Toothache on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Toothache, also known as dental pain,Segen JC. (2002). ''McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine''. The McGraw-Hill Companies. is
pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
in the teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, ...
or their supporting structures, caused by dental diseases or pain referred to the teeth by non-dental diseases. When severe it may impact sleep, eating, and other daily activities.
Common causes include inflammation of the pulp, (usually in response to tooth decay
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complicatio ...
, dental trauma
Dental trauma refers to trauma (injury) to the teeth and/or periodontium (gums, periodontal ligament, alveolar bone), and nearby soft tissues such as the lips, tongue, etc. The study of dental trauma is called dental traumatology.''Textbook an ...
, or other factors), dentin hypersensitivity
Dentin hypersensitivity (DH, DHS) is dental pain which is sharp in character and of short duration, arising from exposed dentin surfaces in response to stimuli, typically thermal, evaporative, tactile, osmotic, chemical or electrical; and which c ...
, apical periodontitis
Periapical periodontitis or apical periodontitis (AP) is an acute or chronic inflammatory lesion around the apex of a tooth root, most commonly caused by bacterial invasion of the pulp of the tooth. It is a likely outcome of untreated denta ...
(inflammation of the periodontal ligament
The periodontal ligament, commonly abbreviated as the PDL, is a group of specialized connective tissue fibers that essentially attach a tooth to the alveolar bone within which it sits. It inserts into root cementum one side and onto alveolar ...
and alveolar bone around the root apex), dental abscesses (localized collections of pus), alveolar osteitis
Alveolar osteitis, also known as dry socket, is inflammation of the alveolar bone (i.e., the alveolar process of the maxilla or mandible). Classically, this occurs as a postoperative complication of tooth extraction.
Alveolar osteitis usually occ ...
("dry socket", a possible complication of tooth extraction), acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG) is a common, non-contagious infection of the gums with sudden onset. The main features are painful, bleeding gums, and ulceration of inter-dental papillae (the sections of gum between adjacent teeth ...
(a gum infection), and temporomandibular disorder.
Pulpitis is reversible when the pain is mild to moderate and lasts for a short time after a stimulus (for instance cold); or irreversible when the pain is severe, spontaneous, and lasts a long time after a stimulus. Left untreated, pulpitis may become irreversible, then progress to pulp necrosis (death of the pulp) and apical periodontitis. Abscesses usually cause throbbing pain. The apical abscess usually occurs after pulp necrosis, the pericoronal abscess is usually associated with acute pericoronitis
Pericoronitis is inflammation of the soft tissues surrounding the crown of a partially erupted tooth, including the gingiva (gums) and the dental follicle. The soft tissue covering a partially erupted tooth is known as an ''operculum'', an ar ...
of a lower wisdom tooth
A third molar, commonly called wisdom tooth, is one of the three molars per quadrant of the human dentition. It is the most posterior of the three. The age at which wisdom teeth come through ( erupt) is variable, but this generally occurs betw ...
, and periodontal abscesses usually represent a complication of chronic periodontitis
Chronic periodontitis is one of the seven categories of periodontitis as defined by the American Academy of Periodontology 1999 classification system. Chronic periodontitis is a common disease of the oral cavity consisting of chronic inflammation ...
(gum disease). Less commonly, non-dental conditions can cause toothache, such as maxillary sinusitis, which can cause pain in the upper back teeth, or angina pectoris
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typically the result of obstru ...
, which can cause pain in the lower teeth. Correct diagnosis can sometimes be challenging.
Proper oral hygiene
Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's mouth clean and free of disease and other problems (e.g. bad breath) by regular brushing of the teeth (dental hygiene) and cleaning between the teeth. It is important that oral hygiene be carried ou ...
helps to prevent toothache by preventing dental disease. The treatment of a toothache depends upon the exact cause, and may involve a filling
Filling may refer to:
* a food mixture used for stuffing
* Frosting used between layers of a cake
* Dental restoration
* Symplectic filling, a kind of cobordism in mathematics
* Part of the leather crusting process
See also
* Fill (disambiguat ...
, root canal treatment, extraction Extraction may refer to:
Science and technology
Biology and medicine
* Comedo extraction, a method of acne treatment
* Dental extraction, the surgical removal of a tooth from the mouth
Computing and information science
* Data extraction, the pr ...
, drainage of pus, or other remedial action. The relief of toothache is considered one of the main responsibilities of dentists. Toothache is the most common type of pain in the mouth or face. It is one of the most common reasons for emergency dental appointments. In 2013, 223 million cases of tooth pain occurred as a result of dental caries in permanent teeth and 53 million cases occurred in baby teeth. Historically, the demand for treatment of toothache is thought to have led to the emergence of dental surgery
Dental surgery is any of a number of medical procedures that involve artificially modifying dentition; in other words, surgery of the teeth, gums and jaw bones.
Types
Some of the more common are:
* Endodontic (surgery involving the pulp or root ...
as the first specialty of medicine.
Causes
Toothache may be caused by ''dental'' (''odontogenic'') conditions (such as those involving the dentin-pulp complex or periodontium), or by ''non-dental'' (''non-odontogenic'') conditions (such as maxillary sinusitis orangina pectoris
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typically the result of obstru ...
). There are many possible non-dental causes, but the vast majority of toothache is dental in origin.
Both the pulp and periodontal ligament have nociceptor
A nociceptor ("pain receptor" from Latin ''nocere'' 'to harm or hurt') is a sensory neuron that responds to damaging or potentially damaging stimuli by sending "possible threat" signals to the spinal cord and the brain. The brain creates the sens ...
s (pain receptors), but the pulp lacks proprioceptors (motion or position receptors) and mechanoreceptor
A mechanoreceptor, also called mechanoceptor, is a sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion. Mechanoreceptors are innervated by sensory neurons that convert mechanical pressure into electrical signals that, in animals, a ...
s (mechanical pressure receptors). Consequently, pain originating from the dentin-pulp complex tends to be poorly localized, whereas pain from the periodontal ligament will typically be well localized, although not always.
For instance, the periodontal ligament can detect the pressure exerted when biting on something smaller than a grain of sand (10–30 µm). When a tooth is intentionally stimulated, about 33% of people can correctly identify the tooth, and about 20% cannot narrow the stimulus location down to a group of three teeth. Another typical difference between pulpal and periodontal pain is that the latter is not usually made worse by thermal stimuli.
Dental

Pulpal
The majority of pulpal toothache falls into one of the following types; however, other rare causes (which do not always fit neatly into these categories) include galvanic pain and barodontalgia.Pulpitis
Pulpitis (inflammation of the pulp) can be triggered by various stimuli (insults), including mechanical, thermal, chemical, and bacterial irritants, or rarely barometric changes andionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation (or ionising radiation), including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel ...
. Common causes include tooth decay, dental trauma (such as a crack or fracture), or a filling with an imperfect seal.
Because the pulp is encased in a rigid outer shell, there is no space to accommodate swelling caused by inflammation. Inflammation therefore increases pressure in the pulp system, potentially compressing the blood vessels which supply the pulp. This may lead to ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems w ...
(lack of oxygen) and necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated diges ...
(tissue death). Pulpitis is termed ''reversible'' when the inflamed pulp is capable of returning to a state of health, and ''irreversible'' when pulp necrosis is inevitable.
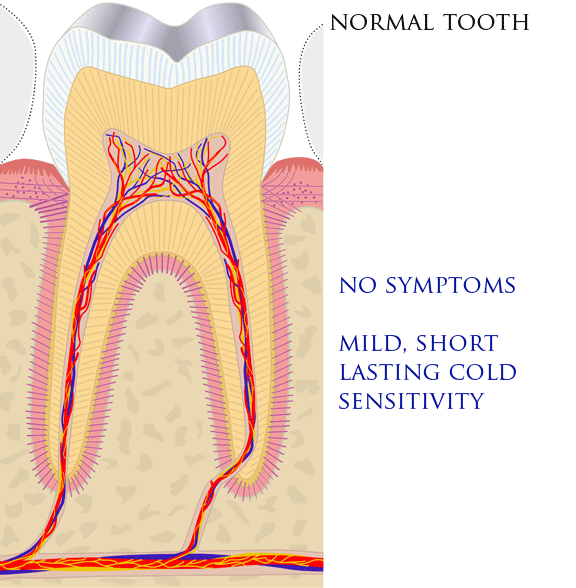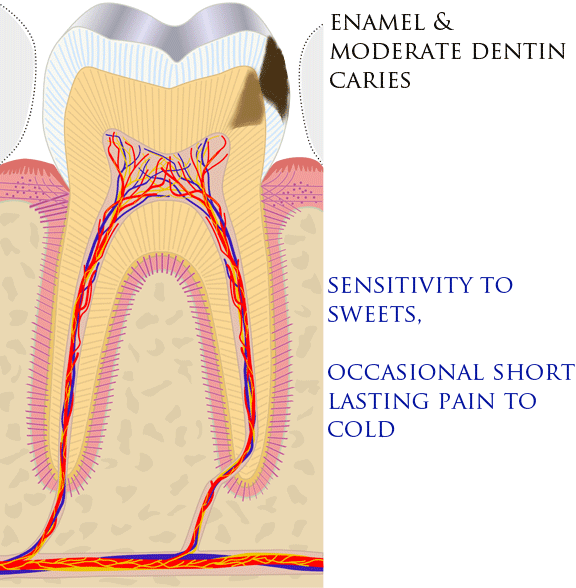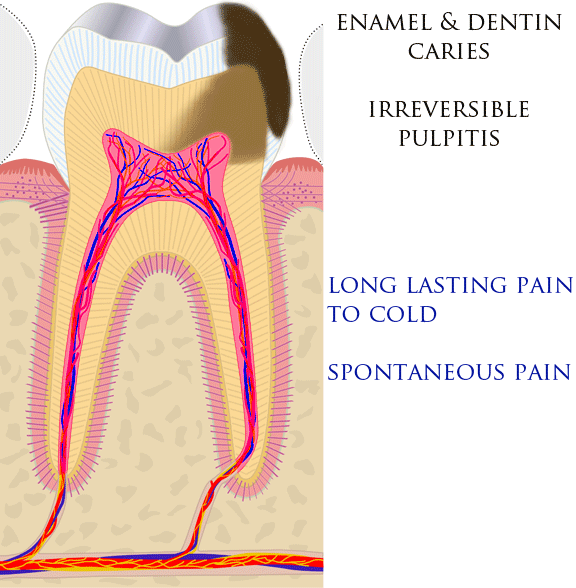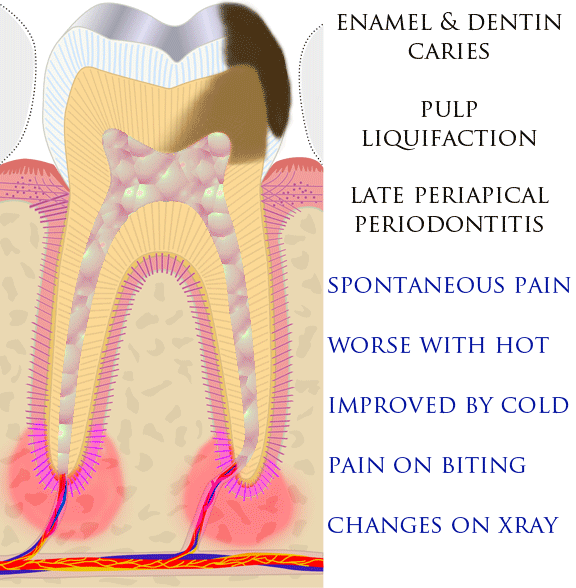
Reversible pulpitis is characterized by short-lasting pain triggered by cold and sometimes heat. The symptoms of reversible pulpitis may disappear, either because the noxious stimulus is removed, such as when dental decay is removed and a filling placed, or because new layers of dentin ( tertiary dentin) have been produced inside the pulp chamber, insulating against the stimulus. Irreversible pulpitis causes spontaneous or lingering pain in response to cold.
