Trepča Mines on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Trepča Mines ( al, Miniera e Trepçës, sr, Рудник Трепча / ''Rudnik Trepča'') is a large industrial complex in
 However, with the closure of several mines and factories in the late 1980s and 1990s, the Trepča mining complex in Kosovo now comprises only seven lead and zinc mines, three concentrators, one smelter, and one zinc plant. Mines are categorized according to their geographic location:
* Northern Chain: Belo Brdo mine,
However, with the closure of several mines and factories in the late 1980s and 1990s, the Trepča mining complex in Kosovo now comprises only seven lead and zinc mines, three concentrators, one smelter, and one zinc plant. Mines are categorized according to their geographic location:
* Northern Chain: Belo Brdo mine,
 During his reign (1243–76), King Uroš invited the
During his reign (1243–76), King Uroš invited the
 After
After
 The Trepča mining complex is derelict in a failing state that has immense potential, but has so far been ignored by serious investors for myriad reasons. The mine effectively went out of production as a result of the 1999 civil war and has been rumored to be part of the reason for the conflict in the first place.
Its economy is in dire straits and there are few options to improve it. Trepča, despite its problems, provides one of the few significant development opportunities. The facility needs major upgrades, but the mineral reserves are great enough to offset the start-up costs. Most importantly, a reactivated Trepča would provide several thousand jobs and increase Kosovo's foreign exchange.
It is estimated that the necessary improvements would cost between 15 and 30 million US dollars.Feraud, J., Gani Maliqi, and Vjolica Meha. (2007). Famous mineral localities: the Trepča mine, Stari Trg, Kosovo. The Mineralogical Record, 38(4), 267+. This would be justifiable if full scale mining were to return as a 2001
The Trepča mining complex is derelict in a failing state that has immense potential, but has so far been ignored by serious investors for myriad reasons. The mine effectively went out of production as a result of the 1999 civil war and has been rumored to be part of the reason for the conflict in the first place.
Its economy is in dire straits and there are few options to improve it. Trepča, despite its problems, provides one of the few significant development opportunities. The facility needs major upgrades, but the mineral reserves are great enough to offset the start-up costs. Most importantly, a reactivated Trepča would provide several thousand jobs and increase Kosovo's foreign exchange.
It is estimated that the necessary improvements would cost between 15 and 30 million US dollars.Feraud, J., Gani Maliqi, and Vjolica Meha. (2007). Famous mineral localities: the Trepča mine, Stari Trg, Kosovo. The Mineralogical Record, 38(4), 267+. This would be justifiable if full scale mining were to return as a 2001
 *
*  *
*  *
*  *
*  *
* "The mineral list of The Trepča Complex"
/ref> The amount of ore mining in Kosovo is continuously in decline, as represented here:
Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Euro ...
, located northeast of Mitrovica. The mine is located on the southern slopes of the Kopaonik
Kopaonik ( sr-cyr, Копаоник, ; sq, Kopaoniku) is a mountain range located in Serbia and Kosovo. The highest point is the Pančić's Peak with . The central part of the Kopaonik plateau was declared a national park in 1981 which today cove ...
mountain, between the peaks of Crni Vrh () and Majdan , and it is Europe's largest lead-zinc and silver ore mine.
With up to 23,000 employees, Trepča was once one of the biggest companies in Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
. In the 1930s, the Selection Trust
Selection Trust was a British mining finance house. It was started in 1913 by A. Chester Beatty, a mining engineer from the United States. After the end of the First World War, Beatty built up a substantial portfolio of mining interests, many of t ...
gained the rights to exploit the Stari Trg mine close to Mitrovica. After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, under socialist management, the company further expanded.
Overview
The enterprise known as Trepča was a conglomerate of 40 mines and factories, located mostly in Kosovo but also in locations inMontenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
. But the heart of its operations, and the source of most of its raw material, is the vast mining complex to the east of Mitrovica in the north of Kosovo, famous since Roman times.
Crnac mine
The Crnac mine is one of the largest lead and zinc mines in Kosovo. The mine is located in Leposavić. The mine has reserves amounting to 1.648 million tonnes of ore grading 7.57% lead, 2.93% zinc and 102gr/t silver thus resulting 125,000 tonnes of ...
and Žuta Prlina
* Middle Chain: Stari Trg mine
* Southern Chain: Hajvalia mine, Novo Brdo mine and Kišnica mine
This is all that remains of the huge complex that during the 1980s employed 20,000 workers, and accounted for 70% of all Yugoslavia's mineral wealth.
The mines still have a reserve of 60.5 million tonnes of ore
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically containing metals, that can be mined, treated and sold at a profit.Encyclopædia Britannica. "Ore". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 7 Apr ...
grading 4.96% lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
, 3.3% zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
and 74.4 gr/tonne silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
, which translates as three million tonnes of lead, two million tonnes of zinc and 4,500 tonnes of silver.http://www.spathfluor.com/_open/open_us/us_op_mines/us_trepca_kosovo_mine.htm "The Trepca Mine - by Jean Feraud - Retrieved 2/23/2013".
