Thomas Holley Chivers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Thomas Holley Chivers (October 18, 1809 – December 18, 1858) was an American doctor-turned-poet from the state of
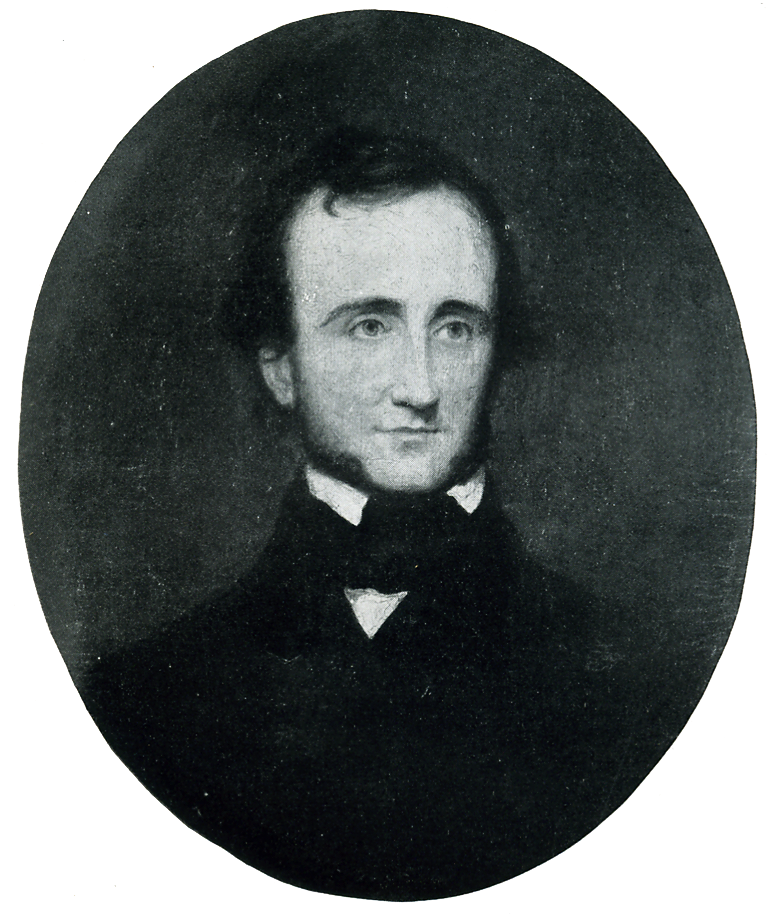 Chivers is best known for his association with Edgar Allan Poe and, in fact, it is through this relationship that Chivers and his work was rediscovered in the 20th century.Hubbell, 550 The first interaction between the two was in 1840 though they did not meet until 1845 in New York.Lombard, 99 The two became friends and Chivers was willing to give Poe lifetime financial support if he moved to the South. Chivers appreciated Poe's ability and wrote that George Rex Graham was seriously underpaying Poe for his work on ''
Chivers is best known for his association with Edgar Allan Poe and, in fact, it is through this relationship that Chivers and his work was rediscovered in the 20th century.Hubbell, 550 The first interaction between the two was in 1840 though they did not meet until 1845 in New York.Lombard, 99 The two became friends and Chivers was willing to give Poe lifetime financial support if he moved to the South. Chivers appreciated Poe's ability and wrote that George Rex Graham was seriously underpaying Poe for his work on ''
 *''The Path of Sorrow; or, the Lament of Youth'' (1832)
*''Conrad and Eudora; or, the Death of Alonzo'' (1834)
*''Nacoochee; or, the Beautiful Star With Other Poems'' (1837)
*''The Lost Pleiad, and Other Poems'' (1845)
*''Search After Truth; or, A New Revelation of the Psycho-Physiological Nature of Man.'' (1848)
*''Eonchs of Ruby: a Gift of Love'' (1851)
*''The Death of the Devil, A Serio-Ludicro, Tragico-Comico, Nigero-Whiteman Extravaganza'' (1852)
*''Atlanta; or, the True Blessed Island of Poesy, a Paul Epic'' (1853
*''The Path of Sorrow; or, the Lament of Youth'' (1832)
*''Conrad and Eudora; or, the Death of Alonzo'' (1834)
*''Nacoochee; or, the Beautiful Star With Other Poems'' (1837)
*''The Lost Pleiad, and Other Poems'' (1845)
*''Search After Truth; or, A New Revelation of the Psycho-Physiological Nature of Man.'' (1848)
*''Eonchs of Ruby: a Gift of Love'' (1851)
*''The Death of the Devil, A Serio-Ludicro, Tragico-Comico, Nigero-Whiteman Extravaganza'' (1852)
*''Atlanta; or, the True Blessed Island of Poesy, a Paul Epic'' (1853
*''Memoralia; or, Phials of Amber Full of the Tears of Love'' (1853) *''Virginalia; or, Songs of My Summer Nights'' (1853) *''The Sons of Usna: a Tragic Apotheosis in Five Acts'' (1858)
The Companion to Southern Literature: Themes, Genres, Places, People
', Joseph M. Flora and Lucinda Hardwick MacKethan (editors). Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 2002. . Accessed January 24, 2008.
