Turkic Migration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Turkic migrations were the spread of Turkic tribes and
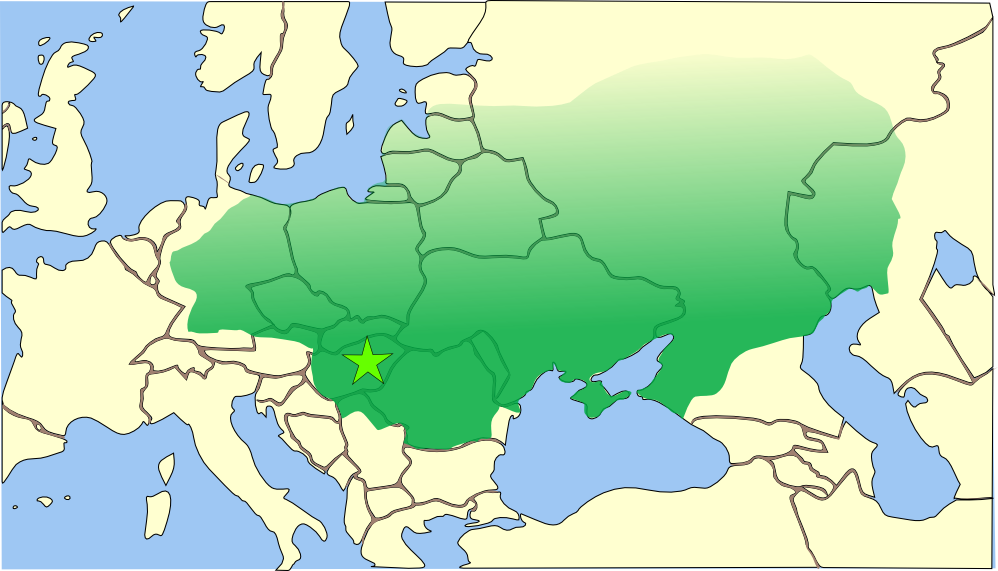 Proposals for the homeland of the Turkic peoples and their language are far-ranging, from the Transcaspian steppe to
Proposals for the homeland of the Turkic peoples and their language are far-ranging, from the Transcaspian steppe to


 The
The
 The Karluks migrated into the area of
The Karluks migrated into the area of
 The Oghuz Turks take their name from the Turkic word for 'clan', 'tribe', or 'kinship'. As such, Oghuz is a common appellation for many Turkic groups, such as the
The Oghuz Turks take their name from the Turkic word for 'clan', 'tribe', or 'kinship'. As such, Oghuz is a common appellation for many Turkic groups, such as the
Turkic languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia ( Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turki ...
across Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
and between the 6th and 11th centuries. In the 6th century, the Göktürks
The Göktürks, Celestial Turks or Blue Turks ( otk, 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰰:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, Türük Bodun; ; ) were a nomadic confederation of Turkic peoples in medieval Inner Asia. The Göktürks, under the leadership of Bumin Qaghan (d. 552) a ...
overthrew the Rouran Khaganate
The Rouran Khaganate, also Juan-Juan Khaganate (), was a tribal confederation and later state founded by a people of Proto-Mongolic Donghu origin.*Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (2000)"Ji 姬 and Jiang 姜: The Role of Exogamic Clans in the Organizati ...
in what is now Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million ...
and expanded in all directions, spreading Turkic culture throughout the Eurasian steppes
The Eurasian Steppe, also simply called the Great Steppe or the steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. It stretches through Hungary, Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova and Transnistria ...
. Although Göktürk empires came to an end in the 8th century, they were succeeded by numerous Turkic empires such as the Uyghur Khaganate
The Uyghur Khaganate (also Uyghur Empire or Uighur Khaganate, self defined as Toquz-Oghuz country; otk, 𐱃𐰆𐰴𐰕:𐰆𐰍𐰕:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, Toquz Oγuz budun, Tang-era names, with modern Hanyu Pinyin: or ) was a Turkic empire that e ...
, Kara-Khanid Khanate, Khazars
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire coverin ...
, and the Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
. Some Turks eventually settled down into sedentary societies such as the Qocho and Ganzhou
Ganzhou (), alternately romanized as Kanchow, is a prefecture-level city in the south of Jiangxi province, China, bordering Fujian to the east, Guangdong to the south, and Hunan to the west. Its administrative seat is at Zhanggong District.
Hist ...
Uyghurs
The Uyghurs; ; ; ; zh, s=, t=, p=Wéiwú'ěr, IPA: ( ), alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central Asia, Cent ...
. The Seljuq dynasty
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
settled in Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
starting in the 11th century, resulting in permanent Turkic settlement and presence there. Modern nations with large Turkic populations include Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the ea ...
, Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the s ...
, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
, Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
and Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, and Turkic populations also exist within other nations, such as Chuvashia
Chuvashia (russian: Чувашия; cv, Чӑваш Ен), officially the Chuvash Republic — Chuvasia,; cv, Чӑваш Республики — Чӑваш Ен is a republic of Russia located in Eastern Europe. It is the homeland of the Chuv ...
, Bashkortostan
The Republic of Bashkortostan or Bashkortostan ( ba, Башҡортостан Республикаһы, Bashqortostan Respublikahy; russian: Республика Башкортостан, Respublika Bashkortostan),; russian: Респу́блик� ...
, Tatarstan
The Republic of Tatarstan (russian: Республика Татарстан, Respublika Tatarstan, p=rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə tətɐrˈstan; tt-Cyrl, Татарстан Республикасы), or simply Tatarstan (russian: Татарстан, tt ...
, the Crimean Tatars, the Kazakhs
The Kazakhs (also spelled Qazaqs; Kazakh: , , , , , ; the English name is transliterated from Russian; russian: казахи) are a Turkic-speaking ethnic group native to northern parts of Central Asia, chiefly Kazakhstan, but also part ...
in Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million ...
