Tolkien's Monsters on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tolkien's monsters are the evil beings, such as
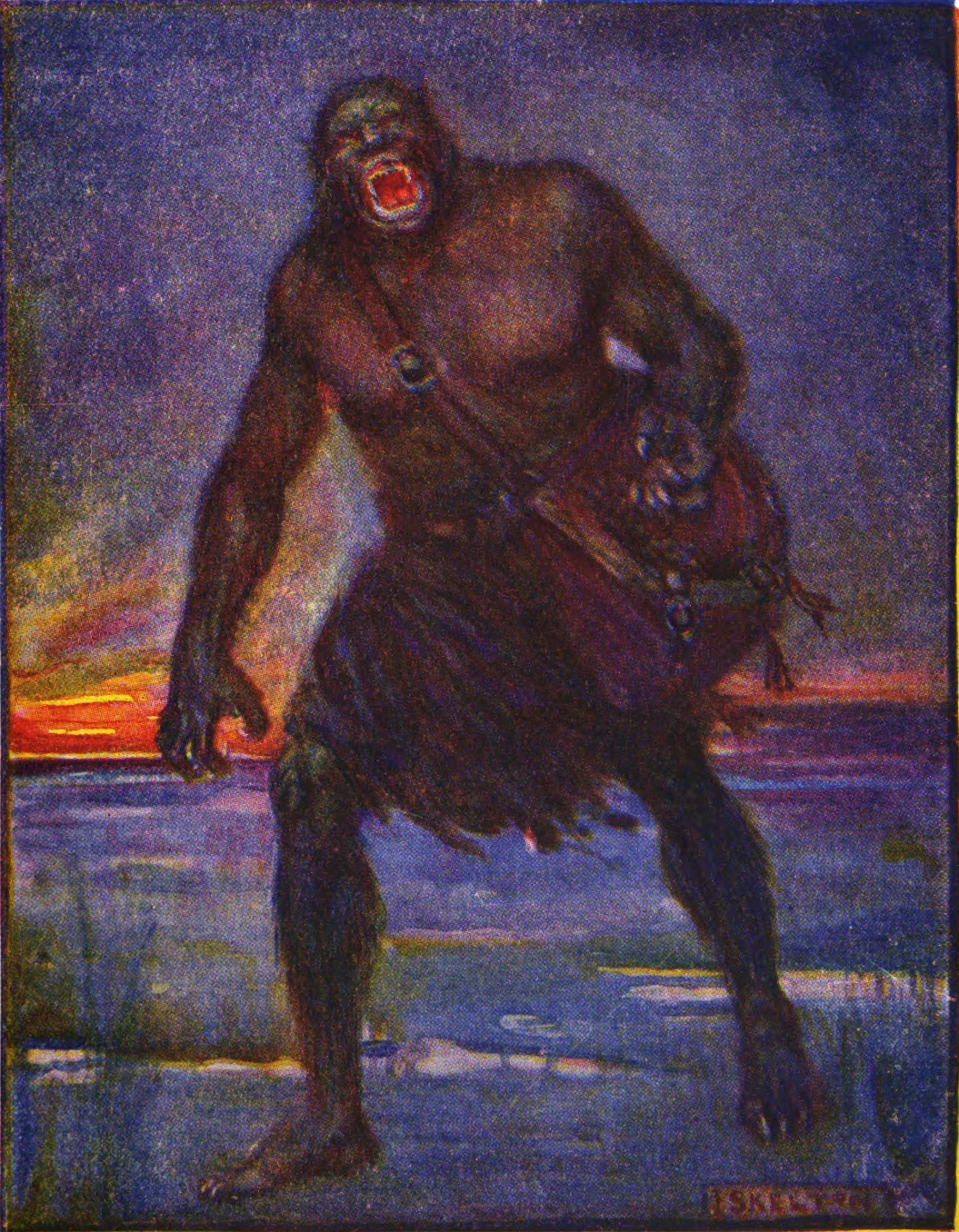 In the ''
In the ''
 Evans notes that "vaguer still", possibly not even living, are the "monstrous Watchers" that guard the gate of the Tower of Cirith Ungol, on a pass into the evil land of
Evans notes that "vaguer still", possibly not even living, are the "monstrous Watchers" that guard the gate of the Tower of Cirith Ungol, on a pass into the evil land of
 Other monsters in ''The Lord of the Rings'' are humanoid, but
Other monsters in ''The Lord of the Rings'' are humanoid, but
 Some of Tolkien's monsters are certainly sentient, as they are
Some of Tolkien's monsters are certainly sentient, as they are
Orcs
An Orc (or Ork) is a fictional humanoid monster like a goblin. Orcs were brought into modern usage by the fantasy writings of J. R. R. Tolkien, especially ''The Lord of the Rings''. In Tolkien's works, Orcs are a brutish, aggressive, ugly, ...
, Trolls
A troll is a being in Nordic folklore, including Norse mythology. In Old Norse sources, beings described as trolls dwell in isolated areas of rocks, mountains, or caves, live together in small family units, and are rarely helpful to human bei ...
