The Democratic Party is one of the
two
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultur ...
major
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators ...
contemporary
political parties in the United States
American electoral politics have been dominated by two major political parties since shortly after the founding of the republic of the United States of America. Since the 1850s, the two have been the Democratic Party and the Republican Party†...
. Founded in 1828, it was predominantly built by
Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren ( ; nl, Maarten van Buren; ; December 5, 1782 – July 24, 1862) was an American lawyer and statesman who served as the eighth president of the United States from 1837 to 1841. A primary founder of the Democratic Party (Uni ...
, who assembled a wide cadre of politicians in every state behind war hero
Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
, making it the world's oldest active political party.
[M. Philip Lucas, "Martin Van Buren as Party Leader and at Andrew Jackson's Right Hand." in ''A Companion to the Antebellum Presidents 1837–1861'' (2014): 107–129.]["The Democratic Party, founded in 1828, is the world's oldest political party" states ] Its main political rival has been the
Republican Party since the 1850s. The party is a
big tent
A big tent party, or catch-all party, is a term used in reference to a political party's policy of permitting or encouraging a broad spectrum of views among its members. This is in contrast to other kinds of parties, which defend a determined i ...
, and though it is often described as
liberal
Liberal or liberalism may refer to:
Politics
* a supporter of liberalism
** Liberalism by country
* an adherent of a Liberal Party
* Liberalism (international relations)
* Sexually liberal feminism
* Social liberalism
Arts, entertainment and m ...
, it is less ideologically uniform than the Republican Party (with major individuals within it frequently holding widely different
political views
An ideology is a set of beliefs or philosophies attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely epistemic, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones." Formerly applied pri ...
) due to the broader list of unique voting blocs that compose it.
The historical predecessor of the Democratic Party is considered to be the
Democratic-Republican Party
The Democratic-Republican Party, known at the time as the Republican Party and also referred to as the Jeffersonian Republican Party among other names, was an American political party founded by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison in the early ...
.
Before 1860, the Democratic Party supported
expansive presidential power,
of
slave states
In the United States before 1865, a slave state was a state in which slavery and the internal or domestic slave trade were legal, while a free state was one in which they were not. Between 1812 and 1850, it was considered by the slave states ...
,
agrarianism
Agrarianism is a political and social philosophy that has promoted subsistence agriculture, smallholdings, and egalitarianism, with agrarian political parties normally supporting the rights and sustainability of small farmers and poor peasants ...
,
and
expansionism
Expansionism refers to states obtaining greater territory through military empire-building or colonialism.
In the classical age of conquest moral justification for territorial expansion at the direct expense of another established polity (who of ...
,
while opposing
a national bank and high
tariff
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government of a country or by a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and poli ...
s.
It split in 1860 over
slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
and won the presidency only twice between 1860 and 1910. In the late 19th century, it continued to oppose high tariffs and had fierce internal debates on the
gold standard
A gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the la ...
. In the early 20th century, it supported
progressive
Progressive may refer to:
Politics
* Progressivism, a political philosophy in support of social reform
** Progressivism in the United States, the political philosophy in the American context
* Progressive realism, an American foreign policy par ...
reforms and opposed
imperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and ...
, with
Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
winning the White House in
1912
Events January
* January 1 – The Republic of China (1912–49), Republic of China is established.
* January 5 – The Prague Conference (6th All-Russian Conference of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party) opens.
* January 6 ...
and
1916
Events
Below, the events of the First World War have the "WWI" prefix.
January
* January 1 – The British Royal Army Medical Corps carries out the first successful blood transfusion, using blood that had been stored and cooled.
* ...
. Since
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
and his
New Deal coalition after 1932, the Democratic Party has promoted a
social liberal
Social liberalism (german: Sozialliberalismus, es, socioliberalismo, nl, Sociaalliberalisme), also known as new liberalism in the United Kingdom, modern liberalism, or simply liberalism in the contemporary United States, left-liberalism ...
platform, including
Social Security
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specificall ...
and
unemployment insurance
Unemployment benefits, also called unemployment insurance, unemployment payment, unemployment compensation, or simply unemployment, are payments made by authorized bodies to unemployed people. In the United States, benefits are funded by a comp ...
.
The
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. Major federal programs agencies included the Civilian Cons ...
attracted strong support for the party from recent European immigrants but caused a decline of the party's conservative pro-business wing. Following the
Great Society
The Great Society was a set of domestic programs in the United States launched by Democratic President Lyndon B. Johnson in 1964–65. The term was first coined during a 1964 commencement address by President Lyndon B. Johnson at the University ...
era of progressive legislation under
Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
, including
Medicare, the
Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
, and the
Voting Rights Act of 1965
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of federal legislation in the United States that prohibits racial discrimination in voting. It was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson during the height of the civil rights movement ...
, the core bases of the parties shifted, with the
Southern states becoming more reliably Republican and the Northeastern states becoming more reliably Democratic.
[ The party's ]labor union
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits ( ...
element has become smaller since the 1970s,Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
's presidency, the election of Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
marked a move for the party toward the Third Way
The Third Way is a centrist political position that attempts to reconcile right-wing and left-wing politics by advocating a varying synthesis of centre-right economic policies with centre-left social policies. The Third Way was born from a ...
, adopting market-oriented economic policies and culturally liberal
Cultural liberalism is a social philosophy which expresses the social dimension of liberalism and advocates the freedom of individuals to choose whether to conform to cultural norms. In the words of Henry David Thoreau, it is often expressed a ...
policies.Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
was the first black president; he oversaw the party's inclusion of same-sex marriage in its platform and its passage of the Affordable Care Act
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and colloquially known as Obamacare, is a landmark U.S. federal statute enacted by the 111th United States Congress and signed into law by Presid ...
.
The Democratic Party's philosophy of modern American liberalism
Modern liberalism in the United States, often simply referred to in the United States as liberalism, is a form of social liberalism found in American politics. It combines ideas of civil liberty and equality with support for social justice and ...
blends notions of civil liberty
Civil liberties are guarantees and freedoms that governments commit not to abridge, either by constitution, legislation, or judicial interpretation, without due process. Though the scope of the term differs between countries, civil liberties may ...
and social equality
Social equality is a state of affairs in which all individuals within a specific society have equal rights, liberties, and status, possibly including civil rights, freedom of expression, autonomy, and equal access to certain public goods and ...
with support for a mixed capitalist economy.[Larry E. Sullivan. ''The SAGE glossary of the social and behavioral sciences'' (2009). p. 291: "This liberalism favors a generous welfare state and a greater measure of social and economic equality. Liberty thus exists when all citizens have access to basic necessities such as education, healthcare, and economic opportunities."] Corporate governance
Corporate governance is defined, described or delineated in diverse ways, depending on the writer's purpose. Writers focused on a disciplinary interest or context (such as accounting, finance, law, or management) often adopt narrow definitions th ...
reform, environmental protection
Environmental protection is the practice of protecting the natural environment by individuals, organizations and governments. Its objectives are to conserve natural resources and the existing natural environment and, where possible, to repair dam ...
, support for organized labor
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and Employee ben ...
, expansion of social programs
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specificall ...
, affordable college tuition
Tuition payments, usually known as tuition in American English and as tuition fees in Commonwealth English, are fees charged by education institutions for instruction or other services. Besides public spending (by governments and other public bo ...
, health care reform
Health care reform is for the most part governmental policy that affects health care delivery in a given place. Health care reform typically attempts to:
* Broaden the population that receives health care coverage through either public sector insur ...
, equal opportunity
Equal opportunity is a state of fairness in which individuals are treated similarly, unhampered by artificial barriers, prejudices, or preferences, except when particular distinctions can be explicitly justified. The intent is that the important ...
, and consumer protection
Consumer protection is the practice of safeguarding buyers of goods and services, and the public, against unfair practices in the marketplace. Consumer protection measures are often established by law. Such laws are intended to prevent business ...
form the core of the party's economic agenda.LGBT rights
Rights affecting lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people vary greatly by country or jurisdiction—encompassing everything from the legal recognition of same-sex marriage to the death penalty for homosexuality.
Notably, , 33 ...
,criminal justice
Criminal justice is the delivery of justice to those who have been accused of committing crimes. The criminal justice system is a series of government agencies and institutions. Goals include the Rehabilitation (penology), rehabilitation of o ...
and immigration reform
Immigration reform is change to the current immigration policy of a country. In its strict definition, ''reform'' means "to change into an improved form or condition, by amending or removing faults or abuses". In the political sense, "immigration ...
, stricter gun laws, abortion rights
Abortion-rights movements, also referred to as pro-choice movements, advocate for the right to have legal access to induced abortion services including elective abortion. They seek to represent and support women who wish to terminate their pre ...
, and the legalization of marijuana
The legality of cannabis for medical and recreational use varies by country, in terms of its possession, distribution, and cultivation, and (in regards to medical) how it can be consumed and what medical conditions it can be used for. These ...
. Since the early 2010s, the Democratic Party has shifted significantly to the left on social, cultural, and religious issues.urban areas
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, t ...
, and college graduates, as well as most racial
A race is a categorization of humans based on shared physical or social qualities into groups generally viewed as distinct within a given society. The term came into common usage during the 1500s, when it was used to refer to groups of variou ...
, religious
Religion is usually defined as a social system, social-cultural system of designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morality, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sacred site, sanctified places, prophecy, prophecie ...
, and sexual minorities
A sexual minority is a group whose sexual identity, sexual orientation, orientation or practices differ from the majority of the surrounding society. Primarily used to refer to lesbian, gay, bisexual, or non-heterosexual individuals, it can als ...
are more likely to support the Democratic Party.government trifecta
A government trifecta is a political situation in which the same political party controls the executive branch and both chambers of the legislative branch in countries that have a bicameral legislature and an executive that is not fused. The t ...
(the presidency and majorities in both the U.S. House
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they ...
and the U.S. Senate
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and powe ...
), as well as 22 state governorships, 17 state legislatures, and 14 state government trifectas. Three of the nine sitting U.S. Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
justices were appointed by Democratic presidents. By registered members (in those states which permit or require registration by party affiliation), the Democratic Party is the largest party in the United States and the third largest in the world. Including the incumbent, Joe Biden, 16 Democrats have served as president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United Stat ...
.
History
 Democratic Party officials often trace its origins to the
Democratic Party officials often trace its origins to the Democratic-Republican Party
The Democratic-Republican Party, known at the time as the Republican Party and also referred to as the Jeffersonian Republican Party among other names, was an American political party founded by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison in the early ...
, founded by Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
, James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
and other influential opponents of the conservative Federalists
The term ''federalist'' describes several political beliefs around the world. It may also refer to the concept of parties, whose members or supporters called themselves ''Federalists''.
History Europe federation
In Europe, proponents of de ...
in 1792.[The party has claimed a founding date of 1792 as noted in S.2047 which passed in the United States Senate in 1991. “ 1992, the Democratic Party of the United States will celebrate the 200th anniversary of its establishment on May 13, 1792.”] That party died out before the modern Democratic Party was organized; the Jeffersonian party also inspired the Whigs and modern Republicans. Historians argue that the modern Democratic Party was first organized in the late 1820s with the election of Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
.[Michael Kazin, ''What It Took to Win: A History of the Democratic Party'' (2022) pp 5, 12.] It was predominately built by Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren ( ; nl, Maarten van Buren; ; December 5, 1782 – July 24, 1862) was an American lawyer and statesman who served as the eighth president of the United States from 1837 to 1841. A primary founder of the Democratic Party (Uni ...
, who assembled a wide cadre of politicians in every state behind war hero Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
of Tennessee, making it the world's oldest active political party.William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan (March 19, 1860 – July 26, 1925) was an American lawyer, orator and politician. Beginning in 1896, he emerged as a dominant force in the History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, running ...
in 1896, the party has generally positioned itself to the left
Left may refer to:
Music
* ''Left'' (Hope of the States album), 2006
* ''Left'' (Monkey House album), 2016
* "Left", a song by Nickelback from the album ''Curb'', 1996
Direction
* Left (direction), the relative direction opposite of right
* L ...
of the Republican Party on economic issues. Democrats have been more liberal on civil rights since 1948, although conservative factions within the Democratic Party that opposed them persisted in the South until the 1960s. On foreign policy, both parties have changed positions several times.
Background
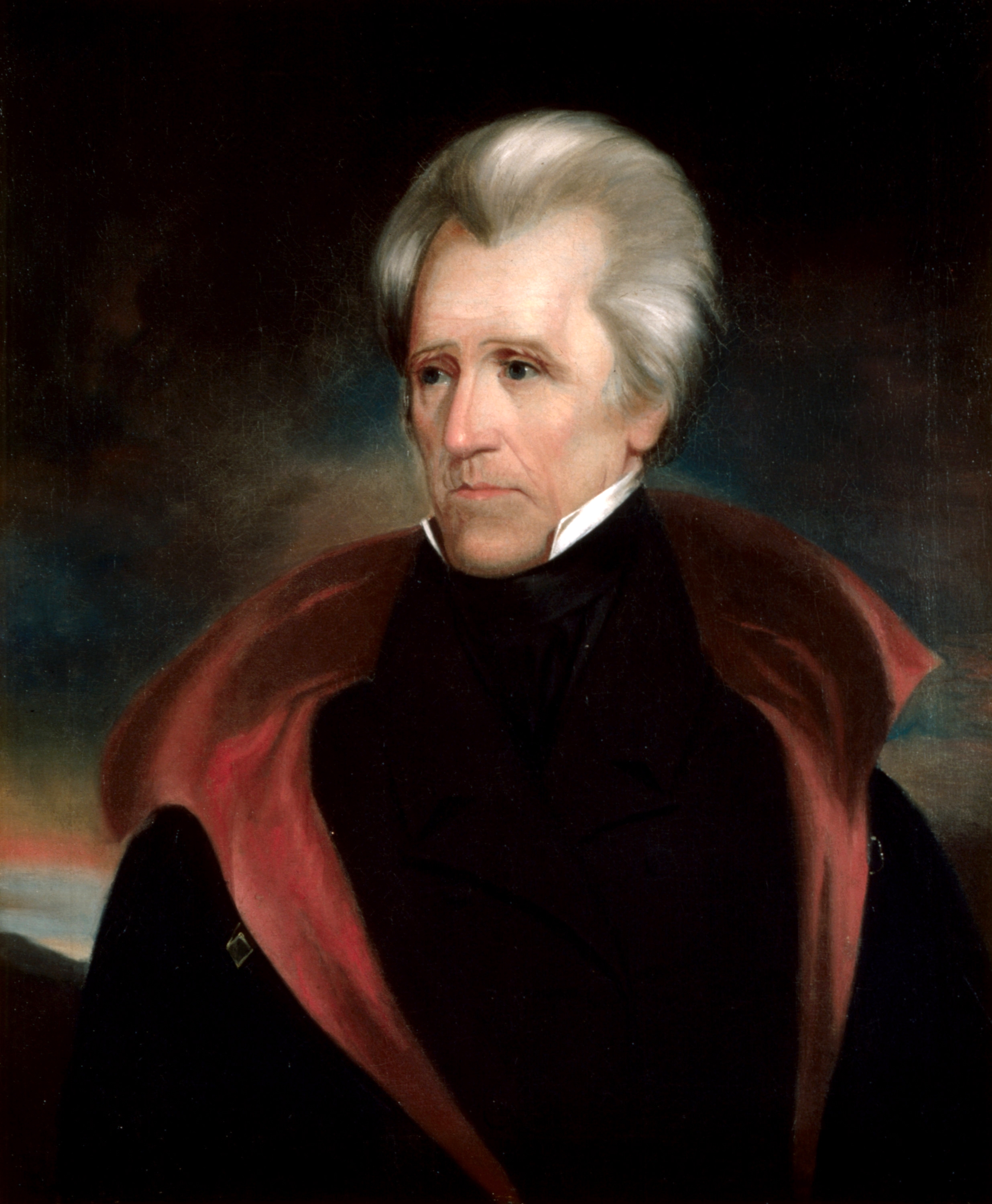 The Democratic Party evolved from the
The Democratic Party evolved from the Jeffersonian Republican
The Democratic-Republican Party, known at the time as the Republican Party and also referred to as the Jeffersonian Republican Party among other names, was an Political parties in the United States, American political party founded by Thomas J ...
or Democratic-Republican Party
The Democratic-Republican Party, known at the time as the Republican Party and also referred to as the Jeffersonian Republican Party among other names, was an American political party founded by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison in the early ...
organized by Jefferson and Madison in opposition to the Federalist Party. The Democratic-Republican Party favored republicanism
Republicanism is a political ideology centered on citizenship in a state organized as a republic. Historically, it emphasises the idea of self-rule and ranges from the rule of a representative minority or oligarchy to popular sovereignty. It ...
; a weak federal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
; states' rights
In American political discourse, states' rights are political powers held for the state governments rather than the federal government according to the United States Constitution, reflecting especially the enumerated powers of Congress and the ...
; agrarian interests (especially Southern planters); and strict adherence to the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of Legal entity, entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When ...
. The party opposed a national bank and Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
. After the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
, the Federalists virtually disappeared and the only national political party left was the Democratic-Republicans, which was prone to splinter along regional lines. The era of one-party rule in the United States, known as the Era of Good Feelings
The Era of Good Feelings marked a period in the political history of the United States that reflected a sense of national purpose and a desire for unity among Americans in the aftermath of the War of 1812. The era saw the collapse of the Fed ...
, lasted from 1816 until 1828, when Andrew Jackson became president. Jackson and Martin Van Buren worked with allies in each state to form a new Democratic Party on a national basis. In the 1830s, the Whig Party coalesced into the main rival to the Democrats.
Before 1860, the Democratic Party supported expansive presidential power,slave states
In the United States before 1865, a slave state was a state in which slavery and the internal or domestic slave trade were legal, while a free state was one in which they were not. Between 1812 and 1850, it was considered by the slave states ...