, the Uyghurs
The Uyghurs; ; ; ; zh, s=, t=, p=Wéiwú'ěr, IPA: ( ), alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central Asia, Cent ...
in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, the Azeri in Iran, and the Sakha Republic
Sakha, officially the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia),, is the largest republic of Russia, located in the Russian Far East, along the Arctic Ocean, with a population of roughly 1 million. Sakha comprises half of the area of its governing Far E ...
in Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
.
Origin theories
 Proposals for the homeland of the Turkic peoples and their language are far-ranging, from the Transcaspian steppe to
Proposals for the homeland of the Turkic peoples and their language are far-ranging, from the Transcaspian steppe to Northeastern Asia
Northeast Asia or Northeastern Asia is a geographical subregion of Asia; its northeastern landmass and islands are bounded by the Pacific Ocean.
The term Northeast Asia was popularized during the 1930s by American historian and political scien ...
(Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
). Peter Benjamin Golden
Peter Benjamin Golden (born 1941) is an American historian who is Professor Emeritus of History, Turkish and Middle Eastern Studies at Rutgers University. He has written many books and articles on Turkic and Central Asian Studies, such as ''An ...
listed Proto-Turkic lexical items about the climate, topography, flora, fauna, people's modes of subsistence in the hypothetical Proto-Turkic Urheimat and proposed that the Proto-Turkic Urheimat was located at the southern, taiga
Taiga (; rus, тайга́, p=tɐjˈɡa; relates to Mongolic and Turkic languages), generally referred to in North America as a boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, sp ...
-steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate gras ...
zone of the Sayan- Altay region. According to Yunusbayev et al. (2015), genetic evidence points to an origin in the region near South Siberia and Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million ...
as the "Inner Asian Homeland" of the Turkic ethnicity. Similarly several linguists, including Juha Janhunen
Juha Janhunen (born 12 February 1952 in Pori, Finland) is a Finnish linguist whose wide interests include Uralic and Mongolic languages. Since 1994 he has been Professor in East Asian studies at the University of Helsinki. He has done fieldwork on ...
, Roger Blench and Matthew Spriggs, suggest that Mongolia is the homeland of the early Turkic language. According to Robbeets, the Turkic people descend from people who lived in a region extending from present-day South Siberia and Mongolia to the West Liao River
The Liao River () is the principal river in southern Northeast China, and one of the seven main river systems in China. Its name derived from the Liao region, a historical name for southern Manchuria, from which the Liaoning province, Liaodong ...
Basin (modern Manchuria). Authors Joo-Yup Lee and Shuntu Kuang analyzed ten years of genetic research on Turkic people and compiled scholarly information about Turkic origins, and said that the early and medieval Turks were a heterogeneous
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts often used in the sciences and statistics relating to the uniformity of a substance or organism. A material or image that is homogeneous is uniform in composition or character (i.e. color, shape, siz ...
group and that the Turkification of Eurasia was a result of language diffusion, not a migration of a homogeneous population.
Hunnic theory
The Huns were anomadic people
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the po ...
who lived in Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
, the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
, and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whi ...
, between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catch ...
, in an area that was part of Scythia
Scythia ( Scythian: ; Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) or Scythica (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Pontic Scythia, was a kingdom created by the Scythians during the 6th to 3rd centuries BC in the Pontic–Caspian steppe.
...
at the time; the Huns' arrival is associated with the migration westward of an Indo-Iranian people, the Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
. The Huns have often been considered a Turkic people, and sometimes associated with the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
. While in Europe, the Huns incorporated others, such as Goths, Slavs, and Alans.
The Huns were not literate (according to Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea ( grc-gre, Προκόπιος ὁ Καισαρεύς ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; la, Procopius Caesariensis; – after 565) was a prominent late antique Greek scholar from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman gen ...
Maenchen-Helfen (1973) page 376.) and left nothing linguistic with which to identify them except their names, which derive from Germanic, Iranian, Turkic, unknown and a mixture. Some, such as Ultinčur and Alpilčur, are like Turkish names ending in -čor, Pecheneg names in - and Kirghiz names in -čoro. Names ending in -gur, such as Utigur
Utigurs were Turkic nomadic equestrians who flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe in the 6th century AD. They possibly were closely related to the Kutrigurs and Bulgars.
Etymology
The name ''Ut(r)igur'', recorded as , and , is generally cons ...
and Onogur, and -gir, such as Ultingir, are like Turkish names of the same endings.
The actual identity of the Huns is still debated. Concerning the cultural genesis of the Huns, the ''Cambridge Ancient History of China'' asserts: "Beginning in about the eighth century BC, throughout inner Asia horse-riding pastoral communities appeared, giving origin to warrior societies." These were part of a larger belt of "equestrian pastoral peoples" stretching from the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
to Mongolia, and known to the Greeks as the Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Cent ...
which were Iranian peoples.
History
Göktürk wave (5th-8th c.)


Tiele and Turk
The earliest Turks mentioned in textual sources are the Xinli (), Gekun (), and Tiele (), the last of which possibly transcribes endonym ''*Tegreg'' ' eople of theCarts', recorded by the Chinese in the 6th century. According to the ''New Book of Tang
The ''New Book of Tang'', generally translated as the "New History of the Tang" or "New Tang History", is a work of official history covering the Tang dynasty in ten volumes and 225 chapters. The work was compiled by a team of scholars of the So ...
'', Tiele is just a mistaken form of ''Chile''/''Gaoche'', who themselves are related to Xiongnu and Dingling. Many scholars believe the Di, Dili, Dingling, and later Tujue mentioned in textual sources are all just Chinese transcriptions of the same Turkic word ''türk'', yet Golden proposes that ''Tujue'' transcribed *''Türküt'' while ''Dili'', ''Dingling'', ''Chile'', ''Tele'', & ''Tiele'' transcribed *''Tegreg''.