Thomas Holley Chivers
at
''Conrad and Eudora; or, the Death of Alonzo''Listing at the New Georgia Encyclopedia
between Poe and Chivers at th
Edgar Allan Poe Society
{{DEFAULTSORT:Chivers, Thomas Holley Poets from Georgia (U.S. state) Edgar Allan Poe 1809 births 1858 deaths Transylvania University alumni 19th-century American poets American male poets
Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
. He is best known for his friendship with Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; Edgar Poe; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic. Poe is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is wid ...
and his controversial defense of the poet after his death.
Born into a wealthy Georgia family, Chivers became interested in poetry at a young age. After he and his first wife separated, he received a medical degree from Transylvania University
Transylvania University is a private university in Lexington, Kentucky. It was founded in 1780 and was the first university in Kentucky. It offers 46 major programs, as well as dual-degree engineering programs, and is accredited by the Southern ...
but focused his energy on publishing rather than medicine. In addition to submitting poems to various magazines and journals, Chivers published several volumes of poetry, including ''The Lost Pleiad'' in 1845, as well as plays. Edgar Allan Poe showed an interest in him and encouraged his work. Chivers spent the last few years of his life defending the reputation of Poe, who had died in 1849, though he also thought Poe had been heavily influenced by his own poetry. Chivers died in Georgia in 1858.
As a literary theorist, Chivers believed in divine inspiration. He encouraged the development of a distinctive American style of literature and especially promoted young writers. His poems were known for religious overtones with an emphasis on death and reunions with lost loved ones in the afterlife. Though he built up a small reputation in his day, he was mostly forgotten after his death.
Life and work
Chivers was born on October 18, 1809, at Digby Manor, his father's plantation nearWashington, Georgia
Washington is the county seat of Wilkes County, Georgia, United States. Under its original name Heard's Fort, it was briefly designated as the state capital during the American Revolutionary War. It is noted as the place where the Confederacy ...
. At age seven, he was introduced to poetry when he read William Cowper's "The Rose". In 1827, Chivers married his 16-year-old cousin Frances Elizabeth Chivers. The two soon separated due to alleged meddling by Frances Chivers Albert, the wife of the poet's uncle, prior to the birth of their daughter in 1828. It has also been suggested their separation was due to abuse, though these rumors originated from the same uncle.Lombard, 13 After this incident, Chivers compared himself to Lord Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824), known simply as Lord Byron, was an English romantic poet and peer. He was one of the leading figures of the Romantic movement, and has been regarded as among the ...
, whose wife had also left him.Hubbell, 551 Chivers went on to receive a degree in medicine in 1830 from Transylvania University
Transylvania University is a private university in Lexington, Kentucky. It was founded in 1780 and was the first university in Kentucky. It offers 46 major programs, as well as dual-degree engineering programs, and is accredited by the Southern ...
in Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia ...
. His thesis was titled "Intermittent and Remittent Fevers".
