Two-dimensional magnetic recording on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Two-dimensional magnetic recording (TDMR) is a technology introduced in 2017 in
Two-dimensional magnetic recording (TDMR) is a technology introduced in 2017 in
/ref> TDMR is a ''read-back'' technology and thus applies equally well to future recording (writing) technologies such as
INSIC
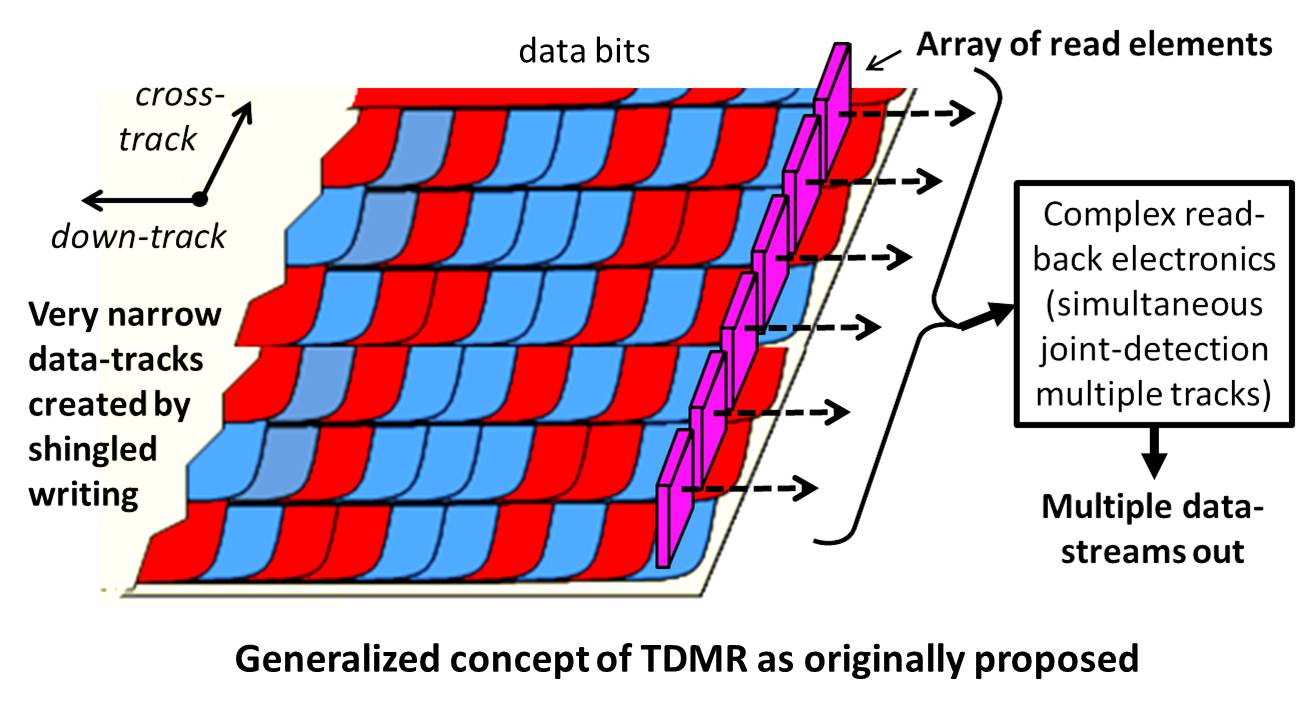
to explore alternative future storage technologies. In the initial concept, the data-tracks were assumed to be very narrow tracks created by shingled recording and subject to considerable mutual interference. The read-heads were assumed to be each centered over a corresponding data-track and a joint detector would optimally recover data from several tracks simultaneously. The technique was viewed as akin to PRML in providing gains similar to and in addition to the gains from PRML but operating across the tracks rather than down the track. A relatively large body of subsequent work has explored this configuration primarily from the perspective of
 In 2017, M. Fatih Erden announced at the TMRC conference that Seagate had been shipping HDDs with TDMR since earlier that year. This was followed by
In 2017, M. Fatih Erden announced at the TMRC conference that Seagate had been shipping HDDs with TDMR since earlier that year. This was followed by
In concept, there is little change to the read electronics except that the equalizer that shapes the signal prior to detection now has two inputs and must be appropriately optimized. However, In practice, there is significant added complexity in the read electronics and in the setup process during manufacturing. This complexity is associated with optimization of the equalization (waveform shaping) and timing recovery for the dynamically varying offtrack conditions - further complicated by the cross-track offset between readers that varies with radius. The HDD servo system also utilizes the position error signals from the two readers. Doing so reduces the repeatable runout, especially when the readers have a wider separation.G. Guo and J. Yu, "Data storage device comprising dual read sensors and dual servo channels to improve servo demodulation", US Patent 901382, Apr. 21, 2015.
