Troyville culture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
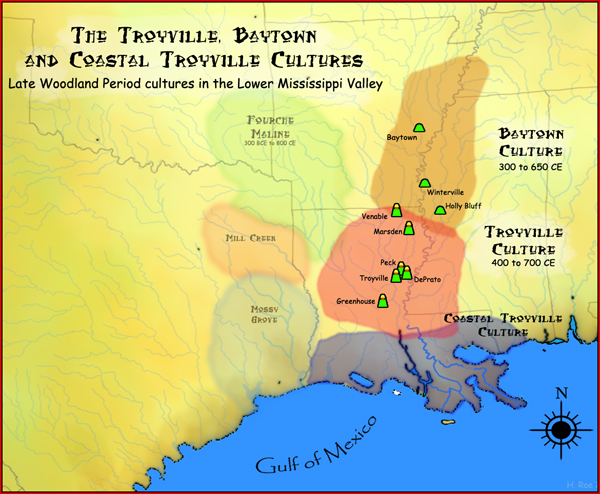 The Troyville culture is an
The Troyville culture is an
 The Troyville culture is an
The Troyville culture is an archaeological culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between thes ...
in areas of Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bord ...
and Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
in the Lower Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
valley in the Southeastern Woodlands
Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, Southeastern cultures, or Southeast Indians are an ethnographic classification for Native Americans who have traditionally inhabited the area now part of the Southeastern United States and the n ...
. It was a Baytown Period culture and lasted from 400 to 700 CE during the Late Woodland period. It was contemporaneous with the Coastal Troyville and Baytown culture
The Baytown culture was a Pre-Columbian Native American culture that existed from 300 to 700 CE in the lower Mississippi River Valley, consisting of sites in eastern Arkansas, western Tennessee, Louisiana, and western Mississippi. The Baytown Sit ...
s (all three had evolved from the Marksville Hopewellian peoples) and was succeeded by the Coles Creek culture
Coles Creek culture is a Late Woodland archaeological culture in the Lower Mississippi valley in the Southeastern Woodlands. It followed the Troyville culture. The period marks a significant change in the cultural history of the area. Population ...
. Where the Baytown peoples built dispersed settlements, the Troyville people instead continued building major earthwork centers.
Subsistence
The Troyville-Coles Creek people lived on gathered wild plants and local domesticates, and maize was of only minor importance. Acorns, persimmons, palmetto, maygrass, and squash were all more important than maize. Tobacco was cultivated as well, and protein came from deer and smaller mammals, but the bounty of the region kept maize from being adopted as a staple until as late as the thirteenth century CE.Known Troyville culture sites
See also
* Culture, phase, and chronological table for the Mississippi ValleyReferences
External links
{{Authority control Late Woodland period Archaeological cultures of North America 4th-century establishments 8th-century disestablishments in North America