History
Middle Ages
Origin
Stari Trg is one of the rare mines which was operational from the Roman period. Many constructions back in theRoman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
were constructed including ''fortresses'', ''wells'', ''dross
Dross is a mass of solid impurities floating on a molten metal or dispersed in the metal, such as in wrought iron. It forms on the surface of low- melting-point metals such as tin, lead, zinc or aluminium or alloys by oxidation of the metal. For ...
es'', etc. The main fortress was built for the Roman city Municipium Dardanorum which was the capital city of a Roman province in Dardani
The Dardani (; grc, Δαρδάνιοι, Δάρδανοι; la, Dardani) or Dardanians were a Paleo-Balkan people, who lived in a region that was named Dardania after their settlement there. They were among the oldest Balkan peoples, and their ...
. With the collapse of the Roman Empire and Slavic migrations, mining activity decreased leading to closure until the late Medieval Era (1000–1492). The long history of the successive influxes of the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, Bulgarian, Serbian, Albanian and Turkish people helps explain the cultural mixing and the legacies of old grievances which underlie the chaos of the 1990s.
Full development
 During his reign (1243–76), King Uroš invited the
During his reign (1243–76), King Uroš invited the Saxon
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
miners to Serbia, in order to develop the state's mines. The Saxons (called ''Sasi'' by the Serbs) built settlements and churches around the mines and were granted with keeping their identity. Trepča mine probably originated in the second half of the 13th century, as it was mentioned for the first time in 1303 in one charter of the Pope Boniface VIII
Pope Boniface VIII ( la, Bonifatius PP. VIII; born Benedetto Caetani, c. 1230 – 11 October 1303) was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 24 December 1294 to his death in 1303. The Caetani family was of baronial ...
. As Stari Trg was one of the Europe's richest mines of lead, zinc, silver and gold, King Milutin
Stefan Uroš II Milutin ( sr-cyr, Стефан Урош II Милутин, Stefan Uroš II Milutin; 1253 – 29 October 1321), known as Stefan Milutin ( sr-cyr, Стефан Милутин, Stefan Milutin), was the King of Serbia between 1282&nd ...
set a coin mint
A mint is an industrial facility which manufactures coins that can be used as currency.
The history of mints correlates closely with the history of coins. In the beginning, hammered coinage or cast coinage were the chief means of coin mint ...
there, which was operational for over a century. Emperor Dušan
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother (empr ...
appointed a special '' knez'' to administer Trepča. The mine reached its pinnacle during the reign of Dušan's successor, Emperor Uroš. On 11 March 1363, Uroš awarded Vuk Branković
Vuk Branković ( sr-cyr, Вук Бранковић, , 1345 – 6 October 1397) was a Serbian medieval nobleman who, during the Fall of the Serbian Empire, inherited a province that extended over present-day southern and southwestern Serbia, enti ...
with the title of "ruler of Drenica, Kosovo and Trepča". Trepča was governed by Branković until 1396 when he was captured by the Ottomans. Also known as a major trading town, Trepča had representatives from the rich, trading cities, like Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, entertai ...
and Kotor
Kotor (Montenegrin Cyrillic: Котор, ), historically known as Cattaro (from Italian: ), is a coastal town in Montenegro. It is located in a secluded part of the Bay of Kotor. The city has a population of 13,510 and is the administrative c ...
on the Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) ...
, while trading city of Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik (), historically known as Ragusa (; see notes on naming), is a city on the Adriatic Sea in the region of Dalmatia, in the southeastern semi-exclave of Croatia. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations in the Mediterran ...
appointed a consul. As with the others mines in the Medieval Serbia (Brskovo
Brskovo ( cnr, Брсково) is a village in northern Montenegro, within the Municipality of Mojkovac which used to have silver mines and a mint. Brskovo encompasses the whole complex of smaller localities, today overgrown with dense wood and w ...
, Rudnik, Janjevo
Janjevo () or Janjevë (in Albanian) is a village or small town in the Lipljan municipality in eastern Kosovo.
The settlement has a long history, having been mentioned for the first time in 1303 as a Catholic parish. The town was prior to the K ...
, Novo Brdo), a square town developed around Trepča.
The mining activity answered the needs of the successive lords and their suzerains
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is cal ...
, for it financed military activities, such as the construction of fortresses along the Ibar valley for protection against the Ottoman threats. On 15 June 1389, a dozen kilometers south from Trepča, the famous Battle of Kosovo occurred. In 1390/91 Serbia became an Ottoman vassal, but the mine continued to function normally. In 1455 the Ottoomans, under the Sultan Mehmed the Conqueror
Mehmed II ( ota, محمد ثانى, translit=Meḥmed-i s̱ānī; tr, II. Mehmed, ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror ( ota, ابو الفتح, Ebū'l-fetḥ, lit=the Father of Conquest, links=no; tr, Fâtih Su ...
, captured Trepča.
Downfall
Under the Ottoman rule, Trepča, and all the other mines (likeNovo Brdo
Novo Brdo ( sr-Cyrl, Ново Брдо), or Novobërda and Artana ( sq-definite, Novobërdë or ''Artanë''), is a municipality located in the Pristina district of Kosovo. According to the 2011 census, it has a population of 6,729 inhabitants. T ...
) began to depopulate and deteriorate. During the Austro-Turkish War from 1683 to 1699, the town of Trepča and its mine were destroyed in 1685. Followed by the massive depopulation as a result of the 1690 Great Migration of the Serbs
The Great Migrations of the Serbs ( sr, Велике сеобе Срба), also known as the Great Exoduses of the Serbs, refers mainly to two large migrations of Serbs from various territories under the rule of the Ottoman Empire to regions u ...
, the mining activity ceased completely.