, and giant spiders, who oppose and sometimes fight the protagonists in J. R. R. Tolkien
John Ronald Reuel Tolkien (, ; 3 January 1892 – 2 September 1973) was an English writer and philologist. He was the author of the high fantasy works ''The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings''.
From 1925 to 1945, Tolkien was the Rawlins ...
's Middle-earth
Middle-earth is the fictional setting of much of the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy. The term is equivalent to the ''Miðgarðr'' of Norse mythology and ''Middangeard'' in Old English works, including ''Beowulf''. Middle-earth is t ...
legendarium.
Tolkien was an expert on Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
, especially ''Beowulf
''Beowulf'' (; ang, Bēowulf ) is an Old English epic poem in the tradition of Germanic heroic legend consisting of 3,182 alliterative lines. It is one of the most important and most often translated works of Old English literature. The ...
'', and several of his monster
A monster is a type of fictional creature found in horror, fantasy, science fiction, folklore, mythology and religion. Monsters are very often depicted as dangerous and aggressive with a strange, grotesque appearance that causes terror and fe ...
s share aspects of the ''Beowulf'' monsters; his Trolls
A troll is a being in Nordic folklore, including Norse mythology. In Old Norse sources, beings described as trolls dwell in isolated areas of rocks, mountains, or caves, live together in small family units, and are rarely helpful to human bei ...
have been likened to Grendel
Grendel is a character in the Anglo-Saxon epic poem '' Beowulf'' (700–1000). He is one of the poem's three antagonists (along with his mother and the dragon), all aligned in opposition against the protagonist Beowulf. Grendel is feared by a ...
, the Orcs' name harks back to the poem's ''orcneas'', and the dragon Smaug
Smaug () is a dragon and the main antagonist in J. R. R. Tolkien's 1937 novel ''The Hobbit'', his treasure and the mountain he lives in being the goal of the quest. Powerful and fearsome, he invaded the Dwarf kingdom of Erebor 150 years prior ...
has multiple attributes of the ''Beowulf'' dragon.
The European medieval tradition of monsters makes them either humanoid but distorted, or like wild beasts, but very large and malevolent; Tolkien follows both traditions, with monsters like Orc
An Orc (or Ork) is a fictional humanoid monster like a goblin. Orcs were brought into modern usage by the fantasy writings of J. R. R. Tolkien, especially '' The Lord of the Rings''. In Tolkien's works, Orcs are a brutish, aggressive, ugl ...
s of the first kind and Warg
In the philologist and fantasy author J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth fiction, a warg is a particularly large and evil kind of wolf that could be ridden by orcs. He derived the name and characteristics of his wargs by combining meanings and myth ...
s of the second. Some scholars add Tolkien's immensely powerful Dark Lords Morgoth
Morgoth Bauglir (; originally Melkor ) is a character, one of the godlike Valar, from Tolkien's legendarium. He is the main antagonist of ''The Silmarillion'', ''The Children of Húrin'', ''Beren and Lúthien'' and ''The Fall of Gondolin''.
...
and Sauron
Sauron (pronounced ) is the title character and the primary antagonist, through the forging of the One Ring, of J. R. R. Tolkien's ''The Lord of the Rings'', where he rules the land of Mordor and has the ambition of ruling the whole of Midd ...
to the list, as monstrous enemies in spirit as well as in body.
Scholars have noted that the monsters' evil nature reflects Tolkien's Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
, a religion which has a clear conception of good and evil.
Origins
The word "monster" has as its origin theLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''monstrum'', "a marvel, prodigy, portent", in turn from Latin ''monstrare'', "to show". Monsters in Medieval Europe were often humanoid, but could also resemble wild beasts, but of enormous size; J. R. R. Tolkien
John Ronald Reuel Tolkien (, ; 3 January 1892 – 2 September 1973) was an English writer and philologist. He was the author of the high fantasy works ''The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings''.
From 1925 to 1945, Tolkien was the Rawlins ...
followed both paths in creating his own monsters.
Some of Tolkien's monsters may derive from his detailed knowledge of the Old English epic poem ''Beowulf
''Beowulf'' (; ang, Bēowulf ) is an Old English epic poem in the tradition of Germanic heroic legend consisting of 3,182 alliterative lines. It is one of the most important and most often translated works of Old English literature. The ...
''; Gollum
Gollum is a fictional Tolkien's monsters, character in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He was introduced in the 1937 Fantasy (genre), fantasy novel ''The Hobbit'', and became important in its sequel, ''The Lord of the Rings''. Gol ...
has some attributes of Grendel
Grendel is a character in the Anglo-Saxon epic poem '' Beowulf'' (700–1000). He is one of the poem's three antagonists (along with his mother and the dragon), all aligned in opposition against the protagonist Beowulf. Grendel is feared by a ...
, while the dragon Smaug
Smaug () is a dragon and the main antagonist in J. R. R. Tolkien's 1937 novel ''The Hobbit'', his treasure and the mountain he lives in being the goal of the quest. Powerful and fearsome, he invaded the Dwarf kingdom of Erebor 150 years prior ...
in ''The Hobbit
''The Hobbit, or There and Back Again'' is a children's fantasy novel by English author J. R. R. Tolkien. It was published in 1937 to wide critical acclaim, being nominated for the Carnegie Medal and awarded a prize from the '' ...
