US Medic Teaches The Heimlich Manuever To Laughing Afghans on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a
 It is generally accepted that the Paleo-indians, first inhabitants of North America migrated from Siberia by way of the Bering land bridge and arrived at least 12,000 years ago; however, some evidence suggests an even earlier date of arrival. The Clovis culture, which appeared around 11,000 BC, is believed to represent the first wave of human settlement of the Americas. This was likely the first of three major waves of migration into North America; later waves brought the ancestors of present-day Alaskan Athabaskans, Athabaskans, Aleuts, and Eskimos.
Over time, indigenous cultures in North America grew increasingly sophisticated, and some, such as the pre-Columbian Mississippian culture in the southeast, developed advanced agriculture, architecture, and complex societies. The city-state of Cahokia is the largest, most complex pre-Columbian archaeological site in the modern-day United States. In the Four Corners region, Ancestral Puebloan culture developed from centuries of agricultural experimentation. The Algonquian peoples, Algonquian are one of the most populous and widespread North American Indigenous peoples of the Americas, native language groups. This grouping consists of the peoples who speak Algonquian languages. Historically, these peoples were prominent along the Atlantic Coast and into the interior along the Saint Lawrence River and around the Great Lakes. Before Europeans came into contact, most Algonquian settlements lived by hunting and fishing, although many supplemented their diet by cultivating maize, corn, beans and Cucurbita, squash (the "Three Sisters (agriculture), Three Sisters"). The Ojibwe cultivated wild rice. The Haudenosaunee confederation of the Iroquoian peoples, Iroquois, located in the southern Great Lakes region, was established at some point between the twelfth and fifteenth centuries.
Population history of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Estimating the native population of North America during European contact is difficult. Douglas H. Ubelaker of the Smithsonian Institution estimated a population of 93,000 in the South Atlantic states and a population of 473,000 in the Gulf states, but most academics regard this figure as too low. Anthropologist Henry F. Dobyns believed the populations were much higher, suggesting around 1.1 million along the shores of the Gulf of Mexico, 2.2 million people living between Florida and Massachusetts, 5.2 million in the Mississippi Valley and tributaries, and around 700,000 people in the Florida peninsula.
It is generally accepted that the Paleo-indians, first inhabitants of North America migrated from Siberia by way of the Bering land bridge and arrived at least 12,000 years ago; however, some evidence suggests an even earlier date of arrival. The Clovis culture, which appeared around 11,000 BC, is believed to represent the first wave of human settlement of the Americas. This was likely the first of three major waves of migration into North America; later waves brought the ancestors of present-day Alaskan Athabaskans, Athabaskans, Aleuts, and Eskimos.
Over time, indigenous cultures in North America grew increasingly sophisticated, and some, such as the pre-Columbian Mississippian culture in the southeast, developed advanced agriculture, architecture, and complex societies. The city-state of Cahokia is the largest, most complex pre-Columbian archaeological site in the modern-day United States. In the Four Corners region, Ancestral Puebloan culture developed from centuries of agricultural experimentation. The Algonquian peoples, Algonquian are one of the most populous and widespread North American Indigenous peoples of the Americas, native language groups. This grouping consists of the peoples who speak Algonquian languages. Historically, these peoples were prominent along the Atlantic Coast and into the interior along the Saint Lawrence River and around the Great Lakes. Before Europeans came into contact, most Algonquian settlements lived by hunting and fishing, although many supplemented their diet by cultivating maize, corn, beans and Cucurbita, squash (the "Three Sisters (agriculture), Three Sisters"). The Ojibwe cultivated wild rice. The Haudenosaunee confederation of the Iroquoian peoples, Iroquois, located in the southern Great Lakes region, was established at some point between the twelfth and fifteenth centuries.
Population history of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Estimating the native population of North America during European contact is difficult. Douglas H. Ubelaker of the Smithsonian Institution estimated a population of 93,000 in the South Atlantic states and a population of 473,000 in the Gulf states, but most academics regard this figure as too low. Anthropologist Henry F. Dobyns believed the populations were much higher, suggesting around 1.1 million along the shores of the Gulf of Mexico, 2.2 million people living between Florida and Massachusetts, 5.2 million in the Mississippi Valley and tributaries, and around 700,000 people in the Florida peninsula.
 Claims of very early colonization of New England#Geography, coastal New England by the Norse colonization of North America, Norse are disputed and controversial. Christopher Columbus had landed in Puerto Rico on his Columbus's second voyage, 1493 voyage, and San Juan, Puerto Rico, San Juan was settled by the Spanish a decade later. The first documented arrival of Europeans in the continental United States is that of Spanish conquistadors such as Juan Ponce de León, who made his first expedition to Spanish Florida, Florida in 1513. The Italian explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano, sent by France to the New World in 1525, encountered native inhabitants of what is now New York Bay. The Spanish set up the first settlements in Florida and New Mexico, such as St. Augustine, Florida, Saint Augustine, often considered the nation's oldest city, and Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe. The French New France, established their own settlements along the Mississippi River and Gulf of Mexico, notably New Orleans and Mobile, Alabama, Mobile.
Successful British colonization of the Americas, English settlement of the eastern coast of North America began with the Colony of Virginia, Virginia Colony in 1607 at Jamestown, Virginia, Jamestown and with the Pilgrims (Plymouth Colony), Pilgrims' Plymouth Colony, colony at Plymouth in 1620. The continent's first elected legislative assembly, Virginia's House of Burgesses, was founded in 1619. Harvard College was established in the Massachusetts Bay Colony in 1636 as the first institution of higher education. The Mayflower Compact and the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut established precedents for representative self-government and constitutionalism that would develop throughout the American colonies. Many English settlers were English Dissenters, dissenting Christians who came seeking Freedom of religion, religious freedom. The Population history of indigenous peoples of the Americas, native population of America declined after European arrival for various reasons, primarily from diseases such as smallpox and measles.
Claims of very early colonization of New England#Geography, coastal New England by the Norse colonization of North America, Norse are disputed and controversial. Christopher Columbus had landed in Puerto Rico on his Columbus's second voyage, 1493 voyage, and San Juan, Puerto Rico, San Juan was settled by the Spanish a decade later. The first documented arrival of Europeans in the continental United States is that of Spanish conquistadors such as Juan Ponce de León, who made his first expedition to Spanish Florida, Florida in 1513. The Italian explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano, sent by France to the New World in 1525, encountered native inhabitants of what is now New York Bay. The Spanish set up the first settlements in Florida and New Mexico, such as St. Augustine, Florida, Saint Augustine, often considered the nation's oldest city, and Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe. The French New France, established their own settlements along the Mississippi River and Gulf of Mexico, notably New Orleans and Mobile, Alabama, Mobile.
Successful British colonization of the Americas, English settlement of the eastern coast of North America began with the Colony of Virginia, Virginia Colony in 1607 at Jamestown, Virginia, Jamestown and with the Pilgrims (Plymouth Colony), Pilgrims' Plymouth Colony, colony at Plymouth in 1620. The continent's first elected legislative assembly, Virginia's House of Burgesses, was founded in 1619. Harvard College was established in the Massachusetts Bay Colony in 1636 as the first institution of higher education. The Mayflower Compact and the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut established precedents for representative self-government and constitutionalism that would develop throughout the American colonies. Many English settlers were English Dissenters, dissenting Christians who came seeking Freedom of religion, religious freedom. The Population history of indigenous peoples of the Americas, native population of America declined after European arrival for various reasons, primarily from diseases such as smallpox and measles.
 In the early days of colonization, many European settlers experienced food shortages, disease, and conflicts with Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native Americans, such as in King Philip's War. Native Americans were also often fighting neighboring tribes and European settlers. In many cases, however, the natives and settlers came to depend on each other. Settlers Columbian exchange, traded for food and animal pelts; natives for guns, tools and other European goods. Natives taught many settlers to cultivate corn, beans, and other foodstuffs. European missionaries and others felt it was important to "civilize" the Native Americans and urged them to adopt European agricultural practices and lifestyles. However, with the increased European settler colonialism, colonization of North America, Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans were displaced and often killed during conflicts.
European settlers also began human trafficking, trafficking Slavery in the colonial United States, African slaves into Colonial America via the Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade. Because of a lower prevalence of tropical diseases and relatively better Treatment of the enslaved in the United States, treatment, slaves had a much higher life expectancy in North America than in South America, leading to a rapid increase in their numbers. Colonial society was largely divided over the religious and moral implications of slavery, and several colonies passed acts for or against the practice.#Lien, Lien, 1913, p. 522#Davis96, Davis, 1996, p. 7 However, by the turn of the 18th century, African slaves had supplanted European Indentured servitude, indentured servants as cash crop labor, especially in the American South.#Quirk, Quirk, 2011, p. 195
The
In the early days of colonization, many European settlers experienced food shortages, disease, and conflicts with Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native Americans, such as in King Philip's War. Native Americans were also often fighting neighboring tribes and European settlers. In many cases, however, the natives and settlers came to depend on each other. Settlers Columbian exchange, traded for food and animal pelts; natives for guns, tools and other European goods. Natives taught many settlers to cultivate corn, beans, and other foodstuffs. European missionaries and others felt it was important to "civilize" the Native Americans and urged them to adopt European agricultural practices and lifestyles. However, with the increased European settler colonialism, colonization of North America, Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans were displaced and often killed during conflicts.
European settlers also began human trafficking, trafficking Slavery in the colonial United States, African slaves into Colonial America via the Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade. Because of a lower prevalence of tropical diseases and relatively better Treatment of the enslaved in the United States, treatment, slaves had a much higher life expectancy in North America than in South America, leading to a rapid increase in their numbers. Colonial society was largely divided over the religious and moral implications of slavery, and several colonies passed acts for or against the practice.#Lien, Lien, 1913, p. 522#Davis96, Davis, 1996, p. 7 However, by the turn of the 18th century, African slaves had supplanted European Indentured servitude, indentured servants as cash crop labor, especially in the American South.#Quirk, Quirk, 2011, p. 195
The
 The
The  In the late 18th century, American settlers began to Territorial evolution of the United States, expand further westward, some of them with a sense of manifest destiny. The 1803 Louisiana Purchase almost doubled the nation's area, Adams–Onís Treaty, Spain ceded Florida and other Gulf Coast territory in 1819, the Republic of Texas was Texas annexation, annexed in 1845 during a period of expansionism, and the 1846 Oregon Treaty with Britain led to U.S. control of the present-day Northwestern United States, American Northwest. Additionally, the Trail of Tears in the 1830s exemplified the Indian Removal Act, Indian removal policy that forcibly resettled Indians. This further expanded acreage under mechanical cultivation, increasing surpluses for international markets. This prompted a long series of American Indian Wars west of the Mississippi River from 1810 to at least 1890. and eventually, conflict with Mexico. Most of these conflicts ended with the cession of Native American territory and their confinement to Indian reservations. Victory in the Mexican–American War resulted in the 1848 Mexican Cession of California and much of the present-day Southwestern United States, American Southwest, and the U.S. spanned the continent. The California Gold Rush of 1848–1849 spurred migration to the Pacific coast, which led to the California Genocide and the creation of additional western states. Economic development was spurred by giving vast quantities of land, nearly 10% of the total area of the United States, to white European settlers as part of the Homestead Acts, as well as making land grants to private railroad companies and Land-grant university, colleges. Prior to the Civil War, Slave states and free states, the prohibition or expansion of slavery into these territories exacerbated tensions over Origins of the American Civil War, the debate around abolitionism.
In the late 18th century, American settlers began to Territorial evolution of the United States, expand further westward, some of them with a sense of manifest destiny. The 1803 Louisiana Purchase almost doubled the nation's area, Adams–Onís Treaty, Spain ceded Florida and other Gulf Coast territory in 1819, the Republic of Texas was Texas annexation, annexed in 1845 during a period of expansionism, and the 1846 Oregon Treaty with Britain led to U.S. control of the present-day Northwestern United States, American Northwest. Additionally, the Trail of Tears in the 1830s exemplified the Indian Removal Act, Indian removal policy that forcibly resettled Indians. This further expanded acreage under mechanical cultivation, increasing surpluses for international markets. This prompted a long series of American Indian Wars west of the Mississippi River from 1810 to at least 1890. and eventually, conflict with Mexico. Most of these conflicts ended with the cession of Native American territory and their confinement to Indian reservations. Victory in the Mexican–American War resulted in the 1848 Mexican Cession of California and much of the present-day Southwestern United States, American Southwest, and the U.S. spanned the continent. The California Gold Rush of 1848–1849 spurred migration to the Pacific coast, which led to the California Genocide and the creation of additional western states. Economic development was spurred by giving vast quantities of land, nearly 10% of the total area of the United States, to white European settlers as part of the Homestead Acts, as well as making land grants to private railroad companies and Land-grant university, colleges. Prior to the Civil War, Slave states and free states, the prohibition or expansion of slavery into these territories exacerbated tensions over Origins of the American Civil War, the debate around abolitionism.
 Irreconcilable sectional conflict regarding Slavery in the United States, the enslavement of Africans and African Americans ultimately Origins of the American Civil War, led to the American Civil War. With the 1860 United States presidential election, 1860 election of Republican Abraham Lincoln, conventions in eleven slave states declared secession and formed the
Irreconcilable sectional conflict regarding Slavery in the United States, the enslavement of Africans and African Americans ultimately Origins of the American Civil War, led to the American Civil War. With the 1860 United States presidential election, 1860 election of Republican Abraham Lincoln, conventions in eleven slave states declared secession and formed the
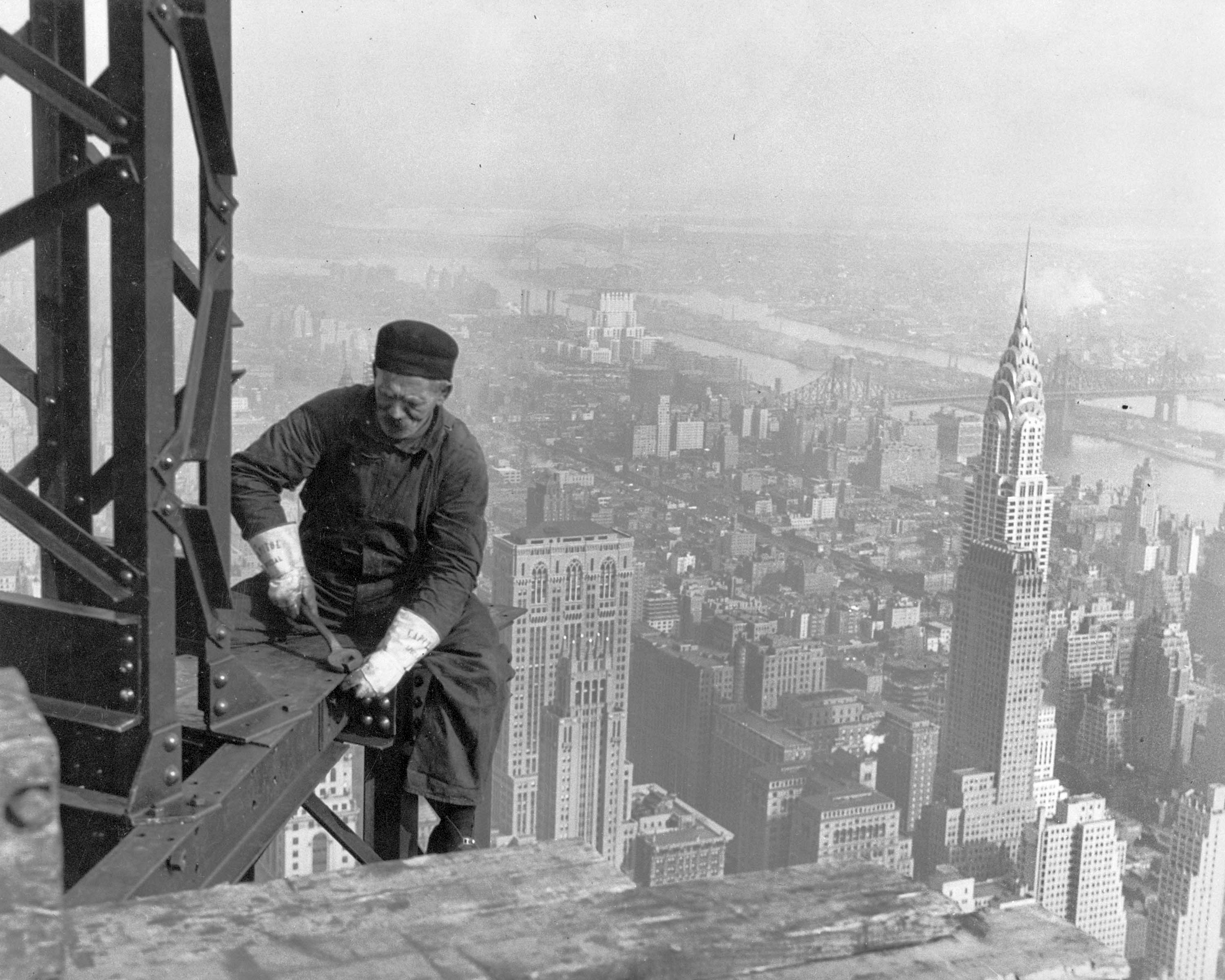

 The United States remained neutral from the outbreak of
The United States remained neutral from the outbreak of
 After World War II, the United States financed and implemented the Marshall Plan to help rebuild western Europe; disbursements paid between 1948 and 1952 would total $13 billion ($115 billion in 2021). Also at this time, Geopolitics, geopolitical tensions between the United States and Soviet Union, Russia led to the Cold War, driven by an ideological divide between capitalism and communism. They dominated the military affairs of Europe, with the U.S. and its
After World War II, the United States financed and implemented the Marshall Plan to help rebuild western Europe; disbursements paid between 1948 and 1952 would total $13 billion ($115 billion in 2021). Also at this time, Geopolitics, geopolitical tensions between the United States and Soviet Union, Russia led to the Cold War, driven by an ideological divide between capitalism and communism. They dominated the military affairs of Europe, with the U.S. and its  The growing
The growing

 The List of states and territories of the United States, 48 contiguous states and the District of Columbia occupy a combined area of . Of this area, is contiguous land, composing 83.65% of total U.S. land area. About 15% is occupied by Alaska, a state in northwestern North America, with the remainder in Hawaii, a state and archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, Pacific, and the five populated but Unincorporated area, unincorporated insular territories of Puerto Rico, American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, and the United States Virgin Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands. Measured by only land area, the United States is third in size behind Russia and China, and just ahead of Canada.
The United States is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third- or fourth-largest nation by total area (land and water), ranking behind Russia and Canada and nearly equal to China. The ranking varies depending on how two territories disputed by China and India are counted, and how the total size of the United States is measured.
The Atlantic coastal plain, coastal plain of the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic seaboard gives way further inland to deciduous forests and the rolling hills of the Piedmont (United States), Piedmont. The Appalachian Mountains and the Adirondack Mountains, Adirondack massif divide the eastern seaboard from the Great Lakes and the grasslands of the Midwestern United States, Midwest. The Mississippi River, Mississippi–Missouri River, the world's List of rivers by length, fourth longest river system, runs mainly north–south through the heart of the country. The flat, fertile prairie of the Great Plains stretches to the west, interrupted by U.S. Interior Highlands, a highland region in the southeast.
The Rocky Mountains, west of the Great Plains, extend north to south across the country, peaking at over in Colorado. Farther west are the rocky Great Basin and deserts such as the Chihuahuan Desert, Chihuahua, Sonoran Desert, Sonoran, and Mojave Desert, Mojave. The Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada and Cascade Range, Cascade mountain ranges run close to the West Coast of the United States, Pacific coast, both ranges also reaching altitudes higher than . The Extreme points of the United States, lowest and highest points in the contiguous United States are in the state of California, and only about apart. At an elevation of , Alaska's Denali is the highest peak in the country and in North America. Active volcanoes are common throughout Alaska's Alexander Archipelago, Alexander and Aleutian Islands, and Hawaii consists of volcanic islands. The supervolcano underlying Yellowstone National Park in the Rockies is the continent's largest volcanic feature.
The List of states and territories of the United States, 48 contiguous states and the District of Columbia occupy a combined area of . Of this area, is contiguous land, composing 83.65% of total U.S. land area. About 15% is occupied by Alaska, a state in northwestern North America, with the remainder in Hawaii, a state and archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, Pacific, and the five populated but Unincorporated area, unincorporated insular territories of Puerto Rico, American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, and the United States Virgin Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands. Measured by only land area, the United States is third in size behind Russia and China, and just ahead of Canada.
The United States is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third- or fourth-largest nation by total area (land and water), ranking behind Russia and Canada and nearly equal to China. The ranking varies depending on how two territories disputed by China and India are counted, and how the total size of the United States is measured.
The Atlantic coastal plain, coastal plain of the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic seaboard gives way further inland to deciduous forests and the rolling hills of the Piedmont (United States), Piedmont. The Appalachian Mountains and the Adirondack Mountains, Adirondack massif divide the eastern seaboard from the Great Lakes and the grasslands of the Midwestern United States, Midwest. The Mississippi River, Mississippi–Missouri River, the world's List of rivers by length, fourth longest river system, runs mainly north–south through the heart of the country. The flat, fertile prairie of the Great Plains stretches to the west, interrupted by U.S. Interior Highlands, a highland region in the southeast.
The Rocky Mountains, west of the Great Plains, extend north to south across the country, peaking at over in Colorado. Farther west are the rocky Great Basin and deserts such as the Chihuahuan Desert, Chihuahua, Sonoran Desert, Sonoran, and Mojave Desert, Mojave. The Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada and Cascade Range, Cascade mountain ranges run close to the West Coast of the United States, Pacific coast, both ranges also reaching altitudes higher than . The Extreme points of the United States, lowest and highest points in the contiguous United States are in the state of California, and only about apart. At an elevation of , Alaska's Denali is the highest peak in the country and in North America. Active volcanoes are common throughout Alaska's Alexander Archipelago, Alexander and Aleutian Islands, and Hawaii consists of volcanic islands. The supervolcano underlying Yellowstone National Park in the Rockies is the continent's largest volcanic feature.
