.

 In the first stage of the invasion, the armies were made up of
In the first stage of the invasion, the armies were made up of
 The Umayyad conquest of Hispania, also known as the Umayyad conquest of the Visigothic Kingdom, was the initial expansion of the Umayyad Caliphate over Hispania (in the Iberian Peninsula) from 711 to 718. The conquest resulted in the decline of the Visigothic Kingdom and the establishment of the Umayyad Wilayah of Al-Andalus.
During the caliphate of the sixth Umayyad caliph
The Umayyad conquest of Hispania, also known as the Umayyad conquest of the Visigothic Kingdom, was the initial expansion of the Umayyad Caliphate over Hispania (in the Iberian Peninsula) from 711 to 718. The conquest resulted in the decline of the Visigothic Kingdom and the establishment of the Umayyad Wilayah of Al-Andalus.
During the caliphate of the sixth Umayyad caliph al-Walid I
Al-Walid ibn Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan ( ar, الوليد بن عبد الملك بن مروان, al-Walīd ibn ʿAbd al-Malik ibn Marwān; ), commonly known as al-Walid I ( ar, الوليد الأول), was the sixth Umayyad Caliphate, Umayyad ca ...
(), forces led by Tariq ibn Ziyad disembarked in early 711 in Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
at the head of an army consisting of Berbers
, image = File:Berber_flag.svg
, caption = The Berber ethnic flag
, population = 36 million
, region1 = Morocco
, pop1 = 14 million to 18 million
, region2 = Algeria
, pop2 ...
from north Africa. After defeating the Visigothic king Roderic
Roderic (also spelled Ruderic, Roderik, Roderich, or Roderick; Spanish and pt, Rodrigo, ar, translit=Ludharīq, لذريق; died 711) was the Visigothic king in Hispania between 710 and 711. He is well-known as "the last king of the Goths". He ...
at the decisive Battle of Guadalete
The Battle of Guadalete was the first major battle of the Umayyad conquest of Hispania, fought in 711 at an unidentified location in what is now southern Spain between the Christian Visigoths under their king, Roderic, and the invading forces of t ...
, Tariq was reinforced by an Arab force led by his superior '' wali'' Musa ibn Nusayr and continued northward. By 717, the combined Arab-Berber force had crossed the Pyrenees into Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septima ...
. They occupied further territory in Gaul until 759.
Background
The historianal-Tabari
( ar, أبو جعفر محمد بن جرير بن يزيد الطبري), more commonly known as al-Ṭabarī (), was a Muslim historian and scholar from Amol, Tabaristan. Among the most prominent figures of the Islamic Golden Age, al-Tabari ...
transmits a tradition attributed to the Caliph Uthman who stated that the road to Constantinople was through Hispania, "Only through Spain can Constantinople be conquered. If you conquer (Spain) you will share the reward of those who conquer (Constantinople)." The conquest of Hispania followed the conquest of the Maghreb. Walter Kaegi
Walter Emil Kaegi (8 november 1937, New Albany, Indiana - February 24, 2022) was a historian and scholar of Byzantine history, professor of history at the University of Chicago, and a Voting Member of The Oriental Institute. He received his B.A. ...
says Tabari's tradition is dubious, arguing that conquest of the far western reaches of the Mediterranean Sea was motivated by military, political and religious opportunities. He considers that it was not a shift in direction due to the Muslims failing to conquer Constantinople in 678.
Precisely what happened in Iberia in the early 8th century is uncertain. There is one contemporary Christian source, the '' Chronicle of 754'' (which ends on that date), regarded as reliable but often vague. There are no contemporary Muslim accounts, and later Muslim compilations, such as that of Al-Maqqari from the 17th century, reflect later ideological influence. Roger Collins writes that this paucity of early sources means that detailed specific claims need to be regarded with caution.
The Umayyads took control of Hispania from the Visigoths, who had ruled for roughly 300 years. At the time of the conquest, the Visigothic upper class was beginning to fracture, and had many problems with succession and maintaining power. This was partially due to the fact that the Visigoths were only one or two percent of the population, making it difficult to maintain control over a rebellious population.
The ruler at the time was King Roderic but the manner of his ascent to the throne is unclear; there are accounts of a dispute with Achila II
Achila II (also spelled Agila, Aquila, or Akhila; died ''c.'' 714) was the Visigothic king of Hispania from 710 or 711 until his death. The kingdom he ruled was restricted to the northeast of the old Hispanic kingdom on account of the Arabo-Berber ...
