The Histories of Herodotus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The ''Histories'' ( el, Ἱστορίαι, ; also known as ''The History'') of
1.2.2
1.2.3
* The rulers of * A description the geographic location of several
* A description the geographic location of several
 * The proof of the antiquity of the
* The proof of the antiquity of the
 * The history of the
* The history of the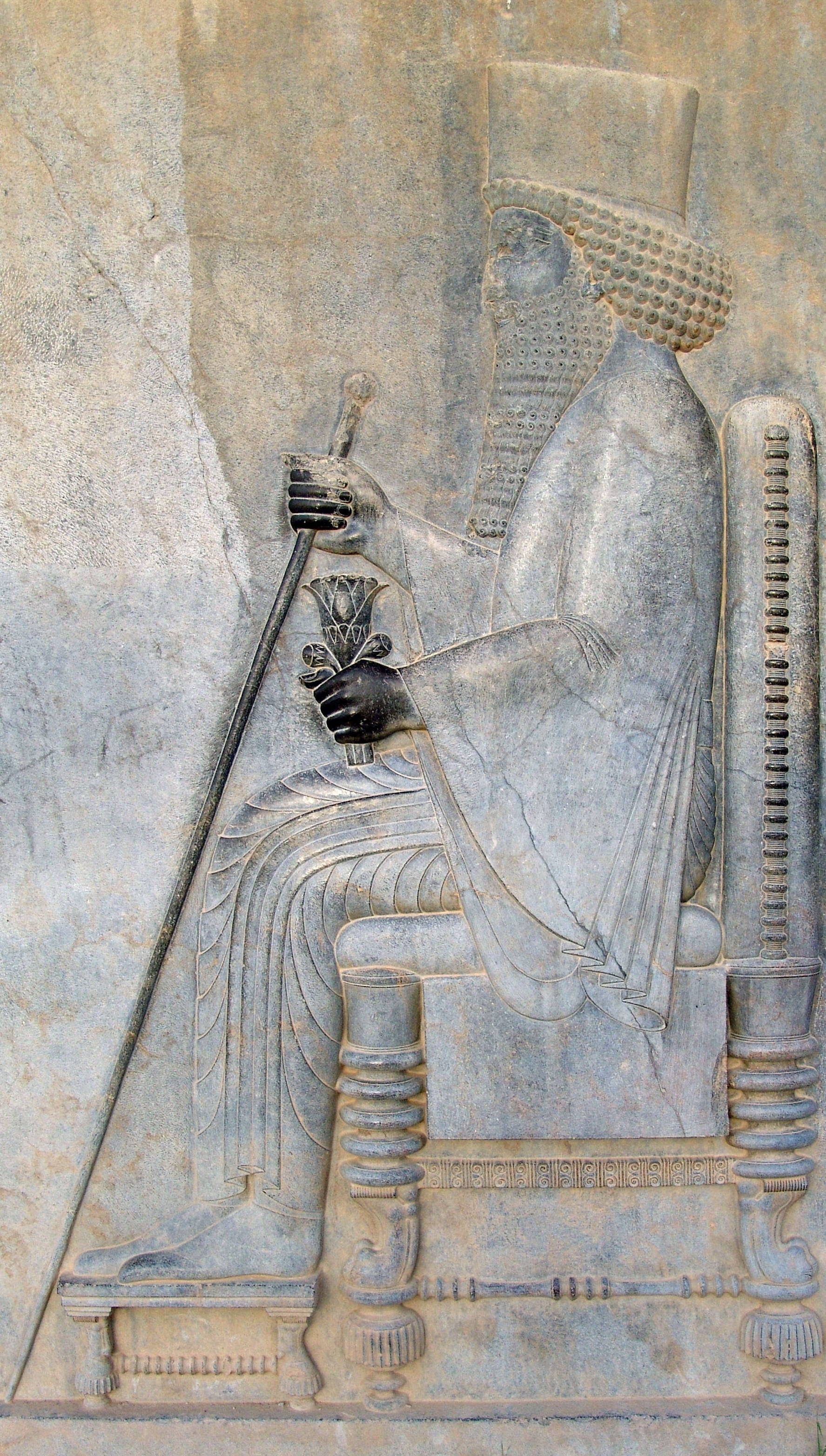  * The beginning of Darius's attack on Scythia, including the
* The beginning of Darius's attack on Scythia, including the 
 * The fleeing of
* The fleeing of  * The order of Darius that the Greeks provide him earth and water, in which most consent, including
* The order of Darius that the Greeks provide him earth and water, in which most consent, including
This section starts roughly around 6.100
* The Spartans late arrival to assist Athens * The history of the
 * The dreams of Xerxes in which a phantom frightens him and Artabanus into choosing invasion
* The preparations for war, including building the
* The dreams of Xerxes in which a phantom frightens him and Artabanus into choosing invasion
* The preparations for war, including building the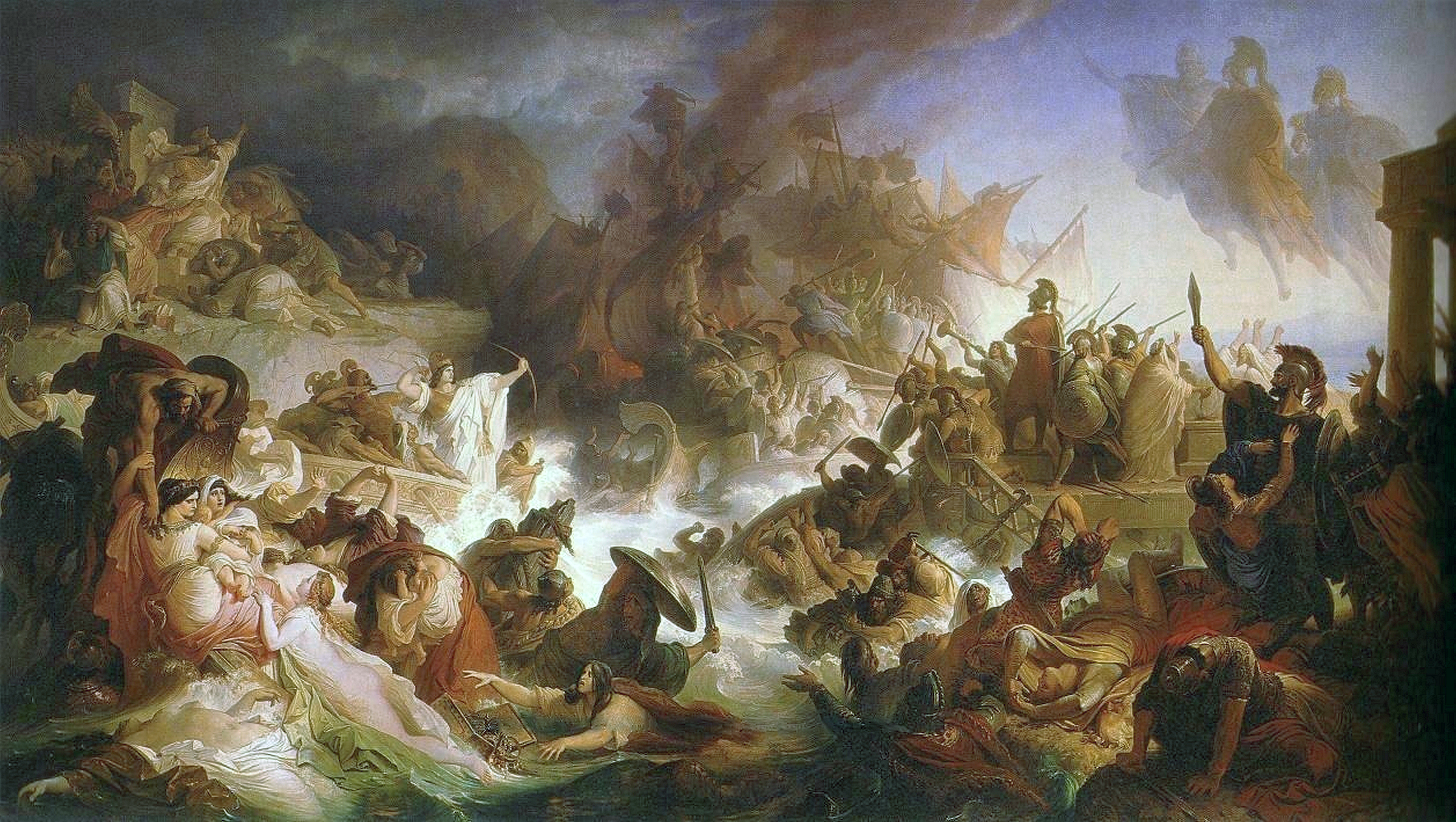 
 * The vengeance of Hermotimus, Xerxes' chief
* The vengeance of Hermotimus, Xerxes' chief
 This points forward to the "folksy" yet "international" outlook typical of Herodotus. However, one modern scholar has described the work of Hecataeus as "a curious false start to history," since despite his critical spirit, he failed to liberate history from myth. Herodotus mentions Hecataeus in his ''Histories'', on one occasion mocking him for his naive genealogy and, on another occasion, quoting Athenian complaints against his handling of their national history. It is possible that Herodotus borrowed much material from Hecataeus, as stated by Porphyry in a quote recorded by
This points forward to the "folksy" yet "international" outlook typical of Herodotus. However, one modern scholar has described the work of Hecataeus as "a curious false start to history," since despite his critical spirit, he failed to liberate history from myth. Herodotus mentions Hecataeus in his ''Histories'', on one occasion mocking him for his naive genealogy and, on another occasion, quoting Athenian complaints against his handling of their national history. It is possible that Herodotus borrowed much material from Hecataeus, as stated by Porphyry in a quote recorded by
 The accuracy of the works of Herodotus has been controversial since his own era. Kenton L. Sparks writes, "In antiquity, Herodotus had acquired the reputation of being unreliable, biased, parsimonious in his praise of heroes, and mendacious". The historian
The accuracy of the works of Herodotus has been controversial since his own era. Kenton L. Sparks writes, "In antiquity, Herodotus had acquired the reputation of being unreliable, biased, parsimonious in his praise of heroes, and mendacious". The historian
 Herodotus claimed to have visited
Herodotus claimed to have visited
 After journeys to India and Pakistan, French ethnologist
After journeys to India and Pakistan, French ethnologist  Peissel reports that, in an isolated region of northern Pakistan on the Deosai Plateau in
Peissel reports that, in an isolated region of northern Pakistan on the Deosai Plateau in
 It is clear from the beginning of Book 1 of the ''Histories'' that Herodotus utilizes (or at least claims to utilize) various sources in his narrative. K. H. Waters relates that "Herodotos did not work from a purely Hellenic standpoint; he was accused by the patriotic but somewhat imperceptive Plutarch of being ''philobarbaros'', a pro-barbarian or pro-foreigner."