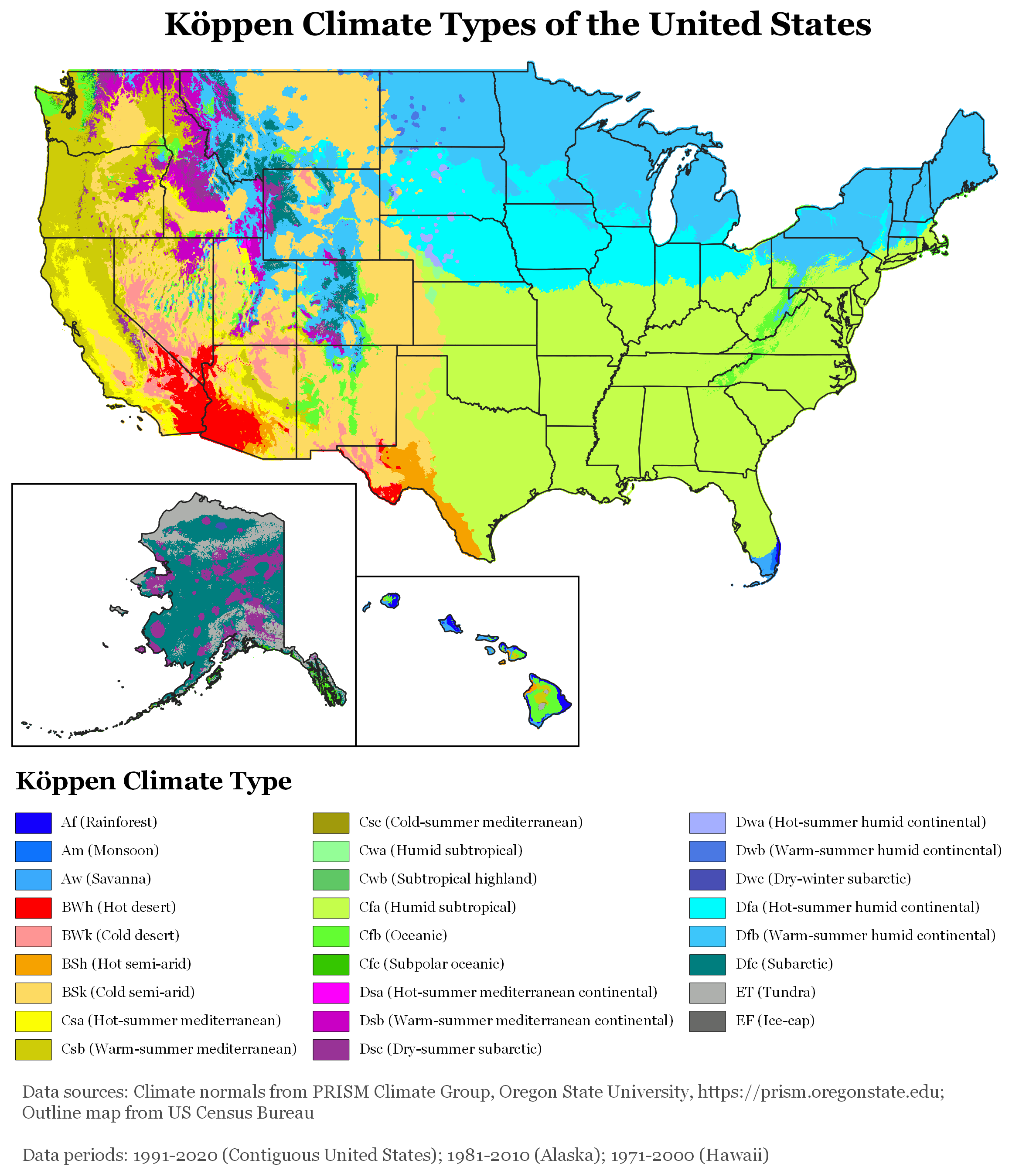 The United States, with its large size and geographic variety, includes most climate types. To the east of the 100th meridian west, 100th meridian, the climate ranges from humid continental climate, humid continental in the north to humid subtropical climate, humid subtropical in the south.
The Great Plains west of the 100th meridian are Semi-arid climate, semi-arid. Many mountainous areas of the American West have an alpine climate. The climate is Desert climate, arid in the Great Basin, desert in the Southwest, Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean in coastal California, and oceanic climate, oceanic in coastal Oregon and Washington (state), Washington and southern Alaska. Most of Alaska is Subarctic climate, subarctic or Polar climate, polar. Hawaii and the southern tip of Florida are Tropical climate, tropical, as well as its territories in the Caribbean and the Pacific.
States bordering the Gulf of Mexico are prone to Tropical cyclone, hurricanes, and most of the world's tornadoes occur in the country, mainly in Tornado Alley areas in the Midwest and South. Overall, the United States receives more high-impact extreme weather incidents than any other country in the world.
Extreme weather has become more frequent in the U.S., with three times the number of reported heat waves as in the 1960s. Of the ten warmest years ever recorded in the 48 contiguous states, eight have occurred since 1998. In the Southwestern United States, American Southwest, droughts have become more persistent and more severe.
The United States, with its large size and geographic variety, includes most climate types. To the east of the 100th meridian west, 100th meridian, the climate ranges from humid continental climate, humid continental in the north to humid subtropical climate, humid subtropical in the south.
The Great Plains west of the 100th meridian are Semi-arid climate, semi-arid. Many mountainous areas of the American West have an alpine climate. The climate is Desert climate, arid in the Great Basin, desert in the Southwest, Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean in coastal California, and oceanic climate, oceanic in coastal Oregon and Washington (state), Washington and southern Alaska. Most of Alaska is Subarctic climate, subarctic or Polar climate, polar. Hawaii and the southern tip of Florida are Tropical climate, tropical, as well as its territories in the Caribbean and the Pacific.
States bordering the Gulf of Mexico are prone to Tropical cyclone, hurricanes, and most of the world's tornadoes occur in the country, mainly in Tornado Alley areas in the Midwest and South. Overall, the United States receives more high-impact extreme weather incidents than any other country in the world.
Extreme weather has become more frequent in the U.S., with three times the number of reported heat waves as in the 1960s. Of the ten warmest years ever recorded in the 48 contiguous states, eight have occurred since 1998. In the Southwestern United States, American Southwest, droughts have become more persistent and more severe.
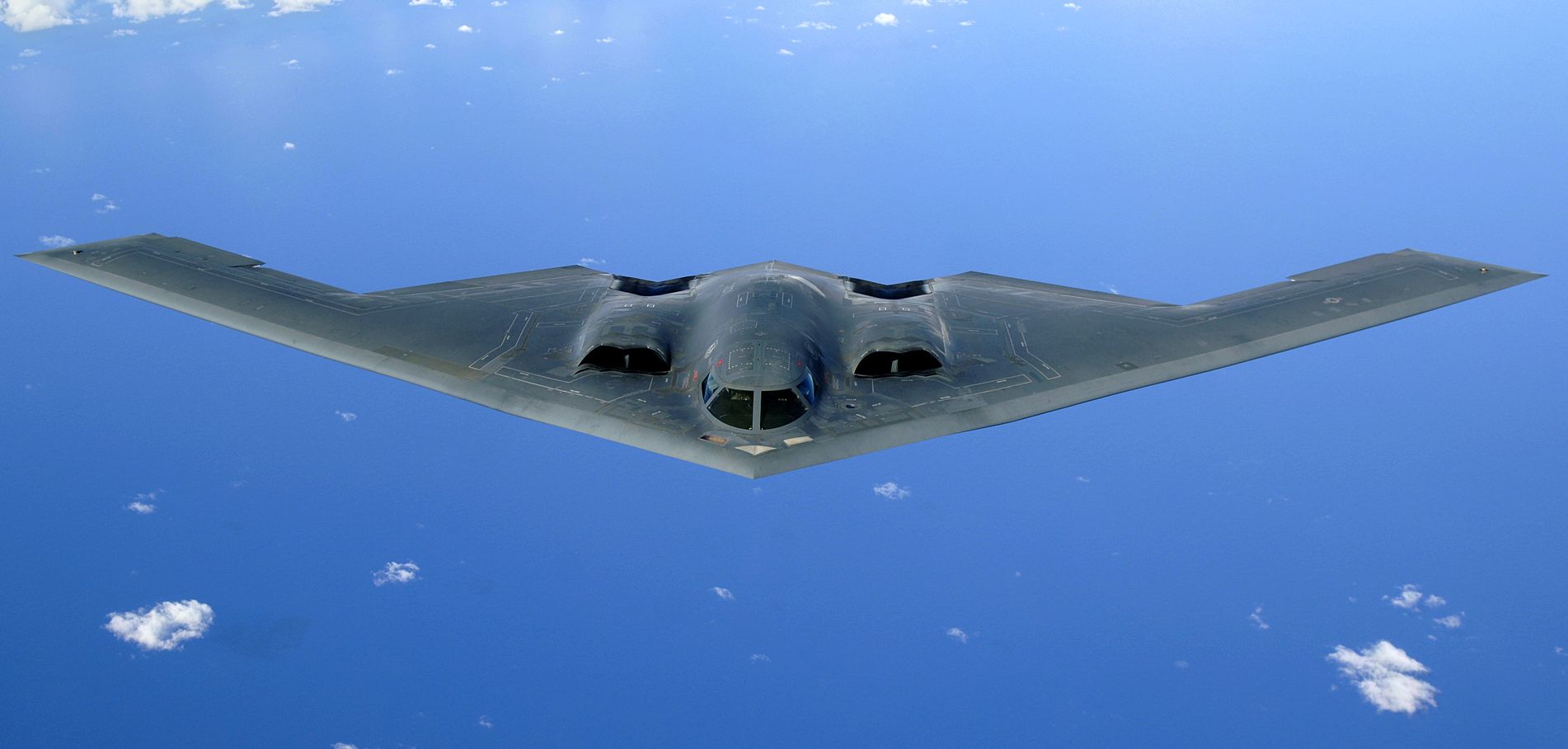
 The president is the Commander-in-Chief of the United States, commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces and appoints its leaders, the United States Secretary of Defense, secretary of defense and the Joint Chiefs of Staff. The United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense, which is headquartered at the Pentagon near Washington, D.C., administers five of the six service branches, which are made up of the United States Army, Army, United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps, United States Navy, Navy, United States Air Force, Air Force, and United States Space Force, Space Force. The United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard is administered by the United States Department of Homeland Security, Department of Homeland Security in peacetime and can be transferred to the United States Department of the Navy, Department of the Navy in wartime. The United States spent $649 billion on its military in 2019, 36% of global military spending. At 4.7% of GDP, the percentage was the second-highest among all countries, after Saudi Arabia. It also has Nuclear weapons of the United States, more than 40% of the world's nuclear weapons, the second-largest after Russia.
In 2019, all six branches of the U.S. Armed Forces reported 1.4 million personnel on active duty. The Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, Reserves and National Guard of the United States, National Guard brought the total number of troops to 2.3 million. The Department of Defense also employed about 700,000 civilians, not including Military-industrial complex, contractors. Military service in the United States is voluntary, although Conscription in the United States, conscription may occur in wartime through the Selective Service System. The United States has the third-largest combined armed forces in the world, behind the People's Liberation Army, Chinese People's Liberation Army and Indian Armed Forces.
Today, American forces can be rapidly deployed by the Air Force's large fleet of transport aircraft, the Navy's 11 active aircraft carriers, and Marine expeditionary units at sea with the Navy, and Army's XVIII Airborne Corps and 75th Ranger Regiment deployed by Air Force transport aircraft. The Air Force can strike targets across the globe through its fleet of strategic bombers, maintains the air defense across the United States, and provides close air support to Army and Marine Corps ground forces.
The Space Force operates the Global Positioning System, operates the Eastern Range, Eastern and Western Range (USSF), Western Ranges for all space launches, and operates the United States's United States Space Surveillance Network, Space Surveillance and United States national missile defense, Missile Warning networks. The military operates about 800 bases and facilities abroad, and maintains United States military deployments, deployments greater than 100 active duty personnel in 25 foreign countries.
The president is the Commander-in-Chief of the United States, commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces and appoints its leaders, the United States Secretary of Defense, secretary of defense and the Joint Chiefs of Staff. The United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense, which is headquartered at the Pentagon near Washington, D.C., administers five of the six service branches, which are made up of the United States Army, Army, United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps, United States Navy, Navy, United States Air Force, Air Force, and United States Space Force, Space Force. The United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard is administered by the United States Department of Homeland Security, Department of Homeland Security in peacetime and can be transferred to the United States Department of the Navy, Department of the Navy in wartime. The United States spent $649 billion on its military in 2019, 36% of global military spending. At 4.7% of GDP, the percentage was the second-highest among all countries, after Saudi Arabia. It also has Nuclear weapons of the United States, more than 40% of the world's nuclear weapons, the second-largest after Russia.
In 2019, all six branches of the U.S. Armed Forces reported 1.4 million personnel on active duty. The Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, Reserves and National Guard of the United States, National Guard brought the total number of troops to 2.3 million. The Department of Defense also employed about 700,000 civilians, not including Military-industrial complex, contractors. Military service in the United States is voluntary, although Conscription in the United States, conscription may occur in wartime through the Selective Service System. The United States has the third-largest combined armed forces in the world, behind the People's Liberation Army, Chinese People's Liberation Army and Indian Armed Forces.
Today, American forces can be rapidly deployed by the Air Force's large fleet of transport aircraft, the Navy's 11 active aircraft carriers, and Marine expeditionary units at sea with the Navy, and Army's XVIII Airborne Corps and 75th Ranger Regiment deployed by Air Force transport aircraft. The Air Force can strike targets across the globe through its fleet of strategic bombers, maintains the air defense across the United States, and provides close air support to Army and Marine Corps ground forces.
The Space Force operates the Global Positioning System, operates the Eastern Range, Eastern and Western Range (USSF), Western Ranges for all space launches, and operates the United States's United States Space Surveillance Network, Space Surveillance and United States national missile defense, Missile Warning networks. The military operates about 800 bases and facilities abroad, and maintains United States military deployments, deployments greater than 100 active duty personnel in 25 foreign countries.
 There are about 18,000 U.S. police agencies from local to federal level in the United States. Law in the United States is mainly Law enforcement in the United States, enforced by local police departments and sheriff's offices. The state police provides broader services, and Federal law enforcement in the United States, federal agencies such as the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the United States Marshals Service, U.S. Marshals Service have specialized duties, such as protecting civil rights, National Security of the United States, national security and enforcing U.S. federal courts' rulings and federal laws. State court (United States), State courts conduct most civil and criminal trials, and federal courts handle designated crimes and appeals from the state criminal courts.
, the United States has an List of countries by intentional homicide rate, intentional homicide rate of 7 per 100,000 people. A cross-sectional analysis of the World Health Organization Mortality Database from 2010 showed that United States homicide rates "were 7.0 times higher than in other high-income countries, driven by a gun homicide rate that was 25.2 times higher."
, the United States has the United States incarceration rate, sixth highest documented incarceration rate and Incarceration in the United States, second largest prison population in the world. In 2019, the total prison population for those sentenced to more than a year is 1,430,800, corresponding to a ratio of 419 per 100,000 residents and the lowest since 1995. Some estimates place that number higher, such Prison Policy Initiative's 2.3 million. Various states have attempted to Decarceration in the United States, reduce their prison populations via government policies and grassroots initiatives.
Although most nations have abolished capital punishment, it is sanctioned in the United States for certain federal and military crimes, and in 27 states out of 50 and in one territory. Several of these states have Moratorium (law), moratoriums on carrying out the penalty, each imposed by the state's governor. Since 1977, there have been more than 1,500 executions, giving the U.S. the sixth-highest number of executions in the world, following Capital punishment in China, China, Capital punishment in Iran, Iran, Capital punishment in Saudi Arabia, Saudi Arabia, Capital punishment in Iraq, Iraq, and Capital punishment in Egypt, Egypt. However, the number is trended down nationally, with Capital punishment in the United States#States without capital punishment, several states recently abolishing the penalty.
There are about 18,000 U.S. police agencies from local to federal level in the United States. Law in the United States is mainly Law enforcement in the United States, enforced by local police departments and sheriff's offices. The state police provides broader services, and Federal law enforcement in the United States, federal agencies such as the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the United States Marshals Service, U.S. Marshals Service have specialized duties, such as protecting civil rights, National Security of the United States, national security and enforcing U.S. federal courts' rulings and federal laws. State court (United States), State courts conduct most civil and criminal trials, and federal courts handle designated crimes and appeals from the state criminal courts.
, the United States has an List of countries by intentional homicide rate, intentional homicide rate of 7 per 100,000 people. A cross-sectional analysis of the World Health Organization Mortality Database from 2010 showed that United States homicide rates "were 7.0 times higher than in other high-income countries, driven by a gun homicide rate that was 25.2 times higher."
, the United States has the United States incarceration rate, sixth highest documented incarceration rate and Incarceration in the United States, second largest prison population in the world. In 2019, the total prison population for those sentenced to more than a year is 1,430,800, corresponding to a ratio of 419 per 100,000 residents and the lowest since 1995. Some estimates place that number higher, such Prison Policy Initiative's 2.3 million. Various states have attempted to Decarceration in the United States, reduce their prison populations via government policies and grassroots initiatives.
Although most nations have abolished capital punishment, it is sanctioned in the United States for certain federal and military crimes, and in 27 states out of 50 and in one territory. Several of these states have Moratorium (law), moratoriums on carrying out the penalty, each imposed by the state's governor. Since 1977, there have been more than 1,500 executions, giving the U.S. the sixth-highest number of executions in the world, following Capital punishment in China, China, Capital punishment in Iran, Iran, Capital punishment in Saudi Arabia, Saudi Arabia, Capital punishment in Iraq, Iraq, and Capital punishment in Egypt, Egypt. However, the number is trended down nationally, with Capital punishment in the United States#States without capital punishment, several states recently abolishing the penalty.
 According to the
According to the
Securities and Exchange Commission (China). The List of the largest trading partners of the United States, largest U.S. trading partners are China, the European Union, Canada, Mexico, India, Japan, South Korea, the United Kingdom, and Taiwan. The U.S. is the world's List of countries by imports, largest importer and the List of countries by exports, second-largest exporter. It has free trade agreements with United States free-trade agreements, several countries, including the United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement, USMCA. The U.S. ranked second in the Global Competitiveness Report in 2019, after Singapore. Of the world's Fortune Global 500, 500 largest companies, 124 are headquartered in the U.S. While its economy has reached a post-industrial society, post-industrial level of development, the United States remains an industrial power. It has a smaller welfare state and redistributes less income through government action than most other World Bank high-income economy, high-income countries. The United States ranked the 41st highest in income inequality among 156 countries in 2017, and the highest compared to the rest of the developed world. As of January 1, 2023, the United States had a national debt of $31.4 trillion.
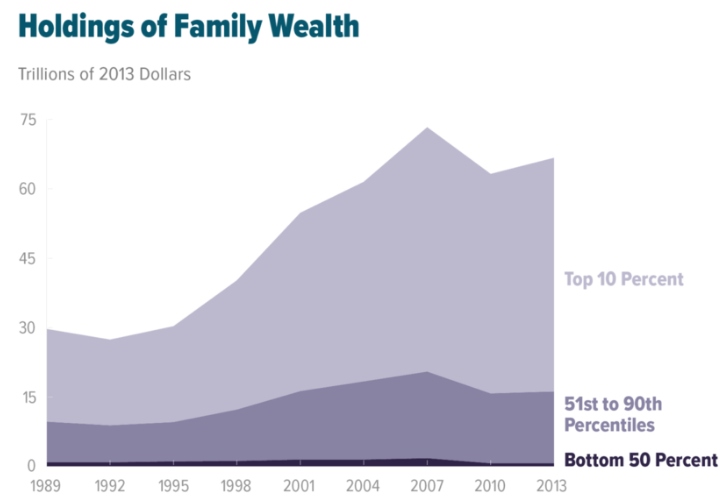 At $46,625 USD in 2021, American citizens have the highest median income in the world. Despite the fact that they only account for 4.24% of the World population, global population, they collectively List of countries by total wealth, possess 30.2% of the world's total wealth as of 2021, the largest percentage of any country. The U.S. also ranks first in the number of dollar billionaires and millionaires in the world, with 724 billionaires (as of 2021) and nearly 22 million millionaires (2021).
Wealth in the United States is Wealth inequality in the United States, highly concentrated; the richest 10% of the adult population own 72% of the country's household wealth, while the bottom 50% own just 2%. Income inequality in the United States, Income inequality in the U.S. remains at record highs, with the top fifth of earners taking home more than half of all income and giving the U.S. one of the widest income distributions among OECD members. The United States is the only advanced economy that does not List of statutory minimum employment leave by country, guarantee its workers paid vacation and is one of a few countries in the world without paid family leave as a legal right. The United States also has a higher percentage of low-income workers than almost any other developed nation, largely because of a weak collective bargaining system and lack of government support for at-risk workers.
There were about 567,715 sheltered and unsheltered Homelessness in the United States, homeless persons in the U.S. in January 2019, with almost two-thirds staying in an emergency shelter or transitional housing program. Attempts to combat homelessness include the Section 8 (housing), Section 8 housing voucher program and implementation of the Housing First strategy across all levels of government.
In 2011, Hunger in the United States#Children, 16.7 million children lived in food-insecure households, about 35% more than 2007 levels, though only 845,000 U.S. children (1.1%) saw reduced food intake or disrupted eating patterns at some point during the year, and most cases were not chronic. 40 million people, roughly 12.7% of the U.S. population, were living in poverty, including 13.3 million children. Of those impoverished, 18.5 million live in "deep poverty", family income below one-half of the federal government's poverty threshold.
At $46,625 USD in 2021, American citizens have the highest median income in the world. Despite the fact that they only account for 4.24% of the World population, global population, they collectively List of countries by total wealth, possess 30.2% of the world's total wealth as of 2021, the largest percentage of any country. The U.S. also ranks first in the number of dollar billionaires and millionaires in the world, with 724 billionaires (as of 2021) and nearly 22 million millionaires (2021).
Wealth in the United States is Wealth inequality in the United States, highly concentrated; the richest 10% of the adult population own 72% of the country's household wealth, while the bottom 50% own just 2%. Income inequality in the United States, Income inequality in the U.S. remains at record highs, with the top fifth of earners taking home more than half of all income and giving the U.S. one of the widest income distributions among OECD members. The United States is the only advanced economy that does not List of statutory minimum employment leave by country, guarantee its workers paid vacation and is one of a few countries in the world without paid family leave as a legal right. The United States also has a higher percentage of low-income workers than almost any other developed nation, largely because of a weak collective bargaining system and lack of government support for at-risk workers.
There were about 567,715 sheltered and unsheltered Homelessness in the United States, homeless persons in the U.S. in January 2019, with almost two-thirds staying in an emergency shelter or transitional housing program. Attempts to combat homelessness include the Section 8 (housing), Section 8 housing voucher program and implementation of the Housing First strategy across all levels of government.
In 2011, Hunger in the United States#Children, 16.7 million children lived in food-insecure households, about 35% more than 2007 levels, though only 845,000 U.S. children (1.1%) saw reduced food intake or disrupted eating patterns at some point during the year, and most cases were not chronic. 40 million people, roughly 12.7% of the U.S. population, were living in poverty, including 13.3 million children. Of those impoverished, 18.5 million live in "deep poverty", family income below one-half of the federal government's poverty threshold.
 The United States has been a leader in technological innovation since the late 19th century and scientific research since the mid-20th century. Methods for producing interchangeable parts and the establishment of a machine tool industry enabled the American system of manufacturing, U.S. to have large-scale manufacturing of sewing machines, bicycles, and other items in the late 19th century. In the early 20th century, factory electrification, the introduction of the assembly line, and other labor-saving techniques created the system of mass production. In the 21st century, approximately two-thirds of research and development funding comes from the private sector. In 2020, the United States was the country with the List of countries by number of scientific and technical journal articles, second-highest number of published scientific papers and second most patents granted, both after China. In 2021, the United States launched a total of 51 spaceflights. (China reported 55.) The U.S. had 2,944 active satellites in space in December 2021, the highest number of any country.