, son of his predecessor Wittiza
Wittiza (''Witiza'', ''Witica'', ''Witicha'', ''Vitiza'', or ''Witiges''; 687 – probably 710) was the Visigothic King of Hispania from 694 until his death, co-ruling with his father, Egica, until 702 or 703.
Joint rule
Early in his reign, Ergi ...
. Later regnal lists, which cite Achila and omit Roderic, are consistent with the contemporary account of civil war. Numismatic
Numismatics is the study or collection of currency, including coins, tokens, paper money, medals and related objects.
Specialists, known as numismatists, are often characterized as students or collectors of coins, but the discipline also includ ...
evidence suggests a division of royal authority, with several coinages being struck, and that Achila II remained king of the Tarraconsense (the Ebro basin) and Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septima ...
until circa 713. The nearly contemporary ''Chronicle of 754'' describes Roderic as a usurper who earned the allegiance of other Goths by deception, while the less reliable late-ninth century ''Chronicle of Alfonso III'' shows a clear hostility towards Oppa, bishop of Seville (or Toledo) and probably a brother of Wittiza, who appears in an unlikely heroic dialogue with Pelagius.
There is also a story of one Julian, count of Ceuta
Julian, Count of Ceuta ( es, Don Julián, Conde de Ceuta,, ar, يليان, (' , ''Youliān Kont Sabteh''; in Ibn 'Abd al-Hakam, بؙلْيان, ''Bulyan'', the latter is treated by the editor of the Arabic text, Torrey, as a copying error. 'A ...
, whose wife or daughter was raped by Roderic and who sought help from Tangier. However, these stories are not included in the earliest accounts of the conquest.
Musa ibn Nusayr's first reconnaissance missions to Hispania returned with reports of "great splendor and beauty" which increased Muslim desires to invade Hispania. During one of the multiple raids in 710, the Muslims “made several inroads into the mainland, which produced a rich spoil and several captives, who were so handsome that Musa and his companions had never seen the like of them.”
The natives of Hispania viewed the Berbers in a similar way as the Byzantines viewed the Arabs: as barbarians. They feared an atttack by them. According to al-Maqqari’s chronicle:
During an early raid, a Berber chieftain “set fire to their houses and fields, and burnt also a church very much venerated amongst them. He then put to the sword such of its inhabitants as he met, and, making a few prisoners, returned safe to Africa.”
Invasion
According to the later chronicler Ibn Abd al-Hakam, the Tangier governor Tariq ibn Ziyad led a raiding force of approximately 1,700 men from North Africa to southern Spain in 711. Ibn Abd al-Hakam reports, one and a half centuries later, that "the people of Andalus did not observe them, thinking that the vessels crossing and recrossing were similar to the trading vessels which for their benefit plied backwards and forwards". They defeated the Visigothic army, led by King Roderic, in a decisive battle at Guadalete in 712. Tariq's forces were then reinforced by those of his superior, the wali Musa ibn Nusayr, who planned a second invasion, and within a few years both took control of more than two-thirds of the Iberian Peninsula. The second invasion comprised 18,000 mostly Arab troops, who rapidly captured Seville and then defeated Roderick's supporters at Mérida and met up with Tariq's troops at Talavera. The following year the combined forces continued intoGalicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
and the northeast, capturing Léon
Leon, Léon (French) or León (Spanish) may refer to:
Places
Europe
* León, Spain, capital city of the Province of León
* Province of León, Spain
* Kingdom of León, an independent state in the Iberian Peninsula from 910 to 1230 and again fro ...
, Astorga and Zaragoza.
According to the Muslim historian Al-Tabari
( ar, أبو جعفر محمد بن جرير بن يزيد الطبري), more commonly known as al-Ṭabarī (), was a Muslim historian and scholar from Amol, Tabaristan. Among the most prominent figures of the Islamic Golden Age, al-Tabari ...
,See: ''History of the Prophets and Kings
The ''History of the Prophets and Kings'' ( ar, تاريخ الرسل والملوك ''Tārīkh al-Rusul wa al-Mulūk''), more commonly known as ''Tarikh al-Tabari'' () or ''Tarikh-i Tabari'' or ''The History of al-Tabari '' ( fa, تاریخ طب� ...