Herodotus at times relates various accounts of the same story. For example, in Book 1 he mentions both the Phoenician and the Persian accounts of Io. However, Herodotus at times arbitrates between varying accounts: "I am not going to say that these events happened one way or the other. Rather, I will point out the man ''who I know for a fact'' began the wrong-doing against the Greeks." Again, later, Herodotus claims himself as an authority: "I know this is how it happened because I heard it from the Delphians myself."
Throughout his work, Herodotus attempts to explain the actions of people. Speaking about Solon the Athenian, Herodotus states " olonsailed away on the pretext of seeing the world, ''but it was really so that he could not be compelled to repeal any of the laws he had laid down''." Again, in the story about Croesus and his son's death, when speaking of Adrastus (the man who accidentally killed Croesus' son), Herodotus states: "Adrastus ... ''believing himself to be the most ill-fated man he had ever known'', cut his own throat over the grave."
It is clear from the beginning of Book 1 of the ''Histories'' that Herodotus utilizes (or at least claims to utilize) various sources in his narrative. K. H. Waters relates that "Herodotos did not work from a purely Hellenic standpoint; he was accused by the patriotic but somewhat imperceptive Plutarch of being ''philobarbaros'', a pro-barbarian or pro-foreigner."
Herodotus at times relates various accounts of the same story. For example, in Book 1 he mentions both the Phoenician and the Persian accounts of Io. However, Herodotus at times arbitrates between varying accounts: "I am not going to say that these events happened one way or the other. Rather, I will point out the man ''who I know for a fact'' began the wrong-doing against the Greeks." Again, later, Herodotus claims himself as an authority: "I know this is how it happened because I heard it from the Delphians myself."
Throughout his work, Herodotus attempts to explain the actions of people. Speaking about Solon the Athenian, Herodotus states " olonsailed away on the pretext of seeing the world, ''but it was really so that he could not be compelled to repeal any of the laws he had laid down''." Again, in the story about Croesus and his son's death, when speaking of Adrastus (the man who accidentally killed Croesus' son), Herodotus states: "Adrastus ... ''believing himself to be the most ill-fated man he had ever known'', cut his own throat over the grave."
Direct link to PDF
{{DEFAULTSORT:Histories Of Herodotus, The 5th-century BC history books Books about civilizations Herodotus, Greco-Roman ethnography Texts in Ionic Greek History books about the Greco-Persian Wars
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
is considered the founding work of history in Western literature
Western literature, also known as European literature, is the literature written in the context of Western culture in the languages of Europe, as well as several geographically or historically related languages such as Basque and Hungarian, an ...
. Written around 430 BC in the Ionic dialect
Ionic Greek ( grc, Ἑλληνικὴ Ἰωνική, Hellēnikē Iōnikē) was a subdialect of the Attic–Ionic or Eastern dialect group of Ancient Greek.
History
The Ionic dialect appears to have originally spread from the Greek mainland acr ...
of classical Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic pe ...
, ''The Histories'' serves as a record of the ancient traditions, politics, geography, and clashes of various cultures that were known in Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
, Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes A ...
and Northern Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in t ...
at that time. Although not a fully impartial record, it remains one of the West's most important sources regarding these affairs. Moreover, it established the genre
Genre () is any form or type of communication in any mode (written, spoken, digital, artistic, etc.) with socially-agreed-upon conventions developed over time. In popular usage, it normally describes a category of literature, music, or other f ...
and study of history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
in the Western world (despite the existence of historical records and chronicle
A chronicle ( la, chronica, from Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historically important events and ...
s beforehand).
''The'' ''Histories'' also stands as one of the earliest accounts of the rise of the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
, as well as the events and causes of the Greco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of th ...
between the Persian Empire and the Greek city-states
''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, πόλις, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means " city" in Greek. In Ancient Greece, it originally referred to an administrative and religious city center, as distinct from the rest of the city. Later, it als ...
in the 5th century BC. Herodotus portrays the conflict as one between the forces of slavery (the Persians) on the one hand, and freedom (the Athenians
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
and the confederacy of Greek city-states which united against the invaders) on the other. ''The Histories'' was at some point divided into the nine books
A book is a medium for recording information in the form of writing or images, typically composed of many pages (made of papyrus, parchment, vellum, or paper) bound together and protected by a cover. The technical term for this physic ...
that appear in modern editions, conventionally named after the nine Muses
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, the Muses ( grc, Μοῦσαι, Moûsai, el, Μούσες, Múses) are the inspirational goddesses of literature, science, and the arts. They were considered the source of the knowledge embodied in the ...
.
Motivation for writing
Herodotus claims to have traveled extensively around theancient world
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cov ...
, conducting interviews and collecting stories for his book, almost all of which covers territories of the Persian Empire. At the beginning of ''The Histories'', Herodotus sets out his reasons for writing it:
Summary
Book I (Clio)
*The rapes of Io,Europa
Europa may refer to:
Places
* Europe
* Europa (Roman province), a province within the Diocese of Thrace
* Europa (Seville Metro), Seville, Spain; a station on the Seville Metro
* Europa City, Paris, France; a planned development
* Europa Clif ...
, and Medea
In Greek mythology, Medea (; grc, Μήδεια, ''Mēdeia'', perhaps implying "planner / schemer") is the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis, a niece of Circe and the granddaughter of the sun god Helios. Medea figures in the myth of Jaso ...
, which motivated Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
to abduct Helen
Helen may refer to:
People
* Helen of Troy, in Greek mythology, the most beautiful woman in the world
* Helen (actress) (born 1938), Indian actress
* Helen (given name), a given name (including a list of people with the name)
Places
* Helen, ...
. The subsequent Trojan War
In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans ( Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology and ...
is marked as a precursor to later conflicts between peoples of Asia and Europe. (–5)
*Colchis
In Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the Colchians are generally though ...
, Colchians
In Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the Colchians are generally thoug ...
and Medea
In Greek mythology, Medea (; grc, Μήδεια, ''Mēdeia'', perhaps implying "planner / schemer") is the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis, a niece of Circe and the granddaughter of the sun god Helios. Medea figures in the myth of Jaso ...
.1.2.2
1.2.3
* The rulers of
Lydia
Lydia ( Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish pro ...
(on the west coast of Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, today modern Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
): Candaules
Candaules (died c.687 BC; el, Κανδαύλης, ''Kandaulēs''), also known as Myrsilos (Μυρσίλος), was a king of the ancient Kingdom of Lydia in the early years of the 7th century BC. According to Herodotus, he succeeded his fath ...
, Gyges Gyges can refer to:
* One of the Hecatoncheires from Greek mythology
* King Gyges of Lydia
* Ogyges
* Ring of Gyges
The Ring of Gyges ( grc, Γύγου Δακτύλιος, ''Gúgou Daktúlios'', ) is a hypothetical magic ring mentioned by the ...