20th-century revival
Selection Trust
 After
After World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
ended, the newly formed Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 ...
(future Yugoslavia), instigated the geological surveys of the medieval ore mines in order to ease the payments of the war credits. Prime minister Nikola Pašić
Nikola Pašić ( sr-Cyrl, Никола Пашић, ; 18 December 1845 – 10 December 1926) was a Serbian and Yugoslav politician and diplomat who was a leading political figure for almost 40 years. He was the leader of the People's Radical ...
, who became the concessionary of the Stari Trg ore deposits, hired P.Tućan to do the explorations. Tućan reported about the massive ore findings.
In 1925 a big exploration program was carried out by the British company, ''Selection Trust'', which assessed the huge potential of the ore deposit and acquired the concession in 1926. The concession was obtained by Sir Alfred Chester Beatty
Sir Alfred Chester Beatty (7 February 1875 – 19 January 1968)Seanad 1985: "Chester Beatty died at the Princess Grace Clinic, Monte Carlo, on 19 January 1968, .. (some sources give this as 20 January). was an American-British mining magnate, p ...
, American-born British industrialist who founded the Selection Trust, nicknamed "King of copper", from Rade Pašić, son of Nikola Pašić. Beatty became the first owner and a head of the modern Trepča mines. On 9 September 1927 he launched the ''Trepča Mines Limited'' subsidiary
A subsidiary, subsidiary company or daughter company is a company owned or controlled by another company, which is called the parent company or holding company. Two or more subsidiaries that either belong to the same parent company or having a s ...
in London and the mines were operational under that name until the end of World War II, so the founding act of the later company said: "Founded on 9 December 1927, Broad and son, 1 Great Winchester Street, London ECZ".
Exploitation of the ore began in 1930 ("First tunnel" in Stari Trg). On 14 August 1930, the flotation in Zvečan (''Stan Trg''), was opened in the same place as the ancient medieval pit. The name ''Stan Trg'' is a misprint by the British administration of the mine, derived from the toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
''Stari Trg'' which in Serbian means ''old place'', or ''old market''. Amazingly, the obvious misprint was not corrected in any later document nor mine plan. The flotation in Zvečan was operational until 31 March 1941. In that period it processed 6 million tons of ore. The ore was transported to the floatation first on the bullock carts
A bullock cart or ox cart (sometimes called a bullock carriage when carrying people in particular) is a two-wheeled or four-wheeled vehicle pulled by oxen. It is a means of transportation used since ancient times in many parts of the world. The ...
, until a long industrial cable car transportation was built. A lead smeltery and refinery became operational in Zvečan in 1939.
During the German occupation of Yugoslavia in World War II, Stari Trg, the centerpiece mine, supplied 40 percent of lead used in the Nazi war industry. After the German-lead Invasion of Yugoslavia
The invasion of Yugoslavia, also known as the April War or Operation 25, or ''Projekt 25'' was a German-led attack on the Kingdom of Yugoslavia by the Axis powers which began on 6 April 1941 during World War II. The order for the invasion was p ...
in April 1941, most of what is today Kosovo was annexed to the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
but the area around Trepča was part of the German-installed Serbian state. The mines were under the direct German administration, allowing the continued flow of minerals for the production of ammunition and submarine batteries. Output of these products was continued in the period after 1945, in the new, Communist Yugoslavia.
Post-WW2 expansion
Since 1939 the complex was expanded and reconstructed on several occasions. After theWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, Tito
Tito may refer to:
People Mononyms
* Josip Broz Tito (1892–1980), commonly known mononymously as Tito, Yugoslav communist revolutionary and statesman
* Roberto Arias (1918–1989), aka Tito, Panamanian international lawyer, diplomat, and journ ...
's SFR Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yug ...
nationalized the enterprise. Marking the 40th anniversary, on 9 December 1967 a new lead smelter was opened (at the time, the 4th largest in the world), so as the zinc electrolysis plant and an automotive battery plant. New flotation in Zvečan was built in 1985, in the First tunnel, closer to Stari Trg. The landmark of the Zvečan complex is a industrial chimney
A flue-gas stack, also known as a smoke stack, chimney stack or simply as a stack, is a type of chimney, a vertical pipe, channel or similar structure through which combustion product gases called flue gases are exhausted to the outside air. Flue ...
.
From 1930 to 1985, 131 million tons of lead and zinc ore was processed. Until the production ceased in 2000, historical total output included: 3,3 million tons of refined lead, 4,100 tons of refined silver and 3,300 tons of bismuth. Calculated in 2017 parity, production of the complex was $360 million in 1975 and $340 million in 1987.
In 1985, Trepča was Europe's 1st and world's 5th largest raw lead smelting facility and one of the largest for processing zinc. Production capacity included: 3.5 million tons of ore, 165,000 tons of raw lead, 110,000 tons of refined lead, 40,000 tons of electrolytic zinc, 100 tons of fine silver, 100 tons of refined bismuth, 72 tons of cadmium, 200 kg of gold, 20,000 tons of lead batteries, 280,000 tons of sulfuric acid, 100,000 tons of sulfur-phosphate and 150,000 tons of composite fertilizers. It produced over 80% of refined lead and over 50% of refined zinc in Yugoslavia.