Dentin hypersensitivity
Dentin hypersensitivity
Dentin hypersensitivity (DH, DHS) is dental pain which is sharp in character and of short duration, arising from exposed dentin surfaces in response to stimuli, typically thermal, evaporative, tactile, osmotic, chemical or electrical; and which c ...
is a sharp, short-lasting dental pain occurring in about 15% of the population, which is triggered by cold (such as liquids
or air), sweet or spicy foods, and beverages. Teeth will normally have some sensation to these triggers, but what separates hypersensitivity from regular tooth sensation is the intensity of the pain. Hypersensitivity is most commonly caused by a lack of insulation from the triggers in the mouth due to gingival recession
Gingival recession, also known as receding gums, is the exposure in the roots of the teeth caused by a loss of gum tissue and/or retraction of the gingival margin from the crown of the teeth.scaling and root planing or dental bleaching, or as a result of
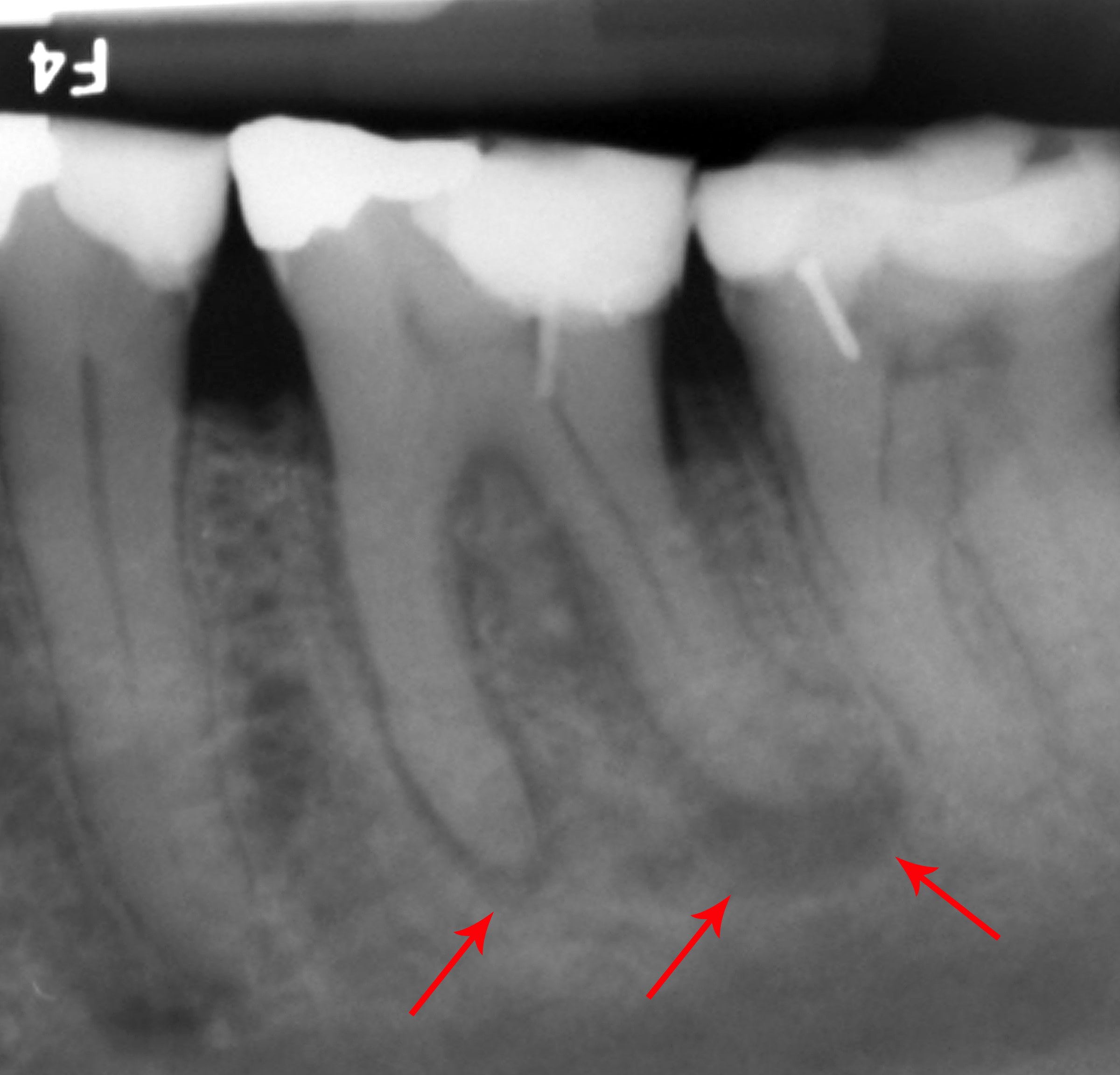
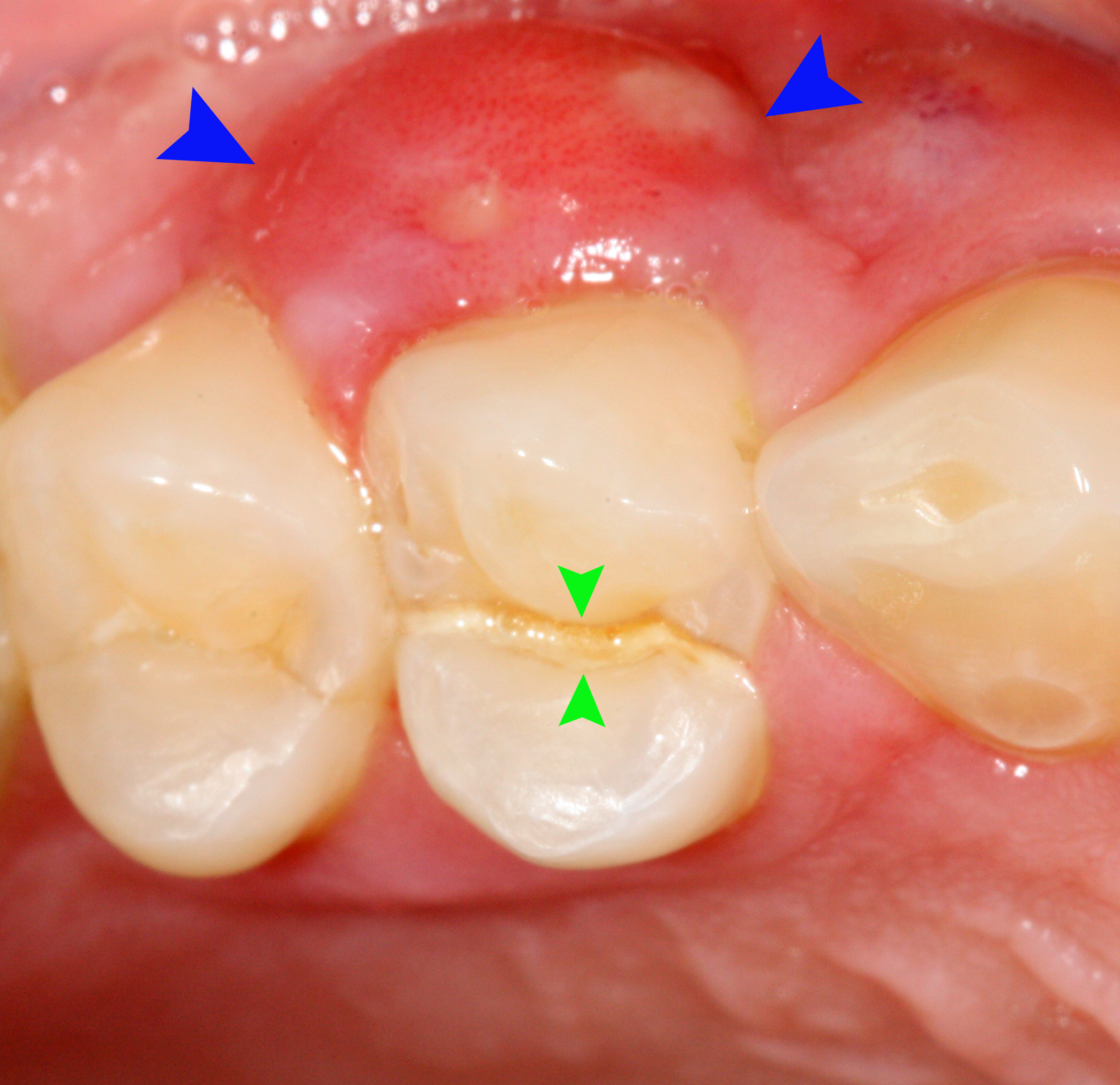 A periodontal abscess (lateral abscess) is a collection of pus that forms in the
A periodontal abscess (lateral abscess) is a collection of pus that forms in the
 Common marginal
Common marginal

 Non-dental causes of toothache are much less common as compared with dental causes. In a toothache of neurovascular origin, pain is reported in the teeth in conjunction with a
Non-dental causes of toothache are much less common as compared with dental causes. In a toothache of neurovascular origin, pain is reported in the teeth in conjunction with a
File:Cold test with ethyl chloride.jpg, Pulp sensibility test using ethyl chloride (cold stimulus)
File:Electric-pulp-testing.gif, Electric pulp tester
File:Tooth sleuth.jpg, Plastic wedge to identify pain on biting from a fractured tooth
File:Transillumination of tooth marked.jpg, Transillumination demonstrating fracture
File:Tooth decay and abscess xray.png, Decay (green) with apical abscess (blue)
File:Sinugram abscessed tooth.jpg, Gutta-percha point indicating abscess origin