, Ardys, Sadyattes, Alyattes, Croesus
Croesus ( ; Lydian: ; Phrygian: ; grc, Κροισος, Kroisos; Latin: ; reigned: c. 585 – c. 546 BC) was the king of Lydia, who reigned from 585 BC until his defeat by the Persian king Cyrus the Great in 547 or 546 BC.
Croesus was r ...
(–7)
*How Candaules
Candaules (died c.687 BC; el, Κανδαύλης, ''Kandaulēs''), also known as Myrsilos (Μυρσίλος), was a king of the ancient Kingdom of Lydia in the early years of the 7th century BC. According to Herodotus, he succeeded his fath ...
made his bodyguard, Gyges Gyges can refer to:
* One of the Hecatoncheires from Greek mythology
* King Gyges of Lydia
* Ogyges
* Ring of Gyges
The Ring of Gyges ( grc, Γύγου Δακτύλιος, ''Gúgou Daktúlios'', ) is a hypothetical magic ring mentioned by the ...
, view the naked body of his wife. Upon discovery, she ordered Gyges to murder Candaules or face death himself
* How Gyges took the kingdom from Candaules
Candaules (died c.687 BC; el, Κανδαύλης, ''Kandaulēs''), also known as Myrsilos (Μυρσίλος), was a king of the ancient Kingdom of Lydia in the early years of the 7th century BC. According to Herodotus, he succeeded his fath ...
(–13)
* The singer Arion
Arion (; grc-gre, Ἀρίων; fl. c. 700 BC) was a kitharode in ancient Greece, a Dionysiac poet credited with inventing the dithyramb. The islanders of Lesbos claimed him as their native son, but Arion found a patron in Periander, tyrant ...
's ride on the dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (the b ...
(–24)
* Solon
Solon ( grc-gre, Σόλων; BC) was an Athenian statesman, constitutional lawmaker and poet. He is remembered particularly for his efforts to legislate against political, economic and moral decline in Archaic Athens.Aristotle ''Politic ...
's answer to Croesus's question that Tellus
Tellus is a Latin word meaning "Earth" and may refer to:
* An alternative name for the planet Earth
* Tellus of Athens, a citizen of ancient Athens who was thought to be the happiest of men
* Tellus Mater or Terra Mater, the ancient Roman earth mo ...
was the happiest person in the world (–33)
* Croesus's efforts to protect his son Atys, his son's accidental death by Adrastus
In Greek mythology, Adrastus or Adrestus (Ancient Greek: Ἄδραστος or Ἄδρηστος), (perhaps meaning "the inescapable"), was a king of Argos, and leader of the Seven against Thebes. He was the son of the Argive king Talaus, but was ...
(–44)
* Croesus's test of the oracles (–54)
* The answer from the Oracle of Delphi
Pythia (; grc, Πυθία ) was the name of the high priestess of the Temple of Apollo at Delphi. She specifically served as its oracle and was known as the Oracle of Delphi. Her title was also historically glossed in English as the Pythoness ...
concerning whether Croesus should attack the Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. ...
(famous for its ambiguity): ''If you attack, a great empire will fall''.
* Peisistratos
Pisistratus or Peisistratus ( grc-gre, Πεισίστρατος ; 600 – 527 BC) was a politician in ancient Athens, ruling as tyrant in the late 560s, the early 550s and from 546 BC until his death. His unification of Attica, the triangular ...
' rises and falls from power as tyrant of Athens (–64)
* The rise of Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referr ...
(–68)
 * A description the geographic location of several
* A description the geographic location of several Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
n tribes, including the Cappadocians
Cappadocian Greeks also known as Greek Cappadocians ( el, Έλληνες-Καππαδόκες, Ελληνοκαππαδόκες, Καππαδόκες; tr, Kapadokyalı Rumlar) or simply Cappadocians are an ethnic Greek community native to the ...
, Matieni, Phrygians
The Phrygians ( Greek: Φρύγες, ''Phruges'' or ''Phryges'') were an ancient Indo-European speaking people, who inhabited central-western Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) in antiquity. They were related to the Greeks.
Ancient Greek authors use ...
, and Paphlagonians
Paphlagonia (; el, Παφλαγονία, Paphlagonía, modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; tr, Paflagonya) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus to the east, an ...
. ()
* The Battle of Halys; Thales
Thales of Miletus ( ; grc-gre, Θαλῆς; ) was a Greek mathematician, astronomer, statesman, and pre-Socratic philosopher from Miletus in Ionia, Asia Minor. He was one of the Seven Sages of Greece. Many, most notably Aristotle, regarded ...
predicts the solar eclipse of May 28, 585 BC ()
* Croesus's defeat by Cyrus II of Persia, and how he later became Cyrus's advisor (–92)
* The Tyrrhenian's descent from the Lydians: "Then the one group, having drawn the lot, left the country and came down to Smyrna and built ships, in which they loaded all their goods that could be transported aboard ship, and sailed away to seek a livelihood and a country; until at last, after sojourning with one people after another, they came to the Ombrici, where they founded cities and have lived ever since. They no longer called themselves Lydians, but Tyrrhenians, after the name of the king's son who had led them there,". ()
* The rulers of the Medes
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, ...
: Deioces
Deioces ( grc, Δηιόκης), from the Old Iranian ''Dahyu-ka-'', meaning "the lands" (above, on and beneath the earth), was the founder and the first ''shah'' as well as priest of the Median Empire. His name has been mentioned in different form ...
, Phraortes
Phraortes ( peo, 𐎳𐎼𐎺𐎼𐎫𐎡𐏁, translit=Fravartiš; grc, Φραόρτης, translit=Phraórtēs; died c. 653 BC), son of Deioces, was the second king of the Median Empire.
Like his father Deioces, Phraortes started wars agains ...
, Cyaxares
Cyaxares (Median language, Median: ; Old Persian: ; Akkadian language, Akkadian: ; Phrygian language, Old Phrygian: ; grc, wikt:Κυαξάρης, Κυαξαρης, Kuaxarēs; Latin: ; reigned 625–585 BCE) was the third king of the Medes.
C ...
, Astyages
Astyages ( Median: ; Akkadian: ; Ancient Greek: grc, Αστυαγης, Astuagēs, , romanized: , , romanized: ; la, Astyages, , ; reigned 585–550 BC) was the last king of the Median Empire. The son of Cyaxares; he was dethroned in 550 BC by ...
, Cyrus II of Persia (–144)
* The rise of Deioces over the Medes
*Astyages
Astyages ( Median: ; Akkadian: ; Ancient Greek: grc, Αστυαγης, Astuagēs, , romanized: , , romanized: ; la, Astyages, , ; reigned 585–550 BC) was the last king of the Median Empire. The son of Cyaxares; he was dethroned in 550 BC by ...
's attempt to destroy Cyrus, and Cyrus's rise to power
*Harpagus
Harpagus, also known as Harpagos or Hypargus ( Ancient Greek Ἅρπαγος; Akkadian: ''Arbaku''), was a Median general from the 6th century BC, credited by Herodotus as having put Cyrus the Great on the throne through his defection during th ...
tricked into eating his son, his revenge against Astyages by assisting Cyrus
* The culture of the Persians
* The history and geography of the Ionia
Ionia () was an ancient region on the western coast of Anatolia, to the south of present-day Izmir. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionia ...
ns, and the attacks on it by Harpagus
* Pactyes' convinces the Lydians to revolt. Rebellion fails and he seeks refuge from Mazares in Cyme (Aeolis)
Cyme ( el, Κύμη) or Cumae was an Aeolian city in Aeolis (Asia Minor) close to the kingdom of Lydia. It was called Phriconian, perhaps from the mountain Phricion in Aeolis, near which the Aeolians had been settled before their migration to A ...
* The culture of Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
, especially the design and improvement of the city of Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
and the ways of its people
* Cyrus's attack on Babylon, including his revenge on the river Gyndes and his famous method for entering the city
* Cyrus's ill-fated attack on the Massagetæ, leading to his death
Book II (Euterpe)
 * The proof of the antiquity of the
* The proof of the antiquity of the Phrygians
The Phrygians ( Greek: Φρύγες, ''Phruges'' or ''Phryges'') were an ancient Indo-European speaking people, who inhabited central-western Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) in antiquity. They were related to the Greeks.
