Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in
Eastern Europe. It is the
second-largest European country after
Russia, which it borders
to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing
Russian invasion, it was the
eighth-most populous country in Europe, with a population of around 41 million people.
It is also bordered by
Belarus to the north; by
Poland,
Slovakia, and
Hungary to the west; and by
Romania and
Moldova to the southwest; with a coastline along the
Black Sea and the
Sea of Azov
The Sea of Azov ( Crimean Tatar: ''Azaq deñizi''; russian: Азовское море, Azovskoye more; uk, Азовське море, Azovs'ke more) is a sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow (about ) Strait of Kerch, ...
to the south and southeast.
Kyiv is the nation's capital and
largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metropo ...
. Ukraine's
state language is
Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
;
Russian is also widely spoken, especially in the
east and
south
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
.
During the
Middle Ages, Ukraine was the site of
early Slavic expansion and the area later became a key centre of
East Slavic culture under the state of
Kievan Rus', which emerged in the 9th century. The state eventually disintegrated into rival regional powers and was ultimately destroyed by the
Mongol invasions of the 13th century. The area was then contested, divided, and ruled by a variety of external powers for the next 600 years, including the
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the
Austrian Empire, the
Ottoman Empire, and the
Tsardom of Russia. The
Cossack Hetmanate emerged in
central Ukraine
Central Ukraine ( uk, Центральна Україна, ''Tsentralna Ukraina'') consists of historical regions of left-bank Ukraine and right-bank Ukraine that reference to the Dnipro River. It is situated away from the Black Sea Littoral N ...
in the 17th century, but was partitioned between Russia and Poland, and ultimately absorbed by the
Russian Empire. Ukrainian nationalism developed, and following the
Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and ad ...
in 1917, the short-lived
Ukrainian People's Republic was formed. The
Bolsheviks consolidated control over much of the former empire and established the
Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, which became a
constituent republic
Administrative division, administrative unit,Article 3(1). country subdivision, administrative region, subnational entity, constituent state, as well as many similar terms, are generic names for geographical areas into which a particular, ind ...
of the
Soviet Union when it was formed in 1922. In the early 1930s, millions of Ukrainians died in the
Holodomor
The Holodomor ( uk, Голодомо́р, Holodomor, ; derived from uk, морити голодом, lit=to kill by starvation, translit=moryty holodom, label=none), also known as the Terror-Famine or the Great Famine, was a man-made famin ...
, a
man-made famine. During
World War II, Ukraine was devastated by the
German occupation
German-occupied Europe refers to the sovereign countries of Europe which were wholly or partly occupied and civil-occupied (including puppet governments) by the military forces and the government of Nazi Germany at various times between 1939 an ...
.
Ukraine gained independence in 1991 as the
Soviet Union dissolved, and declared itself
neutral.
A new
constitution was adopted in 1996. A series of mass demonstrations, known as the
Euromaidan
Euromaidan (; uk, Євромайдан, translit=Yevromaidan, lit=Euro Square, ), or the Maidan Uprising, was a wave of Political demonstration, demonstrations and civil unrest in Ukraine, which began on 21 November 2013 with large protes ...
, led to the establishment of a new government in 2014 after a
revolution. Russia then unilaterally
annexed
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act ...
Ukraine's
Crimean Peninsula; and
pro-Russian unrest culminated in
a war between Russian-backed separatists and government forces in eastern Ukraine. Russia later launched a
full-scale invasion of Ukraine in February 2022. Since the outbreak of
war with Russia, Ukraine has continued to seek closer ties with the
European Union and
NATO.
Ukraine is a
unitary state with a
semi-presidential system
A semi-presidential republic, is a republic in which a president exists alongside a prime minister and a cabinet, with the latter two being responsible to the legislature of the state. It differs from a parliamentary republic in that it has a ...
. It is a
developing country
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
, ranking 77th on the
Human Development Index. Ukraine is the
poorest country in Europe by nominal GDP per capita, and
corruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense which is undertaken by a person or an organization which is entrusted in a position of authority, in order to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's personal gain. Corruption m ...
remains a significant issue. However, due to
its extensive fertile land, pre-war Ukraine was
one of the largest grain exporters in the world.
It is a founding member of the
United Nations, as well as a member of the
Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. ...
, the
World Trade Organization, and the
OSCE. It is in the
process of joining the
European Union and has submitted an application for
NATO membership
NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) is an international military alliance that consists of 30 member states from Europe and North America. It was established at the signing of the North Atlantic Treaty on 4 April 1949. Article 5 of the ...
.
Etymology and orthography
The
name of Ukraine
The name ''Ukraine'' ( uk, Україна, translit=Ukraina , ) was first used in reference to a part of the territory of Kyivan Rus' in the 12th century. The name has been used in a variety of ways since the 12th century, referring to numero ...
likely comes from the
old Slavic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic () was the first Slavic literary language.
Historians credit the 9th-century Byzantine missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius with standardizing the language and using it in translating the Bible and other ...
term for "borderland", as does the word ''
krajina Krajina () is a Slavic toponym, meaning 'frontier' or 'march'. The term is related to ''kraj'' or ''krai'', originally meaning 'edge'Rick Derksen (2008), ''Etymological Dictionary of the Slavic Inherited Lexicon'', Brill: Leiden-Boston, page 244 an ...
''.
In the
English-speaking world during most of the 20th century, Ukraine (whether independent or not) was referred to as "the Ukraine".
This is because the word ''ukraina'' means "borderland" so the
definite article would be natural in the English language; this is similar to "'", which means "low lands" and is rendered in English as "''the''
Netherlands". However, since Ukraine's
declaration of independence in 1991, this usage has become politicised and is now rarer, and
style guide
A style guide or manual of style is a set of standards for the writing, formatting, and design of documents. It is often called a style sheet, although that term also has multiple other meanings. The standards can be applied either for gene ...
s advise against its use.
US ambassador
William Taylor said that using "the Ukraine" implies disregard for Ukrainian sovereignty. The official Ukrainian position is that "the Ukraine" is incorrect, both grammatically and politically.
History
Early history

Settlement by
modern humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, an ...
in Ukraine and its vicinity dates back to 32,000 BC, with evidence of the
Gravettian culture
The Gravettian was an archaeological industry of the European Upper Paleolithic that succeeded the Aurignacian circa 33,000 years BP. It is archaeologically the last European culture many consider unified, and had mostly disappeared by 2 ...
in the
Crimean Mountains
The Crimean Mountains ( uk, Кримські гори, translit. ''Krymski hory''; russian: Крымские горы, translit. ''Krymskie gory''; crh, Qırım dağları) are a range of mountains running parallel to the south-eastern coast o ...
.
By 4,500 BC, the
Neolithic Cucuteni–Trypillia culture was flourishing in wide areas of modern Ukraine, including
Trypillia and the entire
Dnieper-
Dniester region. Ukraine is also considered to be the likely location of the first
domestication of the horse.
The
Kurgan hypothesis places the Volga-Dnieper region of Ukraine and southern Russia as the
urheimat of the
Proto-Indo-Europeans. Early
Indo-European migrations
The Indo-European migrations were hypothesized migrations of Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) speakers, and subsequent migrations of people speaking derived Indo-European languages, which took place approx. 4000 to 1000 BCE, potentially expla ...
from the Pontic steppes in the 3rd millennium BC spread
Yamnaya
The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture (russian: Ямная культура, ua, Ямна культура lit. 'culture of pits'), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archa ...
Steppe pastoralist ancestry and
Indo-European languages across large parts of Europe. During the
Iron Age, the land was inhabited by
Iranian-speaking
Cimmerians,
Scythians, and
Sarmatians. Between 700 BC and 200 BC it was part of the
Scythian kingdom.
From the 6th century BC,
Greek,
Roman, and
Byzantine colonies were established on the north-eastern shore of the
Black Sea, such as at
Tyras,
Olbia, and
Chersonesus. These thrived into the 6th century AD. The
Goths stayed in the area, but came under the sway of the
Huns from the 370s. In the 7th century, the territory that is now eastern Ukraine was the centre of
Old Great Bulgaria. At the end of the century, the majority of Bulgar tribes migrated in different directions, and the
Khazars took over much of the land.
In the 5th and 6th centuries, the
Early Slavic,
Antes people
The Antes, or Antae ( gr, Ἄνται), were an early East Slavic tribal polity of the 6th century CE. They lived on the lower Danube River, in the northwestern Black Sea region (present-day Moldova and central Ukraine), and in the regions aro ...
lived in Ukraine. The Antes were the ancestors of
Ukrainians:
White Croats,
Severians
The Severians or Severyans or Siverians ( be, Севяране; bg, Севери; russian: Северяне; uk, Сiверяни, translit=Siveriany) were a tribe or tribal confederation of early East Slavs occupying areas to the east of the mi ...
,
Eastern Polans
The Polans (, ''Poliany'', ''Polyane'', pl, Polanie), also Polianians, were an East Slavic tribe between the 6th and the 9th century, which inhabited both sides of the Dnieper river from Liubech to Rodnia and also down the lower streams o ...
,
Drevlyans,
Dulebes
The Dulebes, Dulebs, Dudlebi or Dulibyh ( uk, Дуліби) were one of the tribal unions of Early Slavs between the 6th and the 10th centuries. According to medieval sources they lived in Western Volhynia, as well as southern parts of the Duchy o ...
,
Ulichians
The Uliches or Ugliches ( ro, Ulici or ; russian: Уличи or , or ; uk, Уличі , or ) were a tribe of Early East Slavs who, between the eighth and the tenth centuries, inhabited (along with the Tivertsi) Bessarabia, and the territories ...
, and
Tiverians
The Tivertsi ( uk, Тиверці; ro, Tiverți or ), were a tribe of early East Slavs which lived in the lands near the Dniester, and probably the lower Danube, that is in modern-day western Ukraine and Republic of Moldova and possibly in easte ...
. Migrations from the territories of present-day Ukraine throughout the
Balkans established many
South Slavic nations. Northern migrations, reaching almost to
Lake Ilmen
Lake Ilmen ( rus, И́льмень, p=ˈilʲmʲɪnʲ) is a large lake in the Novgorod Oblast of Russia. A historically important lake, it formed a vital part of the medieval trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks. The city of Novgorod - wh ...
, led to the emergence of the
Ilmen Slavs
The Novgorod Slavs, Ilmen Slavs (russian: Ильменские слове́не, ''Il'menskiye slovene''), or Slovenes (not to be confused with the Slovenian Slovenes) were the northernmost tribe of the Early Slavs, and inhabited the shores of L ...
,
Krivichs, and
Radimichs, the groups ancestral to the
Russians. Following an
Avar raid in 602 and the collapse of the Antes Union, most of these peoples survived as separate tribes until the beginning of the second millennium.
Golden Age of Kyiv

The establishment of the state of
Kievan Rus' remains obscure and uncertain. The state included much of present-day Ukraine,
Belarus and the western part of
European Russia
European Russia (russian: Европейская Россия, russian: европейская часть России, label=none) is the western and most populated part of Russia. It is geographically situated in Europe, as opposed to the cou ...
.
According to the ''
Primary Chronicle
The ''Tale of Bygone Years'' ( orv, Повѣсть времѧньныхъ лѣтъ, translit=Pověstĭ vremęnĭnyxŭ lětŭ; ; ; ; ), often known in English as the ''Rus' Primary Chronicle'', the ''Russian Primary Chronicle'', or simply the ...
'', the
Rus' people initially consisted of
Varangians from
Scandinavia. In 882, the pagan
Prince Oleg
Oleg ( orv, Ѡлегъ, Ольгъ; non, Helgi; died 912), also known as Oleg the Wise (russian: Олег Вещий, lit=Oleg the Prophet; uk, Олег Віщий), was a Varangian prince of the Rus' who was ruler of Novgorod. He later con ...
(Oleh) conquered
Kyiv from
Askold and Dir and proclaimed it as the new capital of the Rus'.
Anti-Normanist historians however argue that the East Slavic tribes along the southern parts of the
Dnieper River were already in the process of forming a state independently.
[Martin (2009)]
pp. 37–40
The Varangian elite, including the ruling
Rurik dynasty, later assimilated into the Slavic population.
Kievan Rus' was composed of several
principalities ruled by the interrelated Rurikid ''
kniazes'' ("princes"), who often fought each other for possession of Kyiv.
During the 10th and 11th centuries, Kievan Rus' became the largest and most powerful state in Europe, a period known as its Golden Age.
It began with the reign of
Vladimir the Great (980–1015), who
introduced Christianity. During the reign of his son,
Yaroslav the Wise (1019–1054), Kievan Rus' reached the zenith of its cultural development and military power.
The state soon fragmented as the relative importance of regional powers rose again. After a final resurgence under the rule of
Vladimir II Monomakh
Vladimir II Monomakh (Old East Slavic: Володимѣръ Мономахъ, ''Volodiměrŭ Monomakhŭ''; uk, Володимир Мономах, translit=Volodymyr Monomakh; russian: Владимир Мономах; Christian name: ''Vasiliy'' ...
(1113–1125) and his son
Mstislav (1125–1132), Kievan Rus' finally disintegrated into separate principalities following Mstislav's death, though ownership of Kyiv would still carry great prestige for decades. In the 11th and 12th centuries, the nomadic confederacy of the
Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
-speaking
Cumans and
Kipchaks
The Kipchaks or Qipchaks, also known as Kipchak Turks or Polovtsians, were a Turkic nomadic people and confederation that existed in the Middle Ages, inhabiting parts of the Eurasian Steppe. First mentioned in the 8th century as part of the Se ...
was the dominant force in the
Pontic steppe
Pontic, from the Greek ''pontos'' (, ), or "sea", may refer to:
The Black Sea Places
* The Pontic colonies, on its northern shores
* Pontus (region), a region on its southern shores
* The Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppelands stretching from nor ...
north of the Black Sea.
The
Mongol invasions in the mid-13th century devastated Kievan Rus' and Kyiv was
completely destroyed in 1240. In the western territories, the principalities of
Halych and
Volhynia had arisen earlier, and were merged together to form the
Principality of Galicia–Volhynia
A principality (or sometimes princedom) can either be a monarchical feudatory or a sovereign state, ruled or reigned over by a regnant-monarch with the title of prince and/or princess, or by a monarch with another title considered to fall under ...
.
Daniel of Galicia
Daniel of Galicia ( uk, Данило Романович (Галицький), Danylo Romanovych (Halytskyi); Old Ruthenian: Данило Романовичъ, ''Danylo Romanovyčъ''; pl, Daniel I Romanowicz Halicki; 1201 – 1264) was a King ...
, son of
Roman the Great, re-united much of south-western Rus', including
Volhynia,
Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
, as well as Kyiv. He was subsequently crowned by the
papal
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
as the first
king of Galicia–Volhynia (also known as the Kingdom of Ruthenia) in 1253.
Foreign domination
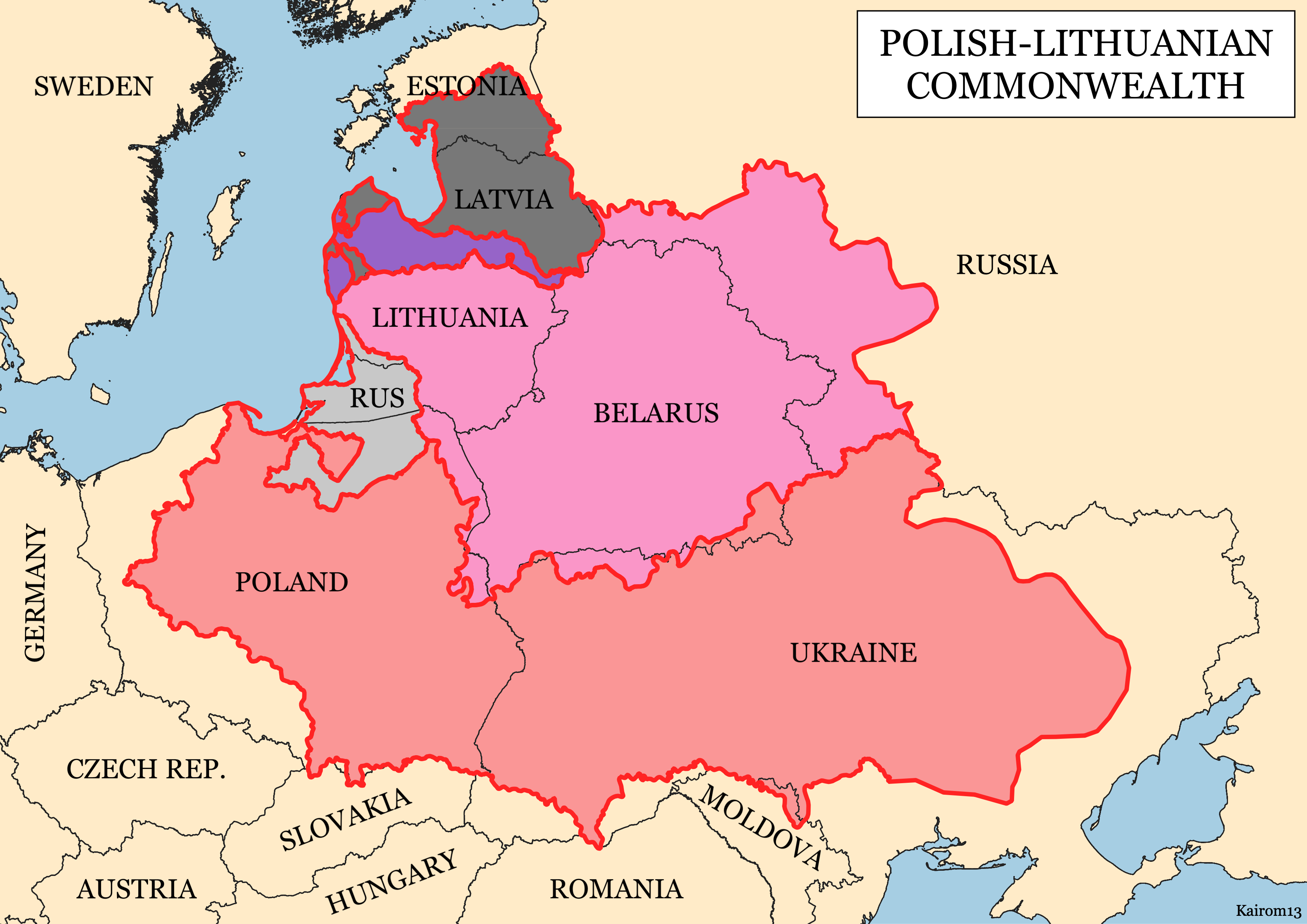
In 1349, in the aftermath of the
Galicia–Volhynia Wars
The Galicia–Volhynia Wars were several wars fought in the years 1340–1392 over the succession in the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia, also known as Ruthenia. After Yuri II Boleslav was poisoned by local Ruthenian nobles in 1340, both the Grand ...