The first reference to ''Türk'' or ''Türküt'' appears in 6th-century Chinese sources as the transcription ''Tūjué'' (). The earliest evidence of Turkic languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia ( Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turki ...
and the use of ''Turk'' as an endonym comes from the Orkhon inscriptions
The Orkhon inscriptions (also known as the Orhon inscriptions, Orhun inscriptions, Khöshöö Tsaidam monuments (also spelled ''Khoshoo Tsaidam'', ''Koshu-Tsaidam'' or ''Höshöö Caidam''), or Kul Tigin steles ( zh, t=闕特勤碑, s=阙特勤� ...
of the Göktürks
The Göktürks, Celestial Turks or Blue Turks ( otk, 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰰:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, Türük Bodun; ; ) were a nomadic confederation of Turkic peoples in medieval Inner Asia. The Göktürks, under the leadership of Bumin Qaghan (d. 552) a ...
( en, 'Celestial Turks') in the early 8th century. Many groups speaking Turkic languages never adopted the name ''Turk'' for their own identity. Among the peoples that came under Göktürk dominance and adopted its political culture and lingua-franca, the name ''Turk'' was not always the preferred identity. Turk, therefore, did not apply to all Turkic peoples at the time, but only referred to the Eastern Turkic Khaganate, while the Western Turkic Khaganate
The Western Turkic Khaganate () or Onoq Khaganate ( otk, 𐰆𐰣:𐰸:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, On oq budun, Ten arrow people) was a Turkic khaganate in Eurasia, formed as a result of the wars in the beginning of the 7th century (593–603 CE) after ...
and Tiele used their own tribal names. Of the Tiele, the ''Book of Sui
The ''Book of Sui'' (''Suí Shū'') is the official history of the Sui dynasty. It ranks among the official Twenty-Four Histories of imperial China. It was written by Yan Shigu, Kong Yingda, and Zhangsun Wuji, with Wei Zheng as the lead author. ...
'' mentions only tribes which were not part a part of the First Turkic Khaganate. There was not a unified expansion of Turkic tribes. Peripheral Turkic peoples in the Göktürk Empire like the Bulgars and even central ones like the Oghuz and Karluks migrated autonomously with migrating traders, soldiers and townspeople.
The precise date of the initial expansion from the early homeland remains unknown. The first state known as ''Turk'', giving its name to the many states and peoples afterward, was that of the Göktürks (''gök'' 'blue' or 'celestial', however in this context ''gök'' refers to the direction 'east'. Therefore, Gökturks only denoted the Eastern Turks in the 6th century. In 439, the head of the Ashina clan led his people from Pingliang (now in modern Gansu province
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
) to the Rouran
The Rouran Khaganate, also Juan-Juan Khaganate (), was a tribal confederation and later state founded by a people of Proto-Mongolic Donghu origin.*Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (2000)"Ji 姬 and Jiang 姜: The Role of Exogamic Clans in the Organizat ...
seeking inclusion in their confederacy and protection. His tribe consisted of famed metalsmiths and was granted land near a mountain quarry that looked like a helmet, from which they got the name Turk/Tujue . In 546, the leader of the Ashina, Bumin, aided the Rouran in putting down a Tiele revolt. Bumin requested a Rouran princess for his service but was denied, after which he declared independence. In 551, Bumin declared himself Khagan and married Princess Changle from Western Wei
Wei (), known in historiography as the Western Wei (), was an imperial dynasty of China that followed the disintegration of the Northern Wei. One of the Northern dynasties during the era of the Northern and Southern dynasties, it ruled the weste ...
. He then dealt a serious blow to the Rouran Khaganate the next year, but died soon after. His sons, Issik Qaghan and Muqan Qaghan, continued to wage war on the Rouran, finishing them off in 554. By 568, their territory had reached the edges of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, where the Avars, possibly related to the Rouran in some fashion, escaped. In 581, Taspar Qaghan died and the khaganate entered a civil war that resulted in two separate Turkic factions. The Eastern Khaganate was defeated by the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
in 630 while the Western Khaganate fell to the Tang in 657. In 682, Ilterish Qaghan rebelled against the Tang and founded the Second Turkic Khaganate, which fell to the Uyghurs
The Uyghurs; ; ; ; zh, s=, t=, p=Wéiwú'ěr, IPA: ( ), alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central Asia, Cent ...
in 744.