Ancient Greek authors use ...
by the use of children unexposed to language
* The geography, customs, and history of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
(Sections 2–182)
* Speculations on the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
river (Sections 2-34)
* The religious practices of Egypt, especially as they differ from the Greeks (sections 35–64)
* The animals of Egypt: cats, dogs, crocodile
Crocodiles (family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term crocodile is sometimes used even more loosely to include all extant me ...
s, hippopotamus
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two exta ...
es, otter
Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine, with diets based on fish and invertebrates. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which also includes we ...
s, phoenixes, sacred serpents, winged snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more ...
s, ibis
The ibises () (collective plural ibis; classical plurals ibides and ibes) are a group of long-legged wading birds in the family Threskiornithidae, that inhabit wetlands, forests and plains. "Ibis" derives from the Latin and Ancient Greek word ...
es
* The culture of Egypt: medicine, funeral rites, food, boats
* The kings of Egypt: Menes
Menes (fl. c. 3200–3000 BC; ; egy, mnj, probably pronounced *; grc, Μήνης) was a pharaoh of the Early Dynastic Period of ancient Egypt credited by classical tradition with having united Upper and Lower Egypt and as the founder of the ...
, Nitocris
Nitocris ( el, Νίτωκρις) possibly was the last pharaoh of ancient Egypt's Sixth Dynasty. Her name is found in Herodotus' '' Histories'' (430BC) and in writings by the 3rd-century BC Manetho, but her historicity has been questioned. If she ...
, Mœris, Sesostris, Pheron, Proteus
In Greek mythology, Proteus (; Ancient Greek: Πρωτεύς, ''Prōteus'') is an early prophetic sea-god or god of rivers and oceanic bodies of water, one of several deities whom Homer calls the "Old Man of the Sea" ''(hálios gérôn)''. ...
* Helen
Helen may refer to:
People
* Helen of Troy, in Greek mythology, the most beautiful woman in the world
* Helen (actress) (born 1938), Indian actress
* Helen (given name), a given name (including a list of people with the name)
Places
* Helen, ...
and Paris's stay in Egypt, just before the Trojan War
In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans ( Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology and ...
(–120)
* More kings of Egypt: Rhampsinit
Rhampsinit (also called Rhampsinitos, Rhampsinitus, Rampsinitus, Rampsinit, derived from Herodotus' Greek Ῥαμψίνιτος ''Rhampsínitos'') is the hellenized name of a fictitious king (pharaoh) from Ancient Egypt. He is named by the ancien ...
(and the story of the clever thief), Cheops
Khufu or Cheops was an ancient Egyptian monarch who was the second pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty, in the first half of the Old Kingdom period (26th century BC). Khufu succeeded his father Sneferu as king. He is generally accepted as having ...
(and the building of the Great Pyramid of Giza
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the biggest Egyptian pyramid and the tomb of Fourth Dynasty pharaoh Khufu. Built in the early 26th century BC during a period of around 27 years, the pyramid is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient Worl ...
using machines
A machine is a physical system using power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromolecul ...
), Chephren
Khafre (also read as Khafra and gr, Χεφρήν Khephren or Chephren) was an ancient Egyptian King (pharaoh) of the 4th Dynasty during the Old Kingdom. He was the son of Khufu and the successor of Djedefre. According to the ancient historian ...
, Mycerinus, Asychis and the Ethiopian conqueror Sabacos
Neferkare Shabaka, or Shabako ( Egyptian: 𓆷𓃞𓂓 ''šꜣ bꜣ kꜣ'', Assyrian: ''Sha-ba-ku-u'') was the third Kushite pharaoh of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, who reigned from 705 to 690 BC.F. Payraudeau, Retour sur la succession Sh ...
, Anysis Anysis was a king of Egypt, mentioned only in book II of '' Histories'' by Herodotus. Herodotus says he came from a city after which he was named. He was blind and was deposed by Ethiopians led by Sabacos. After fifty years of hiding in marshland ...
, Sethos
* The line of priests
* The Labyrinth
In Greek mythology, the Labyrinth (, ) was an elaborate, confusing structure designed and built by the legendary artificer Daedalus for King Minos of Crete at Knossos. Its function was to hold the Minotaur, the monster eventually killed by ...
* More kings of Egypt: the twelve, Psammetichus (and his rise to power), Necôs, Psammis, Apries
Apries ( grc, Ἁπρίης) is the name by which Herodotus (ii. 161) and Diodorus (i. 68) designate Wahibre Haaibre, a pharaoh of Egypt (589 BC570 BC), the fourth king (counting from Psamtik I) of the Twenty-sixth dynasty of Egypt. He was eq ...
, Amasis II
Amasis II ( grc, Ἄμασις ; phn, 𐤇𐤌𐤎 ''ḤMS'') or Ahmose II was a pharaoh (reigned 570526 BCE) of the Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt, the successor of Apries at Sais. He was the last great ruler of Egypt before the Persian conque ...
(and his rise to power)
Book III (Thalia)
*Cambyses II of Persia
Cambyses II ( peo, 𐎣𐎲𐎢𐎪𐎡𐎹 ''Kabūjiya'') was the second King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 530 to 522 BC. He was the son and successor of Cyrus the Great () and his mother was Cassandane.
Before his accession, Cambyses ...
's (son of Cyrus II and king of Persia) attack on Egypt, and the defeat of the Egyptian king Psammetichus III
Psamtik III ( Ancient Egyptian: , pronounced ), known by the Graeco-Romans as Psammetichus or Psammeticus (Ancient Greek: ), or Psammenitus (Ancient Greek: ), was the last Pharaoh of the Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt from 526 BC to 525 BC. Most of ...
.
* Cambyses's abortive attack on Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
* The madness of Cambyses
* The good fortune of Polycrates
Polycrates (; grc-gre, Πολυκράτης), son of Aeaces, was the tyrant of Samos from the 540s BC to 522 BC. He had a reputation as both a fierce warrior and an enlightened tyrant.
Sources
The main source for Polycrates' life and activ ...
, king of Samos
Samos (, also ; el, Σάμος ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the -wide Mycale Strait. It is also a sepa ...
* Periander
Periander (; el, Περίανδρος; died c. 585 BC) was the Second Tyrant of the Cypselid dynasty that ruled over ancient Corinth. Periander's rule brought about a prosperous time in Corinth's history, as his administrative skill made Corinth o ...
, the king of Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part ...
and Corcyra
Corfu (, ) or Kerkyra ( el, Κέρκυρα, Kérkyra, , ; ; la, Corcyra.) is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands, and, including its small satellite islands, forms the margin of the northwestern frontier of Greece. The isl ...
, and his obstinate son
* The revolt of the two Magi
Magi (; singular magus ; from Latin '' magus'', cf. fa, مغ ) were priests in Zoroastrianism and the earlier religions of the western Iranians. The earliest known use of the word ''magi'' is in the trilingual inscription written by Darius t ...
in Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and the death of Cambyses
* The conspiracy of the seven to remove the Magi
* The rise of Darius I of Persia
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a List of monarchs of Persia, Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigni ...
.
* The twenty satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with cons ...
ies
* The culture of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
and their method of collecting gold
* The culture of Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Pl ...
and their method of collecting spices
* The flooded valley with five gates
* Orœtes's (governor of Sardis
Sardis () or Sardes (; Lydian: 𐤳𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣 ''Sfard''; el, Σάρδεις ''Sardeis''; peo, Sparda; hbo, ספרד ''Sfarad'') was an ancient city at the location of modern ''Sart'' (Sartmahmut before 19 October 2005), near Salihli, ...
) scheme against Polycrates
* The physician Democêdes
* The rise of Syloson governor of Samos
* The revolt of Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
and its defeat by the scheme of Zopyrus
Zopyrus (; el, Ζώπυρος) (fl. 522 BC-500 BC) was a Persian nobleman mentioned in Herodotus' '' Histories''.
He was son of Megabyzus I, who helped Darius I in his ascension. According to Herodotus, when Babylon revolted against the ru ...
Book IV (Melpomene)
 * The history of the
* The history of the Scythia
Scythia ( Scythian: ; Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) or Scythica (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Pontic Scythia, was a kingdom created by the Scythians during the 6th to 3rd centuries BC in the Pontic–Caspian steppe.
...
ns (from the land north of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
)
* The miraculous poet Aristeas
* The geography of Scythia
* The inhabitants of regions beyond Scythia: Sauromatae
The Sauromatian culture (russian: Савроматская культура, Savromatskaya kulʹtura) was a Iron Age culture of horse nomads in the area of the lower Volga River in southern Russia, dated to the 6th to 4th centuries BCE. The name o ...
, Budini
The Budini ( Ancient Greek: Βουδίνοι; ''Boudínoi'') was a group of people (a tribe) described by Herodotus and several later classical authors. Described as nomads living near settled Gelonians, Herodotus located them east of the Tanais r ...
, Thyssagetae
The Thyssagetae ( grc, Θυσσαγέται) were an ancient tribe described by Herodotus as occupying a district to the north-east of Scythia, separated from the Budini by a "desert" that took seven days to cross.Herodotus. ''Histories'', 4.22.1: ...