, the area was partitioned between the
Kingdom of Poland and the
Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
From the mid-13th century to the late 1400s, the
Republic of Genoa founded numerous
colonies in the Black Sea region of modern Ukraine and transformed these into large commercial centers headed by the consul, a representative of the Republic. In 1430, the region of
Podolia was incorporated into Poland, and the lands of modern-day Ukraine became increasingly settled by Poles. In 1441,
Genghisid prince
Haci I Giray founded the
Crimean Khanate on the
Crimean Peninsula and the surrounding steppes; the Khanate orchestrated
Tatar slave raids and took an estimated two million slaves from the region.
In 1569, the
Union of Lublin established the
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and most of the Ukrainian lands were transferred from Lithuania to the
Crown of the Kingdom of Poland
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Korona Królestwa Polskiego; Latin: ''Corona Regni Poloniae''), known also as the Polish Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, includ ...
, becoming ''
de jure'' Polish territory. Under the pressures of
Polonisation
Polonization (or Polonisation; pl, polonizacja)In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэя� ...
, many landed gentry of
Ruthenia
Ruthenia or , uk, Рутенія, translit=Rutenia or uk, Русь, translit=Rus, label=none, pl, Ruś, be, Рутэнія, Русь, russian: Рутения, Русь is an exonym, originally used in Medieval Latin as one of several terms ...
converted to
Catholicism and joined the circles of the
Polish nobility
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in the ...
; others still joined the newly created
Ruthenian Uniate Church.
Cossack Hetmanate
Deprived of native protectors among the Ruthenian nobility, the peasants and townspeople began turning for protection to the emerging
Zaporozhian Cossacks. In the mid-17th century, a Cossack military quasi-state, the
Zaporozhian Host, was formed by
Dnieper Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporoz ...
and Ruthenian peasants.
Poland exercised little real control over this population, but found the Cossacks to be useful against the
Turks and
Tatars,
and at times the two were allies in
military campaigns
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
. However, the continued harsh
enserfment of Ruthenian peasantry by Polish
szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in the ...
(many of whom were Polonized
Ruthenian nobles) and the suppression of the Orthodox Church alienated the Cossacks.
The latter did not shy from taking up arms against those they perceived as enemies and occupiers, including the Catholic Church with its local representatives.

In 1648,
Bohdan Khmelnytsky
Bohdan Zynovii Mykhailovych Khmelnytskyi ( Ruthenian: Ѕѣнові Богданъ Хмелнiцкiи; modern ua, Богдан Зиновій Михайлович Хмельницький; 6 August 1657) was a Ukrainian military commander and ...
led the
largest of the Cossack uprisings against the Commonwealth and the
Polish king, which enjoyed wide support from the local population. Khmelnytsky founded the
Cossack Hetmanate, which existed until 1764 (some sources claim until 1782). After Khmelnytsky suffered a crushing defeat at the
Battle of Berestechko in 1651, he turned to the
Russian tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the ter ...
for help. In 1654, Khmelnytsky was subject to the
Pereiaslav Agreement, forming a military and political alliance with Russia that acknowledged loyalty to the Russian monarch.
After his death, the Hetmanate went through a devastating 30-year war amongst Russia, Poland, the
Crimean Khanate, the
Ottoman Empire, and
Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
, known as "
The Ruin" (1657-1686), for control of the Cossack Hetmanate. The
Treaty of Perpetual Peace between Russia and Poland in 1686 divided the lands of the Cossack Hetmanate between them, reducing the portion over which Poland had claimed sovereignty to Ukraine west of the
Dnieper river. In 1686, the
Metropolitanate of Kyiv was
annexed by the Moscow Patriarchate through a synodal letter of the
Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople Dionysius IV, thus placing the
Metropolitanate of Kyiv under the authority of
Moscow. An attempt to reverse the decline was undertaken by Cossack Hetman
Ivan Mazepa (1639–1709), who ultimately defected to the
Swedes
Swedes ( sv, svenskar) are a North Germanic ethnic group native to the Nordic region, primarily their nation state of Sweden, who share a common ancestry, culture, history and language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countr ...
in the
Great Northern War (1700-1721) in a bid to get rid of Russian dependence,
but they were crushed in the
Battle of Poltava (1709).

The Hetmanate's autonomy was severely restricted since Poltava. In the years 1764–1781,
Catherine the Great
, en, Catherine Alexeievna Romanova, link=yes
, house =
, father = Christian August, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst
, mother = Joanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp
, birth_date =
, birth_name = Princess Sophie of Anhal ...
incorporated much of
Central Ukraine
Central Ukraine ( uk, Центральна Україна, ''Tsentralna Ukraina'') consists of historical regions of left-bank Ukraine and right-bank Ukraine that reference to the Dnipro River. It is situated away from the Black Sea Littoral N ...
into the
Russian Empire, abolishing the
Cossack Hetmanate and the
Zaporozhian Sich, and was one of the people responsible for the suppression of the last major Cossack uprising, the
Koliivshchyna. After the
annexation of Crimea by Russia
Annexation of Crimea may refer to:
*Annexation of the Crimean Khanate by the Russian Empire (1783)
*Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation (2014) See also
* 1954 transfer of Crimea
The transfer of the Crimean Oblast in the Soviet Union ...
in 1783, the newly acquired lands, now called
Novorossiya, were opened up to settlement by Russians. The
tsarist autocracy established a policy of
Russification
Russification (russian: русификация, rusifikatsiya), or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians, whether involuntarily or voluntarily, give up their culture and language in favor of the Russian cultur ...
, suppressing the use of the
Ukrainian language and curtailing the Ukrainian national identity.
The western part of present-day Ukraine was subsequently split between Russia and
Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
-ruled
Austria after the
fall of the
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1795.
19th and early 20th century

The 19th century saw the rise of Ukrainian nationalism. With growing urbanization and modernization and a cultural trend toward
romantic nationalism
Romantic nationalism (also national romanticism, organic nationalism, identity nationalism) is the form of nationalism in which the state claims its political legitimacy as an organic consequence of the unity of those it governs. This includes ...
, the Ukrainian
intelligentsia
The intelligentsia is a status class composed of the university-educated people of a society who engage in the complex mental labours by which they critique, shape, and lead in the politics, policies, and culture of their society; as such, the in ...
committed to national rebirth and social justice emerged. The serf-turned-national-poet
Taras Shevchenko (1814–1861) and political theorist
Mykhailo Drahomanov (1841–1895) led the growing nationalist movement. While conditions for its development in Austrian
Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
under the
Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
were relatively lenient, the Russian part (known as
Little Russia) faced severe restrictions, going as far as
banning virtually all books from being published in Ukrainian in 1876.
Ukraine joined the
Industrial Revolution later
Later may refer to:
* Future, the time after the present
Television
* ''Later'' (talk show), a 1988–2001 American talk show
* '' Later... with Jools Holland'', a British music programme since 1992
* ''The Life and Times of Eddie Roberts'', or ...
than most of Western Europe due to the maintenance of
serfdom until 1861. Other than near the newly discovered coal fields of the
Donbas
The Donbas or Donbass (, ; uk, Донба́с ; russian: Донба́сс ) is a historical, cultural, and economic region in eastern Ukraine. Parts of the Donbas are controlled by Russian separatist groups as a result of the Russo-Ukrai ...
, and in some larger cities such as
Odesa and Kyiv, Ukraine largely remained an agricultural and resource extraction economy. The Austrian part of Ukraine
was particularly destitute, which forced hundreds of thousands of peasants into emigration, who created the backbone of an extensive
Ukrainian diaspora in countries such as
Canada, the
United States and
Brazil. Some of the Ukrainians settled in the Far East, too. According to the
1897 census
The first general census of the population of the Russian Empire in 1897 ( pre-reform Russian: ) was the first and only nation-wide census performed in the Russian Empire (the Grand Duchy of Finland was excluded). It recorded demographic data as ...
, there were 223,000 ethnic Ukrainians in
Siberia and 102,000 in
Central Asia. An additional 1.6 million emigrated to the east in the ten years after the opening of the
Trans-Siberian Railway in 1906.
Far Eastern areas with an ethnic Ukrainian population became known as
Green Ukraine
Green Ukraine, also known as Zelenyi Klyn ( uk, Зелений клин, Zelenyi Klyn, russian: Зелёный Клин, Zelyonyy Klin, literally: 'the green gore/wedge') or Zakytaishchyna (Ukrainian and Russian: , literally: 'Trans China'), is ...
.
Ukraine plunged into turmoil with the beginning of
World War I, and fighting on Ukrainian soil persisted until late 1921. Initially, the Ukrainians were split between Austria-Hungary, fighting for the
Central Powers, though the vast majority served in the
Imperial Russian Army
The Imperial Russian Army (russian: Ру́сская импера́торская а́рмия, tr. ) was the armed land force of the Russian Empire, active from around 1721 to the Russian Revolution of 1917. In the early 1850s, the Russian Ar ...
, which was part of the
Triple Entente, under Russia. As the Russian Empire collapsed, the conflict evolved into the
Ukrainian War of Independence, with Ukrainians fighting alongside, or against, the
Red,
White,
Black and
Green armies, with the Poles, Hungarians (in
Transcarpathia), and Germans also intervening at various times.
An attempt to create an independent state, the left-leaning
Ukrainian People's Republic (UNR), was first announced by
Mykhailo Hrushevsky, but the period was plagued by an extremely unstable political and military environment. It was first deposed in a
coup d'état led by
Pavlo Skoropadskyi
Pavlo Petrovych Skoropadskyi ( uk, Павло Петрович Скоропадський, Pavlo Petrovych Skoropadskyi; – 26 April 1945) was a Ukrainian aristocrat, military and state leader, decorated Imperial Russian Army and Ukrainian Army ...
, which yielded the
Ukrainian State under the German protectorate, and the attempt to restore the UNR under the
Directorate
Directorate may refer to:
Contemporary
*Directorates of the Scottish Government
* Directorate-General, a type of specialised administrative body in the European Union
* Directorate-General for External Security, the French external intelligence ag ...
ultimately failed as the Ukrainian army was regularly overrun by other forces. The short-lived West Ukrainian People's Republic and Hutsul Republic also failed to join the rest of Ukraine.
The result of the conflict was a partial victory for the Second Polish Republic, which annexed the Western Ukrainian provinces, as well as a larger-scale victory for the pro-Soviet forces, which succeeded in dislodging the remaining factions and eventually established the
Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic (Soviet Ukraine). Meanwhile, modern-day Bukovina was occupied by Kingdom of Romania, Romania and Carpathian Ruthenia was admitted to First Czechoslovak Republic, Czechoslovakia as an autonomous region.
The conflict over Ukraine, a part of the broader Russian Civil War, devastated the whole of the former
Russian Empire, including eastern and central Ukraine. The fighting left over 1.5 million people dead and hundreds of thousands homeless in the former Russian Empire's territory. The eastern provinces were additionally impacted by a Russian famine of 1921–1922, famine in 1921.
Inter-war Ukraine

In Second Polish Republic, Poland, Marshal Józef Piłsudski and his political allies wanted to gain Ukrainian support by offering limited local autonomy as way to minimise Soviet influences in the borderlands. However, this approach was abandoned after Piłsudski's death in 1935, due to continued unrest among the Ukrainian population, with the Polish government responding by restricting rights of people who declared Ukrainian nationality and belonged to the Eastern Orthodox Church.
In consequence, an underground Ukrainian nationalist and militant movement arose in the 1920s and 1930s, which gradually transformed into the Ukrainian Military Organization and later the Organisation of Ukrainian Nationalists (OUN).
Meanwhile, the recently constituted Soviet Ukraine became one of the founding republics of the
Soviet Union. During the 1920s, under the Ukrainisation policy pursued by the national Communist leadership of Mykola Skrypnyk, Soviet leadership at first encouraged a national renaissance in Culture of Ukraine, Ukrainian culture and Ukrainian language, language. Ukrainisation was part of the Soviet-wide policy of Korenisation (literally ''indigenisation''), which was intended to promote the advancement of native peoples, their language and culture into the governance of their respective republics.
Around the same time, Soviet leader Vladimir Lenin instituted the New Economic Policy (NEP), which introduced a form of market socialism, allowing some private ownership of small and medium-sized productive enterprises, hoping to reconstruct the post-war Soviet Union that had been devastated by both WWI and later the civil war. The NEP was successful at restoring the formerly war-torn nation to pre-WWI levels of production and agricultural output by the mid-1920s, much of the latter based in Ukraine.
These policies attracted many prominent former UNR figures, including former UNR leader Hrushevsky, to return to Soviet Ukraine, where they were accepted, and participated in the advancement of Ukrainian science and culture.
This period was cut short when Joseph Stalin became the leader of the USSR following Lenin's death. Stalin did away with the NEP in what became known as the Great Break (USSR), Great Break. Starting from the late 1920s and now with a planned economy, centrally planned economy, Soviet Ukraine took part in an Industrialization in the USSR, industrialisation scheme which quadrupled its industrial output during the 1930s.
However, as a consequence of Stalin's new policy, the Ukrainian peasantry suffered from the Collectivization in the USSR, programme of collectivization of agricultural crops. Collectivization was part of the first five-year plan and was enforced by regular troops and the secret police known as Cheka. Those who resisted were Population transfer in the Soviet Union, arrested and deported to gulags and work camps. As members of the collective farms were sometimes not allowed to receive any grain until unrealistic quotas were met, millions starved to death in a Droughts and famines in Russia and the Soviet Union, famine known as the
Holodomor
The Holodomor ( uk, Голодомо́р, Holodomor, ; derived from uk, морити голодом, lit=to kill by starvation, translit=moryty holodom, label=none), also known as the Terror-Famine or the Great Famine, was a man-made famin ...
or the "Great Famine", which was recognized by some countries as an act of genocide perpetrated by Joseph Stalin and other Soviet notables.
Following on the Russian Civil War, and collectivisation, the Great Purge, while killing Stalin's perceived political enemies, resulted in a profound loss of a new generation of Ukrainian
intelligentsia
The intelligentsia is a status class composed of the university-educated people of a society who engage in the complex mental labours by which they critique, shape, and lead in the politics, policies, and culture of their society; as such, the in ...
, known today as the Executed Renaissance.
World War II

Following the Invasion of Poland in September 1939, Nazi Germany, German and Soviet Army, Soviet troops divided the territory of Poland. Thus, Eastern
Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
and
Volhynia with their Ukrainian population became part of Ukraine. For the first time in history, the nation was united. Further territorial gains were secured in 1940, when the Ukrainian SSR incorporated the northern and southern districts of Bessarabia, Northern Bukovina, and the Hertsa region from the territories the USSR Soviet occupation of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina, forced Romania to cede, though it handed over the western part of the Moldavian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic to the newly created Moldavian SSR. These territorial gains of the USSR were internationally recognized by the Paris Peace Treaties, 1947, Paris peace treaties of 1947.
Wehrmacht, German armies Operation Barbarossa, invaded the Soviet Union on 22 June 1941, initiating nearly four years of total war. The Axis Powers, Axis initially advanced against desperate but unsuccessful efforts of the Red Army. In the Battle of Kyiv (1941), battle of Kyiv, the city was acclaimed as a "Hero City (Soviet Union), Hero City", because of its fierce Battle of Kyiv (1941), resistance. More than 600,000 Soviet soldiers (or one-quarter of the Soviet Western Front) were killed or taken captive there, with many suffering German mistreatment of Soviet prisoners of war, severe mistreatment. After its conquest, most of the Ukrainian SSR was organised within the Reichskommissariat Ukraine, with the intention of exploiting its resources and eventual German settlement. Some western Ukrainians, who had only joined the Soviet Union in 1939, hailed the Germans as liberators, but that did not last long as the Nazis made little attempt to exploit dissatisfaction with Stalinist policies.
