Timur's invasions of Georgia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The
 Timur's first appearance in the
Timur's first appearance in the 
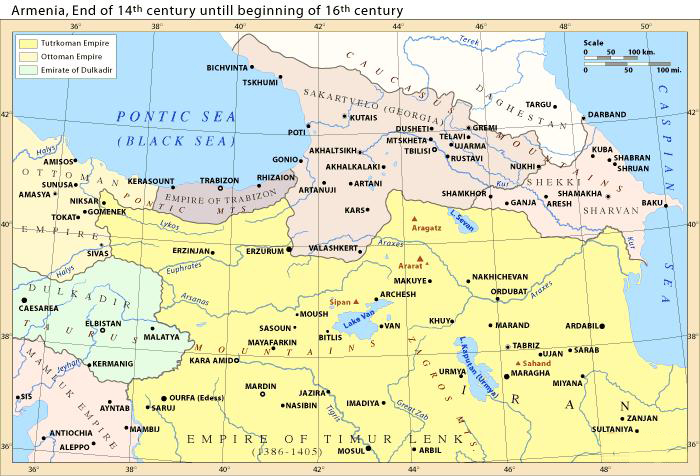 In the spring of 1400, Timur moved back to destroy the Georgian state once and for all. He demanded that George VII should hand over the Jalayirid Tahir. George VII refused and met Timur at the Sagim River in
In the spring of 1400, Timur moved back to destroy the Georgian state once and for all. He demanded that George VII should hand over the Jalayirid Tahir. George VII refused and met Timur at the Sagim River in
Kingdom of Georgia
The Kingdom of Georgia ( ka, საქართველოს სამეფო, tr), also known as the Georgian Empire, was a medieval Eurasian monarchy that was founded in circa 1008 AD. It reached its Golden Age of political and economic ...
, a Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically ...
, was subjected, between 1386 and 1403, to several disastrous invasions by the armies of Turco-Mongol conqueror Timur
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Kür ...
, whose vast empire stretched, at its greatest extent, from Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
into Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
. These conflicts were intimately linked with the wars
''The Wars'' is a 1977 novel by Timothy Findley that follows Robert Ross, a nineteen-year-old Canadian who enlists in World War I after the death of his beloved older sister in an attempt to escape both his grief and the social norms of oppressiv ...
between Timur (Tamerlane) and Tokhtamysh, the last khan
Khan may refer to:
*Khan (inn), from Persian, a caravanserai or resting-place for a travelling caravan
*Khan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Khan (title), a royal title for a ruler in Mongol and Turkic languages and used by ...
of the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fr ...
and Timur's major rival for control over the Islamic world. Timur officially proclaimed his invasions to be jihad
Jihad (; ar, جهاد, jihād ) is an Arabic word which literally means "striving" or "struggling", especially with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it can refer to almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with Go ...
against the region's non-Muslims. Although he was able to invade parts of Georgia, he was never able to make the country Muslim and even recognized Georgia as a Christian state.
In the first of eight invasions, Timur sacked Georgia's capital, Tbilisi
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), is the Capital city, capital and the List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), largest city of Georgia (country), Georgia, lying on the ...
, and captured the king Bagrat V in 1386. Georgian resistance prompted a renewed attack by the Turco-Mongol armies. Bagrat's son and successor, George VII, put up a stiff resistance and had to spend much of his reign (1395–1405) fighting the Timurid invasions. Timur personally led most of these raids to subdue the recalcitrant Georgian monarch. He was not able to establish a firm control over Georgia. By the time George VII was forced to accept Timur's terms of peace
Peace is a concept of societal friendship and harmony in the absence of hostility and violence. In a social sense, peace is commonly used to mean a lack of conflict (such as war) and freedom from fear of violence between individuals or groups. ...
and agree to pay tribute, he was a master of little more than "gutted towns, ravaged countryside and a shattered monarchy." Suny, Ronald Grigor (1994), ''The Making of the Georgian Nation'', p. 45. Indiana University Press
Indiana University Press, also known as IU Press, is an academic publisher founded in 1950 at Indiana University that specializes in the humanities and social sciences. Its headquarters are located in Bloomington, Indiana. IU Press publishes 140 ...