, Argippaeans, Issedones The Issedones (Ἰσσηδόνες) were an ancient people of Central Asia at the end of the trade route leading north-east from Scythia, described in the lost ''Arimaspeia'' of Aristeas, by Herodotus in his ''History'' (IV.16-25) and by Ptolemy in ...
, Arimaspi, Hyperboreans
* A comparison of Libya (Africa), Asia, and Europe
* The rivers of Scythia: the Ister Ister, The Ister, or Der Ister may refer to:
*The Danube river, known as the Ister in Ancient Greek (Ἴστρος) and Thracian
*The Dniester river, known as the Ister in Thracian
*"Der Ister", a poem by Friedrich Hölderlin
**''Hölderlin's Hymn " ...
, the Tyras
Tyras ( grc, Τύρας) was an ancient Greek city on the northern coast of the Black Sea. It was founded by colonists from Miletus, probably about 600 BC. The city was situated some 10 km from the mouth of the Tyras River, which is no ...
, the Hypanis, the Borysthenes, the Panticapes, the Hypacyris, the Gerrhus, and the Tanais
Tanais ( el, Τάναϊς ''Tánaïs''; russian: Танаис) was an ancient Greek city in the Don river delta, called the Maeotian marshes in classical antiquity. It was a bishopric as Tana and remains a Latin Catholic titular see as Tana ...
* The culture of the Scythians: religion, burial rites, xenophobia
Xenophobia () is the fear or dislike of anything which is perceived as being foreign or strange. It is an expression of perceived conflict between an in-group and out-group and may manifest in suspicion by the one of the other's activities, a ...
(the stories of Anacharsis
Anacharsis (; grc, Ἀνάχαρσις) was a Scythian philosopher; he travelled from his homeland on the northern shores of the Black Sea, to Ancient Athens, in the early 6th century BC, and made a great impression as a forthright and outspok ...
and Scylas), population (sections 59–81)
pontoon bridge
A pontoon bridge (or ponton bridge), also known as a floating bridge, uses floats or shallow- draft boats to support a continuous deck for pedestrian and vehicle travel. The buoyancy of the supports limits the maximum load that they can carry ...
over the Bosphorus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
* The brutal worship of Zalmoxis
Zalmoxis ( grc-gre, Ζάλμοξις) also known as Salmoxis (Σάλμοξις), Zalmoxes (Ζάλμοξες), Zamolxis (Ζάμολξις), Samolxis (Σάμολξις), Zamolxes (Ζάμολξες), or Zamolxe (Ζάμολξε) is a divinity of the ...
by the Getae
The Getae ( ) or Gets ( ; grc, Γέται, singular ) were a Thracian-related tribe that once inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube, in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania. Both the singular form ''Get'' an ...
* The customs of the surrounding peoples: Tauri, Agathyrsi
The Agathyrsi ( Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a people belonging to the Scythian cultures. The Agathyrsi were a people of mixed Iranian Scythic and Geto-Thracian origin whose bulk were Thracian while their aristocracy was closely related to ...
, Neuri
The Neuri or Navari were a tribe described by Herodotus in the . Contemporary scholars equate this group with the Yotvingians, a Western Baltic people, and believe they lived near the river Narew in or Belarus.
Primary sources Herodotus's ...
, Androphagi (man-eaters), Melanchlaeni
Melanchlaeni (, meaning "black-cloaks") may refer to three ancient tribes.
The first was a nomad tribe, the name of which first appears in Hecataeus (''ap.'' Steph. B., Fr. 154, ed. Klausen). In the geography of Herodotus (iv. 20,100--103,107) ...
, Geloni
The Gelonians (or Geloni) ( grc, Γελωνοί), also known as Helonians (or Heloni), are mentioned as a nation in northwestern Scythia by Herodotus. Herodotus states that they were originally Hellenes who settled among the Budinoi, and that th ...
, Budini
The Budini ( Ancient Greek: Βουδίνοι; ''Boudínoi'') was a group of people (a tribe) described by Herodotus and several later classical authors. Described as nomads living near settled Gelonians, Herodotus located them east of the Tanais r ...
, Sauromatae
The Sauromatian culture (russian: Савроматская культура, Savromatskaya kulʹtura) was a Iron Age culture of horse nomads in the area of the lower Volga River in southern Russia, dated to the 6th to 4th centuries BCE. The name o ...
* The wooing of the Amazons
In Greek mythology, the Amazons (Ancient Greek: Ἀμαζόνες ''Amazónes'', singular Ἀμαζών ''Amazōn'', via Latin ''Amāzon, -ŏnis'') are portrayed in a number of ancient epic poems and legends, such as the Labours of Hercule ...
by the Scyths, forming the Sauromatae
* Darius's failed attack on Scythia and consequent retreat
* The story of the Minyæ (descendants of the Argonauts
The Argonauts (; Ancient Greek: ) were a band of heroes in Greek mythology, who in the years before the Trojan War (around 1300 BC) accompanied Jason to Colchis in his quest to find the Golden Fleece. Their name comes from their ship, ''Argo ...
) and the founding of Cyrene
* The kings of Cyrene: Battus I, Arcesilaus I, Battus II, Arcesilaus II, Battus III (and the reforms of Demonax
Demonax ( el, Δημώναξ, ''Dēmōnax'', ''gen''.: Δημώνακτος; c. AD 70 – c. 170) was a Greek Cynic philosopher. Born in Cyprus, he moved to Athens, where his wisdom, and his skill in solving disputes, earned him the admiration of ...
), Arcesilaus III
Arcesilaus III of Cyrene ( el, Ἀρκεσίλαος, flourished 6th century BC) was the sixth Greek Cyrenaean King and was a member of the Battiad dynasty. He succeeded his father as king of Cyrene in 530 BC and was ruler until he was killed b ...
(and his flight, restoration, and assassination), Battus IV, and Arcesilaus IV (his revolt and death)
* The peoples of Libya from east to west
* The revenge of Arcesilaus' mother Pheretima

Book V (Terpsichore)
* The attack on theThracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied ...
by Megabazus
* The removal of the Paeonians
Paeonians were an ancient Indo-European people that dwelt in Paeonia. Paeonia was an old country whose location was to the north of Ancient Macedonia, to the south of Dardania, to the west of Thrace and to the east of Illyria, most of their lan ...
to Asia
* The slaughter of the Persian envoys by Alexander I of Macedon
Alexander I of Macedon ( el, Ἀλέξανδρος ὁ Μακεδών), known with the title Philhellene (Greek: φιλέλλην, literally "fond/lover of the Greeks", and in this context "Greek patriot"), was the ruler of the ancient Kingdom of ...
* The failed attack on the Naxians by Aristagoras, tyrant of Miletus
Miletus (; gr, Μῑ́λητος, Mī́lētos; Hittite transcription ''Millawanda'' or ''Milawata'' ( exonyms); la, Mīlētus; tr, Milet) was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in ...
* The revolt of Miletus against Persia
* The background of Cleomenes I
Cleomenes I (; Greek Κλεομένης; died c. 490 BC) was Agiad King of Sparta from c. 524 to c. 490 BC. One of the most important Spartan kings, Cleomenes was instrumental in organising the Greek resistance against the Persian Empire of Dariu ...
, king of Sparta, and his half brother Dorieus
Dorieus (died c.510 BC; grc-gre, Δωριεύς) was a Spartan prince of the Agiad dynasty who is mentioned several times in Herodotus. The second son of Anaxandridas II, he was the younger half-brother of Cleomenes I and the elder full brother ...
* The description of the Persian Royal Road
The Royal Road was an ancient highway reorganized and rebuilt by the Persian king Darius the Great (Darius I) of the first (Achaemenid) Persian Empire in the 5th century BC. Darius built the road to facilitate rapid communication on the western ...
from Sardis
Sardis () or Sardes (; Lydian: 𐤳𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣 ''Sfard''; el, Σάρδεις ''Sardeis''; peo, Sparda; hbo, ספרד ''Sfarad'') was an ancient city at the location of modern ''Sart'' (Sartmahmut before 19 October 2005), near Salihli, ...
to Susa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo- Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ...
* The introduction of writing
Writing is a medium of human communication which involves the representation of a language through a system of physically inscribed, mechanically transferred, or digitally represented symbols.
Writing systems do not themselves constitute h ...
to Greece by the Phoenicians
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their his ...
* The freeing of Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
by Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referr ...
, and its subsequent attacks on Athens
* The reorganizing of the Athenian tribes by Cleisthenes
Cleisthenes ( ; grc-gre, Κλεισθένης), or Clisthenes (c. 570c. 508 BC), was an ancient Athenian lawgiver credited with reforming the constitution of ancient Athens and setting it on a democratic footing in 508 BC. For these accomplishm ...