The 1989 miners' strike
The 1989 Kosovo miners' strike was ahunger strike
A hunger strike is a method of non-violent resistance in which participants fast as an act of political protest, or to provoke a feeling of guilt in others, usually with the objective to achieve a specific goal, such as a policy change. Most ...
initiated by some workers of the Trepča Mines on 20 February 1989 against the abolition of the autonomy of the Province of Kosovo by the Socialist Republic of Serbia
, life_span = 1944–1992
, status = Constituent state of Yugoslavia
, p1 = Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia
, flag_p1 = Flag of German Reich (1935–1945).svg
, p2 ...
. The strike quickly gained support in Slovenia and Croatia, while in Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
protests were held against the Slovenian, Albanian and Croatian demands for decentralization. The strike council articulated ten requirements, which included obeying the 1974 constitution, stopping the alleged chauvinist and hegemonistic politics of the time, amnesty for the strike leaders, etc.
The strike lasted eight days, being known as the longest underground strike to have been held. It eventually ended after the hospitalization of 180 miners and the resignation of the heads of the pro-Milošević leaders Rahman Morina, Ali Shukriu
Ali Shukriu (Serbian: Али Шукрија, ''Ali Šukrija''; 12 September 1919 – 6 January 2005) was a political figure of Kosovo, during its period as an autonomous province of Yugoslavia. He served as the 2nd Chairmen of the Executive Coun ...
and Husamedin Azemi.
Collapse
This complex progressively collapsed during the last fifteen years, for reasons such as outdated installations; neglect and lack of maintenance, repair, and reinvestment; absence of control over production; robbery of equipment and workshops, and " Milosevic apparatchik" mine manager Novak Bjelic. Privatization attempts remained without great follow-up. The downgrade increased from 1990 with the reduction of Kosovo's autonomy by Belgrade, the increasing ethno-political tension and the resignation of most Albanian workers. At the time, an estimated 25,000 tons per year of sulphur dioxide pollution were discharged by the smokestack, and lead levels in the air rose to more than 100 times the acceptable levels in the EU. On 18 September 1999, the mineralogical museum of the mine, where guarded treasures had been accumulated since 1966, was plundered by thieves benefiting from the confusion. It was reported that the most invaluablevivianite
Vivianite () is a hydrated iron phosphate mineral found in a number of geological environments. Small amounts of manganese Mn2+, magnesium Mg and calcium Ca may substitute for iron Fe2+ in the structure.Gaines et al (1997) Dana’s New Minera ...
specimen of the museum, more than 1,500 of the crystals collected inside the mine since 1927, and 150 specimens which had been given by 30 countries from all over the world had disappeared.
UNMIK inherited a large problem through its trusteeship of the assets, and in February 2002, Bjelic suffered from criminal court proceedings brought by the UNMIK-installed management board.
Kosovo War and after
Shutting down
The arrival of KFOR in June 1999 led to an outburst of the mining complex. The northern mines remained owned and operated by Serbs, while the southern mines were in Albanian hands. After the Serbian forces withdrew from Kosovo in 1999, the chaos ensued in the period during the takeover by KFOR andUNMIK
The United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK) is the officially mandated mission of the United Nations in Kosovo. The UNMIK describes its mandate as being to "help the United Nations Security Council achieve an overall ...
, a military and a civilian administration, respectively. The units of UÇK looted and destroyed much of the mine's properties while international forces did nothing to stop it. UNMIK was authorized to take over all the state owned companies. However, Trepča wasn't organized as a plain, state-owned property, but was transformed into the joint-stock company
A joint-stock company is a business entity in which shares of the company's capital stock, stock can be bought and sold by shareholders. Each shareholder owns company stock in proportion, evidenced by their share (finance), shares (certificates ...
in 1996. UNMIK chief Bernard Kouchner
Bernard Kouchner KBE (born 1 November 1939) is a French politician and doctor. He is the co-founder of Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) and Médecins du Monde. From 2007 until 2010, he was the French Minister of Foreign and European Affairs ...
personally asked for the documentation on the ownership of Trepča, but he wasn't authorized to take over the stock company, which French newspaper Le Monde
''Le Monde'' (; ) is a French daily afternoon newspaper. It is the main publication of Le Monde Group and reported an average circulation of 323,039 copies per issue in 2009, about 40,000 of which were sold abroad. It has had its own website si ...
wrote about at the time. Serbian management of the company tried to continue the production in the facilities north of the Ibar river which remained out of Albanian control, as much as it was possible: 9 mines out of 14, 6 out of 8 flotation units, 1 out of 2 metallurgy factories and 9 out of 17 factories or 70% of the capacities. As Kouchner had administrative rule over the electric company, he ordered the shutting down of the power supply to the mine. An alternative power line, which connected the mine with the grid in the Central Serbia was then established. The mine was supplied with water via the long concrete canal from the Gazivode Lake. Claiming that two Albanian children fell into the canal, Kouchner order for the water to be cut, too. The company then organized alternative water supply system which consisted of powerful water pumps which pumped the water from the Ibar river via the two-way pipeline into the pools on the slopes of the Zvečan Hill. From there, using free fall
In Newtonian physics, free fall is any motion of a body where gravity is the only force acting upon it. In the context of general relativity, where gravitation is reduced to a space-time curvature, a body in free fall has no force acting on ...
, the water was conducted to the factories. The official seat of the company was transferred to Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
, but the management remained in Zvečan.