Instead, the Nazis preserved the collective-farm system, carried out Mass graves in the Soviet Union, genocidal policies against History of the Jews in Ukraine, Jews, OST-Arbeiter, deported millions of people to work in Germany, and began a depopulation program to prepare for German colonisation.
They blockaded the transport of food on the Dnieper River.
Although the majority of Ukrainians fought in or alongside the Red Army and Soviet partisans, Soviet resistance,
in Western Ukraine an independent Ukrainian Insurgent Army movement arose (UPA, 1942). It was created as the armed forces of the underground Organization of Ukrainian Nationalists (OUN).
[Vedeneyev, D. ]
Military Field Gendarmerie - special body of the Ukrainian Insurgent Army
'. "Voyenna Istoriya" magazine. 2002. Both organizations, the OUN and the UPA, supported the goal of an Declaration of Ukrainian Independence, 1941, independent Ukrainian state on the territory with a Ukrainian ethnic majority. Although this brought conflict with Nazi Germany, at times the Andriy Atanasovych Melnyk, Melnyk wing of the OUN allied with the Nazi forces. From mid-1943 until the end of the war, the UPA carried out Massacres of Poles in Volhynia and Eastern Galicia, massacres of ethnic Poles in the
Volhynia and Eastern Galicia regions, killing around 100,000 Polish civilians, which brought reprisals.
These organized massacres were an attempt by the OUN to create a homogeneous Ukrainian state without a Polish minority living within its borders, and to prevent the post-war Polish state from asserting its sovereignty over areas that had been part of pre-war Poland. After the war, the UPA continued to fight the USSR until the 1950s. At the same time, the Ukrainian Liberation Army, another nationalist movement, fought alongside the Nazis.

In total, the number of ethnic Ukrainians who fought in the ranks of the Soviet Army is estimated from 4.5 million
to 7 million; half of the Soviet Partisans, Pro-Soviet partisan guerrilla resistance units, which counted up to 500,000 troops in 1944, were also Ukrainian. Generally, the Ukrainian Insurgent Army's figures are unreliable, with figures ranging anywhere from 15,000 to as many as 100,000 fighters.
The vast majority of the fighting in World War II took place on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front. By some estimates, 93% of all German casualties took place there. The World War II casualties of the Soviet Union, total losses inflicted upon the Ukrainian population during the war are estimated at 6 million,
including an estimated one and a half million Jews killed by the Einsatzgruppen, sometimes with the help of local collaborators. Of the estimated 8.6 million Soviet troop losses,
[Кривошеев Г. Ф., ''Россия и СССР в войнах XX века: потери вооруженных сил. Статистическое исследование'' (Krivosheev G. F., ''Russia and the USSR in the wars of the 20th century: losses of the Armed Forces. A Statistical Study'') ] 1.4 million were ethnic
Ukrainians,
and general losses of the Ukrainian people in the war amounted to 40–44% of the total losses of the USSR. The Victory Day over Nazism in World War II, Victory Day is celebrated as one of eleven Ukrainian national holidays.
Post–war Soviet Ukraine
The republic was heavily damaged by the war, and it required significant efforts to recover. More than 700 cities and towns and 28,000 villages were destroyed. The situation was worsened by a famine in 1946–1947, which was caused by a drought and the wartime destruction of infrastructure, killing at least tens of thousands of people.
In 1945, the Ukrainian SSR became one of the founding members of the
United Nations (UN),
part of a special agreement at the Yalta Conference, and, alongside Belarus, had voting rights in the UN even though they were not independent. Moreover, Ukraine once more expanded its borders as it annexed Zakarpattia Oblast, Zakarpattia, and the population became much more homogenized due to post-war Population transfer in the Soviet Union, population transfers, most of which, as in the case of Flight and expulsion of Germans (1944–1950), Germans and Deportation of the Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatars, were forced. As of 1 January 1953, Ukrainians were second only to Russians among adult "Forced settlements in the Soviet Union, special deportees", comprising 20% of the total.
Following the death of Stalin in 1953, Nikita Khrushchev became the new leader of the USSR, who began the policies of De-Stalinization and the Khrushchev Thaw. During his term as head of the Soviet Union, Crimean Oblast, Crimea was 1954 transfer of Crimea, transferred from the Russian SFSR to the Ukrainian SSR, formally as a friendship gift to Ukraine and for economic reasons. This represented the final extension of Ukrainian territory and formed the basis for the internationally recognized borders of Ukraine to this day. Ukraine was one of the most important republics of the Soviet Union, which resulted in many top positions in the Soviet Union occupied by Ukrainians, including notably Leonid Brezhnev, General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1964 to 1982. However, it was him and his Communist Party of Ukraine (Soviet Union), appointee in Ukraine, Volodymyr Shcherbytsky, who presided over extensive Russification of Ukraine, Russification of Ukraine and who were instrumental in repressing a new generation of Ukrainian intellectuals known as the Sixtiers.
By 1950, the republic had fully surpassed pre-war levels of industry and production. Soviet Ukraine soon became a European leader in industrial production and an important centre of the Soviet arms industry and high-tech research, though heavy industry still had an outsided influence. The Soviet government invested in hydroelectric and nuclear power projects to cater to the energy demand that the development carried. On 26 April 1986, however, a reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant exploded, resulting in the Chernobyl disaster, the worst nuclear reactor accident in history.
Independence

Mikhail Gorbachev pursued a policy of limited liberalization of public life, known as ''perestroika,'' and attempted to reform a Era of Stagnation, stagnating economy. The latter failed, but the democratization of the Soviet Union fuelled nationalist and separatist tendencies among the ethnic minorities, including Ukrainians. As part of the so-called parade of sovereignties, on 16 July 1990, the newly elected Supreme Soviet of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic adopted the Declaration of State Sovereignty of Ukraine; after a 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt, putsch of some Communist leaders in Moscow failed to depose Gorbachov, outright independence was Declaration of Independence of Ukraine, proclaimed on 24 August 1991 and approved by 92% of the Ukrainian electorate in a 1991 Ukrainian independence referendum, referendum on 1 December.
[Nohlen & Stöver, p1985] Ukraine's new President of Ukraine, President, Leonid Kravchuk, went on to sign the Belavezha Accords and made Ukraine a founding member of the much looser Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), though Ukraine never became a full member of the latter as it did not ratify the agreement founding CIS.
These documents sealed the fate of the Soviet Union, which formally voted itself out of existence on 26 December.
Ukraine was initially viewed as having favourable economic conditions in comparison to the other regions of the Soviet Union, though it was one of the poorer Soviet republics by the end of the Soviet Union.
However, during its transition to the market economy, the country experienced deeper economic slowdown than almost all of the other former Soviet Republics. During the recession, between 1991 and 1999, Ukraine lost 60% of its GDP
and suffered from hyperinflation that peaked at 10,000% in 1993. The situation only stabilized well after the new currency, the hryvnia, fell sharply in late 1998 partially as a fallout from the Russian debt default earlier that year. The legacy of the economic policies of the nineties was the mass privatization of state property that created a class of extremely powerful and rich individuals known as the Ukrainian oligarch, oligarchs.
The country would then fall into sharp recessions as a result of the 2008 global financial crisis,
then the start of the Russo-Ukrainian War in 2014, and finally, the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, full-scale invasion of Russia in starting from 24 February 2022. Ukraine's economy in general underperformed since the time independence came due to pervasive
corruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense which is undertaken by a person or an organization which is entrusted in a position of authority, in order to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's personal gain. Corruption m ...
and mismanagement, which, particularly in the 1990s, led to protests and organized strikes. The war with Russia impeded meaningful economic recovery in the 2010s, while efforts to combat the COVID-19 pandemic in Ukraine, COVID-19 pandemic, which arrived in 2020, were made much harder by COVID-19 vaccine, low vaccination rates and, later in the pandemic, by the ongoing invasion.

From the political perspective, one of the defining features of the politics of Ukraine is that for most of the time, it has been divided along two issues: the relation between Ukraine, the Western world, West and Russia, and the classical Left–right political spectrum, left-right divide. The first two presidents, Kravchuk and Leonid Kuchma, tended to balance the competing visions of Ukraine, though Yushchenko and Yanukovych were generally pro-Western and pro-Russian, respectively. There were two major protests against Yanukovych: the Orange Revolution in 2004, when tens of thousands of people went in protest of election rigging in his favour (Yushchenko was eventually elected president), and another one in the winter of 2013/2014, when more gathered on the
Euromaidan
Euromaidan (; uk, Євромайдан, translit=Yevromaidan, lit=Euro Square, ), or the Maidan Uprising, was a wave of Political demonstration, demonstrations and civil unrest in Ukraine, which began on 21 November 2013 with large protes ...
to oppose Yanukovych's refusal to sign the European Union–Ukraine Association Agreement. By the end of the 2014 protests, he fled from Ukraine and was removed by the parliament in what is termed the Revolution of Dignity, but Russia refused to recognize the interim pro-Western government, calling it a ''Military junta, junta'' and denouncing the events as a
coup d'état sponsored by the United States.
Even though Russia had signed the so-called Budapest Memorandum on Security Assurances, Budapest memorandum in 1994 that said that Ukraine was to hand over Ukraine and weapons of mass destruction, nuclear weapons in exchange of security guarantees and those of territorial integrity, it reacted violently to these developments and started a Russo-Ukrainian War, war against its western neighbour. In late February and early March 2014, it Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, annexed Crimea using its Russian Navy, Navy in Sevastopol Naval Base, Sevastopol as well as the so-called Little green men (Russo-Ukrainian War), little green men; after this succeeded, it then launched a War in Donbas (2014–2022), proxy war in the Donbas via the breakaway Donetsk People's Republic and Luhansk People's Republic. The first months of the conflict with the Russian-backed separatists were fluid, but Russian forces then started an open invasion in Donbas on 24 August 2014. Together they pushed back Ukrainian troops to the frontline established in February 2015, i.e. after Ukrainian troops Battle of Debaltseve, withdrew from Debaltseve. The conflict remained in a sort of a Frozen conflict, frozen state until the early hours of 24 February 2022, when Russia proceeded with an 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, ongoing invasion of Ukraine. Russian troops control about 20% of Ukraine's internationally recognized territory, though Russia failed with its initial plan, with Ukrainian troops recapturing some territory in counteroffensives.

The military conflict with Russia shifted the government's policy towards the West. Shortly after Yanukovych fled Ukraine, the country signed the EU association agreement in June 2014, and its citizens were granted visa-free travel to the European Union three years later. In January 2019, the Orthodox Church of Ukraine was recognized as independent of Moscow, which reversed the Annexation of the Metropolitanate of Kyiv by the Moscow Patriarchate, 1686 decision of the patriarch of Constantinople and dealt a further blow to Moscow's influence in Ukraine. Finally, amid a full-scale war with Russia, Ukraine was granted Potential enlargement of the European Union, candidate status to the European Union on 23 June 2022.
Geography

Ukraine is the
second-largest European country, after Russia. Lying between latitudes 44th parallel north, 44° and 53rd parallel north, 53° N, and longitudes 22nd meridian east, 22° and 41st meridian east, 41° E., it is mostly in the East European Plain. Ukraine covers an area of , with a coastline of .
The landscape of Ukraine consists mostly of fertile steppes (plains with few trees) and plateaus, crossed by rivers such as the Dnieper River, Dnieper (), Seversky Donets,
Dniester and the Southern Bug as they flow south into the
Black Sea and the smaller
Sea of Azov
The Sea of Azov ( Crimean Tatar: ''Azaq deñizi''; russian: Азовское море, Azovskoye more; uk, Азовське море, Azovs'ke more) is a sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow (about ) Strait of Kerch, ...
. To the southwest, the Danube Delta, delta of the Danube forms the border with Romania. Ukraine's various regions have diverse geographic features ranging from the highlands to the lowlands. The country's only mountains are the Carpathian Mountains in the west, of which the highest is Hoverla at , and the
Crimean Mountains
The Crimean Mountains ( uk, Кримські гори, translit. ''Krymski hory''; russian: Крымские горы, translit. ''Krymskie gory''; crh, Qırım dağları) are a range of mountains running parallel to the south-eastern coast o ...
, in the extreme south along the coast.
Ukraine also has a number of highland regions such as the Volhynian-Podolian Upland, Volyn-Podillia Upland (in the west) and the Near-Dnipro Upland (on the right bank of the Dnieper). To the east there are the south-western spurs of the Central Russian Upland over which runs the border with Russia. Near the
Sea of Azov
The Sea of Azov ( Crimean Tatar: ''Azaq deñizi''; russian: Азовское море, Azovskoye more; uk, Азовське море, Azovs'ke more) is a sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow (about ) Strait of Kerch, ...
are the Donets Ridge and the Near Azov Upland. The snow melt from the mountains feeds the rivers and their waterfalls of Ukraine, waterfalls.
Significant natural resources in Ukraine include lithium, natural gas,
kaolin,
timber and an abundance of arable land. Ukraine has many environmental issues. Some regions lack adequate supplies of potable water. Air and water pollution affects the country, as well as deforestation, and radiation contamination in the northeast from the 1986 accident at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant.
Climate

Ukraine has a mostly temperate climate, except for the southern coast of Crimea which has a subtropical climate.
The climate is influenced by moderately warm, humid air from the Atlantic Ocean.
Average annual temperatures range from in the north, to in the south.
[ precipitation (meteorology), Precipitation is highest in the west and north and lowest in the east and southeast.][ Western Ukraine, particularly in the Carpathian Mountains, receives around of precipitation annually, while Crimea and the coastal areas of the Black Sea receive around .][
Water availability from the major river basins is expected to decrease Effects of climate change, due to climate change, especially in summer. This poses risks to the agricultural sector. The negative Effects of climate change on agriculture, impacts of climate change on agriculture are mostly felt in the south of the country, which has a steppe climate. In the north, some crops may be able to benefit from a longer growing season. The World Bank has stated that Ukraine is highly Climate change vulnerability, vulnerable to climate change.
]
Biodiversity
Ukraine contains six terrestrial ecoregions: Central European mixed forests, Crimean Submediterranean forest complex, East European forest steppe, Pannonian mixed forests, Carpathian montane conifer forests, and Pontic steppe
Pontic, from the Greek ''pontos'' (, ), or "sea", may refer to:
The Black Sea Places
* The Pontic colonies, on its northern shores
* Pontus (region), a region on its southern shores
* The Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppelands stretching from nor ...
.
Urban areas
Ukraine has 457 cities, of which 176 are designated as oblast-class, 279 as smaller -class cities, and two as special legal status cities. There are also 886 urban-type settlements and 28,552 villages.
Politics
Ukraine is a republic under a semi-presidential system with separate legislative branch, legislative, executive branch, executive, and judicial branches.
Constitution
 The Constitution of Ukraine was adopted and ratified at the 5th session of the Verkhovna Rada, the parliament of Ukraine, on 28 June 1996.
The Constitution of Ukraine was adopted and ratified at the 5th session of the Verkhovna Rada, the parliament of Ukraine, on 28 June 1996.[Ukraine celebrating 20th anniversary of Constitution](_blank)
UNIAN (28 June 2016) All other laws and other normative legal acts of Ukraine must conform to the constitution. The right to amend the constitution through a special legislative procedure is vested exclusively in the parliament. The only body that may interpret the constitution and determine whether legislation conforms to it is the Constitutional Court of Ukraine. Since 1996, the public holiday Constitution Day (Ukraine), Constitution Day is celebrated on 28 June.[1996: THE YEAR IN REVIEW](_blank)
, The Ukrainian Weekly (29 December 1996) On 7 February 2019, the Verkhovna Rada voted to amend the constitution to state Ukraine's strategic objectives as joining the European Union and NATO.
Government
The President of Ukraine, president is elected by popular vote for a five-year term and is the formal head of state.
Ukraine's legislative branch includes the 450-seat unicameral parliament, the Verkhovna Rada. The parliament is primarily responsible for the formation of the executive branch and the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine, Cabinet of Ministers, headed by the Prime Minister of Ukraine, prime minister. The president retains the authority to nominate the ministers of foreign affairs and of defence for parliamentary approval, as well as the power to appoint the Prosecutor General of Ukraine, prosecutor general and the head of the Security Service of Ukraine, Security Service.
Laws, acts of the parliament and the cabinet, presidential decrees, and acts of the Verkhovna Rada of Crimea, Crimean parliament may be abrogated by the Constitutional Court of Ukraine, Constitutional Court, should they be found to violate the constitution. Other normative acts are subject to judicial review. The Supreme Court of Ukraine, Supreme Court is the main body in the system of courts of general jurisdiction.
Local self-government is officially guaranteed. Local councils and city mayors are popularly elected and exercise control over local budgets. The heads of regional and district administrations are appointed by the president in accordance with the proposals of the prime minister.
Courts and law enforcement
Martial law in Ukraine, Martial law was declared when Russia invaded in February 2022, and continues.