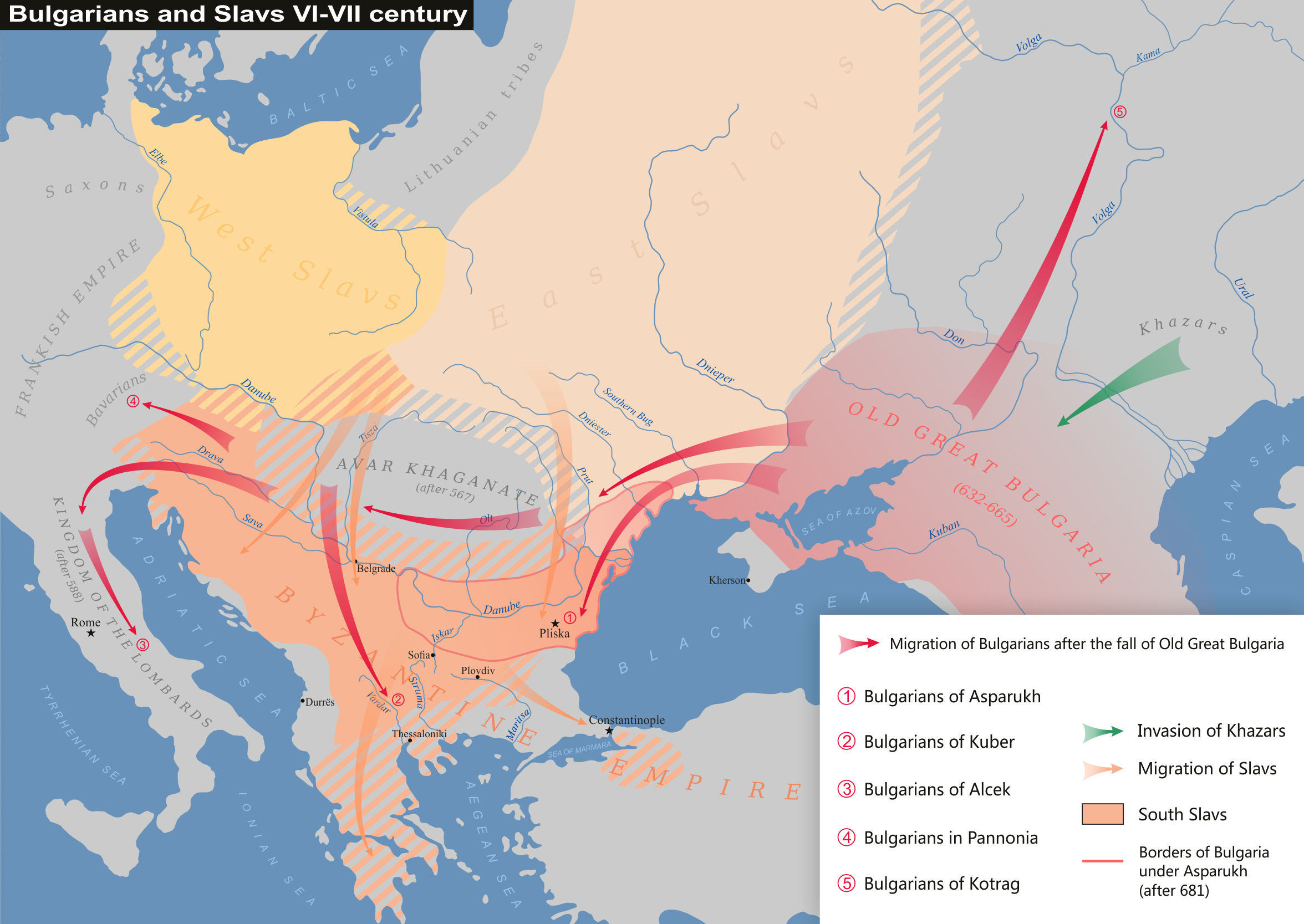
Bulgar
 The
The Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as noma ...
, also known as the Onogur-Bulgars or Onogundurs, arrived in the Kuban steppe
The Kuban steppe is one of the major steppes in Europe, located in southeastern Russia between the city of Rostov on Don and the Caucasus Mountains. The Kuban steppe is the historic home of the Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et ...
zone sometime during the 5th century. By the 7th century, they were under the rule of the Avars, who they revolted against in 635 under the leadership of Kubrat. Prior to this, Kubrat had made an alliance with Heraclius
Heraclius ( grc-gre, Ἡράκλειος, Hērákleios; c. 575 – 11 February 641), was Eastern Roman emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the exarch of Africa, led a revol ...
of the Byzantine Empire. He was baptized in 619. Kubrat died in the 660s and his territory, Old Great Bulgaria, was divided between his sons. Two of them were incorporated by the Khazars
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire coverin ...
, one headed to Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now west ...
, and one became a subject of the Byzantines. The Bulgars in Pannonia revolted against the Pannonian Avars and migrated to Thessalonika by 679. There they formed the First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire ( cu, блъгарьско цѣсарьствиѥ, blagarysko tsesarystviye; bg, Първо българско царство) was a medieval Bulgar- Slavic and later Bulgarian state that existed in Southeastern Eur ...
.
Khazar
The origin of the Khazars is unclear. According toAl-Masudi
Al-Mas'udi ( ar, أَبُو ٱلْحَسَن عَلِيّ ٱبْن ٱلْحُسَيْن ٱبْن عَلِيّ ٱلْمَسْعُودِيّ, '; –956) was an Arab historian, geographer and traveler. He is sometimes referred to as the " Herodotu ...
, the Khazars were called Sabirs in Turkic. Dunlop (1954) suggests a relation to Uyghurs
The Uyghurs; ; ; ; zh, s=, t=, p=Wéiwú'ěr, IPA: ( ), alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central Asia, Cent ...
, some of whom might have migrated west before 555 CE. Because imperial Chinese sources linked Khazars to Göktürks, others believe the Khazars were founded by Irbis Seguy, the penultimate ruler of the Western Turkic Khaganate, since the '' Hudud al-'Alam'' says the Khazar king descended from the Ansa, which has been interpreted as Ashina. By the mid-7th century, the Khazars were located in the North Caucasus
The North Caucasus, ( ady, Темыр Къафкъас, Temır Qafqas; kbd, Ишхъэрэ Къаукъаз, İṩxhərə Qauqaz; ce, Къилбаседа Кавказ, Q̇ilbaseda Kavkaz; , os, Цӕгат Кавказ, Cægat Kavkaz, inh, ...
, where they fought against the Umayyads constantly.
Kyrgyz
According to the '' Book of Tang'', the Yenisei Kyrgyz were tall, red-haired, pale-faced, and green-eyed; black-eyed Kyrgyzes were claimed to be descendants of Han general Li Ling, presumably including the Kyrgyz Khagans who claimed such descent. It also notes that Kyrgyz women outnumbered men, both men and women wore tattoos, and they made weapons which they gave to the Turks. They practiced agriculture but did not grow fruits. The Kyrgyz lived west ofLake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the ...
and east of the Karluks. According to the ''Book of Sui'', the Kyrgyz chaffed at the domination of the First Turkic Khaganate. The Uyghur Khaganate also made war on the Kyrgyz and cut them off from trade with China, which the Uyghurs monopolized. As a result, the Kyrgyz turned to other channels of trade such as with the Tibetans
The Tibetan people (; ) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Tibet. Their current population is estimated to be around 6.7 million. In addition to the majority living in Tibet Autonomous Region of China, significant numbers of Tibetans liv ...
, Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, and Karluks. From 820 onward, the Kyrgyz were constantly at war with the Uyghurs, until 840, when the Uyghur Khaganate was dismantled. Although the Kyrgyz managed to occupy some of the Uyghur lands, they had no great effect on the geopolitical configuration around them. The Chinese paid no heed to them other than to award them with some titles and reasoned that since the Uyghurs were no longer in power, there was no reason to maintain relations with the Kyrgyz any longer. The Kyrgyz themselves seemed to lack any interest in occupying the former territory of the Uyghurs in the east. By 924, the Khitans had occupied Otuken
Ötüken ( otk, 𐰇𐱅𐰜𐰤:𐰖𐰃𐱁, Ötüken yïš, "Ötüken forest", 𐰵𐱅𐰜𐰤:𐰘𐰼, ''Ötüken jer'', "Land of Ötüken", Old Uyghur: 𐰵𐱅𐰜𐰤:𐰘𐰃𐱁 ''Ötüken yïš''; ) was the capital of the First Turkic K ...
in the territory of the former Uyghur Khaganate.
Turgesh
In 699, the Turgesh rulerWuzhile
Wuzhile () (reconstructed Old Turkic *Üç EligS.G. Klyashtorny's reconstruction cited in or *Oçırlıq, ultimately from Pali Vajira) was the first Turgesh Qaghan, from the Sary (Yellow) Türgesh faction.
Early life
He was titled Bagha Tarkh ...
founded a khaganate stretching from Chach to Beshbalik
Beshbalik () is an ancient archaeological site, now located in Jimsar County, Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang, China. The ancient city was initially called Beiting () or Ting Prefecture (), and was the headquarters of the Beiting Protec ...
. He and his successor Saqal campaigned against the Tang dynasty and their Turkic allies until 711 when the resurgent Second Turkic Khaganate crushed the Turgesh in battle. Turgesh remnants under Suluk re-established themselves in Zhetysu
Zhetysu, or Jeti-Suu ( kk, , Жетісу, pronounced ; ky, ''Jeti-Suu'', (), meaning "seven rivers"; also transcribed ''Zhetisu'', ''Jetisuw'', ''Jetysu'', ''Jeti-su'', ''Jity-su'', ''Жетысу'',, National Geospatial-Intelligence Age ...
. Suluk was killed by one of his subordinates in 737 after he was defeated by the Umayyads. The Tang took advantage of the situation to invade Turgesh territory and took the city of Suyab
Suyab ( fa, سوی آب; Middle Chinese: /suʌiH jiᴇp̚/), also known as ''Ordukent'' (modern-day ''Ak-Beshim''), was an ancient Silk Road city located some 50 km east from Bishkek, and 8 km west southwest from Tokmok, in the Chu r ...
. In the 760s, the Karluks drove out the Turgesh.
Karluk
 The Karluks migrated into the area of
The Karluks migrated into the area of Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan c ...
as early as the 7th century. In 744, they participated in the Uyghur Khaganate's rise by overthrowing the Second Turkic Khaganate, but conflict with the Uyghurs forced them to migrate further west into Zhetysu. By 766, they had pushed out the Turgesh and took the Western Turkic capital of Suyab. Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
began spreading in the Karluk tribes during the 9th century. According to the ''Hudud al-'Alam'', written in the 10th century, the Karluks were pleasant nearly civilized people who participated in agriculture as well as herding and hunting. Al-Masudi considered the Karluks to be the most beautiful people among the Turks, being tall in stature, and lordly in appearance. By the 11th century, they had integrated a considerable number of Sogdians into their population, resulting in speech that to Mahmud al-Kashgari
Mahmud ibn Husayn ibn Muhammed al-Kashgari, ''Maḥmūd ibnu 'l-Ḥusayn ibn Muḥammad al-Kāšġarī'', , tr, Kaşgarlı Mahmûd, ug, مەھمۇد قەشقىرى, ''Mehmud Qeshqiri'' / Мәһмуд Қәшқири uz, Mahmud Qashg'ariy / М ...
, sounded slurred. The Karluks, Chigil
The Chigil (Chihil, and also (D)Jigil, Cihil, Chiyal) were a Turkic tribe known from the 7th century CE as living around Issyk Kul lake area. They were considered to be descended from the tribe Chuyue, who were of mixed Yueban- Western Turkic o ...
s, and Yagmas formed the Kara-Khanid Khanate in the 9th century, but it's unclear whether the leadership of the new polity fell to the Karluks or the Yagmas.
=Remarks
=Pecheneg
Paul Pelliot (apud Pritsak, 1975) first proposed that the 7th century Chinese historical ''Book of Sui'' preserved the earliest record on the Pechenegs; the book mentioned a people named Bĕirù (; LMC: * < EMC: *), who had settled near the Ēnqū (; LMC: * < EMC: * < *''On ur'') and Alan (; MC: *) peoples (identified as Onogurs and Alans, respectively), to the east of Fulin () (or theEastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantino ...
). Victor Spinei emphasizes that the Pechenegs' association with the ''Bĕirù'' is "uncertain"; instead, he asserts that an 8th-century Uighur envoy's report, which survives in Tibetan translation, contains the first certain reference to the Pechenegs: the report recorded an armed conflict between the ''Be-ča-nag'' and the ''Hor'' (Uyghurs or Oghuz Turks
The Oghuz or Ghuzz Turks (Middle Turkic: ٱغُز, ''Oγuz'', ota, اوغوز, Oġuz) were a western Turkic people that spoke the Oghuz branch of the Turkic language family. In the 8th century, they formed a tribal confederation conven ...