Chivers wandered throughout the West and North of the United States, publishing poetry in various places before returning to Georgia. In 1832, Chivers published ''The Path of Sorrow'', a collection of poetry based on the events of his troubled first marriage. Two years later, he published ''Conrad and Eudora; or, The Death of Alonzo'', the first fictionalized account of the actual 1825 murder case nicknamed the " Kentucky Tragedy". The work was later renamed ''Leoni, The Orphan of Venice''. On November 21, 1834, Chivers married Harriet Hunt of Springfield, Massachusetts and the couple had four children, though all died young. Chivers and his first wife never legally divorced—one such suit was dismissed in court in 1835—but Georgia law invalidated marriage after a spouse's absence of five years or more. Though Chivers contributed to various newspapers and magazines, his poetry was turned down for publication by the ''Southern Literary Messenger
The ''Southern Literary Messenger'' was a periodical published in Richmond, Virginia, from August 1834 to June 1864, and from 1939 to 1945. Each issue carried a subtitle of "Devoted to Every Department of Literature and the Fine Arts" or some var ...
'' in March 1835, which suggested he return to medicine and the "lancet and pill-box". Though the poems were not printed, unsigned commentary on them was presented in an editorial, referring to verses submitted by "T. H. C., M. D." ''The Lost Pleiad'' was self-published in New York in 1845 to initial success, though sales rapidly declined.Lombard, 46 In 1837, Chivers self-published ''Nacoochee; or, the Beautiful Star, With Other Poems''. The volume was dedicated to his mother, who died a year later.Lombard, 38
Relationship with Edgar Allan Poe
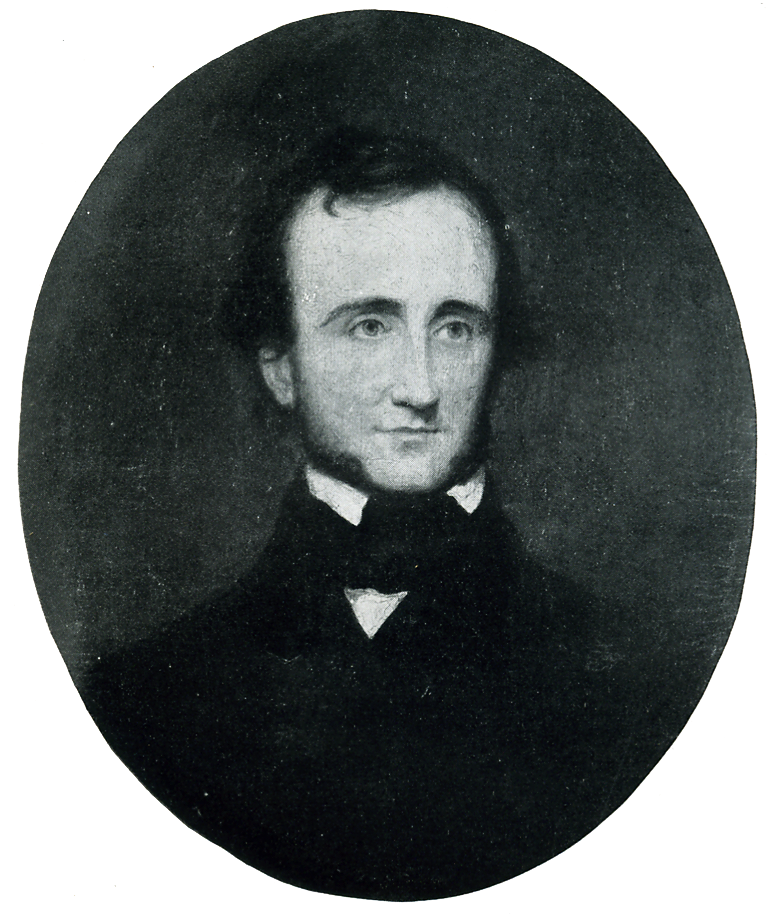 Chivers is best known for his association with Edgar Allan Poe and, in fact, it is through this relationship that Chivers and his work was rediscovered in the 20th century.Hubbell, 550 The first interaction between the two was in 1840 though they did not meet until 1845 in New York.Lombard, 99 The two became friends and Chivers was willing to give Poe lifetime financial support if he moved to the South. Chivers appreciated Poe's ability and wrote that George Rex Graham was seriously underpaying Poe for his work on ''
Chivers is best known for his association with Edgar Allan Poe and, in fact, it is through this relationship that Chivers and his work was rediscovered in the 20th century.Hubbell, 550 The first interaction between the two was in 1840 though they did not meet until 1845 in New York.Lombard, 99 The two became friends and Chivers was willing to give Poe lifetime financial support if he moved to the South. Chivers appreciated Poe's ability and wrote that George Rex Graham was seriously underpaying Poe for his work on ''Graham's Magazine
''Graham's Magazine'' was a nineteenth-century periodical based in Philadelphia established by George Rex Graham and published from 1840 to 1858. It was alternatively referred to as ''Graham's Lady's and Gentleman's Magazine'' (1841–1842, and Ju ...