The courts enjoy legal, financial and constitutional freedom guaranteed by Ukrainian law since 2002. Judges are largely well protected from dismissal (except for gross misconduct). Court justices are appointed by presidential decree for an initial period of five years, after which Ukraine's Supreme Council confirms their positions for life. Although there are still problems, the system is considered to have been much improved since Ukraine's independence in 1991. The Supreme Court is regarded as an independent and impartial body, and has on several occasions ruled against the Ukrainian government. The World Justice Project ranks Ukraine 66 out of 99 countries surveyed in its annual Rule of Law Index.
Prosecutors in Ukraine have greater powers than in most European countries, and according to the European Commission for Democracy through Law "the role and functions of the Prosecutor's Office is not in accordance with Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. ...
standards". The conviction rate is over 99%, equal to the conviction rate of the Soviet Union, with[Moskal: 'Rotten to the core']
Kyiv Post (25 March 2010) suspects often being incarcerated for long periods before trial.[Jackpot]
Kyiv Post, 25 March 2010
On 24 March 2010, Viktor Yanukovych, President Yanukovych formed an expert group to make recommendations on how to "clean up the current mess and adopt a law on court organization".[ One day later, he stated "We can no longer disgrace our country with such a court system."][ The criminal judicial system and the prison system of Ukraine remain quite punitive.]Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
or Russian may use their native language or the services of a translator. Previously all court proceedings had to be held in Ukrainian.
Foreign relations
From 1999 to 2001, Ukraine served as a non-permanent member of the UN Security Council. Historically, Soviet Ukraine joined the United Nations in 1945 as one of the original members following a Western compromise with the Soviet Union.
 The Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Area (DCFTA), which entered into force in January 2016 following the ratification of the Ukraine–European Union Association Agreement, formally integrates Ukraine into the European Single Market and the European Economic Area. Ukraine receives further support and assistance for its Future enlargement of the European Union, EU-accession aspirations from the International Visegrád Fund of the Visegrád Group that consists of Central European Member state of the European Union, EU members the Czech Republic, Poland, Hungary and Slovakia.
In 2020, in Lublin, Lithuania, Poland and Ukraine created the Lublin Triangle initiative, which aims to create further cooperation between the three historical countries of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and further Ukraine's integration and accession to the EU and NATO.
In 2021, the Association Trio was formed by signing a joint memorandum between the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Georgia, Foreign Ministers of Georgia, Ministry of Foreign Affairs and European Integration of Moldova, Moldova and Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Ukraine), Ukraine. The Association Trio is a tripartite format for enhanced cooperation, coordination, and dialogue between the three countries (that have signed the Association Agreement with the EU) with the European Union on issues of common interest related to European integration, enhancing cooperation within the framework of the Eastern Partnership, and committing to the prospect of joining the European Union. As of 2021, Ukraine was preparing to formally apply for European Union, EU membership in 2024, in order to join the European Union in the 2030s,
The Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Area (DCFTA), which entered into force in January 2016 following the ratification of the Ukraine–European Union Association Agreement, formally integrates Ukraine into the European Single Market and the European Economic Area. Ukraine receives further support and assistance for its Future enlargement of the European Union, EU-accession aspirations from the International Visegrád Fund of the Visegrád Group that consists of Central European Member state of the European Union, EU members the Czech Republic, Poland, Hungary and Slovakia.
In 2020, in Lublin, Lithuania, Poland and Ukraine created the Lublin Triangle initiative, which aims to create further cooperation between the three historical countries of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and further Ukraine's integration and accession to the EU and NATO.
In 2021, the Association Trio was formed by signing a joint memorandum between the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Georgia, Foreign Ministers of Georgia, Ministry of Foreign Affairs and European Integration of Moldova, Moldova and Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Ukraine), Ukraine. The Association Trio is a tripartite format for enhanced cooperation, coordination, and dialogue between the three countries (that have signed the Association Agreement with the EU) with the European Union on issues of common interest related to European integration, enhancing cooperation within the framework of the Eastern Partnership, and committing to the prospect of joining the European Union. As of 2021, Ukraine was preparing to formally apply for European Union, EU membership in 2024, in order to join the European Union in the 2030s,
Military
 After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Ukraine inherited a 780,000-man military force on its territory, equipped with the third-largest nuclear weapons and Ukraine, nuclear weapons arsenal in the world.
After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Ukraine inherited a 780,000-man military force on its territory, equipped with the third-largest nuclear weapons and Ukraine, nuclear weapons arsenal in the world. Ukraine played an increasing role in peacekeeping operations. In 2014, the Ukrainian frigate ''Hetman Sagaidachniy'' joined the European Union's counter piracy Operation Atalanta and was part of the EU Naval Force off the coast of Somalia for two months. Ukrainian troops were deployed in Kosovo as part of the Polish-Ukrainian Peace Force Battalion, Ukrainian-Polish Battalion.
A Ukrainian unit was deployed in Lebanon, as part of United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon, UN Interim Force enforcing the mandated ceasefire agreement. There was also a maintenance and training battalion deployed in Sierra Leone. In 2003–05, a Ukrainian unit was deployed as part of the multinational force in Iraq under Polish command.
Military units of other states participated in multinational military exercises with Ukrainian forces in Ukraine regularly, including U.S. military forces.
Following independence, Ukraine declared itself a neutral state.
Ukraine played an increasing role in peacekeeping operations. In 2014, the Ukrainian frigate ''Hetman Sagaidachniy'' joined the European Union's counter piracy Operation Atalanta and was part of the EU Naval Force off the coast of Somalia for two months. Ukrainian troops were deployed in Kosovo as part of the Polish-Ukrainian Peace Force Battalion, Ukrainian-Polish Battalion.
A Ukrainian unit was deployed in Lebanon, as part of United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon, UN Interim Force enforcing the mandated ceasefire agreement. There was also a maintenance and training battalion deployed in Sierra Leone. In 2003–05, a Ukrainian unit was deployed as part of the multinational force in Iraq under Polish command.
Military units of other states participated in multinational military exercises with Ukrainian forces in Ukraine regularly, including U.S. military forces.
Following independence, Ukraine declared itself a neutral state.
Administrative divisions
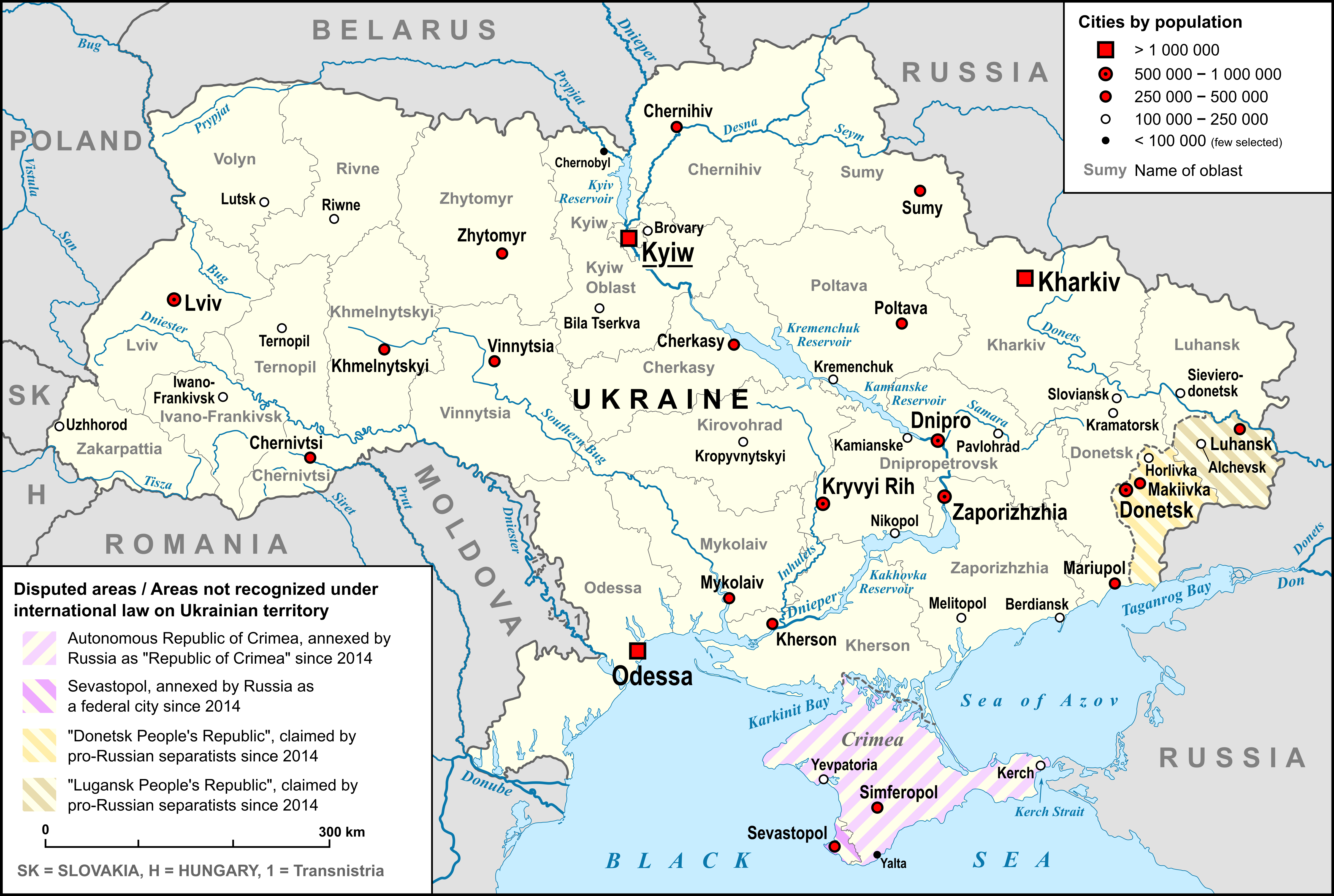 The system of Ukrainian subdivisions reflects the country's status as a unitary state (as stated in the country's constitution) with unified legal and Local government, administrative regimes for each unit.
Including Sevastopol and the Autonomous Republic of Crimea that were annexed by the Russian Federation in 2014, Ukraine consists of 27 regions: twenty-four oblasts (provinces), one autonomous republic (Autonomous Republic of Crimea), and two cities of special status— Kyiv, the capital, and Sevastopol. The 24 oblasts and Crimea are subdivided into 136 (districts) and city municipalities of regional significance, or second-level administrative units.
Populated places in Ukraine are split into two categories: urban and rural. Urban populated places are split further into cities and urban-type settlements (a Soviet administrative invention), while rural populated places consist of villages and settlements (a generally used term). All cities have a certain degree of self-rule depending on their significance such as national significance (as in the case of Kyiv and Sevastopol), regional significance (within each oblast or autonomous republic) or district significance (all the rest of cities). A city's significance depends on several factors such as its population, socio-economic and historical importance and infrastructure.
The system of Ukrainian subdivisions reflects the country's status as a unitary state (as stated in the country's constitution) with unified legal and Local government, administrative regimes for each unit.
Including Sevastopol and the Autonomous Republic of Crimea that were annexed by the Russian Federation in 2014, Ukraine consists of 27 regions: twenty-four oblasts (provinces), one autonomous republic (Autonomous Republic of Crimea), and two cities of special status— Kyiv, the capital, and Sevastopol. The 24 oblasts and Crimea are subdivided into 136 (districts) and city municipalities of regional significance, or second-level administrative units.
Populated places in Ukraine are split into two categories: urban and rural. Urban populated places are split further into cities and urban-type settlements (a Soviet administrative invention), while rural populated places consist of villages and settlements (a generally used term). All cities have a certain degree of self-rule depending on their significance such as national significance (as in the case of Kyiv and Sevastopol), regional significance (within each oblast or autonomous republic) or district significance (all the rest of cities). A city's significance depends on several factors such as its population, socio-economic and historical importance and infrastructure.
Economy
In 2021 agriculture was the biggest sector of the economy and Ukraine was the world's largest Grain trade, wheat exporter.
Agriculture
Ukraine is among the world's top agricultural producers and exporters and is often described as the "bread basket of Europe". During the 2020/21 international wheat marketing season (July–June), it ranked as the sixth largest wheat exporter, accounting for nine percent of world wheat trade.
Tourism
Before the Russo-Ukrainian War, Russo-Ukrainian war the number of tourists visiting Ukraine was eighth in Europe, according to the World Tourism Organization World Tourism rankings, rankings. Ukraine has numerous tourist attractions: mountain ranges suitable for skiing, hiking and fishing; the Black Sea coastline as a popular summer destination; nature reserves of different ecosystems; and churches, castle ruins and other architectural and park landmarks. Kyiv, Lviv, Odesa and Kamyanets-Podilskyi were Ukraine's principal tourist centres, each offering many historical landmarks and extensive hospitality infrastructure. The Seven Wonders of Ukraine and Seven Natural Wonders of Ukraine are selections of the most important landmarks of Ukraine, chosen by Ukrainian experts and an Internet-based public vote. Tourism was the mainstay of Crimea's economy before a major fall in visitor numbers following the Russian annexation in 2014.
Transport
Many roads and bridges were destroyed, and international maritime travel was blocked by the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.Donbas
The Donbas or Donbass (, ; uk, Донба́с ; russian: Донба́сс ) is a historical, cultural, and economic region in eastern Ukraine. Parts of the Donbas are controlled by Russian separatist groups as a result of the Russo-Ukrai ...
region. Although rail freight transport fell in the 1990s, Ukraine is still one of the rail usage statistics by country, world's highest rail users.
Ukraine International Airlines, is the flag carrier and the largest airline, with its head office in Kyiv and its main hub at Kyiv's Boryspil International Airport. It operated domestic and international passenger flights and cargo services to Europe, the Middle East, the United States,
Energy
 Energy in Ukraine is mainly from Natural gas in Ukraine, gas and Coal in Ukraine, coal, followed by Nuclear power in Ukraine, nuclear then oil.
Energy in Ukraine is mainly from Natural gas in Ukraine, gas and Coal in Ukraine, coal, followed by Nuclear power in Ukraine, nuclear then oil.
Information technology
The internet in the country is robust because it is diverse.
Demographics
Before the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine the country had an estimated population of over 41 million people, and was the eighth-most populous country in Europe. It is a Urbanization by country, heavily urbanized country, and its industrial regions in the east and southeast are the most densely populated—about 67% of its total population lives in urban areas. At that time Ukraine had a list of countries by population density, population density of 69.5 inhabitants per square kilometre (180 per square mile), and the overall List of countries by life expectancy, life expectancy in the country at birth was 73 years (68 years for males and 77.8 years for females).
Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Ukraine's population hit a peak of roughly 52 million in 1993. However, due to its death rate exceeding its birth rate, mass emigration, poor living conditions, and low-quality health care,
Language
According to Ukraine's constitution, the state language is Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
.[Serhy Yekelchyk ''Ukraine: Birth of a Modern Nation'', Oxford University Press (2007), ]
 Effective in August 2012, Legislation on languages in Ukraine, a new law on regional languages entitled any local language spoken by at least a 10 percent minority be declared official within that area. Within weeks, Russian was declared a regional language of several southern and eastern Oblasts of Ukraine, oblasts (provinces) and cities. Russian could then be used in the administrative office work and documents of those places.
Effective in August 2012, Legislation on languages in Ukraine, a new law on regional languages entitled any local language spoken by at least a 10 percent minority be declared official within that area. Within weeks, Russian was declared a regional language of several southern and eastern Oblasts of Ukraine, oblasts (provinces) and cities. Russian could then be used in the administrative office work and documents of those places.[Shamshur, pp. 159–168] Following independence, the government of Ukraine began restoring the use of the Ukrainian language in schools and government through a policy of Ukrainisation. Today, most foreign films and TV programs, including Russian ones, are subtitled or dubbed in Ukrainian. Ukraine's 2017 Education in Ukraine, education law bars primary education in public schools in grade five and up in any language but Ukrainian.
Diaspora
Religion
 Ukraine has the world's Eastern Orthodoxy by country, second-largest Eastern Orthodox population, after Russia. A 2021 survey conducted by the Kyiv International Institute of Sociology (KIIS) found that 82% of Ukrainians declared themselves to be religious, while 7% were atheists, and a further 11% found it difficult to answer the question. The level of religiosity in Ukraine was reported to be the highest in Western Ukraine (91%), and the lowest in the
Ukraine has the world's Eastern Orthodoxy by country, second-largest Eastern Orthodox population, after Russia. A 2021 survey conducted by the Kyiv International Institute of Sociology (KIIS) found that 82% of Ukrainians declared themselves to be religious, while 7% were atheists, and a further 11% found it difficult to answer the question. The level of religiosity in Ukraine was reported to be the highest in Western Ukraine (91%), and the lowest in the Donbas
The Donbas or Donbass (, ; uk, Донба́с ; russian: Донба́сс ) is a historical, cultural, and economic region in eastern Ukraine. Parts of the Donbas are controlled by Russian separatist groups as a result of the Russo-Ukrai ...
(57%) and Eastern Ukraine (56%).[ but rose to 2.2% of the population in 2018.
]
Health
Ukraine's healthcare system is state subsidised and freely available to all Ukrainian citizens and registered residents. However, it is not compulsory to be treated in a state-run hospital as a number of private medical complexes do exist nationwide. The public sector employs most healthcare professionals, with those working for private medical centres typically also retaining their state employment as they are mandated to provide care at public health facilities on a regular basis.