Establishing a diagnosis of nondental toothache is initially done by careful questioning about the site, nature, aggravating and relieving factors, and referral of the pain, then ruling out any dental causes. There are no specific treatments for nondental pain (each treatment is directed at the cause of the pain, rather than the toothache itself), but a dentist can assist in offering potential sources of the pain and direct the patient to appropriate care. The most critical nondental source is the radiation of
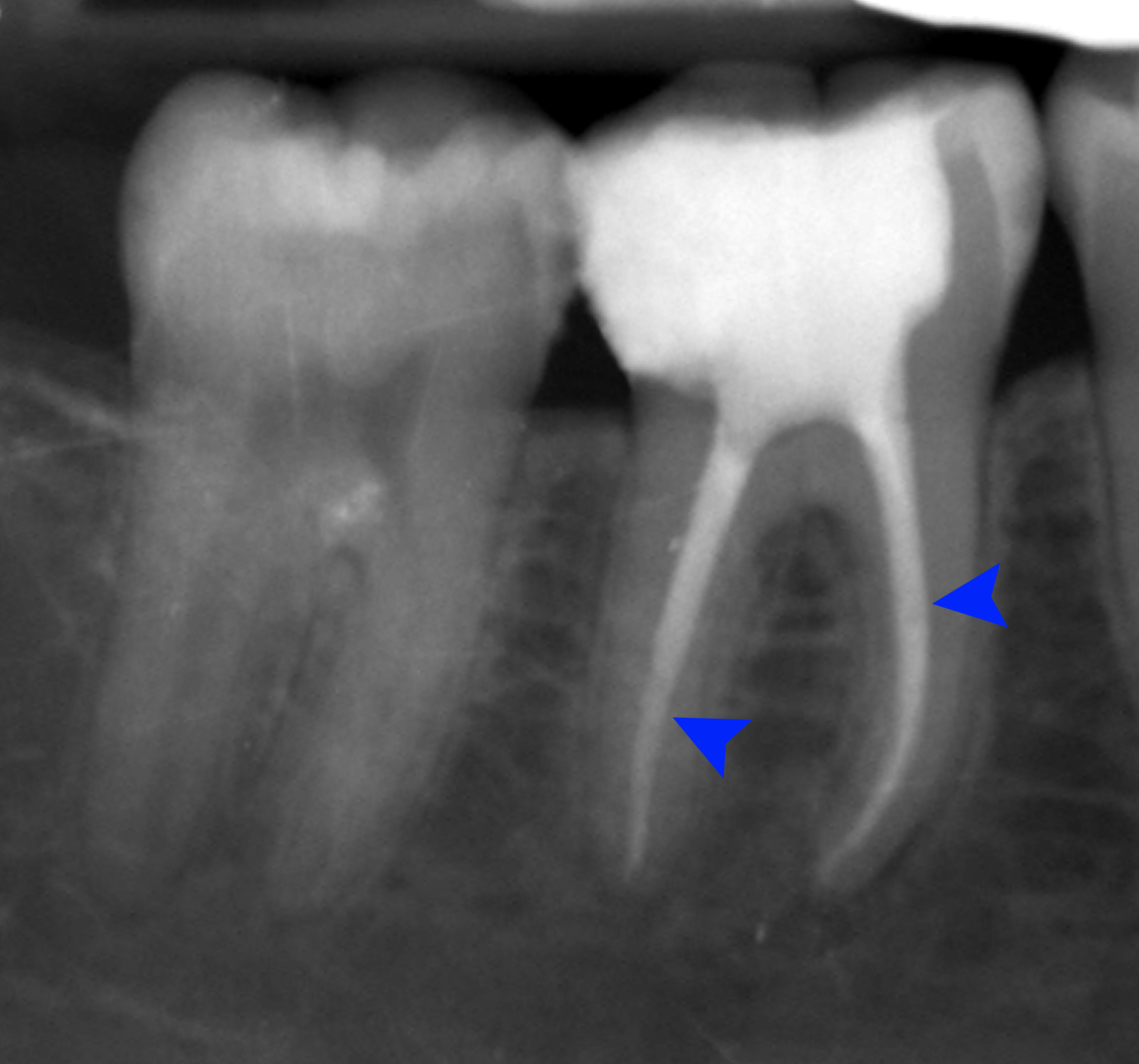

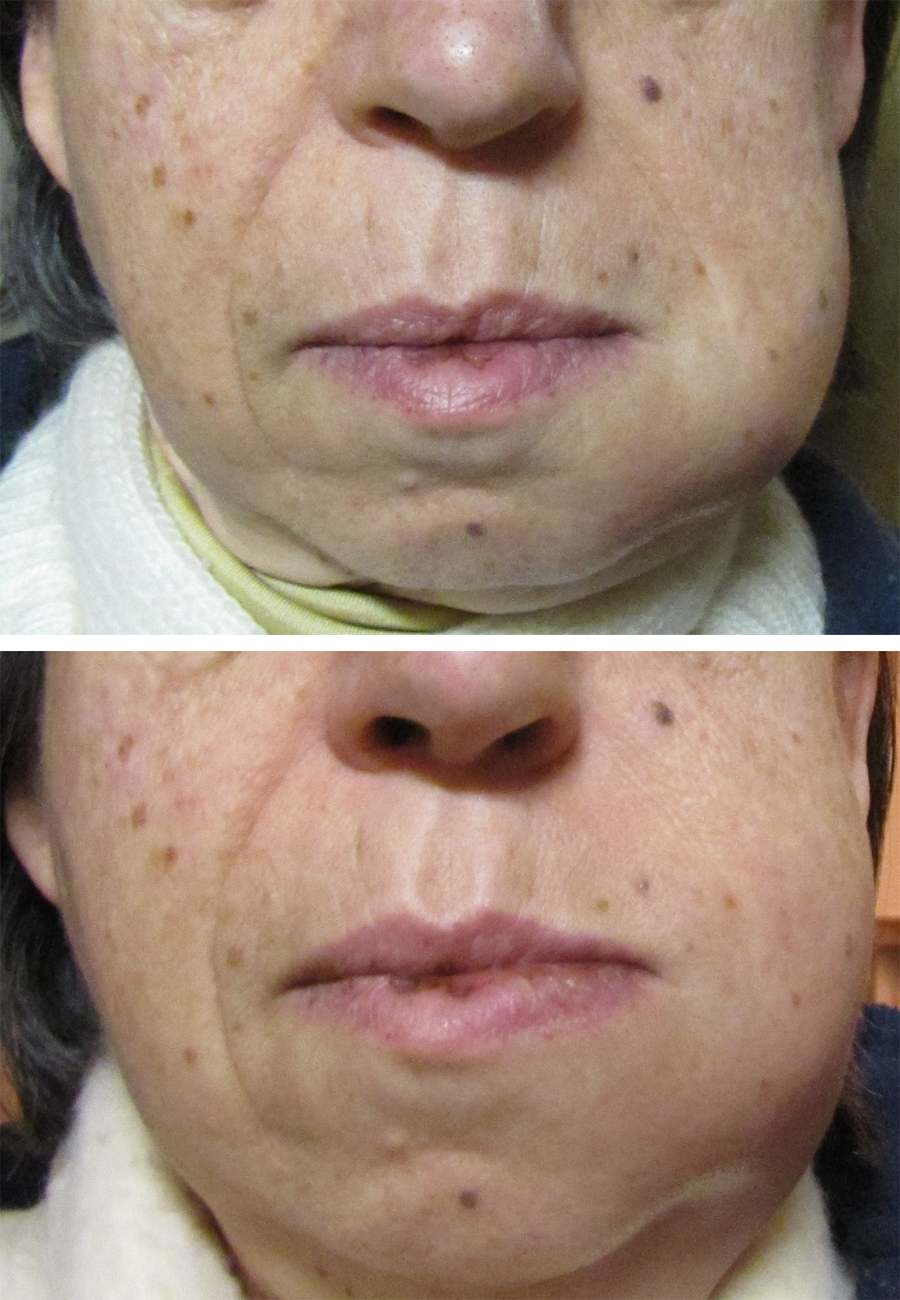 There are many causes of toothache and its diagnosis is a specialist topic, meaning that attendance at a dentist is usually required. Since many cases of toothache are inflammatory in nature,
There are many causes of toothache and its diagnosis is a specialist topic, meaning that attendance at a dentist is usually required. Since many cases of toothache are inflammatory in nature,

 The first known mention of tooth decay and toothache occurs on a
The first known mention of tooth decay and toothache occurs on a  In
In
WebMD Dental Health & ToothachesMayo Clinic Toothache First Aid
{{Pain Pain Headaches Medical emergencies Orofacial pain
erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is d ...
. The pulp of the tooth remains normal and healthy in dentin hypersensitivity.
Many topical treatments for dentin hypersensitivity are available, including desensitizing toothpastes and protective varnishes that coat the exposed dentin surface. Treatment of the root cause Root cause may refer to:
* "Root Cause" (''Person of Interest''), a TV show episode
* Root cause analysis
In science and engineering, root cause analysis (RCA) is a method of problem solving used for identifying the root causes of faults or pro ...
is critical, as topical measures are typically short lasting. Over time, the pulp usually adapts by producing new layers of dentin inside the pulp chamber called tertiary dentin, increasing the thickness between the pulp and the exposed dentin surface and lessening the hypersensitivity.