,agrarianism
Agrarianism is a political and social philosophy that has promoted subsistence agriculture, smallholdings, and egalitarianism, with agrarian political parties normally supporting the rights and sustainability of small farmers and poor peasants ...
,expansionism
Expansionism refers to states obtaining greater territory through military empire-building or colonialism.
In the classical age of conquest moral justification for territorial expansion at the direct expense of another established polity (who of ...
,tariff
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government of a country or by a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and poli ...
s.
19th century
 The
The Democratic-Republican Party
The Democratic-Republican Party, known at the time as the Republican Party and also referred to as the Jeffersonian Republican Party among other names, was an American political party founded by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison in the early ...
split over the choice of a successor to President James Monroe
James Monroe ( ; April 28, 1758July 4, 1831) was an American statesman, lawyer, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, Monroe was ...
. The faction that supported many of the old Jeffersonian principles, led by Andrew Jackson and Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren ( ; nl, Maarten van Buren; ; December 5, 1782 – July 24, 1862) was an American lawyer and statesman who served as the eighth president of the United States from 1837 to 1841. A primary founder of the Democratic Party (Uni ...
, became the modern Democratic Party. Historian Mary Beth Norton
Mary Beth Norton (born 1943) is an American historian, specializing in American colonial history and well known for her work on women's history and the Salem witch trials. She is the Mary Donlon Alger Professor Emeritus of American History at th ...
explains the transformation in 1828:
Behind the platforms issued by state and national parties stood a widely shared political outlook that characterized the Democrats:
Opposing factions led by Henry Clay
Henry Clay Sr. (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American attorney and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the U.S. Senate and House of Representatives. He was the seventh House speaker as well as the ninth secretary of state, al ...
helped form the Whig Party. The Democratic Party had a small yet decisive advantage over the Whigs until the 1850s when the Whigs fell apart over the issue of slavery. In 1854, angry with the Kansas–Nebraska Act
The Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854 () was a territorial organic act that created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska. It was drafted by Democratic Senator Stephen A. Douglas, passed by the 33rd United States Congress, and signed into law by ...
, anti-slavery Democrats left the party and joined Northern Whigs to form the Republican Party.
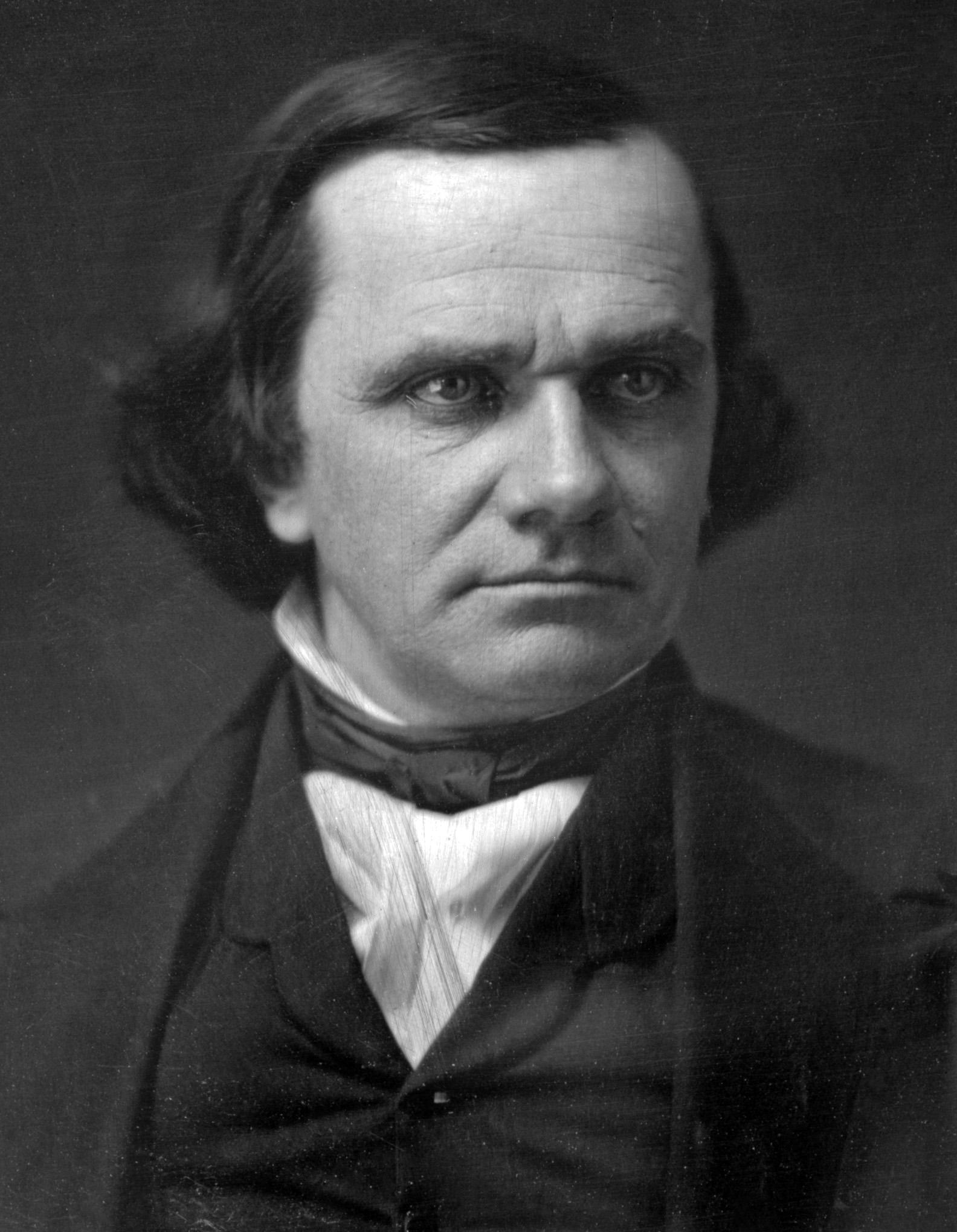 The Democrats split over slavery, with Northern and Southern tickets in the
The Democrats split over slavery, with Northern and Southern tickets in the election of 1860
The following elections occurred in the year 1860. Most notably, the 1860 United States presidential election was one of the events that precipitated the American Civil War.
North America United States
* California's at-large congressional distr ...
, in which the Republican Party gained ascendancy. The radical pro-slavery Fire-Eaters
In American history, the Fire-Eaters were a group of pro-slavery Democrats in the Antebellum South who urged the separation of Southern states into a new nation, which became the Confederate States of America. The dean of the group was Robert R ...
led walkouts at the two conventions when the delegates would not adopt a resolution supporting the extension of slavery into territories even if the voters of those territories did not want it. These Southern Democrats
Southern Democrats, historically sometimes known colloquially as Dixiecrats, are members of the U.S. History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party who reside in the Southern United States. Southern Democrats were generally mu ...
nominated the pro-slavery incumbent vice president
A vice president, also director in British English, is an officer in government or business who is below the president (chief executive officer) in rank. It can also refer to executive vice presidents, signifying that the vice president is on t ...
, John C. Breckinridge
John Cabell Breckinridge (January 16, 1821 – May 17, 1875) was an American lawyer, politician, and soldier. He represented Kentucky in both houses of Congress and became the 14th and youngest-ever vice president of the United States. Serving ...
of Kentucky, for president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
and General Joseph Lane
Joseph "Joe" Lane (December 14, 1801 – April 19, 1881) was an American politician and soldier. He was a state legislator representing Evansville, Indiana, and then served in the Mexican–American War, becoming a general. President James K. P ...
, of Oregon, for vice president. The Northern Democrats
The Northern Democratic Party was a leg of the Democratic Party during the 1860 presidential election, when the party split in two factions because of disagreements over slavery. They held two conventions before the election, in Charleston and ...
nominated Senator Stephen A. Douglas
Stephen Arnold Douglas (April 23, 1813 – June 3, 1861) was an American politician and lawyer from Illinois. A senator, he was one of two nominees of the badly split Democratic Party for president in the 1860 presidential election, which wa ...
of Illinois for president and former Georgia Governor Herschel V. Johnson
Herschel Vespasian Johnson (September 18, 1812August 16, 1880) was an American politician. He was the 41st Governor of Georgia from 1853 to 1857 and the vice presidential nominee of the Douglas wing of the Democratic Party in the 1860 U.S. pre ...
for vice president. This fracturing of the Democrats led to a Republican victory and Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
was elected the 16th president of the United States.[David M. Potter. ''The Impending Crisis, 1848–1861'' (1976). ch. 16.]
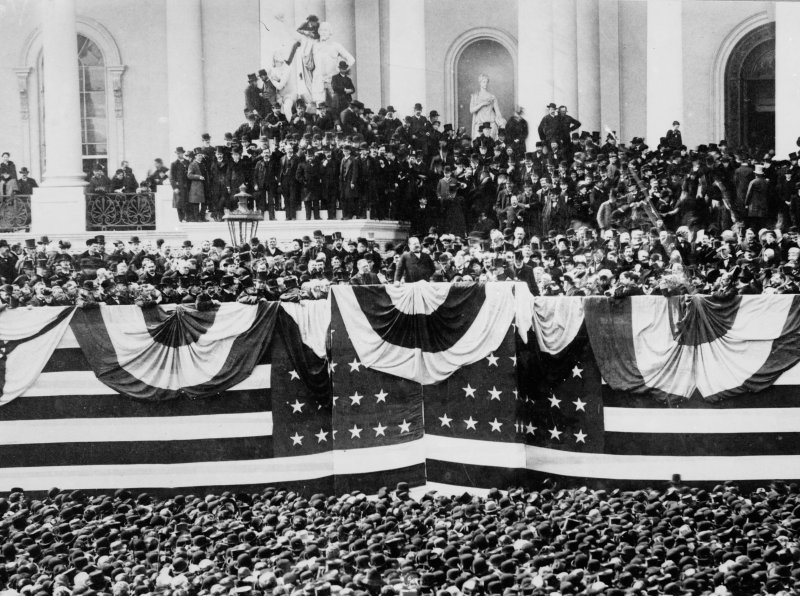 As the
As the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
broke out, Northern Democrats were divided into War Democrats
War Democrats in American politics of the 1860s were members of the Democratic Party who supported the Union and rejected the policies of the Copperheads (or Peace Democrats). The War Democrats demanded a more aggressive policy toward the Con ...
and Peace Democrats
In the 1860s, the Copperheads, also known as Peace Democrats, were a faction of Democrats in the Union who opposed the American Civil War and wanted an immediate peace settlement with the Confederates.
Republicans started calling anti-war De ...
. The Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
deliberately avoided organized political parties. Most War Democrats rallied to Republican President Abraham Lincoln and the Republicans' National Union Party in the election of 1864, which featured Andrew Johnson
Andrew Johnson (December 29, 1808July 31, 1875) was the 17th president of the United States, serving from 1865 to 1869. He assumed the presidency as he was vice president at the time of the assassination of Abraham Lincoln. Johnson was a Dem ...
on the Union ticket to attract fellow Democrats. Johnson replaced Lincoln in 1865, but he stayed independent of both parties.
The Democrats benefited from white Southerners' resentment of Reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
*Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*'' Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Unio ...
after the war and consequent hostility to the Republican Party. After Redeemers
The Redeemers were a political coalition in the Southern United States during the Reconstruction era of the United States, Reconstruction Era that followed the American Civil War, Civil War. Redeemers were the Southern wing of the Democratic Par ...
ended Reconstruction in the 1870s and following the often extremely violent disenfranchisement
Disfranchisement, also called disenfranchisement, or voter disqualification is the restriction of suffrage (the right to vote) of a person or group of people, or a practice that has the effect of preventing a person exercising the right to vote. D ...
of African Americans led by such white supremacist
White supremacy or white supremacism is the belief that white people are superior to those of other Race (human classification), races and thus should dominate them. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any Power (social and polit ...
Democratic politicians as Benjamin Tillman
Benjamin Ryan Tillman (August 11, 1847 – July 3, 1918) was an American politician of the Democratic Party who served as governor of South Carolina from 1890 to 1894, and as a United States Senator from 1895 until his death in 1918. A whit ...
of South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
in the 1880s and 1890s, the South, voting Democratic, became known as the "Solid South
The Solid South or Southern bloc was the electoral voting bloc of the states of the Southern United States for issues that were regarded as particularly important to the interests of Democrats in those states. The Southern bloc existed especial ...
". Although Republicans won all but two presidential elections, the Democrats remained competitive. The party was dominated by pro-business Bourbon Democrat
Bourbon Democrat was a term used in the United States in the later 19th century (1872–1904) to refer to members of the Democratic Party who were ideologically aligned with fiscal conservatism or classical liberalism, especially those who suppo ...
s led by Samuel J. Tilden
Samuel Jones Tilden (February 9, 1814 – August 4, 1886) was an American politician who served as the 25th Governor of New York and was the Democratic candidate for president in the disputed 1876 United States presidential election. Tilden was ...
and Grover Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland (March 18, 1837June 24, 1908) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 22nd and 24th president of the United States from 1885 to 1889 and from 1893 to 1897. Cleveland is the only president in American ...
, who represented mercantile, banking, and railroad interests; opposed imperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and ...
and overseas expansion; fought for the gold standard
A gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the la ...
; opposed bimetallism
Bimetallism, also known as the bimetallic standard, is a monetary standard in which the value of the monetary unit is defined as equivalent to certain quantities of two metals, typically gold and silver, creating a fixed rate of exchange betwee ...
; and crusaded against corruption, high taxes and tariffs. Cleveland was elected to non-consecutive presidential terms in 1884
Events
January–March
* January 4 – The Fabian Society is founded in London.
* January 5 – Gilbert and Sullivan's ''Princess Ida'' premières at the Savoy Theatre, London.
* January 18 – Dr. William Price atte ...
and 1892
Events
January–March
* January 1 – Ellis Island begins accommodating immigrants to the United States.
* February 1 - The historic Enterprise Bar and Grill was established in Rico, Colorado.
* February 27 – Rudolf Diesel applies for ...
.
20th century

Early 20th century
Agrarian Democrats demanding free silver
Free silver was a major economic policy issue in the United States in the late 19th-century. Its advocates were in favor of an expansionary monetary policy featuring the unlimited coinage of silver into money on-demand, as opposed to strict adhe ...
, drawing on Populist ideas, overthrew the Bourbon Democrats in 1896 and nominated William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan (March 19, 1860 – July 26, 1925) was an American lawyer, orator and politician. Beginning in 1896, he emerged as a dominant force in the History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, running ...
for the presidency (a nomination repeated by Democrats in 1900 and 1908). Bryan waged a vigorous campaign attacking Eastern moneyed interests, but he lost to Republican William McKinley
William McKinley (January 29, 1843September 14, 1901) was the 25th president of the United States, serving from 1897 until his assassination in 1901. As a politician he led a realignment that made his Republican Party largely dominant in ...
.
The Democrats took control of the House in 1910, and Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
won election as president in 1912 (when the Republicans split) and 1916. Wilson effectively led Congress to put to rest the issues of tariffs, money, and antitrust, which had dominated politics for 40 years, with new progressive laws. He failed to secure Senate passage of the Versailles Treaty
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
(ending the war with Germany and joining the League of Nations). The weak party was deeply divided by issues such as the KKK and prohibition in the 1920s. However, it did organize new ethnic voters in Northern cities.

Rise of New Deal Coalition (1930s–1960s)
The Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
in 1929 that began under Republican President Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was an American politician who served as the 31st president of the United States from 1929 to 1933 and a member of the Republican Party, holding office during the onset of the Gr ...
and the Republican Congress set the stage for a more liberal government as the Democrats controlled the House of Representatives nearly uninterrupted from 1930 until 1994, the Senate for 44 of 48 years from 1930, and won most presidential elections until 1968. Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
, elected to the presidency in 1932, came forth with federal government programs called the New Deal
The New Deal was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. Major federal programs agencies included the Civilian Cons ...
. New Deal liberalism meant the regulation of business (especially finance and banking) and the promotion of labor unions as well as federal spending to aid the unemployed, help distressed farmers and undertake large-scale public works projects. It marked the start of the American welfare state. The opponents, who stressed opposition to unions, support for business and low taxes, started calling themselves "conservatives".
Until the 1980s, the Democratic Party was a coalition of two parties divided by the Mason–Dixon line: liberal Democrats in the North and culturally conservative voters in the South, who though benefitting from many of the New Deal public works projects opposed increasing civil rights
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' freedom from infringement by governments, social organizations, and private individuals. They ensure one's entitlement to participate in the civil and political life of ...
initiatives advocated by Northeastern liberals. The polarization grew stronger after Roosevelt died. Southern Democrats formed a key part of the bipartisan conservative coalition
The conservative coalition, founded in 1937, was an unofficial alliance of members of the United States Congress which brought together the conservative wings of the Republican and Democratic parties to oppose President Franklin Delano Rooseve ...
in an alliance with most of the Midwestern Republicans. The economically activist philosophy of Franklin D. Roosevelt, which has strongly influenced American liberalism
Liberalism in the United States is a political and moral philosophy based on concepts of unalienable rights of the individual. The fundamental liberal ideals of freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of religion, the separation of chu ...
, shaped much of the party's economic agenda after 1932. From the 1930s to the mid-1960s, the liberal New Deal coalition usually controlled the presidency while the conservative coalition usually controlled Congress.
1960s–1980s, collapse of New Deal Coalition
Issues facing parties and the United States after World War II included the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
and the civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, Racial discrimination ...