/ref>
 Two-dimensional magnetic recording (TDMR) is a technology introduced in 2017 in
Two-dimensional magnetic recording (TDMR) is a technology introduced in 2017 in hard disk drives
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magn ...
(HDD) used for computer data storage
Computer data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers.
The central processing unit (CPU) of a comput ...
. Most of the world's data is recorded on HDDs, and there is continuous pressure on manufacturers to create greater data storage capacity in a given HDD form-factor and for a given cost. In an HDD, data is stored using magnetic recording
Magnetic storage or magnetic recording is the storage of data on a magnetized medium. Magnetic storage uses different patterns of magnetisation in a magnetizable material to store data and is a form of non-volatile memory. The information is ac ...
on a rotating magnetic disk and is accessed through a write-head and read-head (or read-element). TDMR allows greater storage capacity by advantageously combining signals simultaneously from multiple read-back heads to enhance the recovery of one or more of data-tracks. In this manner, data can be stored with higher areal-density on the disks thus providing higher capacity in each HDD.T. Coughlin, "Two-dimensional Magnetic Recording and other HDD news", Forbes: Enterprise Tech., Apr 29, 2018/ref> TDMR is a ''read-back'' technology and thus applies equally well to future recording (writing) technologies such as
Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording
Heat-assisted magnetic recording (HAMR) (pronounced "''hammer")'' is a magnetic storage technology for greatly increasing the amount of data that can be stored on a magnetic device such as a hard disk drive by temporarily heating the disk materia ...
(HAMR) and Microwave-Assisted Magnetic Recording (MAMR).
Overview
The TDMR approach arose from a working group set up undeINSIC
to explore alternative future storage technologies. In the initial concept, the data-tracks were assumed to be very narrow tracks created by shingled recording and subject to considerable mutual interference. The read-heads were assumed to be each centered over a corresponding data-track and a joint detector would optimally recover data from several tracks simultaneously. The technique was viewed as akin to PRML in providing gains similar to and in addition to the gains from PRML but operating across the tracks rather than down the track. A relatively large body of subsequent work has explored this configuration primarily from the perspective of
signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing '' signals'', such as sound, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, ...
. However, the technical challenge of creating an array of closely spaced read-heads and the complexity of jointly detecting data simultaneously on several tracks are both considerable.
Implementations
 In 2017, M. Fatih Erden announced at the TMRC conference that Seagate had been shipping HDDs with TDMR since earlier that year. This was followed by
In 2017, M. Fatih Erden announced at the TMRC conference that Seagate had been shipping HDDs with TDMR since earlier that year. This was followed by Western Digital
Western Digital Corporation (WDC, commonly known as Western Digital or WD) is an American computer drive manufacturer and data storage company, headquartered in San Jose, California. It designs, manufactures and sells data technology produ ...
in 2018 and Toshiba
, commonly known as Toshiba and stylized as TOSHIBA, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. Its diversified products and services include power, industrial and social infrastructure systems, ...
in 2019. These actual first implementations of TDMR are much simpler and very different to the scenario originally envisioned above. Current implementations recover only a single track using a read head with just two read-elements stacked one above the other (i.e. downtrack) and rely on the skew arising from the use of a rotary actuator
A rotary actuator is an actuator that produces a rotary motion or torque.
The simplest actuator is purely mechanical, where linear motion in one direction gives rise to rotation. The most common actuators are electrically powered; others may be p ...
to create some cross-track separation between the sensors. This TDMR approach is being applied to both Shingled (SMR) and conventional PMR HDDs. The gains achieved are quite modest (6 to 12%) but are expected to increase going forward as more complex schemes are implemented .In concept, there is little change to the read electronics except that the equalizer that shapes the signal prior to detection now has two inputs and must be appropriately optimized. However, In practice, there is significant added complexity in the read electronics and in the setup process during manufacturing. This complexity is associated with optimization of the equalization (waveform shaping) and timing recovery for the dynamically varying offtrack conditions - further complicated by the cross-track offset between readers that varies with radius. The HDD servo system also utilizes the position error signals from the two readers. Doing so reduces the repeatable runout, especially when the readers have a wider separation.
/ref>
References
{{Reflist rotating magnetic disk