Chief of the US section of the KFOR, General William L. Nash tried to shut it down, too, giving statements that 700 bodies of dead Albanians were suspected to be in the First Tunnel or that bodies were incinerated in the manhole furnace. After several months of investigation, French, German, Dutch and American investigators concluded that the furnace in question wasn't operational when the alleged crime happened. General Nash then claimed that Trepča needs to be closed because of the environmental pollution, though French minister for environment, Dominique Voynet
Dominique Voynet (born 4 November 1958) is a French politician who is a member of Europe Écologie–The Greens. She is the former mayor of Montreuil and was a French senator for the ''département'' of Seine-Saint-Denis.
Life
Dominique Voy ...
concluded that there is no danger for the surroundings. Expecting military takeover, the management "fortified" the complex with goods wagon
Goods wagons or freight wagons (North America: freight cars), also known as goods carriages, goods trucks, freight carriages or freight trucks, are unpowered railway vehicles that are used for the transportation of cargo. A variety of wagon type ...
s, locomotives and slag
Slag is a by-product of smelting (pyrometallurgical) ores and used metals. Broadly, it can be classified as ferrous (by-products of processing iron and steel), ferroalloy (by-product of ferroalloy production) or non-ferrous/base metals (by-prod ...
, while it was lit with powerful reflector lights, looking like a "space ship". On early 14 August 2000, at 3:45, 3,000 mostly US soldiers stormed the premises, using tanks, amphibians and helicopters. French soldiers, using battering ram
A battering ram is a siege engine that originated in ancient times and was designed to break open the masonry walls of fortifications or splinter their wooden gates. In its simplest form, a battering ram is just a large, heavy log carried b ...
, broke into the central administrative building. Soldiers arrested the CEO, Novak Bjelić, who was 3 hours later expelled into central Serbia on the orders of Kouchner. Kouchner ordered the shut down of Trepča.
On 4 January 2001, Serbian deputy prime minister Nebojša Čović
Nebojša Čović ( sr-Cyrl, Небојша Човић; 2 July 1958) is a Serbian businessman, basketball executive, and politician. Since 2011, he has been serving as the president of Crvena zvezda mts Belgrade.
Early years and education
Čovi ...
signs a document which returns the seat of the company to Zvečan and changes the structure of Trepča, transforming it back to the state owned company, which effectively retroactively legalized the military occupation of the complex.
, the only remaining operational part of the complex were the Kopaonik
Kopaonik ( sr-cyr, Копаоник, ; sq, Kopaoniku) is a mountain range located in Serbia and Kosovo. The highest point is the Pančić's Peak with . The central part of the Kopaonik plateau was declared a national park in 1981 which today cove ...
mines and the flotation in Leposavić.
Privatisation
UNMIK
The United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK) is the officially mandated mission of the United Nations in Kosovo. The UNMIK describes its mandate as being to "help the United Nations Security Council achieve an overall ...
report said that “''29,000,000 tonnes of mine-run ore at grades varying from 3.40 to 3.45% Pb, 2.23 to 2.36% Zn and 74 to 81 grams/tonne Ag, i.e., around 999,000 tonnes Pb, 670,000 tonnes Zn and 2,200 tonnes Ag''” are available. To make use of Trepča, foreign investment is required. Since financial means to upgrade the mines’ facilities themselves are absent, and there is not enough foreign aid still reaching Kosovo to make a difference, the complex still will not be used at its highest level.
The concern that letting in foreign investors will give away their promising source of natural resources since the complex is considered a treasure for the nation needs to be appeased in order for its privatization to happen sooner. In the following years, certain legislation like a new mining law and regulations for investment incentives, will support privatization efforts if approved in order for the complex to work and be used at its highest level.
2015 nationalization attempt
In January 2015, the government of Kosovo said it wouldnationalise
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to pri ...
the Trepča mining complex because the Privatization Agency of Kosovo (KPA) had failed to come up with a plan for the mine's future. Partly due to its murky ownership structure and numerous creditor claims with a draft law, but fearing bankruptcy and liquidation then the government changed this decision, then approved a special draft law except which includes two new articles those for completion changes according to which certain social enterprise could become public by decision of the Assembly. At the request of the Government of the Republic of Kosovo, the Assembly provided two new articles, by which the status of Trepca will be regulated by a special law of Strategy and, while companies that have entered the process of reorganization, bankruptcy or liquidation, terminated with the entry into force of this law without the need for any judicial decision. Albanian employees declared a strike and would not emerge from underground until the parliament adopts the law on public enterprises. They ended their strike when Kosovo government officials said they would consider bringing up nationalization again.
In October 2016, the nationalisation process went ahead over Serbian diplomatic protest. The mine "had been held in trust and readied for sale" since 1999 by the UN-protected Kosovo Privatization Agency. The "legislation makes the government the guarantor of the company’s debt."
As of March 2019, the Serbian managers of RMHK Trepca were still fighting a rearguard action against the nationalization.
Economic impact
The impact on town of Kosovska Mitrovica was a major one. In only one census period of 10 years, from 1961 to 1971, the town grew by 57,7% (26,721 to 42,126). Kosovo has not yet fully recovered from the 1998–99 war and has failed since declaring independence in 2008 to build a stable economy. The Trepča mine complex has not recovered from its lost production during the war. Trepča once accounted for 70 percent of Kosovo'sgross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjec ...
, but since the war ended in 1999, the partition of Mitrovica between Kosovar Albanians and Serbs loyal to Belgrade keeps most of Trepča's facilities closed. According to various statistics, the complex can not be reopened without at least $650 million of foreign investment to repair and update the smelters and refineries.