''. "He ought to give you ten thousand dollars a year... It is richly worth it... rahamis greatly indebted to you. It is not my opinion that you have ever been, or ever will be, paid for your intellectual labours. You need never expect it, until you establish a Magazine of your own", he wrote, referring to Poe's plans to begin ''The Stylus
''The Stylus'', originally intended to be named ''The Penn'', was a would-be periodical owned and edited by Edgar Allan Poe. It had long been a dream of Poe to establish an American journal with very high standards in order to elevate the literatu ...
''. Even so, Chivers was concerned about Poe's reputation as a severe literary critic, cautioning him about "when you tomahawk people".Meyers, 140 Poe, in fact, had been hoping Chivers would lend his wealth as a financial backer for ''The Stylus'' and possibly even serve as a co-editor in its early planning stages. Chivers considered Poe's proposal but was not able to accept because of the death of his three-year-old daughter just over a week later.Silverman, 190
Poe had written about Chivers in the second part of his "Autography" series, published in ''Graham's Magazine
''Graham's Magazine'' was a nineteenth-century periodical based in Philadelphia established by George Rex Graham and published from 1840 to 1858. It was alternatively referred to as ''Graham's Lady's and Gentleman's Magazine'' (1841–1842, and Ju ...
'' in December 1841. Poe said:
The two had corresponded through letters but finally met in June or July 1845. Chivers visited Poe when Poe was sick and bedridden and when Poe's wife Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
was in an especially difficult period of her struggle with tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, i ...
. Chivers later recalled that Poe's voice was "like the soft tones of an Aeolian Harp when the music that has been sleeping in the strings is awakened by the Breezes of Eden laden with sweet Spices from the mountains of the Lord".
By September 1845, however, Chivers was lecturing Poe on the dangers of alcohol. A Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcohol ...
ist, he said Poe was wasting his God-given talents by indulging in drink. "Why should a Man whom God, by nature, has endowed with such transcendent abilities, so degrade himself into the veriest automaton as to be moved only by the poisonous steam of Hell-fire?" he said. While Poe's wife Virginia was sick, Chivers had to carry Poe home after a night of excess.
Moreover, as attested to in an 1848 pamphlet titled ''Search After Truth'', Chivers disagreed with Poe regarding aesthetics
Aesthetics, or esthetics, is a branch of philosophy that deals with the nature of beauty and taste, as well as the philosophy of art (its own area of philosophy that comes out of aesthetics). It examines aesthetic values, often expressed t ...
. This small booklet presents a series of dialogues between the Seer hiversand Politian oe For Chivers, a poet should be a Shelleyan or Swedenborgian visionary intent on capturing mystic realms of experience in language. For Poe, the poet is merely a superior wordsmith. The wise Seer ultimately leads Politan to the truth.
After Poe's death
After Poe's death, Chivers accused Poe of plagiarizing both "The Raven
"The Raven" is a narrative poem by American writer Edgar Allan Poe. First published in January 1845, the poem is often noted for its musicality, stylized language, and supernatural atmosphere. It tells of a distraught lover who is paid a myst ...
" and " Ulalume" from his own work though other critics suggested Chivers's ''Eonchs of Ruby'' were a "mediocre restatement" of Poe's poems. The first poem of the collection, "The Vigil of Aiden", was an homage to Poe, using names like " Lenore" and the refrain "forever more!" On July 30, 1854, Chivers published an essay called "Origin of Poe's Raven" under the pseudonym Fiat Justitia, claiming that he inspired Poe to use trochaic octameter Trochaic octameter is a poetic meter with eight trochaic metrical feet per line. Each foot has one stressed syllable followed by an unstressed syllable. Trochaic octameter is a rarely used meter.