'' shares several features with the ''Beowulf'' dragon. The poem, too, speaks of Orcs, with the Old English compound ''orcneas'', meaning "demon-corpses". In his famous 1936 lecture, " ''Beowulf'': The Monsters and the Critics", Tolkien described the poem's monsters as central to its structure, changing the course of ''Beowulf'' scholarship. Commentators have noted that Tolkien clearly preferred the epic's monsters to the critics.
Humanoid, bestial, and beyond
Evil in mind or body
 In the ''
In the ''J.R.R. Tolkien Encyclopedia
The ''J. R. R. Tolkien Encyclopedia: Scholarship and Critical Assessment'', edited by Michael D. C. Drout, was published by Routledge in 2006. A team of 127 Tolkien scholars on 720 pages cover topics of Tolkien's fiction, his academic works, hi ...
'', Jonathan Evans initially identifies two categories of monster in Tolkien's legendarium
Tolkien's legendarium is the body of J. R. R. Tolkien's mythopoeic writing, unpublished in his lifetime, that forms the background to his ''The Lord of the Rings'', and which his son Christopher summarized in his compilation of ''The Silmaril ...
. The first includes Trolls
A troll is a being in Nordic folklore, including Norse mythology. In Old Norse sources, beings described as trolls dwell in isolated areas of rocks, mountains, or caves, live together in small family units, and are rarely helpful to human bei ...
, Orc
An Orc (or Ork) is a fictional humanoid monster like a goblin. Orcs were brought into modern usage by the fantasy writings of J. R. R. Tolkien, especially '' The Lord of the Rings''. In Tolkien's works, Orcs are a brutish, aggressive, ugl ...
s, and Balrog
A Balrog () is a powerful demonic monster in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth. One first appeared in print in his high-fantasy novel ''The Lord of the Rings'', where the Fellowship of the Ring (characters), Fellowship of the Ring encounter a Bal ...
s, which are humanoid, but distorted in various ways; the second consists of malevolent beasts which resemble those of the natural world, but are much larger, such as the wolflike Warg
In the philologist and fantasy author J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth fiction, a warg is a particularly large and evil kind of wolf that could be ridden by orcs. He derived the name and characteristics of his wargs by combining meanings and myth ...
s, the giant evil spiders – Ungoliant
Ungoliant () is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, described as an evil spirit in the form of a spider. Her name means "dark spider" in Sindarin. She is mentioned briefly in ''The Lord of the Rings'', and plays a supporting ...
and her brood including Shelob
Shelob is a fictional demon in the form of a giant spider from J. R. R. Tolkien's ''The Lord of the Rings''. Her lair lies in Cirith Ungol ("the pass of the spider") leading into Mordor. The creature Gollum deliberately leads the Hobbit protago ...
– and the tentacled Watcher in the Water
The Watcher in the Water is a fictional creature in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth; it appears in '' The Fellowship of the Ring'', the first volume of ''The Lord of the Rings''.'' The Fellowship of the Ring'', book 2, ch. 4 "A Journey in the D ...
. The featherless winged steeds of the Nazgûl
The Nazgûl (from Black Speech , "ring", and , "wraith, spirit"), introduced as Black Riders and also called Ringwraiths, Dark Riders, the Nine Riders, or simply the Nine, are fictional characters in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth. They were ...
are monstrous in the second way, gigantic but evidently based on nature, and "apt to evil". Tolkien never names them, though he alludes to them as "fell beasts", and describes them in a letter as "pterodactyl
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 to 6 ...
ic".
Evans notes that a third kind of monster, Tolkien's dragons, "an especially important monstrous type", does not fit either of these categories, and he treats those "extraordinarily large, reptilian creatures ... preternaturally evil monsters" separately. Dragons are mentioned only in passing in ''The Lord of the Rings'', but dragons that can speak but which are certainly not humanoid are important characters in both ''The Silmarillion
''The Silmarillion'' () is a collection of myths and stories in varying styles by the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien. It was edited and published posthumously by his son Christopher Tolkien in 1977, assisted by the fantasy author Guy Gavriel ...
'' and ''The Hobbit
''The Hobbit, or There and Back Again'' is a children's fantasy novel by English author J. R. R. Tolkien. It was published in 1937 to wide critical acclaim, being nominated for the Carnegie Medal and awarded a prize from the '' ...
''.
Tolkien was not consistent in his allocation of monsters to these categories. In ''The Hobbit'', the hill-trolls are initially comic; they are carnivorous but not particularly malevolent, have vulgar table manners, and speak, with Cockney
Cockney is an accent and dialect of English, mainly spoken in London and its environs, particularly by working-class and lower middle-class Londoners. The term "Cockney" has traditionally been used to describe a person from the East End, or b ...
accents. However, when the Wizard Gandalf
Gandalf is a protagonist in J. R. R. Tolkien's novels ''The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings''. He is a Wizards (Middle-earth), wizard, one of the ''Istari'' order, and the leader of the Fellowship of the Ring (characters), Fellowship of t ...
outwits them, the scholar Christina Fawcett writes, these Trolls are seen as "monstrous, a warning against vice, captured forever in stone for their greed and anger". The critic Gregory Hartley adds that the Trolls in ''The Silmarillion'' and ''The Lord of the Rings'' are "more bestial" and much less like the trolls of Norse mythology
Norse, Nordic, or Scandinavian mythology is the body of myths belonging to the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Old Norse religion and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia, and into the Nordic folklore of the modern period ...