Periodontal
In general, chronic periodontal conditions do not cause any pain. Rather, it is acute inflammation which is responsible for the pain.=Apical periodontitis
=
Apical periodontitis
Periapical periodontitis or apical periodontitis (AP) is an acute or chronic inflammatory lesion around the apex of a tooth root, most commonly caused by bacterial invasion of the pulp of the tooth. It is a likely outcome of untreated denta ...
is acute or chronic inflammation around the apex of a tooth caused by an immune response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which coul ...
to bacteria within an infected pulp. It does not occur because of pulp necrosis, meaning that a tooth that tests as if it's alive (vital) may cause apical periodontitis, and a pulp which has become non-vital due to a sterile
Sterile or sterility may refer to:
*Asepsis
Asepsis is the state of being free from disease-causing micro-organisms (such as pathogenic bacteria, viruses, pathogenic fungi, and parasites). There are two categories of asepsis: medical and surgi ...
, non-infectious processes (such as trauma) may not cause any apical periodontitis. Bacterial cytotoxin
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are an immune cell or some types of venom, e.g. from the puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') or brown recluse spider (''Loxosceles reclusa'').
Cell physiology
Treating c ...
s reach the region around the roots of the tooth via the apical foramina and lateral canals, causing vasodilation
Vasodilation is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasoconstrictio ...
, sensitization of nerves, osteolysis
Osteolysis is an active resorption of bone matrix by osteoclasts and can be interpreted as the reverse of ossification. Although osteoclasts are active during the natural formation of healthy bone the term "osteolysis" specifically refers to a pa ...
(bone resorption) and potentially abscess or cyst formation.
The periodontal ligament becomes inflamed and there may be pain when biting or tapping on the tooth. On an X-ray, bone resorption appears as a radiolucent
Radiodensity (or radiopacity) is opacity to the radio wave and X-ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum: that is, the relative inability of those kinds of electromagnetic radiation to pass through a particular material. Radiolucency or hypod ...
area around the end of the root, although this does not manifest immediately. Acute apical periodontitis is characterized by well-localized, spontaneous, persistent, moderate to severe pain. The alveolar process may be tender to palpation over the roots. The tooth may be raised in the socket and feel more prominent than the adjacent teeth.
=Food impaction
= Food impaction occurs when food debris, especially fibrous food such as meat, becomes trapped between two teeth and is pushed into the gums during chewing. The usual cause of food impaction is disruption of the normal interproximal contour or drifting of teeth so that a gap is created (an open contact). Decay can lead to collapse of part of the tooth, or a dental restoration may not accurately reproduce the contact point. Irritation, localized discomfort or mild pain and a feeling of pressure from between the two teeth results. The gingival papilla is swollen, tender and bleeds when touched. The pain occurs during and after eating, and may slowly disappear before being evoked again at the next meal,This pattern of pain should be distinguished from the "meal time syndrome" of certainsalivary gland disease
Salivary gland diseases (SGDs) are multiple and varied in cause. There are three paired major salivary glands in humans – the parotid glands, the submandibular glands, and the sublingual glands. In addition there are about 800-1000 minor saliv ...
s. or relieved immediately by using a tooth pick or dental floss in the involved area. A gingival or periodontal abscess may develop from this situation.
=Periodontal abscess
= A periodontal abscess (lateral abscess) is a collection of pus that forms in the
A periodontal abscess (lateral abscess) is a collection of pus that forms in the gingival crevice
The gingival sulcus is an area of potential space between a tooth and the surrounding gingival tissue and is lined by sulcular epithelium. The depth of the sulcus (Latin for ''groove'') is bounded by two entities: apically by the gingival f ...
s, usually as a result of chronic periodontitis where the pockets are pathologically deepened greater than 3mm. A healthy gingival pocket will contain bacteria and some calculus
Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizati ...
kept in check by the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
. As the pocket deepens, the balance is disrupted, and an acute inflammatory response results, forming pus. The debris and swelling then disrupt the normal flow of fluids into and out of the pocket, rapidly accelerating the inflammatory cycle. Larger pockets also have a greater likelihood of collecting food debris, creating additional sources of infection.
Periodontal abscesses are less common than apical abscesses, but are still frequent. The key difference between the two is that the pulp of the tooth tends to be alive, and will respond normally to pulp tests. However, an untreated periodontal abscess may still cause the pulp to die if it reaches the tooth apex in a periodontic-endodontic lesion. A periodontal abscess can occur as the result of tooth fracture, food packing into a periodontal pocket (with poorly shaped fillings), calculus build-up, and lowered immune responses (such as in diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
). Periodontal abscess can also occur after periodontal scaling, which causes the gums to tighten around the teeth and trap debris in the pocket. Toothache caused by a periodontal abscess is generally deep and throbbing. The oral mucosa
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed '' lamina propria''. The oral cavity has sometimes been de ...
covering an early periodontal abscess appears erythema
Erythema (from the Greek , meaning red) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not asso ...
tous (red), swollen, shiny, and painful to touch.
A variant of the periodontal abscess is the gingival abscess, which is limited to the gingival margin, has a quicker onset, and is typically caused by trauma from items such as a fishbone, toothpick, or toothbrush, rather than chronic periodontitis. The treatment of a periodontal abscess is similar to the management of dental abscesses in general (see: Treatment). However, since the tooth is typically alive, there is no difficulty in accessing the source of infection and, therefore, antibiotics are more routinely used in conjunction with scaling and root planing. The occurrence of a periodontal abscess usually indicates advanced periodontal disease, which requires correct management to prevent recurrent abscesses, including daily cleaning below the gumline to prevent the buildup of subgingival plaque and calculus.
=Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
= Common marginal
Common marginal gingivitis
Gingivitis is a non-destructive disease that causes inflammation of the gums. The most common form of gingivitis, and the most common form of periodontal disease overall, is in response to bacterial biofilms (also called plaque) that is attac ...
in response to subgingival plaque is usually a painless condition. However, an acute form of gingivitis/periodontitis, termed acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG) is a common, non-contagious infection of the gums with sudden onset. The main features are painful, bleeding gums, and ulceration of inter-dental papillae (the sections of gum between adjacent teeth ...
(ANUG), can develop, often suddenly. It is associated with severe periodontal pain, bleeding gums, "punched out" ulceration, loss of the interdental papillae, and possibly also halitosis
Bad breath, also known as halitosis, is a symptom in which a noticeably unpleasant breath odour is present. It can result in anxiety among those affected. It is also associated with depression and symptoms of obsessive compulsive disorder.
...
(bad breath) and a bad taste. Predisposing factors include poor oral hygiene
Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's mouth clean and free of disease and other problems (e.g. bad breath) by regular brushing of the teeth (dental hygiene) and cleaning between the teeth. It is important that oral hygiene be carried ou ...
, smoking, malnutrition, psychological stress, and immunosuppression. This condition is not contagious, but multiple cases may simultaneously occur in populations who share the same risk factors (such as students in a dormitory during a period of examination). ANUG is treated over several visits, first with debridement
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), and by maggot therapy.
I ...
of the necrotic gingiva, homecare with hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3 ...
mouthwash, analgesics and, when the pain has subsided sufficiently, cleaning below the gumline, both professionally and at home. Antibiotics are not indicated in ANUG management unless there is underlying systemic disease.
=Pericoronitis
=Pericoronitis
Pericoronitis is inflammation of the soft tissues surrounding the crown of a partially erupted tooth, including the gingiva (gums) and the dental follicle. The soft tissue covering a partially erupted tooth is known as an ''operculum'', an ar ...
is inflammation of the soft tissues surrounding the crown of a partially erupted tooth. The lower wisdom tooth
A third molar, commonly called wisdom tooth, is one of the three molars per quadrant of the human dentition. It is the most posterior of the three. The age at which wisdom teeth come through ( erupt) is variable, but this generally occurs betw ...
is the last tooth to erupt into the mouth, and is, therefore, more frequently impacted, or stuck, against the other teeth. This leaves the tooth partially erupted into the mouth, and there frequently is a flap of gum (an operculum), overlying the tooth. Bacteria and food debris accumulate beneath the operculum, which is an area that is difficult to keep clean because it is hidden and far back in the mouth. The opposing upper wisdom tooth also tends to have sharp cusps and over-erupt because it has no opposing tooth to bite into, and instead traumatizes the operculum further. Periodontitis and dental caries may develop on either the third or second molars, and chronic inflammation develops in the soft tissues. Chronic pericoronitis may not cause any pain, but an acute pericoronitis episode is often associated with pericoronal abscess formation. Typical signs and symptoms of a pericoronal abscess include severe, throbbing pain, which may radiate to adjacent areas in the head and neck, redness, swelling and tenderness of the gum over the tooth. There may be trismus (difficulty opening the mouth), facial swelling, and rubor (flushing) of the cheek that overlies the angle of the jaw. Persons typically develop pericoronitis in their late teens and early 20s, as this is the age that the wisdom teeth are erupting. Treatment for acute conditions includes cleaning the area under the operculum with an antiseptic solution, painkillers, and antibiotics if indicated. After the acute episode has been controlled, the definitive treatment is usually by tooth extraction or, less commonly, the soft tissue is removed (operculectomy). If the tooth is kept, good oral hygiene is required to keep the area free of debris to prevent recurrence of the infection.
=Occlusal trauma
= Occlusal trauma results from excessive biting forces exerted on teeth, which overloads the periodontal ligament, causing periodontal pain and a reversible increase in tooth mobility. Occlusal trauma may occur withbruxism
Bruxism is excessive teeth grinding or jaw clenching. It is an oral parafunctional activity; i.e., it is unrelated to normal function such as eating or talking. Bruxism is a common behavior; reports of prevalence range from 8% to 31% in the gen ...
, the parafunctional (abnormal) clenching and grinding of teeth during sleep or while awake. Over time, there may be attrition ( tooth wear), which may also cause dentin hypersensitivity, and possibly formation of a periodontal abscess, as the occlusal trauma causes adaptive changes in the alveolar bone.