Description and uses
The best known work in trocha ...
and the word "nevermore" in "The Raven". Chivers also suggested in the ''Georgia Citizen'' that Poe learned to write poetry from him. As literary scholar Randy Nelson wrote: "anybody who's read both Poe and Thomas Holley Chivers can see that one of them 'influenced' the other, but just who took what from whom isn't clear."
Even so, Chivers continued to praise and admire Poe (albeit careful to point out Poe's literary debt to him) and was one of the first to present a picture of the "real Poe" in the face of the sustained attacks on Poe's reputation by the Reverend Rufus Wilmot Griswold
Rufus Wilmot Griswold (February 13, 1815 – August 27, 1857) was an American anthologist, editor, poet, and critic. Born in Vermont, Griswold left home when he was 15 years old. He worked as a journalist, editor, and critic in Philadelphia, New Y ...
, the poet's literary executor
The literary estate of a deceased author consists mainly of the copyright and other intellectual property rights of published works, including film, translation rights, original manuscripts of published work, unpublished or partially completed w ...
. This correction took the form of a memoir now titled ''Chivers' Life of Poe'', not published until 1952. Chivers said of Griswold that he "is not only incompetent to Edit any of oe'sworks, but totally unconscious of the duties which he and every man who sets himself up as a Literary Executor, owe the dead." Chivers continued to defend Poe's reputation until the end of his life.
Final years and death
From 1845 to 1850, Chivers had been living with his wife in Georgia, then spent the next five years in the North. His poetry collection ''Eonchs of Ruby, A Gift of Love'' was published in 1851 with a subtitle meant to capitalize on thegift book
Gift books, literary annuals, or keepsakes were 19th-century books, often lavishly decorated, which collected essays, short fiction, and poetry. They were primarily published in the autumn, in time for the holiday season and were intended to be g ...
trend. Chivers explained the title: "The Word ''Eonch'' is the same as ''Concha Marina—Shell of the Sea''. ''Eonch'' is used... merely for its euphony." Throughout the collection, Chivers experiments with the sonic effects of words rather than their literal meaning. ''Atlanta: or the True Blessed Island of Poesy: A Paul Epic in Three Lustra'' was first published in three installments in the ''Georgia Citizen'' beginning in January 1853. Later that year, ''Memoralia; or, Philas of Amber Full of the Tears of Love'' was printed in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
and generally received unfavorably. Very shortly after, the same publisher brought out ''Virginalia; or, Songs of My Summer Nights'', a collection made up of poems that were generally under 200 lines each, about half of which had previously been published in magazines.
By 1855, Chivers and his wife had moved back to Georgia and he predicted that the slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
issue would soon force his home state to break from the United States.Lombard, 97 A slaveholder himself, Chivers did not believe that slaves should be abused, though he still defended the institution against abolitionists
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The Britis ...
. Struck with sudden illness, Chivers wrote his will before dying on December 18, 1858, in Decatur, Georgia.Lombard, 18 His last words were, "All is perfect peace with me." His last published work, a drama titled ''The Sons of Usna'', had been published earlier that year. At the time of his death, Chivers had prepared several manuscripts of his literary theory with the intention of publishing them in several volumes of books and as part of a lecture series. In his will, he left one dollar for his first wife and their daughter. He is buried in Decatur Cemetery.
Poetic theory and literary reputation
In his poetry, Chivers made use of legends and themes from Native American culture, particularly theCherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
, though often with Christian overtones. He was also heavily influenced by the work of François-René de Chateaubriand
François-René, vicomte de Chateaubriand (4 September 1768 – 4 July 1848) was a French writer, politician, diplomat and historian who had a notable influence on French literature of the nineteenth century. Descended from an old aristocrati ...
and Emanuel Swedenborg
Emanuel Swedenborg (, ; born Emanuel Swedberg; 29 March 1772) was a Swedish pluralistic-Christian theologian, scientist, philosopher and mystic. He became best known for his book on the afterlife, ''Heaven and Hell'' (1758).
Swedenborg had a ...
. Many of Chivers's poems included themes of death and sorrow, often using images of shrouds, coffins, angels, and reunions with lost loves in the afterlife.Silverman, 259 Religious conventions at the time made discussion of death popular, as was reflected in poetry. Because of his background as a doctor, Chivers was able to graphically depict the last moments before someone's death.