All of Ukraine's medical service providers and hospitals are subordinate to the Ministry of Healthcare (Ukraine), Ministry of Healthcare, which provides oversight and scrutiny of general medical practice as well as being responsible for the day-to-day administration of the healthcare system. Despite this, standards of hygiene and patient-care have fallen.
Ukraine faces a number of major public health issues and is considered to be in a demographic crisis because of its high death rate and low birth rate (the Ukrainian birth rate is 11 births/1,000 population, and the death rate is 16.3 deaths/1,000 population). A factor contributing to the high death rate is a high mortality rate among working-age males from preventable causes such as alcohol poisoning and smoking.
Education
According to the Constitution of Ukraine, Ukrainian constitution, access to free education is granted to all citizens. Complete general secondary education is compulsory in the state schools which constitute the overwhelming majority. Free higher education in state and communal educational establishments is provided on a competitive basis.
Because of the Soviet Union's emphasis on total access of education for all citizens, which continues today, the literacy rate is an estimated 99.4%.[ Since 2005, an eleven-year school programme has been replaced with a twelve-year one: primary education takes four years to complete (starting at age six), middle education (secondary) takes five years to complete; upper secondary then takes three years. Students in the 12th grade take Government tests, which are also referred to as school-leaving exams. These tests are later used for university admissions.
Among the oldest is also the Lviv University, founded in 1661. More higher education institutions were set up in the 19th century, beginning with universities in Kharkiv University, Kharkiv (1805), Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, Kyiv (1834), Odessa University, Odesa (1865) and Chernivtsi University, Chernivtsi (1875) and a number of professional higher education institutions, e.g.: Nizhyn Pedagogical University, Nizhyn Historical and Philological Institute (originally established as the Gymnasium of Higher Sciences in 1805), a Veterinary Institute (1873) and a Kharkiv Polytechnical Institute, Technological Institute (1885) in Kharkiv, a Igor Sikorsky Kyiv Polytechnic Institute, Polytechnic Institute in Kyiv (1898) and a Higher Mining School (1899) in Dnipro, Katerynoslav. Rapid growth followed in the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet period. By 1988 the number of higher education institutions increased to 146 with over 850,000 students.
The Ukrainian higher education system comprises higher educational establishments, scientific and methodological facilities under national, municipal government, municipal and self-governing bodies in charge of education. The organisation of higher education in Ukraine is built up in accordance with the structure of education of the world's higher developed countries, as is defined by UNESCO and the UN.
Ukraine produces the fourth largest number of Tertiary education, post-secondary graduates in Europe, while being ranked seventh in population. Higher education in Ukraine, Higher education is either state funded or private. Most universities provide subsidised housing for out-of-city students. It is common for libraries to supply required books for all registered students. Ukrainian universities confer two degrees: the bachelor's degree (4 years) and the master's degree (5–6th year), in accordance with the Bologna process. Historically, Specialist degree (usually 5 years) is still also granted; it was the only degree awarded by universities in Soviet times. Ukraine was ranked 57th in 2022 in the Global Innovation Index, down from 49th in 2021
]
Regional differences

Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
is the dominant language in Western Ukraine and in Central Ukraine
Central Ukraine ( uk, Центральна Україна, ''Tsentralna Ukraina'') consists of historical regions of left-bank Ukraine and right-bank Ukraine that reference to the Dnipro River. It is situated away from the Black Sea Littoral N ...
, while Russian language, Russian is the dominant language in the cities of Eastern Ukraine and Southern Ukraine. In the Ukrainian SSR schools, learning Russian language, Russian was mandatory; in modern Ukraine, schools with Ukrainian as the language of instruction offer classes in Russian and in the other minority languages.[ Surveys of regional identities in Ukraine have shown that the feeling of belonging to a "Soviet identity" is strongest in the ]Donbas
The Donbas or Donbass (, ; uk, Донба́с ; russian: Донба́сс ) is a historical, cultural, and economic region in eastern Ukraine. Parts of the Donbas are controlled by Russian separatist groups as a result of the Russo-Ukrai ...
(about 40%) and the Crimea (about 30%).
During Elections in Ukraine, elections voters of Western and Central Ukrainian Oblasts of Ukraine, oblasts (provinces) vote mostly for parties (Our Ukraine–People's Self-Defense Bloc, Our Ukraine, All-Ukrainian Union "Fatherland", Batkivshchyna) and presidential candidates (Viktor Yuschenko, Yulia Tymoshenko) with a pro-Western and state reform Political platform, platform, while voters in Southern and Eastern oblasts vote for parties (Communist Party of Ukraine, CPU, Party of Regions) and presidential candidates (Viktor Yanukovych) with a pro-Russian and status quo platform.
Culture
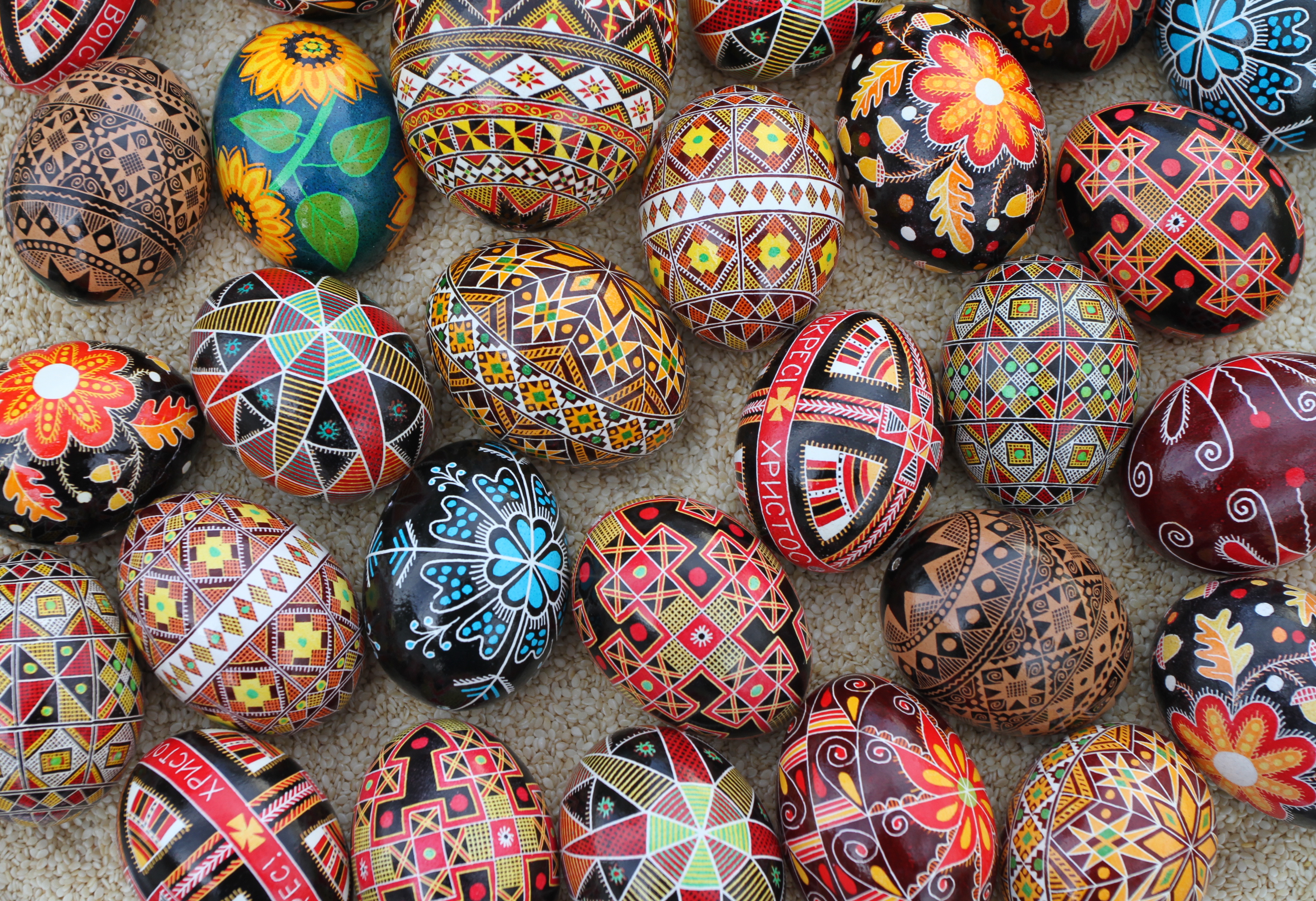 Ukrainian customs are heavily influenced by Orthodox Christianity, the dominant religion in the country. Gender roles also tend to be more traditional, and grandparents play a greater role in bringing up children, than in the West. The culture of Ukraine has also been influenced by its eastern and western neighbours, reflected in its Ukrainian architecture, architecture, music and art.
The Communist era had quite a strong effect on the art and writing of Ukraine. In 1932, Stalin made socialist realism state policy in the Soviet Union when he promulgated the decree "On the Reconstruction of Literary and Art Organisations". This greatly stifled creativity. During the 1980s glasnost (openness) was introduced and Soviet artists and writers again became free to express themselves as they wanted.
, UNESCO inscribed List of World Heritage Sites in Ukraine, seven properties in Ukraine on the World Heritage List. Ukraine is also known for its decorative and folk traditions such as Petrykivka painting, Kosiv ceramics, and Cossack's songs of Dnipropetrovsk Region, Cossack songs.
The tradition of the Easter egg, known as pysanky, has long roots in Ukraine. These eggs were drawn on with wax to create a pattern; then, the dye was applied to give the eggs their pleasant colours, the dye did not affect the previously wax-coated parts of the egg. After the entire egg was dyed, the wax was removed leaving only the colourful pattern. This tradition is thousands of years old, and precedes the arrival of Christianity to Ukraine. In the city of Kolomyia near the foothills of the Carpathian Mountains, the museum of Pysanka was built in 2000 and won a nomination as the monument of modern Ukraine in 2007, part of the Seven Wonders of Ukraine action.
Ukrainian customs are heavily influenced by Orthodox Christianity, the dominant religion in the country. Gender roles also tend to be more traditional, and grandparents play a greater role in bringing up children, than in the West. The culture of Ukraine has also been influenced by its eastern and western neighbours, reflected in its Ukrainian architecture, architecture, music and art.
The Communist era had quite a strong effect on the art and writing of Ukraine. In 1932, Stalin made socialist realism state policy in the Soviet Union when he promulgated the decree "On the Reconstruction of Literary and Art Organisations". This greatly stifled creativity. During the 1980s glasnost (openness) was introduced and Soviet artists and writers again became free to express themselves as they wanted.
, UNESCO inscribed List of World Heritage Sites in Ukraine, seven properties in Ukraine on the World Heritage List. Ukraine is also known for its decorative and folk traditions such as Petrykivka painting, Kosiv ceramics, and Cossack's songs of Dnipropetrovsk Region, Cossack songs.
The tradition of the Easter egg, known as pysanky, has long roots in Ukraine. These eggs were drawn on with wax to create a pattern; then, the dye was applied to give the eggs their pleasant colours, the dye did not affect the previously wax-coated parts of the egg. After the entire egg was dyed, the wax was removed leaving only the colourful pattern. This tradition is thousands of years old, and precedes the arrival of Christianity to Ukraine. In the city of Kolomyia near the foothills of the Carpathian Mountains, the museum of Pysanka was built in 2000 and won a nomination as the monument of modern Ukraine in 2007, part of the Seven Wonders of Ukraine action.
Libraries
The Vernadsky National Library of Ukraine, is the main academic library and main scientific information centre in Ukraine.
During the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine the Russians bombed the Maksymovych Scientific Library of the Taras Shevchenko Kyiv National University, Vernadsky National Library of Ukraine, the National Scientific Medical Library of Ukraine and the Kyiv city youth library.
Literature
Ukrainian literature has origins in Old Church Slavonic writings, which was used as a Liturgy, liturgical and literary language following Christianization of Kievan Rus', Christianization in the 10th and 11th centuries.Primary Chronicle
The ''Tale of Bygone Years'' ( orv, Повѣсть времѧньныхъ лѣтъ, translit=Pověstĭ vremęnĭnyxŭ lětŭ; ; ; ; ), often known in English as the ''Rus' Primary Chronicle'', the ''Russian Primary Chronicle'', or simply the ...
''. Literary activity faced a sudden decline after the Mongol invasion of Kievan Rus', before seeing a revival beginning in the 14th century, and was advanced in the 16th century with the invention of the printing press.[
The ]Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
established an independent society and popularized a Duma (epic), new kind of epic poetry, epic poem, which marked a high point of Ukrainian oral literature.[ These advances were then set back in the 17th and early 18th centuries, as many Ukrainian authors wrote in Russian or Polish. Nonetheless, by the late 18th century, the modern literary Ukrainian language finally emerged.][ In 1798, the modern era of the Ukrainian literary tradition began with Ivan Kotlyarevsky's publication of Eneida in the Ukrainian vernacular.
By the 1830s, a Ukrainian romanticism, romantic literature began to develop, and the nation's most renowned cultural figure, romanticist poet-painter Taras Shevchenko emerged. Whereas Ivan Kotliarevsky is considered to be the father of literature in the Ukrainian vernacular; Shevchenko is the father of a national revival.
Then, in 1863, the use of the Ukrainian language in print was effectively Ems Ukaz, prohibited by the Russian Empire.][ This severely curtailed literary activity in the area, and Ukrainian writers were forced to either publish their works in Russian or release them in Austrian controlled Galicia (Central Europe), Galicia. The ban was never officially lifted, but it became obsolete after the revolution and the Bolsheviks' coming to power.][
Ukrainian literature continued to flourish in the early Soviet years when nearly all literary trends were approved. These policies faced a steep decline in the 1930s, when prominent representatives as well as many others were killed by the NKVD during the Great Purge. In general around 223 writers were repressed by what was known as the Executed Renaissance. These repressions were part of Stalin's implemented policy of socialist realism. The doctrine did not necessarily repress the use of the Ukrainian language, but it required that writers follow a certain style in their works.
Literary freedom grew in the late 1980s and early 1990s alongside the decline and collapse of the USSR and the reestablishment of Ukrainian independence in 1991.][
]
Architecture
 Ukrainian architecture includes the motifs and styles that are found in structures built in modern Ukraine, and by Ukrainians worldwide. These include initial roots which were established in the state of Kievan Rus'. Following the Christianization of Kievan Rus', Ukrainian architecture has been influenced by Byzantine architecture. After the Mongol invasion of Kievan Rus', it continued to develop in the Kingdom of Galicia-Volhynia.
Ukrainian architecture includes the motifs and styles that are found in structures built in modern Ukraine, and by Ukrainians worldwide. These include initial roots which were established in the state of Kievan Rus'. Following the Christianization of Kievan Rus', Ukrainian architecture has been influenced by Byzantine architecture. After the Mongol invasion of Kievan Rus', it continued to develop in the Kingdom of Galicia-Volhynia.
Weaving and embroidery
 Artisan textile arts play an important role in Ukrainian culture, especially in Ukrainian wedding traditions. Ukrainian embroidery, weaving and lace-making are used in traditional folk dress and in traditional celebrations. Ukrainian embroidery varies depending on the region of origin and the designs have a long history of motifs, compositions, choice of colours and types of stitches.
Artisan textile arts play an important role in Ukrainian culture, especially in Ukrainian wedding traditions. Ukrainian embroidery, weaving and lace-making are used in traditional folk dress and in traditional celebrations. Ukrainian embroidery varies depending on the region of origin and the designs have a long history of motifs, compositions, choice of colours and types of stitches.
Music
 Music is a major part of Ukrainian culture, with a long history and many influences. From traditional folk music, to classical music, classical and modern rock, Ukraine has produced several internationally recognised musicians including Kirill Karabits, Okean Elzy and Ruslana. Elements from traditional Ukrainian folk music made their way into Western music and even into modern jazz. Ukrainian music sometimes presents a perplexing mix of exotic melismatic singing with chordal harmony. The most striking general characteristic of authentic ethnic Ukrainian folk music is the wide use of minor modes or keys which incorporate augmented second intervals.
Music is a major part of Ukrainian culture, with a long history and many influences. From traditional folk music, to classical music, classical and modern rock, Ukraine has produced several internationally recognised musicians including Kirill Karabits, Okean Elzy and Ruslana. Elements from traditional Ukrainian folk music made their way into Western music and even into modern jazz. Ukrainian music sometimes presents a perplexing mix of exotic melismatic singing with chordal harmony. The most striking general characteristic of authentic ethnic Ukrainian folk music is the wide use of minor modes or keys which incorporate augmented second intervals. The first dedicated musical academy was set up in Hlukhiv in 1738 and students were taught to sing and play violin and bandura from manuscripts. As a result, many of the earliest composers and performers within the Russian empire were ethnically Ukrainian, having been born or educated in Hlukhiv or having been closely associated with this music school.
The first dedicated musical academy was set up in Hlukhiv in 1738 and students were taught to sing and play violin and bandura from manuscripts. As a result, many of the earliest composers and performers within the Russian empire were ethnically Ukrainian, having been born or educated in Hlukhiv or having been closely associated with this music school.