In 1876, Alexander Graham Bell was awarded the first U.S. Invention of the telephone, patent for the telephone. Thomas Edison's Research institute, research laboratory developed the phonograph, the first Incandescent light bulb, long-lasting light bulb, and the first viable Kinetoscope, movie camera. The Wright brothers in 1903 made the Wright Flyer, first sustained and controlled heavier-than-air powered flight, and the automobile companies of Ransom E. Olds and Henry Ford popularized the assembly line in the early 20th century. The rise of fascism and Nazism in the 1920s and 30s led many European scientists, such as Albert Einstein, Enrico Fermi, and John von Neumann, to immigrate to the United States. During World War II, the Manhattan Project developed nuclear weapons, ushering in the Atomic Age. During the Cold War, competition for superior missile capability ushered in the
The United States has been a leader in technological innovation since the late 19th century and scientific research since the mid-20th century. Methods for producing interchangeable parts and the establishment of a machine tool industry enabled the American system of manufacturing, U.S. to have large-scale manufacturing of sewing machines, bicycles, and other items in the late 19th century. In the early 20th century, factory electrification, the introduction of the assembly line, and other labor-saving techniques created the system of mass production. In the 21st century, approximately two-thirds of research and development funding comes from the private sector. In 2020, the United States was the country with the List of countries by number of scientific and technical journal articles, second-highest number of published scientific papers and second most patents granted, both after China. In 2021, the United States launched a total of 51 spaceflights. (China reported 55.) The U.S. had 2,944 active satellites in space in December 2021, the highest number of any country.
In 1876, Alexander Graham Bell was awarded the first U.S. Invention of the telephone, patent for the telephone. Thomas Edison's Research institute, research laboratory developed the phonograph, the first Incandescent light bulb, long-lasting light bulb, and the first viable Kinetoscope, movie camera. The Wright brothers in 1903 made the Wright Flyer, first sustained and controlled heavier-than-air powered flight, and the automobile companies of Ransom E. Olds and Henry Ford popularized the assembly line in the early 20th century. The rise of fascism and Nazism in the 1920s and 30s led many European scientists, such as Albert Einstein, Enrico Fermi, and John von Neumann, to immigrate to the United States. During World War II, the Manhattan Project developed nuclear weapons, ushering in the Atomic Age. During the Cold War, competition for superior missile capability ushered in the
 The United States's Rail transport in the United States, rail network, nearly all Standard-gauge railway, standard gauge, is the List of countries by rail transport network size, longest in the world, and exceeds . It handles mostly freight, with intercity passenger service provided by Amtrak to all but four states. The country's Inland waterways of the United States, inland waterways are the world's List of countries by waterways length, fifth-longest, and total .
Personal transportation is dominated by automobiles, which operate on a network of of public roads. The United States has the world's second-largest automobile market, and has the highest vehicle ownership per capita in the world, with 816.4 vehicles per 1,000 Americans (2014). In 2017, there were 255 million non-two wheel motor vehicles, or about 910 vehicles per 1,000 people.
The List of airlines of the United States, civil airline industry is entirely privately owned and has been largely Airline Deregulation Act, deregulated since 1978, while List of airports in the United States, most major airports are publicly owned. The three largest airlines in the world by passengers carried are U.S.-based; American Airlines is number one after its 2013 acquisition by US Airways. Of the List of the world's busiest airports by passenger traffic, world's 50 busiest passenger airports, 16 are in the United States, including the busiest, Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport. Of the List of busiest container ports, fifty busiest container ports, four are located in the United States, of which the busiest is the Port of Los Angeles.
The United States's Rail transport in the United States, rail network, nearly all Standard-gauge railway, standard gauge, is the List of countries by rail transport network size, longest in the world, and exceeds . It handles mostly freight, with intercity passenger service provided by Amtrak to all but four states. The country's Inland waterways of the United States, inland waterways are the world's List of countries by waterways length, fifth-longest, and total .
Personal transportation is dominated by automobiles, which operate on a network of of public roads. The United States has the world's second-largest automobile market, and has the highest vehicle ownership per capita in the world, with 816.4 vehicles per 1,000 Americans (2014). In 2017, there were 255 million non-two wheel motor vehicles, or about 910 vehicles per 1,000 people.
The List of airlines of the United States, civil airline industry is entirely privately owned and has been largely Airline Deregulation Act, deregulated since 1978, while List of airports in the United States, most major airports are publicly owned. The three largest airlines in the world by passengers carried are U.S.-based; American Airlines is number one after its 2013 acquisition by US Airways. Of the List of the world's busiest airports by passenger traffic, world's 50 busiest passenger airports, 16 are in the United States, including the busiest, Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport. Of the List of busiest container ports, fifty busiest container ports, four are located in the United States, of which the busiest is the Port of Los Angeles.
 American state school, public education is operated by state and local governments and regulated by the United States Department of Education through restrictions on federal grants. In most states, children are required to attend school from the age of five or six (beginning with kindergarten or first grade) until they turn 18 (generally bringing them through twelfth grade, the end of high school); some states allow students to leave school at 16 or 17. Of Americans 25 and older, 84.6% graduated from high school, 52.6% attended some college, 27.2% earned a bachelor's degree, and 9.6% earned graduate degrees. The basic literacy rate is approximately 99%.
The United States has many private and public Lists of American institutions of higher education, institutions of higher education. The majority of the world's top Public university, public and Private university, private universities, as listed by various ranking organizations, are in the United States. There are also local community colleges with generally more open admission policies, shorter academic programs, and lower tuition. The U.S. spends more on education per student than any nation in the world, spending an average of $12,794 per year on public elementary and secondary school students in the 2016–2017 school year. As for public expenditures on higher education, the U.S. spends more per student than the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD average, and more than all nations in combined public and private spending. Despite some student loan forgiveness programs in place, Student debt, student loan debt has increased by 102% in the last decade, and exceeded 1.7 trillion dollars as of 2022.
American state school, public education is operated by state and local governments and regulated by the United States Department of Education through restrictions on federal grants. In most states, children are required to attend school from the age of five or six (beginning with kindergarten or first grade) until they turn 18 (generally bringing them through twelfth grade, the end of high school); some states allow students to leave school at 16 or 17. Of Americans 25 and older, 84.6% graduated from high school, 52.6% attended some college, 27.2% earned a bachelor's degree, and 9.6% earned graduate degrees. The basic literacy rate is approximately 99%.
The United States has many private and public Lists of American institutions of higher education, institutions of higher education. The majority of the world's top Public university, public and Private university, private universities, as listed by various ranking organizations, are in the United States. There are also local community colleges with generally more open admission policies, shorter academic programs, and lower tuition. The U.S. spends more on education per student than any nation in the world, spending an average of $12,794 per year on public elementary and secondary school students in the 2016–2017 school year. As for public expenditures on higher education, the U.S. spends more per student than the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD average, and more than all nations in combined public and private spending. Despite some student loan forgiveness programs in place, Student debt, student loan debt has increased by 102% in the last decade, and exceeded 1.7 trillion dollars as of 2022.
 In a preliminary report, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced that U.S. life expectancy at birth had dropped to 76.4 years in 2021 (73.2 years for men and 79.1 years for women), down 0.9 years from 2020. This was the second year of overall decline, and the chief causes listed were the COVID-19 pandemic, accidents, drug overdoses, heart and liver disease, and suicides. Life expectancy was highest among Asians and Hispanics and lowest among Blacks and American Indian–Alaskan Native (AIAN (U.S. Census), AIAN) peoples. Starting in 1998, the average life expectancy in the U.S. fell behind that of other wealthy industrialized countries, and Americans' "health disadvantage" gap has been increasing ever since. The U.S. also has one of the highest Suicide in the United States, suicide rates among high-income countries, and approximately one-third of the U.S. adult population is obese and another third is overweight.
In 2010, coronary artery disease, lung cancer, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, and traffic collisions caused the most years of life lost in the U.S. Low back pain, major depressive disorder, depression, musculoskeletal disorders, neck pain, and anxiety caused the most years lost to disability. The most harmful risk factors were poor diet, tobacco smoking, obesity, Hypertension, high blood pressure, Hyperglycemia, high blood sugar, physical inactivity, and Alcohol consumption and health, alcohol consumption. Alzheimer's disease, substance use disorders, kidney disease, cancer, and falls caused the most additional years of life lost over their age-adjusted 1990 per-capita rates. Teenage pregnancy in the United States, Teenage pregnancy and Abortion in the United States, abortion rates in the U.S. are substantially higher than in other Western nations, especially among blacks and Hispanics.
The U.S. health care system far List of countries by total health expenditure (PPP) per capita, outspends that of any other nation, measured both in per capita spending and as a percentage of GDP but attains worse healthcare outcomes when compared to peer nations. The United States is the only developed nation Healthcare reform in the United States, without a system of universal health care, and a Health insurance coverage in the United States, significant proportion of the population that does not carry health insurance. The U.S., however, is a global leader in medical innovation, measured either in terms of revenue or the number of new drugs and devices introduced.Stats from 2007 Europ.Fed.of Pharm.Indust.and Assoc. Retrieved June 17, 2009, fro
In a preliminary report, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced that U.S. life expectancy at birth had dropped to 76.4 years in 2021 (73.2 years for men and 79.1 years for women), down 0.9 years from 2020. This was the second year of overall decline, and the chief causes listed were the COVID-19 pandemic, accidents, drug overdoses, heart and liver disease, and suicides. Life expectancy was highest among Asians and Hispanics and lowest among Blacks and American Indian–Alaskan Native (AIAN (U.S. Census), AIAN) peoples. Starting in 1998, the average life expectancy in the U.S. fell behind that of other wealthy industrialized countries, and Americans' "health disadvantage" gap has been increasing ever since. The U.S. also has one of the highest Suicide in the United States, suicide rates among high-income countries, and approximately one-third of the U.S. adult population is obese and another third is overweight.
In 2010, coronary artery disease, lung cancer, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, and traffic collisions caused the most years of life lost in the U.S. Low back pain, major depressive disorder, depression, musculoskeletal disorders, neck pain, and anxiety caused the most years lost to disability. The most harmful risk factors were poor diet, tobacco smoking, obesity, Hypertension, high blood pressure, Hyperglycemia, high blood sugar, physical inactivity, and Alcohol consumption and health, alcohol consumption. Alzheimer's disease, substance use disorders, kidney disease, cancer, and falls caused the most additional years of life lost over their age-adjusted 1990 per-capita rates. Teenage pregnancy in the United States, Teenage pregnancy and Abortion in the United States, abortion rates in the U.S. are substantially higher than in other Western nations, especially among blacks and Hispanics.
The U.S. health care system far List of countries by total health expenditure (PPP) per capita, outspends that of any other nation, measured both in per capita spending and as a percentage of GDP but attains worse healthcare outcomes when compared to peer nations. The United States is the only developed nation Healthcare reform in the United States, without a system of universal health care, and a Health insurance coverage in the United States, significant proportion of the population that does not carry health insurance. The U.S., however, is a global leader in medical innovation, measured either in terms of revenue or the number of new drugs and devices introduced.Stats from 2007 Europ.Fed.of Pharm.Indust.and Assoc. Retrieved June 17, 2009, fro
/ref> Government-funded health care coverage for the poor (Medicaid, established in 1965) and for those age 65 and older (Medicare (United States), Medicare, begun in 1966) is available to Americans who meet the programs' income or age qualifications. In 2010, former President Obama passed the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act or ACA, which the CDC said that the law roughly halved the uninsured share of the population and multiple studies have concluded that ACA had reduced the mortality of enrollees. However, its legacy Criticism of Obamacare, remains controversial.
 Americans have traditionally Stereotypes of Americans, been characterized by a strong work ethic, competitiveness, and individualism, as well as a unifying belief in an "American civil religion, American creed" emphasizing liberty, social equality, property rights, democracy, equality under the law, and a preference for limited government. Americans are extremely charitable by global standards: according to a 2016 study by the Charities Aid Foundation, Americans donated 1.44% of total GDP to charity, the List of countries by charitable donation, highest in the world by a large margin. The United States is home to a Multiculturalism, wide variety of ethnic groups, traditions, and values, and exerts major cultural influence Americanization, on a global scale. The country has been described as a society "built on a Moral universalism, universalistic cultural frame rooted in the natural laws of science and human rights."
The United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence has become a well-known statement on human rights, particularly its second sentence: "We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by Higher Power, their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness." Stephen Lucas called it "one of the best-known sentences in the English language", with historian Joseph Ellis writing that the document contains "the most potent and consequential words in American history". The passage has since came to represent a moral standard to which the United States should strive. This view was notably promoted by Lincoln, who considered it to be the foundation of his political philosophy and argued that it is a statement of principles through which the Constitution should be interpreted.
Aside from the Native American, Native Hawaiians, Native Hawaiian, and Alaska Natives, Native Alaskan populations, nearly all Americans or their ancestors immigrated or were imported as slaves within the past five centuries. wikt:mainstream, Mainstream American culture is a Western culture largely derived from the European American, traditions of European immigrants with influences from many other sources, such as African-American culture, traditions brought by slaves from Africa. More recent immigration from Asian American, Asia and especially Latin American culture, Latin America has added to a cultural mix that has been described as a homogenizing melting pot, and a heterogeneous salad bowl (cultural idea), salad bowl, with immigrants contributing to, and often Assimilation (phonology), assimilating into, mainstream American culture. Nevertheless, there is a high degree of social inequality related to Racial inequality in the United States, race and Wealth inequality in the United States, wealth. The American Dream, or the perception that Americans enjoy high Socio-economic mobility in the United States, social mobility, plays a key role in attracting immigrants. Whether this perception is accurate has been a topic of debate.*
*
*
* While mainstream culture holds that the United States is a classless society, scholars identify significant differences between Social class in the United States, the country's social classes, affecting socialization, language, and values.
Americans tend to greatly value socioeconomics, socioeconomic achievement, but being Average Joe, ordinary or average is promoted by some as a noble condition.
In the modern day, the country is considered to have Permissive society, permissive attitudes surrounding human sexuality. LGBT rights in the United States are among the most socially, culturally, and legally permissive and advanced in the world, with Public opinion of same-sex marriage in the United States, public opinion and jurisprudence on the issue changing significantly since the late 1980s. A late 2022 ''Grinnell College National Poll'' found that 74% of Americans agree that same-sex marriage should be a guaranteed right while 13% disagree.
Americans have traditionally Stereotypes of Americans, been characterized by a strong work ethic, competitiveness, and individualism, as well as a unifying belief in an "American civil religion, American creed" emphasizing liberty, social equality, property rights, democracy, equality under the law, and a preference for limited government. Americans are extremely charitable by global standards: according to a 2016 study by the Charities Aid Foundation, Americans donated 1.44% of total GDP to charity, the List of countries by charitable donation, highest in the world by a large margin. The United States is home to a Multiculturalism, wide variety of ethnic groups, traditions, and values, and exerts major cultural influence Americanization, on a global scale. The country has been described as a society "built on a Moral universalism, universalistic cultural frame rooted in the natural laws of science and human rights."
The United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence has become a well-known statement on human rights, particularly its second sentence: "We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by Higher Power, their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness." Stephen Lucas called it "one of the best-known sentences in the English language", with historian Joseph Ellis writing that the document contains "the most potent and consequential words in American history". The passage has since came to represent a moral standard to which the United States should strive. This view was notably promoted by Lincoln, who considered it to be the foundation of his political philosophy and argued that it is a statement of principles through which the Constitution should be interpreted.
Aside from the Native American, Native Hawaiians, Native Hawaiian, and Alaska Natives, Native Alaskan populations, nearly all Americans or their ancestors immigrated or were imported as slaves within the past five centuries. wikt:mainstream, Mainstream American culture is a Western culture largely derived from the European American, traditions of European immigrants with influences from many other sources, such as African-American culture, traditions brought by slaves from Africa. More recent immigration from Asian American, Asia and especially Latin American culture, Latin America has added to a cultural mix that has been described as a homogenizing melting pot, and a heterogeneous salad bowl (cultural idea), salad bowl, with immigrants contributing to, and often Assimilation (phonology), assimilating into, mainstream American culture. Nevertheless, there is a high degree of social inequality related to Racial inequality in the United States, race and Wealth inequality in the United States, wealth. The American Dream, or the perception that Americans enjoy high Socio-economic mobility in the United States, social mobility, plays a key role in attracting immigrants. Whether this perception is accurate has been a topic of debate.*
*
*
* While mainstream culture holds that the United States is a classless society, scholars identify significant differences between Social class in the United States, the country's social classes, affecting socialization, language, and values.
Americans tend to greatly value socioeconomics, socioeconomic achievement, but being Average Joe, ordinary or average is promoted by some as a noble condition.
In the modern day, the country is considered to have Permissive society, permissive attitudes surrounding human sexuality. LGBT rights in the United States are among the most socially, culturally, and legally permissive and advanced in the world, with Public opinion of same-sex marriage in the United States, public opinion and jurisprudence on the issue changing significantly since the late 1980s. A late 2022 ''Grinnell College National Poll'' found that 74% of Americans agree that same-sex marriage should be a guaranteed right while 13% disagree.
 In the 18th and early 19th centuries, American art and literature took most of their cues from Europe, contributing to Western culture. Writers such as Washington Irving, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Edgar Allan Poe, and Henry David Thoreau established a distinctive American literary voice by the middle of the 19th century. Mark Twain and poet Walt Whitman were major figures in the century's second half; Emily Dickinson, virtually unknown during her lifetime, is recognized as an essential American poet.
A work seen as capturing fundamental aspects of the national experience and character—such as Herman Melville's ''Moby-Dick'' (1851), Twain's ''Adventures of Huckleberry Finn, The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn'' (1885), F. Scott Fitzgerald's ''The Great Gatsby'' (1925) and Harper Lee's ''To Kill a Mockingbird'' (1960)—may be dubbed the "Great American Novel."
Thirteen U.S. citizens have won the Nobel Prize in Literature. William Faulkner, Ernest Hemingway and John Steinbeck are often named among the most influential writers of the 20th century. The Beat Generation writers opened up new literary approaches, as have postmodern literature, postmodernist authors such as John Barth, Thomas Pynchon, and Don DeLillo.
In the visual arts, the Hudson River School was a mid-19th-century movement in the tradition of European Realism (arts), naturalism. The 1913 Armory Show in New York City, an exhibition of European modern art, modernist art, shocked the public and transformed the U.S. art scene. Georgia O'Keeffe, Marsden Hartley, and others experimented with new, individualistic styles.
Major artistic movements such as the abstract expressionism of Jackson Pollock and Willem de Kooning and the pop art of Andy Warhol and Roy Lichtenstein developed largely in the United States. The tide of modernism and then postmodernism has brought fame to American architects such as Frank Lloyd Wright, Philip Johnson, and Frank Gehry. Americans have long been important in the modern artistic medium of photography, with major photographers including Alfred Stieglitz, Edward Steichen, Edward Weston, and Ansel Adams.
In the 18th and early 19th centuries, American art and literature took most of their cues from Europe, contributing to Western culture. Writers such as Washington Irving, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Edgar Allan Poe, and Henry David Thoreau established a distinctive American literary voice by the middle of the 19th century. Mark Twain and poet Walt Whitman were major figures in the century's second half; Emily Dickinson, virtually unknown during her lifetime, is recognized as an essential American poet.
A work seen as capturing fundamental aspects of the national experience and character—such as Herman Melville's ''Moby-Dick'' (1851), Twain's ''Adventures of Huckleberry Finn, The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn'' (1885), F. Scott Fitzgerald's ''The Great Gatsby'' (1925) and Harper Lee's ''To Kill a Mockingbird'' (1960)—may be dubbed the "Great American Novel."
Thirteen U.S. citizens have won the Nobel Prize in Literature. William Faulkner, Ernest Hemingway and John Steinbeck are often named among the most influential writers of the 20th century. The Beat Generation writers opened up new literary approaches, as have postmodern literature, postmodernist authors such as John Barth, Thomas Pynchon, and Don DeLillo.
In the visual arts, the Hudson River School was a mid-19th-century movement in the tradition of European Realism (arts), naturalism. The 1913 Armory Show in New York City, an exhibition of European modern art, modernist art, shocked the public and transformed the U.S. art scene. Georgia O'Keeffe, Marsden Hartley, and others experimented with new, individualistic styles.
Major artistic movements such as the abstract expressionism of Jackson Pollock and Willem de Kooning and the pop art of Andy Warhol and Roy Lichtenstein developed largely in the United States. The tide of modernism and then postmodernism has brought fame to American architects such as Frank Lloyd Wright, Philip Johnson, and Frank Gehry. Americans have long been important in the modern artistic medium of photography, with major photographers including Alfred Stieglitz, Edward Steichen, Edward Weston, and Ansel Adams.
 Hollywood, Los Angeles, Hollywood, a northern district of Los Angeles, California, is the leader in motion picture production and the most recognizable movie industry in the world. The major film studios of the United States are the primary source of the List of highest grossing films, most commercially successful and most ticket selling movies in the world.
The world's first commercial motion picture exhibition was given in New York City in 1894, using the Kinetoscope. Since the early 20th century, the U.S. film industry has largely been based in and around Hollywood, although in the 21st century an increasing number of films are not made there, and film companies have been subject to the forces of globalization. The Academy Awards, popularly known as the Oscars, have been held annually by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences since 1929, and the Golden Globe Awards have been held annually since January 1944.
Director D. W. Griffith, an American filmmaker during the silent film period, was central to the development of film grammar, and producer/entrepreneur Walt Disney was a leader in both animation, animated film and movie merchandising. Directors such as John Ford redefined the image of the American Old West, and, like others such as John Huston, broadened the possibilities of cinema with location shooting. The industry enjoyed its golden years, in what is commonly referred to as the "Classical Hollywood cinema, Golden Age of Hollywood", from the early sound period until the early 1960s, with screen actors such as John Wayne and Marilyn Monroe becoming iconic figures. In the 1970s, "New Hollywood" or the "Hollywood Renaissance" was defined by grittier films influenced by French and Italian realist pictures of the Aftermath of World War II, post-war period.
Theater in the United States derives from the old European theatrical tradition and has been heavily influenced by the Theatre of the United Kingdom, British theater. The central hub of the American theater scene has been Manhattan, with its divisions of Broadway theatre, Broadway, off-Broadway, and off-off-Broadway. Many movie and television stars have gotten their big break working in New York productions. Outside New York City, many cities have professional Regional theater in the United States, regional or resident theater companies that produce their own seasons, with some works being produced regionally with hopes of eventually moving to New York. The biggest-budget theatrical productions are musical theatre, musicals. U.S. theater also has an active community theater culture, which relies mainly on local volunteers who may not be actively pursuing a theatrical career.
Hollywood, Los Angeles, Hollywood, a northern district of Los Angeles, California, is the leader in motion picture production and the most recognizable movie industry in the world. The major film studios of the United States are the primary source of the List of highest grossing films, most commercially successful and most ticket selling movies in the world.
The world's first commercial motion picture exhibition was given in New York City in 1894, using the Kinetoscope. Since the early 20th century, the U.S. film industry has largely been based in and around Hollywood, although in the 21st century an increasing number of films are not made there, and film companies have been subject to the forces of globalization. The Academy Awards, popularly known as the Oscars, have been held annually by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences since 1929, and the Golden Globe Awards have been held annually since January 1944.