. Republicans attracted conservatives and, after the 1960s, white Southerners from the Democratic coalition with their use of the Southern strategy
In American politics, the Southern strategy was a Republican Party electoral strategy to increase political support among white voters in the South by appealing to racism against African Americans. As the civil rights movement and dismantling of ...
and resistance to New Deal and Great Society
The Great Society was a set of domestic programs in the United States launched by Democratic President Lyndon B. Johnson in 1964–65. The term was first coined during a 1964 commencement address by President Lyndon B. Johnson at the University ...
liberalism. Until the 1950s, African Americans had traditionally supported the Republican Party because of its anti-slavery civil rights policies. Following the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
and Voting Rights Act of 1965
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of federal legislation in the United States that prohibits racial discrimination in voting. It was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson during the height of the civil rights movement ...
, the Southern states became more reliably Republican in presidential politics, while Northeastern states became more reliably Democratic. The election of President
The election of President John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination ...
from Massachusetts in 1960 partially reflected this shift. In the campaign, Kennedy attracted a new generation of younger voters. In his agenda dubbed the New Frontier
The term ''New Frontier'' was used by Democratic presidential candidate John F. Kennedy in his acceptance speech in the 1960 United States presidential election to the Democratic National Convention at the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum as the D ...
, Kennedy introduced a host of social programs and public works projects, along with enhanced support of the space program
A space program is an organized effort by a government or a company with a goal related to outer space.
Lists of space programs include:
* List of government space agencies
* List of private spaceflight companies
* List of human spaceflight prog ...
, proposing a crewed spacecraft trip to the moon by the end of the decade. He pushed for civil rights initiatives and proposed the Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
, but with his assassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
in November 1963, he was not able to see its passage.
Kennedy's successor Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
was able to persuade the largely conservative Congress to pass the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and with a more progressive Congress in 1965 passed much of the Great Society
The Great Society was a set of domestic programs in the United States launched by Democratic President Lyndon B. Johnson in 1964–65. The term was first coined during a 1964 commencement address by President Lyndon B. Johnson at the University ...
, including Medicare, which consisted of an array of social programs designed to help the poor, sick, and elderly. Kennedy and Johnson's advocacy of civil rights further solidified black support for the Democrats but had the effect of alienating Southern whites who would eventually gravitate toward the Republican Party, particularly after the election of Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
to the presidency in 1980. The United States' involvement in the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
in the 1960s was another divisive issue that further fractured the fault lines of the Democrats' coalition. After the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution
The Gulf of Tonkin Resolution or the Southeast Asia Resolution, , was a joint resolution that the United States Congress passed on August 7, 1964, in response to the Gulf of Tonkin incident.
It is of historic significance because it gave U.S. p ...
in 1964, President Johnson committed a large contingency of combat troops to Vietnam, but the escalation failed to drive the Viet Cong
,
, war = the Vietnam War
, image = FNL Flag.svg
, caption = The flag of the Viet Cong, adopted in 1960, is a variation on the flag of North Vietnam. Sometimes the lower stripe was green.
, active ...
from South Vietnam, resulting in an increasing quagmire, which by 1968 had become the subject of widespread anti-war protests in the United States and elsewhere. With increasing casualties and nightly news reports bringing home troubling images from Vietnam, the costly military engagement became increasingly unpopular, alienating many of the kinds of young voters that the Democrats had attracted in the early 1960s. The protests that year along with assassinations of Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. (born Michael King Jr.; January 15, 1929 – April 4, 1968) was an American Baptist minister and activist, one of the most prominent leaders in the civil rights movement from 1955 until his assassination in 1968 ...
and Democratic presidential candidate Senator Robert F. Kennedy
Robert Francis Kennedy (November 20, 1925June 6, 1968), also known by his initials RFK and by the nickname Bobby, was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 64th United States Attorney General from January 1961 to September 1964, ...
(younger brother of John F. Kennedy) climaxed in turbulence at the hotly-contested Democratic National Convention
The Democratic National Convention (DNC) is a series of presidential nominating conventions held every four years since 1832 by the United States Democratic Party. They have been administered by the Democratic National Committee since the 1852 ...
that summer in Chicago (which amongst the ensuing turmoil inside and outside of the convention hall nominated Vice President Hubert Humphrey
Hubert Horatio Humphrey Jr. (May 27, 1911 – January 13, 1978) was an American pharmacist and politician who served as the 38th vice president of the United States from 1965 to 1969. He twice served in the United States Senate, representing Mi ...
) in a series of events that proved to mark a significant turning point in the decline of the Democratic Party's broad coalition.
Republican presidential nominee Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California and was ...
was able to capitalize on the confusion of the Democrats that year, and won the 1968 election to become the 37th president. He won re-election in a landslide
Landslides, also known as landslips, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, deep-seated grade (slope), slope failures, mudflows, and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of ...
in 1972 against Democratic nominee George McGovern
George Stanley McGovern (July 19, 1922 – October 21, 2012) was an American historian and South Dakota politician who was a U.S. representative and three-term U.S. senator, and the Democratic Party presidential nominee in the 1972 pres ...
, who like Robert F. Kennedy, reached out to the younger anti-war and counterculture voters, but unlike Kennedy, was not able to appeal to the party's more traditional white working-class constituencies. During Nixon's second term, his presidency was rocked by the Watergate
The Watergate scandal was a major political scandal in the United States involving the administration of President Richard Nixon from 1972 to 1974 that led to Nixon's resignation. The scandal stemmed from the Nixon administration's continual ...
scandal, which forced him to resign in 1974. He was succeeded by vice president Gerald Ford
Gerald Rudolph Ford Jr. ( ; born Leslie Lynch King Jr.; July 14, 1913December 26, 2006) was an American politician who served as the 38th president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. He was the only president never to have been elected ...
, who served a brief tenure. Watergate offered the Democrats an opportunity to recoup, and their nominee Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (born October 1, 1924) is an American politician who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he previously served as th ...
won the 1976 presidential election. With the initial support of evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide Interdenominationalism, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being "bor ...
Christian voters in the South, Carter was temporarily able to reunite the disparate factions within the party, but inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reductio ...
and the Iran Hostage Crisis
On November 4, 1979, 52 United States diplomats and citizens were held hostage after a group of militarized Iranian college students belonging to the Muslim Student Followers of the Imam's Line, who supported the Iranian Revolution, took over t ...
of 1979–1980 took their toll, resulting in a landslide
Landslides, also known as landslips, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, deep-seated grade (slope), slope failures, mudflows, and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of ...
victory for Republican presidential nominee Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
in 1980, which shifted the political landscape in favor of the Republicans for years to come.
1990s and Third Way centrism
 With the ascendancy of the Republicans under Ronald Reagan, the Democrats searched for ways to respond yet were unable to succeed by running traditional candidates, such as former vice president and Democratic presidential nominee
With the ascendancy of the Republicans under Ronald Reagan, the Democrats searched for ways to respond yet were unable to succeed by running traditional candidates, such as former vice president and Democratic presidential nominee Walter Mondale
Walter Frederick "Fritz" Mondale (January 5, 1928 – April 19, 2021) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 42nd vice president of the United States from 1977 to 1981 under President Jimmy Carter. A U.S. senator from Minnesota ...
, who lost to Reagan in the 1984 presidential election. Many Democrats attached their hopes to the future star of Gary Hart
Gary Warren Hart (''né'' Hartpence; born November 28, 1936) is an American politician, diplomat, and lawyer. He was the front-runner for the 1988 Democratic presidential nomination until he dropped out amid revelations of extramarital affairs. ...
, who had challenged Mondale in the 1984 primaries running on a theme of "New Ideas"; and in the subsequent 1988 primaries became the de facto front-runner and virtual "shoo-in" for the Democratic presidential nomination before a sex scandal ended his campaign. The party nevertheless began to seek out a younger generation of leaders, who like Hart had been inspired by the pragmatic idealism of John F. Kennedy.
Arkansas governor Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
was one such figure, who was elected president in 1992 as the Democratic nominee. The Democratic Leadership Council
The Democratic Leadership Council (DLC) was founded in 1985 and closed in 2011. Founded and directed by Al From, prominent members include Arkansas Governor Bill Clinton (who was elected president in 1992 and 1996), Delaware Senator Joe Biden (e ...
was a campaign organization connected to Clinton that advocated a realignment and triangulation
In trigonometry and geometry, triangulation is the process of determining the location of a point by forming triangles to the point from known points.
Applications
In surveying
Specifically in surveying, triangulation involves only angle me ...
under the re-branded "New Democrat
New Democrats, also known as centrist Democrats, Clinton Democrats, or moderate Democrats, are a centrist ideological faction within the Democratic Party in the United States. As the Third Way faction of the party, they are seen as culturall ...
" label.neoliberal
Neoliberalism (also neo-liberalism) is a term used to signify the late 20th century political reappearance of 19th-century ideas associated with free-market capitalism after it fell into decline following the Second World War. A prominent fa ...
economic policies
The economy of governments covers the systems for setting levels of taxation, government budgets, the money supply and interest rates as well as the labour market, national ownership, and many other areas of government interventions into the e ...
with cultural liberalism
Cultural liberalism is a social philosophy which expresses the social dimension of liberalism and advocates the freedom of individuals to choose whether to conform to cultural norms. In the words of Henry David Thoreau, it is often expressed a ...
, with the voter base after Reagan having shifted considerably to the right
Rights are law, legal, social, or ethics, ethical principles of Liberty, freedom or entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people according to some legal system, social convent ...
.balanced budget
A balanced budget (particularly that of a government) is a budget in which revenues are equal to expenditures. Thus, neither a budget deficit nor a budget surplus exists (the accounts "balance"). More generally, it is a budget that has no budge ...
and market economy
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand, where all suppliers and consumers ...
tempered by government intervention
Economic interventionism, sometimes also called state interventionism, is an economic policy position favouring government intervention in the market process with the intention of correcting market failures and promoting the general welfare of ...
(mixed economy
A mixed economy is variously defined as an economic system blending elements of a market economy with elements of a planned economy, markets with state interventionism, or private enterprise with public enterprise. Common to all mixed economi ...
), along with a continued emphasis on social justice
Social justice is justice in terms of the distribution of wealth, opportunities, and privileges within a society. In Western and Asian cultures, the concept of social justice has often referred to the process of ensuring that individuals fu ...
and affirmative action. The economic policy adopted by the Democratic Party, including the former Clinton administration
Bill Clinton's tenure as the 42nd president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1993, and ended on January 20, 2001. Clinton, a Democrat from Arkansas, took office following a decisive election victory over Re ...
, has been referred to as "Third Way
The Third Way is a centrist political position that attempts to reconcile right-wing and left-wing politics by advocating a varying synthesis of centre-right economic policies with centre-left social policies. The Third Way was born from a ...
".
The Democrats lost control of Congress in the election of 1994 to the Republican Party. Re-elected in 1996, Clinton was the first Democratic president since Franklin D. Roosevelt to be elected to two terms.
21st century
2000s
In the wake of the 2001 terrorist attacks
The following is a list of terrorist incidents that have not been carried out by a state or its forces (see state terrorism and state-sponsored terrorism). Assassinations are listed at List of assassinated people.
Definitions of terrori ...
on the World Trade Center
World Trade Centers are sites recognized by the World Trade Centers Association.
World Trade Center may refer to:
Buildings
* List of World Trade Centers
* World Trade Center (2001–present), a building complex that includes five skyscrapers, a ...
and the Pentagon
The Pentagon is the headquarters building of the United States Department of Defense. It was constructed on an accelerated schedule during World War II. As a symbol of the U.S. military, the phrase ''The Pentagon'' is often used as a metony ...
as well as the growing concern over global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
, some of the party's key issues in the early 21st century have included combating terrorism
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violen ...
while preserving human rights
Human rights are Morality, moral principles or Social norm, normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for ce ...
, expanding access to health care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
, labor rights
Labor rights or workers' rights are both legal rights and human rights relating to labor relations between workers and employers. These rights are codified in national and international labor and employment law. In general, these rights influen ...
, and environmental protection. Democrats regained majority control of both the House and the Senate in the 2006 elections. Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
won the Democratic Party's nomination and was elected as the first African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
president in 2008. Under the Obama presidency, the party moved forward reforms including an economic stimulus
In economics, stimulus refers to attempts to use monetary policy or fiscal policy (or stabilization policy in general) to stimulate the economy. Stimulus can also refer to monetary policies such as lowering interest rates and quantitative easi ...
package, the Dodd–Frank financial reform act, and the Affordable Care Act
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and colloquially known as Obamacare, is a landmark U.S. federal statute enacted by the 111th United States Congress and signed into law by Presid ...
.
2010s
In the 2010 midterm elections
The 2010 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 2, 2010, in the middle of Democratic President Barack Obama's first term. Republicans ended unified Democratic control of Congress and the presidency by winning a majority in the H ...
, the Democratic Party lost control of the House and lost its majority in state legislatures and state governorships. In the 2012 elections, President Obama was re-elected, but the party remained in the minority in the House of Representatives and lost control of the Senate in the 2014 midterm elections. After the 2016 election of Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021.
Trump graduated from the Wharton School of the University of Pe ...
, the Democratic Party transitioned into the role of an opposition party and held neither the presidency nor the Senate but won back a majority in the House in the 2018 midterm elections
The 2018 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 6, 2018. These midterm elections occurred during Republican Donald Trump's term. Democrats made a net gain of 41 seats in the United States House of Representatives, gaining a majo ...
. Democrats were extremely critical of President Trump, particularly his policies on immigration, healthcare, and abortion, as well as his response to the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
.
2020s
Since the early 2010s, the party has shifted significantly to the left on social, cultural, and religious issues and attracted support from college-educated white Americans.2020 presidential election
This national electoral calendar for 2020 lists the national/federal elections held in 2020 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.
January
*5 January:
**C ...
. He began his term with narrow Democratic majorities in the House and the Senate. The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022
The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (IRA) is a landmark United States federal law which aims to curb inflation by reducing the deficit, lowering prescription drug prices, and investing into domestic energy production while promoting clean ener ...
was negotiated by Biden, Majority Leader Chuck Schumer
Charles Ellis Schumer ( ; born November 23, 1950) is an American politician serving as Senate Majority Leader since January 20, 2021. A member of the Democratic Party, Schumer is in his fourth Senate term, having held his seat since 1999, and ...
, Joe Manchin
Joseph Manchin III (born August 24, 1947) is an American politician and businessman serving as the senior United States senator from West Virginia, a seat he has held since 2010. A member of the Democratic Party, Manchin was the 34th governor of ...
, Kyrsten Sinema
Kyrsten Lea Sinema (; born July 12, 1976) is an American politician and former social worker serving as the senior United States senator from Arizona since January 2019. A former member of the Democratic Party, Sinema became an independent in ...
and other Democrats and is the largest allocation of funds for climate to date.
Name and symbols
The Democratic-Republican Party
The Democratic-Republican Party, known at the time as the Republican Party and also referred to as the Jeffersonian Republican Party among other names, was an American political party founded by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison in the early ...
splintered in 1824 into the short-lived National Republican Party
The National Republican Party, also known as the Anti-Jacksonian Party or simply Republicans, was a political party in the United States that evolved from a conservative-leaning faction of the Democratic-Republican Party that supported John Qu ...
and the Jacksonian movement which in 1828 became the Democratic Party. Under the Jacksonian era, the term "The Democracy" was in use by the party, but the name "Democratic Party" was eventually settled upon and became the official name in 1844. Members of the party are called "Democrats" or "Dems".
The term "Democrat Party" has also been in local use but has usually been used by opponents since 1952 as a disparaging term.
The most common mascot symbol for the party has been the donkey
The domestic donkey is a hoofed mammal in the family Equidae, the same family as the horse. It derives from the African wild ass, ''Equus africanus'', and may be classified either as a subspecies thereof, ''Equus africanus asinus'', or as a ...
, or jackass. Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
's enemies twisted his name to "jackass" as a term of ridicule regarding a stupid and stubborn animal. However, the Democrats liked the common-man implications and picked it up too, therefore the image persisted and evolved. Its most lasting impression came from the cartoons of Thomas Nast
Thomas Nast (; ; September 26, 1840December 7, 1902) was a German-born American caricaturist and editorial cartoonist often considered to be the "Father of the American Cartoon".
He was a critic of Democratic Party (United States), Democratic U ...
from 1870 in ''Harper's Weekly
''Harper's Weekly, A Journal of Civilization'' was an American political magazine based in New York City. Published by Harper & Brothers from 1857 until 1916, it featured foreign and domestic news, fiction, essays on many subjects, and humor, ...
''. Cartoonists followed Nast and used the donkey to represent the Democrats and the elephant to represent the History of the Republican Party (United States), Republicans.
In the early 20th century, the traditional symbol of the Democratic Party in Indiana, Kentucky, Oklahoma and Ohio was the rooster, as opposed to the Republican eagle. This symbol still appears on Oklahoma, Kentucky, Indiana, and West Virginia ballots. The rooster was adopted as the official symbol of the national Democratic Party. In New York (state), New York, the Democratic ballot symbol is a five-pointed star.
Although both major political parties (and many minor ones) use the traditional American colors of red, white, and blue in their marketing and representations, since 2000 United States presidential election, election night 2000 blue has become the identifying color for the Democratic Party while red has become the identifying color for the Republican Party. That night, for the first time all major broadcast television networks used the same color scheme for the electoral map: Red states and blue states, blue states for Al Gore (Democratic nominee) and red states for George W. Bush (Republican nominee). Since then, the color blue has been widely used by the media to represent the party. This is contrary to common practice outside of the United States where blue is the traditional color of the right-wing politics, right and red the color of the left-wing politics, left.Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
and Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
, whom the party regards as its distinguished early leaders.
The song "Happy Days Are Here Again" is the unofficial song of the Democratic Party. It was used prominently when Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
was nominated for president at the 1932 Democratic National Convention and remains a sentimental favorite for Democrats today. For example, Paul Shaffer played the theme on the ''Late Show with David Letterman'' after the Democrats won Congress in 2006. "Don't Stop (Fleetwood Mac song), Don't Stop" by Fleetwood Mac was adopted by Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
's presidential campaign in 1992 and has endured as a popular Democratic song. The emotionally similar song "Beautiful Day" by the band U2 has also become a favorite theme song for Democratic candidates. John Kerry used the song during his 2004 presidential campaign and several Democratic Congressional candidates used it as a celebratory tune in 2006.
