U.S. Census 2000 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The United States census of 2000, conducted by the

 (maps not to scale)
(maps not to scale)
 The results of the census are used to determine how many
The results of the census are used to determine how many
 The census forms did not include any questions regarding
The census forms did not include any questions regarding
Constitution Article I Section II re Enumeration and Apportionment
Population Profile Introductory slide show
in
State and County QuickFacts
the most requested information
for population, housing, economic, and geographic data
2000 United States Census Form
2001 U.S Census Report
Contains 2000 census results
MLA Language Map
from the Modern Language Association
How the Census Works
via Howstuffworks.com {{Authority control
Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal Statistical System of the United States, U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the Americans, Ame ...
, determined the resident population of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
on April 1, 2000
File:2000 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Protests against Bush v. Gore after the 2000 United States presidential election; Heads of state meet for the Millennium Summit; The International Space Station in its infant form as seen from S ...
, to be 281,421,906, an increase of 13.2 percent over the 248,709,873 people enumerated during the 1990 census. This was the twenty-second federal census and was at the time the largest civilly administered peacetime effort in the United States.
Approximately 16 percent of households received a "long form" of the 2000 census, which contained over 100 questions. Full documentation on the 2000 census, including census forms and a procedural history, is available from the Integrated Public Use Microdata Series
Integrated Public Use Microdata Series (IPUMS) is the world's largest individual-level population database. IPUMS consists of microdata samples from United States ''(IPUMS-USA)'' and international ''(IPUMS-International)'' census records, as well ...
.
This was the first census in which a state – California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
– recorded a population of over 30 million, as well as the first in which two states – California and Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
– recorded populations of more than 20 million.
Data availability
Microdata from the 2000 census is freely available through theIntegrated Public Use Microdata Series
Integrated Public Use Microdata Series (IPUMS) is the world's largest individual-level population database. IPUMS consists of microdata samples from United States ''(IPUMS-USA)'' and international ''(IPUMS-International)'' census records, as well ...
. Aggregate data
Aggregate data is high-level data which is acquired by combining individual-level data. For instance, the output of an industry is an aggregate of the firms’ individual outputs within that industry. Aggregate data are applied in statistics, d ...
for small areas, together with electronic boundary files, can be downloaded from the National Historical Geographic Information System
The National Historical Geographic Information System (NHGIS) is a historical GIS project to create and freely disseminate a database incorporating all available aggregate census information for the United States between 1790 and 2010. The proj ...
.
Personally identifiable information will be available in 2072.
State rankings

City rankings
Top 100
Population profile
The U.S. resident population includes the total number of people in the50 states
The United States of America is a federal republic consisting of 50 states, a federal district ( Washington, D.C., the capital city of the United States), five major territories, and various minor islands. Both the states and the United ...
and the District of Columbia
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
. The Bureau also enumerated the residents of the U.S. territory
In the United States, a territory is any extent of region under the sovereign jurisdiction of the federal government of the United States, including all waters (around islands or continental tracts). The United States asserts sovereign rights for ...
of Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
; its population was 3,808,610, an 8.1% increase over the number from a decade earlier.
In an introduction to a more detailed population profile (see references below), the Census Bureau highlighted the following facts about U.S. population dynamics:
* 75% of respondents said they were White or Caucasian and no other race;
* Hispanics
The term ''Hispanic'' ( es, hispano) refers to people, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or Hispanidad.
The term commonly applies to countries with a cultural and historical link to Spain and to viceroyalties forme ...
accounted for 12.5% of the U.S. population, up from 9% in 1990;
* 12.4% (34.5 million Americans) were of German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
descent;
* 12.3% were of Black or African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
descent;
* 3.6% of respondents were Asian
Asian may refer to:
* Items from or related to the continent of Asia:
** Asian people, people in or descending from Asia
** Asian culture, the culture of the people from Asia
** Asian cuisine, food based on the style of food of the people from Asi ...
;
* 2.4% (6.8 million Americans) of respondents were multiracial (2 or more races). The 2000 census was the first time survey options for multiracial Americans were provided.