,
History
 Timur's first appearance in the
Timur's first appearance in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically ...
was a response to Khan Tokhtamysh's marauding inroad into Northern Iran
Northern Iran consists of the southern border of the Caspian Sea and the Alborz mountains.
It includes the provinces of Gilan, Mazandaran, and Golestan. (Ancient kingdom of Hyrcania, medieval region of Tabaristan). The major provinces, Gilan ...
through the Caucasian lands in 1385. This marked an outbreak of outright hostility between the two Islamic monarchs. Timur responded by launching a full-scale invasion of the small frontier countries, which lay between the western border of his emerging empire and Tokhtamysh's khanate. After having overrun Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
and Kars
Kars (; ku, Qers; ) is a city in northeast Turkey and the capital of Kars Province. Its population is 73,836 in 2011. Kars was in the ancient region known as ''Chorzene'', (in Greek Χορζηνή) in classical historiography ( Strabo), part of ...
, Timur marched into Georgia. The official history of his reign, ''Zafarnama'', represents this campaign in Georgia as a jihad
Jihad (; ar, جهاد, jihād ) is an Arabic word which literally means "striving" or "struggling", especially with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it can refer to almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with Go ...
. Timur set out from Kars and assailed Samtskhe
Meskheti ( ka, მესხეთი) or Samtskhe ( ka, სამცხე) (Moschia in ancient sources), is a mountainous area in southwestern Georgia.
History
Ancient tribes known as the Mushki (or Moschi) and Mosiniks (or Mossynoeci) were the ...
, the southernmost principality within the Kingdom of Georgia
The Kingdom of Georgia ( ka, საქართველოს სამეფო, tr), also known as the Georgian Empire, was a medieval Eurasian monarchy that was founded in circa 1008 AD. It reached its Golden Age of political and economic ...
later in 1386. From there, he marched against Tbilisi which the Georgian king Bagrat V had fortified. The city fell on November 21, 1386, and King Bagrat V was captured and converted to Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
at sword point. The '' Georgian Chronicles'' and Thomas of Metsoph
Thomas of Metsoph ( hy, Թովմա Մեծոփեցի, Thovma Metsopetsi) (1378–1446) was an Armenian cleric and chronicler who left an account of Timur’s invasions of the Caucasus (1386–1403). What we know of Thomas's life comes from a biograp ...
mention the apostasy
Apostasy (; grc-gre, ἀποστασία , 'a defection or revolt') is the formal disaffiliation from, abandonment of, or renunciation of a religion by a person. It can also be defined within the broader context of embracing an opinion that i ...
of the king but represent it as a clever ruse which enabled him to earn a degree of Timur's trust. Bagrat was given some 12,000 troops to reestablish himself in Georgia, whose government was run by Bagrat's son and co-ruler George VII during his father's absence at Timur's court. The old king, however, entered into secret negotiations with George, who ambushed Bagrat's Islamic escort, and freed his father. Minorsky, Vladimir, "Tiflis", in: M. Th. Houtsma, E. van Donzel (1993), ''E. J. Brill's First Encyclopaedia of Islam
The ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'' (''EI'') is an encyclopaedia of the academic discipline of Islamic studies published by Brill. It is considered to be the standard reference work in the field of Islamic studies. The first edition was published in ...
, 1913–1936'', p. 757. Brill, .