Occlusal trauma often occurs when a newly placed dental restoration
Dental restoration, dental fillings, or simply fillings are treatments used to restore the function, integrity, and morphology of missing tooth structure resulting from caries or external trauma as well as to the replacement of such structure sup ...
is built too "high", concentrating the biting forces on one tooth. Height differences measuring less than a millimeter can cause pain. Dentists, therefore, routinely check that any new restoration is in harmony with the bite and forces are distributed correctly over many teeth using articulating paper. If the high spot is quickly eliminated, the pain disappears and there is no permanent harm. Over-tightening of braces can cause periodontal pain and, occasionally, a periodontal abscess.
=Alveolar osteitis
=Alveolar osteitis
Alveolar osteitis, also known as dry socket, is inflammation of the alveolar bone (i.e., the alveolar process of the maxilla or mandible). Classically, this occurs as a postoperative complication of tooth extraction.
Alveolar osteitis usually occ ...
is a complication of tooth extraction (especially lower wisdom teeth) in which the blood clot is not formed or is lost, leaving the socket where the tooth used to be empty, and bare bone is exposed to the mouth. The pain is moderate to severe, and dull, aching, and throbbing in character. The pain is localized to the socket, and may radiate. It normally starts two to four days after the extraction, and may last 10–40 days. Healing is delayed, and it is treated with local anesthetic dressings, which are typically required for five to seven days. There is some evidence that chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine (CHX) (commonly known by the salt forms chlorhexidine gluconate and chlorhexidine digluconate (CHG) or chlorhexidine acetate) is a disinfectant and antiseptic that is used for skin disinfection before surgery and to sterilize surgi ...
mouthwash used prior to extractions prevents alveolar osteitis.
Combined pulpal-periodontal
=Dental trauma and cracked tooth syndrome
=
Cracked tooth syndrome
Cracked tooth syndrome (CTS) is where a tooth has incompletely cracked but no part of the tooth has yet broken off. Sometimes it is described as a greenstick fracture. The symptoms are very variable, making it a notoriously difficult condition to d ...
refers to a highly variable set of pain-sensitivity symptoms that may accompany a tooth fracture, usually sporadic, sharp pain that occurs during biting or with release of biting pressure, or relieved by releasing pressure on the tooth. The term is falling into disfavor and has given way to the more generalized description of fractures and cracks of the tooth, which allows for the wide variations in signs, symptoms, and prognosis for traumatized teeth. A fracture of a tooth can involve the enamel, dentin, and/or pulp, and can be orientated horizontally or vertically. Fractured or cracked teeth can cause pain via several mechanisms, including dentin hypersensitivity, pulpitis (reversible or irreversible), or periodontal pain. Accordingly, there is no single test or combination of symptoms that accurately diagnose a fracture or crack, although when pain can be stimulated by causing separation of the cusps of the tooth, it's highly suggestive of the disorder. Vertical fractures can be very difficult to identify because the crack can rarely be probed or seen on radiographs, as the fracture runs in the plane of conventional films (similar to how the split between two adjacent panes of glass is invisible when facing them).
When toothache results from dental trauma
Dental trauma refers to trauma (injury) to the teeth and/or periodontium (gums, periodontal ligament, alveolar bone), and nearby soft tissues such as the lips, tongue, etc. The study of dental trauma is called dental traumatology.''Textbook an ...
(regardless of the exact pulpal or periodontal diagnosis), the treatment and prognosis is dependent on the extent of damage to the tooth, the stage of development of the tooth, the degree of displacement or, when the tooth is avulsed, the time out of the socket and the starting health of the tooth and bone. Because of the high variation in treatment and prognosis, dentists often use trauma guides to help determine prognosis and direct treatment decisions.
The prognosis for a cracked tooth varies with the extent of the fracture. Those cracks that are irritating the pulp but do not extend through the pulp chamber can be amenable to stabilizing dental restorations such as a crown or composite resin
Dental composite resins (better referred to as "resin-based composites" or simply "filled resins") are dental cements made of synthetic resins. Synthetic resins evolved as restorative materials since they were insoluble, of good tooth-like appea ...
. Should the fracture extend though the pulp chamber and into the root, the prognosis of the tooth is hopeless.
=Periodontic-endodontic lesion
= Apical abscesses can spread to involve periodontal pockets around a tooth, and periodontal pockets cause eventual pulp necrosis via accessory canals or the apical foramen at the bottom of the tooth. Such lesions are termed periodontic-endodontic lesions, and they may be acutely painful, sharing similar signs and symptoms with a periodontal abscess, or they may cause mild pain or no pain at all if they are chronic and free-draining. Successful root canal therapy is required before periodontal treatment is attempted. Generally, the long-term prognosis of perio-endo lesions is poor.Non-dental
 Non-dental causes of toothache are much less common as compared with dental causes. In a toothache of neurovascular origin, pain is reported in the teeth in conjunction with a
Non-dental causes of toothache are much less common as compared with dental causes. In a toothache of neurovascular origin, pain is reported in the teeth in conjunction with a migraine
Migraine (, ) is a common neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches. Typically, the associated headache affects one side of the head, is pulsating in nature, may be moderate to severe in intensity, and could last from a few hou ...
. Local and distant structures (such as ear, brain, carotid artery Carotid artery may refer to:
* Common carotid artery, often "carotids" or "carotid", an artery on each side of the neck which divides into the external carotid artery and internal carotid artery
* External carotid artery, an artery on each side of ...
, or heart) can also refer pain to the teeth. Other non-dental causes of toothache include myofascial pain (muscle pain) and angina pectoris
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typically the result of obstru ...
(which classically refers pain to the lower jaw). Very rarely, toothache can be psychogenic in origin.
Disorders of the maxillary sinus
The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus (or antrum of Highmore) is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, and drains into the middle meatus of the nose through the osteomeatal complex.Human Anatomy, Jacobs, Elsevier, 2008, page 209-210
Structure
It i ...
can be referred to the upper back teeth. The posterior, middle and anterior superior alveolar nerves are all closely associated with the lining of the sinus. The bone between the floor of the maxillary sinus and the roots of the upper back teeth is very thin, and frequently the apices of these teeth disrupt the contour of the sinus floor. Consequently, acute or chronic maxillary sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, head ...
can be perceived as maxillary toothache, and neoplasm
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s of the sinus (such as adenoid cystic carcinoma) can cause similarly perceived toothache if malignant invasion of the superior alveolar nerves occurs. Classically, sinusitis pain increases upon Valsalva maneuver
The Valsalva maneuver is performed by a forceful attempt of exhalation against a closed airway, usually done by closing one's mouth and pinching one's nose shut while expelling air out as if blowing up a balloon. Variations of the maneuver can ...
s or tilting the head forward.
Painful conditions which do not originate from the teeth or their supporting structures may affect the oral mucosa of the gums and be interpreted by the individual as toothache. Examples include neoplasms of the gingival or alveolar mucosa
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed '' lamina propria''. The oral cavity has sometimes been des ...
(usually squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinomas (SCCs), also known as epidermoid carcinomas, comprise a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the ...
), conditions which cause gingivostomatitis
Stomatitis is inflammation of the mouth and lips. It refers to any inflammatory process affecting the mucous membranes of the mouth and lips, with or without oral ulceration.
In its widest meaning, stomatitis can have a multitude of different ca ...
and desquamative gingivitis. Various conditions may involve the alveolar bone, and cause non-odontogenic toothache, such as Burkitt's lymphoma
Burkitt lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system, particularly B lymphocytes found in the germinal center. It is named after Denis Parsons Burkitt, the Irish surgeon who first described the disease in 1958 while working in equatorial Africa. ...
, infarcts in the jaws caused by sickle cell disease, and osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the ...
. Various conditions of the trigeminal nerve can masquerade as toothache, including trigeminal zoster (maxillary or mandibular division), trigeminal neuralgia, cluster headache
Cluster headache (CH) is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent severe headaches on one side of the head, typically around the eye(s). There is often accompanying eye watering, nasal congestion, or swelling around the eye on the af ...
, and trigeminal neuropathies
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or o ...
. Very rarely, a brain tumor
A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and seco ...
might cause toothache. Another chronic facial pain syndrome which can mimic toothache is temporomandibular disorder (temporomandibular joint pain-dysfunction syndrome), which is very common. Toothache which has no identifiable dental or medical cause is often termed atypical odontalgia
Atypical facial pain (AFP) is a type of chronic facial pain which does not fulfill any other diagnosis. There is no consensus as to a globally accepted definition, and there is even controversy as to whether the term should be continued to be use ...
, which, in turn, is usually considered a type of atypical facial pain (or persistent idiopathic facial pain). Atypical odontalgia may give very unusual symptoms, such as pain which migrates from one tooth to another and which crosses anatomical boundaries (such as from the left teeth to the right teeth).
Pathophysiology
A tooth is composed of an outer shell ofcalcified
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature Ma ...
hard tissues (from hardest to softest: enamel, dentin
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by e ...
, and cementum), and an inner soft tissue
Soft tissue is all the tissue in the body that is not hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. Soft tissue connects, surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ...
core (the pulp system), which contains nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system.
A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the ...
s and blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide awa ...
s. The visible parts of the teeth in the mouth – the crowns (covered by enamel) – are anchored into the bone by the roots
A root is the part of a plant, generally underground, that anchors the plant body, and absorbs and stores water and nutrients.
Root or roots may also refer to:
Art, entertainment, and media
* ''The Root'' (magazine), an online magazine focusing ...
(covered by cementum). Underneath the cementum and enamel layers, dentin forms the bulk of the tooth and surrounds the pulp system. The part of the pulp inside the crown is the pulp chamber, and the central soft tissue nutrient canals within each root are root canals, exiting through one or more holes at the root end ( apical foramen/foramina). The periodontal ligament
The periodontal ligament, commonly abbreviated as the PDL, is a group of specialized connective tissue fibers that essentially attach a tooth to the alveolar bone within which it sits. It inserts into root cementum one side and onto alveolar ...
connects the roots to the bony socket. The gingiva
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue l ...
covers the alveolar process
The alveolar process () or alveolar bone is the thickened ridge of bone that contains the tooth sockets on the jaw bones (in humans, the maxilla and the mandible). The structures are covered by gums as part of the oral cavity.
The synonymous ...
es, the tooth-bearing arches of the jaws.