; Fawcett compares them to the monster Grendel
Grendel is a character in the Anglo-Saxon epic poem '' Beowulf'' (700–1000). He is one of the poem's three antagonists (along with his mother and the dragon), all aligned in opposition against the protagonist Beowulf. Grendel is feared by a ...
in ''Beowulf
''Beowulf'' (; ang, Bēowulf ) is an Old English epic poem in the tradition of Germanic heroic legend consisting of 3,182 alliterative lines. It is one of the most important and most often translated works of Old English literature. The ...
''. Tolkien's description runs: "Olog-hai they were called in the Black Speech. That Sauron bred them none doubted, though from what stock was not known... Trolls they were, but filled with the evil will of their master: a fell race, strong, agile, fierce and cunning, but harder than stone. Unlike the older race of the Twilight they could endure the Sun, so long as the will of Sauron held sway over them. They spoke little, and the only tongue that they knew was the Black Speech of Barad-dûr
In J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional world of Middle-earth, Mordor (pronounced ; from Sindarin ''Black Land'' and Quenya ''Land of Shadow'') is the realm and base of the evil Sauron. It lay to the east of Gondor and the great river Anduin, and to ...
."
Evil in spirit
Other scholars sometimes add the Legendarium's powerful opponents to the list of monsters; Joe Abbott, writing in ''Mythlore
''Mythlore'' is a biannual (originally quarterly) peer-reviewed academic journal founded by Glen GoodKnight and published by the Mythopoeic Society. Although it publishes articles that explore the genres of myth and fantasy in general, special a ...
'', describes the Dark Lords Morgoth
Morgoth Bauglir (; originally Melkor ) is a character, one of the godlike Valar, from Tolkien's legendarium. He is the main antagonist of ''The Silmarillion'', ''The Children of Húrin'', ''Beren and Lúthien'' and ''The Fall of Gondolin''.
...
and Sauron
Sauron (pronounced ) is the title character and the primary antagonist, through the forging of the One Ring, of J. R. R. Tolkien's ''The Lord of the Rings'', where he rules the land of Mordor and has the ambition of ruling the whole of Midd ...
as monsters, intelligent and powerful but wholly gone over to evil. Abbott notes that in ''The Monsters and the Critics
"''Beowulf'': The Monsters and the Critics" was a 1936 lecture given by J. R. R. Tolkien on literary criticism on the Old English heroic epic poem '' Beowulf''. It was first published as a paper in the ''Proceedings of the British Academy'', ...
'', Tolkien distinguished between ordinary monsters in the body, and monsters also in spirit:
By going beyond the limits of the body with these monstrous Dark Lords, Tolkien had in Abbott's view made the "ultimate transformation" for a Christian author, creating "a far more terrifying monster".
Themes
Evil and darkness
Tolkien'sRoman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
gave him a clear sense of good and evil, and a ready symbolism to hand: light symbolises good, and darkness evil, as it does in the Bible.
In ''The Fellowship of the Ring
''The Fellowship of the Ring'' is the first of three volumes of the epic novel ''The Lord of the Rings'' by the English author J. R. R. Tolkien. It is followed by ''The Two Towers'' and ''The Return of the King''. It takes place in the fiction ...
'', the first evil being that the Hobbits encounter after leaving the Shire
The Shire is a region of J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional Middle-earth, described in ''The Lord of the Rings'' and other works. The Shire is an inland area settled exclusively by hobbits, the Shire-folk, largely sheltered from the goings-on in the ...
on the quest to destroy the One Ring
The One Ring, also called the Ruling Ring and Isildur's Bane, is a central plot element in J. R. R. Tolkien's ''The Lord of the Rings'' (1954–55). It first appeared in the earlier story ''The Hobbit'' (1937) as a magic ring that grants the w ...
is Old Man Willow
In J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy ''The Lord of the Rings'', Old Man Willow is a malign tree-spirit of great age in Tom Bombadil's Old Forest, appearing physically as a large willow tree beside the River Withywindle, but spreading his influence throug ...
, a powerful tree or tree-spirit who controls much of the Old Forest
In J. R. R. Tolkien’s fictional universe of Middle-earth, the Old Forest was a daunting and ancient woodland just beyond the eastern borders of the Shire. Its first and main appearance in print was in ''The Fellowship of the Ring'', especia ...
. He is wholly malevolent. Outside the entrance to Moria, the Fellowship is again attacked, this time by the Watcher in the Water
The Watcher in the Water is a fictional creature in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth; it appears in '' The Fellowship of the Ring'', the first volume of ''The Lord of the Rings''.'' The Fellowship of the Ring'', book 2, ch. 4 "A Journey in the D ...