* The attack on Athens by the Thebans
Thebes (; ell, Θήβα, ''Thíva'' ; grc, Θῆβαι, ''Thêbai'' .) is a city in Boeotia, Central Greece. It played an important role in Greek myths, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus, Heracles and others. Archaeol ...
and Eginetans
* The backgrounds of the tyrants of Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part ...
Cypselus
Cypselus ( grc-gre, Κύψελος, ''Kypselos'') was the first tyrant of Corinth in the 7th century BC.
With increased wealth and more complicated trade relations and social structures, Greek city-states tended to overthrow their traditional her ...
and his son Periander
Periander (; el, Περίανδρος; died c. 585 BC) was the Second Tyrant of the Cypselid dynasty that ruled over ancient Corinth. Periander's rule brought about a prosperous time in Corinth's history, as his administrative skill made Corinth o ...
* Aristagoras's failed request for help from Sparta, and successful attempt with Athens
* The burning of Sardis, and Darius's vow for revenge against the Athenians
* Persia's attempts to quell the Ionian revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisf ...
Book VI (Erato)
 * The fleeing of
* The fleeing of Histiaeus
Histiaeus (, died 493 BC), the son of Lysagoras, was a Greek ruler of Miletus in the late 6th century BC. Histiaeus was tyrant of Miletus under Darius I, king of Persia, who had subjugated Miletus and the other Ionian states in Asia Mi ...
to Chios
Chios (; el, Χίος, Chíos , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greek island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea. The island is separated from Turkey by the Chios Strait. Chios is notable for its exports of mast ...
* The training of the Ionia
Ionia () was an ancient region on the western coast of Anatolia, to the south of present-day Izmir. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionia ...
n fleet by Dionysius of Phocaea
Dionysius the Phocaean or Dionysius of Phocaea ( el, Διονύσιος) ( fl. 494 BC) was a Phocaean admiral of ancient Greece during the Persian Wars of 5th century BC, and was the commander of the Ionian fleet at the Battle of Lade in 494 BC. ...
* The abandonment of the Ionian fleet by the Samians
Samos (, also ; el, Σάμος ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the -wide Mycale Strait. It is also a separate ...
during battle
* The defeat of the Ionian fleet by the Persians
* The capture and death of Histiaeus by Harpagus
Harpagus, also known as Harpagos or Hypargus ( Ancient Greek Ἅρπαγος; Akkadian: ''Arbaku''), was a Median general from the 6th century BC, credited by Herodotus as having put Cyrus the Great on the throne through his defection during th ...
* The invasion of Greek lands under Mardonius and enslavement of Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled ...
* The destruction of 300 ships in Mardonius's fleet near Athos
 * The order of Darius that the Greeks provide him earth and water, in which most consent, including
* The order of Darius that the Greeks provide him earth and water, in which most consent, including Aegina
Aegina (; el, Αίγινα, ''Aígina'' ; grc, Αἴγῑνα) is one of the Saronic Islands of Greece in the Saronic Gulf, from Athens. Tradition derives the name from Aegina, the mother of the hero Aeacus, who was born on the island an ...
* The Athenian request for assistance of Cleomenes of Sparta in dealing with the traitors
* The history behind Sparta having two kings and their powers
* The dethronement of Demaratus
Demaratus ( el, Δημάρατος ; Doric: ) was a king of Sparta from around 515 BC to 491 BC. The 15th of the Eurypontid line, he was the first son born to his father, King Ariston.
As king, Demaratus is known chiefly for his opposition t ...
, the other king of Sparta, due to his supposed false lineage
* The arrest of the traitors in Aegina by Cleomenes and the new king Leotychides
Leotychidas II ( grc-gre, Λεωτυχίδας; Doric: ; c. 545 – c. 469 BC) was king of Sparta between 491–476 BC, alongside Cleomenes I and later Leonidas I and Pleistarchus. He led Spartan forces during the Persian Wars from 490 BC to 478 ...
* The suicide of Cleomenes in a fit of madness, possibly caused by his war with Argos, drinking unmixed wine, or his involvement in dethroning Demaratus
* The battle between Aegina and Athens
* The taking of Eretria
Eretria (; el, Ερέτρια, , grc, Ἐρέτρια, , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th centur ...
by the Persians after the Eretrians sent away Athenian help
* Pheidippides
Pheidippides ( grc-gre, Φειδιππίδης, , ; "Son of Pheídippos") or Philippides (Φιλιππίδης) is the central figure in the story that inspired a modern sporting event, the marathon race. Pheidippides is said to have run from ...
's encounter with the god Pan on a journey to Sparta to request aid
* The assistance of the Plataeans
Plataea or Plataia (; grc, Πλάταια), also Plataeae or Plataiai (; grc, Πλαταιαί), was an ancient city, located in Greece in southeastern Boeotia, south of Thebes.Mish, Frederick C., Editor in Chief. “Plataea.” '' Webst ...
, and the history behind their alliance with Athens
* The Athenian win at the Battle of Marathon
The Battle of Marathon took place in 490 BC during the first Persian invasion of Greece. It was fought between the citizens of Athens, aided by Plataea, and a Persian force commanded by Datis and Artaphernes. The battle was the culmination o ...
, led by Miltiades
Miltiades (; grc-gre, Μιλτιάδης; c. 550 – 489 BC), also known as Miltiades the Younger, was a Greek Athenian citizen known mostly for his role in the Battle of Marathon, as well as for his downfall afterwards. He was the son of Cimon ...
and other ''strategoi
''Strategos'', plural ''strategoi'', Latinized ''strategus'', ( el, στρατηγός, pl. στρατηγοί; Doric Greek: στραταγός, ''stratagos''; meaning "army leader") is used in Greek to mean military general. In the Hellenist ...
''This section starts roughly around 6.100
* The Spartans late arrival to assist Athens * The history of the
Alcmaeonidae
The Alcmaeonidae or Alcmaeonids ( grc-gre, Ἀλκμαιωνίδαι ; Attic: ) were a wealthy and powerful noble family of ancient Athens, a branch of the Neleides who claimed descent from the mythological Alcmaeon, the great-grandson of Nes ...
and how they came about their wealth and status
* The death of Miltiades after a failed attack on Paros
Paros (; el, Πάρος; Venetian: ''Paro'') is a Greek island in the central Aegean Sea. One of the Cyclades island group, it lies to the west of Naxos, from which it is separated by a channel about wide. It lies approximately south-east of ...
and the successful taking of Lemnos
Lemnos or Limnos ( el, Λήμνος; grc, Λῆμνος) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within the Lemnos regional unit, which is part of the North Aegean region. The p ...

Book VII (Polymnia)
* The amassing of an army by Darius after learning about the defeat atMarathon
The marathon is a long-distance foot race with a distance of , usually run as a road race, but the distance can be covered on trail routes. The marathon can be completed by running or with a run/walk strategy. There are also wheelchair div ...
()
* The quarrel between Ariabignes
Ariabignes ( peo, Ariyabigna, el, Ἀριαβίγνης) was one of the sons of the Persian king Darius I and his mother was a daughter of Gobryas (). He participated in the Second Persian invasion of Greece, as one of the four admirals of the ...
and Xerxes over which son should succeed Darius in which Xerxes is chosen (-3)
* The death of Darius in 486 BC ()
* The defeat of the Egyptian rebels by Xerxes
* The advice given to Xerxes on invading Greece: Mardonius for invasion, Artabanus against (-10)
 * The dreams of Xerxes in which a phantom frightens him and Artabanus into choosing invasion
* The preparations for war, including building the
* The dreams of Xerxes in which a phantom frightens him and Artabanus into choosing invasion
* The preparations for war, including building the Xerxes Canal
The Xerxes Canal ( el, Διώρυγα του Ξέρξη) was a navigable canal through the base of the Mount Athos peninsula in Chalkidiki, northern Greece, built by king Xerxes I of Persia in the 5th century BC. It is one of the few monuments lef ...
and Xerxes' Pontoon Bridges
Xerxes' Pontoon Bridges were constructed in 480 BC during the second Persian invasion of Greece upon the order of Xerxes I of Persia for the purpose of Xerxes’ army to traverse the Hellespont (the present-day Dardanelles) from Asia into Thra ...
across the Hellespont
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; ...
* The offer by Pythius
Pythius is a Lydian mentioned in book VII of Herodotus' '' Histories'', chh. 27-29 and 38-39. He is the son of Atys, and the grandson of Croesus, the last native king of Lydia before the Persian conquest.