Media
The Ukrainian legal framework on media freedom is deemed "among the most progressive in eastern Europe", although implementation has been uneven.[Freedom House]
Ukraine 2015 Freedom of the Press
report The constitution and laws provide for freedom of speech and Freedom of the press in Ukraine, press. The main regulatory authority for the broadcast media is the National Television and Radio Broadcasting Council of Ukraine (NTRBCU), tasked with licensing media outlets and ensure their compliance with the law.
Kyiv dominates the media sector in Ukraine: National List of newspapers in Ukraine, newspapers ''Den (newspaper), Den'', ''Dzerkalo Tyzhnia'', tabloids, such as ''The Ukrainian Week'' or ''Focus (Ukrainian magazine), Focus'', and television and radio are largely based there, although Lviv is also a significant national media centre. The National News Agency of Ukraine, Ukrinform was founded here in 1918. BBC Ukrainian started its broadcasts in 1992. 75% of the population use the internet, and social media is widely used by government and people.
Sport
 Ukraine greatly benefited from the Soviet emphasis on physical education. These policies left Ukraine with hundreds of stadia, swimming pools, gymnasia and many other athletic facilities. The most popular sport is Association football, football. The top professional league is the Ukrainian Premier League, Vyscha Liha ("premier league").
Many Ukrainians also played for the Soviet national football team, most notably Ballon d'Or winners Ihor Belanov and Oleh Blokhin. This award was only presented to one Ukrainian after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Andriy Shevchenko. The national team made its debut in the 2006 FIFA World Cup, and reached the quarterfinals before losing to eventual champions, Italy national football team, Italy.
Ukraine greatly benefited from the Soviet emphasis on physical education. These policies left Ukraine with hundreds of stadia, swimming pools, gymnasia and many other athletic facilities. The most popular sport is Association football, football. The top professional league is the Ukrainian Premier League, Vyscha Liha ("premier league").
Many Ukrainians also played for the Soviet national football team, most notably Ballon d'Or winners Ihor Belanov and Oleh Blokhin. This award was only presented to one Ukrainian after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Andriy Shevchenko. The national team made its debut in the 2006 FIFA World Cup, and reached the quarterfinals before losing to eventual champions, Italy national football team, Italy.
 Ukrainian boxing, boxers are amongst the best in the world. Since becoming the undisputed cruiserweight champion in 2018, Oleksandr Usyk has also gone on to win the unified WBA (Super), IBF, WBO and IBO heavyweight titles. This feat made him one of only three boxers to have unified the cruiserweight world titles and become a world heavyweight champion. The brothers Vitali Klitschko, Vitali and Wladimir Klitschko are former heavyweight world champions who held multiple world titles throughout their careers. Also hailing from Ukraine is Vasyl Lomachenko, a 2008 Summer Olympics, 2008 and 2012 Olympic games, 2012 Olympic gold medalist. He is the Unified champion, unified lightweight world champion who ties the record for winning a world title in the fewest professional fights; three. As of September 2018, he is ranked as the world's best active boxer, pound for pound, by boxing pound for pound rankings#ESPN, ESPN.
Sergey Bubka held the record in the Pole vault from 1993 to 2014; with great strength, speed and gymnastic abilities, he was voted the world's best athlete on several occasions.
Basketball has gained popularity in Ukraine. In 2011, Ukraine was granted a right to organize EuroBasket 2015. Two years later the Ukraine national basketball team finished sixth in EuroBasket 2013 and qualified to 2014 FIBA Basketball World Cup, FIBA World Cup for the first time in its history. Euroleague participant BC Budivelnyk, Budivelnyk Kyiv is the strongest professional basketball club in Ukraine.
Chess is a popular sport in Ukraine. Ruslan Ponomariov is the former world champion. There are about 85 Grandmaster (chess), Grandmasters and 198 International Masters in Ukraine. Rugby league is played throughout Ukraine.
Ukrainian boxing, boxers are amongst the best in the world. Since becoming the undisputed cruiserweight champion in 2018, Oleksandr Usyk has also gone on to win the unified WBA (Super), IBF, WBO and IBO heavyweight titles. This feat made him one of only three boxers to have unified the cruiserweight world titles and become a world heavyweight champion. The brothers Vitali Klitschko, Vitali and Wladimir Klitschko are former heavyweight world champions who held multiple world titles throughout their careers. Also hailing from Ukraine is Vasyl Lomachenko, a 2008 Summer Olympics, 2008 and 2012 Olympic games, 2012 Olympic gold medalist. He is the Unified champion, unified lightweight world champion who ties the record for winning a world title in the fewest professional fights; three. As of September 2018, he is ranked as the world's best active boxer, pound for pound, by boxing pound for pound rankings#ESPN, ESPN.
Sergey Bubka held the record in the Pole vault from 1993 to 2014; with great strength, speed and gymnastic abilities, he was voted the world's best athlete on several occasions.
Basketball has gained popularity in Ukraine. In 2011, Ukraine was granted a right to organize EuroBasket 2015. Two years later the Ukraine national basketball team finished sixth in EuroBasket 2013 and qualified to 2014 FIBA Basketball World Cup, FIBA World Cup for the first time in its history. Euroleague participant BC Budivelnyk, Budivelnyk Kyiv is the strongest professional basketball club in Ukraine.
Chess is a popular sport in Ukraine. Ruslan Ponomariov is the former world champion. There are about 85 Grandmaster (chess), Grandmasters and 198 International Masters in Ukraine. Rugby league is played throughout Ukraine.
Cuisine
 The traditional Ukrainian diet includes chicken, pork, beef, fish and mushrooms. Ukrainians also tend to eat a lot of potatoes; grains; and fresh, boiled or pickled vegetables. Popular traditional dishes ' (boiled dumplings with mushrooms, potatoes, sauerkraut, cottage cheese, cherries or berries), ''nalysnyky'' (pancakes with cottage cheese, poppy seeds, mushrooms, caviar or meat), ''Cabbage soup, kapusnyak'' (cabbage soup made with meat, potatoes, carrots, onions, millet, tomato paste, spices and fresh herbs), borscht (soup made of beets, cabbage and mushrooms or meat) and (stuffed cabbage rolls filled with rice, carrots, onion and minced meat). Among traditional baked goods are decorated korovais and Paska (bread), paska Easter bread. Ukrainian specialties also include Chicken Kiev and Kyiv cake.
Ukrainians drink kompot, stewed fruit compote, juices, milk, buttermilk, mineral water, tea and coffee, beer, wine and .
The traditional Ukrainian diet includes chicken, pork, beef, fish and mushrooms. Ukrainians also tend to eat a lot of potatoes; grains; and fresh, boiled or pickled vegetables. Popular traditional dishes ' (boiled dumplings with mushrooms, potatoes, sauerkraut, cottage cheese, cherries or berries), ''nalysnyky'' (pancakes with cottage cheese, poppy seeds, mushrooms, caviar or meat), ''Cabbage soup, kapusnyak'' (cabbage soup made with meat, potatoes, carrots, onions, millet, tomato paste, spices and fresh herbs), borscht (soup made of beets, cabbage and mushrooms or meat) and (stuffed cabbage rolls filled with rice, carrots, onion and minced meat). Among traditional baked goods are decorated korovais and Paska (bread), paska Easter bread. Ukrainian specialties also include Chicken Kiev and Kyiv cake.
Ukrainians drink kompot, stewed fruit compote, juices, milk, buttermilk, mineral water, tea and coffee, beer, wine and .
See also
*Outline of Ukraine
Notes
a. Among the Ukrainians that rose to the highest offices in the Russian Empire were Aleksey Razumovsky, Alexander Bezborodko and Ivan Paskevich. Among the Ukrainians who greatly influenced the Russian Orthodox Church in this period were Stephen Yavorsky, Feofan Prokopovich and Dimitry of Rostov.
b. Estimates on the number of deaths vary. Official Soviet data is not available because the Soviet government denied the existence of the famine. See the Holodomor
The Holodomor ( uk, Голодомо́р, Holodomor, ; derived from uk, морити голодом, lit=to kill by starvation, translit=moryty holodom, label=none), also known as the Terror-Famine or the Great Famine, was a man-made famin ...
article for details. Sources differ on interpreting various statements from different branches of different governments as to whether they amount to the official recognition of the Famine as Genocide by the country. For example, after the statement issued by the Latvian Sejm on 13 March 2008, the total number of countries is given as 19 (according to ''Ukrainian BBC''
, 16 (according to ''Korrespondent'', Russian edition
, "more than 10" (according to ''Korrespondent'', Ukrainian edition
Retrieved 27 January 2008.
c. These figures are likely to be much higher, as they do not include Ukrainians of other nationalities or Ukrainian Jews, but only ethnic Ukrainians, from the Ukrainian SSR.
d. This figure excludes POW deaths.
e. Several countries with territory in Europe have a larger total area, but all of those also include territory outside of Europe. Only Russia's European territory is larger than Ukraine.
f. According to the official Ukrainian Census (2001), 2001 census data (by nationality; by language
g. Such writings were also the base for Russian and Belarusian literature.
References
Print sources
Reference books
* ''Encyclopedia of Ukraine'' (University of Toronto Press, 1984–1993) 5 vol
partial online version
from Canadian Institute of Ukrainian Studies
*
Ukraine: A Concise Encyclopedia Vol.1
' ed by Volodymyr E. KubijovyC; University of Toronto Press. 1963; 1188pp
Recent (since 1991)
* Aslund, Anders, and Michael McFaul. ''Revolution in Orange: The Origins of Ukraine's Democratic Breakthrough'' (2006)
* Birch, Sarah. ''Elections and Democratization in Ukraine'' Macmillan, 200
online edition
* Edwards Mike: "Ukraine – Running on empty" National Geographic Magazine March 1993
* Ivan Katchanovski: ''Cleft Countries: Regional Political Divisions and Cultures in Post-Soviet Ukraine and Moldova'', Ibidem-Verlag, 2006,
* Kuzio, Taras: ''Contemporary Ukraine: Dynamics of Post-Soviet Transformation'', M.E. Sharpe, 1998,
* Kuzio, Taras. ''Ukraine: State and Nation Building'', Routledge, 199
online edition
* Shamshur O. V., Ishevskaya T. I., ''Multilingual education as a factor of inter-ethnic relations: the case of the Ukraine'', in ''Language Education for Intercultural Communication'', by D. E. Ager, George Muskens, Sue Wright, Multilingual Matters, 1993,
*
* Whitmore, Sarah. ''State Building in Ukraine: The Ukrainian Parliament, 1990–2003'' Routledge, 200
online edition
* Andrew Wilson (historian), Wilson, Andrew, ''Ukraine's Orange Revolution'' (2005)
* Wilson, Andrew, ''The Ukrainians: Unexpected Nation,'' 2nd ed. 2002;
* Wilson, Andrew, ''Ukrainian Nationalism in the 1990s: A Minority Faith'', Cambridge University Press,
* Zon, Hans van. ''The Political Economy of Independent Ukraine''. 200
online edition
History
UKRAINIAN UPPER PALAEOLITHIC BETWEEN 40/10.000 BP
* Bilinsky, Yaroslav ''The Second Soviet Republic: The Ukraine after World War II'' (Rutgers University Press, 1964
online
* Hrushevsky, Michael. ''A History of Ukraine'' (1986)
* Katchanovski Ivan; Kohut, Zenon E.; Nebesio, Bohdan Y.; and Yurkevich, Myroslav. ''Historical Dictionary of Ukraine.'' Second Edition. Scarecrow Press, 2013. 968 pp.
* Kononenko, Konstantyn. ''Ukraine and Russia: A History of the Economic Relations between Ukraine and Russia, 1654–1917'' (Marquette University Press 1958
online
* Luckyj, George S. ''Towards an Intellectual History of Ukraine: An Anthology of Ukrainian Thought from 1710 to 1995.'' (1996)
* Magocsi, Paul Robert, ''A History of Ukraine''. University of Toronto Press, 1996
* Reid, Anna. ''Borderland: A Journey Through the History of Ukraine'' (2003
online edition
* Orest Subtelny, Subtelny, Orest. ''Ukraine: A History'', 1st edition. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 1988. .
* Yekelchyk, Serhy. ''Ukraine: Birth of a Modern Nation'' (Oxford University Press 2007
online
World War II
*
* Berkhoff, Karel C. ''Harvest of Despair: Life and Death in Ukraine Under Nazi Rule.'' Harvard U. Press, 2004. 448 pp.
*
* Gross, Jan T. ''Revolution from Abroad: The Soviet Conquest of Poland's Western Ukraine and Western Belorussia'' (1988).
* Wendy Lower, Lower, Wendy. ''Nazi Empire-Building and the Holocaust in Ukraine.'' U. of North Carolina Press, 2005. 307 pp.
* Piotrowski Tadeusz, ''Poland's Holocaust: Ethnic Strife, Collaboration with Occupying Forces and Genocide in the Second Republic, 1918–1947'', McFarland & Company, 1998,
* Redlich, Shimon. ''Together and Apart in Brzezany: Poles, Jews, and Ukrainians, 1919–1945.'' Indiana U. Press, 2002. 202 pp.
* Zabarko, Boris, ed. ''Holocaust In The Ukraine'', Mitchell Vallentine & Co, 2005. 394 pp.
External links
Ukraine Corruption Profile
from the Risk & Compliance Portal
Ukraine
information from the United States Department of State
Key Development Forecasts for Ukraine
from International Futures
Encyclopedia of Ukraine
; Government
The President of Ukraine
Government Portal of Ukraine
The Parliament of Ukraine
Ukrainian art. Most famous modern painters
; Trade
World Bank Summary Trade Statistics Ukraine
{{Authority control
Ukraine,
1991 establishments in Ukraine, *
Countries in Europe
Eastern European countries
Member states of the Council of Europe
Member states of the United Nations
Republics
States and territories established in 1991
Ukrainian-speaking countries and territories
Post-Soviet states
 Settlement by
Settlement by  The establishment of the state of Kievan Rus' remains obscure and uncertain. The state included much of present-day Ukraine, Belarus and the western part of
The establishment of the state of Kievan Rus' remains obscure and uncertain. The state included much of present-day Ukraine, Belarus and the western part of  In 1349, in the aftermath of the
In 1349, in the aftermath of the  In 1648,
In 1648,  The 19th century saw the rise of Ukrainian nationalism. With growing urbanization and modernization and a cultural trend toward
The 19th century saw the rise of Ukrainian nationalism. With growing urbanization and modernization and a cultural trend toward  In Second Polish Republic, Poland, Marshal Józef Piłsudski and his political allies wanted to gain Ukrainian support by offering limited local autonomy as way to minimise Soviet influences in the borderlands. However, this approach was abandoned after Piłsudski's death in 1935, due to continued unrest among the Ukrainian population, with the Polish government responding by restricting rights of people who declared Ukrainian nationality and belonged to the Eastern Orthodox Church. In consequence, an underground Ukrainian nationalist and militant movement arose in the 1920s and 1930s, which gradually transformed into the Ukrainian Military Organization and later the Organisation of Ukrainian Nationalists (OUN).
Meanwhile, the recently constituted Soviet Ukraine became one of the founding republics of the Soviet Union. During the 1920s, under the Ukrainisation policy pursued by the national Communist leadership of Mykola Skrypnyk, Soviet leadership at first encouraged a national renaissance in Culture of Ukraine, Ukrainian culture and Ukrainian language, language. Ukrainisation was part of the Soviet-wide policy of Korenisation (literally ''indigenisation''), which was intended to promote the advancement of native peoples, their language and culture into the governance of their respective republics.
Around the same time, Soviet leader Vladimir Lenin instituted the New Economic Policy (NEP), which introduced a form of market socialism, allowing some private ownership of small and medium-sized productive enterprises, hoping to reconstruct the post-war Soviet Union that had been devastated by both WWI and later the civil war. The NEP was successful at restoring the formerly war-torn nation to pre-WWI levels of production and agricultural output by the mid-1920s, much of the latter based in Ukraine. These policies attracted many prominent former UNR figures, including former UNR leader Hrushevsky, to return to Soviet Ukraine, where they were accepted, and participated in the advancement of Ukrainian science and culture.
This period was cut short when Joseph Stalin became the leader of the USSR following Lenin's death. Stalin did away with the NEP in what became known as the Great Break (USSR), Great Break. Starting from the late 1920s and now with a planned economy, centrally planned economy, Soviet Ukraine took part in an Industrialization in the USSR, industrialisation scheme which quadrupled its industrial output during the 1930s.
However, as a consequence of Stalin's new policy, the Ukrainian peasantry suffered from the Collectivization in the USSR, programme of collectivization of agricultural crops. Collectivization was part of the first five-year plan and was enforced by regular troops and the secret police known as Cheka. Those who resisted were Population transfer in the Soviet Union, arrested and deported to gulags and work camps. As members of the collective farms were sometimes not allowed to receive any grain until unrealistic quotas were met, millions starved to death in a Droughts and famines in Russia and the Soviet Union, famine known as the
In Second Polish Republic, Poland, Marshal Józef Piłsudski and his political allies wanted to gain Ukrainian support by offering limited local autonomy as way to minimise Soviet influences in the borderlands. However, this approach was abandoned after Piłsudski's death in 1935, due to continued unrest among the Ukrainian population, with the Polish government responding by restricting rights of people who declared Ukrainian nationality and belonged to the Eastern Orthodox Church. In consequence, an underground Ukrainian nationalist and militant movement arose in the 1920s and 1930s, which gradually transformed into the Ukrainian Military Organization and later the Organisation of Ukrainian Nationalists (OUN).