* Between 1990 and 2000, the population aged 45 to 54 grew by 49% and those aged 85 and older grew 38%;
* Women outnumbered men two to one among those aged 85 and older;
* Almost one in five adults had some type of disability
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be cognitive, developmental, intellectual, mental, physical, ...
in 1997 and the likelihood of having a disability increased with age;
* Families (as opposed to men or women living alone) still dominated American households, but less so than they did thirty years ago;
* Since 1993, both families and non-families have seen median household incomes rise, with "households headed by a woman without a spouse present" growing the fastest;
* People in married-couple families had the lowest poverty rates;
* The poor of any age were more likely than others to lack health insurance coverage;
* The number of elementary
Elementary may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music
* ''Elementary'' (Cindy Morgan album), 2001
* ''Elementary'' (The End album), 2007
* ''Elementary'', a Melvin "Wah-Wah Watson" Ragin album, 1977
Other uses in arts, entertainment, a ...
and high school
A secondary school describes an institution that provides secondary education and also usually includes the building where this takes place. Some secondary schools provide both '' lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper seconda ...
students in 2000 fell just short of the all-time high of 49 million reached in 1970;
* Improvements in educational attainment cross racial and ethnic lines; and
* The majority (51%) of U.S. households had access to computers; 42% had Internet access.
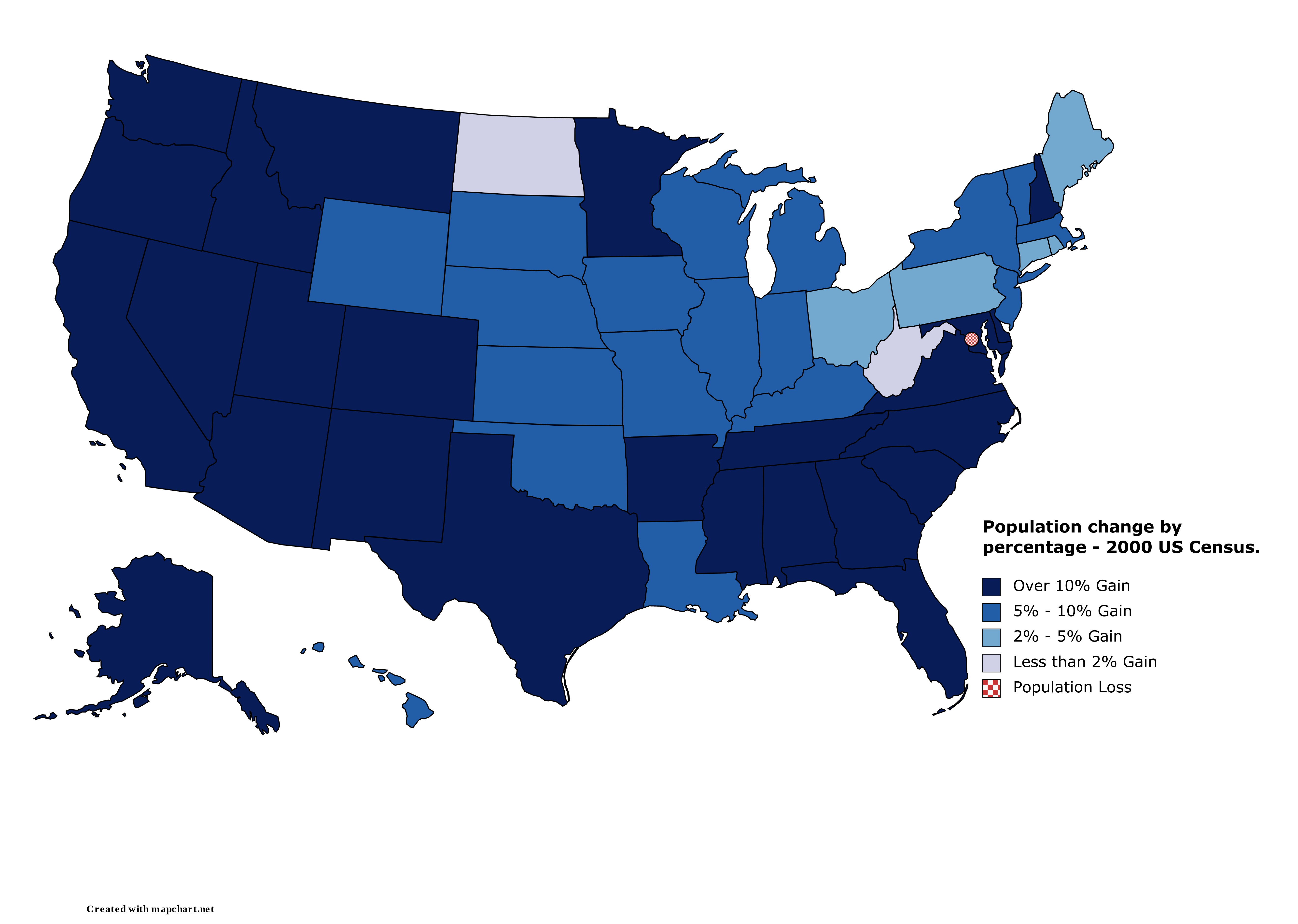
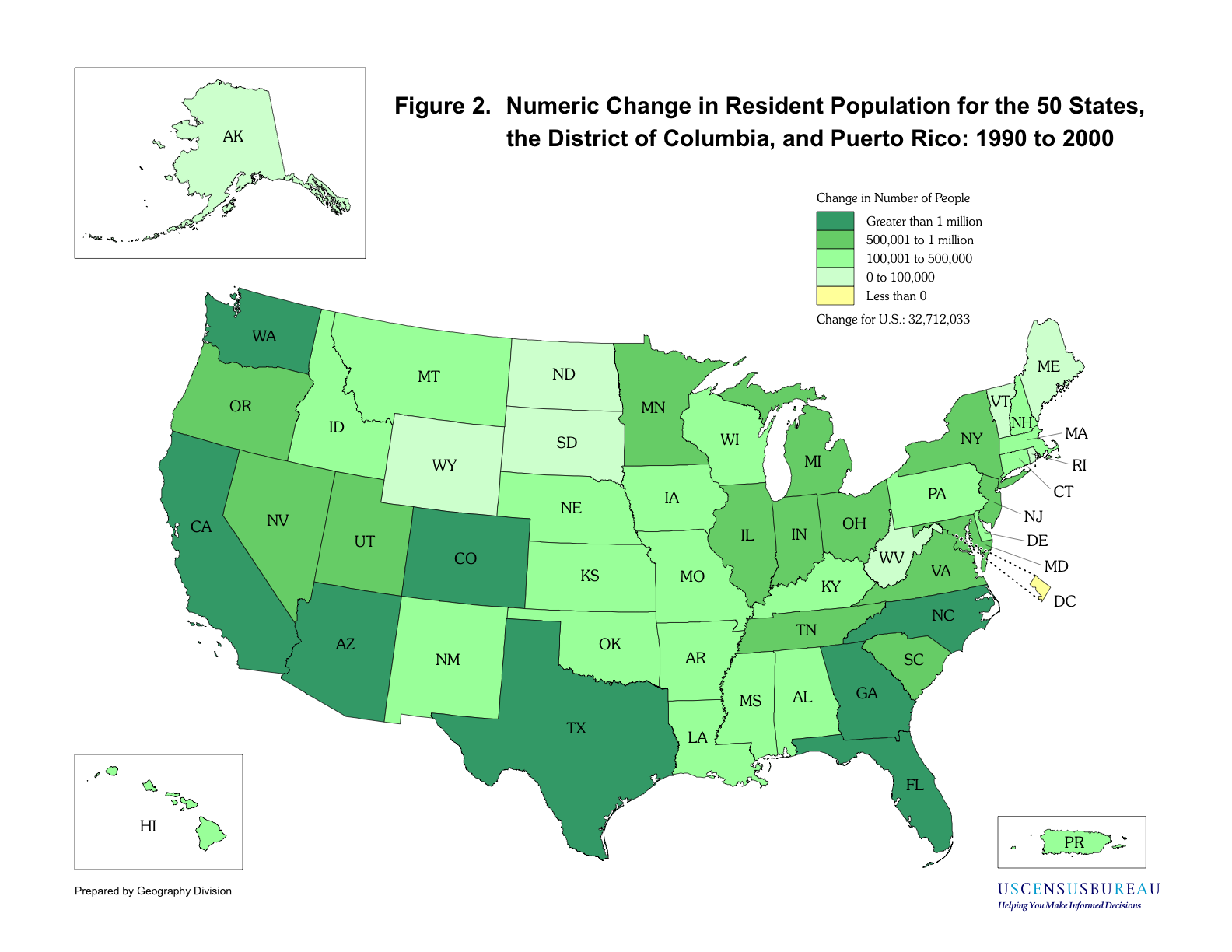
Changes in population
Regionally, the South andWest
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...