Enamel is not a vital tissue, as it lacks blood vessels, nerves, and living cells. Consequently, pathologic processes involving only enamel, such as shallow cavities or cracks, tend to be painless. Dentin contains many microscopic tubes containing fluid and the processes of odontoblast
In vertebrates, an odontoblast is a cell of neural crest origin that is part of the outer surface of the dental pulp, and whose biological function is dentinogenesis, which is the formation of dentin, the substance beneath the tooth enamel on t ...
cells, which communicate with the pulp. Mechanical, osmotic
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region ...
, or other stimuli cause movement of this fluid, triggering nerves in the pulp (the "hydrodynamic
In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids— liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including ''aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) ...
theory" of pulp sensitivity). Due to the close relationship between dentin and pulp, they are frequently considered together as the ''dentin-pulp complex''.
The teeth and gums exhibit normal sensations in health. Such sensations are generally sharp, lasting as long as the stimulus. There is a continuous spectrum from physiologic sensation to pain in disease. Pain is an unpleasant sensation caused by intense or damaging events. In a toothache, nerves are stimulated by either exogenous
In a variety of contexts, exogeny or exogeneity () is the fact of an action or object originating externally. It contrasts with endogeneity or endogeny, the fact of being influenced within a system.
Economics
In an economic model, an exogen ...
sources (for instance, bacterial toxins, metabolic
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
byproducts, chemicals, or trauma) or endogenous
Endogenous substances and processes are those that originate from within a living system such as an organism, tissue, or cell.
In contrast, exogenous substances and processes are those that originate from outside of an organism.
For example, ...
factors (such as inflammatory mediators).
The pain pathway is mostly transmitted via myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can ...
ated Aδ (sharp or stabbing pain) and unmyelinated C nerve fiber
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action p ...
s (slow, dull, aching, or burning pain) of the trigeminal nerve
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve ( lit. ''triplet'' nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and che ...
, which supplies sensation to the teeth and gums via many divisions and branches. Initially, pain is felt while noxious stimuli are applied (such as cold). Continued exposure decreases firing thresholds of the nerves, allowing normally non-painful stimuli to trigger pain (allodynia
Allodynia is a condition in which pain is caused by a stimulus that does not normally elicit pain. For example, bad sunburn can cause temporary allodynia, and touching sunburned skin, or running cold or warm water over it, can be very painful. It i ...
). Should the insult continue, noxious stimuli produce larger discharges in the nerve, perceived as more intense pain. Spontaneous pain may occur if the firing threshold is decreased so it can fire without stimulus ( hyperalgesia). The physical component of pain is processed in the medullary spinal cord and perceived in the frontal cortex
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove be ...
. Because pain perception involves overlapping sensory systems and an emotional component, individual responses to identical stimuli are variable.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of toothache can be challenging, not only because the list of potential causes is extensive, but also because dental pain may be extremely variable, and pain can be referred to and from the teeth. Dental pain can simulate virtually any facial pain syndrome. However, the vast majority of toothache is caused by dental, rather than non-dental, sources. Consequently, the saying " horses, not zebras" has been applied to thedifferential diagnosis
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (abbreviated DDx) is a method of analysis of a patient's history and physical examination to arrive at the correct diagnosis. It involves distinguishing a particular disease or condition from others that p ...
of orofacial pain. That is, everyday dental causes (such as pulpitis) should always be considered before unusual, non-dental causes (such as myocardial infarction). In the wider context of orofacial pain, all cases of orofacial pain may be considered as having a dental origin until proven otherwise. The diagnostic approach for toothache is generally carried out in the following sequence: history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
, followed by examination, and investigations. All this information is then collated and used to build a clinical picture, and a differential diagnosis can be carried out.
Symptoms
Thechief complaint The chief complaint, formally known as CC in the medical field, or termed presenting complaint (PC) in Europe and Canada, forms the second step of medical history taking. It is sometimes also referred to as reason for encounter (RFE), presenting pr ...
, and the onset of the complaint, are usually important in the diagnosis of toothache. For example, the key distinction between reversible and irreversible pulpitis is given in the history, such as pain following a stimulus in the former, and lingering pain following a stimulus and spontaneous pain in the latter. History is also important in recent filling or other dental treatment, and trauma to the teeth. Based on the most common causes of toothache (dentin hypersensitivity, periodontitis, and pulpitis), the key indicators become localization of the pain (whether the pain is perceived as originating in a specific tooth), thermal sensitivity, pain on biting, spontaneity of the pain, and factors that make the pain worse.The various qualities of the toothache, such as the effect of biting and chewing on the pain, the effect of thermal stimuli, and the effect of the pain on sleep, are verbally established by the clinician, usually in a systematic fashion, such as using the Socrates pain assessment method (see table).
From the history, indicators of pulpal, periodontal, a combination of both, or non-dental causes can be observed. Periodontal pain is frequently localized to a particular tooth, which is made much worse by biting on the tooth, sudden in onset, and associated with bleeding and pain when brushing. More than one factor may be involved in the toothache. For example, a pulpal abscess (which is typically severe, spontaneous and localized) can cause periapical periodontitis (which results in pain on biting). Cracked tooth syndrome may also cause a combination of symptoms. Lateral periodontitis (which is usually without any thermal sensitivity and sensitive to biting) can cause pulpitis and the tooth becomes sensitive to cold.
Non-dental sources of pain often cause multiple teeth to hurt and have an epicenter that is either above or below the jaws. For instance, cardiac pain (which can make the bottom teeth hurt) usually radiates up from the chest and neck, and sinusitis (which can make the back top teeth hurt) is worsened by bending over. As all of these conditions may mimic toothache, it is possible that dental treatment, such as fillings, root canal treatment, or tooth extraction may be carried out unnecessarily by dentists in an attempt to relieve the individual's pain, and as a result the correct diagnosis is delayed. A hallmark is that there is no obvious dental cause, and signs and symptoms elsewhere in the body may be present. As migraines are typically present for many years, the diagnosis is easier to make. Often the character of the pain is the differentiator between dental and non-dental pain.
Irreversible pulpitis progresses to pulp necrosis, wherein the nerves are non-functional, and a pain-free period following the severe pain of irreversible pulpitis may be experienced. However, it is common for irreversible pulpitis to progress to apical periodontitis, including an acute apical abscess, without treatment. As irreversible pulpitis generates an apical abscess, the character of the toothache may simply change without any pain-free period. For instance, the pain becomes well localized, and biting on the tooth becomes painful. Hot drinks can make the tooth feel worse because they expand the gases and likewise, cold can make it feel better, thus some will sip cold water.
Examination
The clinical examination narrows the source down to a specific tooth, teeth, or a non-dental cause. Clinical examination moves from the outside to the inside, and from the general to the specific. Outside of the mouth, thesinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the spheno ...
, muscles of the face
The face is the front of an animal's head that features the eyes, nose and mouth, and through which animals express many of their emotions. The face is crucial for human identity, and damage such as scarring or developmental deformities may aff ...
and neck
The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In ...
, the temporomandibular joints, and cervical lymph nodes are palpated for pain or swelling. In the mouth, the soft tissues of the gingiva
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue l ...
, mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It i ...
, tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste ...
, and pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its st ...
are examined for redness, swelling or deformity. Finally, the teeth are examined. Each tooth that may be painful is percussed (tapped), palpated at the base of the root, and probed with a dental explorer for dental caries and a periodontal probe for periodontitis
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main cau ...
, then wiggled for mobility.
Sometimes the symptoms reported in the history are misleading and point the examiner to the wrong area of the mouth. For instance, sometimes people may mistake pain from pulpitis in a lower tooth as pain in the upper teeth, and ''vice versa''. In other instances, the apparent examination findings may be misleading and lead to the wrong diagnosis and wrong treatment. Pus from a pericoronal abscess associated with a lower third molar may drain along the submucosa
The submucosa (or tela submucosa) is a thin layer of tissue in various organs of the gastrointestinal, respiratory, and genitourinary tracts. It is the layer of dense irregular connective tissue that supports the mucosa (mucous membrane) and j ...
l plane and discharge as a parulis
Intraoral dental sinus (also termed a parulis and commonly, a gumboil) is an oral lesion characterized by a soft erythematous papule (red spot) that develops on the alveolar process in association with a non-vital tooth and accompanying dental abs ...
over the roots of the teeth towards the front of the mouth (a "migratory abscess"). Another example is decay of the tooth root which is hidden from view below the gumline, giving the casual appearance of a sound tooth if careful periodontal examination is not carried out.
Factors indicating infection include movement of fluid in the tissues during palpation (''fluctuance''), swollen lymph nodes in the neck, and fever with an oral temperature more than 37.7 °C.
Investigations
Any tooth that is identified, in either the history of pain or base clinical exam, as a source for toothache may undergo further testing for vitality of the dental pulp, infection, fractures, or periodontitis. These tests may include: * Pulp sensitivity tests, usually carried out with a cotton wool pledget sprayed with ethyl chloride to serve as a cold stimulus, or with an electric pulp tester. The air spray from a three-in-one syringe may also be used to demonstrate areas of dentin hypersensitivity. Heat tests can also be applied with hotGutta-percha
Gutta-percha is a tree of the genus '' Palaquium'' in the family Sapotaceae. The name also refers to the rigid, naturally biologically inert, resilient, electrically nonconductive, thermoplastic latex derived from the tree, particularly fr ...
. A healthy tooth will feel the cold but the pain will be mild and disappear once the stimulus is removed. The accuracy of these tests has been reported as 86% for cold testing, 81% for electric pulp testing, and 71% for heat testing. Because of the lack of test sensitivity, a second symptom should be present or a positive test before making a diagnosis.
* Radiograph
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeut ...
s utilized to find dental caries and bone loss laterally or at the apex.
* Assessment of biting on individual teeth (which sometimes helps to localize the problem) or the separate cusps (may help to detect cracked cusp syndrome).
Less commonly used tests might include trans-illumination (to detect congestion of the maxillary sinus or to highlight a crack in a tooth), dyes (to help visualize a crack), a test cavity, selective anaesthesia and laser doppler flowmetry.
angina pectoris
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typically the result of obstru ...
into the lower teeth and the potential need for urgent cardiac care.