Chivers believed in a close connection between poetry and God and that true poetry could only be written through divine inspiration. He once wrote: "Poets are the apostles of divine thought, who are clothed with an authority from the Most High, to work miracles in the minds of men". He also wrote: "Poetry is the power given by God to man of manifesting... the wise relations that subsist between him and God", and it "is that crystal river of the soul which runs through all the avenues of life, and after purifying the affections of the heart, empties itself into the Sea of God". In ''Nacoochee'', the preface states: "Poetry is that crystal river of the soul which runs through all the avenues of life, and after purifying the affections of the heart, empties itself into the Sea of God." In his introduction to ''Atlanta'', written in 1842 but not published until 1853, Chivers gives a lengthy discussion of his poetic theory, pre-dating many ideas Poe would suggest in "The Poetic Principle "The Poetic Principle" is an essay by Edgar Allan Poe, written near the end of his life and published posthumously in 1850, the year after his death. It is a work of literary criticism, in which Poe presents his literary theory. It is based on a s ...
" (1850). Chivers, for example, suggests that poems should be short to be successful: "No poem of any considerable length... can be pleasing to any well-educated person for any length of time". He also experimented with blank verse
Blank verse is poetry written with regular metrical but unrhymed lines, almost always in iambic pentameter. It has been described as "probably the most common and influential form that English poetry has taken since the 16th century", and Pa ...
as early as 1832 and his 1853 collection, ''Virginalia'', included mostly poems using blank verse.
At least for a time, he considered Elizabeth Barrett Browning the best contemporary English poet. Like many from his time, Chivers called for the development of a distinctive American literature and he especially encouraged young writers. Poe called the 1845 poetry collection ''The Lost Pleiad'' "the honest and fervent utterance of an exquisitely sensitive heart." Overall, he called Chivers "one of the best and one of the worst poets in America". William Gilmore Simms
William Gilmore Simms (April 17, 1806 – June 11, 1870) was an American writer and politician from the American South who was a "staunch defender" of slavery. A poet, novelist, and historian, his ''History of South Carolina'' served as the defin ...
offered conditional praise of Chivers's poetry as well: "He possesses a poetic ardor sufficiently fervid, and a singularly marked command of language. But he should have been caught young, and well-bitted, and subjected to the severest training... As an artist, Dr. Chivers is yet in his accidence." Simms also commented that his works were too gloomy and melancholy. Chivers was one of a group of poets criticized for "intensity of epithet" in Bayard Taylor's verse parody ''The Echo Club and Other Literary Diversions'' (1876).
Though Chivers built up a mild reputation during his lifetime, counting Algernon Charles Swinburne among his admirers, his fame faded away quickly after his death. Other writers that acknowledged his influence included Dante Gabriel Rossetti
Gabriel Charles Dante Rossetti (12 May 1828 – 9 April 1882), generally known as Dante Gabriel Rossetti (), was an English poet, illustrator, painter, translator and member of the Rossetti family. He founded the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhoo ...
and William Michael Rossetti
William Michael Rossetti (25 September 1829 – 5 February 1919) was an English writer and critic.
Early life
Born in London, Rossetti was a son of immigrant Italian scholar Gabriele Rossetti and his wife Frances Rossetti ''née'' Polidor ...
. Others, however, were more critical. One anonymous reviewer, possibly Evert Augustus Duyckinck
Evert Augustus Duyckinck (pronounced DIE-KINK) (November 23, 1816 – August 13, 1878) was an American publisher and biographer. He was associated with the literary side of the Young America movement in New York.
Biography
He was born on Novem ...
, joked that Chivers was formulaic and suggested the formula included 30% Percy Bysshe Shelley, 20% Poe, 20% "mild idiocy", 10% "gibbering idiocy", 10% "raving mania" and 10% "sweetness and originality".Moore, Rayburn S. "A New Look at Thomas Holley Chivers", ''The Southern Literary Journal'', vol. 13, no. 1. Fall 1980: University of North Carolina Press: 131. Literary scholar S. Foster Damon wrote that Chivers would have had a stronger reputation if he were born in the North and "the literary coteries there would surely have pruned and preserved him... But the time and space were against him."