As a traditional anthem for its presidential nominating convention, Aaron Copland's "Fanfare for the Common Man" is traditionally performed at the beginning of the Democratic National Convention.
Current structure and composition
National committee
The Democratic National Committee (DNC) is responsible for promoting Democratic campaign activities. While the DNC is responsible for overseeing the process of writing the Democratic Platform, the DNC is more focused on campaign and organizational strategy than public policy. In presidential elections, it supervises the Democratic National Convention. The national convention is subject to the charter of the party and the ultimate authority within the Democratic Party when it is in session, with the DNC running the party's organization at other times. The DNC is chaired by Jaime Harrison.
State parties
Each state also has a state committee, made up of elected committee members as well as ex officio committee members (usually elected officials and representatives of major constituencies), which in turn elects a chair. County, town, city, and ward committees generally are composed of individuals elected at the local level. State and local committees often coordinate campaign activities within their jurisdiction, oversee local conventions, and in some cases primaries or caucuses, and may have a role in nominating candidates for elected office under state law. Rarely do they have much funding, but in 2005 DNC Chairman Dean began a program (called the "50 State Strategy") of using DNC national funds to assist all state parties and pay for full-time professional staffers.
Major party groups
 The Democratic Congressional Campaign Committee (DCCC) assists party candidates in House races and its current chairman (selected by the party caucus) is Representative Sean Patrick Maloney of New York. Similarly, the Democratic Senatorial Campaign Committee (DSCC), headed by Senator Gary Peters of Michigan, raises funds for Senate races. The Democratic Legislative Campaign Committee (DLCC), chaired by Majority Leader of the New York State Senate Andrea Stewart-Cousins, is a smaller organization that focuses on state legislative races. The DNC sponsors the College Democrats of America (CDA), a student-outreach organization with the goal of training and engaging a new generation of Democratic activists. Democrats Abroad is the organization for Americans living outside the United States. They work to advance the party's goals and encourage Americans living abroad to support the Democrats. The Young Democrats of America (YDA) and the High School Democrats of America (HSDA) are young adult and youth-led organizations respectively that attempt to draw in and mobilize young people for Democratic candidates but operates outside of the DNC. The Democratic Governors Association (DGA) is an organization supporting the candidacies of Democratic gubernatorial nominees and incumbents. Likewise, the mayors of the largest cities and urban centers convene as the National Conference of Democratic Mayors.
The Democratic Congressional Campaign Committee (DCCC) assists party candidates in House races and its current chairman (selected by the party caucus) is Representative Sean Patrick Maloney of New York. Similarly, the Democratic Senatorial Campaign Committee (DSCC), headed by Senator Gary Peters of Michigan, raises funds for Senate races. The Democratic Legislative Campaign Committee (DLCC), chaired by Majority Leader of the New York State Senate Andrea Stewart-Cousins, is a smaller organization that focuses on state legislative races. The DNC sponsors the College Democrats of America (CDA), a student-outreach organization with the goal of training and engaging a new generation of Democratic activists. Democrats Abroad is the organization for Americans living outside the United States. They work to advance the party's goals and encourage Americans living abroad to support the Democrats. The Young Democrats of America (YDA) and the High School Democrats of America (HSDA) are young adult and youth-led organizations respectively that attempt to draw in and mobilize young people for Democratic candidates but operates outside of the DNC. The Democratic Governors Association (DGA) is an organization supporting the candidacies of Democratic gubernatorial nominees and incumbents. Likewise, the mayors of the largest cities and urban centers convene as the National Conference of Democratic Mayors.
Ideology
Upon foundation, the Democratic Party supported agrarianism
Agrarianism is a political and social philosophy that has promoted subsistence agriculture, smallholdings, and egalitarianism, with agrarian political parties normally supporting the rights and sustainability of small farmers and poor peasants ...
and the Jacksonian democracy movement of President Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
, representing farmers and rural interests and traditional Jeffersonian democracy, Jeffersonian democrats. Since the 1890s, especially in northern states, the party began to favor more liberal positions (the term "liberal" in this sense describes Modern liberalism in the United States, modern liberalism, rather than classical liberalism or economic liberalism). In recent exit polls, the Democratic Party has had broad appeal across all socio-ethno-economic demographics.social programs
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specificall ...
targeted at the poor. The party had a Fiscal conservatism, fiscally conservative, Economic liberalism, pro-business wing, typified by Grover Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland (March 18, 1837June 24, 1908) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 22nd and 24th president of the United States from 1885 to 1889 and from 1893 to 1897. Cleveland is the only president in American ...
and Al Smith, and a Southern Democrats, Southern conservative wing that shrank after President Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
supported the Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
. The major influences for liberalism were labor unions (which peaked in the 1936–1952 era) and African Americans. Environmentalism has been a major component since the 1970s. The 21st century Democratic Party is predominantly a coalition of centrists, liberals, and progressives, with significant overlap between the three groups. Political scientists characterize the Democratic Party as less ideologically cohesive than the Republican Party due to the broader diversity of coalitions that compose the Democratic Party.
Centrists
Centrist Democrats, or New Democrats, are an ideologically Centrism, centrist faction within the Democratic Party that emerged after the victory of Republican Party (United States), Republican George H. W. Bush in the 1988 United States presidential election, 1988 presidential election. They are an economically Economic liberalism, liberal and "Third Way
The Third Way is a centrist political position that attempts to reconcile right-wing and left-wing politics by advocating a varying synthesis of centre-right economic policies with centre-left social policies. The Third Way was born from a ...
" faction which dominated the party for around 20 years starting in the late 1980s after the United States populace turned much further to the political right. They are represented by organizations such as the New Democrat Network and the New Democrat Coalition. The New Democrat Coalition is a pro-growth and fiscally moderate congressional coalition.
One of the most influential centrist groups was the Democratic Leadership Council
The Democratic Leadership Council (DLC) was founded in 1985 and closed in 2011. Founded and directed by Al From, prominent members include Arkansas Governor Bill Clinton (who was elected president in 1992 and 1996), Delaware Senator Joe Biden (e ...
(DLC), a nonprofit organization that advocated centrist positions for the party. The DLC hailed President Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
as proof of the viability of "Third Way" politicians and a DLC success story. The DLC disbanded in 2011 and much of the former DLC is now represented in the think tank Third Way (United States), Third Way.
Some Democratic elected officials have self-declared as being centrists, including former President Bill Clinton, former Vice President Al Gore, Senator Mark Warner, former Pennsylvania governor Ed Rendell, former Senator Jim Webb, President Joe Biden, congresswoman Ann Kirkpatrick, and former congressman Dave McCurdy.Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
was self-described as a New Democrat.
Conservatives
A conservative Democrat is a member of the Democratic Party with Conservatism in the United States, conservative political views, or with views relatively conservative with respect to those of the national party. While such members of the Democratic Party can be found throughout the nation, actual elected officials are disproportionately found within the Southern United States, Southern states and to a lesser extent within Rural United States, rural regions of the United States generally, more commonly in the Western United States, West. Historically, Southern Democrats were generally much more ideologically conservative than conservative Democrats are now.
 Many conservative Southern Democrats defected to the Republican Party, beginning with the passage of the
Many conservative Southern Democrats defected to the Republican Party, beginning with the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
and the general leftward shift of the party. Strom Thurmond of South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
, Billy Tauzin of Louisiana, Kent Hance and Ralph Hall of Texas and Richard Shelby of Alabama are examples of this. The influx of conservative Democrats into the Republican Party is often cited as a reason for the Republican Party's shift further to the right during the late 20th century as well as the shift of its base from the Northeast and Midwest to the South.
Into the 1980s, the Democratic Party had a conservative element, mostly from the South and Border regions. Their numbers declined sharply as the Republican Party built up its Southern base. They were sometimes humorously called "Yellow dog Democrats", or "Boll weevil (politics), boll weevils" and "Dixiecrats". In the United States House of Representatives, House, they form the Blue Dog Coalition, a caucus of conservatives and centrists willing to broker compromises with the Republican leadership. They have acted as a unified voting bloc in the past, giving its members some ability to change legislation, depending on their numbers in Congress.
Split-ticket voting was common among conservative Southern Democrats in the 1970s and 1980s. These voters supported conservative Democrats for local and statewide office while simultaneously voting for Republican presidential candidates.
Liberals
Social liberalism, Social liberals (Modern liberalism in the United States, modern liberals) are a large portion of the Democratic base. According to 2018 exit polls, liberals constituted 27% of the electorate, and 91% of American liberals favored the candidate of the Democratic Party.
Progressives
Progressivism in the United States, Progressives are the most left-leaning faction in the party and support strong business regulations, social programs
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specificall ...
, and workers' rights. Progressive ideological stances have much in common with the programs of European countries as well as many East Asian countries. Many progressive Democrats are descendants of the New Left of Democratic presidential candidate Senator George McGovern
George Stanley McGovern (July 19, 1922 – October 21, 2012) was an American historian and South Dakota politician who was a U.S. representative and three-term U.S. senator, and the Democratic Party presidential nominee in the 1972 pres ...
of South Dakota whereas others were involved in the Bernie Sanders 2016 presidential campaign, 2016 presidential candidacy of Vermont Senator Bernie Sanders. Progressives are often considered to have ideas similar to social democracy due to heavy inspiration from the nordic model, believing in federal top marginal income taxes ranging from 52% to 70%, rent control, increased collective bargaining power, a $15 an hour minimum wage, as well as free tuition and Universal Healthcare (typically Single-payer healthcare, Medicare for All).
In 2014, progressive Senator Elizabeth Warren set out "Eleven Commandments of Progressivism": tougher regulation on corporations, affordable education, scientific investment and environmentalism, net neutrality, increased wages, equal pay for women, collective bargaining rights, defending social programs, same-sex marriage, Immigration reform in the US, immigration reform, and unabridged access to reproductive healthcare. In addition, progressives strongly oppose political corruption and seek to advance electoral reforms such as campaign finance rules and voting rights protections. Today, many progressives have made combating Economic inequality in the United States, economic inequality their top priority.
The Congressional Progressive Caucus (CPC) is a caucus of progressive Democrats chaired by Pramila Jayapal of Washington (state), Washington. Its members have included Representatives Dennis Kucinich of Ohio, John Conyers of Michigan, Jim McDermott of Washington (state), Washington, Barbara Lee of California, and Senator Paul Wellstone of Minnesota. Senators Sherrod Brown of Ohio, Tammy Baldwin of Wisconsin, Mazie Hirono of Hawaii, and Ed Markey of Massachusetts were members of the caucus when in the House of Representatives. While no Democratic senators currently belong to the CPC, independent Senator Bernie Sanders is a member.
Political positions
; Economic policy:
* Expand Social Security
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specificall ...
and safety net programs.
* Increase the Capital gains tax in the United States, capital gains tax rate to 39.6% for taxpayers with annual income above $1 million.
* Cut taxes for the working and middle classes as well as small businesses.
Economic issues
Equal opportunity employment, Equal economic opportunity, a social safety net, and strong Labor unions in the United States, labor unions have historically been at the heart of Democratic economic policy.Social Security
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specificall ...
, universal health care, Education in the United States, public education, and Subsidized housing in the United States, subsidized housing.
Fiscal policy
Democrats support a more progressive tax structure to provide more services and reduce economic inequality by making sure that the wealthiest Americans pay the highest amount in taxes.Social Security
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specificall ...
, Medicare, and Medicaid, believing it to be harmful to efficiency and social justice
Social justice is justice in terms of the distribution of wealth, opportunities, and privileges within a society. In Western and Asian cultures, the concept of social justice has often referred to the process of ensuring that individuals fu ...
. Democrats believe the benefits of social services in monetary and non-monetary terms are a more Productive and unproductive labour, productive labor force and cultured population and believe that the benefits of this are greater than any benefits that could be derived from lower taxes, especially on top earners, or cuts to social services. Furthermore, Democrats see social services as essential toward providing Positive liberty, positive freedom, freedom derived from economic opportunity. The Democratic-led House of Representatives reinstated the PAYGO (pay-as-you-go) budget rule at the start of the 110th United States Congress, 110th Congress.
Minimum wage
The Democratic Party favors raising the minimum wage. The Fair Minimum Wage Act of 2007 was an early component of the Democrats' agenda during the 110th United States Congress, 110th Congress. In 2006, the Democrats supported six state ballot initiatives to increase the minimum wage and all six initiatives passed.
Health care
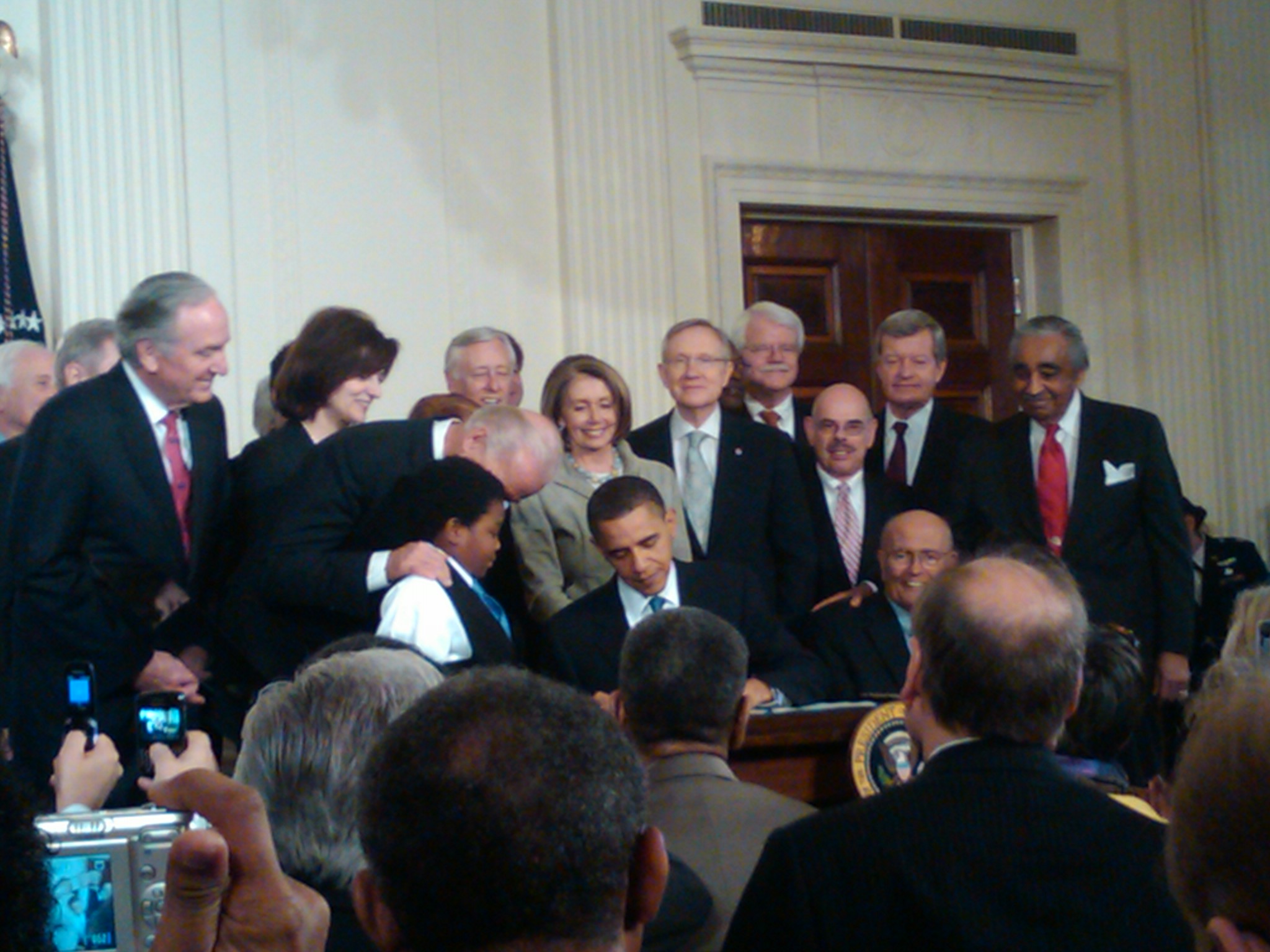 Democrats call for "affordable and quality health care" and favor moving toward universal health care in a variety of forms to address rising healthcare costs. Some Democratic politicians favor a single-payer health care, single-payer program or Medicare for All, while others prefer creating a public health insurance option.
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, signed into law by President
Democrats call for "affordable and quality health care" and favor moving toward universal health care in a variety of forms to address rising healthcare costs. Some Democratic politicians favor a single-payer health care, single-payer program or Medicare for All, while others prefer creating a public health insurance option.
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, signed into law by President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
on March 23, 2010, has been one of the most significant pushes for universal health care. As of December 2019, more than 20 million Americans have gained health insurance under the Affordable Care Act.
Education
Democrats favor improving public education by raising school standards and reforming the Head Start (program), Head Start program. They also support universal preschool and expanding access to primary education, including through charter schools. They call for addressing student loan debt and reforms to reduce college tuition. Other proposals have included tuition-free public universities and reform of standardized testing. Democrats have the long-term aim of having publicly funded college education with low tuition fees (like in much of Europe and Canada), which would be available to every eligible American student. Alternatively, they encourage expanding access to post-secondary education by increasing state funding for student financial aid such as Pell Grants and college tuition tax deductions.
Environment
Democrats believe that the government should protect the environment and have a history of environmentalism. In more recent years, this stance has emphasized renewable energy generation as the basis for an improved economy, greater national security, and general environmental benefits. The Democratic Party is substantially more likely than the Republican Party to support environmental regulation and policies that are supportive of renewable energy.