Differential diagnoses
When it becomes extremely painful and decayed the tooth may be known as a hot tooth.Prevention
Since most toothache is the result of plaque-related diseases, such as tooth decay and periodontal disease, the majority of cases could be prevented by avoidance of acariogenic
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complicatio ...
diet and maintenance of good oral hygiene
Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's mouth clean and free of disease and other problems (e.g. bad breath) by regular brushing of the teeth (dental hygiene) and cleaning between the teeth. It is important that oral hygiene be carried ou ...
. That is, reduction in the number times that refined sugars are consumed per day and brushing the teeth twice a day with fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an inorganic, monatomic anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose salts are typically white or colorless. Fluoride salts ty ...
toothpaste and interdental cleaning. Regular visits to a dentist also increases the likelihood that problems are detected early and averted before toothache occurs. Dental trauma could also be significantly reduced by routine use of mouthguard
A mouthguard is a protective device for the mouth that covers the teeth and gums to prevent and reduce injury to the teeth, arches, lips and gums. An effective mouthguard is like a crash helmet for teeth and jaws. It also prevents the jaws co ...
s in contact sport
Contact sports are sports that emphasize or require physical contact between players. Some sports, such as mixed martial arts, are scored on impacting an opponent, while others, including rugby football, gridiron football and Australian rules f ...
s.
Management


 There are many causes of toothache and its diagnosis is a specialist topic, meaning that attendance at a dentist is usually required. Since many cases of toothache are inflammatory in nature,
There are many causes of toothache and its diagnosis is a specialist topic, meaning that attendance at a dentist is usually required. Since many cases of toothache are inflammatory in nature, over the counter
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are medicines sold directly to a consumer without a requirement for a prescription from a healthcare professional, as opposed to prescription drugs, which may be supplied only to consumers possessing a valid prescr ...
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
s (NSAIDs) may help (unless contraindicated
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition that serves as a reason not to take a certain medical treatment due to the harm that it would cause the patient. Contraindication is the opposite of indication, which is a reason to use a certain tre ...
, such as with a peptic ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines ...
). Generally, NSAIDs are as effective as aspirin
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and/or inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat inc ...
alone or in combination with codeine
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, ''Papaver somniferum''. It is typically ...
. However, simple analgesics may have little effect on some causes of toothache, and the severe pain can drive individuals to exceed the maximum dose. For example, when acetaminophen
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol.
At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferior ...
(paracetamol) is taken for toothache, an accidental overdose is more likely to occur when compared to people who are taking acetaminophen for other reasons. Another risk in persons with toothache is a painful chemical burn of the oral mucosa
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed '' lamina propria''. The oral cavity has sometimes been de ...
caused by holding a caustic substance such as aspirin tablets and toothache remedies containing eugenol
Eugenol is an allyl chain-substituted guaiacol, a member of the allylbenzene class of chemical compounds. It is a colorless to pale yellow, aromatic oily liquid extracted from certain essential oils especially from clove, nutmeg, cinnamon, bas ...
(such as clove oil
Oil of clove, also known as clove oil, is an essential oil extracted from the clove plant, '' Syzygium aromaticum''. Clove oil is commonly used in aromatherapy and for flavoring food and some medicines. Madagascar and Indonesia are the main produc ...
) against the gum. Although the logic of placing a tablet against the painful tooth is understandable, an aspirin tablet needs to be swallowed to have any pain-killing effect. Caustic toothache remedies require careful application to the tooth only, without coming into excessive contact with the soft tissues of the mouth.
For the dentist, the goal of treatment generally is to relieve the pain, and wherever possible to preserve or restore function. The treatment depends on the cause of the toothache, and frequently a clinical decision regarding the current state and long-term prognosis of the affected tooth, as well as the individual's wishes and ability to cope with dental treatment, will influence the treatment choice. Often, administration of an intra-oral local anesthetic such as lidocaine
Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia. When used for local anaesthesia or in nerve blocks, lid ...
and epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and ...
is indicated in order to carry out pain-free treatment. Treatment may range from simple advice, removal of dental decay with a dental drill
A dental drill or handpiece is a hand-held, mechanical instrument used to perform a variety of common dental procedures, including removing decay, polishing fillings, performing cosmetic dentistry, and altering prostheses.
The handpiece itse ...
and subsequent placement of a filling, to root canal treatment, tooth extraction, or debridement.
Pulpitis and its sequalae
In pulpitis, an important distinction in regard to treatment is whether the inflammation is reversible or irreversible. Treatment of reversible pulpitis is by removing or correcting the causative factor. Usually, the decay is removed, and a sedative dressing is used to encourage the pulp to return to a state of health, either as a base underneath a permanent filling or as a temporary filling intended to last for a period while the tooth is observed to see if pulpitis resolves. Irreversible pulpitis and its sequalae pulp necrosis and apical periodontitis require treatment with root canal therapy or tooth extraction, as the pulp acts as a nidus of infection, which will lead to a chronic infection if not removed. Generally, there is no difference in outcomes between whether the root canal treatment is completed in one or multiple appointments. The field of regenerative endodontics is now developing ways to clean the pulp chamber and regenerate the soft and hard tissues to either regrow or simulate pulp structure. This has proved especially helpful in children where the tooth root has not yet finished developing and root canal treatments have lower success rates. Reversible/irreversible pulpitis is a distinct concept from whether the tooth is restorable or unrestorable, e.g. a tooth may only have reversible pulpitis, but has been structurally weakened by decay or trauma to the point that it is impossible to restore the tooth in the long term.Dental abscesses
A general principle concerning dental abscesses is '' ubi pus, ibi evacua'' ("where there is pus, drain it"), which applies to any case where there is a collection of pus in the tissues (such as a periodontal abscess, pericoronal abscess, or apical abscess). The pus within the abscess is under pressure, and the surrounding tissues are deformed and stretched to accommodate the swelling. This leads to a sensation of throbbing (often in time with the pulse) and constant pain. Pus may be evacuated via the tooth by drilling into the pulp chamber (an endodontic access cavity). Such a treatment is sometimes termed open drainage. Drainage can also be performed via the tooth socket, once the causative tooth is extracted. If neither of those measures succeeds, or they are impossible, incision and drainage may be required, in which a small incision is made in the soft tissues directly over the abscess at the most dependent point. A surgical instrument such as a pair of tweezers is gently inserted into the incision and opened, while the abscess is massaged to encourage the pus to drain out. Usually, the reduction in pain when the pus drains is immediate and marked as the built up pressure is relieved. If the pus drains into the mouth, there is usually a bad or offensive taste.Antibiotics
Antibiotics tend to be extensively used for emergency dental problems. As samples for microbiologic culture and sensitivity are hardly ever carried out in general dental practice,broad-spectrum antibiotic
A broad-spectrum antibiotic is an antibiotic that acts on the two major bacterial groups, Gram-positive and Gram-negative, or any antibiotic that acts against a wide range of disease-causing bacteria. These medications are used when a bacterial ...
s such as amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is an antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infection, strep throat, pneumonia, skin infections, and urinary tract infections among others. It is taken by mouth, or less c ...
are typically used for a short course of about three to seven days. Antibiotics are seen as a "quick fix" by both dentists, who generally only have a very short time to manage dental emergencies, and by patients, who tend to want to avoid treatments (such as tooth extraction) which are perceived negatively. However, antibiotics typically only temporarily suppress an infection, and the need for definitive treatment is only postponed for an unpredictable length of time. An estimated 10% of all antibiotic prescriptions are made by dentists, a major factor in antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. ...
. They are often used inappropriately, in conditions for which they are ineffective, or their risks outweigh the benefits, such as irreversible pulpitis, apical abscess, dry socket, or mild pericoronitis. However, the reality is that antibiotics are rarely needed, and they should be used restrictively in dentistry. Local measures such as incision and drainage, and removal of the cause of the infection (such as a necrotic tooth pulp) have a greater therapeutic benefit and are much more important. If abscess drainage has been achieved, antibiotics are not usually necessary.
Antibiotics tend to be used when local measures cannot be carried out immediately. In this role, antibiotics suppress the infection until local measures can be carried out. Severe trismus may occur in when the muscles of mastication
There are four classical muscles of mastication. During mastication, three muscles of mastication (''musculi masticatorii'') are responsible for adduction of the jaw, and one (the lateral pterygoid) helps to abduct it. All four move the jaw lat ...
are involved in an odontogenic infection, making any surgical treatment impossible. Immunocompromised
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that a ...
individuals are less able to fight off infections, and antibiotics are usually given. Evidence of systemic involvement (such as a fever higher than 38.5 °C, cervical lymphadenopathy, or malaise
As a medical term, malaise is a feeling of general discomfort, uneasiness or lack of wellbeing and often the first sign of an infection or other disease. The word has existed in French since at least the 12th century.
The term is often used ...
) also indicates antibiotic therapy, as do rapidly spreading infections, cellulitis
Cellulitis is usually a bacterial infection involving the inner layers of the skin. It specifically affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat. Signs and symptoms include an area of redness which increases in size over a few days. The borders of ...
, or severe pericoronitis. Drooling
Drooling, or slobbering, is the flow of saliva outside the mouth. Drooling can be caused by excess production of saliva, inability to retain saliva within the mouth (incontinence of saliva), or problems with swallowing (dysphagia or odynophagia ...
and difficulty swallowing
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or liqui ...
are signs that the airway may be threatened, and may precede difficulty in breathing. Ludwig's angina and cavernous sinus thrombosis
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.
Structure
The ...
are rare but serious complications of odontogenic infections. Severe infections tend to be managed in hospital.
Prognosis
Most dental pain can be treated with routine dentistry. In rare cases, toothache can be a symptom representing a life-threatening condition, such as a deep neck infection (compression of theairway
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose t ...
by a spreading odontogenic infection) or something more remote like a heart attack.