experienced the bulk of the nation's population increase: 14,790,890 and 10,411,850, respectively. This meant that the mean center of U.S. population
The mean center of the United States population is determined by the United States Census Bureau from the results of each national census. The Bureau defines it as follows:
After moving roughly Boxing the compass, west by south during the ...
moved to Phelps County, Missouri
Phelps County is a county in the central portion of the U.S. state of Missouri. As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 44,638. The largest city and county seat is Rolla. The county was organized on November 13, 1857, and was ...
. The Northeastern United States grew by 2,785,149; the Midwest by 4,724,144.

 (maps not to scale)
(maps not to scale)
Reapportionment
congressional district
Congressional districts, also known as electoral districts and legislative districts, electorates, or wards in other nations, are divisions of a larger administrative region that represent the population of a region in the larger congressional bod ...
s each state is apportioned. Congress defines the formula, in accordance with Title 2 of the U.S. Code, to reapportion among the states the 435 seats in the United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they ...
. The apportionment population consists of the resident population of the fifty states, plus the overseas military and federal civilian employees and their dependents living with them who could be allocated to a state. Each member of the House represents a population of about 647,000. The populations of the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico are excluded from the apportionment population because they do not have voting seats in the U. S. House of Representatives.
Since the first census in 1790, the decennial count has been the basis for the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
representative form of government. Article I, Section II specifies that "The Number of Representatives shall not exceed one for every thirty Thousand, but each State shall have at Least one Representative." In 1790, each member of the House represented about 34,000 residents. Since then, the House more than quadrupled in size, and in 1911 the number of representatives was fixed at 435. Today, each member represents about 20 times as many constituents.
Adjustment controversy
In the years leading up to the 2000 census, there was substantial controversy over whether the Bureau should adjust census figures based on a follow-up survey, called the post-enumeration survey, of a sample of blocks. (In 1999, the Supreme Court ruled 5–4 that the Constitution prohibits the use of such figures for apportionment purposes, but it may be permissible for other purposes where feasible.) The controversy was partly technical, but also partly political, since based on data from the 1990 census both parties believed that adjustment would likely have the effect, after redistricting, of slightly increasing Democratic representation in legislative bodies, but would also give Utah an additional, probably Republican, representative to Congress. Following the census, discrepancies between the adjusted census figures and demographic estimates of population change could not be resolved in time to meet legal deadlines for the provision of redistricting data, and the Census Bureau therefore recommended that the unadjusted results be used for this purpose. This recommendation was followed by the Secretary of Commerce (the official in charge of making the determination).Utah controversy
After the census was tabulated,Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
challenged the results in two different ways. Utah was extremely close to gaining a fourth congressional seat, falling 857 people short, which in turn was allocated to North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and ...
. The margin was later shortened to 80 people, after the federal government discovered that it overcounted the population of North Carolina by 2,673 residents. The Census Bureau counted members of the military and other federal civilian employees serving abroad as residents of their home state but did not count other people living outside the United States. Utah claimed that people traveling abroad as religious missionaries should be counted as residents and that the failure to do so imposed a burden on Mormon
Mormons are a religious and cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's death in 1844, the movement split into severa ...
religious practice. Almost half of all Mormon missionaries, more than 11,000 people, were from Utah; only 102 came from North Carolina. If this policy were changed, then Utah would have received an additional seat instead of North Carolina. On November 26, 2002, the Supreme Court affirmed the lower court ruling that rejected Utah's efforts to have Mormon missionaries counted.