The Democratic Party also favors expansion of conservation lands and encourages open space and rail travel to relieve highway and airport congestion and improve air quality and the economy as it "believe[s] that communities, environmental interests, and the government should work together to protect resources while ensuring the vitality of local economies. Once Americans were led to believe they had to make a choice between the economy and the environment. They now know this is a false choice".
The foremost environmental concern of the Democratic Party is climate change. Democrats, most notably former Vice President Al Gore, have pressed for stern regulation of greenhouse gases. On October 15, 2007, Gore won the Nobel Peace Prize for his efforts to build greater knowledge about man-made climate change and laying the foundations for the measures needed to counteract it.
Renewable energy and fossil fuels
Democrats have supported increased domestic renewable energy development, including wind and solar power farms, in an effort to reduce carbon pollution. The party's platform calls for an "all of the above" energy policy including clean energy, natural gas and domestic oil, with the desire of becoming energy independent.
Trade agreements
Many Democrats support fair trade policies when it comes to the issue of international trade agreements and some in the party have started supporting free trade in recent decades.[Rorty, R. (1997). ''Achieving Our Country: Leftist Thought In Twentieth Century America''. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. ] In the 1990s, the Clinton administration and a number of prominent Democrats pushed through a number of agreements such as the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). Since then, the party's shift away from free trade became evident in the Dominican Republic – Central America Free Trade Agreement, Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA) vote, with 15 House Democrats voting for the agreement and 187 voting against.
Social issues
 The modern Democratic Party emphasizes
The modern Democratic Party emphasizes social equality
Social equality is a state of affairs in which all individuals within a specific society have equal rights, liberties, and status, possibly including civil rights, freedom of expression, autonomy, and equal access to certain public goods and ...
and equal opportunity
Equal opportunity is a state of fairness in which individuals are treated similarly, unhampered by artificial barriers, prejudices, or preferences, except when particular distinctions can be explicitly justified. The intent is that the important ...
. Democrats support Voting rights in the United States, voting rights and minority rights, including LGBT rights
Rights affecting lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people vary greatly by country or jurisdiction—encompassing everything from the legal recognition of same-sex marriage to the death penalty for homosexuality.
Notably, , 33 ...
. The party championed the Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
, which for the first time outlawed segregation. Carmines and Stimson wrote "the Democratic Party appropriated racial liberalism and assumed federal responsibility for ending racial discrimination."
Ideological social elements in the party include cultural liberalism
Cultural liberalism is a social philosophy which expresses the social dimension of liberalism and advocates the freedom of individuals to choose whether to conform to cultural norms. In the words of Henry David Thoreau, it is often expressed a ...
, civil libertarianism, and feminism. Some Democratic social policies are immigration reform, electoral reform, and women's reproductive rights.
Equal opportunity
The Democratic Party supports equal opportunity
Equal opportunity is a state of fairness in which individuals are treated similarly, unhampered by artificial barriers, prejudices, or preferences, except when particular distinctions can be explicitly justified. The intent is that the important ...
for all Americans regardless of sex, age, race, ethnicity, sexual orientation, gender identity, religion, creed, or national origin. Many Democrats support affirmative action programs to further this goal. Democrats also strongly support the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990, Americans with Disabilities Act to prohibit discrimination against people based on physical or mental disability. As such, the Democrats pushed as well the ADA Amendments Act of 2008, a disability rights expansion that became law.
Voting rights
The party is very supportive of improving voting rights as well as election accuracy and accessibility. They support extensions of voting time, including making election day a holiday. They support reforming the electoral system to eliminate gerrymandering, abolishing the United States Electoral College, electoral college, as well as passing comprehensive campaign finance reform.
Abortion and reproductive rights
The Democratic Party believes that all women should have access to birth control and supports public funding of contraception for poor women. In its national platforms from 1992 to 2004, the Democratic Party has called for abortion to be "safe, legal and rare"—namely, keeping it legal by rejecting laws that allow governmental interference in abortion decisions and reducing the number of abortions by promoting both knowledge of reproduction and contraception and incentives for adoption. The wording changed in the 2008 platform. When Congress voted on the Partial-Birth Abortion Ban Act in 2003, Congressional Democrats were split, with a minority (including former Party leaders of the United States Senate, Senate Majority Leader Harry Reid) supporting the ban and the majority of Democrats opposing the legislation.
The Democratic Party opposes attempts to reverse the 1973 Supreme Court decision ''Roe v. Wade'', which declared abortion covered by the constitutionally protected individual right to privacy under the Ninth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Ninth Amendment; and ''Planned Parenthood v. Casey'', which lays out the legal framework in which government action alleged to violate that right is assessed by courts. As a matter of the right to privacy and of gender equality, many Democrats believe all women should have the ability to choose to abort without governmental interference. They believe that each woman, conferring with her conscience, has the right to choose for herself whether abortion is morally correct.
Former Party leaders of the United States Senate, Senate Minority Leader Harry Reid was anti-abortion, while former President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
and Speaker of the United States House of Representatives, Speaker of the House Nancy Pelosi favor abortion rights
Abortion-rights movements, also referred to as pro-choice movements, advocate for the right to have legal access to induced abortion services including elective abortion. They seek to represent and support women who wish to terminate their pre ...
. Groups such as Democrats for Life of America represent the anti-abortion political faction, faction of the party while groups such as EMILY's List represent the abortion rights faction. A ''Newsweek'' poll from October 2006 found that 25% of Democrats were anti-abortion while a 69% majority was in favor of abortion rights.
According to the 2020 Democratic Party platform, "Democrats believe every woman should be able to access high-quality reproductive health care services, including safe and legal abortion."
Immigration
Many Democratic politicians have called for systematic reform of the immigration system such that residents that have Illegal immigration to the United States, come into the United States illegally have a pathway to legal citizenship. President Obama remarked in November 2013 that he felt it was "long past time to fix our broken immigration system," particularly to allow "incredibly bright young people" that came over as students to become full citizens. The Public Religion Research Institute found in a late 2013 study that 73% of Democrats supported the pathway concept, compared to 63% of Americans as a whole.
LGBT rights
The Democratic Party is supportive of LGBT rights. Most support for same-sex marriage in the United States has come from Democrats. Support for same-sex marriage has increased in the past decade according to ABC News. An April 2009 ABC News/''Washington Post'' public opinion poll put support among Democrats at 62% whereas a June 2008 ''Newsweek'' poll found that 42% of Democrats support same-sex marriage while 23% support civil unions or domestic partnership laws and 28% oppose any legal recognition at all. A broad majority of Democrats have supported other LGBT-related laws such as extending hate crime statutes, Employment Non-Discrimination Act, legally preventing discrimination against LGBT people in the workforce and repealing the "don't ask, don't tell" military policy. A 2006 Pew Research Center poll of Democrats found that 55% supported gays adopting children with 40% opposed while 70% support Sexual orientation and military service, gays in the military, with only 23% opposed. Gallup polling from May 2009 stated that 82% of Democrats support open enlistment.
The 2004 Democratic National Platform stated that marriage should be defined at the state level and it repudiated the Federal Marriage Amendment.[ ] While not stating support of same-sex marriage, the 2008 platform called for repeal of the Defense of Marriage Act, which banned federal recognition of same-sex marriage and removed the need for interstate recognition, supported antidiscrimination laws and the extension of hate crime laws to LGBT people and opposed "don't ask, don't tell". The 2012 platform included support for same-sex marriage and for the repeal of DOMA.Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
became the first sitting president to say he supports same-sex marriage.[ Earlier, when running for the Illinois Senate in 1996 he said, "I favor legalizing same-sex marriages, and would fight efforts to prohibit such marriages". John Kerry, Democratic presidential candidate in 2004, did not support same-sex marriage. Former presidents ]Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
and Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (born October 1, 1924) is an American politician who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he previously served as th ...
and former vice presidents Al Gore and Walter Mondale
Walter Frederick "Fritz" Mondale (January 5, 1928 – April 19, 2021) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 42nd vice president of the United States from 1977 to 1981 under President Jimmy Carter. A U.S. senator from Minnesota ...
also support gay marriage. President Joe Biden has been in favor of same-sex marriage since 2012 when he became the highest-ranking government official to support it.
Puerto Rico
The 2016 Democratic Party platform declares: "We are committed to addressing the extraordinary challenges faced by our fellow citizens in Puerto Rico. Many stem from the fundamental question of Puerto Rico's political status. Democrats believe that the people of Puerto Rico should determine their ultimate political status from permanent options that do not conflict with the Constitution, laws, and policies of the United States. Democrats are committed to promoting economic opportunity and good-paying jobs for the hardworking people of Puerto Rico. We also believe that Puerto Ricans must be treated equally by Medicare, Medicaid, and other programs that benefit families. Puerto Ricans should be able to vote for the people who make their laws, just as they should be treated equally. All American citizens, no matter where they reside, should have the right to vote for the president of the United States. Finally, we believe that federal officials must respect Puerto Rico's local self-government as laws are implemented and Puerto Rico's budget and debt are restructured so that it can get on a path towards stability and prosperity".
Legal issues
Gun control
 With a stated goal of reducing crime and homicide, the Democratic Party has introduced various Gun politics in the United States, gun control measures, most notably the Gun Control Act of 1968, the Brady Handgun Violence Prevention Act, Brady Bill of 1993 and Crime Control Act of 1994. However, some Democrats, especially rural, Southern, and Western Democrats, favor fewer restrictions on firearm possession and warned the party was defeated in the 2000 presidential election in rural areas because of the issue. In the national platform for 2008, the only statement explicitly favoring gun control was a plan calling for renewal of the 1994 Federal Assault Weapons Ban, Assault Weapons Ban. In 2022, Democratic president Joe Biden signed the Bipartisan Safer Communities Act, which among other things expanded background checks and provided incentives for states to pass red flag laws.
With a stated goal of reducing crime and homicide, the Democratic Party has introduced various Gun politics in the United States, gun control measures, most notably the Gun Control Act of 1968, the Brady Handgun Violence Prevention Act, Brady Bill of 1993 and Crime Control Act of 1994. However, some Democrats, especially rural, Southern, and Western Democrats, favor fewer restrictions on firearm possession and warned the party was defeated in the 2000 presidential election in rural areas because of the issue. In the national platform for 2008, the only statement explicitly favoring gun control was a plan calling for renewal of the 1994 Federal Assault Weapons Ban, Assault Weapons Ban. In 2022, Democratic president Joe Biden signed the Bipartisan Safer Communities Act, which among other things expanded background checks and provided incentives for states to pass red flag laws.
Death penalty
The Democratic Party currently opposes the death penalty.Clinton administration
Bill Clinton's tenure as the 42nd president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1993, and ended on January 20, 2001. Clinton, a Democrat from Arkansas, took office following a decisive election victory over Re ...
, Democrats led the expansion of the federal death penalty. These efforts resulted in the passage of the Antiterrorism and Effective Death Penalty Act of 1996, signed into law by Bill Clinton, President Clinton, which heavily limited appeals in death penalty cases.
In 1972, the Democratic Party platform called for the abolition of capital punishment.
In 1992, 1993 and 1995, Democratic Texas Congressman Henry B. Gonzalez, Henry González unsuccessfully introduced the s:Death Penalty Abolition Amendment, Death Penalty Abolition Amendment which prohibited the use of capital punishment in the United States. Democratic Missouri Congressman Bill Clay, William Lacy Clay, Sr. cosponsored the amendment in 1993.
During his Illinois Senate career of Barack Obama, Illinois Senate career, former President of the United States, President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
successfully introduced legislation intended to reduce the likelihood of Miscarriage of justice, wrongful convictions in capital cases, requiring videotaping of confessions. When Barack Obama 2008 presidential campaign, campaigning for the presidency, Obama stated that he supports the limited use of the death penalty, including for people who have been convicted of raping a minor under the age of 12, having opposed the Supreme Court of the United States, Supreme Court's ruling in ''Kennedy v. Louisiana'' that the death penalty was unconstitutional in child rape cases. Obama has stated that he thinks the "death penalty does little to deter crime" and that it is used too frequently and too inconsistently.
In June 2016, the Democratic Platform Drafting Committee unanimously adopted an amendment to abolish the death penalty.
Torture
Many Democrats are opposed to the Torture and the United States, use of torture against individuals apprehended and held prisoner by the United States armed forces, United States military and hold that categorizing such prisoners as unlawful combatants does not release the United States from its obligations under the Geneva Conventions. Democrats contend that torture is inhumane, damages the United States' moral standing in the world, and produces questionable results. Democrats are largely against waterboarding.
Torture became a divisive issue in the party after Barack Obama was elected president.
Patriot Act
Many Democrats are opposed to the Patriot Act, but when the law was passed most Democrats were supportive of it and all but two Democrats in the Senate voted for the original Patriot Act legislation in 2001. The lone nay vote was from Russ Feingold of Wisconsin as Mary Landrieu of Louisiana did not vote. In the House, the Democrats voted for the Act by 145 yea and 62 nay. Democrats were split on the renewal in 2006. In the Senate, Democrats voted 34 for the 2006 renewal and nine against. In the House, Democrats voted 66 voted for the renewal and 124 against.
Privacy
The Democratic Party believes that individuals should have a privacy law, right to privacy. For example, many Democrats have opposed the NSA warrantless surveillance (2001–07), NSA warrantless surveillance of American citizens.
Some Democratic officeholders have championed consumer protection
Consumer protection is the practice of safeguarding buyers of goods and services, and the public, against unfair practices in the marketplace. Consumer protection measures are often established by law. Such laws are intended to prevent business ...
laws that limit the sharing of consumer data between corporations. Democrats have opposed Sodomy laws in the United States, sodomy laws since the 1972 platform which stated that "Americans should be free to make their own choice of life-styles and private habits without being subject to discrimination or prosecution", and believe that government should not regulate consensual noncommercial sexual conduct among adults as a matter of personal privacy.
Foreign policy issues
The foreign policy of the voters of the two major parties has largely overlapped since the 1990s. A Gallup poll in early 2013 showed broad agreement on the top issues, albeit with some divergence regarding human rights and international cooperation through agencies such as the United Nations.
In June 2014, the Quinnipiac Poll asked Americans which foreign policy they preferred:
Democrats chose A over B by 65% to 32%; Republicans chose A over B by 56% to 39%; and independents chose A over B by 67% to 29%.
Iraq War
 In 2002, Congressional Democrats were divided on the Iraq Resolution, Authorization for Use of Military Force Against Iraq: 147 voted against it (21 in the Senate and 126 in the House) and 110 voted for it (29 in the Senate and 81 in the House). Since then, many prominent Democrats, such as former senator John Edwards, have expressed regret about this decision and have called it a mistake while others, such as Senator Hillary Clinton, have criticized the conduct of the war yet not repudiated their initial vote for it (though Clinton later went on to repudiate her stance during the 2008 primaries). Referring to Iraq, Party leaders of the United States Senate, Senate Majority Leader Harry Reid declared in April 2007 the war to be "lost" while other Democrats (especially during the 2004 presidential election cycle) accused the President of lying to the public about weapons of mass destruction in Iraq. Among lawmakers, Democrats are the most vocal opponents of Operation Iraqi Freedom VI, Operation Iraqi Freedom and campaigned on a platform of withdrawal ahead of the United States elections, 2006, 2006 midterm elections.
A March 2003 CBS News poll taken a few days before the 2003 invasion of Iraq, invasion of Iraq found that 34% of Democrats nationwide would support it without United Nations backing, 51% would support it only with its backing and 14% would not support it at all. The ''Los Angeles Times'' stated in early April 2003 that 70% of Democrats supported the decision to invade while 27% opposed it. The Pew Research Center stated in August 2007 that opposition increased from 37% during the initial invasion to 74%. In April 2008, a CBS News poll found that about 90% of Democrats disapprove of the Presidency of George W. Bush, Bush administration's conduct and want to end the war within the next year.
Democrats in the House of Representatives near-unanimously supported a non-binding resolution disapproving of President Bush's decision to send Iraq War troop surge of 2007, additional troops into Iraq in 2007. Congressional Democrats overwhelmingly supported military funding legislation that included a provision that set "a timeline for the withdrawal of all US combat troops from Iraq" by March 31, 2008, but also would leave combat forces in Iraq for purposes such as targeted counter-terrorism operations. After a veto from the President and a failed attempt in Congress to override the veto, the U.S. Troop Readiness, Veterans' Care, Katrina Recovery, and Iraq Accountability Appropriations Act, 2007 was passed by Congress and signed by the President after the timetable was dropped. Criticism of the Iraq War subsided after the Iraq War troop surge of 2007 led to a dramatic decrease in Iraqi violence. The Democratic-controlled 110th Congress continued to fund efforts in both Iraq and Afghanistan. Presidential candidate
In 2002, Congressional Democrats were divided on the Iraq Resolution, Authorization for Use of Military Force Against Iraq: 147 voted against it (21 in the Senate and 126 in the House) and 110 voted for it (29 in the Senate and 81 in the House). Since then, many prominent Democrats, such as former senator John Edwards, have expressed regret about this decision and have called it a mistake while others, such as Senator Hillary Clinton, have criticized the conduct of the war yet not repudiated their initial vote for it (though Clinton later went on to repudiate her stance during the 2008 primaries). Referring to Iraq, Party leaders of the United States Senate, Senate Majority Leader Harry Reid declared in April 2007 the war to be "lost" while other Democrats (especially during the 2004 presidential election cycle) accused the President of lying to the public about weapons of mass destruction in Iraq. Among lawmakers, Democrats are the most vocal opponents of Operation Iraqi Freedom VI, Operation Iraqi Freedom and campaigned on a platform of withdrawal ahead of the United States elections, 2006, 2006 midterm elections.