'' (''Tarikh al-Tabari)'' Iberia was first invaded some sixty years earlier during the caliphate of Uthman (Rashidun
, image = تخطيط كلمة الخلفاء الراشدون.png
, caption = Calligraphic representation of Rashidun Caliphs
, birth_place = Mecca, Hejaz, Arabia present-day Saudi Arabia
, known_for = Companions of t ...
era). Another prominent Muslim historian of the 13th century, Ibn Kathir
Abū al-Fiḍā’ ‘Imād ad-Dīn Ismā‘īl ibn ‘Umar ibn Kathīr al-Qurashī al-Damishqī (Arabic: إسماعيل بن عمر بن كثير القرشي الدمشقي أبو الفداء عماد; – 1373), known as Ibn Kathīr (, was ...
, quoted the same narration, pointing to a campaign led by Abd Allah bin Nafi al Husayn and Abd Allah bin Nafi al Abd al Qays in 32 AH (654 CE), but there is no solid evidence about this campaign.
The first expedition led by Tariq consisted mainly of Berbers
, image = File:Berber_flag.svg
, caption = The Berber ethnic flag
, population = 36 million
, region1 = Morocco
, pop1 = 14 million to 18 million
, region2 = Algeria
, pop2 ...
, who had themselves only recently come under Muslim influence. It is probable that this army represented a continuation of a historic pattern of large-scale raids into Iberia dating to the pre-Islamic period, and hence it has been suggested that actual conquest was not originally planned. Both the ''Chronicle of 754'' and later Muslim sources speak of raiding activity in previous years, and Tariq's army may have been present for some time before the decisive battle. It has been argued that this possibility is supported by the fact that the army was led by a Berber and that Musa, who was the Umayyad Governor of North Africa, only arrived the following year – the governor had not deigned to lead a mere raid, but hurried across once the unexpected triumph became clear. The historian Abd al-Wāḥid Dhannūn Ṭāhā mentions that several Arab-Muslim writers mention the fact that Tariq decided to cross the strait without informing his superior and wali Musa. The Chronicle of 754 states that many townspeople fled to the hills rather than defend their cities, which might support the view that this was expected to be a temporary raid rather than a permanent change of government. The Chronicle of 754 stated that "the entire army of the Goths, which had come with him odericfraudulently and in rivalry out of hopes of the Kingship, fled". This is the only contemporary account of the battle and the paucity of detail led many later historians to invent their own. The location of the battle, though not clear, was probably the
The Chronicle of 754 stated that "the entire army of the Goths, which had come with him odericfraudulently and in rivalry out of hopes of the Kingship, fled". This is the only contemporary account of the battle and the paucity of detail led many later historians to invent their own. The location of the battle, though not clear, was probably the Guadalete River
The Guadalete River is located almost entirely in the Spanish Province of Cádiz, rising in the Sierra de Grazalema Natural Park at an elevation of about , and running for into the Bay of Cádiz at El Puerto de Santa Maria, north of the city of ...
.
Roderic was believed to have been killed, and a crushing defeat would have left the Visigoths largely leaderless and disorganized, partly because the ruling Visigoth population is estimated to have been a mere 1 to 2% of the total population. While this isolation is said to have been "a reasonably strong and effective instrument of government"; it was highly "centralised to the extent that the defeat of the royal army left the entire land open to the invaders". The resulting power vacuum, which may have indeed caught Tariq completely by surprise, would have aided the Muslim conquest. It may have been equally welcome to the Hispano-Roman peasants who were probably – as D.W. Lomax claims – disillusioned by the prominent legal, linguistic and social divide between them and the "barbaric" and "decadent" Visigoth royal family. In 714, Musa ibn Nusayr headed north-west up the Ebro river to overrun the western Basque regions and the Cantabrian mountains all the way to Gallaecia, with no relevant or attested opposition. During the period of the second (or first, depending on the sources) Arab governor Abd al-Aziz ibn Musa (714–716), the principal urban centres of Catalonia surrendered. In 714, his father, Musa ibn Nusayr, advanced and overran Soria, the western Basque regions, Palencia, and as far west as Gijón or León, where a Berber governor was appointed with no recorded opposition. The northern areas of Iberia drew little attention from the conquerors and were hard to defend when taken. The high western and central sub-Pyrenean valleys remained unconquered.
At this time, Umayyad troops reached Pamplona, and the Basque town submitted after a compromise was brokered with Arab commanders to respect the town and its inhabitants, a practice that was common in many towns of the Iberian Peninsula. The Umayyad troops met little resistance. Considering that era's communication capabilities, three years was a reasonable time spent almost reaching the Pyrenees, after making the necessary arrangements for the towns' submissions and their future governance.