Director D. W. Griffith, an American filmmaker during the silent film period, was central to the development of film grammar, and producer/entrepreneur Walt Disney was a leader in both animation, animated film and movie merchandising. Directors such as John Ford redefined the image of the American Old West, and, like others such as John Huston, broadened the possibilities of cinema with location shooting. The industry enjoyed its golden years, in what is commonly referred to as the "Classical Hollywood cinema, Golden Age of Hollywood", from the early sound period until the early 1960s, with screen actors such as John Wayne and Marilyn Monroe becoming iconic figures. In the 1970s, "New Hollywood" or the "Hollywood Renaissance" was defined by grittier films influenced by French and Italian realist pictures of the Aftermath of World War II, post-war period.
Theater in the United States derives from the old European theatrical tradition and has been heavily influenced by the Theatre of the United Kingdom, British theater. The central hub of the American theater scene has been Manhattan, with its divisions of Broadway theatre, Broadway, off-Broadway, and off-off-Broadway. Many movie and television stars have gotten their big break working in New York productions. Outside New York City, many cities have professional Regional theater in the United States, regional or resident theater companies that produce their own seasons, with some works being produced regionally with hopes of eventually moving to New York. The biggest-budget theatrical productions are musical theatre, musicals. U.S. theater also has an active community theater culture, which relies mainly on local volunteers who may not be actively pursuing a theatrical career.
 American folk music encompasses numerous music genres, variously known as traditional music, traditional folk music, contemporary folk music, or roots music. Many traditional songs have been sung within the same family or folk group for generations, and sometimes trace back to such origins as the British Isles, Mainland Europe, or Africa."Folk Music and Song", American Folklife Center, Library of Congress
American folk music encompasses numerous music genres, variously known as traditional music, traditional folk music, contemporary folk music, or roots music. Many traditional songs have been sung within the same family or folk group for generations, and sometimes trace back to such origins as the British Isles, Mainland Europe, or Africa."Folk Music and Song", American Folklife Center, Library of Congress
/ref> Among America's earliest composers was a man named William Billings who, born in Boston, composed patriotic hymns in the 1770s; Billings was a part of the Yankee tunesmiths, First New England School, who dominated American music during its earliest stages. Anthony Heinrich was the most prominent composer before the Civil War. From the mid- to late 1800s, John Philip Sousa of the late Romantic music, Romantic era composed numerous military songs—List of marches by John Philip Sousa, particularly marches—and is regarded as one of America's greatest composers. The rhythmic and lyrical styles of African-American music have significantly influenced Music of the United States, American music at large, distinguishing it from European and African traditions. Elements from folk idioms such as the blues and what is known as old-time music were adopted and transformed into popular music, popular genres with global audiences. Jazz was developed by innovators such as Louis Armstrong and Duke Ellington early in the 20th century. Country music developed in the 1920s, and rhythm and blues in the 1940s. Elvis Presley and Chuck Berry were among the pioneers of rock and roll in the mid-1950s. Rock bands such as Metallica, the Eagles (band), Eagles, and Aerosmith are among the List of best-selling music artists, highest grossing in worldwide sales. In the 1960s, Bob Dylan emerged from the American folk music revival, folk revival to become one of America's most celebrated songwriters. Mid-20th-century American pop stars such as Bing Crosby, Frank Sinatra, and Elvis Presley became global celebrities, as have artists of the late 20th century such as Prince (musician), Prince, Michael Jackson, Madonna, Whitney Houston, and Mariah Carey.
 The four major broadcasters in the U.S. are the National Broadcasting Company (NBC), Columbia Broadcasting System (CBS), American Broadcasting Company (ABC), and Fox Broadcasting Company (FOX). The four major broadcast television networks are all commercial entities. Cable television in the United States, Cable television offers hundreds of channels catering to a variety of niches. , about 83% of Americans over age 12 listen to radio broadcasting, broadcast radio, while about 41% listen to podcasts. , there are 15,433 licensed full-power radio stations in the U.S. according to the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Much of the public radio broadcasting is supplied by NPR, incorporated in February 1970 under the Public Broadcasting Act of 1967.
Well-known U.S. newspapers include ''The Wall Street Journal'', ''The New York Times'', and ''USA Today''. More than 800 publications are produced in Spanish, the second most commonly used language in the United States behind English. With very few exceptions, all the newspapers in the U.S. are privately owned, either by large chains such as Gannett Company, Gannett or The McClatchy Company, McClatchy, which own dozens or even hundreds of newspapers; by small chains that own a handful of papers; or, in a situation that is increasingly rare, by individuals or families. Major cities often have alternative newspapers to complement the mainstream daily papers, such as New York City's ''The Village Voice'' or Los Angeles' ''LA Weekly''. The five most popular websites used in the U.S. are Google, YouTube, Amazon (company), Amazon, Yahoo, and Facebook.
The Video games in the United States, American video game industry is the world's 2nd largest by revenue. It generated $90 billion in annual economic output in 2020. Furthermore, the video game industry contributed $12.6 billion in federal, state, and municipal taxes annually. Some of the largest video game companies like Activision Blizzard, Xbox, Sony Interactive Entertainment, Rockstar Games, and Electronic Arts are based in the United States. Some of the most popular and best selling video games like The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim, Call of Duty: Modern Warfare (2019 video game), Call of Duty: Modern Warfare and Diablo III are made by American Video game developer, developers. The American video gaming business is still a significant employer. More than 143,000 individuals are employed directly and indirectly by video game companies throughout 50 states. The national compensation for direct workers is US$2.9 billion, or an average wage of US$121,000.
The four major broadcasters in the U.S. are the National Broadcasting Company (NBC), Columbia Broadcasting System (CBS), American Broadcasting Company (ABC), and Fox Broadcasting Company (FOX). The four major broadcast television networks are all commercial entities. Cable television in the United States, Cable television offers hundreds of channels catering to a variety of niches. , about 83% of Americans over age 12 listen to radio broadcasting, broadcast radio, while about 41% listen to podcasts. , there are 15,433 licensed full-power radio stations in the U.S. according to the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Much of the public radio broadcasting is supplied by NPR, incorporated in February 1970 under the Public Broadcasting Act of 1967.
Well-known U.S. newspapers include ''The Wall Street Journal'', ''The New York Times'', and ''USA Today''. More than 800 publications are produced in Spanish, the second most commonly used language in the United States behind English. With very few exceptions, all the newspapers in the U.S. are privately owned, either by large chains such as Gannett Company, Gannett or The McClatchy Company, McClatchy, which own dozens or even hundreds of newspapers; by small chains that own a handful of papers; or, in a situation that is increasingly rare, by individuals or families. Major cities often have alternative newspapers to complement the mainstream daily papers, such as New York City's ''The Village Voice'' or Los Angeles' ''LA Weekly''. The five most popular websites used in the U.S. are Google, YouTube, Amazon (company), Amazon, Yahoo, and Facebook.
The Video games in the United States, American video game industry is the world's 2nd largest by revenue. It generated $90 billion in annual economic output in 2020. Furthermore, the video game industry contributed $12.6 billion in federal, state, and municipal taxes annually. Some of the largest video game companies like Activision Blizzard, Xbox, Sony Interactive Entertainment, Rockstar Games, and Electronic Arts are based in the United States. Some of the most popular and best selling video games like The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim, Call of Duty: Modern Warfare (2019 video game), Call of Duty: Modern Warfare and Diablo III are made by American Video game developer, developers. The American video gaming business is still a significant employer. More than 143,000 individuals are employed directly and indirectly by video game companies throughout 50 states. The national compensation for direct workers is US$2.9 billion, or an average wage of US$121,000.
 Early settlers were introduced by Native Americans to such indigenous, non-European foods as turkey, sweet potatoes, maize, corn, Cucurbita, squash, and maple syrup. They and later immigrants combined these with foods they had known, such as wheat flour, beef, and milk to create a distinctive American cuisine. Homegrown foods are part of a shared national menu on one of America's most popular holidays, Thanksgiving (United States), Thanksgiving, when many Americans make or purchase traditional foods to celebrate the occasion.
The American fast food industry, the world's largest, pioneered the drive-through format in the 1940s. Characteristic American dishes such as apple pie, fried chicken, doughnuts, french fries, macaroni and cheese, ice cream, pizza, hamburgers, and hot dogs derive from the recipes of various immigrants. Mexican cuisine, Mexican dishes such as burritos and tacos and pasta dishes freely adapted from Italian cuisine, Italian sources are widely consumed.
Americans drink three times as much coffee as tea. Marketing by U.S. industries is largely responsible for making orange juice and milk standard List of breakfast drinks, breakfast beverages.
Early settlers were introduced by Native Americans to such indigenous, non-European foods as turkey, sweet potatoes, maize, corn, Cucurbita, squash, and maple syrup. They and later immigrants combined these with foods they had known, such as wheat flour, beef, and milk to create a distinctive American cuisine. Homegrown foods are part of a shared national menu on one of America's most popular holidays, Thanksgiving (United States), Thanksgiving, when many Americans make or purchase traditional foods to celebrate the occasion.
The American fast food industry, the world's largest, pioneered the drive-through format in the 1940s. Characteristic American dishes such as apple pie, fried chicken, doughnuts, french fries, macaroni and cheese, ice cream, pizza, hamburgers, and hot dogs derive from the recipes of various immigrants. Mexican cuisine, Mexican dishes such as burritos and tacos and pasta dishes freely adapted from Italian cuisine, Italian sources are widely consumed.
Americans drink three times as much coffee as tea. Marketing by U.S. industries is largely responsible for making orange juice and milk standard List of breakfast drinks, breakfast beverages.
 The most popular sports in the U.S. are American football, basketball, baseball and ice hockey.
While most major U.S. sports such as baseball and American football have evolved out of European practices, basketball, volleyball, skateboarding, and snowboarding are American inventions, some of which have become popular worldwide. Lacrosse and surfing arose from Native American and Native Hawaiian activities that predate European contact.Liss, Howard. ''Lacrosse'' (Funk & Wagnalls, 1970) pg 13. The market for professional sports in the United States is roughly $69 billion, roughly 50% larger than that of all of Europe, the Middle East, and Africa combined.
American football is by several measures the most popular spectator sport in the United States; the National Football League (NFL) has the highest average attendance of any sports league in the world, and the Super Bowl is watched by tens of millions globally. Baseball has been regarded as the U.S. national sport since the late 19th century, with Major League Baseball being the top league. Basketball and ice hockey are the country's next two most popular professional team sports, with the top leagues being the National Basketball Association and the National Hockey League. The most-watched individual sports in the U.S. are golf and auto racing, particularly NASCAR and IndyCar.
Eight Olympic Games have taken place in the United States. The 1904 Summer Olympics in St. Louis, Missouri, were the first-ever Olympic Games held outside of Europe. The Olympic Games will be held in the U.S. for a ninth time when Los Angeles hosts the 2028 Summer Olympics. , the United States has won 2,629 medals at the Summer Olympic Games, more than any other country, and 330 in the Winter Olympic Games, the second most behind Norway. In Association football, soccer, the United States men's national soccer team, men's national soccer team qualified for United States at the FIFA World Cup, eleven World Cups and the United States women's national soccer team, women's team has United States at the FIFA Women's World Cup, won the FIFA Women's World Cup four times. The United States hosted the 1994 FIFA World Cup and will host the 2026 FIFA World Cup along with Canada and Mexico. On the collegiate athletics, collegiate level, earnings for the member institutions exceed $1 billion annually,Sports Illustrated: NCAA Reports $1.1 Billion in Revenues
The most popular sports in the U.S. are American football, basketball, baseball and ice hockey.
While most major U.S. sports such as baseball and American football have evolved out of European practices, basketball, volleyball, skateboarding, and snowboarding are American inventions, some of which have become popular worldwide. Lacrosse and surfing arose from Native American and Native Hawaiian activities that predate European contact.Liss, Howard. ''Lacrosse'' (Funk & Wagnalls, 1970) pg 13. The market for professional sports in the United States is roughly $69 billion, roughly 50% larger than that of all of Europe, the Middle East, and Africa combined.
American football is by several measures the most popular spectator sport in the United States; the National Football League (NFL) has the highest average attendance of any sports league in the world, and the Super Bowl is watched by tens of millions globally. Baseball has been regarded as the U.S. national sport since the late 19th century, with Major League Baseball being the top league. Basketball and ice hockey are the country's next two most popular professional team sports, with the top leagues being the National Basketball Association and the National Hockey League. The most-watched individual sports in the U.S. are golf and auto racing, particularly NASCAR and IndyCar.
Eight Olympic Games have taken place in the United States. The 1904 Summer Olympics in St. Louis, Missouri, were the first-ever Olympic Games held outside of Europe. The Olympic Games will be held in the U.S. for a ninth time when Los Angeles hosts the 2028 Summer Olympics. , the United States has won 2,629 medals at the Summer Olympic Games, more than any other country, and 330 in the Winter Olympic Games, the second most behind Norway. In Association football, soccer, the United States men's national soccer team, men's national soccer team qualified for United States at the FIFA World Cup, eleven World Cups and the United States women's national soccer team, women's team has United States at the FIFA Women's World Cup, won the FIFA Women's World Cup four times. The United States hosted the 1994 FIFA World Cup and will host the 2026 FIFA World Cup along with Canada and Mexico. On the collegiate athletics, collegiate level, earnings for the member institutions exceed $1 billion annually,Sports Illustrated: NCAA Reports $1.1 Billion in Revenues
/ref> and college football and College basketball, basketball attract large audiences, as the NCAA Division I men's basketball tournament, NCAA Final Four is one of the most watched sporting events.
United States
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
United States
from the BBC News
Key Development Forecasts for the United States
from International Futures ; Government
Official U.S. Government Web Portal
Gateway to government sites
House
Official site of the United States House of Representatives
Senate
Official site of the United States Senate
White House
Official site of the president of the United States * [ Supreme Court] Official site of the Supreme Court of the United States ; History
Historical Documents
Collected by the National Center for Public Policy Research
Analysis by the Ontario Consultants on Religious Tolerance
Collected links to historical data ; Maps
National Atlas of the United States
Official maps from the U.S. Department of the Interior * *
Measure of America
A variety of mapped information relating to health, education, income, and demographics for the U.S. ; Photos
Photos of the USA
{{Coord, 40, -100, dim:10000000_region:region:US_type:country, name=United States of America, display=title United States Countries in North America English-speaking countries and territories Federal constitutional republics Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas Former confederations G20 nations Member states of NATO Member states of the United Nations States and territories established in 1776 Transcontinental countries
federal district
A federal district is a type of administrative division of a federation, usually under the direct control of a federal government and organized sometimes with a single municipal body. Federal districts often include capital districts, and they ...
, five major unincorporated territories
Territories of the United States are sub-national administrative divisions overseen by the federal government of the United States. The various American territories differ from the U.S. states and tribal reservations as they are not sover ...
, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island
Collectively called the Pacific Islands, the islands in the Pacific Ocean are further categorized into three major island groups: Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Depending on the context, the term ''Pacific Islands'' may refer to one of se ...
sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
, the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
, and the Republic of Palau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the Caro ...
. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the ar ...
, Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
.
Paleo-Americans migrated from Siberia to the North American mainland at least 12,000 years ago, and advanced cultures began to appear later on. These societies had almost completely declined when Europeans arrived in North America and began colonizing it. Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It i ...
's Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th cent ...
quarreled with the British Crown over taxation and political representation
Political representation is the activity of making citizens "present" in public policy-making processes when political actors act in the best interest of citizens. This definition of political representation is consistent with a wide variety of vie ...
, leading to the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
(1765–1791). After the Revolution, the United States gained independence, the first nation-state founded on Enlightenment principles of liberal democracy
Liberal democracy is the combination of a liberal political ideology that operates under an indirect democratic form of government. It is characterized by elections between multiple distinct political parties, a separation of powers into ...
.
In the late 18th century, the U.S. began expanding across North America, gradually obtaining new territories, sometimes through war, frequently displacing Native Americans, and admitting new states. By 1848, the United States spanned the continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas t ...
from east to west. The controversy surrounding the practice of slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
culminated in the secession of the Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
, which fought the remaining states of the Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states ...
(1861–1865). With the Union's victory and preservation, slavery was abolished by the Thirteenth Amendment.
By 1890, the United States had grown to become the world's largest economy, and the Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (cloc ...
and World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
established the country as a world power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power inf ...
. After Japan's surprise attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941, the U.S. entered World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
on the Allied side. The aftermath of the war left the United States and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
as the world's two superpowers, and led to the Cold War, which commenced in 1945 and ended in 1991 with the Soviet Union's dissolution. During the Cold War, both countries engaged in a struggle for ideological dominance but avoided direct military conflict. They also competed in the Space Race
The Space Race was a 20th-century competition between two Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between the t ...
, which culminated in the 1969 American spaceflight in which the U.S. was the first nation to land humans on the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
. Simultaneously, the civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional racial segregation, discrimination, and disenfranchisement throughout the Unite ...
(1954–1968) led to legislation abolishing state and local Jim Crow laws
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws enforcing racial segregation in the Southern United States. Other areas of the United States were affected by formal and informal policies of segregation as well, but many states outside the Sout ...
and other codified racial discrimination against African Americans. With the Soviet Union's dissolution in 1991 and the end of the Cold War, the United States emerged as the world's sole superpower. In 2001, following the September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commer ...
, the United States became a lead member of the Global War on Terrorism
The war on terror, officially the Global War on Terrorism (GWOT), is an ongoing international counterterrorism military campaign initiated by the United States following the September 11 attacks. The main targets of the campaign are militant ...
, which included the War in Afghanistan
War in Afghanistan, Afghan war, or Afghan civil war may refer to:
*Conquest of Afghanistan by Alexander the Great (330 BC – 327 BC)
* Muslim conquests of Afghanistan (637–709)
*Conquest of Afghanistan by the Mongol Empire (13th century), see al ...
(2001–2021) and the Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, حرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, شەڕی عێراق ( Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict and the War on terror
, image ...
(2003–2011).
The United States is a federal republic with three separate branches of government, including a bicameral legislature. It is a liberal democracy and has a market economy. It ranks very high in international measures of quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
, income
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. Fo ...
and wealth
Wealth is the abundance of valuable financial assets or physical possessions which can be converted into a form that can be used for transactions. This includes the core meaning as held in the originating Old English word , which is from an I ...
, economic competitiveness, human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
, innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entit ...
, and education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty ...
; it has low levels of perceived corruption. The United States has the highest median income per person of any polity in the world. It has high levels of incarceration and inequality
Inequality may refer to:
Economics
* Attention inequality, unequal distribution of attention across users, groups of people, issues in etc. in attention economy
* Economic inequality, difference in economic well-being between population groups
* ...
and lacks universal health care
Universal health care (also called universal health coverage, universal coverage, or universal care) is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized ar ...
. As a melting pot of cultures
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tylo ...
and ethnicities
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
, the U.S. has been shaped by centuries of immigration.
The United States is a highly developed country, and its economy accounts for approximately a quarter of global GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
and is the world's largest
Large means of great size.
Large may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Arbitrarily large, a phrase in mathematics
* Large cardinal, a property of certain transfinite numbers
* Large category, a category with a proper class of objects and morphisms (o ...
by GDP at market exchange rates. By value, the United States is the world's largest
Large means of great size.
Large may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Arbitrarily large, a phrase in mathematics
* Large cardinal, a property of certain transfinite numbers
* Large category, a category with a proper class of objects and morphisms (o ...
importer and second-largest exporter. Although it accounts for just over 4.2% of the world's total population, the U.S. holds over 30% of the total wealth in the world, the largest share held by any country. The United States is a founding member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
, World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
, International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glo ...
, Organization of American States, NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
, the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue
The Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QSD), commonly known as the Quad, is a strategic security dialogue between Australia, India, Japan and the United States that is maintained by talks between member countries. The dialogue was initiated in ...
, and is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
. The country is responsible for more than a third of global military spending and is the foremost military power in the world and a leading Politics of the United States, political, cultural, and Science and technology in the United States, scientific force.
Etymology
The first known use of the name "Americas, America" dates to 1507, when it appeared on Waldseemüller map, a world map produced by the German cartographer Martin Waldseemüller in Saint-Dié-des-Vosges, Saint Dié, Duchy of Lorraine, Lorraine (now northeastern France). On his map, the name is shown in large letters on what would now be considered South America, honoring Amerigo Vespucci. The Italian explorer was the first to postulate that the West Indies did not represent Asia's eastern limit but were part of a previously unknown landmass. In 1538, the Flemish cartographer Gerardus Mercator used the name "America" to refer to the entire Western Hemisphere. The first documentary evidence of the phrase "United States of America" dates back to a letter from January 2, 1776, written by Stephen Moylan to Joseph Reed (politician), Joseph Reed, George Washington's aide-de-camp. Moylan expressed his wish to go "with full and ample powers from the United States of America to Spain" to seek assistance in the revolutionary war effort. The first known publication of the phrase "United States of America" was in an anonymous essay in ''The Virginia Gazette'' newspaper in Williamsburg, Virginia, Williamsburg, on April 6, 1776. The second draft of the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, prepared by John Dickinson and completed no later than June 17, 1776, declared "The name of this Confederation shall be the 'United States of America'." The final version of the Articles, sent to the states for ratification in late 1777, stated that "The Stile of this Confederacy shall be 'The United States of America'." In June 1776, Thomas Jefferson wrote the phrase "UNITED STATES OF AMERICA" in the headline of his "original Rough draught" of the United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence. This draft of the document did not surface until June 21, 1776, and it is unclear whether it was written before or after Dickinson used the term in his June 17 draft of the Articles of Confederation. The phrase "United States" was originally plural in American usage. It described a collection of states—e.g., "the United States are..." The singular form became popular after the end of the Civil War and is now standard usage. A Citizenship of the United States, citizen of the United States is called an "Americans, American". "United States", "American", and "U.S." refer to the country adjectivally ("American values", "U.S. forces"). In English, the word "American" rarely refers to topics or subjects not directly connected with the United States.History
Early history
 It is generally accepted that the Paleo-indians, first inhabitants of North America migrated from Siberia by way of the Bering land bridge and arrived at least 12,000 years ago; however, some evidence suggests an even earlier date of arrival. The Clovis culture, which appeared around 11,000 BC, is believed to represent the first wave of human settlement of the Americas. This was likely the first of three major waves of migration into North America; later waves brought the ancestors of present-day Alaskan Athabaskans, Athabaskans, Aleuts, and Eskimos.
Over time, indigenous cultures in North America grew increasingly sophisticated, and some, such as the pre-Columbian Mississippian culture in the southeast, developed advanced agriculture, architecture, and complex societies. The city-state of Cahokia is the largest, most complex pre-Columbian archaeological site in the modern-day United States. In the Four Corners region, Ancestral Puebloan culture developed from centuries of agricultural experimentation. The Algonquian peoples, Algonquian are one of the most populous and widespread North American Indigenous peoples of the Americas, native language groups. This grouping consists of the peoples who speak Algonquian languages. Historically, these peoples were prominent along the Atlantic Coast and into the interior along the Saint Lawrence River and around the Great Lakes. Before Europeans came into contact, most Algonquian settlements lived by hunting and fishing, although many supplemented their diet by cultivating maize, corn, beans and Cucurbita, squash (the "Three Sisters (agriculture), Three Sisters"). The Ojibwe cultivated wild rice. The Haudenosaunee confederation of the Iroquoian peoples, Iroquois, located in the southern Great Lakes region, was established at some point between the twelfth and fifteenth centuries.