Dental caries, if left untreated, follows a predictable natural history as it nears the pulp of the tooth. First it causes reversible pulpitis, which transitions to irreversible pulpitis, then to necrosis, then to necrosis with periapical periodontitis and, finally, to necrosis with periapical abscess. Reversible pulpitis can be stopped by removal of the cavity and the placement of a sedative dressing of any part of the cavity that is near the pulp chamber. Irreversible pulpitis and pulp necrosis are treated with either root canal therapy or extraction. Infection of the periapical tissue will generally resolve with the treatment of the pulp, unless it has expanded to cellulitis
Cellulitis is usually a bacterial infection involving the inner layers of the skin. It specifically affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat. Signs and symptoms include an area of redness which increases in size over a few days. The borders of ...
or a radicular cyst
Radicular pain, or radiculitis, is pain "radiated" along the dermatome (sensory distribution) of a nerve due to inflammation or other irritation of the nerve root (radiculopathy) at its connection to the spinal column. A common form of radicu ...
. The success rate of restorative treatment and sedative dressings in reversible pulpitis, depends on the extent of the disease, as well as several technical factors, such as the sedative agent used and whether a rubber dam was used. The success rate of root canal treatment also depends on the degree of disease (root canal therapy for irreversible pulpitis has a generally higher success rate than necrosis with periapical abscess) and many other technical factors.
Epidemiology
In the United States, an estimated 12% of people reported that they had a toothache at some point in the six months before questioning. Individuals aged 18–34 reported much higher rates toothache than those aged 75 or over. In a survey of Australian schoolchildren, 12% had experienced toothache before the age of five, and 32% by the age of 12. Dental trauma is extremely common and tends to occur more often in children than adults. Toothache may occur at any age, in any gender and in any geographic region. Diagnosing and relieving toothache is considered one of the main responsibilities of dentists. Irreversible pulpitis is thought to be the most common reason that people seek emergency dental treatment. Since dental caries associated with pulpitis is the most common cause, toothache is more common in populations that are at higher risk of dental caries. The prevalence of caries in a population is dependent upon factors such as diet (refined sugars), socioeconomic status, and exposure to fluoride (such as areas withoutwater fluoridation
Water fluoridation is the controlled adjustment of fluoride to a public water supply solely to reduce tooth decay. Fluoridated water contains fluoride at a level that is effective for preventing cavities; this can occur naturally or by adding ...
).
History, society and culture

 The first known mention of tooth decay and toothache occurs on a
The first known mention of tooth decay and toothache occurs on a Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of ...
ian clay tablet now referred to as the "Legend of the worm". It was written in cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo- syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge- ...
, recovered from the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
valley, and dates from around 5000 BC. The belief that tooth decay and dental pain is caused by tooth worms is found in ancient India, Egypt, Japan, and China, and persists until the Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
. Although toothache is an ancient problem, it is thought that ancient people suffered less dental decay due to a lack of refined sugars in their diet. On the other hand, diets were frequently coarser, leading to more tooth wear. For example, hypotheses hold that ancient Egyptians had a lot of tooth wear due to desert sand blown on the wind mixing with the dough of their bread. The ancient Egyptians also wore amulet
An amulet, also known as a good luck charm or phylactery, is an object believed to confer protection upon its possessor. The word "amulet" comes from the Latin word amuletum, which Pliny's ''Natural History'' describes as "an object that protect ...
s to prevent toothache. The Ebers papyrus (1500 BC) details a recipe to treat "gnawing of the blood in the tooth", which included fruit of the gebu plant, onion, cake, and dough, to be chewed for four days.
Archigenes of Apamea describes use of a mouthwash made by boiling gallnut
Galls (from the Latin , 'oak-apple') or ''cecidia'' (from the Greek , anything gushing out) are a kind of swelling growth on the external tissues of plants, fungi, or animals. Plant galls are abnormal outgrowths of plant tissues, similar to be ...
s and hallicacabum in vinegar, and a mixture of roasted earthworms, spikenard ointment, and crushed spider eggs. Pliny advises toothache sufferers to ask a frog to take away the pain by moonlight. Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Drusus and Antonia Minor ...
' physician Scribonius Largus recommends ''"fumigations made with the seeds of the hyoscyamus scattered on burning charcoal ... followed by rinsings of the mouth with hot water, in this way ... small worms are expelled."''
In Christianity, Saint Apollonia is the patron saint of toothache and other dental problems. She was an early Christian martyr
A martyr (, ''mártys'', "witness", or , ''marturia'', stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an externa ...
who was persecuted for her beliefs in Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
during the Imperial Roman age. A mob struck her repeatedly in the face until all her teeth were smashed. She was threatened with being burned alive unless she renounced Christianity, but she instead chose to throw herself onto the fire. Supposedly, toothache sufferers who invoke her name will find relief.
In the 15th century, priest-physician Andrew Boorde describes a "deworming technique" for the teeth: "''And if it oothachedo come by worms, make a candle of wax with Henbane seeds and light it and let the perfume of the candle enter into the tooth and gape over a dish of cold water and then you may take the worms out of the water and kill them on your nail."''
Albucasis (Abu al-Qasim Khalaf ibn al-Abbas Al-Zahrawi) used cautery for toothache, inserting a red-hot needle into the pulp of the tooth. The medieval surgeon Guy de Chauliac used a camphor
Camphor () is a waxy, colorless solid with a strong aroma. It is classified as a terpenoid and a cyclic ketone. It is found in the wood of the camphor laurel (''Cinnamomum camphora''), a large evergreen tree found in East Asia; and in the k ...
, sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
, myrrh
Myrrh (; from Semitic, but see '' § Etymology'') is a gum-resin extracted from a number of small, thorny tree species of the genus '' Commiphora''. Myrrh resin has been used throughout history as a perfume, incense and medicine. Myrrh m ...
, and asafetida mixture to fill teeth and cure toothworm and toothache. French anatomist Ambroise Paré
Ambroise Paré (c. 1510 – 20 December 1590) was a French barber surgeon who served in that role for kings Henry II, Francis II, Charles IX and Henry III. He is considered one of the fathers of surgery and modern forensic pathology and a pi ...
recommended: ''"Toothache is, of all others, the most atrocious pain that can torment a man, being followed by death. Erosion (i.e. dental decay) is the effect of an acute and acrid humour. To combat this, one must recourse to cauterization ... by means of cauterization ... one burns the nerve, thus rendering it incapable of again feeling or causing pain."''
In the Elizabethan era
The Elizabethan era is the epoch in the Tudor period of the history of England during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I (1558–1603). Historians often depict it as the golden age in English history. The symbol of Britannia (a female personific ...
, toothache was an ailment associated with lovers, as in Massinger Massinger is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Philip Massinger
Philip Massinger (1583 – 17 March 1640) was an English dramatist. His finely plotted plays, including ''A New Way to Pay Old Debts'', '' The City Madam ...
and Fletcher's play ''The False One
''The False One'' is a late Jacobean stage play by John Fletcher and Philip Massinger, though formerly placed in the Beaumont and Fletcher canon. It was first published in the first Beaumont and Fletcher folio of 1647.
This classical histor ...
''. Toothache also appears in a number of William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
's plays, such as ''Othello
''Othello'' (full title: ''The Tragedy of Othello, the Moor of Venice'') is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare, probably in 1603, set in the contemporary Ottoman–Venetian War (1570–1573) fought for the control of the Island of Cyp ...
'' and ''Cymbeline
''Cymbeline'' , also known as ''The Tragedie of Cymbeline'' or ''Cymbeline, King of Britain'', is a play by William Shakespeare set in Ancient Britain () and based on legends that formed part of the Matter of Britain concerning the early Celti ...
''. In ''Much Ado About Nothing
''Much Ado About Nothing'' is a comedy by William Shakespeare thought to have been written in 1598 and 1599.See textual notes to ''Much Ado About Nothing'' in ''The Norton Shakespeare'' ( W. W. Norton & Company, 1997 ) p. 1387 The play ...
'', Act III scene 2, when asked by his companions why he is feeling sad, a character replies that he has toothache so as not to admit the truth that he is in love. There is reference to "toothworm" as the cause of toothache and to tooth extraction as a cure ("draw it"). In Act V, scene 1, another character remarks: ''"For there was never yet philosopher That could endure the toothache patiently."'' In modern parlance, this translates to the observation that philosophers are still human and feel pain, even though they claim they have transcended human suffering and misfortune. In effect, the character is rebuking his friend for trying to make him feel better with philosophical platitudes.
The Scottish poet, Robert Burns
Robert Burns (25 January 175921 July 1796), also known familiarly as Rabbie Burns, was a Scottish poet and lyricist. He is widely regarded as the national poet of Scotland and is celebrated worldwide. He is the best known of the poets who hav ...
wrote "Address to the Toothache" in 1786, inspired after he suffered from it. The poem elaborates on the severity of toothache, describing it as the "hell o' a' diseases" (hell of all diseases).
A number of plants and trees include "toothache" in their common name. Prickly ash ( Zanthoxylum americanum) is sometimes termed "toothache tree", and its bark, "toothache bark"; whilst Ctenium Americanum is sometimes termed "toothache grass", and Acmella oleracea is called "toothache plant". Pellitory ( Anacyclus pyrethrum) was traditionally used to relieve toothache.
 In
In Kathmandu
, pushpin_map = Nepal Bagmati Province#Nepal#Asia
, coordinates =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name =
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 = Bagmati Prov ...
, Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
, there is a shrine to Vaishya Dev, the Newar
Newar (; new, नेवार, endonym: Newa; new, नेवा, Pracalit script:) or Nepami, are the historical inhabitants of the Kathmandu Valley and its surrounding areas in Nepal and the creators of its historic heritage and civilisat ...
god of toothache. The shrine consists of part of an old tree to which sufferers of toothache nail a rupee
Rupee is the common name for the currencies of
India, Mauritius, Nepal, Pakistan, Seychelles, and Sri Lanka, and of former currencies of Afghanistan, Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, the United Arab Emirates (as the Gulf rupee), British East Africa, ...
coin in order to ask the god to relieve their pain. The lump of wood is called the "toothache tree" and is said to have been cut from the legendary tree, Bangemudha. On this street, many traditional tooth pullers still work and many of the city's dentists have advertisements placed next to the tree.
The phrase ''toothache in the bones'' is sometimes used to describe the pain in certain types of diabetic neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is various types of nerve damage associated with diabetes mellitus. Symptoms depend on the site of nerve damage and can include motor changes such as weakness; sensory symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or pain; or autonomic c ...
.
Notes
References
External links
*WebMD Dental Health & Toothaches
{{Pain Pain Headaches Medical emergencies Orofacial pain