In 714, Musa ibn Nusayr headed north-west up the Ebro river to overrun the western Basque regions and the Cantabrian mountains all the way to Gallaecia, with no relevant or attested opposition. During the period of the second (or first, depending on the sources) Arab governor Abd al-Aziz ibn Musa (714–716), the principal urban centres of Catalonia surrendered. In 714, his father, Musa ibn Nusayr, advanced and overran Soria, the western Basque regions, Palencia, and as far west as Gijón or León, where a Berber governor was appointed with no recorded opposition. The northern areas of Iberia drew little attention from the conquerors and were hard to defend when taken. The high western and central sub-Pyrenean valleys remained unconquered.
At this time, Umayyad troops reached Pamplona, and the Basque town submitted after a compromise was brokered with Arab commanders to respect the town and its inhabitants, a practice that was common in many towns of the Iberian Peninsula. The Umayyad troops met little resistance. Considering that era's communication capabilities, three years was a reasonable time spent almost reaching the Pyrenees, after making the necessary arrangements for the towns' submissions and their future governance.
New territorial and civil administration

A preference for treaties
In 713, Abd al-Aziz ibn Musa subdued the forces of the Visigothic count Theodemir (or ''Tudmir''), who had taken over southeastern Iberia from his base in Murcia after the power vacuum following king Roderic's defeat. Theudimer then signed a conditional capitulation by which his lands were made into an autonomous client state under Umayyad rule ("the rule of God"). Abd Al-Aziz sent messages to the governors of the different Islamic provinces, denouncing non-Muslims: His government and the Christian beliefs of his subjects were respected; in exchange, he pledged to pay a tax (''jizya
Jizya ( ar, جِزْيَة / ) is a per capita yearly taxation historically levied in the form of financial charge on dhimmis, that is, permanent Kafir, non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The jizya tax has been unde ...
'') and to hand over any rebels plotting against Umayyad rule or the Islamic religion. In this way, the life of many inhabitants remained much the same as before Tariq's and Musa's campaigns. The treaty signed with Theudimer set a precedent for the whole of Iberia, and towns surrendering to Umayyad troops experienced a similar fate, including probably the '' muwallad'' Banu Qasi
The Banu Qasi, Banu Kasi, Beni Casi ( ar, بني قسي or بنو قسي, meaning "sons" or "heirs of Cassius"), Banu Musa, or al-Qasawi were a Muladí (local convert) dynasty that in the 9th century ruled the Upper March, a frontier ter ...
based in the Ebro valley, and other counts and landowners.
In exception to this pattern, some towns (Cordova, Toledo, etc.) were stormed and captured unconditionally by the Umayyads, to be governed by direct Arab rule. In the area thought to be part of King Roderic's territory, Mérida also staged a prolonged resistance to the Umayyad advance, but was ultimately conquered in mid-summer 712. As of 713 (or 714), the last Visigothic king, Ardo
Ardo (or ''Ardonus'', possibly short for ''Ardabastus''; died 720/721) is attested as the last of all Visigothic kings of Hispania, reigning from 713 or likely 714 until his death. The Visigothic Kingdom was already severely reduced in power and a ...
, took over from Achila II, with effective control just over Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septima ...
, and probably the eastern Pyrenean threshold and coastal areas of the Tarraconense.
Islamic laws did not apply to all the subjects of the new rulers. Christians were ruled by their own Visigothic law code (''Forum Iudicum'') as before. In most of the towns, ethnic communities remained segregated, and newly arriving ethnic groups (Syrians, Yemenites, Berbers and others) would erect new boroughs outside existing urban areas. However, this would not apply to towns under direct Umayyad rule. In Cordova, the cathedral was partitioned and shared to provide for the religious needs of Christians and Muslims. This situation lasted some 40 years until Abd ar-Rahman's conquest of southern Spain (756).
Taxation
An early governor (wali) of al-Andalus, al-Hurr ibn Abd al-Rahman al-Thaqafi, spread the rule of the Umayyad Caliphate up to the Ebro valley and the northeastern borders of Iberia, pacifying most of the territory and initiating in 717 the first forays across the Pyrenees intoSeptimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septima ...
. In addition, he laid out the foundations of Umayyad civil administration in Iberia, by sending civil administration officials (''judges'') to conquered towns and lands guarded by garrisons established usually next to the population nuclei.