. It specifically seizes Frodo
Frodo Baggins is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's writings, and one of the protagonists in ''The Lord of the Rings''. Frodo is a hobbit of the Shire who inherits the One Ring from his cousin Bilbo Baggins, described familiarly a ...
, the ring-bearer, as if it knew and opposed the quest. Evans comments that though clearly deadly dangerous, the monster is vague, only sketchily described in the text.
 Evans notes that "vaguer still", possibly not even living, are the "monstrous Watchers" that guard the gate of the Tower of Cirith Ungol, on a pass into the evil land of
Evans notes that "vaguer still", possibly not even living, are the "monstrous Watchers" that guard the gate of the Tower of Cirith Ungol, on a pass into the evil land of Mordor
In J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional world of Middle-earth, Mordor (pronounced ; from Sindarin ''Black Land'' and Quenya ''Land of Shadow'') is the realm and base of the evil Sauron. It lay to the east of Gondor and the great river Anduin, and to t ...
. Tolkien describes them as aware, but immobile, with an indwelling "spirit of evil vigilance":
The monstrous Watchers are defeated by the Elvish light of the Phial of Galadriel
Shelob is a fictional demon in the form of a giant spider from J. R. R. Tolkien's ''The Lord of the Rings''. Her lair lies in Cirith Ungol ("the pass of the spider") leading into Mordor. The creature Gollum deliberately leads the Hobbit protag ...
; Sam holds it up "and the shadows under the dark arch fled"; Sam sees "a glitter in the black stones of their eyes", full of malice, and their will is broken.
The light of the Phial of Galadriel
Galadriel (IPA: Help:IPA, �aˈladri.ɛl is a Character (arts), character created by J. R. R. Tolkien in his Middle-earth writings. She appears in ''The Lord of the Rings'', ''The Silmarillion'', and ''Unfinished Tales''.
She ...
is effective, too, against Middle-earth's giant spider Shelob
Shelob is a fictional demon in the form of a giant spider from J. R. R. Tolkien's ''The Lord of the Rings''. Her lair lies in Cirith Ungol ("the pass of the spider") leading into Mordor. The creature Gollum deliberately leads the Hobbit protago ...
, daughter of the line of the evil Ungoliant
Ungoliant () is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, described as an evil spirit in the form of a spider. Her name means "dark spider" in Sindarin. She is mentioned briefly in ''The Lord of the Rings'', and plays a supporting ...
. Shelob is both evil and ancient, "bloated and grown fat with endless brooding on her feasts, weaving webs of shadow; for all living things were her food, and her vomit darkness".
The opposition of Galadriel and Shelob has been interpreted psychologically in terms of Jungian archetypes.
The medievalist Alaric Hall
Alaric Hall (born 1979) is a British philologist who is an associate professor of English and director of the Institute for Medieval Studies at the University of Leeds. He has, since 2009, been the editor of the academic journal '' Leeds Studies ...
states more generally that in ''The Lord of the Rings'', as in ''Beowulf'' and the ''Grettis saga
''Grettis saga Ásmundarsonar'' (modern , reconstructed ), also known as ''Grettla'', ''Grettir's Saga'' or ''The Saga of Grettir the Strong'', is one of the Icelanders' sagas. It details the life of Grettir Ásmundarson, a bellicose Icelandic ou ...
'', the opposition of protagonists and monsters is psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between t ...
as much as physical, since "heroes cannot defeat their enemies without taking something from them to themselves."
The Tolkien scholar Verlyn Flieger Verlyn Flieger (born 1933) is an author, editor, and Professor Emerita in the Department of English at the University of Maryland at College Park, where she taught courses in comparative mythology, medieval literature, and the works of J. R. R. Tol ...
writes that Galadriel's light is a splintered remnant of that of the Two Trees of Valinor, which were consumed into the limitless darkness of Shelob's earliest ancestor, Ungoliant. That light contained and symbolised divine power; its destruction was the embodiment of evil.
Undead
 Other monsters in ''The Lord of the Rings'' are humanoid, but
Other monsters in ''The Lord of the Rings'' are humanoid, but undead
The undead are beings in mythology, legend, or fiction that are deceased but behave as if alive. Most commonly the term refers to corporeal forms of formerly-alive humans, such as mummies, vampires, and zombies, who have been reanimated by super ...
, like the barrow-wight who traps the Hobbits soon after they have left Tom Bombadil
Tom Bombadil is a character in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium. He first appeared in print in a 1934 poem called " The Adventures of Tom Bombadil", which also included ''The Lord of the Rings'' characters Goldberry (Tom's wife), Old Man Willow ...
's house. Such wights are found in Norse mythology.
Far more powerful are the Nazgûl, undead and invisible but still physical ringwraiths, able to ride horses and to wield weapons; they were once kings of Men
A man is an adult male human. Prior to adulthood, a male human is referred to as a boy (a male child or adolescent). Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chro ...
, but were trapped by Sauron with the gift of Rings of Power
The Rings of Power are magical artefacts in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, most prominently in his high fantasy novel ''The Lord of the Rings''. The One Ring first appeared as a plot device, a magic ring in Tolkien's children's fantasy n ...