Population history of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Estimating the native population of North America during European contact is difficult. Douglas H. Ubelaker of the Smithsonian Institution estimated a population of 93,000 in the South Atlantic states and a population of 473,000 in the Gulf states, but most academics regard this figure as too low. Anthropologist Henry F. Dobyns believed the populations were much higher, suggesting around 1.1 million along the shores of the Gulf of Mexico, 2.2 million people living between Florida and Massachusetts, 5.2 million in the Mississippi Valley and tributaries, and around 700,000 people in the Florida peninsula.
It is generally accepted that the Paleo-indians, first inhabitants of North America migrated from Siberia by way of the Bering land bridge and arrived at least 12,000 years ago; however, some evidence suggests an even earlier date of arrival. The Clovis culture, which appeared around 11,000 BC, is believed to represent the first wave of human settlement of the Americas. This was likely the first of three major waves of migration into North America; later waves brought the ancestors of present-day Alaskan Athabaskans, Athabaskans, Aleuts, and Eskimos.
Over time, indigenous cultures in North America grew increasingly sophisticated, and some, such as the pre-Columbian Mississippian culture in the southeast, developed advanced agriculture, architecture, and complex societies. The city-state of Cahokia is the largest, most complex pre-Columbian archaeological site in the modern-day United States. In the Four Corners region, Ancestral Puebloan culture developed from centuries of agricultural experimentation. The Algonquian peoples, Algonquian are one of the most populous and widespread North American Indigenous peoples of the Americas, native language groups. This grouping consists of the peoples who speak Algonquian languages. Historically, these peoples were prominent along the Atlantic Coast and into the interior along the Saint Lawrence River and around the Great Lakes. Before Europeans came into contact, most Algonquian settlements lived by hunting and fishing, although many supplemented their diet by cultivating maize, corn, beans and Cucurbita, squash (the "Three Sisters (agriculture), Three Sisters"). The Ojibwe cultivated wild rice. The Haudenosaunee confederation of the Iroquoian peoples, Iroquois, located in the southern Great Lakes region, was established at some point between the twelfth and fifteenth centuries.
Population history of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Estimating the native population of North America during European contact is difficult. Douglas H. Ubelaker of the Smithsonian Institution estimated a population of 93,000 in the South Atlantic states and a population of 473,000 in the Gulf states, but most academics regard this figure as too low. Anthropologist Henry F. Dobyns believed the populations were much higher, suggesting around 1.1 million along the shores of the Gulf of Mexico, 2.2 million people living between Florida and Massachusetts, 5.2 million in the Mississippi Valley and tributaries, and around 700,000 people in the Florida peninsula.
Colonial America
 Claims of very early colonization of New England#Geography, coastal New England by the Norse colonization of North America, Norse are disputed and controversial. Christopher Columbus had landed in Puerto Rico on his Columbus's second voyage, 1493 voyage, and San Juan, Puerto Rico, San Juan was settled by the Spanish a decade later. The first documented arrival of Europeans in the continental United States is that of Spanish conquistadors such as Juan Ponce de León, who made his first expedition to Spanish Florida, Florida in 1513. The Italian explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano, sent by France to the New World in 1525, encountered native inhabitants of what is now New York Bay. The Spanish set up the first settlements in Florida and New Mexico, such as St. Augustine, Florida, Saint Augustine, often considered the nation's oldest city, and Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe. The French New France, established their own settlements along the Mississippi River and Gulf of Mexico, notably New Orleans and Mobile, Alabama, Mobile.
Successful British colonization of the Americas, English settlement of the eastern coast of North America began with the Colony of Virginia, Virginia Colony in 1607 at Jamestown, Virginia, Jamestown and with the Pilgrims (Plymouth Colony), Pilgrims' Plymouth Colony, colony at Plymouth in 1620. The continent's first elected legislative assembly, Virginia's House of Burgesses, was founded in 1619. Harvard College was established in the Massachusetts Bay Colony in 1636 as the first institution of higher education. The Mayflower Compact and the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut established precedents for representative self-government and constitutionalism that would develop throughout the American colonies. Many English settlers were English Dissenters, dissenting Christians who came seeking Freedom of religion, religious freedom. The Population history of indigenous peoples of the Americas, native population of America declined after European arrival for various reasons, primarily from diseases such as smallpox and measles.
Claims of very early colonization of New England#Geography, coastal New England by the Norse colonization of North America, Norse are disputed and controversial. Christopher Columbus had landed in Puerto Rico on his Columbus's second voyage, 1493 voyage, and San Juan, Puerto Rico, San Juan was settled by the Spanish a decade later. The first documented arrival of Europeans in the continental United States is that of Spanish conquistadors such as Juan Ponce de León, who made his first expedition to Spanish Florida, Florida in 1513. The Italian explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano, sent by France to the New World in 1525, encountered native inhabitants of what is now New York Bay. The Spanish set up the first settlements in Florida and New Mexico, such as St. Augustine, Florida, Saint Augustine, often considered the nation's oldest city, and Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe. The French New France, established their own settlements along the Mississippi River and Gulf of Mexico, notably New Orleans and Mobile, Alabama, Mobile.
Successful British colonization of the Americas, English settlement of the eastern coast of North America began with the Colony of Virginia, Virginia Colony in 1607 at Jamestown, Virginia, Jamestown and with the Pilgrims (Plymouth Colony), Pilgrims' Plymouth Colony, colony at Plymouth in 1620. The continent's first elected legislative assembly, Virginia's House of Burgesses, was founded in 1619. Harvard College was established in the Massachusetts Bay Colony in 1636 as the first institution of higher education. The Mayflower Compact and the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut established precedents for representative self-government and constitutionalism that would develop throughout the American colonies. Many English settlers were English Dissenters, dissenting Christians who came seeking Freedom of religion, religious freedom. The Population history of indigenous peoples of the Americas, native population of America declined after European arrival for various reasons, primarily from diseases such as smallpox and measles.
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th cent ...
that would become the United States of America were administered by the British as overseas dependencies. Colonial government in the Thirteen Colonies, All nonetheless had local governments with elections open to most free men. With very high birth rates, low death rates, and steady settlement, the colonial population grew rapidly, eclipsing Native American populations. The Christian revivalist movement of the 1730s and 1740s known as the First Great Awakening, Great Awakening fueled interest both in religion and in religious liberty.
During the Seven Years' War (1756–1763), known in the U.S. as the French and Indian War, British forces captured Canada from the French. With the creation of the Province of Quebec (1763–1791), Province of Quebec, Canada's French language, francophone population would remain isolated from the English-speaking colonial dependencies of Nova Scotia, Newfoundland Colony, Newfoundland and the Thirteen Colonies. Excluding the Native Americans who lived there, the Thirteen Colonies had a population of over 2.1 million in 1770, about a third that of Britain. Despite continuing new arrivals, the rate of natural increase was such that by the 1770s only a small minority of Americans had been born overseas. The colonies' distance from Britain had allowed the development of self-government, but their unprecedented success motivated British monarchs to periodically seek to reassert royal authority.
American Revolution and the early federal republic
 The
The American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
separated the Thirteen Colonies from the British Empire, and was the first successful war of independence by a non-European entity against a European power in modern history. By the 18th century the American Enlightenment and Liberalism in the United States, the political philosophies of liberalism were pervasive among leaders. Americans began to develop an ideology of "Republicanism in the United States, republicanism", asserting that government rested on the consent of the governed. They demanded their "Rights of Englishmen, rights as Englishmen" and "no taxation without representation". The British insisted on administering the colonies through a Parliament of Great Britain, Parliament that did not have a single representative responsible for any American constituency, and the conflict escalated into war.
In 1774, the First Continental Congress passed the Continental Association, which mandated a Thirteen Colonies, colonies-wide boycott of British goods. The American Revolutionary War began the following year, catalyzed by events like the Stamp Act 1765, Stamp Act and the Boston Tea Party that were rooted in colonial disagreement with British governance. The Second Continental Congress, an assembly representing the United Colonies, unanimously adopted the United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776 (annually celebrated as Independence Day (United States), Independence Day). In 1781, the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union established a decentralized government that operated until 1789. A celebrated early turn in the war for the Americans was George Washington leading the Americans to George Washington's crossing of the Delaware River, cross the frozen Delaware River in a surprise attack the night of December 25–26, 1776. Another victory, in 1777, at the Battles of Saratoga, Battle of Saratoga resulted in the capture of a British army, and led to France in the American Revolutionary War, France and Spain in the American Revolutionary War, Spain joining in the war against them. After the surrender of a second British army at the Siege of Yorktown (1781), siege of Yorktown in 1781, Britain signed a Treaty of Paris (1783), peace treaty. American sovereignty became internationally recognized, and the new nation took possession of substantial territory east of the Mississippi River, from what is today Canada in the north and Florida in the south.
As it became increasingly apparent that the Confederation was insufficient to govern the new country, Nationalism, nationalists advocated for and led the Constitutional Convention (United States), Philadelphia Convention of 1787 in writing the United States Constitution to replace it, Ratification of the United States Constitution, ratified in state conventions in 1788. Going into force in 1789, this constitution reorganized the government into a federation administered by Separation of powers, three equal branches (executive, judicial and legislative), on the principle of creating salutary checks and balances. George Washington, who had led the Continental Army to victory and then willingly relinquished power, was the first President of the United States, president elected under the new constitution. The United States Bill of Rights, Bill of Rights, forbidding federal restriction of Natural and legal rights, personal freedoms and guaranteeing a range of legal protections, was adopted in 1791.#Boyer, Boyer, 2007, pp. 192–193 Origins of the War of 1812, Tensions with Britain remained, however, leading to the War of 1812, which was fought to a draw.
Although the federal government Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves, outlawed American participation in the Atlantic slave trade in 1807, after 1820, cultivation of the highly profitable cotton crop exploded in the Deep South, and along with it, the use of Slavery in the United States, slave labor. The Second Great Awakening, especially in the period 1800–1840, converted millions to Evangelicalism in the United States, evangelical Protestantism. In the North, it energized multiple social reform movements, including Abolitionism in the United States, abolitionism; in the South, History of Methodism in the United States, Methodists and Baptists in the United States, Baptists proselytized among slave populations.  In the late 18th century, American settlers began to Territorial evolution of the United States, expand further westward, some of them with a sense of manifest destiny. The 1803 Louisiana Purchase almost doubled the nation's area, Adams–Onís Treaty, Spain ceded Florida and other Gulf Coast territory in 1819, the Republic of Texas was Texas annexation, annexed in 1845 during a period of expansionism, and the 1846 Oregon Treaty with Britain led to U.S. control of the present-day Northwestern United States, American Northwest. Additionally, the Trail of Tears in the 1830s exemplified the Indian Removal Act, Indian removal policy that forcibly resettled Indians. This further expanded acreage under mechanical cultivation, increasing surpluses for international markets. This prompted a long series of American Indian Wars west of the Mississippi River from 1810 to at least 1890. and eventually, conflict with Mexico. Most of these conflicts ended with the cession of Native American territory and their confinement to Indian reservations. Victory in the Mexican–American War resulted in the 1848 Mexican Cession of California and much of the present-day Southwestern United States, American Southwest, and the U.S. spanned the continent. The California Gold Rush of 1848–1849 spurred migration to the Pacific coast, which led to the California Genocide and the creation of additional western states. Economic development was spurred by giving vast quantities of land, nearly 10% of the total area of the United States, to white European settlers as part of the Homestead Acts, as well as making land grants to private railroad companies and Land-grant university, colleges. Prior to the Civil War, Slave states and free states, the prohibition or expansion of slavery into these territories exacerbated tensions over Origins of the American Civil War, the debate around abolitionism.
In the late 18th century, American settlers began to Territorial evolution of the United States, expand further westward, some of them with a sense of manifest destiny. The 1803 Louisiana Purchase almost doubled the nation's area, Adams–Onís Treaty, Spain ceded Florida and other Gulf Coast territory in 1819, the Republic of Texas was Texas annexation, annexed in 1845 during a period of expansionism, and the 1846 Oregon Treaty with Britain led to U.S. control of the present-day Northwestern United States, American Northwest. Additionally, the Trail of Tears in the 1830s exemplified the Indian Removal Act, Indian removal policy that forcibly resettled Indians. This further expanded acreage under mechanical cultivation, increasing surpluses for international markets. This prompted a long series of American Indian Wars west of the Mississippi River from 1810 to at least 1890. and eventually, conflict with Mexico. Most of these conflicts ended with the cession of Native American territory and their confinement to Indian reservations. Victory in the Mexican–American War resulted in the 1848 Mexican Cession of California and much of the present-day Southwestern United States, American Southwest, and the U.S. spanned the continent. The California Gold Rush of 1848–1849 spurred migration to the Pacific coast, which led to the California Genocide and the creation of additional western states. Economic development was spurred by giving vast quantities of land, nearly 10% of the total area of the United States, to white European settlers as part of the Homestead Acts, as well as making land grants to private railroad companies and Land-grant university, colleges. Prior to the Civil War, Slave states and free states, the prohibition or expansion of slavery into these territories exacerbated tensions over Origins of the American Civil War, the debate around abolitionism.
The Civil War and Reconstruction
Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
, while the federal government (the "Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
") maintained that Perpetual Union, secession was unconstitutional and illegal. On April 12, 1861, the Confederacy initiated military conflict by Battle of Fort Sumter, bombarding Fort Sumter, a federal garrison in Charleston, South Carolina, Charleston harbor, South Carolina. This would be the spark of the Civil War, which lasted for four years (1861–1865) and became the deadliest military conflict in American history. The war would result in the deaths of approximately 620,000 soldiers from both sides and upwards of 50,000 civilians, almost all of them in the South.
Reconstruction (United States), Reconstruction began in earnest following the war. While President Lincoln attempted to foster friendship and forgiveness between the Union and the former Confederacy, Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination on April 14, 1865 drove a wedge between North and South again. Republicans in the federal government made it their goal to oversee the rebuilding of the South and to ensure the rights of African Americans. They persisted until the Compromise of 1877, when the Republicans agreed to cease protecting the rights of African Americans in the South in order for Democrats to concede the 1876 United States presidential election, presidential election of 1876. Southern white Democrats, calling themselves "Redeemers", took control of the South after the end of Reconstruction, beginning the nadir of American race relations. From 1890 to 1910, the Redeemers established so-called Jim Crow laws
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws enforcing racial segregation in the Southern United States. Other areas of the United States were affected by formal and informal policies of segregation as well, but many states outside the Sout ...
, Disenfranchisement after the Reconstruction Era, disenfranchising almost all blacks and some impoverished whites throughout the region. Blacks would face Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation nationwide, especially in the South. They also lived under constant threat of vigilante violence, including Lynching in the United States, lynching.
Industrial Age and the Progressive Era
In the North, urbanization and an unprecedented History of immigration to the United States, influx of immigrants from Southern Europe, Southern and Eastern Europe supplied a surplus of labor for the country's industrialization and transformed its culture. National infrastructure, including First Transcontinental Telegraph, telegraph and First transcontinental railroad, transcontinental railroads, spurred economic growth and greater settlement and development of the American frontier, American Old West. After theAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states ...
, new transcontinental Rail transportation in the United States#History, railways made relocation easier for settlers, expanded internal trade, and increased conflicts with Native Americans. The later inventions of Incandescent light bulb, electric light and the telephone would also affect communication and urban life.
Mainland expansion also included the Alaska Purchase, purchase of Alaska from Russian Empire, Russia in 1867. In 1893, pro-American elements in Hawaii Overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii, overthrew the Kingdom of Hawaii, Hawaiian monarchy and formed the Republic of Hawaii, which the U.S. Newlands Resolution, annexed in 1898. Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines were ceded by Spain in the same year, following the Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (cloc ...
. American Samoa was acquired by the United States in 1900 after the end of the Second Samoan Civil War. The United States Virgin Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands were purchased from Denmark in 1917.
Gilded Age, Rapid economic development during the late 19th and early 20th centuries fostered the rise of many prominent industrialists. Business magnate, Tycoons like Cornelius Vanderbilt, John D. Rockefeller, and Andrew Carnegie led the nation's progress in the Railways, railroad, Petroleum industry, petroleum, and History of the steel industry (1850–1970), steel industries. Banking became a major part of the economy, with J. P. Morgan playing a notable role. The American economy boomed, becoming the world's largest.
These dramatic changes were accompanied by Economic inequality, growing inequality and social unrest, which prompted the rise of Labor history of the United States, organized labor along with Populism in the United States, populist, History of the socialist movement in the United States, socialist, and Anarchism in the United States, anarchist movements. This period eventually ended with the advent of the Progressive Era, which saw significant reforms including Consumer protection, health and safety regulation of consumer goods, the rise of Labor unions in the United States, labor unions, and greater United States antitrust law, antitrust measures to ensure competition among businesses and attention to worker conditions.
The rise to world power, The New Deal, and World War II

 The United States remained neutral from the outbreak of
The United States remained neutral from the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
in 1914 until 1917 when it joined the war as an "associated power" alongside the Allies of World War I, helping to turn the tide against the Central Powers. In 1919, President Woodrow Wilson took a leading diplomatic role at the Paris Peace Conference, 1919, Paris Peace Conference and advocated strongly for the U.S. to join the League of Nations. However, the Senate refused to approve this and did not ratify the Treaty of Versailles that established the League of Nations.McDuffie, Jerome; Piggrem, Gary Wayne; Woodworth, Steven E. (2005). ''U.S. History Super Review''. Piscataway, NJ: Research & Education Association. p. 418. .
Around this time, millions of rural African Americans began Great Migration (African American), a mass migration from the South to northern urban centers; it would continue until about 1970. The last vestiges of the Progressive Era resulted in women's suffrage and Prohibition in the United States, alcohol prohibition. In 1920, the women's rights movement won passage of a Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, constitutional amendment granting Women's suffrage in the United States, women's suffrage. The 1920s and 1930s saw the rise of radio for mass communication and the invention of early television. The prosperity of the Roaring Twenties ended with the Wall Street Crash of 1929 and the onset of the Great Depression in the United States, Great Depression. After his election as president in 1932, Franklin D. Roosevelt responded with the New Deal. The Dust Bowl of the mid-1930s impoverished many farming communities and spurred a new wave of western migration.
At first United States non-interventionism before entering World War II, neutral during World War II, the United States in March 1941 Lend-Lease, began supplying materiel to the Allies of World War II, Allies. On December 7, 1941, the Empire of Japan launched a surprise attack on Pearl Harbor, prompting the United States to join the Allies against the Axis powers, and in the following year, to Internment of Japanese Americans, intern about 120,000 Japanese and Japanese Americans. The U.S. pursued a "Europe first" defense policy, leaving the Philippines, an History of the Philippines (1898–1946), American colony, isolated and alone to fight Japan's Japanese occupation of the Philippines, invasion and occupation until the U.S.-led Philippines campaign (1944–1945). During the war, the United States was one of the "Four Policemen, Four Powers" who met to plan the postwar world, along with Britain, the Soviet Union, and China. The United States emerged World War II casualties#Human losses by country, relatively unscathed from the war, and with even greater economic and military influence.
The United States played a leading role in the Bretton Woods Conference, Bretton Woods and Yalta Conference, Yalta conferences, which signed agreements on new international financial institutions and Europe's postwar reorganization. As an Victory in Europe Day, Allied victory was won in Europe, a 1945 United Nations Conference on International Organization, international conference held in San Francisco produced the United Nations Charter, which became active after the war. The United States and Japan then fought each other in the largest naval battle in history, the Battle of Leyte Gulf. The United States developed the Manhattan Project, first nuclear weapons and used them on Japan Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, in the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945; the Japanese Surrender of Japan, surrendered on September 2, ending World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
.
Cold War and late 20th century
 After World War II, the United States financed and implemented the Marshall Plan to help rebuild western Europe; disbursements paid between 1948 and 1952 would total $13 billion ($115 billion in 2021). Also at this time, Geopolitics, geopolitical tensions between the United States and Soviet Union, Russia led to the Cold War, driven by an ideological divide between capitalism and communism. They dominated the military affairs of Europe, with the U.S. and its
After World War II, the United States financed and implemented the Marshall Plan to help rebuild western Europe; disbursements paid between 1948 and 1952 would total $13 billion ($115 billion in 2021). Also at this time, Geopolitics, geopolitical tensions between the United States and Soviet Union, Russia led to the Cold War, driven by an ideological divide between capitalism and communism. They dominated the military affairs of Europe, with the U.S. and its NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
allies on one side and the Soviet Union and its Warsaw Pact allies on the other. The U.S. often opposed Third World movements that it viewed as Soviet-sponsored, sometimes pursuing direct action for United States involvement in regime change, regime change against Left-wing politics, left-wing governments. American troops fought the communist forces in the Korean War of 1950–1953, and the U.S. became increasingly involved in the Vietnam War (1955–1975), introducing combat forces in 1965. Their competition to achieve superior spaceflight capability led to the Space Race
The Space Race was a 20th-century competition between two Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between the t ...
, which culminated in the U.S. becoming the first nation to Apollo 11, land people on the Moon in 1969. While both countries engaged in proxy wars and developed powerful nuclear weapons, they avoided direct military conflict.
At home, the United States experienced Post–World War II economic expansion, sustained economic expansion, Urbanization in the United States, urbanization, and a Post–World War II baby boom, rapid growth of its population and American middle class, middle class following World War II. Construction of an Interstate Highway System transformed the nation's transportation infrastructure in decades to come. In 1959, the United States admitted Alaska and Hawaii to become the 49th and 50th states, formally expanding beyond the contiguous United States.
 The growing
The growing civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional racial segregation, discrimination, and disenfranchisement throughout the Unite ...
used nonviolence to confront Racism in the United States, racism, with Martin Luther King Jr. becoming a prominent leader and figurehead. President Lyndon B. Johnson initiated legislation that led to a series of policies addressing poverty and racial inequalities, in what he termed the "Great Society". The launch of a "War on Poverty" expanded Social programs in the United States, entitlements and welfare spending, leading to the creation of the Food Stamp Program, Aid to Families with Dependent Children, along with national health insurance programs Medicare (United States), Medicare and Medicaid. A combination of court decisions and legislation, culminating in the Civil Rights Act of 1968, made significant improvements. Meanwhile, a counterculture of the 1960s, counterculture movement grew, which was fueled by Opposition to United States involvement in the Vietnam War, opposition to the Vietnam War, the Black Power movement, and the sexual revolution. The Women's Movement in the United States (1963-1982), women's movement in the U.S. broadened the debate on women's rights and made gender equality a major social goal. The Sexual revolution in 1960s United States, 1960s Sexual Revolution liberalized American attitudes to sexuality; the 1969 Stonewall riots in New York City marked the beginning of the fledgling gay liberation, gay rights movement.
The United States supported Israel during the Yom Kippur War; in response, the country faced an oil embargo from OPEC nations, sparking the 1973 oil crisis. After a surge in female labor participation around the 1970s, by 1985, the majority of women aged 16 and over were employed. The 1970s and early 1980s also saw the onset of stagflation. The presidency of Richard Nixon saw the American withdrawal from Vietnam but also the Watergate scandal which led to a decline in public trust of government.Sam Ervin, Ervin, Sam, et al., ''Final Report of the Watergate Committee]''.