Moreover, al-Hurr restored lands to their previous Christian landowners, which may have added greatly to the revenue of the Umayyad governors and the caliph of Damascus, by increasingly imposing the vectigalia
Octroi (; fro, octroyer, to grant, authorize; Lat. ''auctor'') is a local tax collected on various articles brought into a district for consumption.
Antiquity
The word itself is of French origin. Octroi taxes have a respectable antiquity, being ...
on the former; this was a tax applied on a specific region or estate, and not per capitation (''jizya''). Only non-Muslims were subject to taxation, apart from a Muslim subject's compulsory alms-giving. The task of establishing a civil administration in conquered al-Andalus was essentially completed by the governor Yahya ibn Salama al-Kalbi 10 years later.
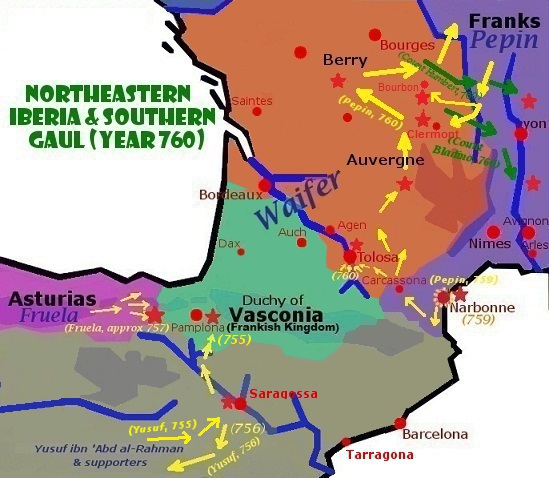
The period following al-Hurr's office saw the establishment of the Arabs in southern Septimania during Al-Samh ibn Malik al-Khawlani's tenure as wali. Narbonne fell (720), and no sooner had he garrisoned it than the Arab commander led an offensive against Toulouse. During this Umayyad thrust or its aftermath, King Ardo died (721).
Ethnic groups and the rise of conflicting internal tensions
 In the first stage of the invasion, the armies were made up of
In the first stage of the invasion, the armies were made up of Berbers
, image = File:Berber_flag.svg
, caption = The Berber ethnic flag
, population = 36 million
, region1 = Morocco
, pop1 = 14 million to 18 million
, region2 = Algeria
, pop2 ...
from northern regions of North Africa, together with different groups of Arabs from Western Asia. These peoples, clustered around the banner of the Umayyads did not mix together, remaining in separate towns and boroughs. The Berbers, recently subdued and superficially Islamized, were usually in charge of the most difficult tasks and the most rugged terrains, similar to the ones found in their North African homeland, while the Arabs occupied the gentler plains of southern Iberia.
Consequently, the Berbers went on to stations in Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
(possibly including Asturias) and the Upper Marches ( Ebro basin), but these lands remained unpleasant, humid and cold. The grievances resented by the Berbers under Arab rulers (attempts to impose a tax on Muslim Berbers, etc.) sparked rebellions in north Africa that expanded into Iberia. An early uprising took place in 730 when Uthman ibn Naissa
Uthman ibn Naissa () better known as Munuza, was a Berber governor depicted in different contradictory chronicles during the Umayyad conquest of Hispania.
Munuza in Asturias
One account says that he was the governor of Gijón (or possibly León) ...
(Munuza), master of the eastern Pyrenees (Cerretanya), allied with the duke Odo of Aquitaine and detached from Cordova.
Those internal frictions continually threatened (or sometimes may have spurred) the ever-expanding Umayyad military effort in al-Andalus during the conquest period. Around 739, on learning the news of Charles Martel's second intervention in Provence, Uqba ibn al-Hajjaj had to call off an expedition to the Lower Rhone in order to deal with the Berber revolt in the south instead. The following year, the Berber garrisons stationed in León, Astorga and other north-western outposts gave up their positions, and some of them even embraced the Christian religion. The Muslim settlement was thereafter established permanently south of the Douro's banks.
The Berber rebellions swept the whole of al-Andalus during Abd al-Malik ibn Katan al-Fihri's term as governor. Reinforcements were then called from the other end of the Mediterranean in a military capacity: the "Syrian" (actually Yemeni Arabs). The Berber rebellions were quelled in blood, and the Arab commanders came up reinforced after 742. Different Arab factions reached an agreement to alternate in office, but this did not last long, since Yusuf ibn 'Abd al-Rahman al-Fihri (opposed to the Umayyads) remained in power up to his defeat by Abd al-Rahman I in 756, and the establishment of the independent Umayyad Emirate of Cordova. It was in this period of unrest that the Frankish king Pepin finally captured Narbonne from the Andalusians (759).