) peoples in the region of the river Syr Darya. The Pecheneg tribes were possibly related to the Kangly. In the late 9th century, conflict with the Khazars drove the Pechenegs into the Pontic steppes. In the 10th century, they had substantial interactions with the Byzantine Empire, who depended on them for keeping control of their neighbors. Byzantine and Muslim sources confirm that the Pechenegs had a leader, but the position was not passed down from father to son. In the 10th century, the Pechenegs came into military conflict with the Rus', and in the early 11th century, military conflict with the Oghuz Turks drove them further west across the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
into Byzantine territory.
Uyghur wave (8th-9th c.)
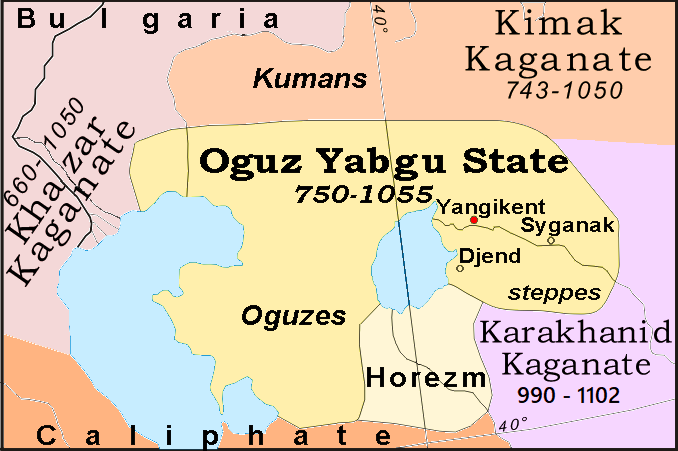
Oghuz
 The Oghuz Turks take their name from the Turkic word for 'clan', 'tribe', or 'kinship'. As such, Oghuz is a common appellation for many Turkic groups, such as the
The Oghuz Turks take their name from the Turkic word for 'clan', 'tribe', or 'kinship'. As such, Oghuz is a common appellation for many Turkic groups, such as the Toquz Oghuz
The Toquz Oghuz ( otk, 𐱃𐰸𐰆𐰔:𐰆𐰍𐰔, Toquz Oγuz; ; "Turks of Nine Bones") was a political alliance of nine Turkic-speaking Tiele tribes in Inner Asia, during the early Middle Ages. The Toquz Oghuz was consolidated and subordi ...
(nine tribes), Sekiz Oghuz (eight tribes), and Uch Oghuz (three tribes). Oghuz has been used to refer to many different Turkic tribes, causing much confusion. For example, the ruler of the Oghuz was called the Toquz Khagan, even though there were twelve tribes instead of nine. It is uncertain if the Oghuz Turks were directly descended from the Toquz Oghuz. They may have been under the direct leadership of the Toquz at some point, but by the 11th century, the Oghuz were already linguistically distinct from their neighbors such as the Kipchaks
The Kipchaks or Qipchaks, also known as Kipchak Turks or Polovtsians, were a Turkic nomadic people and confederation that existed in the Middle Ages, inhabiting parts of the Eurasian Steppe. First mentioned in the 8th century as part of the ...
and Karakhanids. Zuev (1960) connects the Oghuzes to the Western Turkic tribe (< MC *) mentioned in the Chinese encyclopedia Tongdian, as well as the 'Three ' (< MC *) in the 8th-century () 'Venus's Secret Classic' and the three hordes mentioned in Al-Masudi's Meadows of Gold and Mines of Gems.
The Oghuz migration westward began with the fall of the Second Turkic Khaganate and the rise of the Uyghur Khaganate in 744. Under the Uyghur rule, the Oghuz leader obtained the title of "right yabgu
Yabghu ( otk, 𐰖𐰉𐰍𐰆, yabγu,Entrabγu">"𐰖𐰉𐰍𐰆_[yabγuйабғұ"in_"Ethno-Cultural_Dictionary"_''Türik_Bitig''_),_also_rendered_as_Jabgu,_Djabgu_or_Yabgu,_was_a_state_office_in_the_early_Turkic_peoples.html" ;"title="abγuй ...
". When they appeared in Muslim textual sources in the 9th century, they were described using the same title. The Oghuz fought a series of wars with the Pechenegs, Khalaj people, Khalaj, Charuk, and Khazars for the steppes, emerging victorious and establishing the Oghuz Yabgu State. The Oghuz were in constant conflict with the Pechenegs and Khazars throughout the 10th century, as recorded by Muslim texts, but they also cooperated at times. In one instance, the Khazars hired the Oghuz to fight off an attack by the Alans. In 965, the Oghuz took part in a Rus' attack on the Khazars and in 985 they joined the Rus' again in attacking Volga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria or Volga–Kama Bulgaria, was a historic Bulgar state that existed between the 7th and 13th centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama River, in what is now European Russia. Volga Bulgaria was a multi-ethnic state ...
. The Yabgu State of the Oghuz did not have a central leadership and there is no evidence of the Yabgu acting as a spokesman for the entire Oghuz people. By the 10th century, some Oghuz had settled in towns and converted to Islam, although many tribes still followed Tengrism
Tengrism (also known as Tengriism, Tengerism, or Tengrianism) is an ethnic and old state Turko- Mongolic religion originating in the Eurasian steppes, based on folk shamanism, animism and generally centered around the titular sky god Tengri. ...
.
Cuman Kipchak
The relationship and origins of theCumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
and Kipchaks is uncertain. Probably, Cumans and Kipchaks had originally been two distinct Turkic peoples who joined one same confederation, with Cumans constituting the western part and Kipchaks the eastern part. According to Rashid al-Din Hamadani
Rashīd al-Dīn Ṭabīb ( fa, رشیدالدین طبیب; 1247–1318; also known as Rashīd al-Dīn Faḍlullāh Hamadānī, fa, links=no, رشیدالدین فضلالله همدانی) was a statesman, historian and physician in Ilk ...