A March 2003 CBS News poll taken a few days before the 2003 invasion of Iraq, invasion of Iraq found that 34% of Democrats nationwide would support it without United Nations backing, 51% would support it only with its backing and 14% would not support it at all. The ''Los Angeles Times'' stated in early April 2003 that 70% of Democrats supported the decision to invade while 27% opposed it. The Pew Research Center stated in August 2007 that opposition increased from 37% during the initial invasion to 74%. In April 2008, a CBS News poll found that about 90% of Democrats disapprove of the Presidency of George W. Bush, Bush administration's conduct and want to end the war within the next year.
Democrats in the House of Representatives near-unanimously supported a non-binding resolution disapproving of President Bush's decision to send Iraq War troop surge of 2007, additional troops into Iraq in 2007. Congressional Democrats overwhelmingly supported military funding legislation that included a provision that set "a timeline for the withdrawal of all US combat troops from Iraq" by March 31, 2008, but also would leave combat forces in Iraq for purposes such as targeted counter-terrorism operations. After a veto from the President and a failed attempt in Congress to override the veto, the U.S. Troop Readiness, Veterans' Care, Katrina Recovery, and Iraq Accountability Appropriations Act, 2007 was passed by Congress and signed by the President after the timetable was dropped. Criticism of the Iraq War subsided after the Iraq War troop surge of 2007 led to a dramatic decrease in Iraqi violence. The Democratic-controlled 110th Congress continued to fund efforts in both Iraq and Afghanistan. Presidential candidate Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
advocated a withdrawal of combat troops within Iraq by late 2010 with a residual force of peacekeeping troops left in place.[Obama says conditions to dictate final Iraq force](_blank)
. Reuters. July 27, 2008.
On February 27, 2009, President Obama announced: "As a candidate for president, I made clear my support for a timeline of 16 months to carry out this drawdown, while pledging to consult closely with our military commanders upon taking office to ensure that we preserve the gains we've made and protect our troops ... Those consultations are now complete, and I have chosen a timeline that will remove our combat brigades over the next 18 months".[ Around 50,000 non-combat-related forces would remain.][ Obama's plan drew wide bipartisan support, including that of defeated Republican presidential candidate Senator John McCain.][Top Republicans embrace Iraq plan]
. ''The Politico''. February 27, 2009.
Iran sanctions
The Democratic Party has been critical of the Iran's nuclear weapon program and supported economic sanctions against the Iranian government. In 2013, the Democratic-led administration worked to reach a diplomatic agreement with the government of Iran to halt the Iranian nuclear weapon program in exchange for Sanctions against Iran, international economic sanction relief. , negotiations had been successful and the party called for more cooperation with Iran in the future. In 2015, the Obama administration agreed to the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, which provides sanction relief in exchange for international oversight of the Iranian nuclear program. In February 2019, the Democratic National Committee passed a resolution calling on the United States to re-enter the JCPOA, which President Trump withdrew from in 2018.
Invasion of Afghanistan
Democrats in the House of Representatives and in the Senate near-unanimously voted for the Authorization for Use of Military Force Against Terrorists against "those responsible for the September 11 attacks, recent attacks launched against the United States" in Afghanistan in 2001, supporting the NATO coalition Operation Enduring Freedom, invasion of the nation. Most elected Democrats continued to support the War in Afghanistan (2001–present), Afghanistan conflict for its duration, with some, such as a Democratic National Committee spokesperson, voicing concerns that the Invasion of Iraq, Iraq War shifted too many resources away from the presence in Afghanistan.["John McCain & Barack Obama urge Afghanistan surge"](_blank)
. ''New York Daily News''. July 15, 2008. Retrieved August 23, 2008. During the 2008 United States presidential election, 2008 Presidential Election, then-candidate Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
called for a "surge" of troops into Afghanistan.["Afghan War Edges Out Iraq as Most Important for U.S."](_blank)
by Frank Newport. Gallup poll, Gallup. July 30, 2008. Retrieved August 24, 2009. A CNN survey in August 2009 stated that a majority of Democrats opposed the war. CNN polling director Keating Holland said: "Nearly two thirds of Republicans support the war in Afghanistan. Three quarters of Democrats oppose the war".[Most Americans oppose Afghanistan war: poll]
. ''The Australian''. August 7, 2009. Retrieved August 24, 2009. An August 2009 ''Washington Post'' poll found similar results, and the paper stated that Obama's policies would anger his closest supporters.
During the 2020 United States presidential election, 2020 Presidential Election, then-candidate Joe Biden promised to "end the forever wars in Afghanistan and the Middle East." Biden went on to win the election, and in April 2021, he announced he would withdraw all US troops from Afghanistan by September 11 of that year. The last troops left in August, bringing America's 20-year-long military campaign in the country to a close.
Israel
The Democratic Party has both recently and historically supported Israel.[ A 2008 Gallup poll found that 64% of Americans have a favorable image of Israel while only 16% say that they have a favorable image of the Palestinian Authority.][Americans' Most and Least Favored Nations]
. By Lydia Saad. Gallup. March 3, 2008. A pro-Israel view is held by the party leadership although some Democrats, including former President of the United States, President Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (born October 1, 1924) is an American politician who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he previously served as th ...
, have criticized Israel.[Left could push pro-Israel voters to GOP]
. By Jennifer Rubin (journalist), Jennifer Rubin. ''Politico''. July 18, 2007.
The 2008 Democratic Party platform acknowledges a "special relationship with Israel, grounded in shared interests and shared values, and a clear, strong, fundamental commitment to the security of Israel, our strongest ally in the region and its only established democracy." It also included:
It is in the best interests of all parties, including the United States, that we take an active role to help secure a lasting settlement of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict with a democratic, viable Palestinian state dedicated to living in peace and security side by side with the Jewish State of Israel. To do so, we must help Israel identify and strengthen those partners who are truly committed to peace while isolating those who seek conflict and instability, and stand with Israel against those who seek its destruction. The United States and its Quartet partners should continue to isolate Hamas until it renounces terrorism, recognizes Israel's right to exist, and abides by past agreements. Sustained American leadership for peace and security will require patient efforts and the personal commitment of the President of the United States. The creation of a Palestinian state through final status negotiations, together with an international compensation mechanism, should resolve the issue of Palestinian refugees by allowing them to settle there, rather than in Israel. All understand that it is unrealistic to expect the outcome of final status negotiations to be a full and complete return to the armistice lines of 1949. Jerusalem is and will remain the capital of Israel. The parties have agreed that Jerusalem is a matter for final status negotiations. It should remain an undivided city accessible to people of all faiths.
 A January 2009 Pew Research Center study found that when asked "which side do you sympathize with more", 42% of Democrats and 33% of liberals (a plurality in both groups) sympathize most with the Israelis. Around half of all political moderates or independents sided with Israel. The years leading up to the 2016 election have brought more discussion of the party's stance on Israel as polls reported declining support for Israel among the party faithful.
A January 2009 Pew Research Center study found that when asked "which side do you sympathize with more", 42% of Democrats and 33% of liberals (a plurality in both groups) sympathize most with the Israelis. Around half of all political moderates or independents sided with Israel. The years leading up to the 2016 election have brought more discussion of the party's stance on Israel as polls reported declining support for Israel among the party faithful.
Composition
By income and class
 The relationship between income, class, and partisan support has changed dramatically in recent years.
The relationship between income, class, and partisan support has changed dramatically in recent years.Blue America is an increasingly wealthy and well-educated place.
Throughout the second half of the 20th century, Americans without college degrees were more likely than university graduates to vote Democratic. But that gap began narrowing in the late 1960s before finally flipping in 2004... A more educated Democratic coalition is, naturally, a more affluent one... In every presidential election from 1948 to 2012, white voters in the top 5 percent of America's income distribution were more Republican than those in the bottom 95 percent. Now, the opposite is true: Among America's white majority, the rich voted to the left of the middle class and the poor in 2016 and 2020, while the poor voted to the right of the middle class and the rich.
Since 1980, there has been a significant decline in support for the Democratic Party among white working class voters. Since the 2010s, similar trends have been observed among working class minority groups, particularly among those who are Hispanic.2020 presidential election
This national electoral calendar for 2020 lists the national/federal elections held in 2020 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.
January
*5 January:
**C ...
, Democratic-plurality voting counties composed 70% of the Economy of the United States, total United States GDP.
Professionals
 Professionals, those who have a Higher education, college education and those whose work revolves around the conception of ideas, have tended to support the Democratic Party since 2000. While the professional class was once a stronghold of the Republican Party, it has become increasingly in favor of the Democratic Party. Support for Democratic candidates among professionals may be traced to the prevalence of liberal cultural values among this group:
Professionals, those who have a Higher education, college education and those whose work revolves around the conception of ideas, have tended to support the Democratic Party since 2000. While the professional class was once a stronghold of the Republican Party, it has become increasingly in favor of the Democratic Party. Support for Democratic candidates among professionals may be traced to the prevalence of liberal cultural values among this group:
Labor
 Since the 1930s, a critical component of the Democratic Party coalition has been Labor unions in the United States, organized labor. Labor unions supply a great deal of the money, Grassroots, grass roots Political organisation, political organization, and voters for the party. Democrats are far more likely to be represented by unions, although union membership has declined in general during the last few decades. This trend is depicted in the following graph from the book ''Democrats and Republicans—Rhetoric and Reality''. It is based on surveys conducted by the National Election Studies (NES).
The three most significant labor groupings in the Democratic coalition today are the AFL–CIO and Change to Win Federation, Change to Win National trade union center, labor federations as well as the National Education Association, a large, unaffiliated teacher, teachers' union. Important issues for labor unions include supporting industrial policy that sustains unionized manufacturing jobs, raising the minimum wage, and promoting broad social programs such as
Since the 1930s, a critical component of the Democratic Party coalition has been Labor unions in the United States, organized labor. Labor unions supply a great deal of the money, Grassroots, grass roots Political organisation, political organization, and voters for the party. Democrats are far more likely to be represented by unions, although union membership has declined in general during the last few decades. This trend is depicted in the following graph from the book ''Democrats and Republicans—Rhetoric and Reality''. It is based on surveys conducted by the National Election Studies (NES).
The three most significant labor groupings in the Democratic coalition today are the AFL–CIO and Change to Win Federation, Change to Win National trade union center, labor federations as well as the National Education Association, a large, unaffiliated teacher, teachers' union. Important issues for labor unions include supporting industrial policy that sustains unionized manufacturing jobs, raising the minimum wage, and promoting broad social programs such as Social Security
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specificall ...
and Medicare.
In the 2020 presidential election, 57% of union households voted for Joe Biden.
Younger Americans
 Younger Americans, including millennials and Generation Z, tend to vote mostly for Democratic candidates in recent years.
Younger Americans, including millennials and Generation Z, tend to vote mostly for Democratic candidates in recent years.Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
in 1992 and are more likely to identify as liberals than the general population.Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
carry 66% of their votes in 2008. In the 2018 midterm elections
The 2018 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 6, 2018. These midterm elections occurred during Republican Donald Trump's term. Democrats made a net gain of 41 seats in the United States House of Representatives, gaining a majo ...
, 67% of those in the 18–29 age range voted for the Democratic candidate. Democrats also won those in the 30–44 age range by a 19-point margin.
Women
 Although the gender gap has varied over many years, women of all ages are more likely than men to identify as Democrats.
Since the 1990s, women have supported Democratic Party candidates to various offices at higher rates than men. Polls in 2009 indicated that 41% of women identify as Democrats while only 25% of women identify as Republicans and 26% as independents whereas 32% of men identify as Democrats, 28% as Republicans and 34% as independents. Among ethnic minorities, women also are more likely than men to identify as Democrats.
The National Federation of Democratic Women is an affiliated organization meant to advocate for women's issues. National women's organizations that support Democratic candidates include EMILY's List, which aims to help elect pro-choice female Democratic candidates to office.
Of the 118 women in the United States House of Representatives at the start of the 117th United States Congress, 117th Congress, there were 89 Democrats. After special elections between June 2021 and September 2022, where four more female Democrats were elected as U.S. Representatives, there have been 123 women in the House, 93 of whom are Democratic.
Although the gender gap has varied over many years, women of all ages are more likely than men to identify as Democrats.
Since the 1990s, women have supported Democratic Party candidates to various offices at higher rates than men. Polls in 2009 indicated that 41% of women identify as Democrats while only 25% of women identify as Republicans and 26% as independents whereas 32% of men identify as Democrats, 28% as Republicans and 34% as independents. Among ethnic minorities, women also are more likely than men to identify as Democrats.
The National Federation of Democratic Women is an affiliated organization meant to advocate for women's issues. National women's organizations that support Democratic candidates include EMILY's List, which aims to help elect pro-choice female Democratic candidates to office.
Of the 118 women in the United States House of Representatives at the start of the 117th United States Congress, 117th Congress, there were 89 Democrats. After special elections between June 2021 and September 2022, where four more female Democrats were elected as U.S. Representatives, there have been 123 women in the House, 93 of whom are Democratic.
Marital status and parenthood
Americans that identify as single, living with a domestic partner, divorced, separated, or widowed are more likely to vote Democratic in contrast to married Americans who split about equally between Democrats and Republicans.[
]
LGBT Americans
 According to exit polling, LGBT Americans typically vote Democratic in national elections within the 70–80% range. In heavily gay precincts in large cities across the nation, the average was higher, ranging from 85% to 94%. This trend has continued since 1996 when Bill Clinton won 71% of the LGBT vote compared to Bob Dole's 16%. In 2000 Al Gore won 70% to George W. Bush's 25%, in 2004 John Kerry won 77% to George W. Bush's 23%, in 2008 Barack Obama won 70% to John McCain's 27%,
According to exit polling, LGBT Americans typically vote Democratic in national elections within the 70–80% range. In heavily gay precincts in large cities across the nation, the average was higher, ranging from 85% to 94%. This trend has continued since 1996 when Bill Clinton won 71% of the LGBT vote compared to Bob Dole's 16%. In 2000 Al Gore won 70% to George W. Bush's 25%, in 2004 John Kerry won 77% to George W. Bush's 23%, in 2008 Barack Obama won 70% to John McCain's 27%,Kyrsten Sinema
Kyrsten Lea Sinema (; born July 12, 1976) is an American politician and former social worker serving as the senior United States senator from Arizona since January 2019. A former member of the Democratic Party, Sinema became an independent in ...
of Arizona, Representative David Cicilline of Rhode Island, Governor Kate Brown of Oregon, and Governor Jared Polis of Colorado. The late activist and San Francisco Supervisor Harvey Milk was a Democrat as is former Representative Barney Frank of Massachusetts.
The Stonewall Democrats is an LGBT advocacy group associated with the Democratic Party. The Congressional LGBT Equality Caucus, Congressional LGBTQ+ Equality Caucus is a congressional caucus of 172 Democrats that advocate for LGBT rights within the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives.
African Americans
 From the end of the American Civil War, Civil War to the early 20th century, African Americans primarily favored the Republican Party due to its role in achieving the abolition of
From the end of the American Civil War, Civil War to the early 20th century, African Americans primarily favored the Republican Party due to its role in achieving the abolition of slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
, particularly through Abraham Lincoln, President Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation.Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
was elected president.civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, Racial discrimination ...
in the 1960s by Democratic presidents John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination ...
and Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
helped give the Democrats even greater support in the African-American community, which has consistently voted between 85% and 95% Democratic from the 1960s to the present day, making African Americans one of the biggest support groups in any US party.Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
, who managed to win over 95% of the African-American vote in the 2008 election. Despite not having a partisan affiliation, the NAACP often participates in organizing voter turnout drives and advocates for progressive causes, especially, those that affect people of color.
Within the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, the Congressional Black Caucus, consisting of 55 black Democrats, serves to represent the interests of African Americans and advocate on issues that affect them.
Latino Americans
 The Hispanic and Latino Americans, Latino population, particularly the large Mexican Americans, Mexican American population in the Southwestern United States, Southwest and the large Puerto Ricans in the United States, Puerto Rican and Dominican American, Dominican populations in the Northeastern United States, Northeast, have been strong supporters of the Democratic Party. In the 1996 United States presidential election, 1996 presidential election, Democratic President
The Hispanic and Latino Americans, Latino population, particularly the large Mexican Americans, Mexican American population in the Southwestern United States, Southwest and the large Puerto Ricans in the United States, Puerto Rican and Dominican American, Dominican populations in the Northeastern United States, Northeast, have been strong supporters of the Democratic Party. In the 1996 United States presidential election, 1996 presidential election, Democratic President Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
received 72% of the Latino vote. In following years, the Republican Party gained increasing support from the Latino community, especially among Latino Protestants and Pentecostalism, Pentecostals. With his much more liberal views on immigration, President Bush was the first Republican president to gain 40% of the Latino vote in the 2004 United States presidential election, 2004 presidential election. But the Republican Party's support among Hispanics eroded in the United States House of Representatives elections, 2006, 2006 midterm elections, dropping from 44% to 30%, with the Democrats gaining in the Latino vote from 55% in 2004 to 69% in 2006.Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
receiving 67%. According to exit polls by Edison Research, Obama increased his support again in 2012, winning 71% of Latino voters.
Cuban Americans still tend to vote Republican, though there has been a noticeable change starting with the 2008 elections. During the 2008 elections, Barack Obama received 47% of the Cuban American vote in Florida. According to Bendixen's exit polls, 84% of Miami-Dade Cuban-American voters 65 or older backed McCain, while 55% of those 29 or younger backed Obama, showing that the younger Cuban-American generation has become more liberal.
Unaffiliated Latino advocacy groups that often support progressive candidates and causes include the National Council of La Raza and the League of United Latin American Citizens. In the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, the Democratic caucus of Latino Americans is the Congressional Hispanic Caucus.
In the 2018 United States House of Representatives elections, 2018 elections, 69% of Latino Americans voted for the Democratic House candidate.