After his election in 1980 President Ronald Reagan responded to economic stagnation with Reaganomics, neoliberal reforms and initiated the more aggressive rollback, rollback strategy towards the Soviet Union. During Reagan's presidency, the federal debt held by the public nearly tripled in nominal terms, from $738 billion to $2.1 trillion. This led to the United States moving from the world's largest international creditor to the world's largest debtor nation. The dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 ended the Cold War, ensuring a global unipolarity in which the U.S. was unchallenged as the world's dominant superpower.
Fearing the spread of Middle East, regional international instability from the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait, in August 1991, President George H. W. Bush launched and led the Gulf War against Iraq, expelling Iraqi forces and restoring the Emir of Kuwait, Kuwaiti monarchy. During the administration of President Bill Clinton in 1994, the U.S. signed the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), causing trade among the U.S., Canada, and Mexico to soar. Due to the dot-com bubble, dot-com boom, stable monetary policy, and Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Act, reduced social welfare spending, the 1990s saw the 1990s United States boom, longest economic expansion in modern U.S. history.
21st century
On September 11 attacks, September 11, 2001, al-Qaeda terrorist hijackers flew passenger planes into the World Trade Center (1973–2001), World Trade Center in New York City and the Pentagon near Washington, D.C., killing nearly 3,000 people. In response, President George W. Bush launched the War on Terror, which included a nearly 20-year War in Afghanistan (2001–present), war in Afghanistan from 2001 to 2021 and the 2003–2011Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, حرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, شەڕی عێراق ( Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict and the War on terror
, image ...
. Government policy designed to promote affordable housing, widespread failures in corporate and regulatory governance, and historically low interest rates set by the Federal Reserve led to a United States housing bubble, housing bubble in 2006. This culminated in the financial crisis of 2007–2008 and the Great Recession, the nation's largest economic contraction since the Great Depression.
Barack Obama, the first Multiracial American, multiracial president with African-American ancestry, 2008 United States presidential election, was elected in 2008 amid the financial crisis. By the end of his second term, the stock market, median household income and net worth, and the number of persons with jobs were all at record levels, while the unemployment rate was well below the historical average. His signature legislative accomplishment was the Affordable Care Act (ACA), popularly known as "Obamacare". It represented the U.S. healthcare system's most significant regulatory overhaul and expansion of coverage since Medicare in 1965. As a result, the uninsured share of the population was cut in half, while the number of newly insured Americans was estimated to be between 20 and 24 million. After Obama served two terms, Republican Donald Trump was elected as the List of Presidents of the United States, 45th president in 2016. 2016 United States presidential election, His election is viewed as one of the biggest political upsets in American history. Trump held office through Timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, the first waves of the COVID-19 pandemic and the resulting COVID-19 recession starting in 2020 that exceeded even the Great Recession earlier in the century.
The early 2020s saw the country become more divided, with various social issues sparking debate and protest. The murder of George Floyd in 2020 led to George Floyd protests, widespread civil unrest in urban centers and a national debate about Police brutality in the United States, police brutality and lingering institutional racism. The nationwide increase in the frequency of instances and number of deaths related to Mass shootings in the United States, mass shootings added to the societal tensions. On January 6, 2021, supporters of the outgoing president, Trump, 2021 United States Capitol attack, stormed the U.S. Capitol in an unsuccessful effort to disrupt the U.S. Electoral College, Electoral College vote count that would confirm Democrat Joe Biden as the 46th president. In 2022, the Supreme Court Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization, ruled that there is no constitutional right to an abortion, causing 2022 abortion protests, another wave of protests across the country and stoking international reactions as well. Despite these divisions, the country has remained unified against Union State, Russia after Vladimir Putin's 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, 2022 invasion of Ukraine, with politicians and individuals across the political spectrum supporting arms shipments to Ukraine and many large American corporations pulling out of Russia and Belarus altogether.
Geography

 The List of states and territories of the United States, 48 contiguous states and the District of Columbia occupy a combined area of . Of this area, is contiguous land, composing 83.65% of total U.S. land area. About 15% is occupied by Alaska, a state in northwestern North America, with the remainder in Hawaii, a state and archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, Pacific, and the five populated but Unincorporated area, unincorporated insular territories of Puerto Rico, American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, and the United States Virgin Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands. Measured by only land area, the United States is third in size behind Russia and China, and just ahead of Canada.
The United States is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third- or fourth-largest nation by total area (land and water), ranking behind Russia and Canada and nearly equal to China. The ranking varies depending on how two territories disputed by China and India are counted, and how the total size of the United States is measured.
The Atlantic coastal plain, coastal plain of the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic seaboard gives way further inland to deciduous forests and the rolling hills of the Piedmont (United States), Piedmont. The Appalachian Mountains and the Adirondack Mountains, Adirondack massif divide the eastern seaboard from the Great Lakes and the grasslands of the Midwestern United States, Midwest. The Mississippi River, Mississippi–Missouri River, the world's List of rivers by length, fourth longest river system, runs mainly north–south through the heart of the country. The flat, fertile prairie of the Great Plains stretches to the west, interrupted by U.S. Interior Highlands, a highland region in the southeast.
The Rocky Mountains, west of the Great Plains, extend north to south across the country, peaking at over in Colorado. Farther west are the rocky Great Basin and deserts such as the Chihuahuan Desert, Chihuahua, Sonoran Desert, Sonoran, and Mojave Desert, Mojave. The Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada and Cascade Range, Cascade mountain ranges run close to the West Coast of the United States, Pacific coast, both ranges also reaching altitudes higher than . The Extreme points of the United States, lowest and highest points in the contiguous United States are in the state of California, and only about apart. At an elevation of , Alaska's Denali is the highest peak in the country and in North America. Active volcanoes are common throughout Alaska's Alexander Archipelago, Alexander and Aleutian Islands, and Hawaii consists of volcanic islands. The supervolcano underlying Yellowstone National Park in the Rockies is the continent's largest volcanic feature.
The List of states and territories of the United States, 48 contiguous states and the District of Columbia occupy a combined area of . Of this area, is contiguous land, composing 83.65% of total U.S. land area. About 15% is occupied by Alaska, a state in northwestern North America, with the remainder in Hawaii, a state and archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, Pacific, and the five populated but Unincorporated area, unincorporated insular territories of Puerto Rico, American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, and the United States Virgin Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands. Measured by only land area, the United States is third in size behind Russia and China, and just ahead of Canada.
The United States is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third- or fourth-largest nation by total area (land and water), ranking behind Russia and Canada and nearly equal to China. The ranking varies depending on how two territories disputed by China and India are counted, and how the total size of the United States is measured.
The Atlantic coastal plain, coastal plain of the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic seaboard gives way further inland to deciduous forests and the rolling hills of the Piedmont (United States), Piedmont. The Appalachian Mountains and the Adirondack Mountains, Adirondack massif divide the eastern seaboard from the Great Lakes and the grasslands of the Midwestern United States, Midwest. The Mississippi River, Mississippi–Missouri River, the world's List of rivers by length, fourth longest river system, runs mainly north–south through the heart of the country. The flat, fertile prairie of the Great Plains stretches to the west, interrupted by U.S. Interior Highlands, a highland region in the southeast.
The Rocky Mountains, west of the Great Plains, extend north to south across the country, peaking at over in Colorado. Farther west are the rocky Great Basin and deserts such as the Chihuahuan Desert, Chihuahua, Sonoran Desert, Sonoran, and Mojave Desert, Mojave. The Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada and Cascade Range, Cascade mountain ranges run close to the West Coast of the United States, Pacific coast, both ranges also reaching altitudes higher than . The Extreme points of the United States, lowest and highest points in the contiguous United States are in the state of California, and only about apart. At an elevation of , Alaska's Denali is the highest peak in the country and in North America. Active volcanoes are common throughout Alaska's Alexander Archipelago, Alexander and Aleutian Islands, and Hawaii consists of volcanic islands. The supervolcano underlying Yellowstone National Park in the Rockies is the continent's largest volcanic feature.
Climate
 The United States, with its large size and geographic variety, includes most climate types. To the east of the 100th meridian west, 100th meridian, the climate ranges from humid continental climate, humid continental in the north to humid subtropical climate, humid subtropical in the south.
The Great Plains west of the 100th meridian are Semi-arid climate, semi-arid. Many mountainous areas of the American West have an alpine climate. The climate is Desert climate, arid in the Great Basin, desert in the Southwest, Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean in coastal California, and oceanic climate, oceanic in coastal Oregon and Washington (state), Washington and southern Alaska. Most of Alaska is Subarctic climate, subarctic or Polar climate, polar. Hawaii and the southern tip of Florida are Tropical climate, tropical, as well as its territories in the Caribbean and the Pacific.
States bordering the Gulf of Mexico are prone to Tropical cyclone, hurricanes, and most of the world's tornadoes occur in the country, mainly in Tornado Alley areas in the Midwest and South. Overall, the United States receives more high-impact extreme weather incidents than any other country in the world.
Extreme weather has become more frequent in the U.S., with three times the number of reported heat waves as in the 1960s. Of the ten warmest years ever recorded in the 48 contiguous states, eight have occurred since 1998. In the Southwestern United States, American Southwest, droughts have become more persistent and more severe.
The United States, with its large size and geographic variety, includes most climate types. To the east of the 100th meridian west, 100th meridian, the climate ranges from humid continental climate, humid continental in the north to humid subtropical climate, humid subtropical in the south.
The Great Plains west of the 100th meridian are Semi-arid climate, semi-arid. Many mountainous areas of the American West have an alpine climate. The climate is Desert climate, arid in the Great Basin, desert in the Southwest, Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean in coastal California, and oceanic climate, oceanic in coastal Oregon and Washington (state), Washington and southern Alaska. Most of Alaska is Subarctic climate, subarctic or Polar climate, polar. Hawaii and the southern tip of Florida are Tropical climate, tropical, as well as its territories in the Caribbean and the Pacific.
States bordering the Gulf of Mexico are prone to Tropical cyclone, hurricanes, and most of the world's tornadoes occur in the country, mainly in Tornado Alley areas in the Midwest and South. Overall, the United States receives more high-impact extreme weather incidents than any other country in the world.
Extreme weather has become more frequent in the U.S., with three times the number of reported heat waves as in the 1960s. Of the ten warmest years ever recorded in the 48 contiguous states, eight have occurred since 1998. In the Southwestern United States, American Southwest, droughts have become more persistent and more severe.
Biodiversity and conservation
The U.S. is one of 17 megadiverse countries containing large numbers of List of endangered species in North America, endemic species: about 17,000 species of vascular plants occur in the contiguous United States and Alaska, and more than 1,800 species of flowering plants are found in Hawaii, few of which occur on the mainland. The United States is home to 428 mammal species, 784 birds, 311 reptiles, and 295 amphibians, and 91,000 insect species. There are 63 List of areas in the United States National Park System, national parks and hundreds of other federally managed parks, forests, and wilderness areas, which are managed by the National Park Service. Altogether, the government owns about 28% of the country's land area, mostly in the Western United States, western states. Most of this land is protected area, protected, though some is leased for oil and gas drilling, mining, logging, or cattle ranching, and about .86% is used for military purposes. Environmental issues in the United States, Environmental issues include debates on oil and nuclear binding energy, nuclear energy, dealing with air and water pollution, the economic costs of protecting wildlife, logging and deforestation, and Climate change in the United States, climate change. The most prominent environmental agency is the United States Environmental Protection Agency, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), created by presidential order in 1970. The idea of wilderness has shaped the management of public lands since 1964, with the Wilderness Act. The Endangered Species Act of 1973 is intended to protect threatened and endangered species and their habitats, which are monitored by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. As of 2020, the U.S. ranked 24th among nations in the Environmental Performance Index. The country joined the Paris Agreement on climate change in 2016, and has many other environmental commitments. It United States withdrawal from the Paris Agreement, withdrew from the Paris Agreement in 2020 but rejoined it in 2021.Government and politics
The United States is a federal republic of 50 states, a District of Columbia, federal district, Territories of the United States, five territories and several uninhabited United States Minor Outlying Islands, island possessions. It is the world's oldest surviving federation. It is a federal republic and a representative democracy "in which majority rule is tempered by minority rights protected by Law of the United States, law."Scheb, John M.; Scheb, John M. II (2002). ''An Introduction to the American Legal System''. Florence, KY: Delmar, p. 6. . In the American federalism, federal system, sovereignty is shared between Political divisions of the United States, two levels of government: federal and state. Citizens of the states are also governed by local governments, which are administrative divisions of the states. The territories are administrative divisions of the federal government. The Constitution of the United States, U.S. Constitution serves as the country's supreme legal document. The Constitution establishes the structure and responsibilities of the federal government and its relationship with the individual states. The Constitution has been amended 27 times; the first ten amendments (United States Bill of Rights, Bill of Rights) and the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Fourteenth Amendment form the central basis of Americans' individual rights. All laws and governmental procedures are subject to judicial review, and any law can be voided if the courts determine that it violates the Constitution. The principle of judicial review, not explicitly mentioned in the Constitution, was established by the Supreme Court in ''Marbury v. Madison'' (1803). The United States has operated under a two-party system for most of its history. In American political culture, the Center-right politics, center-right Republican Party is considered "Conservatism in the United States, conservative" and the Centre-left politics, center-left Democratic Party is considered "Modern liberalism in the United States, liberal". On Transparency International's 2019 Corruption Perceptions Index, its public sector position deteriorated from a score of 76 in 2015 to 69 in 2019. In 2021, the U.S. ranked 26th on the Democracy Index, and is described as a "flawed democracy".Federal government
The federal government comprises three branches, which are headquartered in Washington, D.C. and regulated by a system of separation of powers, checks and balances defined by the Constitution. * Legislature, Legislative: The United States Congress, bicameral Congress, made up of the United States Senate, Senate and the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, makes federal law, declaration of war, declares war, approves treaties, has the power of the purse, and has the power of impeachment, by which it can remove sitting members of the federal government. * Executive (government), Executive: President of the United States, The president is the commander-in-chief of the military, can veto bill (law), legislative bills before they become law (subject to congressional override), and appoints the Cabinet of the United States, members of the Cabinet (subject to Senate approval) and other officers, who administer and enforce federal laws and policies. * Judiciary, Judicial: The Supreme Court of the United States, Supreme Court and lower Federal judiciary of the United States, federal courts, whose judges are appointed by the president with Senate approval, interpret laws and overturn those they find constitutionality, unconstitutional. The lower house, the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, has 435 voting members, each representing a congressional district for a two-year term. House seats are United States congressional apportionment, apportioned among the states by population. Each state then draws single-member districts to conform with the census apportionment. The District of Columbia and the five major U.S. territories each have Non-voting members of the United States House of Representatives, one member of Congress—these members are not allowed to vote. The upper house, the United States Senate, Senate, has 100 members with each state having two senators, elected at-large, at large to six-year terms; one-third of Senate seats are up for election every two years. The District of Columbia and the five major U.S. territories do not have senators. The Senate is unique among upper houses in being the most prestigious and powerful portion of the country's Bicameralism, bicameral system; political scientists have frequently labeled it the "most powerful upper house" of any government. The president serves a four-year term and may be elected to the office Term limits in the United States, no more than twice. The president is United States presidential election, not elected by direct vote, but by an indirect Electoral College (United States), electoral college system in which the determining votes are apportioned to the states and the District of Columbia. The Supreme Court, led by the Chief Justice of the United States, chief justice of the United States, has nine members, who serve for life.Political divisions
Each of the 50 states holds jurisdiction over a geographic territory, where it shares sovereignty with the federal government. They are subdivided into List of United States counties and county equivalents, counties or county equivalents, and further divided into Municipality, municipalities. The District of Columbia is a federal district that contains the capital of the United States, the Washington, D.C., city of Washington. Each state has the amount presidential electors equal to the number of their representatives plus senators in Congress, and the District of Columbia has three electors. Territories of the United States do not have presidential electors, therefore people there cannot vote for the president. Citizenship of the United States, Citizenship is granted at birth in all states, the District of Columbia, and all major U.S. territories except American Samoa. The United States observes limited Tribal sovereignty in the United States, tribal sovereignty of the American Indian nations, like states' sovereignty. American Indians are U.S. citizens and tribal lands are subject to the jurisdiction of the U.S. Congress and the federal courts. Like the states, tribes have some autonomy restrictions. They are prohibited from making war, engaging in their own foreign relations, and printing or issuing independent currency. Indian reservations are usually contained within one state, but there are 12 reservations that cross state boundaries.Foreign relations
The United States has an established structure of foreign relations, and it had the world's second-largest diplomatic corps in 2019. It is a permanent member of theUnited Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
, and home to the Headquarters of the United Nations, United Nations headquarters. The United States is also a member of the G7, G-20 major economies, G20, and OECD intergovernmental organizations. Almost all countries have List of diplomatic missions in the United States, embassies and many have consul (representative), consulates (official representatives) in the country. Likewise, nearly all nations host formal diplomatic missions with United States, except Iran–United States relations, Iran, North Korea–United States relations, North Korea, and Foreign relations of Bhutan#Other countries, Bhutan. Though Taiwan–United States relations, Taiwan does not have formal diplomatic relations with the U.S., it maintains close, if unofficial, relations. The United States also regularly supplies Taiwan with Six Assurances, military equipment.
The United States has a "Special Relationship" with the United Kingdom–United States relations, United Kingdom and strong ties with Canada–United States relations, Canada, Australia–United States relations, Australia, New Zealand–United States relations, New Zealand, Philippines–United States relations, the Philippines, Japan–United States relations, Japan, South Korea–United States relations, South Korea, Israel–United States relations, Israel, and several European Union countries (France–United States relations, France, Italy–United States relations, Italy, Germany–United States relations, Germany, Spain–United States relations, Spain, and Poland–United States relations, Poland). The U.S. works closely with its NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
allies on military and national security issues, and with nations in the Americas through the Organization of American States and the United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement, United States–Mexico–Canada Free Trade Agreement. In South America, Colombia is traditionally considered to be the closest ally of the United States. The U.S. exercises full international defense authority and responsibility for Federated States of Micronesia, Micronesia, the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
and Palau through the Compact of Free Association. Since the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, the U.S. has become a key ally of Ukraine since Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, annexed Crimea in 2014 and began an 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, invasion of Ukraine in 2022, significantly deteriorating relations with Russia in the process. The U.S. has also experienced a deterioration of relations with China and grown closer to Taiwan.
Military

 The president is the Commander-in-Chief of the United States, commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces and appoints its leaders, the United States Secretary of Defense, secretary of defense and the Joint Chiefs of Staff. The United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense, which is headquartered at the Pentagon near Washington, D.C., administers five of the six service branches, which are made up of the United States Army, Army, United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps, United States Navy, Navy, United States Air Force, Air Force, and United States Space Force, Space Force. The United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard is administered by the United States Department of Homeland Security, Department of Homeland Security in peacetime and can be transferred to the United States Department of the Navy, Department of the Navy in wartime. The United States spent $649 billion on its military in 2019, 36% of global military spending. At 4.7% of GDP, the percentage was the second-highest among all countries, after Saudi Arabia. It also has Nuclear weapons of the United States, more than 40% of the world's nuclear weapons, the second-largest after Russia.
In 2019, all six branches of the U.S. Armed Forces reported 1.4 million personnel on active duty. The Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, Reserves and National Guard of the United States, National Guard brought the total number of troops to 2.3 million. The Department of Defense also employed about 700,000 civilians, not including Military-industrial complex, contractors. Military service in the United States is voluntary, although Conscription in the United States, conscription may occur in wartime through the Selective Service System. The United States has the third-largest combined armed forces in the world, behind the People's Liberation Army, Chinese People's Liberation Army and Indian Armed Forces.
Today, American forces can be rapidly deployed by the Air Force's large fleet of transport aircraft, the Navy's 11 active aircraft carriers, and Marine expeditionary units at sea with the Navy, and Army's XVIII Airborne Corps and 75th Ranger Regiment deployed by Air Force transport aircraft. The Air Force can strike targets across the globe through its fleet of strategic bombers, maintains the air defense across the United States, and provides close air support to Army and Marine Corps ground forces.
The Space Force operates the Global Positioning System, operates the Eastern Range, Eastern and Western Range (USSF), Western Ranges for all space launches, and operates the United States's United States Space Surveillance Network, Space Surveillance and United States national missile defense, Missile Warning networks. The military operates about 800 bases and facilities abroad, and maintains United States military deployments, deployments greater than 100 active duty personnel in 25 foreign countries.
The president is the Commander-in-Chief of the United States, commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces and appoints its leaders, the United States Secretary of Defense, secretary of defense and the Joint Chiefs of Staff. The United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense, which is headquartered at the Pentagon near Washington, D.C., administers five of the six service branches, which are made up of the United States Army, Army, United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps, United States Navy, Navy, United States Air Force, Air Force, and United States Space Force, Space Force. The United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard is administered by the United States Department of Homeland Security, Department of Homeland Security in peacetime and can be transferred to the United States Department of the Navy, Department of the Navy in wartime. The United States spent $649 billion on its military in 2019, 36% of global military spending. At 4.7% of GDP, the percentage was the second-highest among all countries, after Saudi Arabia. It also has Nuclear weapons of the United States, more than 40% of the world's nuclear weapons, the second-largest after Russia.
In 2019, all six branches of the U.S. Armed Forces reported 1.4 million personnel on active duty. The Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, Reserves and National Guard of the United States, National Guard brought the total number of troops to 2.3 million. The Department of Defense also employed about 700,000 civilians, not including Military-industrial complex, contractors. Military service in the United States is voluntary, although Conscription in the United States, conscription may occur in wartime through the Selective Service System. The United States has the third-largest combined armed forces in the world, behind the People's Liberation Army, Chinese People's Liberation Army and Indian Armed Forces.
Today, American forces can be rapidly deployed by the Air Force's large fleet of transport aircraft, the Navy's 11 active aircraft carriers, and Marine expeditionary units at sea with the Navy, and Army's XVIII Airborne Corps and 75th Ranger Regiment deployed by Air Force transport aircraft. The Air Force can strike targets across the globe through its fleet of strategic bombers, maintains the air defense across the United States, and provides close air support to Army and Marine Corps ground forces.
The Space Force operates the Global Positioning System, operates the Eastern Range, Eastern and Western Range (USSF), Western Ranges for all space launches, and operates the United States's United States Space Surveillance Network, Space Surveillance and United States national missile defense, Missile Warning networks. The military operates about 800 bases and facilities abroad, and maintains United States military deployments, deployments greater than 100 active duty personnel in 25 foreign countries.
Law enforcement and crime
Economy
 According to the
According to the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glo ...
, the U.S. gross domestic product (GDP) of $22.7 trillion constitutes 24% of the gross world product at market exchange rates and over 16% of the gross world product at purchasing power parity (PPP). From 1983 to 2008, U.S. real compounded annual GDP growth was 3.3%, compared to a 2.3% weighted average for the rest of the G7. The country ranks fifth in the world in List of countries by GDP (nominal) per capita, nominal GDP per capita and seventh in List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, GDP per capita at PPP. The country has been the world's largest economy since at least 1900.