The Persian king Xerxes I, son of Dariu ...
to give Xerxes all his money, in which Xerxes rewards him
* The request by Pythius to allow one son to stay at home, Xerxes's anger, and the march out between the butchered halves of Pythius's sons
* The destruction and rebuilding of the bridges built by the Egyptians
Egyptians ( arz, المَصرِيُون, translit=al-Maṣriyyūn, ; arz, المَصرِيِين, translit=al-Maṣriyyīn, ; cop, ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, remenkhēmi) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian ...
and Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their his ...
ns at Abydos Abydos may refer to:
*Abydos, a progressive metal side project of German singer Andy Kuntz
*Abydos (Hellespont), an ancient city in Mysia, Asia Minor
* Abydos (''Stargate''), name of a fictional planet in the ''Stargate'' science fiction universe ...
* The siding with Persia of many Greek states, including Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thes ...
, Thebes, Melia, and Argos
* The refusal of aid after negotiations by Gelo
Gelon also known as Gelo (Greek: Γέλων ''Gelon'', ''gen.'': Γέλωνος; died 478 BC), son of Deinomenes, was a Greek tyrant of the Sicilian cities Gela and Syracuse, and first of the Deinomenid rulers.
Early life
Gelon was the son o ...
of Syracuse
Syracuse may refer to:
Places Italy
* Syracuse, Sicily, or spelled as ''Siracusa''
* Province of Syracuse
United States
*Syracuse, New York
**East Syracuse, New York
** North Syracuse, New York
* Syracuse, Indiana
*Syracuse, Kansas
*Syracuse, M ...
, and the refusal from Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, ...
* The destruction of 400 Persian ships due to a storm
* The small Greek force (approx. 7,000) led by Leonidas I
Leonidas I (; grc-gre, Λεωνίδας; died 19 September 480 BC) was a king of the Greek city-state of Sparta, and the 17th of the Agiad line, a dynasty which claimed descent from the mythological demigod Heracles. Leonidas I was son of Kin ...
, sent to Thermopylae
Thermopylae (; Ancient Greek and Katharevousa: (''Thermopylai'') , Demotic Greek (Greek): , (''Thermopyles'') ; "hot gates") is a place in Greece where a narrow coastal passage existed in antiquity. It derives its name from its hot sulphur ...
to delay the Persian army (~5,283,220 (Herodotus) )
* The Battle of Thermopylae
The Battle of Thermopylae ( ; grc, Μάχη τῶν Θερμοπυλῶν, label= Greek, ) was fought in 480 BC between the Achaemenid Persian Empire under Xerxes I and an alliance of Greek city-states led by Sparta under Leonidas I. Lastin ...
in which the Greeks hold the pass for 3 days
* The secret pass divulged by Ephialtes of Trachis
Ephialtes (; el, Ἐφιάλτης, ''Ephialtēs''; although Herodotus spelled it as , ''Epialtes'') was the son of Eurydemus ( el, Εὐρύδημος) of Malis. He betrayed his homeland, in hope of receiving some kind of reward from the Persian ...
, which Hydarnes
Hydarnes ( peo, 𐎻𐎡𐎭𐎼𐎴, Vidṛna), also known as Hydarnes the Elder, was a Persian nobleman, who was one of the seven conspirators who overthrew the Pseudo-Smerdis. His name is the Greek transliteration of the Old Persian name ''Vid� ...
uses to lead forces around the mountains to encircle the Greeks
* The retreat of all but the Spartans, Thespians, and Thebans (forced to stay by the Spartans).
* The Greek defeat and order by Xerxes to remove Leonidas's head and attach his torso to a cross
Book VIII (Urania)
* Greek fleet is led byEurybiades
Eurybiades (; grc-gre, Εὐρυβιάδης) was the Spartan navarch in charge of the Greek navy during the Second Persian invasion of Greece (480–479 BC).
Biography
Eurybiades was the son of Eurycleides, and was chosen as commander in 48 ...
, a Spartan commander who led the Greek fleet after the meeting at the Isthmus 481 BC,
* The destruction by storm of two hundred ships sent to block the Greeks from escaping
* The retreat of the Greek fleet after word of a defeat at Thermopylae
Thermopylae (; Ancient Greek and Katharevousa: (''Thermopylai'') , Demotic Greek (Greek): , (''Thermopyles'') ; "hot gates") is a place in Greece where a narrow coastal passage existed in antiquity. It derives its name from its hot sulphur ...
* The supernatural rescue of Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), in ancient times was a sacred precinct that served as the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient classical world. The orac ...
from a Persian attack
* The evacuation of Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
assisted by the fleet
* The reinforcement of the Greek fleet at Salamis Island
Salamis ( ; el, Σαλαμίνα, Salamína; grc, label= Ancient and Katharevousa, Σαλαμίς, Salamís) is the largest Greek island in the Saronic Gulf, about off-coast from Piraeus and about west of central Athens. The chief city, S ...
, bringing the total ships to 378
* The destruction of Athens by the Persian land force after difficulties with those who remained
* The Battle of Salamis
The Battle of Salamis ( ) was a naval battle fought between an alliance of Greek city-states under Themistocles and the Persian Empire under King Xerxes in 480 BC. It resulted in a decisive victory for the outnumbered Greeks. The battle was ...
, the Greeks have the advantage due to better organization, and fewer losses due to ability to swim
* The description of the Angarum, the Persian riding post
* The rise in favor of Artemisia, the Persian woman commander, and her council to Xerxes in favor of returning to Persia
 * The vengeance of Hermotimus, Xerxes' chief
* The vengeance of Hermotimus, Xerxes' chief eunuch
A eunuch ( ) is a male who has been castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function.
The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2nd millenni ...
, against Panionius
* The attack on Andros
Andros ( el, Άνδρος, ) is the northernmost island of the Greek Cyclades archipelago, about southeast of Euboea, and about north of Tinos. It is nearly long, and its greatest breadth is . It is for the most part mountainous, with many ...
by Themistocles
Themistocles (; grc-gre, Θεμιστοκλῆς; c. 524–459 BC) was an Athenian politician and general. He was one of a new breed of non-aristocratic politicians who rose to prominence in the early years of the Athenian democracy. As ...
, the Athenian fleet commander and most valiant Greek at Salamis
* The escape of Xerxes and leaving behind of 300,000 picked troops under Mardonius in Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thes ...
* The ancestry of Alexander I of Macedon
Alexander I of Macedon ( el, Ἀλέξανδρος ὁ Μακεδών), known with the title Philhellene (Greek: φιλέλλην, literally "fond/lover of the Greeks", and in this context "Greek patriot"), was the ruler of the ancient Kingdom of ...
, including Perdiccas
Perdiccas ( el, Περδίκκας, ''Perdikkas''; 355 BC – 321/320 BC) was a general of Alexander the Great. He took part in the Macedonian campaign against the Achaemenid Empire, and, following Alexander's death in 323 BC, rose to becom ...
* The refusal of an attempt by Alexander to seek a Persian alliance with Athens
Book IX (Calliope)
* The second taking of an evacuatedAthens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
* The evacuation to Thebes by Mardonius after the sending of Lacedaemonian
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
troops
* The slaying of Masistius
Masistius (Macistius to the Greeks) was a Persian cavalry commander best known for his role in the second Persian invasion of Greece.
Biography
Masistius was the son of a man named Siromitras. He was reportedly a very tall and handsome man. He be ...
, leader of the Persian cavalry, by the Athenians
* The warning from Alexander
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
to the Greeks of an impending attack
* The death of Mardonius by Aeimnestus
Aeimnestus ( grc, Ἀείμνηστος) is an Ancient Greek word, also spelled and that means "unforgettable", literally "of everlasting memory". It was the name of multiple revered Greek warriors.
A Spartan soldier Aeimnestus killed the Pers ...
* The Persian retreat to Thebes where they are afterwards slaughtered (Battle of Plataea
The Battle of Plataea was the final land battle during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place in 479 BC near the city of Plataea in Boeotia, and was fought between an alliance of the Greek city-states (including Sparta, Athens, ...
)
* The description and dividing of the spoils
* The speedy escape of Artabazus into Asia.
* The Persian defeat in Ionia
Ionia () was an ancient region on the western coast of Anatolia, to the south of present-day Izmir. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionia ...
by the Greek fleet (Battle of Mycale
The Battle of Mycale ( grc, Μάχη τῆς Μυκάλης; ''Machē tēs Mykalēs'') was one of the two major battles (the other being the Battle of Plataea) that ended the second Persian invasion of Greece during the Greco-Persian Wars. It ...
), and the Ionian revolt
* The mutilation of the wife of Masistes
Masistes (Old Persian 𐎶𐎰𐎡𐏁𐎫, ''Maθišta''; Greek Μασίστης, ''Masístēs''; Old Iranian *''Masišta'') (?- c. 478 BC) was a Persian prince of the Achaemenid Dynasty, son of king Darius I (reign: 520-486 BC) and of his wi ...
ordered by Amestris
Amestris ( el, Άμηστρις, ''Amēstris'', perhaps the same as Άμαστρις, ''Amāstris'', from Old Persian ''Amāstrī-'', "strong woman"; died c. 424 BC) was a Persian queen, the wife of Xerxes I of Persia, mother of Achaemenid King ...