.}
Gollum
Gollum is a fictional Tolkien's monsters, character in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He was introduced in the 1937 Fantasy (genre), fantasy novel ''The Hobbit'', and became important in its sequel, ''The Lord of the Rings''. Gol ...
, too, once a member of a peaceful group of Hobbits, has become a desperate monster, alive but with his mind almost destroyed, constantly seeking the One Ring
The One Ring, also called the Ruling Ring and Isildur's Bane, is a central plot element in J. R. R. Tolkien's ''The Lord of the Rings'' (1954–55). It first appeared in the earlier story ''The Hobbit'' (1937) as a magic ring that grants the w ...
, after bearing it for many centuries. Flieger suggests that Gollum is Tolkien's central monster-figure, likening him to both Grendel and the ''Beowulf'' dragon, "the twisted, broken, outcast hobbit whose manlike shape and dragonlike greed combine both the ''Beowulf'' kinds of monster in one figure".
Souls and sentience
Orcs
An Orc (or Ork) is a fictional humanoid monster like a goblin. Orcs were brought into modern usage by the fantasy writings of J. R. R. Tolkien, especially ''The Lord of the Rings''. In Tolkien's works, Orcs are a brutish, aggressive, ugly, ...
are depicted as wholly evil, meaning that they could be slaughtered without regret. All the same, Orcs are human-like in being able to speak, and in having a similar concept of good and evil, a moral sense of fairness, even if they are not able to apply their morals to themselves. This presented Tolkien, a devout Roman Catholic, with a problem: since "evil cannot make, only mock", the at least somewhat sentient and morally-aware Orcs could not have been created by evil as a genuinely new and separate species; but the alternative, that they were corrupted from one of Middle-earth's free peoples, such as Elves, which would imply that they were fully sentient and had immortal souls, was equally unpalatable to him. Tolkien realized that some of the decisions he had made in his 1937 children's book ''The Hobbit'', showing his goblins (orcs) as even slightly civilised, and giving his animals the power of speech, clearly implied sentience; this conflicted with the more measured theology
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the ...
behind his Legendarium.
The Tolkien scholar Tom Shippey
Thomas Alan Shippey (born 9 September 1943) is a British medievalist, a retired scholar of Middle and Old English literature as well as of modern fantasy and science fiction. He is considered one of the world's leading academic experts on the ...
writes that the orcs in ''The Lord of the Rings'' were almost certainly created just to equip Middle-earth with "a continual supply of enemies over whom one need feel no compunction
Remorse is a distressing emotion experienced by an individual who regrets actions which they have done in the past that they deem to be shameful, hurtful, or wrong. Remorse is closely allied to guilt and self-directed resentment. When a perso ...
", or in Tolkien's words from "''Beowulf'': The Monsters and the Critics", "the infantry of the old war", ready to be slaughtered. Shippey states that all the same, orcs share the human concept of good and evil, with a familiar sense of morality, though he comments that, like many people, orcs are quite unable to apply their morals to themselves. In his view, Tolkien, as a Catholic, took it as a given that "evil cannot make, only mock", so orcs could not have an equal and opposite morality to that of men or elves. Shippey notes that in ''The Two Towers'', Tolkien has the orc Gorbag disapprove of the "regular elvish trick" of seeming to abandon a comrade, as he wrongly supposes Sam has done with Frodo. Shippey describes the implied view of evil as Boethian
Anicius Manlius Severinus Boethius, commonly known as Boethius (; Latin: ''Boetius''; 480 – 524 AD), was a Roman senator, consul, ''magister officiorum'', historian, and philosopher of the Early Middle Ages. He was a central figure in the tran ...
, that evil is the absence of good; he notes however that Tolkien did not agree with that point of view, believing that evil had to be actively combatted, with war if necessary, the Manichean
Manichaeism (;
in New Persian ; ) is a former major religionR. van den Broek, Wouter J. Hanegraaff ''Gnosis and Hermeticism from Antiquity to Modern Times''SUNY Press, 1998 p. 37 founded in the 3rd century AD by the Parthian prophet Mani (AD ...
position.
Wargs
In the philologist and fantasy author J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth fiction, a warg is a particularly large and evil kind of wolf that could be ridden by orcs. He derived the name and characteristics of his wargs by combining meanings and myth ...
, great wolf-like beasts, can attack independently, as they do while the Fellowship of the Ring is going south from Rivendell
Rivendell ('' sjn, Imladris'') is a valley in J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional world of Middle-earth, representing both a homely place of sanctuary and a magical Elvish otherworld. It is an important location in ''The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of th ...
, and soon after Thorin's Company emerged from the Misty Mountains. The group of wargs in ''The Hobbit'' could speak, though never pleasantly. Hartley treats wargs as "personified animals", noting that Tolkien writes about their actions using verbs like " oplan" and " oguard", implying in his view that the wargs are monstrous, "more than mere beasts"; but all the same, he denies that they "possess autonomous wills".
Fallen angels
 Some of Tolkien's monsters are certainly sentient, as they are
Some of Tolkien's monsters are certainly sentient, as they are angel
In various theistic religious traditions an angel is a supernatural spiritual being who serves God.