Geology
Geologically, the Trepča area belongs to theMississippi Valley-Type
Carbonate-hosted lead-zinc ore deposits are important and highly valuable concentrations of lead and zinc sulfide ores hosted within carbonate (limestone, marl, dolomite) formations and which share a common genetic origin.
These ore bodies ran ...
of mineral deposits. It has beautiful occurrence of skarn
Skarns or tactites are hard, coarse-grained metamorphic rocks that form by a process called metasomatism. Skarns tend to be rich in calcium-magnesium-iron-manganese-aluminium silicate minerals, which are also referred to as calc-silicate mineral ...
, so as the Novo Brdo mine.
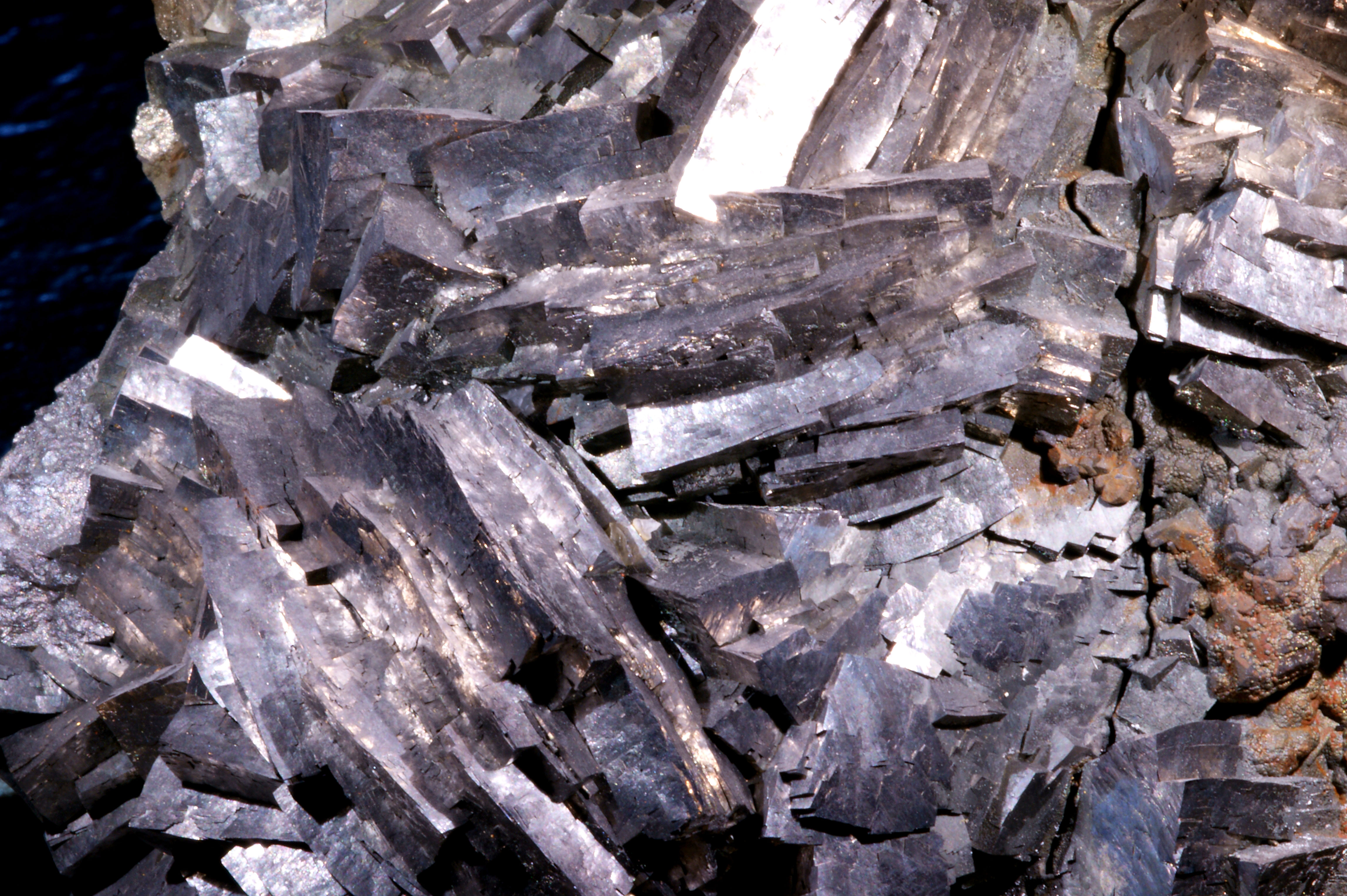
Trepča was the largest Galena
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver.
Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It cryst ...
and Sphalerite
Sphalerite (sometimes spelled sphaelerite) is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in Sedimentary exhalative deposits, sedimen ...
mine in Yugoslavia.
More than sixty minerals are listed up to date, most of which from a museological viewpoint are of exceptional quality.
They include:
* Actinolite
Actinolite is an amphibole silicate mineral with the chemical formula .
Etymology
The name ''actinolite'' is derived from the Greek word ''aktis'' (), meaning "beam" or "ray", because of the mineral's fibrous nature.
Mineralogy
Actinolite is ...