In Yusuf's and Abd-ar-Rahman's fight for power in al-Andalus, the "Syrian" troops, a mainstay of the Umayyad Caliphate, split. For the most part, Arabs from the Mudhar
The Mudar ( ar, مُضَر) are one of the most powerful Adnanites, northern Arab tribal groupings.
History
The Mudar and Rabi'ah ibn Nizar, Rabi'a are recorded in central Arabia in the Arabic histories of the Pre-Islamic Arabia, pre-Islamic pe ...
and Qais Qais ( ar, قیس) is an Arabic given name. 'Qays' and 'Qai' are alternatives of Qais.
Notable people with the name include:
*Imru' al-Qais, Arabic poet in the 6th century
*Kais Saied (born 1958), Tunisian President
*Qais Ashfaq (born 1993), Britis ...
tribes sided with Yusuf, as did the indigenous (second or third generation) Arabs from northern Africa, while Yemeni units and some Berbers sided with Abd-ar-Rahman, probably born to a North African Berber mother himself. By 756, south and central al-Andalus (Cordova, Sevilla) were in the hands of Abd-ar-Rahman, but it took another 25 years for him to hold sway over the Upper Marches (Pamplona, Zaragoza, and all the northeast).
Aftermath and consequences
The Iberian Peninsula was the westernmost tip of the Umayyad Caliphate of Damascus and was under the rule of the governor of Ifriqiya. In 720, the caliph even considered abandoning the territory. The conquest was followed by a period of several hundred years during which most of the Iberian peninsula was known as Al-Andalus, dominated by Muslim rulers. Only a handful of new small Christian realms managed to reassert their authority across the faraway mountainous north of the peninsula. In 756, Abd al-Rahman I, a survivor of the recently overthrown Umayyad dynasty, landed in al-Andalus and seized power in Cordova and Seville, and proclaimed himself '' emir'' or ''malik'', removing any mentions of the Abbasid Caliphs from the Friday prayers. In the wake of these events, southern Iberia became ''de jure'' and ''de facto'' independent from the Abbasid Caliphate. Although this was not accepted outside al-Andalus and those North African territories with which it was affiliated, Abd al-Rahman, and especially his successors, considered that they were the legitimate continuation of the Umayyad caliphate, i.e. that their rule was more legitimate than that of the Abbasids. It seems that Abd ar-Rahman never considered establishing a separate principality. (See Caliphate of Córdoba.) During the unification of al-Andalus in the reign of Abd ar-Rahman before his death in 788, al-Andalus underwent centralization and slow but steady homogenization. The autonomous status of many towns and regions negotiated in the first years of the conquest was reversed by 778, in some cases much earlier (Pamplona by 742, for example). The Hispanic Church based in Toledo, whose status remained largely undiminished under the new rulers, fell out with the Roman Church during the Adoptionist controversy (late 8th century). Rome relied on an alliance with Charlemagne (in war with the Cordovan emirs) to defend its political authority and possessions, and went on to recognize the northern Asturian principality (''Gallaecia'') as a kingdom apart from Cordova, and Alfonso II as king. The population of al-Andalus, especially local nobles who aspired to a share in power, began to embraceIslam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
and the Arabic language. However, the majority of the population remained Christian (using the Mozarabic Rite), and Latin ( Mozarabic) remained the principal language until the 11th century. Historian Jessica Coope of University of Nebraska argues that the pre-modern Islamic conquest was unlike Christianization because the latter was "imposed on everyone as part of a negotiated surrender, and thus lacked the element of personal conviction that modern ideas about religious faith would require" while conquest of ''dar al-harb
In classical Islamic law, the major divisions are ''dar al-Islam'' (lit. territory of Islam/voluntary submission to God), denoting regions where Islamic law prevails, ''dar al-sulh'' (lit. territory of treaty) denoting non-Islamic lands which have ...
'' was not motivated by a goal of converting the population to Islam, but by the belief that everyone was better off under Islamic rule.