The United States is the most technologically powerful and Science and technology in the United States, innovative nation, especially in artificial intelligence, computers, pharmaceuticals, and medical, aerospace, and military equipment. The nation's economy is fueled by abundant natural resources, a well-developed infrastructure, and high productivity.Wright, Gavin, and Jesse Czelusta, "Resource-Based Growth Past and Present", in ''Natural Resources: Neither Curse Nor Destiny'', ed. Daniel Lederman and William Maloney (World Bank, 2007), p. 185. . It has the second-highest total-estimated value of natural resources, valued at United States dollar, US$ 44.98trillion in 2019, although sources differ on their estimates. Americans have the highest average Household income, household and List of countries by average wage, employee income among OECD member states. In 2013, they had the sixth-highest median household income, down from fourth-highest in 2010.
The United States dollar, U.S. dollar is the currency most used in international trade, international transactions and is the world's foremost reserve currency, backed by its economy, its United States Armed Forces, military, the petrodollar, petrodollar system and its linked eurodollar and large U.S. Treasury, U.S. treasuries market. Several countries International use of the US dollar, use it as their official currency and in others it is the de facto currency, ''de facto'' currency.Benjamin J. Cohen, ''The Future of Money'', Princeton University Press, 2006, ; ''cf.'' "the dollar is the de facto currency in Cambodia", Charles Agar, ''Frommer's Vietnam'', 2006, , p. 17 The New York Stock Exchange and Nasdaq are the world's List of stock exchanges, largest stock exchanges by market capitalization and trade volume.Table A – Market Capitalization of the World's Top Stock Exchanges (As at end of June 2012)Securities and Exchange Commission (China). The List of the largest trading partners of the United States, largest U.S. trading partners are China, the European Union, Canada, Mexico, India, Japan, South Korea, the United Kingdom, and Taiwan. The U.S. is the world's List of countries by imports, largest importer and the List of countries by exports, second-largest exporter. It has free trade agreements with United States free-trade agreements, several countries, including the United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement, USMCA. The U.S. ranked second in the Global Competitiveness Report in 2019, after Singapore. Of the world's Fortune Global 500, 500 largest companies, 124 are headquartered in the U.S. While its economy has reached a post-industrial society, post-industrial level of development, the United States remains an industrial power. It has a smaller welfare state and redistributes less income through government action than most other World Bank high-income economy, high-income countries. The United States ranked the 41st highest in income inequality among 156 countries in 2017, and the highest compared to the rest of the developed world. As of January 1, 2023, the United States had a national debt of $31.4 trillion.
Income and poverty
 At $46,625 USD in 2021, American citizens have the highest median income in the world. Despite the fact that they only account for 4.24% of the World population, global population, they collectively List of countries by total wealth, possess 30.2% of the world's total wealth as of 2021, the largest percentage of any country. The U.S. also ranks first in the number of dollar billionaires and millionaires in the world, with 724 billionaires (as of 2021) and nearly 22 million millionaires (2021).
Wealth in the United States is Wealth inequality in the United States, highly concentrated; the richest 10% of the adult population own 72% of the country's household wealth, while the bottom 50% own just 2%. Income inequality in the United States, Income inequality in the U.S. remains at record highs, with the top fifth of earners taking home more than half of all income and giving the U.S. one of the widest income distributions among OECD members. The United States is the only advanced economy that does not List of statutory minimum employment leave by country, guarantee its workers paid vacation and is one of a few countries in the world without paid family leave as a legal right. The United States also has a higher percentage of low-income workers than almost any other developed nation, largely because of a weak collective bargaining system and lack of government support for at-risk workers.
There were about 567,715 sheltered and unsheltered Homelessness in the United States, homeless persons in the U.S. in January 2019, with almost two-thirds staying in an emergency shelter or transitional housing program. Attempts to combat homelessness include the Section 8 (housing), Section 8 housing voucher program and implementation of the Housing First strategy across all levels of government.
In 2011, Hunger in the United States#Children, 16.7 million children lived in food-insecure households, about 35% more than 2007 levels, though only 845,000 U.S. children (1.1%) saw reduced food intake or disrupted eating patterns at some point during the year, and most cases were not chronic. 40 million people, roughly 12.7% of the U.S. population, were living in poverty, including 13.3 million children. Of those impoverished, 18.5 million live in "deep poverty", family income below one-half of the federal government's poverty threshold.
At $46,625 USD in 2021, American citizens have the highest median income in the world. Despite the fact that they only account for 4.24% of the World population, global population, they collectively List of countries by total wealth, possess 30.2% of the world's total wealth as of 2021, the largest percentage of any country. The U.S. also ranks first in the number of dollar billionaires and millionaires in the world, with 724 billionaires (as of 2021) and nearly 22 million millionaires (2021).
Wealth in the United States is Wealth inequality in the United States, highly concentrated; the richest 10% of the adult population own 72% of the country's household wealth, while the bottom 50% own just 2%. Income inequality in the United States, Income inequality in the U.S. remains at record highs, with the top fifth of earners taking home more than half of all income and giving the U.S. one of the widest income distributions among OECD members. The United States is the only advanced economy that does not List of statutory minimum employment leave by country, guarantee its workers paid vacation and is one of a few countries in the world without paid family leave as a legal right. The United States also has a higher percentage of low-income workers than almost any other developed nation, largely because of a weak collective bargaining system and lack of government support for at-risk workers.
There were about 567,715 sheltered and unsheltered Homelessness in the United States, homeless persons in the U.S. in January 2019, with almost two-thirds staying in an emergency shelter or transitional housing program. Attempts to combat homelessness include the Section 8 (housing), Section 8 housing voucher program and implementation of the Housing First strategy across all levels of government.
In 2011, Hunger in the United States#Children, 16.7 million children lived in food-insecure households, about 35% more than 2007 levels, though only 845,000 U.S. children (1.1%) saw reduced food intake or disrupted eating patterns at some point during the year, and most cases were not chronic. 40 million people, roughly 12.7% of the U.S. population, were living in poverty, including 13.3 million children. Of those impoverished, 18.5 million live in "deep poverty", family income below one-half of the federal government's poverty threshold.
Science, technology, and energy
 The United States has been a leader in technological innovation since the late 19th century and scientific research since the mid-20th century. Methods for producing interchangeable parts and the establishment of a machine tool industry enabled the American system of manufacturing, U.S. to have large-scale manufacturing of sewing machines, bicycles, and other items in the late 19th century. In the early 20th century, factory electrification, the introduction of the assembly line, and other labor-saving techniques created the system of mass production. In the 21st century, approximately two-thirds of research and development funding comes from the private sector. In 2020, the United States was the country with the List of countries by number of scientific and technical journal articles, second-highest number of published scientific papers and second most patents granted, both after China. In 2021, the United States launched a total of 51 spaceflights. (China reported 55.) The U.S. had 2,944 active satellites in space in December 2021, the highest number of any country.
In 1876, Alexander Graham Bell was awarded the first U.S. Invention of the telephone, patent for the telephone. Thomas Edison's Research institute, research laboratory developed the phonograph, the first Incandescent light bulb, long-lasting light bulb, and the first viable Kinetoscope, movie camera. The Wright brothers in 1903 made the Wright Flyer, first sustained and controlled heavier-than-air powered flight, and the automobile companies of Ransom E. Olds and Henry Ford popularized the assembly line in the early 20th century. The rise of fascism and Nazism in the 1920s and 30s led many European scientists, such as Albert Einstein, Enrico Fermi, and John von Neumann, to immigrate to the United States. During World War II, the Manhattan Project developed nuclear weapons, ushering in the Atomic Age. During the Cold War, competition for superior missile capability ushered in the
The United States has been a leader in technological innovation since the late 19th century and scientific research since the mid-20th century. Methods for producing interchangeable parts and the establishment of a machine tool industry enabled the American system of manufacturing, U.S. to have large-scale manufacturing of sewing machines, bicycles, and other items in the late 19th century. In the early 20th century, factory electrification, the introduction of the assembly line, and other labor-saving techniques created the system of mass production. In the 21st century, approximately two-thirds of research and development funding comes from the private sector. In 2020, the United States was the country with the List of countries by number of scientific and technical journal articles, second-highest number of published scientific papers and second most patents granted, both after China. In 2021, the United States launched a total of 51 spaceflights. (China reported 55.) The U.S. had 2,944 active satellites in space in December 2021, the highest number of any country.
In 1876, Alexander Graham Bell was awarded the first U.S. Invention of the telephone, patent for the telephone. Thomas Edison's Research institute, research laboratory developed the phonograph, the first Incandescent light bulb, long-lasting light bulb, and the first viable Kinetoscope, movie camera. The Wright brothers in 1903 made the Wright Flyer, first sustained and controlled heavier-than-air powered flight, and the automobile companies of Ransom E. Olds and Henry Ford popularized the assembly line in the early 20th century. The rise of fascism and Nazism in the 1920s and 30s led many European scientists, such as Albert Einstein, Enrico Fermi, and John von Neumann, to immigrate to the United States. During World War II, the Manhattan Project developed nuclear weapons, ushering in the Atomic Age. During the Cold War, competition for superior missile capability ushered in the Space Race
The Space Race was a 20th-century competition between two Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between the t ...
between the U.S. and Soviet Union. The invention of the transistor in the 1950s, a key component in almost all modern electronics, led to the development of microprocessors, software, personal computers and the Internet. In 2022, the United States ranked 2nd in the Global Innovation Index.
, the United States receives approximately 80% of its energy from fossil fuels. In 2019, the largest source of the country's energy came from petroleum (36.6%), followed by natural gas (32%), coal (11.4%), renewable sources (11.4%) and nuclear power (8.4%). Americans constitute less than 5% of the world population, world's population, but consume 17% of the Energy use in the United States, world's energy. They account for about 25% of the world's Oil consumption, petroleum consumption, while producing only 6% of the world's annual petroleum supply. The U.S. ranks as second-highest emitter of greenhouse gases, exceeded only by China.
Transportation
 The United States's Rail transport in the United States, rail network, nearly all Standard-gauge railway, standard gauge, is the List of countries by rail transport network size, longest in the world, and exceeds . It handles mostly freight, with intercity passenger service provided by Amtrak to all but four states. The country's Inland waterways of the United States, inland waterways are the world's List of countries by waterways length, fifth-longest, and total .
Personal transportation is dominated by automobiles, which operate on a network of of public roads. The United States has the world's second-largest automobile market, and has the highest vehicle ownership per capita in the world, with 816.4 vehicles per 1,000 Americans (2014). In 2017, there were 255 million non-two wheel motor vehicles, or about 910 vehicles per 1,000 people.
The List of airlines of the United States, civil airline industry is entirely privately owned and has been largely Airline Deregulation Act, deregulated since 1978, while List of airports in the United States, most major airports are publicly owned. The three largest airlines in the world by passengers carried are U.S.-based; American Airlines is number one after its 2013 acquisition by US Airways. Of the List of the world's busiest airports by passenger traffic, world's 50 busiest passenger airports, 16 are in the United States, including the busiest, Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport. Of the List of busiest container ports, fifty busiest container ports, four are located in the United States, of which the busiest is the Port of Los Angeles.
The United States's Rail transport in the United States, rail network, nearly all Standard-gauge railway, standard gauge, is the List of countries by rail transport network size, longest in the world, and exceeds . It handles mostly freight, with intercity passenger service provided by Amtrak to all but four states. The country's Inland waterways of the United States, inland waterways are the world's List of countries by waterways length, fifth-longest, and total .
Personal transportation is dominated by automobiles, which operate on a network of of public roads. The United States has the world's second-largest automobile market, and has the highest vehicle ownership per capita in the world, with 816.4 vehicles per 1,000 Americans (2014). In 2017, there were 255 million non-two wheel motor vehicles, or about 910 vehicles per 1,000 people.
The List of airlines of the United States, civil airline industry is entirely privately owned and has been largely Airline Deregulation Act, deregulated since 1978, while List of airports in the United States, most major airports are publicly owned. The three largest airlines in the world by passengers carried are U.S.-based; American Airlines is number one after its 2013 acquisition by US Airways. Of the List of the world's busiest airports by passenger traffic, world's 50 busiest passenger airports, 16 are in the United States, including the busiest, Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport. Of the List of busiest container ports, fifty busiest container ports, four are located in the United States, of which the busiest is the Port of Los Angeles.
Demographics
Population
The United States Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau reported 331,449,281 residents as of April 1, 2020, making the United States the third most populous nation in the world, after China and India. According to the Bureau's U.S. and World Population Clock, U.S. Population Clock, on January 28, 2021, the U.S. population had a net gain of one person every 100 seconds, or about 864 people per day. In 2018, 52% of Americans age 15 and over were married, 6% were widowed, 10% were divorced, and 32% had never been married. In 2020, the U.S. had a total fertility rate stood at 1.64 children per woman and the world's highest rate (23%) of children living in Single parents in the United States, single-parent households. The United States of America has a diverse population; 37 American ancestries, ancestry groups have more than one million members. White Americans with ancestry from Europe, the Middle East or North Africa, form the largest race (human classification), racial and ethnic group at 57.8% of the United States population. Hispanic and Latino Americans form the second-largest group and are 18.7% of the United States population. African Americans constitute the nation's third-largest ancestry group and are 12.1% of the total United States population. Asian Americans are the country's fourth-largest group, composing 5.9% of the United States population, while the country's 3.7 million Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans account for about 1%. In 2020, the median age of the United States population was 38.5 years. In 2018, there were almost 90 million immigrants and Second-generation immigrants in the United States, U.S.-born children of immigrants in the United States, accounting for 28% of the overall U.S. population. In 2017, out of the U.S. foreign-born population, some 45% (20.7 million) were naturalized citizens, 27% (12.3 million) were lawful permanent residents, 6% (2.2 million) were temporary lawful residents, and 23% (10.5 million) were unauthorized immigrants. The United States led the world in refugee resettlement for decades, admitting more refugees than the rest of the world combined.Language
English (specifically, American English) is the de facto national language of the United States. Although there is no official language at the federal level, some laws—such as Naturalized citizen of the United States, U.S. naturalization requirements—standardize English, and most states have declared English as the official language. Three states and four U.S. territories have recognized local or indigenous languages in addition to English, including Hawaii (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian), Alaska (Alaska Native languages, twenty Native languages), South Dakota (Sioux language, Sioux), American Samoa (Samoan language, Samoan), Puerto Rico (Spanish language, Spanish), Guam (Chamorro language, Chamorro), and the Northern Mariana Islands (Carolinian language, Carolinian and Chamorro). In Puerto Rico, Spanish is more widely spoken than English. According to the American Community Survey, in 2010 some 229 million people (out of the total U.S. population of 308 million) spoke only English at home. More than 37 million spoke Spanish language in the United States, Spanish at home, making it the second most commonly used language in the United States. Other languages spoken at home by one million people or more include Chinese language, Chinese (2.8 million), Tagalog language, Tagalog (1.6 million), Vietnamese language, Vietnamese (1.4 million), French language, French (1.3 million), Korean language, Korean (1.1 million), and German language, German (1 million). The List of most commonly learned foreign languages in the United States, most widely taught foreign languages in the United States, in terms of enrollment numbers from kindergarten through university undergraduate education, are Spanish (around 7.2 million students), French (1.5 million), and German language in the United States, German (500,000). Other commonly taught languages include Latin, Japanese language education in the United States, Japanese, American Sign Language, Italian language in the United States, Italian, and Chinese language in the United States, Chinese.Religion
A large variety of faiths have historically flourished within the country. According to the World Values Survey in 2017, the United States is more Secularity, secular than the median country; they ranked the United States the 32nd least religious country in the world. Until the 1990s, the country was a substantial outlier among other Developed country, highly developed countries: uniquely Wealth and religion, combining a high level of religiosity and wealth, although this has lessened significantly since then. Studies during the early 2020s found that about 81% of Americans believe in some conception of God, 45% report Prayer, praying on a daily basis, 41% report that religion plays a very important role in their lives, and 31% report attending religious services weekly or near weekly. According to ''Gallup, Inc., Gallup'' in December 2022, 58% of Americans report "seldom" or "never" attending religious services. According to the ''Institute for Family Studies'' in 2022, around 28% of Americans attended at least once or twice a month''.'' In a 2020 survey, about 64% of adults in the United States identified themselves as Christianity in the United States, Christians making it the country with the Christianity by country, largest Christian population. Protestantism in the United States, Protestantism is the largest Christian religious grouping in the United States, accounting for around a third of all Americans. In the so-called Bible Belt, located primarily within the Southern United States, socially conservative evangelical Protestantism plays a significant role culturally. By contrast, religion plays the least important role in New England and the Western United States. Another 6% claimed a non-Christian faith; the largest of which are American Jews, Judaism, Islam in the United States, Islam, Hinduism in the United States, Hinduism, and Buddhism in the United States, Buddhism. Around 30% of Americans describe themselves as having irreligion, no religion. Membership in a house of worship fell from 70% in 1999 to 47% in 2020, much of the decline related to the number of Americans expressing no religious preference. Membership also fell among those who identified with a specific religious group. According to ''Gallup'', trust in "the church or organized religion" has declined significantly since the 1970s. The First Amendment to the United States Constitution, First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution guarantees the Free Exercise Clause, free exercise of religion and forbids Congress from passing laws respecting its Establishment Clause, establishment.Urbanization
About 82% of Americans live in United States urban area, urban areas, including suburbs; about half of those reside in cities with populations over 50,000. In 2008, 273 List of United States cities by population, incorporated municipalities had populations over 100,000, nine cities had more than one million residents, and four cities (New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
, Los Angeles, Chicago, and Houston) had populations exceeding two million. Many U.S. metropolitan populations are growing rapidly, particularly in the South and West.
Education
 American state school, public education is operated by state and local governments and regulated by the United States Department of Education through restrictions on federal grants. In most states, children are required to attend school from the age of five or six (beginning with kindergarten or first grade) until they turn 18 (generally bringing them through twelfth grade, the end of high school); some states allow students to leave school at 16 or 17. Of Americans 25 and older, 84.6% graduated from high school, 52.6% attended some college, 27.2% earned a bachelor's degree, and 9.6% earned graduate degrees. The basic literacy rate is approximately 99%.
The United States has many private and public Lists of American institutions of higher education, institutions of higher education. The majority of the world's top Public university, public and Private university, private universities, as listed by various ranking organizations, are in the United States. There are also local community colleges with generally more open admission policies, shorter academic programs, and lower tuition. The U.S. spends more on education per student than any nation in the world, spending an average of $12,794 per year on public elementary and secondary school students in the 2016–2017 school year. As for public expenditures on higher education, the U.S. spends more per student than the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD average, and more than all nations in combined public and private spending. Despite some student loan forgiveness programs in place, Student debt, student loan debt has increased by 102% in the last decade, and exceeded 1.7 trillion dollars as of 2022.
American state school, public education is operated by state and local governments and regulated by the United States Department of Education through restrictions on federal grants. In most states, children are required to attend school from the age of five or six (beginning with kindergarten or first grade) until they turn 18 (generally bringing them through twelfth grade, the end of high school); some states allow students to leave school at 16 or 17. Of Americans 25 and older, 84.6% graduated from high school, 52.6% attended some college, 27.2% earned a bachelor's degree, and 9.6% earned graduate degrees. The basic literacy rate is approximately 99%.
The United States has many private and public Lists of American institutions of higher education, institutions of higher education. The majority of the world's top Public university, public and Private university, private universities, as listed by various ranking organizations, are in the United States. There are also local community colleges with generally more open admission policies, shorter academic programs, and lower tuition. The U.S. spends more on education per student than any nation in the world, spending an average of $12,794 per year on public elementary and secondary school students in the 2016–2017 school year. As for public expenditures on higher education, the U.S. spends more per student than the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD average, and more than all nations in combined public and private spending. Despite some student loan forgiveness programs in place, Student debt, student loan debt has increased by 102% in the last decade, and exceeded 1.7 trillion dollars as of 2022.
Health
 In a preliminary report, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced that U.S. life expectancy at birth had dropped to 76.4 years in 2021 (73.2 years for men and 79.1 years for women), down 0.9 years from 2020. This was the second year of overall decline, and the chief causes listed were the COVID-19 pandemic, accidents, drug overdoses, heart and liver disease, and suicides. Life expectancy was highest among Asians and Hispanics and lowest among Blacks and American Indian–Alaskan Native (AIAN (U.S. Census), AIAN) peoples. Starting in 1998, the average life expectancy in the U.S. fell behind that of other wealthy industrialized countries, and Americans' "health disadvantage" gap has been increasing ever since. The U.S. also has one of the highest Suicide in the United States, suicide rates among high-income countries, and approximately one-third of the U.S. adult population is obese and another third is overweight.
In 2010, coronary artery disease, lung cancer, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, and traffic collisions caused the most years of life lost in the U.S. Low back pain, major depressive disorder, depression, musculoskeletal disorders, neck pain, and anxiety caused the most years lost to disability. The most harmful risk factors were poor diet, tobacco smoking, obesity, Hypertension, high blood pressure, Hyperglycemia, high blood sugar, physical inactivity, and Alcohol consumption and health, alcohol consumption. Alzheimer's disease, substance use disorders, kidney disease, cancer, and falls caused the most additional years of life lost over their age-adjusted 1990 per-capita rates. Teenage pregnancy in the United States, Teenage pregnancy and Abortion in the United States, abortion rates in the U.S. are substantially higher than in other Western nations, especially among blacks and Hispanics.
The U.S. health care system far List of countries by total health expenditure (PPP) per capita, outspends that of any other nation, measured both in per capita spending and as a percentage of GDP but attains worse healthcare outcomes when compared to peer nations. The United States is the only developed nation Healthcare reform in the United States, without a system of universal health care, and a Health insurance coverage in the United States, significant proportion of the population that does not carry health insurance. The U.S., however, is a global leader in medical innovation, measured either in terms of revenue or the number of new drugs and devices introduced.Stats from 2007 Europ.Fed.of Pharm.Indust.and Assoc. Retrieved June 17, 2009, fro
In a preliminary report, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced that U.S. life expectancy at birth had dropped to 76.4 years in 2021 (73.2 years for men and 79.1 years for women), down 0.9 years from 2020. This was the second year of overall decline, and the chief causes listed were the COVID-19 pandemic, accidents, drug overdoses, heart and liver disease, and suicides. Life expectancy was highest among Asians and Hispanics and lowest among Blacks and American Indian–Alaskan Native (AIAN (U.S. Census), AIAN) peoples. Starting in 1998, the average life expectancy in the U.S. fell behind that of other wealthy industrialized countries, and Americans' "health disadvantage" gap has been increasing ever since. The U.S. also has one of the highest Suicide in the United States, suicide rates among high-income countries, and approximately one-third of the U.S. adult population is obese and another third is overweight.
In 2010, coronary artery disease, lung cancer, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, and traffic collisions caused the most years of life lost in the U.S. Low back pain, major depressive disorder, depression, musculoskeletal disorders, neck pain, and anxiety caused the most years lost to disability. The most harmful risk factors were poor diet, tobacco smoking, obesity, Hypertension, high blood pressure, Hyperglycemia, high blood sugar, physical inactivity, and Alcohol consumption and health, alcohol consumption. Alzheimer's disease, substance use disorders, kidney disease, cancer, and falls caused the most additional years of life lost over their age-adjusted 1990 per-capita rates. Teenage pregnancy in the United States, Teenage pregnancy and Abortion in the United States, abortion rates in the U.S. are substantially higher than in other Western nations, especially among blacks and Hispanics.