Asian Americans
 The Democratic Party has supermajority support in the Asian Americans, Asian-American population. Asian Americans had been a stronghold of the Republican Party up to and including the 1992 presidential election, in which George H. W. Bush won 55% of the Asian-American vote. Originally, the vast majority of Asian Americans were strongly anti-communist Vietnamese American, Vietnamese refugees, Chinese Americans, Taiwanese Americans, Korean Americans, and Filipino Americans, and the Republican Party's positions resonated with this demographic.
The Democratic Party made gains among Asian Americans starting in 1996 and in 2006 won 62% of the Asian-American vote. Exit polls after the 2008 presidential election indicated that Democratic candidate,
The Democratic Party has supermajority support in the Asian Americans, Asian-American population. Asian Americans had been a stronghold of the Republican Party up to and including the 1992 presidential election, in which George H. W. Bush won 55% of the Asian-American vote. Originally, the vast majority of Asian Americans were strongly anti-communist Vietnamese American, Vietnamese refugees, Chinese Americans, Taiwanese Americans, Korean Americans, and Filipino Americans, and the Republican Party's positions resonated with this demographic.
The Democratic Party made gains among Asian Americans starting in 1996 and in 2006 won 62% of the Asian-American vote. Exit polls after the 2008 presidential election indicated that Democratic candidate, Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
, won 62% of the Asian-American vote. In the 2012 presidential election, 73% of the Asian-American electorate voted for Obama's re-election. Barack Obama had the support of 85% of Indian Americans, 68% of Chinese Americans, and 57% of Filipino Americans. The Asian-American community's increasing number of young voters has also helped to erode traditionally reliably Republican voting blocs such as Vietnamese and Filipino Americans, leading to an increase in support for Democrats.
Prominent past and present Asian-American Democrats include Vice President of the United States, Vice President Kamala Harris, U.S. Senators Tammy Duckworth, Daniel Inouye, Daniel Akaka, and Mazie Hirono, former Governor and Secretary of Commerce Gary Locke, and U.S. Representatives Mike Honda, Judy Chu, Doris Matsui, Ro Khanna, Pramila Jayapal, Norman Mineta, and Dalip Singh Saund. Saund was the first Asian-American U.S. Representative.
In the 2018 United States House of Representatives elections, 2018 elections, 77% of Asian Americans voted for the Democratic candidate.
Native Americans
 The Democratic Party also has strong support among the Native Americans in the United States, Native American population, particularly in Arizona, New Mexico, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Washington (U.S. state), Washington, Alaska, Idaho, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Oklahoma, and North Carolina. Although now a small percentage of the population (virtually non-existent in some regions), most Native American precincts vote Democratic in margins exceeded only by African Americans.
Modern-day Democratic Native American politicians include former Congressman Brad Carson of Oklahoma as well as Principal Chief Bill John Baker of the Cherokee Nation, Governor Bill Anoatubby of the Chickasaw Nation, and Chief Gary Batton of the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma.
In 2018 United States House of Representatives elections, 2018, Democrats Deb Haaland of New Mexico and Sharice Davids of Kansas became the first Native American women to be elected to Congress. Democrat Peggy Flanagan was also elected in 2018 and currently serves as List of lieutenant governors of Minnesota, Lieutenant Governor of Minnesota. Flanagan is the second Native American woman to be elected to statewide executive office in U.S. history and the highest-ranking Native woman to be elected to executive office.
In December 2020, Joe Biden chose Deb Haaland to serve as United States Secretary of the Interior; she became the first Native American Cabinet secretary in March 2021.
The Democratic Party also has strong support among the Native Americans in the United States, Native American population, particularly in Arizona, New Mexico, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Washington (U.S. state), Washington, Alaska, Idaho, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Oklahoma, and North Carolina. Although now a small percentage of the population (virtually non-existent in some regions), most Native American precincts vote Democratic in margins exceeded only by African Americans.
Modern-day Democratic Native American politicians include former Congressman Brad Carson of Oklahoma as well as Principal Chief Bill John Baker of the Cherokee Nation, Governor Bill Anoatubby of the Chickasaw Nation, and Chief Gary Batton of the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma.
In 2018 United States House of Representatives elections, 2018, Democrats Deb Haaland of New Mexico and Sharice Davids of Kansas became the first Native American women to be elected to Congress. Democrat Peggy Flanagan was also elected in 2018 and currently serves as List of lieutenant governors of Minnesota, Lieutenant Governor of Minnesota. Flanagan is the second Native American woman to be elected to statewide executive office in U.S. history and the highest-ranking Native woman to be elected to executive office.
In December 2020, Joe Biden chose Deb Haaland to serve as United States Secretary of the Interior; she became the first Native American Cabinet secretary in March 2021.
Christian Americans
 Black churches, mainline Protestants, Evangelicalism in the United States, evangelicals, and Catholic Church in the United States, Catholics contributed to
Black churches, mainline Protestants, Evangelicalism in the United States, evangelicals, and Catholic Church in the United States, Catholics contributed to Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
's New Deal coalition. During the New Deal
The New Deal was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. Major federal programs agencies included the Civilian Cons ...
era, President Roosevelt appealed to notions of Christian charity.John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination ...
and Joe Biden, have been Democrats. Speaker of the United States House of Representatives, Speaker of the House Nancy Pelosi is also Catholic.
In response to high white evangelical support for Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021.
Trump graduated from the Wharton School of the University of Pe ...
and the Republican Party, Hillary Scholten, a member of the Christian Reformed Church in North America, Christian Reformed Church, founded the Christian Democrats of America.
Religious minorities
Secular Americans
 The Democratic Party receives support from secular organizations such as the Secular Coalition for America and many agnostic and atheist Americans. Exit polls from the 2008 election showed that voters with a religious affiliation of "Irreligion, none" accounted for the 12% of the electorate and voted for Democratic candidate Barack Obama by a 75–25% margin. In his first inaugural address, Obama acknowledged atheists by saying that the United States is not just "Christians and Muslims, Jews and Hindus but non-believers as well". In the 2012 United States presidential election, 2012 election cycle, Democratic president Barack Obama, who was running for re-election, had moderate to high ratings with the Secular Coalition for America while the majority of the Republican candidates had ratings in the low-to-failing range.
In the 2020 United States presidential election, exit polls show that voters with no religious affiliation accounted for 22% of the electorate and voted for Biden by a 65–31% margin.
The Democratic Party receives support from secular organizations such as the Secular Coalition for America and many agnostic and atheist Americans. Exit polls from the 2008 election showed that voters with a religious affiliation of "Irreligion, none" accounted for the 12% of the electorate and voted for Democratic candidate Barack Obama by a 75–25% margin. In his first inaugural address, Obama acknowledged atheists by saying that the United States is not just "Christians and Muslims, Jews and Hindus but non-believers as well". In the 2012 United States presidential election, 2012 election cycle, Democratic president Barack Obama, who was running for re-election, had moderate to high ratings with the Secular Coalition for America while the majority of the Republican candidates had ratings in the low-to-failing range.
In the 2020 United States presidential election, exit polls show that voters with no religious affiliation accounted for 22% of the electorate and voted for Biden by a 65–31% margin.
Jewish Americans
 American Jews, Jewish American communities tend to be a stronghold for the Democratic Party. Al Gore received 79% of the Jewish votes in 2000, and Barack Obama won about 77% of the Jewish vote in 2008. In the 2018 United States House of Representatives elections, 2018 House of Representatives elections, 79% of Jewish Americans voted for the Democratic candidate.
American Jews, Jewish American communities tend to be a stronghold for the Democratic Party. Al Gore received 79% of the Jewish votes in 2000, and Barack Obama won about 77% of the Jewish vote in 2008. In the 2018 United States House of Representatives elections, 2018 House of Representatives elections, 79% of Jewish Americans voted for the Democratic candidate.Chuck Schumer
Charles Ellis Schumer ( ; born November 23, 1950) is an American politician serving as Senate Majority Leader since January 20, 2021. A member of the Democratic Party, Schumer is in his fourth Senate term, having held his seat since 1999, and ...
, Carl Levin, Abraham Ribicoff, Ben Cardin, Henry Waxman, Joseph Lieberman, Bernie Sanders, Dianne Feinstein, Barney Frank, Barbara Boxer, Paul Wellstone, Rahm Emanuel, Russ Feingold, Herb Kohl, and Howard Metzenbaum.[Survey]
American Jewish Committee September 2008. Retrieved April 30, 2009.
Arab and Muslim Americans
Arab Americans and Islam in the United States, Muslim Americans have leaned Democratic since the 2003 invasion of Iraq.[Arab-American Voters Say Iraq Top Issue in 2008 Campaign](_blank)
By Mohamed Elshinnawi. Voice of America. July 23, 2007, Zogby International, Zogby found in June 2007 that 39% of Arab Americans identify as Democrats, 26% as Republicans, and 28% as Independent (voter), independents.
Democratic presidents
, there have been a total of 16 Democratic Party presidents.
Current Supreme Court justices appointed by Democratic presidents
, three of the nine seats on the Supreme Court of the United States are filled by Justices appointed by Democratic Presidents Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
and Joe Biden.
Recent electoral history
In congressional elections: 1950–present
In presidential elections: 1828–present
See also
* Democratic Party (United States) organizations
* List of political parties in the United States
*List of United States Democratic Party presidential candidates
* List of United States Democratic Party presidential tickets
* Political party strength in U.S. states
* Politics of the United States
Notes
References
Further reading
* ''The Almanac of American Politics 2022'' (2022) details on members of Congress, and the governors: their records and election results; also state and district politics; revised every two years since 1975
details
see The Almanac of American Politics
* ''American National Biography'' (20 volumes, 1999) covers all politicians no longer alive; online at many academic libraries and a
Wikipedia Library
* Andelic, Patrick. ''Donkey Work: Congressional Democrats in Conservative America, 1974–1994'' (2019
excerpt
* Baker, Jean H. ''Affairs of party: The political culture of northern Democrats in the mid-nineteenth century'' (Fordham UP, 1998).
* Bass Jr, Harold F. ''Historical dictionary of United States political parties'' (Scarecrow Press, 2009).
*
* Burner, David. ''The Politics of Provincialism: The Democratic Party in Transition, 1918–1932'' (Knopf, 1968).
* Congressional Quarterly. ''National Party Conventions, 1831–2000'' (2001).
* Congressional Quarterly. ''Presidential Elections 1789–2008'' (10th edition, 2009)
* Craig, Douglas. "Newton D. Baker and the Democratic Malaise, 1920–1937." ''Australasian Journal of American Studies'' (2006): 49–64
in JSTOR
* Dowe, Pearl K. Ford, et al. ''Remaking the Democratic Party: Lyndon B. Johnson as a Native-Son Presidential Candidate'' (University of Michigan Press, 2016).
* Feller, David. "Politics and Society: Toward a Jacksonian Synthesis" ''Journal of the Early Republic'' 10#2 (1990), pp. 135–16
in JSTOR
* Frymer, Paul. ''Black and blue: African Americans, the labor movement, and the decline of the Democratic party'' (Princeton UP, 2008).
* Gerring, John. "A chapter in the history of American party ideology: The nineteenth-century Democratic Party (1828–1892)." ''Polity'' 26.4 (1994): 729–768
online
*
online
* Kazin, Michael. ''What It Took to Win: A History of the Democratic Party'' (2022
excerpt
* Landis, Michael Todd. ''Northern Men with Southern Loyalties: The Democratic Party and the Sectional Crisis''. (Cornell UP, 2014).
* Lawrence, David G. ''The collapse of the democratic presidential majority: Realignment, dealignment, and electoral change from Franklin Roosevelt to Bill Clinton''. (Westview Press, 1997).
*
* Maisel, L. Sandy, and Jeffrey M. Berry, eds. ''The Oxford handbook of American political parties and interest groups'' (Oxford UP, 2010).
* Mieczkowski, Yanek, and Mark C Carnes. ''The Routledge historical atlas of presidential elections'' (2001).
* Neal, Steven. ''Happy Days are Here Again: The 1932 Democratic Convention, the Emergence of FDR—and how America was Changed Forever'' (Harper Collins, 2010).
* Remini, Robert V. ''Martin Van Buren and the making of the Democratic Party'' (Columbia UP, 1961).
* Savage, Sean J. ''Roosevelt: The Party Leader, 1932–1945'' (U Press of Kentucky, 2015).
* Savage, Sean J. ''JFK, LBJ, and the Democratic Party'' (SUNY Press, 2012).
* Savage, Sean J. ''Truman and the Democratic Party'' (U Press of Kentucky, 2015).
* Woods, Randall B. ''Prisoners of Hope: Lyndon B. Johnson, the Great Society, and the Limits of Liberalism'' (Basic Books, 2016).
External links
*
* .
{{DEFAULTSORT:Democratic Party
Democratic Party (United States),
1828 establishments in Maryland
Liberal parties in the United States
Political parties established in 1828
Political parties in the United States
Social liberal parties in the United States
 The Democratic Party evolved from the
The Democratic Party evolved from the  The
The  The Democrats split over slavery, with Northern and Southern tickets in the
The Democrats split over slavery, with Northern and Southern tickets in the  As the
As the 

 The election of President
The election of President  With the ascendancy of the Republicans under Ronald Reagan, the Democrats searched for ways to respond yet were unable to succeed by running traditional candidates, such as former vice president and Democratic presidential nominee
With the ascendancy of the Republicans under Ronald Reagan, the Democrats searched for ways to respond yet were unable to succeed by running traditional candidates, such as former vice president and Democratic presidential nominee  The Democratic Congressional Campaign Committee (DCCC) assists party candidates in House races and its current chairman (selected by the party caucus) is Representative Sean Patrick Maloney of New York. Similarly, the Democratic Senatorial Campaign Committee (DSCC), headed by Senator Gary Peters of Michigan, raises funds for Senate races. The Democratic Legislative Campaign Committee (DLCC), chaired by Majority Leader of the New York State Senate Andrea Stewart-Cousins, is a smaller organization that focuses on state legislative races. The DNC sponsors the College Democrats of America (CDA), a student-outreach organization with the goal of training and engaging a new generation of Democratic activists. Democrats Abroad is the organization for Americans living outside the United States. They work to advance the party's goals and encourage Americans living abroad to support the Democrats. The Young Democrats of America (YDA) and the High School Democrats of America (HSDA) are young adult and youth-led organizations respectively that attempt to draw in and mobilize young people for Democratic candidates but operates outside of the DNC. The Democratic Governors Association (DGA) is an organization supporting the candidacies of Democratic gubernatorial nominees and incumbents. Likewise, the mayors of the largest cities and urban centers convene as the National Conference of Democratic Mayors.
The Democratic Congressional Campaign Committee (DCCC) assists party candidates in House races and its current chairman (selected by the party caucus) is Representative Sean Patrick Maloney of New York. Similarly, the Democratic Senatorial Campaign Committee (DSCC), headed by Senator Gary Peters of Michigan, raises funds for Senate races. The Democratic Legislative Campaign Committee (DLCC), chaired by Majority Leader of the New York State Senate Andrea Stewart-Cousins, is a smaller organization that focuses on state legislative races. The DNC sponsors the College Democrats of America (CDA), a student-outreach organization with the goal of training and engaging a new generation of Democratic activists. Democrats Abroad is the organization for Americans living outside the United States. They work to advance the party's goals and encourage Americans living abroad to support the Democrats. The Young Democrats of America (YDA) and the High School Democrats of America (HSDA) are young adult and youth-led organizations respectively that attempt to draw in and mobilize young people for Democratic candidates but operates outside of the DNC. The Democratic Governors Association (DGA) is an organization supporting the candidacies of Democratic gubernatorial nominees and incumbents. Likewise, the mayors of the largest cities and urban centers convene as the National Conference of Democratic Mayors.
 Many conservative Southern Democrats defected to the Republican Party, beginning with the passage of the
Many conservative Southern Democrats defected to the Republican Party, beginning with the passage of the  Democrats call for "affordable and quality health care" and favor moving toward universal health care in a variety of forms to address rising healthcare costs. Some Democratic politicians favor a single-payer health care, single-payer program or Medicare for All, while others prefer creating a public health insurance option.
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, signed into law by President
Democrats call for "affordable and quality health care" and favor moving toward universal health care in a variety of forms to address rising healthcare costs. Some Democratic politicians favor a single-payer health care, single-payer program or Medicare for All, while others prefer creating a public health insurance option.
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, signed into law by President  The modern Democratic Party emphasizes
The modern Democratic Party emphasizes  In 2002, Congressional Democrats were divided on the Iraq Resolution, Authorization for Use of Military Force Against Iraq: 147 voted against it (21 in the Senate and 126 in the House) and 110 voted for it (29 in the Senate and 81 in the House). Since then, many prominent Democrats, such as former senator John Edwards, have expressed regret about this decision and have called it a mistake while others, such as Senator Hillary Clinton, have criticized the conduct of the war yet not repudiated their initial vote for it (though Clinton later went on to repudiate her stance during the 2008 primaries). Referring to Iraq, Party leaders of the United States Senate, Senate Majority Leader Harry Reid declared in April 2007 the war to be "lost" while other Democrats (especially during the 2004 presidential election cycle) accused the President of lying to the public about weapons of mass destruction in Iraq. Among lawmakers, Democrats are the most vocal opponents of Operation Iraqi Freedom VI, Operation Iraqi Freedom and campaigned on a platform of withdrawal ahead of the United States elections, 2006, 2006 midterm elections.
A March 2003 CBS News poll taken a few days before the 2003 invasion of Iraq, invasion of Iraq found that 34% of Democrats nationwide would support it without United Nations backing, 51% would support it only with its backing and 14% would not support it at all. The ''Los Angeles Times'' stated in early April 2003 that 70% of Democrats supported the decision to invade while 27% opposed it. The Pew Research Center stated in August 2007 that opposition increased from 37% during the initial invasion to 74%. In April 2008, a CBS News poll found that about 90% of Democrats disapprove of the Presidency of George W. Bush, Bush administration's conduct and want to end the war within the next year.