Abrahamic religions often depict angels as benevolent celestial intermediaries between God (or Heaven) and humanity. Other roles include ...
-like beings, powerful Ainur Ainur may refer to:
* Ainur, a given name in several languages, such as Arabic, Kazakh and Albanian. The Turkish version of it is Aynur
Aynur is a Turkish and Azerbaijani given name for females. As it is derived from the Turkish word " ay" and t ...
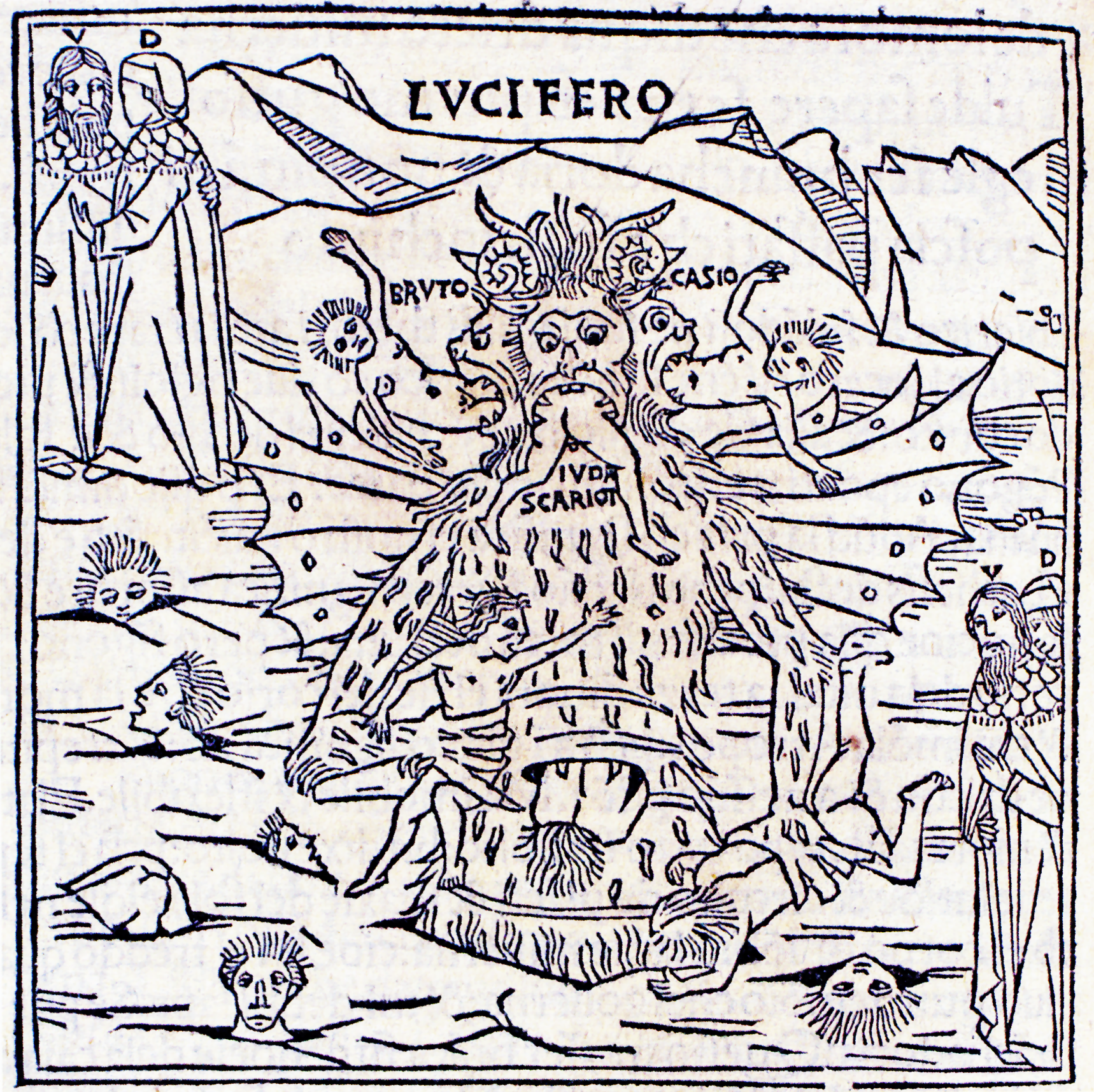
, fallen into evil. This is just as in Christianity, where the devil Lucifer
Lucifer is one of various figures in folklore associated with the planet Venus. The entity's name was subsequently absorbed into Christianity as a name for the devil. Modern scholarship generally translates the term in the relevant Bible passage ...
is understood to be a fallen angel, having been indeed once the greatest of the angels. These characters had immortal souls, were created good by the one God (Eru Iluvatar
The cosmology of J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium combines aspects of Christian theology and metaphysics with pre-modern cosmological concepts in the flat Earth paradigm, along with the modern spherical Earth view of the Solar System.
The created ...
in the Legendarium), but had made the choice of evil by their own free will
Free will is the capacity of agents to choose between different possible courses of action unimpeded.