Meanwhile, the recently constituted Soviet Ukraine became one of the founding republics of the Soviet Union. During the 1920s, under the Ukrainisation policy pursued by the national Communist leadership of Mykola Skrypnyk, Soviet leadership at first encouraged a national renaissance in Culture of Ukraine, Ukrainian culture and Ukrainian language, language. Ukrainisation was part of the Soviet-wide policy of Korenisation (literally ''indigenisation''), which was intended to promote the advancement of native peoples, their language and culture into the governance of their respective republics.
Around the same time, Soviet leader Vladimir Lenin instituted the New Economic Policy (NEP), which introduced a form of market socialism, allowing some private ownership of small and medium-sized productive enterprises, hoping to reconstruct the post-war Soviet Union that had been devastated by both WWI and later the civil war. The NEP was successful at restoring the formerly war-torn nation to pre-WWI levels of production and agricultural output by the mid-1920s, much of the latter based in Ukraine. These policies attracted many prominent former UNR figures, including former UNR leader Hrushevsky, to return to Soviet Ukraine, where they were accepted, and participated in the advancement of Ukrainian science and culture.
This period was cut short when Joseph Stalin became the leader of the USSR following Lenin's death. Stalin did away with the NEP in what became known as the Great Break (USSR), Great Break. Starting from the late 1920s and now with a planned economy, centrally planned economy, Soviet Ukraine took part in an Industrialization in the USSR, industrialisation scheme which quadrupled its industrial output during the 1930s.
However, as a consequence of Stalin's new policy, the Ukrainian peasantry suffered from the Collectivization in the USSR, programme of collectivization of agricultural crops. Collectivization was part of the first five-year plan and was enforced by regular troops and the secret police known as Cheka. Those who resisted were Population transfer in the Soviet Union, arrested and deported to gulags and work camps. As members of the collective farms were sometimes not allowed to receive any grain until unrealistic quotas were met, millions starved to death in a Droughts and famines in Russia and the Soviet Union, famine known as the  Following the Invasion of Poland in September 1939, Nazi Germany, German and Soviet Army, Soviet troops divided the territory of Poland. Thus, Eastern
Following the Invasion of Poland in September 1939, Nazi Germany, German and Soviet Army, Soviet troops divided the territory of Poland. Thus, Eastern  In total, the number of ethnic Ukrainians who fought in the ranks of the Soviet Army is estimated from 4.5 million to 7 million; half of the Soviet Partisans, Pro-Soviet partisan guerrilla resistance units, which counted up to 500,000 troops in 1944, were also Ukrainian. Generally, the Ukrainian Insurgent Army's figures are unreliable, with figures ranging anywhere from 15,000 to as many as 100,000 fighters.
The vast majority of the fighting in World War II took place on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front. By some estimates, 93% of all German casualties took place there. The World War II casualties of the Soviet Union, total losses inflicted upon the Ukrainian population during the war are estimated at 6 million, including an estimated one and a half million Jews killed by the Einsatzgruppen, sometimes with the help of local collaborators. Of the estimated 8.6 million Soviet troop losses,Кривошеев Г. Ф., ''Россия и СССР в войнах XX века: потери вооруженных сил. Статистическое исследование'' (Krivosheev G. F., ''Russia and the USSR in the wars of the 20th century: losses of the Armed Forces. A Statistical Study'') 1.4 million were ethnic Ukrainians, and general losses of the Ukrainian people in the war amounted to 40–44% of the total losses of the USSR. The Victory Day over Nazism in World War II, Victory Day is celebrated as one of eleven Ukrainian national holidays.
In total, the number of ethnic Ukrainians who fought in the ranks of the Soviet Army is estimated from 4.5 million to 7 million; half of the Soviet Partisans, Pro-Soviet partisan guerrilla resistance units, which counted up to 500,000 troops in 1944, were also Ukrainian. Generally, the Ukrainian Insurgent Army's figures are unreliable, with figures ranging anywhere from 15,000 to as many as 100,000 fighters.
The vast majority of the fighting in World War II took place on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front. By some estimates, 93% of all German casualties took place there. The World War II casualties of the Soviet Union, total losses inflicted upon the Ukrainian population during the war are estimated at 6 million, including an estimated one and a half million Jews killed by the Einsatzgruppen, sometimes with the help of local collaborators. Of the estimated 8.6 million Soviet troop losses,Кривошеев Г. Ф., ''Россия и СССР в войнах XX века: потери вооруженных сил. Статистическое исследование'' (Krivosheev G. F., ''Russia and the USSR in the wars of the 20th century: losses of the Armed Forces. A Statistical Study'') 1.4 million were ethnic Ukrainians, and general losses of the Ukrainian people in the war amounted to 40–44% of the total losses of the USSR. The Victory Day over Nazism in World War II, Victory Day is celebrated as one of eleven Ukrainian national holidays.
 Mikhail Gorbachev pursued a policy of limited liberalization of public life, known as ''perestroika,'' and attempted to reform a Era of Stagnation, stagnating economy. The latter failed, but the democratization of the Soviet Union fuelled nationalist and separatist tendencies among the ethnic minorities, including Ukrainians. As part of the so-called parade of sovereignties, on 16 July 1990, the newly elected Supreme Soviet of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic adopted the Declaration of State Sovereignty of Ukraine; after a 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt, putsch of some Communist leaders in Moscow failed to depose Gorbachov, outright independence was Declaration of Independence of Ukraine, proclaimed on 24 August 1991 and approved by 92% of the Ukrainian electorate in a 1991 Ukrainian independence referendum, referendum on 1 December.Nohlen & Stöver, p1985 Ukraine's new President of Ukraine, President, Leonid Kravchuk, went on to sign the Belavezha Accords and made Ukraine a founding member of the much looser Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), though Ukraine never became a full member of the latter as it did not ratify the agreement founding CIS. These documents sealed the fate of the Soviet Union, which formally voted itself out of existence on 26 December.
Ukraine was initially viewed as having favourable economic conditions in comparison to the other regions of the Soviet Union, though it was one of the poorer Soviet republics by the end of the Soviet Union. However, during its transition to the market economy, the country experienced deeper economic slowdown than almost all of the other former Soviet Republics. During the recession, between 1991 and 1999, Ukraine lost 60% of its GDP and suffered from hyperinflation that peaked at 10,000% in 1993. The situation only stabilized well after the new currency, the hryvnia, fell sharply in late 1998 partially as a fallout from the Russian debt default earlier that year. The legacy of the economic policies of the nineties was the mass privatization of state property that created a class of extremely powerful and rich individuals known as the Ukrainian oligarch, oligarchs. The country would then fall into sharp recessions as a result of the 2008 global financial crisis, then the start of the Russo-Ukrainian War in 2014, and finally, the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, full-scale invasion of Russia in starting from 24 February 2022. Ukraine's economy in general underperformed since the time independence came due to pervasive
Mikhail Gorbachev pursued a policy of limited liberalization of public life, known as ''perestroika,'' and attempted to reform a Era of Stagnation, stagnating economy. The latter failed, but the democratization of the Soviet Union fuelled nationalist and separatist tendencies among the ethnic minorities, including Ukrainians. As part of the so-called parade of sovereignties, on 16 July 1990, the newly elected Supreme Soviet of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic adopted the Declaration of State Sovereignty of Ukraine; after a 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt, putsch of some Communist leaders in Moscow failed to depose Gorbachov, outright independence was Declaration of Independence of Ukraine, proclaimed on 24 August 1991 and approved by 92% of the Ukrainian electorate in a 1991 Ukrainian independence referendum, referendum on 1 December.Nohlen & Stöver, p1985 Ukraine's new President of Ukraine, President, Leonid Kravchuk, went on to sign the Belavezha Accords and made Ukraine a founding member of the much looser Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), though Ukraine never became a full member of the latter as it did not ratify the agreement founding CIS. These documents sealed the fate of the Soviet Union, which formally voted itself out of existence on 26 December.
Ukraine was initially viewed as having favourable economic conditions in comparison to the other regions of the Soviet Union, though it was one of the poorer Soviet republics by the end of the Soviet Union. However, during its transition to the market economy, the country experienced deeper economic slowdown than almost all of the other former Soviet Republics. During the recession, between 1991 and 1999, Ukraine lost 60% of its GDP and suffered from hyperinflation that peaked at 10,000% in 1993. The situation only stabilized well after the new currency, the hryvnia, fell sharply in late 1998 partially as a fallout from the Russian debt default earlier that year. The legacy of the economic policies of the nineties was the mass privatization of state property that created a class of extremely powerful and rich individuals known as the Ukrainian oligarch, oligarchs. The country would then fall into sharp recessions as a result of the 2008 global financial crisis, then the start of the Russo-Ukrainian War in 2014, and finally, the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, full-scale invasion of Russia in starting from 24 February 2022. Ukraine's economy in general underperformed since the time independence came due to pervasive  From the political perspective, one of the defining features of the politics of Ukraine is that for most of the time, it has been divided along two issues: the relation between Ukraine, the Western world, West and Russia, and the classical Left–right political spectrum, left-right divide. The first two presidents, Kravchuk and Leonid Kuchma, tended to balance the competing visions of Ukraine, though Yushchenko and Yanukovych were generally pro-Western and pro-Russian, respectively. There were two major protests against Yanukovych: the Orange Revolution in 2004, when tens of thousands of people went in protest of election rigging in his favour (Yushchenko was eventually elected president), and another one in the winter of 2013/2014, when more gathered on the
From the political perspective, one of the defining features of the politics of Ukraine is that for most of the time, it has been divided along two issues: the relation between Ukraine, the Western world, West and Russia, and the classical Left–right political spectrum, left-right divide. The first two presidents, Kravchuk and Leonid Kuchma, tended to balance the competing visions of Ukraine, though Yushchenko and Yanukovych were generally pro-Western and pro-Russian, respectively. There were two major protests against Yanukovych: the Orange Revolution in 2004, when tens of thousands of people went in protest of election rigging in his favour (Yushchenko was eventually elected president), and another one in the winter of 2013/2014, when more gathered on the  After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Ukraine inherited a 780,000-man military force on its territory, equipped with the third-largest nuclear weapons and Ukraine, nuclear weapons arsenal in the world. In 1992, Ukraine signed the Lisbon Protocol in which the country agreed to give up all nuclear weapons to Russia for disposal and to join the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty as a non-nuclear weapon state. By 1996 the country had become free of nuclear weapons.
Ukraine took consistent steps toward reduction of conventional weapons. It signed the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe, which called for reduction of tanks, artillery, and armoured vehicles (army forces were reduced to 300,000). The country plans to convert the current conscript-based military into a professional volunteer military. Ukraine's current military consist of 196,600 active personnel and around 900,000 reservists.
After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Ukraine inherited a 780,000-man military force on its territory, equipped with the third-largest nuclear weapons and Ukraine, nuclear weapons arsenal in the world. In 1992, Ukraine signed the Lisbon Protocol in which the country agreed to give up all nuclear weapons to Russia for disposal and to join the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty as a non-nuclear weapon state. By 1996 the country had become free of nuclear weapons.
Ukraine took consistent steps toward reduction of conventional weapons. It signed the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe, which called for reduction of tanks, artillery, and armoured vehicles (army forces were reduced to 300,000). The country plans to convert the current conscript-based military into a professional volunteer military. Ukraine's current military consist of 196,600 active personnel and around 900,000 reservists.
 Ukraine played an increasing role in peacekeeping operations. In 2014, the Ukrainian frigate ''Hetman Sagaidachniy'' joined the European Union's counter piracy Operation Atalanta and was part of the EU Naval Force off the coast of Somalia for two months. Ukrainian troops were deployed in Kosovo as part of the Polish-Ukrainian Peace Force Battalion, Ukrainian-Polish Battalion.
A Ukrainian unit was deployed in Lebanon, as part of United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon, UN Interim Force enforcing the mandated ceasefire agreement. There was also a maintenance and training battalion deployed in Sierra Leone. In 2003–05, a Ukrainian unit was deployed as part of the multinational force in Iraq under Polish command.
Military units of other states participated in multinational military exercises with Ukrainian forces in Ukraine regularly, including U.S. military forces.
Following independence, Ukraine declared itself a neutral state. The country had a limited military partnership with Russian Federation and other CIS countries and has had a Partnership for Peace, partnership with NATO since 1994. In the 2000s, the government was leaning towards NATO, and deeper cooperation with the alliance was set by the NATO-Ukraine Action Plan signed in 2002. It was later agreed that the question of joining NATO should be answered by a national referendum at some point in the future. Deposed Ukrainian President, President Viktor Yanukovych considered the current level of co-operation between Ukraine–NATO relations, Ukraine and NATO sufficient, and was against Ukraine joining NATO. During the 2008 Bucharest summit, NATO declared that Ukraine would eventually become a member of NATO when it meets the criteria for accession.
As part of modernization after the beginning of the Russo-Ukrainian War in 2014, junior officers were allowed to take more initiative and a Territorial defence battalions (Ukraine), territorial defense force of volunteers was established. Various defensive weapons including Unmanned combat aerial vehicle, drones were supplied by many countries, but not fighter jets. During the first few weeks of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, 2022 Russian invasion the military found it difficult to defend against shelling, missiles and high level bombing; but light infantry used shoulder-mounted weapons effectively to destroy tanks, armoured vehicles and low-flying aircraft.
Ukraine played an increasing role in peacekeeping operations. In 2014, the Ukrainian frigate ''Hetman Sagaidachniy'' joined the European Union's counter piracy Operation Atalanta and was part of the EU Naval Force off the coast of Somalia for two months. Ukrainian troops were deployed in Kosovo as part of the Polish-Ukrainian Peace Force Battalion, Ukrainian-Polish Battalion.
A Ukrainian unit was deployed in Lebanon, as part of United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon, UN Interim Force enforcing the mandated ceasefire agreement. There was also a maintenance and training battalion deployed in Sierra Leone. In 2003–05, a Ukrainian unit was deployed as part of the multinational force in Iraq under Polish command.
Military units of other states participated in multinational military exercises with Ukrainian forces in Ukraine regularly, including U.S. military forces.
Following independence, Ukraine declared itself a neutral state. The country had a limited military partnership with Russian Federation and other CIS countries and has had a Partnership for Peace, partnership with NATO since 1994. In the 2000s, the government was leaning towards NATO, and deeper cooperation with the alliance was set by the NATO-Ukraine Action Plan signed in 2002. It was later agreed that the question of joining NATO should be answered by a national referendum at some point in the future. Deposed Ukrainian President, President Viktor Yanukovych considered the current level of co-operation between Ukraine–NATO relations, Ukraine and NATO sufficient, and was against Ukraine joining NATO. During the 2008 Bucharest summit, NATO declared that Ukraine would eventually become a member of NATO when it meets the criteria for accession.
As part of modernization after the beginning of the Russo-Ukrainian War in 2014, junior officers were allowed to take more initiative and a Territorial defence battalions (Ukraine), territorial defense force of volunteers was established. Various defensive weapons including Unmanned combat aerial vehicle, drones were supplied by many countries, but not fighter jets. During the first few weeks of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, 2022 Russian invasion the military found it difficult to defend against shelling, missiles and high level bombing; but light infantry used shoulder-mounted weapons effectively to destroy tanks, armoured vehicles and low-flying aircraft.
 The system of Ukrainian subdivisions reflects the country's status as a unitary state (as stated in the country's constitution) with unified legal and Local government, administrative regimes for each unit.
Including Sevastopol and the Autonomous Republic of Crimea that were annexed by the Russian Federation in 2014, Ukraine consists of 27 regions: twenty-four oblasts (provinces), one autonomous republic (Autonomous Republic of Crimea), and two cities of special status— Kyiv, the capital, and Sevastopol. The 24 oblasts and Crimea are subdivided into 136 (districts) and city municipalities of regional significance, or second-level administrative units.
Populated places in Ukraine are split into two categories: urban and rural. Urban populated places are split further into cities and urban-type settlements (a Soviet administrative invention), while rural populated places consist of villages and settlements (a generally used term). All cities have a certain degree of self-rule depending on their significance such as national significance (as in the case of Kyiv and Sevastopol), regional significance (within each oblast or autonomous republic) or district significance (all the rest of cities). A city's significance depends on several factors such as its population, socio-economic and historical importance and infrastructure.
The system of Ukrainian subdivisions reflects the country's status as a unitary state (as stated in the country's constitution) with unified legal and Local government, administrative regimes for each unit.
Including Sevastopol and the Autonomous Republic of Crimea that were annexed by the Russian Federation in 2014, Ukraine consists of 27 regions: twenty-four oblasts (provinces), one autonomous republic (Autonomous Republic of Crimea), and two cities of special status— Kyiv, the capital, and Sevastopol. The 24 oblasts and Crimea are subdivided into 136 (districts) and city municipalities of regional significance, or second-level administrative units.
Populated places in Ukraine are split into two categories: urban and rural. Urban populated places are split further into cities and urban-type settlements (a Soviet administrative invention), while rural populated places consist of villages and settlements (a generally used term). All cities have a certain degree of self-rule depending on their significance such as national significance (as in the case of Kyiv and Sevastopol), regional significance (within each oblast or autonomous republic) or district significance (all the rest of cities). A city's significance depends on several factors such as its population, socio-economic and historical importance and infrastructure.