The U.S. health care system far List of countries by total health expenditure (PPP) per capita, outspends that of any other nation, measured both in per capita spending and as a percentage of GDP but attains worse healthcare outcomes when compared to peer nations. The United States is the only developed nation Healthcare reform in the United States, without a system of universal health care, and a Health insurance coverage in the United States, significant proportion of the population that does not carry health insurance. The U.S., however, is a global leader in medical innovation, measured either in terms of revenue or the number of new drugs and devices introduced.Stats from 2007 Europ.Fed.of Pharm.Indust.and Assoc. Retrieved June 17, 2009, fro/ref> Government-funded health care coverage for the poor (Medicaid, established in 1965) and for those age 65 and older (Medicare (United States), Medicare, begun in 1966) is available to Americans who meet the programs' income or age qualifications. In 2010, former President Obama passed the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act or ACA, which the CDC said that the law roughly halved the uninsured share of the population and multiple studies have concluded that ACA had reduced the mortality of enrollees. However, its legacy Criticism of Obamacare, remains controversial.
Culture and society
 Americans have traditionally Stereotypes of Americans, been characterized by a strong work ethic, competitiveness, and individualism, as well as a unifying belief in an "American civil religion, American creed" emphasizing liberty, social equality, property rights, democracy, equality under the law, and a preference for limited government. Americans are extremely charitable by global standards: according to a 2016 study by the Charities Aid Foundation, Americans donated 1.44% of total GDP to charity, the List of countries by charitable donation, highest in the world by a large margin. The United States is home to a Multiculturalism, wide variety of ethnic groups, traditions, and values, and exerts major cultural influence Americanization, on a global scale. The country has been described as a society "built on a Moral universalism, universalistic cultural frame rooted in the natural laws of science and human rights."
The United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence has become a well-known statement on human rights, particularly its second sentence: "We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by Higher Power, their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness." Stephen Lucas called it "one of the best-known sentences in the English language", with historian Joseph Ellis writing that the document contains "the most potent and consequential words in American history". The passage has since came to represent a moral standard to which the United States should strive. This view was notably promoted by Lincoln, who considered it to be the foundation of his political philosophy and argued that it is a statement of principles through which the Constitution should be interpreted.
Aside from the Native American, Native Hawaiians, Native Hawaiian, and Alaska Natives, Native Alaskan populations, nearly all Americans or their ancestors immigrated or were imported as slaves within the past five centuries. wikt:mainstream, Mainstream American culture is a Western culture largely derived from the European American, traditions of European immigrants with influences from many other sources, such as African-American culture, traditions brought by slaves from Africa. More recent immigration from Asian American, Asia and especially Latin American culture, Latin America has added to a cultural mix that has been described as a homogenizing melting pot, and a heterogeneous salad bowl (cultural idea), salad bowl, with immigrants contributing to, and often Assimilation (phonology), assimilating into, mainstream American culture. Nevertheless, there is a high degree of social inequality related to Racial inequality in the United States, race and Wealth inequality in the United States, wealth. The American Dream, or the perception that Americans enjoy high Socio-economic mobility in the United States, social mobility, plays a key role in attracting immigrants. Whether this perception is accurate has been a topic of debate.*
*
*
* While mainstream culture holds that the United States is a classless society, scholars identify significant differences between Social class in the United States, the country's social classes, affecting socialization, language, and values.
Americans tend to greatly value socioeconomics, socioeconomic achievement, but being Average Joe, ordinary or average is promoted by some as a noble condition.
In the modern day, the country is considered to have Permissive society, permissive attitudes surrounding human sexuality. LGBT rights in the United States are among the most socially, culturally, and legally permissive and advanced in the world, with Public opinion of same-sex marriage in the United States, public opinion and jurisprudence on the issue changing significantly since the late 1980s. A late 2022 ''Grinnell College National Poll'' found that 74% of Americans agree that same-sex marriage should be a guaranteed right while 13% disagree.
Americans have traditionally Stereotypes of Americans, been characterized by a strong work ethic, competitiveness, and individualism, as well as a unifying belief in an "American civil religion, American creed" emphasizing liberty, social equality, property rights, democracy, equality under the law, and a preference for limited government. Americans are extremely charitable by global standards: according to a 2016 study by the Charities Aid Foundation, Americans donated 1.44% of total GDP to charity, the List of countries by charitable donation, highest in the world by a large margin. The United States is home to a Multiculturalism, wide variety of ethnic groups, traditions, and values, and exerts major cultural influence Americanization, on a global scale. The country has been described as a society "built on a Moral universalism, universalistic cultural frame rooted in the natural laws of science and human rights."
The United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence has become a well-known statement on human rights, particularly its second sentence: "We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by Higher Power, their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness." Stephen Lucas called it "one of the best-known sentences in the English language", with historian Joseph Ellis writing that the document contains "the most potent and consequential words in American history". The passage has since came to represent a moral standard to which the United States should strive. This view was notably promoted by Lincoln, who considered it to be the foundation of his political philosophy and argued that it is a statement of principles through which the Constitution should be interpreted.
Aside from the Native American, Native Hawaiians, Native Hawaiian, and Alaska Natives, Native Alaskan populations, nearly all Americans or their ancestors immigrated or were imported as slaves within the past five centuries. wikt:mainstream, Mainstream American culture is a Western culture largely derived from the European American, traditions of European immigrants with influences from many other sources, such as African-American culture, traditions brought by slaves from Africa. More recent immigration from Asian American, Asia and especially Latin American culture, Latin America has added to a cultural mix that has been described as a homogenizing melting pot, and a heterogeneous salad bowl (cultural idea), salad bowl, with immigrants contributing to, and often Assimilation (phonology), assimilating into, mainstream American culture. Nevertheless, there is a high degree of social inequality related to Racial inequality in the United States, race and Wealth inequality in the United States, wealth. The American Dream, or the perception that Americans enjoy high Socio-economic mobility in the United States, social mobility, plays a key role in attracting immigrants. Whether this perception is accurate has been a topic of debate.*
*
*
* While mainstream culture holds that the United States is a classless society, scholars identify significant differences between Social class in the United States, the country's social classes, affecting socialization, language, and values.
Americans tend to greatly value socioeconomics, socioeconomic achievement, but being Average Joe, ordinary or average is promoted by some as a noble condition.
In the modern day, the country is considered to have Permissive society, permissive attitudes surrounding human sexuality. LGBT rights in the United States are among the most socially, culturally, and legally permissive and advanced in the world, with Public opinion of same-sex marriage in the United States, public opinion and jurisprudence on the issue changing significantly since the late 1980s. A late 2022 ''Grinnell College National Poll'' found that 74% of Americans agree that same-sex marriage should be a guaranteed right while 13% disagree.
Literature and visual arts
 In the 18th and early 19th centuries, American art and literature took most of their cues from Europe, contributing to Western culture. Writers such as Washington Irving, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Edgar Allan Poe, and Henry David Thoreau established a distinctive American literary voice by the middle of the 19th century. Mark Twain and poet Walt Whitman were major figures in the century's second half; Emily Dickinson, virtually unknown during her lifetime, is recognized as an essential American poet.
A work seen as capturing fundamental aspects of the national experience and character—such as Herman Melville's ''Moby-Dick'' (1851), Twain's ''Adventures of Huckleberry Finn, The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn'' (1885), F. Scott Fitzgerald's ''The Great Gatsby'' (1925) and Harper Lee's ''To Kill a Mockingbird'' (1960)—may be dubbed the "Great American Novel."
Thirteen U.S. citizens have won the Nobel Prize in Literature. William Faulkner, Ernest Hemingway and John Steinbeck are often named among the most influential writers of the 20th century. The Beat Generation writers opened up new literary approaches, as have postmodern literature, postmodernist authors such as John Barth, Thomas Pynchon, and Don DeLillo.
In the visual arts, the Hudson River School was a mid-19th-century movement in the tradition of European Realism (arts), naturalism. The 1913 Armory Show in New York City, an exhibition of European modern art, modernist art, shocked the public and transformed the U.S. art scene. Georgia O'Keeffe, Marsden Hartley, and others experimented with new, individualistic styles.
Major artistic movements such as the abstract expressionism of Jackson Pollock and Willem de Kooning and the pop art of Andy Warhol and Roy Lichtenstein developed largely in the United States. The tide of modernism and then postmodernism has brought fame to American architects such as Frank Lloyd Wright, Philip Johnson, and Frank Gehry. Americans have long been important in the modern artistic medium of photography, with major photographers including Alfred Stieglitz, Edward Steichen, Edward Weston, and Ansel Adams.
In the 18th and early 19th centuries, American art and literature took most of their cues from Europe, contributing to Western culture. Writers such as Washington Irving, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Edgar Allan Poe, and Henry David Thoreau established a distinctive American literary voice by the middle of the 19th century. Mark Twain and poet Walt Whitman were major figures in the century's second half; Emily Dickinson, virtually unknown during her lifetime, is recognized as an essential American poet.
A work seen as capturing fundamental aspects of the national experience and character—such as Herman Melville's ''Moby-Dick'' (1851), Twain's ''Adventures of Huckleberry Finn, The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn'' (1885), F. Scott Fitzgerald's ''The Great Gatsby'' (1925) and Harper Lee's ''To Kill a Mockingbird'' (1960)—may be dubbed the "Great American Novel."
Thirteen U.S. citizens have won the Nobel Prize in Literature. William Faulkner, Ernest Hemingway and John Steinbeck are often named among the most influential writers of the 20th century. The Beat Generation writers opened up new literary approaches, as have postmodern literature, postmodernist authors such as John Barth, Thomas Pynchon, and Don DeLillo.
In the visual arts, the Hudson River School was a mid-19th-century movement in the tradition of European Realism (arts), naturalism. The 1913 Armory Show in New York City, an exhibition of European modern art, modernist art, shocked the public and transformed the U.S. art scene. Georgia O'Keeffe, Marsden Hartley, and others experimented with new, individualistic styles.
Major artistic movements such as the abstract expressionism of Jackson Pollock and Willem de Kooning and the pop art of Andy Warhol and Roy Lichtenstein developed largely in the United States. The tide of modernism and then postmodernism has brought fame to American architects such as Frank Lloyd Wright, Philip Johnson, and Frank Gehry. Americans have long been important in the modern artistic medium of photography, with major photographers including Alfred Stieglitz, Edward Steichen, Edward Weston, and Ansel Adams.
Cinema and theater
 Hollywood, Los Angeles, Hollywood, a northern district of Los Angeles, California, is the leader in motion picture production and the most recognizable movie industry in the world. The major film studios of the United States are the primary source of the List of highest grossing films, most commercially successful and most ticket selling movies in the world.
The world's first commercial motion picture exhibition was given in New York City in 1894, using the Kinetoscope. Since the early 20th century, the U.S. film industry has largely been based in and around Hollywood, although in the 21st century an increasing number of films are not made there, and film companies have been subject to the forces of globalization. The Academy Awards, popularly known as the Oscars, have been held annually by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences since 1929, and the Golden Globe Awards have been held annually since January 1944.
Director D. W. Griffith, an American filmmaker during the silent film period, was central to the development of film grammar, and producer/entrepreneur Walt Disney was a leader in both animation, animated film and movie merchandising. Directors such as John Ford redefined the image of the American Old West, and, like others such as John Huston, broadened the possibilities of cinema with location shooting. The industry enjoyed its golden years, in what is commonly referred to as the "Classical Hollywood cinema, Golden Age of Hollywood", from the early sound period until the early 1960s, with screen actors such as John Wayne and Marilyn Monroe becoming iconic figures. In the 1970s, "New Hollywood" or the "Hollywood Renaissance" was defined by grittier films influenced by French and Italian realist pictures of the Aftermath of World War II, post-war period.
Theater in the United States derives from the old European theatrical tradition and has been heavily influenced by the Theatre of the United Kingdom, British theater. The central hub of the American theater scene has been Manhattan, with its divisions of Broadway theatre, Broadway, off-Broadway, and off-off-Broadway. Many movie and television stars have gotten their big break working in New York productions. Outside New York City, many cities have professional Regional theater in the United States, regional or resident theater companies that produce their own seasons, with some works being produced regionally with hopes of eventually moving to New York. The biggest-budget theatrical productions are musical theatre, musicals. U.S. theater also has an active community theater culture, which relies mainly on local volunteers who may not be actively pursuing a theatrical career.
Hollywood, Los Angeles, Hollywood, a northern district of Los Angeles, California, is the leader in motion picture production and the most recognizable movie industry in the world. The major film studios of the United States are the primary source of the List of highest grossing films, most commercially successful and most ticket selling movies in the world.
The world's first commercial motion picture exhibition was given in New York City in 1894, using the Kinetoscope. Since the early 20th century, the U.S. film industry has largely been based in and around Hollywood, although in the 21st century an increasing number of films are not made there, and film companies have been subject to the forces of globalization. The Academy Awards, popularly known as the Oscars, have been held annually by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences since 1929, and the Golden Globe Awards have been held annually since January 1944.
Director D. W. Griffith, an American filmmaker during the silent film period, was central to the development of film grammar, and producer/entrepreneur Walt Disney was a leader in both animation, animated film and movie merchandising. Directors such as John Ford redefined the image of the American Old West, and, like others such as John Huston, broadened the possibilities of cinema with location shooting. The industry enjoyed its golden years, in what is commonly referred to as the "Classical Hollywood cinema, Golden Age of Hollywood", from the early sound period until the early 1960s, with screen actors such as John Wayne and Marilyn Monroe becoming iconic figures. In the 1970s, "New Hollywood" or the "Hollywood Renaissance" was defined by grittier films influenced by French and Italian realist pictures of the Aftermath of World War II, post-war period.
Theater in the United States derives from the old European theatrical tradition and has been heavily influenced by the Theatre of the United Kingdom, British theater. The central hub of the American theater scene has been Manhattan, with its divisions of Broadway theatre, Broadway, off-Broadway, and off-off-Broadway. Many movie and television stars have gotten their big break working in New York productions. Outside New York City, many cities have professional Regional theater in the United States, regional or resident theater companies that produce their own seasons, with some works being produced regionally with hopes of eventually moving to New York. The biggest-budget theatrical productions are musical theatre, musicals. U.S. theater also has an active community theater culture, which relies mainly on local volunteers who may not be actively pursuing a theatrical career.
Music
 American folk music encompasses numerous music genres, variously known as traditional music, traditional folk music, contemporary folk music, or roots music. Many traditional songs have been sung within the same family or folk group for generations, and sometimes trace back to such origins as the British Isles, Mainland Europe, or Africa."Folk Music and Song", American Folklife Center, Library of Congress
American folk music encompasses numerous music genres, variously known as traditional music, traditional folk music, contemporary folk music, or roots music. Many traditional songs have been sung within the same family or folk group for generations, and sometimes trace back to such origins as the British Isles, Mainland Europe, or Africa."Folk Music and Song", American Folklife Center, Library of Congress/ref> Among America's earliest composers was a man named William Billings who, born in Boston, composed patriotic hymns in the 1770s; Billings was a part of the Yankee tunesmiths, First New England School, who dominated American music during its earliest stages. Anthony Heinrich was the most prominent composer before the Civil War. From the mid- to late 1800s, John Philip Sousa of the late Romantic music, Romantic era composed numerous military songs—List of marches by John Philip Sousa, particularly marches—and is regarded as one of America's greatest composers. The rhythmic and lyrical styles of African-American music have significantly influenced Music of the United States, American music at large, distinguishing it from European and African traditions. Elements from folk idioms such as the blues and what is known as old-time music were adopted and transformed into popular music, popular genres with global audiences. Jazz was developed by innovators such as Louis Armstrong and Duke Ellington early in the 20th century. Country music developed in the 1920s, and rhythm and blues in the 1940s. Elvis Presley and Chuck Berry were among the pioneers of rock and roll in the mid-1950s. Rock bands such as Metallica, the Eagles (band), Eagles, and Aerosmith are among the List of best-selling music artists, highest grossing in worldwide sales. In the 1960s, Bob Dylan emerged from the American folk music revival, folk revival to become one of America's most celebrated songwriters. Mid-20th-century American pop stars such as Bing Crosby, Frank Sinatra, and Elvis Presley became global celebrities, as have artists of the late 20th century such as Prince (musician), Prince, Michael Jackson, Madonna, Whitney Houston, and Mariah Carey.
Mass media
Food
 Early settlers were introduced by Native Americans to such indigenous, non-European foods as turkey, sweet potatoes, maize, corn, Cucurbita, squash, and maple syrup. They and later immigrants combined these with foods they had known, such as wheat flour, beef, and milk to create a distinctive American cuisine. Homegrown foods are part of a shared national menu on one of America's most popular holidays, Thanksgiving (United States), Thanksgiving, when many Americans make or purchase traditional foods to celebrate the occasion.
The American fast food industry, the world's largest, pioneered the drive-through format in the 1940s. Characteristic American dishes such as apple pie, fried chicken, doughnuts, french fries, macaroni and cheese, ice cream, pizza, hamburgers, and hot dogs derive from the recipes of various immigrants. Mexican cuisine, Mexican dishes such as burritos and tacos and pasta dishes freely adapted from Italian cuisine, Italian sources are widely consumed.
Americans drink three times as much coffee as tea. Marketing by U.S. industries is largely responsible for making orange juice and milk standard List of breakfast drinks, breakfast beverages.
Early settlers were introduced by Native Americans to such indigenous, non-European foods as turkey, sweet potatoes, maize, corn, Cucurbita, squash, and maple syrup. They and later immigrants combined these with foods they had known, such as wheat flour, beef, and milk to create a distinctive American cuisine. Homegrown foods are part of a shared national menu on one of America's most popular holidays, Thanksgiving (United States), Thanksgiving, when many Americans make or purchase traditional foods to celebrate the occasion.
The American fast food industry, the world's largest, pioneered the drive-through format in the 1940s. Characteristic American dishes such as apple pie, fried chicken, doughnuts, french fries, macaroni and cheese, ice cream, pizza, hamburgers, and hot dogs derive from the recipes of various immigrants. Mexican cuisine, Mexican dishes such as burritos and tacos and pasta dishes freely adapted from Italian cuisine, Italian sources are widely consumed.
Americans drink three times as much coffee as tea. Marketing by U.S. industries is largely responsible for making orange juice and milk standard List of breakfast drinks, breakfast beverages.
Sports
 The most popular sports in the U.S. are American football, basketball, baseball and ice hockey.
While most major U.S. sports such as baseball and American football have evolved out of European practices, basketball, volleyball, skateboarding, and snowboarding are American inventions, some of which have become popular worldwide. Lacrosse and surfing arose from Native American and Native Hawaiian activities that predate European contact.Liss, Howard. ''Lacrosse'' (Funk & Wagnalls, 1970) pg 13. The market for professional sports in the United States is roughly $69 billion, roughly 50% larger than that of all of Europe, the Middle East, and Africa combined.
American football is by several measures the most popular spectator sport in the United States; the National Football League (NFL) has the highest average attendance of any sports league in the world, and the Super Bowl is watched by tens of millions globally. Baseball has been regarded as the U.S. national sport since the late 19th century, with Major League Baseball being the top league. Basketball and ice hockey are the country's next two most popular professional team sports, with the top leagues being the National Basketball Association and the National Hockey League. The most-watched individual sports in the U.S. are golf and auto racing, particularly NASCAR and IndyCar.
Eight Olympic Games have taken place in the United States. The 1904 Summer Olympics in St. Louis, Missouri, were the first-ever Olympic Games held outside of Europe. The Olympic Games will be held in the U.S. for a ninth time when Los Angeles hosts the 2028 Summer Olympics. , the United States has won 2,629 medals at the Summer Olympic Games, more than any other country, and 330 in the Winter Olympic Games, the second most behind Norway. In Association football, soccer, the United States men's national soccer team, men's national soccer team qualified for United States at the FIFA World Cup, eleven World Cups and the United States women's national soccer team, women's team has United States at the FIFA Women's World Cup, won the FIFA Women's World Cup four times. The United States hosted the 1994 FIFA World Cup and will host the 2026 FIFA World Cup along with Canada and Mexico. On the collegiate athletics, collegiate level, earnings for the member institutions exceed $1 billion annually,Sports Illustrated: NCAA Reports $1.1 Billion in Revenues
The most popular sports in the U.S. are American football, basketball, baseball and ice hockey.
While most major U.S. sports such as baseball and American football have evolved out of European practices, basketball, volleyball, skateboarding, and snowboarding are American inventions, some of which have become popular worldwide. Lacrosse and surfing arose from Native American and Native Hawaiian activities that predate European contact.Liss, Howard. ''Lacrosse'' (Funk & Wagnalls, 1970) pg 13. The market for professional sports in the United States is roughly $69 billion, roughly 50% larger than that of all of Europe, the Middle East, and Africa combined.
American football is by several measures the most popular spectator sport in the United States; the National Football League (NFL) has the highest average attendance of any sports league in the world, and the Super Bowl is watched by tens of millions globally. Baseball has been regarded as the U.S. national sport since the late 19th century, with Major League Baseball being the top league. Basketball and ice hockey are the country's next two most popular professional team sports, with the top leagues being the National Basketball Association and the National Hockey League. The most-watched individual sports in the U.S. are golf and auto racing, particularly NASCAR and IndyCar.
Eight Olympic Games have taken place in the United States. The 1904 Summer Olympics in St. Louis, Missouri, were the first-ever Olympic Games held outside of Europe. The Olympic Games will be held in the U.S. for a ninth time when Los Angeles hosts the 2028 Summer Olympics. , the United States has won 2,629 medals at the Summer Olympic Games, more than any other country, and 330 in the Winter Olympic Games, the second most behind Norway. In Association football, soccer, the United States men's national soccer team, men's national soccer team qualified for United States at the FIFA World Cup, eleven World Cups and the United States women's national soccer team, women's team has United States at the FIFA Women's World Cup, won the FIFA Women's World Cup four times. The United States hosted the 1994 FIFA World Cup and will host the 2026 FIFA World Cup along with Canada and Mexico. On the collegiate athletics, collegiate level, earnings for the member institutions exceed $1 billion annually,Sports Illustrated: NCAA Reports $1.1 Billion in Revenues/ref> and college football and College basketball, basketball attract large audiences, as the NCAA Division I men's basketball tournament, NCAA Final Four is one of the most watched sporting events.
See also
* Index of United States–related articles * Lists of U.S. state topics * Outline of the United StatesNotes
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Internet sources * * * * * * * * * * *External links
United States
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
United States
from the BBC News
Key Development Forecasts for the United States
from International Futures ; Government
Official U.S. Government Web Portal
Gateway to government sites
House
Official site of the United States House of Representatives
Senate
Official site of the United States Senate
White House
Official site of the president of the United States * [ Supreme Court] Official site of the Supreme Court of the United States ; History
Historical Documents
Collected by the National Center for Public Policy Research
Analysis by the Ontario Consultants on Religious Tolerance
Collected links to historical data ; Maps
National Atlas of the United States
Official maps from the U.S. Department of the Interior * *
Measure of America
A variety of mapped information relating to health, education, income, and demographics for the U.S. ; Photos
Photos of the USA
{{Coord, 40, -100, dim:10000000_region:region:US_type:country, name=United States of America, display=title United States Countries in North America English-speaking countries and territories Federal constitutional republics Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas Former confederations G20 nations Member states of NATO Member states of the United Nations States and territories established in 1776 Transcontinental countries