 *
* Anglesite
Anglesite is a lead sulfate mineral with the chemical formula PbSO4. It occurs as an oxidation product of primary lead sulfide ore, galena. Anglesite occurs as prismatic orthorhombic crystals and earthy masses, and is isomorphous with barite and ...
* Ankerite
* Aragonite
Aragonite is a carbonate mineral, one of the three most common naturally occurring crystal forms of calcium carbonate, (the other forms being the minerals calcite and vaterite). It is formed by biological and physical processes, including prec ...
 *
* Arsenopyrite
Arsenopyrite ( IMA symbol: Apy) is an iron arsenic sulfide (FeAsS). It is a hard ( Mohs 5.5-6) metallic, opaque, steel grey to silver white mineral with a relatively high specific gravity of 6.1. When dissolved in nitric acid, it releases eleme ...
* Barite
Baryte, barite or barytes ( or ) is a mineral consisting of barium sulfate ( Ba S O4). Baryte is generally white or colorless, and is the main source of the element barium. The ''baryte group'' consists of baryte, celestine (strontium sulfate), ...
* Bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental ...
* Bornite
Bornite, also known as peacock ore, is a sulfide mineral with chemical composition Cu5 Fe S4 that crystallizes in the orthorhombic system (pseudo-cubic).
Appearance
Bornite has a brown to copper-red color on fresh surfaces that tarnishes to v ...
* Boulangerite
Boulangerite is an uncommon monoclinic orthorhombic sulfosalt mineral, lead antimony sulfide, formula Pb5Sb4S11. It was named in 1837 in honor of French mining engineer Charles Boulanger (1810–1849),http://www.mindat.org/min-738.html Mindat a ...
* Bournonite
Bournonite is a Sulfosalt minerals, sulfosalt mineral species, trithioantimoniate of lead and copper with the formula PbCuSbS3.
It was first mentioned by Philip Rashleigh (1729–1811), Philip Rashleigh in 1797 as an ore of antimony and was mor ...
* Calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
* Chalcanthite
Chalcanthite (, ) is a richly colored blue-green water-soluble sulfate mineral . It is commonly found in the late-stage oxidation zones of copper deposits. Due to its ready solubility, chalcanthite is more common in arid regions.
Chalcanthite i ...
* Chalcedony
Chalcedony ( , or ) is a cryptocrystalline form of silica, composed of very fine intergrowths of quartz and moganite. These are both silica minerals, but they differ in that quartz has a trigonal crystal structure, while moganite is monocli ...
 *
* Chalcopyrite
Chalcopyrite ( ) is a copper iron sulfide mineral and the most abundant copper ore mineral. It has the chemical formula CuFeS2 and crystallizes in the tetragonal system. It has a brassy to golden yellow color and a hardness of 3.5 to 4 on the Mo ...
* Childrenite
* Chlorite
* Covellite
Covellite (also known as covelline) is a rare copper sulfide mineral with the formula CuS. This indigo blue mineral is commonly a secondary mineral in limited abundance and although it is not an important ore of copper itself, it is well known t ...
 *
* Cubanite
Cubanite is a copper iron sulfide mineral that commonly occurs as a minor alteration mineral in magmatic sulfide deposits. It has the chemical formula CuFe2S3 and when found, it has a bronze to brass-yellow appearance. On the Mohs hardness scale, ...
* Diopside
Diopside is a monoclinic pyroxene mineral with composition . It forms complete solid solution series with hedenbergite () and augite, and partial solid solutions with orthopyroxene and pigeonite. It forms variably colored, but typically dull ...
* Dolomite Dolomite may refer to:
*Dolomite (mineral), a carbonate mineral
*Dolomite (rock), also known as dolostone, a sedimentary carbonate rock
*Dolomite, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community
*Dolomite, California, United States, an unincor ...
* Enargite
Enargite is a copper arsenic sulfosalt mineral with formula Cu3AsS4. It takes its name from the Greek word , "distinct". Enargite is a steel gray, blackish gray, to violet black mineral with metallic luster. It forms slender orthorhombic prisms as ...
* Epidote
Epidote is a calcium aluminium iron sorosilicate mineral.
Description
Well developed crystals of epidote, Ca2Al2(Fe3+;Al)(SiO4)(Si2O7)O(OH), crystallizing in the monoclinic system, are of frequent occurrence: they are commonly prismatic in hab ...
* Galena
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver.
Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It cryst ...
 *
* Garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives.
All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different s ...
s
* Gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywall. ...
* Hedenbergite
Hedenbergite, Ca Fe Si2 O6, is the iron rich end member of the pyroxene group having a monoclinic crystal system. The mineral is extremely rarely found as a pure substance, and usually has to be synthesized in a lab. It was named in 1819 after M ...
* Hematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of . ...
* Illite
Illite is a group of closely related non-expanding clay minerals. Illite is a secondary mineral precipitate, and an example of a phyllosilicate, or layered alumino-silicate. Its structure is a 2:1 sandwich of silica tetrahedron (T) – alumina ...
* Indium
Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. Indium is the softest metal that is not an alkali metal. It is a silvery-white metal that resembles tin in appearance. It is a post-transition metal that makes up 0.21 parts p ...
* Jamesonite
Jamesonite is a sulfosalt mineral, a lead, iron, antimony sulfide with formula Pb4FeSb6S14. With the addition of manganese it forms a series with benavidesite.http://rruff.geo.arizona.edu/doclib/hom/jamesonite.pdf Handbook of Mineralogy It is a ...