, writing much later in the Ilkhanate
The Ilkhanate, also spelled Il-khanate ( fa, ایل خانان, ''Ilxānān''), known to the Mongols as ''Hülegü Ulus'' (, ''Qulug-un Ulus''), was a khanate established from the southwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanid realm ...
, ''Kipchak'' is derived from a Turkic word which means 'hollow rotted out tree'. Cuman may be derived from the Turkic word , which means 'pale' or 'yellow". Some scholars associate the Cumans-Kipchaks with the Kankalis
The Kangly (康曷利; pinyin: Kānghélì; Middle Chinese ( ZS): /kʰɑŋ-ɦɑt̚-liɪH/ or 康里 pinyin: ''Kānglĭ'' < MC-ZS: /kʰɑŋ-lɨX/; Moyun Chur inscription, though this was uncertain as only the letters 𐰲𐰴 (čq *''čaq''?) were readable on the damaged inscription; they were first definitely mentioned in the 9th century by


 Later Turkic peoples include the Khazars,
Later Turkic peoples include the Khazars,
The Turkic Expansion
{{DEFAULTSORT:Turkic Migration History of the Turkic peoples Migration Period History of Central Asia Historical migrations
Ibn Khordadbeh
Abu'l-Qasim Ubaydallah ibn Abdallah ibn Khordadbeh ( ar, ابوالقاسم عبیدالله ابن خرداذبه; 820/825–913), commonly known as Ibn Khordadbeh (also spelled Ibn Khurradadhbih; ), was a high-ranking Persian bureaucrat and ...
, who placed them next to the Toquz Oghuz, while Al-Biruni claimed that the Qun were further east of them. Habash al-Hasib al-Marwazi
Ahmad ibn 'Abdallah Habash Hasib Marwazi (766 - d. after 869 in Samarra, Iraq ) was a north-eastern Iranian astronomer, geographer, and mathematician from Merv in Khorasan who for the first time described the trigonometric ratios: sine, cosine, t ...
writes that the Qun came from the lands of Cathay
Cathay (; ) is a historical name for China that was used in Europe. During the early modern period, the term ''Cathay'' initially evolved as a term referring to what is now Northern China, completely separate and distinct from China, which ...
which they fled from in fear of the Khitans. This may have been what the Armenian chronicler Matthew of Edessa was referring to when he recounted Pale Ones being driven out by the people of the Snakes, whom Golden identified as a Mongolic or para-Mongolic people known as in Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
, in Old Turkic, and ''Kumo Xi
The Kumo Xi (Xu Elina-Qian, p.296b), also known as the Tatabi, were a Mongolic steppe people located in current Northeast China from 207 CE to 907 CE. After the death of their ancestor Tadun in 207, they were no longer called Wuhuan but joined ...
'' in Chinese language
Chinese (, especially when referring to written Chinese) is a group of languages spoken natively by the ethnic Han Chinese majority and many minority ethnic groups in Greater China. About 1.3 billion people (or approximately 16% of the ...
.
Kimek
In the mid-9th century, the Kimek-Kipchak confederation emerged in the northern steppes stretching from Lake Balkhash in the east to theAral Sea
The Aral Sea ( ; kk, Арал теңізі, Aral teñızı; uz, Орол денгизи, Orol dengizi; kaa, Арал теңизи, Aral teńizi; russian: Аральское море, Aral'skoye more) was an endorheic lake lying between Kazak ...
in the west. They were a confederation of seven minor tribes: Yemeks, Imur, Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turki ...
, Bayandur, Kipchaks, Lanikaz, and in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turki ...
Ajlad
The Ajlad was a Turkic tribe or clan. They were one of seven original tribes that made up the Kimek confederation. They originated from the Central Asian steppes.
The Ajlad were one of seven original tribes that made up the Kimek confederation, ...
; and whose leader held the title of "Shad Tutuk", derived from the Middle Chinese
Middle Chinese (formerly known as Ancient Chinese) or the Qieyun system (QYS) is the historical variety of Chinese recorded in the '' Qieyun'', a rime dictionary first published in 601 and followed by several revised and expanded editions. The ...
military title 'military governor' (> standard Chinese
Standard Chinese ()—in linguistics Standard Northern Mandarin or Standard Beijing Mandarin, in common speech simply Mandarin, better qualified as Standard Mandarin, Modern Standard Mandarin or Standard Mandarin Chinese—is a modern standa ...
: ), but started using the title of "Yabgu" instead when remnants of the Uyghur Khaganate fled to them in 840. By the early 10th century, the Kimeks bordered the Oghuz to the south, where the Ural formed the boundary. According to the ''Hudud al-'Alam'', written in the 10th century, the Kimeks used the title of Khagan. They were the most removed from the sedentary civilization of all the Turks and had only one town within their territory. In the 11th century, the Kimeks were displaced by the Cumans.
Later Turkic peoples


 Later Turkic peoples include the Khazars,
Later Turkic peoples include the Khazars, Turkmens
Turkmens ( tk, , , , ; historically "the Turkmen"), sometimes referred to as Turkmen Turks ( tk, , ), are a Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia, living mainly in Turkmenistan, northern and northeastern regions of Iran and north-weste ...
: either Karluks (mainly 8th century) or Oghuz Turks, Uyghurs, Yenisei Kyrgyz, Pechenegs, Cumans-Kipchaks, etc. As these peoples were founding states in the area between Mongolia and Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (Land beyond the Oxus) is the Latin name for a region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to modern-day eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
, they came into contact with Muslims, and most gradually adopted Islam. However, most groups of Turkic people who belonged to other religions, including Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ� ...