Abd ar-Rahman I founded an independent dynasty that survived until the 11th century. That line was succeeded by a variety of short and small emirates (''taifas'') unable to stop the push of the expanding northern Christian kingdoms. The Almoravids (1086–1094) and the Almohads (1146–1173) occupied al-Andalus next, and the Marinids in 1269, but that could not prevent the fragmentation of Muslim-ruled territory. The last Muslim emirate, Granada
Granada (,, DIN 31635, DIN: ; grc, Ἐλιβύργη, Elibýrgē; la, Illiberis or . ) is the capital city of the province of Granada, in the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. Granada is located at the fo ...
, was defeated by the armies of Castile (successor to Asturias) and Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to sou ...
under Isabella
Isabella may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Isabella (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters
* Isabella (surname), including a list of people
Places
United States
* Isabella, Alabama, an unincorpora ...
and Ferdinand in 1492. The last wave of expulsions of Spaniards of Muslim descent took place in 1614.
Chronology
As discussed above, much of the traditional narrative of the Conquest is more legend than reliable history. Some of the key events and the stories around them are outlined below. * 710 – Tariq ibn Ziyad, a Berber '' mawla'' of Musa ibn Nusayr, lands with 400 men and 100 horses on the tiny peninsula now calledGibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
(Jebel al Tarik : Mountain of Tariq), after his name.
* 711 – Musa ibn Nusayr, Governor of Ifriqiya in North Africa, dispatches Tariq into the Iberian Peninsula.
* 711 (July 19) – King Roderic
Roderic (also spelled Ruderic, Roderik, Roderich, or Roderick; Spanish and pt, Rodrigo, ar, translit=Ludharīq, لذريق; died 711) was the Visigothic king in Hispania between 710 and 711. He is well-known as "the last king of the Goths". He ...
k's army utterly routed in the Battle of Guadalete
The Battle of Guadalete was the first major battle of the Umayyad conquest of Hispania, fought in 711 at an unidentified location in what is now southern Spain between the Christian Visigoths under their king, Roderic, and the invading forces of t ...
somewhere in the Guadalquivir valley.
* 712 – Musa ibn Nusayr joins Tariq after the Battle of Guadalete
The Battle of Guadalete was the first major battle of the Umayyad conquest of Hispania, fought in 711 at an unidentified location in what is now southern Spain between the Christian Visigoths under their king, Roderic, and the invading forces of t ...
and both go on to attack towns and strongholds previously avoided. Abu Zora Tarif Abu Zora Tarif (fl. about 700) was an Umayyad general. He is best known for his participation in the Umayyad conquest of Hispania from July 710-712 AD and was near Algeciras
Algeciras ( , ) is a municipality of Spain belonging to the province of ...
lands in Algeciras.
* 713 – Theudimer Theodemir, Theodemar, Theudemer or Theudimer was a Germanic name common among the various Germanic peoples of early medieval Europe. According to Smaragdus of Saint-Mihiel (9th century), the form ''Theudemar'' is Frankish and ''Theudemir'' is Gothi ...
's conditional surrender, allowing him to remain lord of his south-eastern region around Murcia (Tudmir).
* 715 – Abd al-Aziz ibn Musa announces first wali of Andalus and marries the widow of King Roderick, Egilona Egilona (or Egilo) was a Visigothic noblewoman and the last known queen of the Visigoths. She was the wife first of Roderic, the Visigothic king (710–11), and then of ʿAbd al-ʿAzīz, Muslim governor (''wālī'') of al-Andalus (714–16). Her na ...
. Seville becomes the capital.
* 717–18 – Al-Hurr ibn Abd al-Rahman al-Thaqafi starts the first military campaigns into Gothic Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septima ...
.
* 719 – Al-Samh ibn Malik al-Khawlani, 4th wali, transfers the seat of Governor from Seville to Cordova. Barcelona and Narbonne captured.
* 721 – An Umayyad army led by Al-Samh crushed by duke Odo's Aquitanian army at the Battle of Toulouse ("Balat Al Shuhada" of Toulouse).
* 722 – An Umayyad patrol defeated by Pelagius at the Battle of Covadonga in the mountains of Asturias.
* 725 – Anbasa ibn Suhaym Al-Kalbi subdues all Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septima ...
, raids the Lower Rhone, and captures Autun and Sens
Sens () is a Communes of France, commune in the Yonne Departments of France, department in Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in north-central France, 120 km from Paris.
Sens is a Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture and the second city of the d ...
.