In the spring of 1387, Timur returned to Georgia to take revenge for the ambush and escape. Bagrat and George managed to evacuate the civilian population of the frontier regions to the mountains and forests, and began organising their defences. Khan Tokhtamysh's reappearance in Iran forced Timur to temporarily withdraw. However once the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fr ...
was defeated, Timur returned to attack Georgia again. In 1394, he dispatched four generals to the province of Samtskhe, with orders to apply the Islamic law of ghaza
A ''ghazi'' ( ar, غازي, , plural ''ġuzāt'') is an individual who participated in ''ghazw'' (, ''wikt:ghazwa, ''), meaning military expeditions or raiding. The latter term was applied in early Islamic literature to expeditions led by the Is ...
(i.e. the systematic raiding of non-Muslim lands). The same year, Timur in person punished the mountainous Georgian communities in the Aragvi Valley whom the ''Zafarnama'' calls ''Kara-Kalkanlik'' ("with black bucklers”, i.e., the eastern Georgian mountaineers, the Pshavs and Khevsurs
Khevsurians ( ka, ხევსურები) are an ethnic sub-group of Georgians, mainly living in Khevsureti, on both sides of the Caucasus Mountains, Caucasus Mountain Chain in the watersheds of the rivers Aragvi River, Aragvi and Argun Rive ...
), and returned via Tbilisi to Shekki upon hearing of yet another offensive by Tokhtamysh.
In 1395 the desperate Georgians allied themselves with Sidi Ali of Shekki and inflicted a crushing defeat on the invading armies of Miran Shah, a son of Timur, who was besieging Alindjak (near Nakhichevan), and captured the Jalayirid prince Tahir, who was shut up in it. This event prompted Timur
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Kür ...
to return, later in 1399, to inflict massive revenge on the general population of the region. He took Shekki and devastated the neighboring region of Kakheti
Kakheti ( ka, კახეთი ''K’akheti''; ) is a region (mkhare) formed in the 1990s in eastern Georgia from the historical province of Kakheti and the small, mountainous province of Tusheti. Telavi is its capital. The region comprises eigh ...
.

Lower Kartli
Kvemo Kartli ( ka, ქვემო ქართლი, az, Aşağı Kartli) or "Lower Kartli", is a historic province and current administrative region (mkhare) in southeastern Georgia. The city of Rustavi is the regional capital.
Location
Kvem ...
, but suffered a defeat and retreated deeper into the country, relentlessly chased by Timur. Timur destroyed the Georgian capital Tbilisi, left a garrison there, and laid siege to Gori, where George was entrenched. The king made a bold sortie westward, but having failed to thwart the enemy's advance at the fortresses of Dzami and Savaneti, fled to the inaccessible forests of western Georgia, where the armies of the Islamic ruler could not penetrate. Timur turned back in fury and thoroughly pillaged the rest of Georgia. This bloody campaign lasted for several months, with Timur's armies systematically moving from province to province. Virtually all major cities and towns were destroyed and their populations decimated; the countryside (with its villages and food sources) was burnt; monasteries and churches were systematically razed to the ground. Of those who survived the fighting and reprisals, many thousands died of hunger and disease, and 60,000 survivors were enslaved and carried away by Timur's troops.
In late 1401, Timur invaded the Caucasus once again. George VII had to sue for peace, and sent his brother with tribute. Timur was preparing for a major confrontation with the Ottoman dynasty and apparently wished to freeze the currently prevailing situation in Georgia, until he could return to deal with it more decisively and thoroughly at his leisure. Thus, he made peace
Peace is a concept of societal friendship and harmony in the absence of hostility and violence. In a social sense, peace is commonly used to mean a lack of conflict (such as war) and freedom from fear of violence between individuals or groups. ...
with George on condition that the king of Georgia supplied him with troops and granted Muslims special privileges. Timur nonetheless undertook some preventive measures and attacked the Georgian garrison of Tortum
Tortum ( ota, تورتوم) is a town and district of Erzurum Province in the Eastern Anatolia Region of Turkey. The population is 4,507 as of 2010. The current mayor is Muammer Yiğider from the Great Unity Party (BBP).