* Limonite
Limonite () is an iron ore consisting of a mixture of hydrated iron(III) oxide-hydroxides in varying composition. The generic formula is frequently written as FeO(OH)·H2O, although this is not entirely accurate as the ratio of oxide to hydroxid ...
* Löllingite
Loellingite, also spelled löllingite, is an iron arsenide mineral with formula FeAs2. It is often found associated with arsenopyrite (FeAsS) from which it is hard to distinguish. Cobalt, nickel and sulfur substitute in the structure. The orthorho ...
* Ludlamite
* Magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2O4. It is one of the oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself. With the ...
* Marcasite
The mineral marcasite, sometimes called “white iron pyrite”, is iron sulfide (FeS2) with orthorhombic crystal structure. It is physically and crystallographically distinct from pyrite, which is iron sulfide with cubic crystal structure. Both ...
* Melanterite
Melanterite is a mineral form of hydrous iron(II) sulfate: FeSO4·7H2O. It is the iron analogue of the copper sulfate chalcanthite. It alters to siderotil by loss of water. It is a secondary sulfate mineral which forms from the oxidation of pri ...
* Native gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
* Psilomelane
Psilomelane is a group name for hard black manganese oxides including hollandite and romanechite. Psilomelane consists of hydrous manganese oxide with variable amounts of barium and potassium. Psilomelane is erroneously, and uncommonly, known as ...
* Pyrargyrite
Pyrargyrite is a sulfosalt mineral consisting of silver sulfantimonite, Ag3SbS3. Known also as dark red silver ore or ruby silver, it is an important source of the metal.
It is closely allied to, and isomorphous with, the corresponding sulfarse ...
* Pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), lust ...
* Pyrrhotite
Pyrrhotite is an iron sulfide mineral with the formula Fe(1-x)S (x = 0 to 0.2). It is a nonstoichiometric variant of FeS, the mineral known as troilite.
Pyrrhotite is also called magnetic pyrite, because the color is similar to pyrite and it is ...
* Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical form ...
* Rhodochrosite
Rhodochrosite is a manganese carbonate mineral with chemical composition MnCO3. In its (rare) pure form, it is typically a rose-red color, but impure specimens can be shades of pink to pale brown. It streaks white, and its Mohs hardness varies bet ...
* Scheelite
Scheelite is a calcium tungstate mineral with the chemical formula Ca W O4. It is an important ore of tungsten (wolfram). Scheelite is originally named after Swedish chemist K. Scheele (1742-1786). Well-formed crystals are sought by collectors ...
* Siderite
Siderite is a mineral composed of iron(II) carbonate (FeCO3). It takes its name from the Greek word σίδηρος ''sideros,'' "iron". It is a valuable iron mineral, since it is 48% iron and contains no sulfur or phosphorus. Zinc, magnesium and ...
* Smithsonite
Smithsonite, also known as zinc spar, is the mineral form of zinc carbonate ( Zn CO3). Historically, smithsonite was identified with hemimorphite before it was realized that they were two different minerals. The two minerals are very similar in a ...
* Sphalerite
Sphalerite (sometimes spelled sphaelerite) is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in Sedimentary exhalative deposits, sedimen ...
* Stannite
* Stibnite
Stibnite, sometimes called antimonite, is a sulfide mineral with the formula Sb2 S3. This soft grey material crystallizes in an orthorhombic space group. It is the most important source for the metalloid antimony. The name is derived from the ...
* Struvite
* Tennantite
Tennantite is a copper arsenic sulfosalt mineral with an ideal formula . Due to variable substitution of the copper by iron and zinc the formula is . It is gray-black, steel-gray, iron-gray or black in color. A closely related mineral, tetrahedri ...
* Tetrahedrite
Tetrahedrite is a copper antimony sulfosalt mineral with formula: . It is the antimony endmember of the continuous solid solution series with arsenic-bearing tennantite. Pure endmembers of the series are seldom if ever seen in nature. Of the two, ...
* Thallium
Thallium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Tl and atomic number 81. It is a gray post-transition metal that is not found free in nature. When isolated, thallium resembles tin, but discolors when exposed to air. Chemists W ...
* Valleriite
Valleriite is an uncommon sulfide mineral (hydroxysulfide) of iron and copper with formula: or . It is an opaque, soft, bronze-yellow to brown mineral which occurs as nodules or encrustations.
Discovery and occurrence
Valleriite was first describ ...
* Vivianite
Vivianite () is a hydrated iron phosphate mineral found in a number of geological environments. Small amounts of manganese Mn2+, magnesium Mg and calcium Ca may substitute for iron Fe2+ in the structure.Gaines et al (1997) Dana’s New Minera ...
* Wollastonite
Wollastonite is a calcium inosilicate mineral ( Ca Si O3) that may contain small amounts of iron, magnesium, and manganese substituting for calcium. It is usually white. It forms when impure limestone or dolomite is subjected to high temperature ...
/ref> The amount of ore mining in Kosovo is continuously in decline, as represented here:
Notes
References
Bibliography
* C. A. Kidd (1982), ''A History of the Trepča Mines in Yugoslavia'' * Ian Bancroft (2020), ''Dragon’s Teeth: Tales from North Kosovo'' {{Commons category, Trepca Complex History of Kosovo Mines in Kosovo Zinc smelters Lead smelters Smelters of Yugoslavia Smelters of Kosovo