Free will is closely linked to the concepts of moral responsibility, praise, culpability, sin, and other judgements which apply only to actio ...
.
The evil Lords of the Legendarium are extremely powerful. Melkor
Morgoth Bauglir (; originally Melkor ) is a character, one of the godlike Valar, from Tolkien's legendarium. He is the main antagonist of ''The Silmarillion'', ''The Children of Húrin'', '' Beren and Lúthien'' and ''The Fall of Gondolin''.
...
or as he became, Morgoth, particularly resembles Lucifer, as he is described as having been the most powerful of the Ainur, before he turned to darkness. He has indeed been interpreted as being analogous to Satan
Satan,, ; grc, ὁ σατανᾶς or , ; ar, شيطانالخَنَّاس , also known as Devil in Christianity, the Devil, and sometimes also called Lucifer in Christianity, is an non-physical entity, entity in the Abrahamic religions ...
, as like Lucifer, he rebels against his creator. He physically and symbolically destroys the Two Trees of Valinor
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the Two Trees of Valinor are Telperion and Laurelin, the Silver Tree and the Gold Tree, which brought light to Valinor, a paradisiacal realm also known as the Undying Lands where angelic beings lived. The Two ...
, which brought light to the world. When some of their light is captured and embodied in the jewel-like Silmaril
The Silmarils (Quenya in-universe ''pl''. ''Silmarilli'', ''radiance of pure light''J. R. R. Tolkien, Tolkien, J. R. R., "Addenda and Corrigenda to the Etymologies — Part Two" (edited by Carl F. Hostetter and Patrick H. Wynne), in ''Vinyar Teng ...
s, he steals them and places them in his crown.
Morgoth's servant, Sauron
Sauron (pronounced ) is the title character and the primary antagonist, through the forging of the One Ring, of J. R. R. Tolkien's ''The Lord of the Rings'', where he rules the land of Mordor and has the ambition of ruling the whole of Midd ...
, was similarly described as the Dark Lord; he had been a Maia
Maia (; Ancient Greek: Μαῖα; also spelled Maie, ; la, Maia), in ancient Greek religion and mythology, is one of the Pleiades and the mother of Hermes, one of the major Greek gods, by Zeus, the king of Olympus.
Family
Maia is the daugh ...
serving the Vala Aulë
The Valar (; singular Vala) are characters in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium. They are "angelic powers" or "gods", #154 to Naomi Mitchison, September 1954 subordinate to the one God ( Eru Ilúvatar). The Ainulindalë describes how those of the ...
, but on betraying the other Maiar, became Morgoth's principal lieutenant, and then in the absence of Morgoth, the Dark Lord of Middle-earth in his own right. Tolkien has a character in ''The Lord of the Rings'', Elrond
Elrond Half-elven is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. Both of his parents, Eärendil and Elwing, were half-elven, having both Men and Elves as ancestors. He is the bearer of the elven-ring Vilya, the Ring ...
, state that "Nothing is evil in the beginning. Even Sauron was not so."
The fire-demons or Balrog
A Balrog () is a powerful demonic monster in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth. One first appeared in print in his high-fantasy novel ''The Lord of the Rings'', where the Fellowship of the Ring (characters), Fellowship of the Ring encounter a Bal ...
s, too, come into this category, at least in Tolkien's later writings, where they were described as Maia corrupted by Melkor. In ''The Lord of the Rings'', the Wizard Gandalf
Gandalf is a protagonist in J. R. R. Tolkien's novels ''The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings''. He is a Wizards (Middle-earth), wizard, one of the ''Istari'' order, and the leader of the Fellowship of the Ring (characters), Fellowship of t ...
names the Balrog of Khazad-Dum as "a foe beyond any of you" and "flame of Udûn", meaning an immortal but evil being, with power similar to his own.
Adaptations and legacy
Tolkien's Middle-earth and its monsters have been documented in ''Clash of the Gods: Tolkien's Monsters'', a 2009 television programme in theHistory Channel
History (formerly The History Channel from January 1, 1995 to February 15, 2008, stylized as HISTORY) is an American pay television network and flagship channel owned by A&E Networks, a joint venture between Hearst Communications and the Disney ...
's ''Clash of the Gods'' series. Jason Seratino, writing on ''Complex'', has listed his ten favourite Tolkien monsters in movies, describing the Great Goblin as "a slimy cross between Sloth and the Elephant Man
Joseph Carey Merrick (5 August 1862 – 11 April 1890), often erroneously called John Merrick, was an English man known for having severe deformities. He was first exhibited at a freak show under the stage name "the Elephant Man" and then wen ...
". Artists including Alan Lee, John Howe, and Ted Nasmith
Ted Nasmith (born 1956) is a Canadians, Canadian artist, illustrator and architectural rendering, architectural renderer. He is best known as an illustrator of J. R. R. Tolkien's works ''The Hobbit'', ''The Lord of the Rings'' and ''The Silmaril ...
have created paintings of Tolkien's monsters, including those published in ''Tolkien's Dragons & Monsters: A Book of 20 Postcards''.
Notes
References
Primary
::''This list identifies each item's location in Tolkien's writings.''Secondary
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Lord of the Rings *