, Judaists, Buddhists
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
, Manichaeans, and Zoroastrians.
Turkmens
While the Karakhanid state remained in this territory until its conquest byGenghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; ; xng, Temüjin, script=Latn; ., name=Temujin – August 25, 1227) was the founder and first Great Khan (Emperor) of the Mongol Empire, which became the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in history a ...
, the Turkmen group of tribes was formed around the core of the Karluks and the more westward Oghuzes. The current majority view for the etymology of the name is that it comes from ''Türk'' and the Turkic emphasizing suffix ''-men'', meaning 'most Turkish of the Turks' or 'pure-blooded Turks.', Thus, the ethnic consciousness among some, but not all Turkic tribes as "Turkmens" in the Islamic era came long after the fall of the non-Muslim Gokturk (and Eastern and Western) Khanates.
Turkic soldiers in the army of the Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Mutta ...
caliphs emerged as the ''de facto'' rulers of much of the Muslim Middle East (apart from Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
and North Africa) from the 13th century. The Oghuz and other tribes captured and dominated various countries under the leadership of the Seljuk dynasty
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
, and eventually captured the territories of the Abbasid dynasty and the Byzantine Empire.
Meanwhile, the Kyrgyz and Uyghurs were struggling with one another and with the Chinese Empire. The Kyrgyz people ultimately settled in the region now referred to as Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the ea ...
. The Batu hordes conquered the Volga Bulgars
Volga Bulgaria or Volga–Kama Bulgaria, was a historic Bulgar state that existed between the 7th and 13th centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama River, in what is now European Russia. Volga Bulgaria was a multi-ethnic state ...
in what is today Tatarstan
The Republic of Tatarstan (russian: Республика Татарстан, Respublika Tatarstan, p=rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə tətɐrˈstan; tt-Cyrl, Татарстан Республикасы), or simply Tatarstan (russian: Татарстан, tt ...
and Kypchaks
The Kipchaks or Qipchaks, also known as Kipchak Turks or Polovtsians, were a Turkic nomadic people and confederation that existed in the Middle Ages, inhabiting parts of the Eurasian Steppe. First mentioned in the 8th century as part of the Sec ...
in what is now Southern Russia, following the westward sweep of the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
in the 13th century. Other Bulgars settled in Europe in the seventh and eighth centuries, but were assimilated by the Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
, giving the name to the Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe.
Etymology
Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not completely underst ...
and the Slavic Bulgarian language
Bulgarian (, ; bg, label=none, български, bălgarski, ) is an Eastern South Slavic language spoken in Southeastern Europe, primarily in Bulgaria. It is the language of the Bulgarians.
Along with the closely related Macedonian l ...
.
It was under Seljuq suzerainty that numerous Turkmen tribes, especially those that came through the Caucasus via Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
, acquired fiefdoms (beyliks
Anatolian beyliks ( tr, Anadolu beylikleri, Ottoman Turkish: ''Tavâif-i mülûk'', ''Beylik'' ) were small principalities (or petty kingdoms) in Anatolia governed by beys, the first of which were founded at the end of the 11th century. A secon ...
) in newly conquered areas of Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
and even the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
. Thus, the ancestors of the founding stock of the modern Turkish nation were most closely related to the Oghuz Turkmen groups that settled in the Caucasus and later became the Azerbaijani nation.
By early modern times, the name ''Turkestan'' has several definitions:
# land of sedentary Turkic-speaking townspeople that have been subjects of the Central Asian Chagatayids, i.e. Sarts, Central Asian Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
, Central Asian Timurids, Taranchi of Chinese Turkestan, and the later invading East Kipchak Tatars who mixed with local Sarts and Chagatais to form the Uzbeks
The Uzbeks ( uz, , , , ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the wider Central Asian region, being among the largest Turkic ethnic group in the area. They comprise the majority population of Uzbekistan, next to Kazakh and Karakalpak mino ...
; This area roughly coincides with Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
in the widest sense, plus Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hyd ...
which was known as Chinese Turkestan. It is ethnically diverse, and includes homelands of non-Turkic peoples like the Tajiks, Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
, Dungans
Dungan, Xiao'erjing: ; zh, s=东干族, t=東干族, p=Dōnggān zú, w=Tung1kan1-tsu2, , Xiao'erjing: ; russian: Дунгане, ''Dungane''; ky, Дуңгандар, ''Duñgandar'', دۇنغاندار; kk, Дүңгендер, ''Düñgende ...
, and Dzungars
The Dzungar people (also written as Zunghar; from the Mongolian words , meaning 'left hand') were the many Mongol Oirat tribes who formed and maintained the Dzungar Khanate in the 17th and 18th centuries. Historically they were one of major tr ...
. Turkic peoples of the Kypchak branch, i.e. Kazakhs and Kyrgyz, are not normally considered Turkestanis but are also populous (as pastoralists) in many parts of Turkestan.
# a specific district governed by a 17th-century Kazakh Khan, in modern-day Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, which were more sedentary than other Kazakh areas, and were populated by towns-dwelling Sarts
See also
*Migration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roma ...
*Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
*Nomadic empire
Nomadic empires, sometimes also called steppe empires, Central or Inner Asian empires, were the empires erected by the bow-wielding, horse-riding, nomadic people in the Eurasian Steppe, from classical antiquity (Scythia) to the early modern era ...
*Eurasian nomads
The Eurasian nomads were a large group of nomadic peoples from the Eurasian Steppe, who often appear in history as invaders of Europe, Western Asia, Central Asia, Eastern Asia, and South Asia.
A nomad is a member of people having no permanent ab ...
* Turkic tribal confederations
* History of Central Asia
*Hephthalites
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during th ...
* Xionites
* Tatar invasions
*Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * *External links
The Turkic Expansion
{{DEFAULTSORT:Turkic Migration History of the Turkic peoples Migration Period History of Central Asia Historical migrations