List of works
 *''The Path of Sorrow; or, the Lament of Youth'' (1832)
*''Conrad and Eudora; or, the Death of Alonzo'' (1834)
*''Nacoochee; or, the Beautiful Star With Other Poems'' (1837)
*''The Lost Pleiad, and Other Poems'' (1845)
*''Search After Truth; or, A New Revelation of the Psycho-Physiological Nature of Man.'' (1848)
*''Eonchs of Ruby: a Gift of Love'' (1851)
*''The Death of the Devil, A Serio-Ludicro, Tragico-Comico, Nigero-Whiteman Extravaganza'' (1852)
*''Atlanta; or, the True Blessed Island of Poesy, a Paul Epic'' (1853
*''The Path of Sorrow; or, the Lament of Youth'' (1832)
*''Conrad and Eudora; or, the Death of Alonzo'' (1834)
*''Nacoochee; or, the Beautiful Star With Other Poems'' (1837)
*''The Lost Pleiad, and Other Poems'' (1845)
*''Search After Truth; or, A New Revelation of the Psycho-Physiological Nature of Man.'' (1848)
*''Eonchs of Ruby: a Gift of Love'' (1851)
*''The Death of the Devil, A Serio-Ludicro, Tragico-Comico, Nigero-Whiteman Extravaganza'' (1852)
*''Atlanta; or, the True Blessed Island of Poesy, a Paul Epic'' (1853*''Memoralia; or, Phials of Amber Full of the Tears of Love'' (1853) *''Virginalia; or, Songs of My Summer Nights'' (1853) *''The Sons of Usna: a Tragic Apotheosis in Five Acts'' (1858)
Further reading
*Bell, Landon C. ''Poe and Chivers.''Columbus: Charles A. Trowbridge Co., 1931. *Brown, Ellen Firsching. "The Genius and Tragedy of Georgia's Lost Poet". ''Georgia Backroads'', Vol. 8 No. 3, Autumn 2009. *Damon, S. Foster. ''Thomas Holley Chivers, Friend of Poe''. New York, 1930 *Davis, Richard Beale, editor. ''Chivers' Life of Poe''. New York: E. P. Dutton & Co., Inc., 1952.Notes
Sources
* Chivers, Thomas Holley. ''Chivers' Life of Poe'', Richard Beale Davis (editor). New York: E. P. Dutton & Co., Inc., 1952. * Hubbell, Jay B. ''The South in American Literature: 1607–1900''. Durham, North Carolina: Duke University Press, 1954. * Kennedy, J. Gerald. "A Brief Biography", ''A Historical Guide to Edgar Allan Poe'' New York: Oxford University Press, 2001. * Lombard, Charles M. ''Thomas Holley Chivers''. Boston: Twayne Publishers, 1979. * Meyers, Jeffrey. ''Edgar Allan Poe: His Life and Legacy'' New York: Cooper Square Press, 1992. * Moss, Sidney P. ''Poe's Literary Battles: The Critic in the Context of His Literary Milieu''. Carbondale, Ill: Southern Illinois University Press, 1969. * Nelson, Randy F. ''The Almanac of American Letters''. Los Altos, California: William Kaufmann, Inc., 1981. * Parks, Edd Winfield. ''Ante-Bellum Southern Literary Critics''. Athens, GA: University of Georgia Press, 1962. * Silverman, Kenneth. ''Edgar A. Poe: Mournful and Never-ending Remembrance'' New York: Harper Perennial, 1991. * Thomas, Dwight and David K. Jackson. ''The Poe Log: A Documentary Life of Edgar Allan Poe 1809–1849''. New York: G. K. Hall & Co., 1987. * Watts, Charles Henry. ''Thomas Holley Chivers; His Literary Career and His Poetry''. Athens: University of Georgia Press, 1956. *Whited, Stephen R. "Kentucky Tragedy",The Companion to Southern Literature: Themes, Genres, Places, People
', Joseph M. Flora and Lucinda Hardwick MacKethan (editors). Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 2002. . Accessed January 24, 2008.
External links
Thomas Holley Chivers
at
Google Book Search
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical ...
* Full text o''Conrad and Eudora; or, the Death of Alonzo''
between Poe and Chivers at th
Edgar Allan Poe Society
{{DEFAULTSORT:Chivers, Thomas Holley Poets from Georgia (U.S. state) Edgar Allan Poe 1809 births 1858 deaths Transylvania University alumni 19th-century American poets American male poets