Democrats in the House of Representatives near-unanimously supported a non-binding resolution disapproving of President Bush's decision to send Iraq War troop surge of 2007, additional troops into Iraq in 2007. Congressional Democrats overwhelmingly supported military funding legislation that included a provision that set "a timeline for the withdrawal of all US combat troops from Iraq" by March 31, 2008, but also would leave combat forces in Iraq for purposes such as targeted counter-terrorism operations. After a veto from the President and a failed attempt in Congress to override the veto, the U.S. Troop Readiness, Veterans' Care, Katrina Recovery, and Iraq Accountability Appropriations Act, 2007 was passed by Congress and signed by the President after the timetable was dropped. Criticism of the Iraq War subsided after the Iraq War troop surge of 2007 led to a dramatic decrease in Iraqi violence. The Democratic-controlled 110th Congress continued to fund efforts in both Iraq and Afghanistan. Presidential candidate
In 2002, Congressional Democrats were divided on the Iraq Resolution, Authorization for Use of Military Force Against Iraq: 147 voted against it (21 in the Senate and 126 in the House) and 110 voted for it (29 in the Senate and 81 in the House). Since then, many prominent Democrats, such as former senator John Edwards, have expressed regret about this decision and have called it a mistake while others, such as Senator Hillary Clinton, have criticized the conduct of the war yet not repudiated their initial vote for it (though Clinton later went on to repudiate her stance during the 2008 primaries). Referring to Iraq, Party leaders of the United States Senate, Senate Majority Leader Harry Reid declared in April 2007 the war to be "lost" while other Democrats (especially during the 2004 presidential election cycle) accused the President of lying to the public about weapons of mass destruction in Iraq. Among lawmakers, Democrats are the most vocal opponents of Operation Iraqi Freedom VI, Operation Iraqi Freedom and campaigned on a platform of withdrawal ahead of the United States elections, 2006, 2006 midterm elections.
A March 2003 CBS News poll taken a few days before the 2003 invasion of Iraq, invasion of Iraq found that 34% of Democrats nationwide would support it without United Nations backing, 51% would support it only with its backing and 14% would not support it at all. The ''Los Angeles Times'' stated in early April 2003 that 70% of Democrats supported the decision to invade while 27% opposed it. The Pew Research Center stated in August 2007 that opposition increased from 37% during the initial invasion to 74%. In April 2008, a CBS News poll found that about 90% of Democrats disapprove of the Presidency of George W. Bush, Bush administration's conduct and want to end the war within the next year.
Democrats in the House of Representatives near-unanimously supported a non-binding resolution disapproving of President Bush's decision to send Iraq War troop surge of 2007, additional troops into Iraq in 2007. Congressional Democrats overwhelmingly supported military funding legislation that included a provision that set "a timeline for the withdrawal of all US combat troops from Iraq" by March 31, 2008, but also would leave combat forces in Iraq for purposes such as targeted counter-terrorism operations. After a veto from the President and a failed attempt in Congress to override the veto, the U.S. Troop Readiness, Veterans' Care, Katrina Recovery, and Iraq Accountability Appropriations Act, 2007 was passed by Congress and signed by the President after the timetable was dropped. Criticism of the Iraq War subsided after the Iraq War troop surge of 2007 led to a dramatic decrease in Iraqi violence. The Democratic-controlled 110th Congress continued to fund efforts in both Iraq and Afghanistan. Presidential candidate  A January 2009 Pew Research Center study found that when asked "which side do you sympathize with more", 42% of Democrats and 33% of liberals (a plurality in both groups) sympathize most with the Israelis. Around half of all political moderates or independents sided with Israel. The years leading up to the 2016 election have brought more discussion of the party's stance on Israel as polls reported declining support for Israel among the party faithful. Gallup suggested that the decline in support might be due to tensions between Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and President Barack Obama.
The rise of the progressive Bernie Sanders-aligned faction of the party, which tends to trend more pro-Palestine, is also likely responsible for the decline in support for Israel. A 2016 Pew Research poll found that while Clinton supporters sympathized more with Israel than Palestinians by a 20-point margin, Sanders supporters sympathized more with Palestinians than with Israel by a 6-point margin. In June 2016, DNC members voted against an amendment to the party platform proposed by Sanders supporter James Zogby calling for an "end to occupation and illegal settlements". In August 2018, Rashida Tlaib, who supports a one-state solution, and Ilhan Omar, who has referred to Israel as an "apartheid regime" won Democratic primaries in Michigan and Minnesota. In November 2018, shortly after being elected to Congress, Omar came out in support of the Boycott, Divestment and Sanctions (BDS) campaign against Israel.
A January 2009 Pew Research Center study found that when asked "which side do you sympathize with more", 42% of Democrats and 33% of liberals (a plurality in both groups) sympathize most with the Israelis. Around half of all political moderates or independents sided with Israel. The years leading up to the 2016 election have brought more discussion of the party's stance on Israel as polls reported declining support for Israel among the party faithful. Gallup suggested that the decline in support might be due to tensions between Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and President Barack Obama.
The rise of the progressive Bernie Sanders-aligned faction of the party, which tends to trend more pro-Palestine, is also likely responsible for the decline in support for Israel. A 2016 Pew Research poll found that while Clinton supporters sympathized more with Israel than Palestinians by a 20-point margin, Sanders supporters sympathized more with Palestinians than with Israel by a 6-point margin. In June 2016, DNC members voted against an amendment to the party platform proposed by Sanders supporter James Zogby calling for an "end to occupation and illegal settlements". In August 2018, Rashida Tlaib, who supports a one-state solution, and Ilhan Omar, who has referred to Israel as an "apartheid regime" won Democratic primaries in Michigan and Minnesota. In November 2018, shortly after being elected to Congress, Omar came out in support of the Boycott, Divestment and Sanctions (BDS) campaign against Israel.
 The relationship between income, class, and partisan support has changed dramatically in recent years. Since the mid-2010s, affluent white voters have been more likely to vote for the Democratic Party. Eric Levitz of ''New York (magazine), New York Magazine'' writes that:
The relationship between income, class, and partisan support has changed dramatically in recent years. Since the mid-2010s, affluent white voters have been more likely to vote for the Democratic Party. Eric Levitz of ''New York (magazine), New York Magazine'' writes that: Younger Americans, including millennials and Generation Z, tend to vote mostly for Democratic candidates in recent years.
The young have voted in favor of the Democratic presidential candidate in every election since
Younger Americans, including millennials and Generation Z, tend to vote mostly for Democratic candidates in recent years.
The young have voted in favor of the Democratic presidential candidate in every election since  Although the gender gap has varied over many years, women of all ages are more likely than men to identify as Democrats.
Since the 1990s, women have supported Democratic Party candidates to various offices at higher rates than men. Polls in 2009 indicated that 41% of women identify as Democrats while only 25% of women identify as Republicans and 26% as independents whereas 32% of men identify as Democrats, 28% as Republicans and 34% as independents. Among ethnic minorities, women also are more likely than men to identify as Democrats.
The National Federation of Democratic Women is an affiliated organization meant to advocate for women's issues. National women's organizations that support Democratic candidates include EMILY's List, which aims to help elect pro-choice female Democratic candidates to office.
Of the 118 women in the United States House of Representatives at the start of the 117th United States Congress, 117th Congress, there were 89 Democrats. After special elections between June 2021 and September 2022, where four more female Democrats were elected as U.S. Representatives, there have been 123 women in the House, 93 of whom are Democratic.
Although the gender gap has varied over many years, women of all ages are more likely than men to identify as Democrats.
Since the 1990s, women have supported Democratic Party candidates to various offices at higher rates than men. Polls in 2009 indicated that 41% of women identify as Democrats while only 25% of women identify as Republicans and 26% as independents whereas 32% of men identify as Democrats, 28% as Republicans and 34% as independents. Among ethnic minorities, women also are more likely than men to identify as Democrats.
The National Federation of Democratic Women is an affiliated organization meant to advocate for women's issues. National women's organizations that support Democratic candidates include EMILY's List, which aims to help elect pro-choice female Democratic candidates to office.
Of the 118 women in the United States House of Representatives at the start of the 117th United States Congress, 117th Congress, there were 89 Democrats. After special elections between June 2021 and September 2022, where four more female Democrats were elected as U.S. Representatives, there have been 123 women in the House, 93 of whom are Democratic.
 According to exit polling, LGBT Americans typically vote Democratic in national elections within the 70–80% range. In heavily gay precincts in large cities across the nation, the average was higher, ranging from 85% to 94%. This trend has continued since 1996 when Bill Clinton won 71% of the LGBT vote compared to Bob Dole's 16%. In 2000 Al Gore won 70% to George W. Bush's 25%, in 2004 John Kerry won 77% to George W. Bush's 23%, in 2008 Barack Obama won 70% to John McCain's 27%, in 2012 Barack Obama won 76% to Mitt Romney's 22%, in 2016 Hillary Clinton won 78% to Donald Trump's 14%, and in 2020 Joe Biden won 73% to Donald Trump's 25%. Patrick Egan, a professor at New York University specializing in LGBT voting patterns, calls this a "remarkable continuity", saying that "about three-fourths vote Democratic and one-fourth Republican from year to year".
Notable LGBT Democrats include Senator Tammy Baldwin of Wisconsin, Senator
According to exit polling, LGBT Americans typically vote Democratic in national elections within the 70–80% range. In heavily gay precincts in large cities across the nation, the average was higher, ranging from 85% to 94%. This trend has continued since 1996 when Bill Clinton won 71% of the LGBT vote compared to Bob Dole's 16%. In 2000 Al Gore won 70% to George W. Bush's 25%, in 2004 John Kerry won 77% to George W. Bush's 23%, in 2008 Barack Obama won 70% to John McCain's 27%, in 2012 Barack Obama won 76% to Mitt Romney's 22%, in 2016 Hillary Clinton won 78% to Donald Trump's 14%, and in 2020 Joe Biden won 73% to Donald Trump's 25%. Patrick Egan, a professor at New York University specializing in LGBT voting patterns, calls this a "remarkable continuity", saying that "about three-fourths vote Democratic and one-fourth Republican from year to year".
Notable LGBT Democrats include Senator Tammy Baldwin of Wisconsin, Senator  From the end of the American Civil War, Civil War to the early 20th century, African Americans primarily favored the Republican Party due to its role in achieving the abolition of
From the end of the American Civil War, Civil War to the early 20th century, African Americans primarily favored the Republican Party due to its role in achieving the abolition of  The Hispanic and Latino Americans, Latino population, particularly the large Mexican Americans, Mexican American population in the Southwestern United States, Southwest and the large Puerto Ricans in the United States, Puerto Rican and Dominican American, Dominican populations in the Northeastern United States, Northeast, have been strong supporters of the Democratic Party. In the 1996 United States presidential election, 1996 presidential election, Democratic President
The Hispanic and Latino Americans, Latino population, particularly the large Mexican Americans, Mexican American population in the Southwestern United States, Southwest and the large Puerto Ricans in the United States, Puerto Rican and Dominican American, Dominican populations in the Northeastern United States, Northeast, have been strong supporters of the Democratic Party. In the 1996 United States presidential election, 1996 presidential election, Democratic President  The Democratic Party has supermajority support in the Asian Americans, Asian-American population. Asian Americans had been a stronghold of the Republican Party up to and including the 1992 presidential election, in which George H. W. Bush won 55% of the Asian-American vote. Originally, the vast majority of Asian Americans were strongly anti-communist Vietnamese American, Vietnamese refugees, Chinese Americans, Taiwanese Americans, Korean Americans, and Filipino Americans, and the Republican Party's positions resonated with this demographic.
The Democratic Party made gains among Asian Americans starting in 1996 and in 2006 won 62% of the Asian-American vote. Exit polls after the 2008 presidential election indicated that Democratic candidate,
The Democratic Party has supermajority support in the Asian Americans, Asian-American population. Asian Americans had been a stronghold of the Republican Party up to and including the 1992 presidential election, in which George H. W. Bush won 55% of the Asian-American vote. Originally, the vast majority of Asian Americans were strongly anti-communist Vietnamese American, Vietnamese refugees, Chinese Americans, Taiwanese Americans, Korean Americans, and Filipino Americans, and the Republican Party's positions resonated with this demographic.
The Democratic Party made gains among Asian Americans starting in 1996 and in 2006 won 62% of the Asian-American vote. Exit polls after the 2008 presidential election indicated that Democratic candidate,  The Democratic Party also has strong support among the Native Americans in the United States, Native American population, particularly in Arizona, New Mexico, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Washington (U.S. state), Washington, Alaska, Idaho, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Oklahoma, and North Carolina. Although now a small percentage of the population (virtually non-existent in some regions), most Native American precincts vote Democratic in margins exceeded only by African Americans.
Modern-day Democratic Native American politicians include former Congressman Brad Carson of Oklahoma as well as Principal Chief Bill John Baker of the Cherokee Nation, Governor Bill Anoatubby of the Chickasaw Nation, and Chief Gary Batton of the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma.
In 2018 United States House of Representatives elections, 2018, Democrats Deb Haaland of New Mexico and Sharice Davids of Kansas became the first Native American women to be elected to Congress. Democrat Peggy Flanagan was also elected in 2018 and currently serves as List of lieutenant governors of Minnesota, Lieutenant Governor of Minnesota. Flanagan is the second Native American woman to be elected to statewide executive office in U.S. history and the highest-ranking Native woman to be elected to executive office.
In December 2020, Joe Biden chose Deb Haaland to serve as United States Secretary of the Interior; she became the first Native American Cabinet secretary in March 2021.
The Democratic Party also has strong support among the Native Americans in the United States, Native American population, particularly in Arizona, New Mexico, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Washington (U.S. state), Washington, Alaska, Idaho, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Oklahoma, and North Carolina. Although now a small percentage of the population (virtually non-existent in some regions), most Native American precincts vote Democratic in margins exceeded only by African Americans.
Modern-day Democratic Native American politicians include former Congressman Brad Carson of Oklahoma as well as Principal Chief Bill John Baker of the Cherokee Nation, Governor Bill Anoatubby of the Chickasaw Nation, and Chief Gary Batton of the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma.
In 2018 United States House of Representatives elections, 2018, Democrats Deb Haaland of New Mexico and Sharice Davids of Kansas became the first Native American women to be elected to Congress. Democrat Peggy Flanagan was also elected in 2018 and currently serves as List of lieutenant governors of Minnesota, Lieutenant Governor of Minnesota. Flanagan is the second Native American woman to be elected to statewide executive office in U.S. history and the highest-ranking Native woman to be elected to executive office.
In December 2020, Joe Biden chose Deb Haaland to serve as United States Secretary of the Interior; she became the first Native American Cabinet secretary in March 2021.
 Black churches, mainline Protestants, Evangelicalism in the United States, evangelicals, and Catholic Church in the United States, Catholics contributed to
Black churches, mainline Protestants, Evangelicalism in the United States, evangelicals, and Catholic Church in the United States, Catholics contributed to  The Democratic Party receives support from secular organizations such as the Secular Coalition for America and many agnostic and atheist Americans. Exit polls from the 2008 election showed that voters with a religious affiliation of "Irreligion, none" accounted for the 12% of the electorate and voted for Democratic candidate Barack Obama by a 75–25% margin. In his first inaugural address, Obama acknowledged atheists by saying that the United States is not just "Christians and Muslims, Jews and Hindus but non-believers as well". In the 2012 United States presidential election, 2012 election cycle, Democratic president Barack Obama, who was running for re-election, had moderate to high ratings with the Secular Coalition for America while the majority of the Republican candidates had ratings in the low-to-failing range.
In the 2020 United States presidential election, exit polls show that voters with no religious affiliation accounted for 22% of the electorate and voted for Biden by a 65–31% margin.
The Democratic Party receives support from secular organizations such as the Secular Coalition for America and many agnostic and atheist Americans. Exit polls from the 2008 election showed that voters with a religious affiliation of "Irreligion, none" accounted for the 12% of the electorate and voted for Democratic candidate Barack Obama by a 75–25% margin. In his first inaugural address, Obama acknowledged atheists by saying that the United States is not just "Christians and Muslims, Jews and Hindus but non-believers as well". In the 2012 United States presidential election, 2012 election cycle, Democratic president Barack Obama, who was running for re-election, had moderate to high ratings with the Secular Coalition for America while the majority of the Republican candidates had ratings in the low-to-failing range.
In the 2020 United States presidential election, exit polls show that voters with no religious affiliation accounted for 22% of the electorate and voted for Biden by a 65–31% margin.
 American Jews, Jewish American communities tend to be a stronghold for the Democratic Party. Al Gore received 79% of the Jewish votes in 2000, and Barack Obama won about 77% of the Jewish vote in 2008. In the 2018 United States House of Representatives elections, 2018 House of Representatives elections, 79% of Jewish Americans voted for the Democratic candidate.
Jewish Americans as an important Democratic constituency are especially politically active and influential in large cities such as New York City, Los Angeles, Boston, and Chicago and play critical roles in large cities within presidential swing states, such as Philadelphia, Miami, and Las Vegas Valley, Las Vegas. Many prominent national Democrats in recent decades have been Jewish, including
American Jews, Jewish American communities tend to be a stronghold for the Democratic Party. Al Gore received 79% of the Jewish votes in 2000, and Barack Obama won about 77% of the Jewish vote in 2008. In the 2018 United States House of Representatives elections, 2018 House of Representatives elections, 79% of Jewish Americans voted for the Democratic candidate.
Jewish Americans as an important Democratic constituency are especially politically active and influential in large cities such as New York City, Los Angeles, Boston, and Chicago and play critical roles in large cities within presidential swing states, such as Philadelphia, Miami, and Las Vegas Valley, Las Vegas. Many prominent national Democrats in recent decades have been Jewish, including