* 731 – Munuza defeated in Cerdanya
Cerdanya () or often La Cerdanya ( la, Ceretani or ''Ceritania''; french: Cerdagne; es, Cerdaña), is a natural comarca and historical region of the eastern Pyrenees divided between France and Spain. Historically it was one of the counties ...
by Abdul Rahman Al Ghafiqi.
* Spring 732 – An expedition led by the wali Al Ghafiqi vanquishes duke Odo at the Battle of the River Garonne
The Battle of the River Garonne, also known as the Battle of Bordeaux,Matthew Bennett ''The Hutchinson Dictionary of Ancient & Medieval Warfare'' 1579581161 1998 p319 "In 732 a large army of (70,000-80,000) men led by Abd ar-Rahman defeated the Aq ...
.
* October 732 – Al Ghafiqi totally routed by Charles Martel ( Mayor of the Palace at the Merovingian court) at the Battle of Tours ("Balat Al Shuhada" of Poitiers).
* 734 – Count Maurontus calls Umayyad forces on a military capacity into Arles, Avignon
Avignon (, ; ; oc, Avinhon, label=Provençal dialect, Provençal or , ; la, Avenio) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Vaucluse Departments of France, department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region of So ...
, and probably Marseille.
* 740–42 – Berbers
, image = File:Berber_flag.svg
, caption = The Berber ethnic flag
, population = 36 million
, region1 = Morocco
, pop1 = 14 million to 18 million
, region2 = Algeria
, pop2 ...
in northern Iberia (Galicia, Leon, Astorga, upper Ebro) give up their positions to join the Berber Revolts.
* 743–757 – Alfonso I of Asturias raids the territory between the rivers Duero and Ebro but doesn't retain it.
* 743 – Mudari
The Mudar ( ar, مُضَر) are one of the most powerful northern Arab tribal groupings.
History
The Mudar and Rabi'a are recorded in central Arabia in the Arabic histories of the pre-Islamic period; the kings of the Kindah bore the title o ...
tes and Yemenites agree on choosing alternately one of their numbers each year to rule Al–Andalus.
* 747 – Governor Yusuf ibn 'Abd al-Rahman al-Fihri, a Mudarite and descendant of Uqbah ibn Nafia, refuses to give turn to the Yemenite candidate and rules autonomously.
* 755 – Rebellion in Zaragoza quashed, and Yusuf's detachment annihilated by the Basques
The Basques ( or ; eu, euskaldunak ; es, vascos ; french: basques ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Bas ...
near Pamplona.
* 755 – Abd Al-Rahman Al Dakhel ("''Saqr Quraysh''") lands on the southern coast, taking in a quick succession Granada
Granada (,, DIN 31635, DIN: ; grc, Ἐλιβύργη, Elibýrgē; la, Illiberis or . ) is the capital city of the province of Granada, in the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. Granada is located at the fo ...
, Seville and Cordova.
* 756 – After refusing to compromise with Yusuf, Abd ar-Rahman I independent Umayyad emir of Córdova. Yusuf defeated.
* 759 – Narbonne captured by the Frankish king Pepin the Short
the Short (french: Pépin le Bref; – 24 September 768), also called the Younger (german: Pippin der Jüngere), was King of the Franks from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian to become king.
The younger was the son of ...
.
* 763 – Pro-Abbasid army defeated by Abd ar-Rahman I in Carmona
Carmona may refer to:
Places Angola
* the former name of the town of Uíge
Costa Rica
* Carmona District, Nandayure, a district in Guanacaste Province
India
* Carmona, Goa, a village located in the Salcette district of South Goa, India
...
.
* 778 – Charlemagne repelled in Zaragoza by Muslim local lords.
* 779 – Abd ar-Rahman I campaigns to the Upper Marches and subdues its main city, Zaragoza.
* 781 – Pamplona and the Basque lords south of the Pyrenean fringes subdued. All of Al Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
unified.
* 788 – Abd ar-Rahman I dies.
See also
*Timeline of the Muslim presence in the Iberian peninsula
This is a timeline of notable events during the period of Muslim presence in Iberia, starting with the Umayyad conquest in the 8th century.
Conquest (711–756)
* 711A Muslim force consisting of Arabs and Berbers of about 7,000 soldiers under ge ...
* Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent
References
Sources
* {{Umayyad Caliphate topics Hispania Invasions of Europe 8th-century conflicts 8th-century military history 8th century in the Visigothic Kingdom 8th century in Al-Andalus 8th century in the Umayyad Caliphate Wars involving the Goths Islam in Portugal Islam in Spain Invasions of Spain