 Effective in August 2012, Legislation on languages in Ukraine, a new law on regional languages entitled any local language spoken by at least a 10 percent minority be declared official within that area. Within weeks, Russian was declared a regional language of several southern and eastern Oblasts of Ukraine, oblasts (provinces) and cities. Russian could then be used in the administrative office work and documents of those places.
On 23 February 2014, following the Revolution of Dignity, the Ukrainian Parliament voted to repeal the law on regional languages, making Ukrainian the sole state language at all levels; however, the repeal was not signed by acting Oleksandr Turchynov, President Turchynov or by President Poroshenko. In February 2019, the law allowing for official use of regional languages was found unconstitutional. According to the Council of Europe, this act fails to achieve fair protection of the linguistic rights of Minority language, minorities.
Ukrainian is the primary language used in the vast majority of Ukraine (see "Linguistic map of Ukraine" above.) 67% of Ukrainians speak Ukrainian as their primary language, while 30% speak Russian as their primary language. In eastern and southern Ukraine, Russian is the primary language in some cities, while Ukrainian is used in rural areas. Hungarian language, Hungarian is spoken in the Zakarpattia Oblast.
For a large part of the Soviet era, the number of Ukrainian speakers declined from generation to generation, and by the mid-1980s, the usage of the Ukrainian language in public life had decreased significantly.Shamshur, pp. 159–168 Following independence, the government of Ukraine began restoring the use of the Ukrainian language in schools and government through a policy of Ukrainisation. Today, most foreign films and TV programs, including Russian ones, are subtitled or dubbed in Ukrainian. Ukraine's 2017 Education in Ukraine, education law bars primary education in public schools in grade five and up in any language but Ukrainian.
Effective in August 2012, Legislation on languages in Ukraine, a new law on regional languages entitled any local language spoken by at least a 10 percent minority be declared official within that area. Within weeks, Russian was declared a regional language of several southern and eastern Oblasts of Ukraine, oblasts (provinces) and cities. Russian could then be used in the administrative office work and documents of those places.
On 23 February 2014, following the Revolution of Dignity, the Ukrainian Parliament voted to repeal the law on regional languages, making Ukrainian the sole state language at all levels; however, the repeal was not signed by acting Oleksandr Turchynov, President Turchynov or by President Poroshenko. In February 2019, the law allowing for official use of regional languages was found unconstitutional. According to the Council of Europe, this act fails to achieve fair protection of the linguistic rights of Minority language, minorities.
Ukrainian is the primary language used in the vast majority of Ukraine (see "Linguistic map of Ukraine" above.) 67% of Ukrainians speak Ukrainian as their primary language, while 30% speak Russian as their primary language. In eastern and southern Ukraine, Russian is the primary language in some cities, while Ukrainian is used in rural areas. Hungarian language, Hungarian is spoken in the Zakarpattia Oblast.
For a large part of the Soviet era, the number of Ukrainian speakers declined from generation to generation, and by the mid-1980s, the usage of the Ukrainian language in public life had decreased significantly.Shamshur, pp. 159–168 Following independence, the government of Ukraine began restoring the use of the Ukrainian language in schools and government through a policy of Ukrainisation. Today, most foreign films and TV programs, including Russian ones, are subtitled or dubbed in Ukrainian. Ukraine's 2017 Education in Ukraine, education law bars primary education in public schools in grade five and up in any language but Ukrainian.
 Ukraine has the world's Eastern Orthodoxy by country, second-largest Eastern Orthodox population, after Russia. A 2021 survey conducted by the Kyiv International Institute of Sociology (KIIS) found that 82% of Ukrainians declared themselves to be religious, while 7% were atheists, and a further 11% found it difficult to answer the question. The level of religiosity in Ukraine was reported to be the highest in Western Ukraine (91%), and the lowest in the
Ukraine has the world's Eastern Orthodoxy by country, second-largest Eastern Orthodox population, after Russia. A 2021 survey conducted by the Kyiv International Institute of Sociology (KIIS) found that 82% of Ukrainians declared themselves to be religious, while 7% were atheists, and a further 11% found it difficult to answer the question. The level of religiosity in Ukraine was reported to be the highest in Western Ukraine (91%), and the lowest in the 
 Ukrainian architecture includes the motifs and styles that are found in structures built in modern Ukraine, and by Ukrainians worldwide. These include initial roots which were established in the state of Kievan Rus'. Following the Christianization of Kievan Rus', Ukrainian architecture has been influenced by Byzantine architecture. After the Mongol invasion of Kievan Rus', it continued to develop in the Kingdom of Galicia-Volhynia.
After the union with the Tsardom of Russia, architecture in Ukraine began to develop in different directions, with many structures in the larger eastern, Russian-ruled area built in the styles of Russian architecture of that period, whilst the western region of Galicia (Central Europe), Galicia developed under Architecture of Poland, Polish and Architecture of Austria, Austro-Hungarian architectural influences. Ukrainian national motifs would eventually be used during the period of the Soviet Union and in modern independent Ukraine. However, much of the contemporary architectural skyline of Ukraine is dominated by Soviet-style Khrushchyovkas, or low-cost apartment buildings.
Ukrainian architecture includes the motifs and styles that are found in structures built in modern Ukraine, and by Ukrainians worldwide. These include initial roots which were established in the state of Kievan Rus'. Following the Christianization of Kievan Rus', Ukrainian architecture has been influenced by Byzantine architecture. After the Mongol invasion of Kievan Rus', it continued to develop in the Kingdom of Galicia-Volhynia.
After the union with the Tsardom of Russia, architecture in Ukraine began to develop in different directions, with many structures in the larger eastern, Russian-ruled area built in the styles of Russian architecture of that period, whilst the western region of Galicia (Central Europe), Galicia developed under Architecture of Poland, Polish and Architecture of Austria, Austro-Hungarian architectural influences. Ukrainian national motifs would eventually be used during the period of the Soviet Union and in modern independent Ukraine. However, much of the contemporary architectural skyline of Ukraine is dominated by Soviet-style Khrushchyovkas, or low-cost apartment buildings.
 Artisan textile arts play an important role in Ukrainian culture, especially in Ukrainian wedding traditions. Ukrainian embroidery, weaving and lace-making are used in traditional folk dress and in traditional celebrations. Ukrainian embroidery varies depending on the region of origin and the designs have a long history of motifs, compositions, choice of colours and types of stitches. Use of colour is very important and has roots in Ukrainian folklore. Embroidery motifs found in different parts of Ukraine are preserved in the Rushnyk Museum in Pereiaslav.
National dress is woven and highly decorated. Weaving with handmade looms is still practised in the village of Krupove, situated in Rivne Oblast. The village is the birthplace of two famous personalities in the scene of national crafts fabrication. Nina Myhailivna and Uliana Petrivna with international recognition.
Artisan textile arts play an important role in Ukrainian culture, especially in Ukrainian wedding traditions. Ukrainian embroidery, weaving and lace-making are used in traditional folk dress and in traditional celebrations. Ukrainian embroidery varies depending on the region of origin and the designs have a long history of motifs, compositions, choice of colours and types of stitches. Use of colour is very important and has roots in Ukrainian folklore. Embroidery motifs found in different parts of Ukraine are preserved in the Rushnyk Museum in Pereiaslav.
National dress is woven and highly decorated. Weaving with handmade looms is still practised in the village of Krupove, situated in Rivne Oblast. The village is the birthplace of two famous personalities in the scene of national crafts fabrication. Nina Myhailivna and Uliana Petrivna with international recognition.
 Music is a major part of Ukrainian culture, with a long history and many influences. From traditional folk music, to classical music, classical and modern rock, Ukraine has produced several internationally recognised musicians including Kirill Karabits, Okean Elzy and Ruslana. Elements from traditional Ukrainian folk music made their way into Western music and even into modern jazz. Ukrainian music sometimes presents a perplexing mix of exotic melismatic singing with chordal harmony. The most striking general characteristic of authentic ethnic Ukrainian folk music is the wide use of minor modes or keys which incorporate augmented second intervals.
During the Baroque period, music had a place of considerable importance in the curriculum of the Kyiv-Mohyla Academy. Much of the nobility was well versed in music with many Ukrainian Cossack leaders such as (Ivan Mazepa, Mazepa, Semen Paliy, Paliy, Antin Holovaty, Holovatyj, Ivan Sirko, Sirko) being accomplished players of the kobza, bandura or torban.
Music is a major part of Ukrainian culture, with a long history and many influences. From traditional folk music, to classical music, classical and modern rock, Ukraine has produced several internationally recognised musicians including Kirill Karabits, Okean Elzy and Ruslana. Elements from traditional Ukrainian folk music made their way into Western music and even into modern jazz. Ukrainian music sometimes presents a perplexing mix of exotic melismatic singing with chordal harmony. The most striking general characteristic of authentic ethnic Ukrainian folk music is the wide use of minor modes or keys which incorporate augmented second intervals.
During the Baroque period, music had a place of considerable importance in the curriculum of the Kyiv-Mohyla Academy. Much of the nobility was well versed in music with many Ukrainian Cossack leaders such as (Ivan Mazepa, Mazepa, Semen Paliy, Paliy, Antin Holovaty, Holovatyj, Ivan Sirko, Sirko) being accomplished players of the kobza, bandura or torban.
 The first dedicated musical academy was set up in Hlukhiv in 1738 and students were taught to sing and play violin and bandura from manuscripts. As a result, many of the earliest composers and performers within the Russian empire were ethnically Ukrainian, having been born or educated in Hlukhiv or having been closely associated with this music school. Ukrainian classical music differs considerably depending on whether the composer was of Ukrainian ethnicity living in Ukraine, a composer of non-Ukrainian ethnicity who was a citizen of Ukraine, or part of the Ukrainian diaspora.
Since the mid-1960s, Western-influenced pop music has been growing in popularity in Ukraine. Folk singer and harmonium player Mariana Sadovska is prominent. Ukrainian pop and folk music arose with the international popularity of groups and performers like Vopli Vidoplyasova, Dakh Daughters, Dakha Brakha, Ivan Dorn and Okean Elzy.
The first dedicated musical academy was set up in Hlukhiv in 1738 and students were taught to sing and play violin and bandura from manuscripts. As a result, many of the earliest composers and performers within the Russian empire were ethnically Ukrainian, having been born or educated in Hlukhiv or having been closely associated with this music school. Ukrainian classical music differs considerably depending on whether the composer was of Ukrainian ethnicity living in Ukraine, a composer of non-Ukrainian ethnicity who was a citizen of Ukraine, or part of the Ukrainian diaspora.
Since the mid-1960s, Western-influenced pop music has been growing in popularity in Ukraine. Folk singer and harmonium player Mariana Sadovska is prominent. Ukrainian pop and folk music arose with the international popularity of groups and performers like Vopli Vidoplyasova, Dakh Daughters, Dakha Brakha, Ivan Dorn and Okean Elzy.
 Ukraine greatly benefited from the Soviet emphasis on physical education. These policies left Ukraine with hundreds of stadia, swimming pools, gymnasia and many other athletic facilities. The most popular sport is Association football, football. The top professional league is the Ukrainian Premier League, Vyscha Liha ("premier league").
Many Ukrainians also played for the Soviet national football team, most notably Ballon d'Or winners Ihor Belanov and Oleh Blokhin. This award was only presented to one Ukrainian after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Andriy Shevchenko. The national team made its debut in the 2006 FIFA World Cup, and reached the quarterfinals before losing to eventual champions, Italy national football team, Italy.
Ukraine greatly benefited from the Soviet emphasis on physical education. These policies left Ukraine with hundreds of stadia, swimming pools, gymnasia and many other athletic facilities. The most popular sport is Association football, football. The top professional league is the Ukrainian Premier League, Vyscha Liha ("premier league").
Many Ukrainians also played for the Soviet national football team, most notably Ballon d'Or winners Ihor Belanov and Oleh Blokhin. This award was only presented to one Ukrainian after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Andriy Shevchenko. The national team made its debut in the 2006 FIFA World Cup, and reached the quarterfinals before losing to eventual champions, Italy national football team, Italy.
 Ukrainian boxing, boxers are amongst the best in the world. Since becoming the undisputed cruiserweight champion in 2018, Oleksandr Usyk has also gone on to win the unified WBA (Super), IBF, WBO and IBO heavyweight titles. This feat made him one of only three boxers to have unified the cruiserweight world titles and become a world heavyweight champion. The brothers Vitali Klitschko, Vitali and Wladimir Klitschko are former heavyweight world champions who held multiple world titles throughout their careers. Also hailing from Ukraine is Vasyl Lomachenko, a 2008 Summer Olympics, 2008 and 2012 Olympic games, 2012 Olympic gold medalist. He is the Unified champion, unified lightweight world champion who ties the record for winning a world title in the fewest professional fights; three. As of September 2018, he is ranked as the world's best active boxer, pound for pound, by boxing pound for pound rankings#ESPN, ESPN.
Sergey Bubka held the record in the Pole vault from 1993 to 2014; with great strength, speed and gymnastic abilities, he was voted the world's best athlete on several occasions.
Basketball has gained popularity in Ukraine. In 2011, Ukraine was granted a right to organize EuroBasket 2015. Two years later the Ukraine national basketball team finished sixth in EuroBasket 2013 and qualified to 2014 FIBA Basketball World Cup, FIBA World Cup for the first time in its history. Euroleague participant BC Budivelnyk, Budivelnyk Kyiv is the strongest professional basketball club in Ukraine.
Chess is a popular sport in Ukraine. Ruslan Ponomariov is the former world champion. There are about 85 Grandmaster (chess), Grandmasters and 198 International Masters in Ukraine. Rugby league is played throughout Ukraine.
Ukrainian boxing, boxers are amongst the best in the world. Since becoming the undisputed cruiserweight champion in 2018, Oleksandr Usyk has also gone on to win the unified WBA (Super), IBF, WBO and IBO heavyweight titles. This feat made him one of only three boxers to have unified the cruiserweight world titles and become a world heavyweight champion. The brothers Vitali Klitschko, Vitali and Wladimir Klitschko are former heavyweight world champions who held multiple world titles throughout their careers. Also hailing from Ukraine is Vasyl Lomachenko, a 2008 Summer Olympics, 2008 and 2012 Olympic games, 2012 Olympic gold medalist. He is the Unified champion, unified lightweight world champion who ties the record for winning a world title in the fewest professional fights; three. As of September 2018, he is ranked as the world's best active boxer, pound for pound, by boxing pound for pound rankings#ESPN, ESPN.
Sergey Bubka held the record in the Pole vault from 1993 to 2014; with great strength, speed and gymnastic abilities, he was voted the world's best athlete on several occasions.
Basketball has gained popularity in Ukraine. In 2011, Ukraine was granted a right to organize EuroBasket 2015. Two years later the Ukraine national basketball team finished sixth in EuroBasket 2013 and qualified to 2014 FIBA Basketball World Cup, FIBA World Cup for the first time in its history. Euroleague participant BC Budivelnyk, Budivelnyk Kyiv is the strongest professional basketball club in Ukraine.
Chess is a popular sport in Ukraine. Ruslan Ponomariov is the former world champion. There are about 85 Grandmaster (chess), Grandmasters and 198 International Masters in Ukraine. Rugby league is played throughout Ukraine.
 The traditional Ukrainian diet includes chicken, pork, beef, fish and mushrooms. Ukrainians also tend to eat a lot of potatoes; grains; and fresh, boiled or pickled vegetables. Popular traditional dishes ' (boiled dumplings with mushrooms, potatoes, sauerkraut, cottage cheese, cherries or berries), ''nalysnyky'' (pancakes with cottage cheese, poppy seeds, mushrooms, caviar or meat), ''Cabbage soup, kapusnyak'' (cabbage soup made with meat, potatoes, carrots, onions, millet, tomato paste, spices and fresh herbs), borscht (soup made of beets, cabbage and mushrooms or meat) and (stuffed cabbage rolls filled with rice, carrots, onion and minced meat). Among traditional baked goods are decorated korovais and Paska (bread), paska Easter bread. Ukrainian specialties also include Chicken Kiev and Kyiv cake.
Ukrainians drink kompot, stewed fruit compote, juices, milk, buttermilk, mineral water, tea and coffee, beer, wine and .
The traditional Ukrainian diet includes chicken, pork, beef, fish and mushrooms. Ukrainians also tend to eat a lot of potatoes; grains; and fresh, boiled or pickled vegetables. Popular traditional dishes ' (boiled dumplings with mushrooms, potatoes, sauerkraut, cottage cheese, cherries or berries), ''nalysnyky'' (pancakes with cottage cheese, poppy seeds, mushrooms, caviar or meat), ''Cabbage soup, kapusnyak'' (cabbage soup made with meat, potatoes, carrots, onions, millet, tomato paste, spices and fresh herbs), borscht (soup made of beets, cabbage and mushrooms or meat) and (stuffed cabbage rolls filled with rice, carrots, onion and minced meat). Among traditional baked goods are decorated korovais and Paska (bread), paska Easter bread. Ukrainian specialties also include Chicken Kiev and Kyiv cake.
Ukrainians drink kompot, stewed fruit compote, juices, milk, buttermilk, mineral water, tea and coffee, beer, wine and .