The state of Utah then filed another lawsuit alleging that the statistical methods used in computing the state populations were improper and cost Utah the seat. The Bureau uses a method called imputation to assign a number of residents to addresses where residents cannot be reached after multiple efforts. While nationwide the imputation method added 0.4% to the population, the rate in Utah was 0.2%. The state challenged that the use of imputation violates the Census Act of 1957 and that it also fails the Constitution's requirement in Article I, Section 2 that an "actual enumeration" be used for apportionment. This case, '' Utah v. Evans'', made it to the Supreme Court, but Utah was again defeated.
Gay and lesbian controversy
 The census forms did not include any questions regarding
The census forms did not include any questions regarding sexual orientation
Sexual orientation is an enduring pattern of romantic or sexual attraction (or a combination of these) to persons of the opposite sex or gender, the same sex or gender, or to both sexes or more than one gender. These attractions are generall ...
, making it impossible to compile data comparing heterosexual and homosexual populations. However, two questions ''were'' asked that allowed same-sex partnerships to be counted. The questionnaires asked the sex of each person in a household and they asked what the relationship was between each of the members of the household. Respondents could check "Husband/wife" or "unmarried partner" or a number of other relationships. Responses were tabulated and the Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal Statistical System of the United States, U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the Americans, Ame ...
reported that there were more than 658,000 same-sex couples heading households in the United States. However, only about 25% of gay men and 40% of lesbians are in shared-household partnerships at any one time, according to non-census surveys. For every same-sex couple tallied in the census, there could be three to six more homosexual un-partnered individuals who would not be counted as gay. The census reported that same-sex male couples numbered 336,001 and female same-sex couples numbered 329,522. Extrapolating from those figures and the surveyed partnering habits of homosexuals, as many as 4.3 million homosexual adults could have been living in the U.S. in 2000. The exact number cannot be known because the census did not count them specifically. Bisexual and transgender populations were not counted, either, because there were no questions regarding this information. Also unavailable is the number of additional same-sex couples living under the same roof as the first, though this applies to additional heterosexual couples as well. The lack of accurate numbers makes it difficult for lawmakers who are considering legislation on hate crimes or social services for gay families with children. It also makes for less accuracy when predicting the fertility of a population.
Another issue that concerned gay rights advocates involved the automatic changing of data during the tabulation process. This automatic software data compiling method, called ''allocation'', was designed to counteract mistakes and discrepancies in returned questionnaires. Forms that were filled out by two same-sex persons who checked the "Husband/wife" relationship box were treated as a discrepancy. The Census Bureau explained that same-sex "Husband/wife" data samples were changed to "unmarried partner" by computer processing methods in 99% of the cases. In the remaining 1%, computer systems used one of two possibilities: a) one of the two listed sexes was changed, making the partnership appear heterosexual, or b) if the two partners were more than 15 years apart in age, they might have been reassigned into a familial parent/child relationship. The process of automatic reassignment of same-sex marriage data was initiated so that the Census Bureau would not contravene the Defense of Marriage Act
The Defense of Marriage Act (DOMA) was a United States federal law passed by the 104th United States Congress and signed into law by President Bill Clinton. It banned federal recognition of same-sex marriage by limiting the definition of marr ...
passed in 1996. The Act states:
With allocation moving married same-sex couples to the unmarried partner category, social scientists lost information that could have been extracted relating to the social stability of a same-gender couple who identify themselves as married.
References
SourcesConstitution Article I Section II re Enumeration and Apportionment
Further reading
* .External links
United States Census Bureau
Population Profile Introductory slide show
in
MS Powerpoint
Microsoft PowerPoint is a presentation program, created by Robert Gaskins and Dennis Austin at a software company named Forethought, Inc. It was released on April 20, 1987, initially for Macintosh computers only. Microsoft acquired PowerPoi ...
format
State and County QuickFacts
the most requested information
for population, housing, economic, and geographic data
2000 United States Census Form
2001 U.S Census Report
Contains 2000 census results
Other 2000 census websites
MLA Language Map
from the Modern Language Association
How the Census Works
via Howstuffworks.com {{Authority control
Census 2000
The United States census of 2000, conducted by the Census Bureau, determined the resident population of the United States on April 1, 2000, to be 281,421,906, an increase of 13.2 percent over the 248,709,873 people enumerated during the 1990 ce ...
United States census
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...