History
Tortum was par ...
i, demolishing the citadel and looting the surrounding area.
Once the Ottomans were defeated, Timur, back in Erzurum in 1402, decided to punish the king of Georgia for not having come to present his congratulations on his victory. George VII's brother, Constantine
Constantine most often refers to:
* Constantine the Great, Roman emperor from 306 to 337, also known as Constantine I
* Constantine, Algeria, a city in Algeria
Constantine may also refer to:
People
* Constantine (name), a masculine given na ...
, who was then on bad terms with his brother, arrived with gifts, as did the king's defiant vassal Iwane Jaqeli, prince of Samtskhe. Sheikh Ibrahim I of Shirvan
Ibrahim I ( fa, ابراهیم) was the 33rd Shirvanshah (ruler of Shirvan, r. 1382–1418). Because of his cunning politics he managed to remain independent and avoid being deposed by the Turko-Mongol ruler Timur.
Family and accession to the thr ...
went to estimate the revenues and expenses of Georgia. George sent new presents but Timur refused them and summoned George to appear in person. In the meantime, he himself laid siege to the previously impregnable fortress of Birtvisi
Birtvisi ( ka, ბირთვისი) is a ruined medieval fortress in Kvemo Kartli, Georgia, nested within limestone cliffs in the Algeti river gorge. It is now within the boundaries of the Tetritsqaro Municipality, adjacent to the Algeti Nati ...
, stubbornly defended by a tiny Georgian garrison. Having captured the fortress in August 1403, Timur sent his army to plunder and clear the frontier regions of Georgia and set out in pursuit of the retreating king George VII as far as Abkhazia
Abkhazia, ka, აფხაზეთი, tr, , xmf, აბჟუა, abzhua, or ( or ), officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, recognised by most countries as part of Georgia, which vi ...
. Timur's historian reports that 700 towns were destroyed and their inhabitants massacred.Grousset, René (1970), The Empire of the Steppes: A History of Central Asia, pp. 433–4. Rutgers University Press, .
Timur only stopped his army when the ulema
In Islam, the ''ulama'' (; ar, علماء ', singular ', "scholar", literally "the learned ones", also spelled ''ulema''; feminine: ''alimah'' ingularand ''aalimath'' lural are the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious ...
and the mufti decided it was possible to grant the king of Georgia clemency (''aman''). George VII had to pay a huge tribute, including 1,000 tankas of gold struck in the name of Timur, 1,000 horses, a ruby weighing 18 mithkal The mithkal or sextula (in Persian and Arabic: مثقال) is an Arabic unit of weight used in Middle East, mostly for weighing gold and Saffron. It is equivalent to a little over 4.6 grams.
Conversion
one Mithkal equal to:
:4.6875 g = =
See ...
s, etc, in exchange Timur would recognize Georgia as a Christian kingdom and the kingdom could retain its independence. Timur then passed through Tbilisi, destroying all monasteries and churches on his way, and went to Beylagan early in 1404. All the territories from Beylagan to Trebizond were officially given by Timur as an appanage to his grandson Khalil Mirza
Khalil, Khelil, or Khaleel may refer to:
People
* Khalil (Pashtun tribe)
* Kahlil Gibran (1883–1931), Lebanese-American writer, poet, visual artist, and Lebanese nationalist
* Khalil (scholar), 19th century Islamic scholar in the Emirate of Har ...
. Timur then finally left the Caucasus and headed for Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
, where he died on February 19, 1405, while preparing for a massive invasion of China.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Timur's Invasions Of Georgia Wars involving the Kingdom of Georgia Invasions of Georgia (country) Georgia Spread of Islam Religion-based wars Military history of Islam Islam and violence Invasions Georgia 1380s conflicts 1390s conflicts 1400s conflicts 14th century in the Kingdom of Georgia 15th century in the Kingdom of Georgia 1380s in Asia 1390s in Asia 1400s in Asia 1400s in Europe