, wife of Xerxes
* The death of Masistes after his intent to rebel
* The Athenian blockade of Sestos
Sestos ( el, Σηστός, la, Sestus) was an ancient city in Thrace. It was located at the Thracian Chersonese peninsula on the European coast of the Hellespont, opposite the ancient city of Abydos, and near the town of Eceabat in Turkey.
In ...
and the capture of Artayctes
Artaÿctes is a historical figure described in Herodotus' '' The Histories''. Artayctes, the son of Cherasmis, was a Persian general who commanded the Macrones and Mossynoeci forces in the army of Xerxes during the second Persian invasion of Gr ...
* The Persians' abortive suggestion to Cyrus to migrate from rocky Persis
Style
In his introduction to Hecataeus' work, ''Genealogies
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kins ...
'':
 This points forward to the "folksy" yet "international" outlook typical of Herodotus. However, one modern scholar has described the work of Hecataeus as "a curious false start to history," since despite his critical spirit, he failed to liberate history from myth. Herodotus mentions Hecataeus in his ''Histories'', on one occasion mocking him for his naive genealogy and, on another occasion, quoting Athenian complaints against his handling of their national history. It is possible that Herodotus borrowed much material from Hecataeus, as stated by Porphyry in a quote recorded by
This points forward to the "folksy" yet "international" outlook typical of Herodotus. However, one modern scholar has described the work of Hecataeus as "a curious false start to history," since despite his critical spirit, he failed to liberate history from myth. Herodotus mentions Hecataeus in his ''Histories'', on one occasion mocking him for his naive genealogy and, on another occasion, quoting Athenian complaints against his handling of their national history. It is possible that Herodotus borrowed much material from Hecataeus, as stated by Porphyry in a quote recorded by Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος ; 260/265 – 30 May 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilus (from the grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος τοῦ Παμφίλου), was a Greek historian of Christianity, exegete, and Chris ...
. In particular, it is possible that he copied descriptions of the crocodile
Crocodiles (family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term crocodile is sometimes used even more loosely to include all extant me ...
, hippopotamus
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two exta ...
, and phoenix
Phoenix most often refers to:
* Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore
* Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States
Phoenix may also refer to:
Mythology
Greek mythological figures
* Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ...
from Hecataeus's ''Circumnavigation of the Known World'' (''Periegesis'' / ''Periodos ges''), even misrepresenting the source as "Heliopolitans" (''Histories'' 2.73).
But Hecataeus did not record events that had occurred in living memory, unlike Herodotus, nor did he include the oral traditions of Greek history within the larger framework of oriental history. There is no proof that Herodotus derived the ambitious scope of his own work, with its grand theme of civilizations in conflict, from any predecessor, despite much scholarly speculation about this in modern times. Herodotus claims to be better informed than his predecessors by relying on empirical observation to correct their excessive schematism. For example, he argues for continental asymmetry as opposed to the older theory of a perfectly circular earth with Europe and Asia/Africa equal in size (''Histories'' 4.36 and 4.42). However, he retains idealizing tendencies, as in his symmetrical notions of the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
and Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
.
His debt to previous authors of prose "histories" might be questionable, but there is no doubt that Herodotus owed much to the example and inspiration of poets and story-tellers. For example, Athenian tragic poets provided him with a world-view of a balance between conflicting forces, upset by the hubris
Hubris (; ), or less frequently hybris (), describes a personality quality of extreme or excessive pride or dangerous overconfidence, often in combination with (or synonymous with) arrogance. The term ''arrogance'' comes from the Latin ', mean ...
of kings, and they provided his narrative with a model of episodic structure. His familiarity with Athenian tragedy is demonstrated in a number of passages echoing Aeschylus
Aeschylus (, ; grc-gre, Αἰσχύλος ; c. 525/524 – c. 456/455 BC) was an ancient Greek tragedian, and is often described as the father of tragedy. Academic knowledge of the genre begins with his work, and understanding of earlier Gree ...
's ''Persae
''The Persians'' ( grc, Πέρσαι, ''Persai'', Latinised as ''Persae'') is an ancient Greek tragedy written during the Classical period of Ancient Greece by the Greek tragedian Aeschylus. It is the second and only surviving part of a now othe ...
'', including the epigrammatic observation that the defeat of the Persian navy at Salamis caused the defeat of the land army (''Histories'' 8.68 ~ ''Persae'' 728). The debt may have been repaid by Sophocles because there appear to be echoes of ''The Histories'' in his plays, especially a passage in ''Antigone
In Greek mythology, Antigone ( ; Ancient Greek: Ἀντιγόνη) is the daughter of Oedipus and either his mother Jocasta or, in another variation of the myth, Euryganeia. She is a sister of Polynices, Eteocles, and Ismene.Roman, L., ...
'' that resembles Herodotus's account of the death of Intaphernes (''Histories'' 3.119 ~ ''Antigone'' 904–920). However, this point is one of the most contentious issues in modern scholarship.
Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
was another inspirational source. Just as Homer drew extensively on a tradition of oral poetry, sung by wandering minstrels, so Herodotus appears to have drawn on an Ionian tradition of story-telling, collecting and interpreting the oral histories he chanced upon in his travels. These oral histories often contained folk-tale motifs and demonstrated a moral, yet they also contained substantial facts relating to geography, anthropology, and history, all compiled by Herodotus in an entertaining style and format.
Mode of explanation
Herodotus writes with the purpose of explaining; that is, he discusses the reason for or cause of an event. He lays this out in the preamble: "This is the publication of the research of Herodotus of Halicarnassus, so that the actions of people shall not fade with time, so that the great and admirable achievements of both Greeks and barbarians shall not go unrenowned, and, among other things, ''to set forth the reasons why they waged war on each other''." This mode of explanation traces itself all the way back to Homer, who opened the ''Iliad'' by asking: :''Which of the immortals set these two at each other's throats?'' :''Zeus' son and Leto's, offended'' :''by the warlord. Agamemnon had dishonored'' :''Chryses, Apollo's priest, so the god'' :''struck the Greek camp with plague,'' :''and the soldiers were dying of it.'' Both Homer and Herodotus begin with a question of causality. In Homer's case, "who set these two at each other's throats?" In Herodotus's case, "Why did the Greeks and barbarians go to war with each other?" Herodotus's means of explanation does not necessarily posit a simple cause; rather, his explanations cover a host of potential causes and emotions. It is notable, however, that "the obligations of gratitude and revenge are the fundamental human motives for Herodotus, just as ... they are the primary stimulus to the generation of narrative itself." Some readers of Herodotus believe that his habit of tying events back to personal motives signifies an inability to see broader and more abstract reasons for action.Gould
Gould may refer to:
People
* Gould (name), a surname
Places United States
* Gould, Arkansas, a city
* Gould, Colorado, an unincorporated community
* Gould, Ohio, an unincorporated community
* Gould, Oklahoma, a town
* Gould, West Virginia, ...
argues to the contrary that this is likely because Herodotus attempts to provide the rational reasons, as understood by his contemporaries, rather than providing more abstract reasons.
Types of causality
Herodotus attributes cause to both divine and human agents. These are not perceived as mutually exclusive, but rather mutually interconnected. This is true of Greek thinking in general, at least fromHomer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
onward. Gould notes that invoking the supernatural in order to explain an event does not answer the question "why did this happen?" but rather "why did this happen to me?" By way of example, faulty craftsmanship is the human cause for a house collapsing. However, divine will is the reason that the house collapses at the particular moment when I am inside. It was the will of the gods that the house collapsed while a particular individual was within it, whereas it was the cause of man that the house had a weak structure and was prone to falling.
Some authors, including Geoffrey de Ste-Croix
Geoffrey Ernest Maurice de Ste. Croix, (; 8 February 1910 – 5 February 2000), known informally as Croicks, was a British historian who specialised in examining Ancient Greece from a Marxist perspective. He was Fellow and Tutor in Ancient Hist ...
and Mabel Lang
Mabel Louise Lang (November 12, 1917 – July 21, 2010) was an American archaeologist and scholar of Classical Greek and Mycenaean culture.
Biography
Lang took her first degree at Cornell University in 1939 and was awarded her PhD at Bryn M ...
, have argued that Fate, or the belief that "this is how it had to be," is Herodotus's ultimate understanding of causality. Herodotus's explanation that an event "was going to happen" maps well on to Aristotelean and Homeric means of expression. The idea of "it was going to happen" reveals a "tragic discovery" associated with fifth-century drama. This tragic discovery can be seen in Homer's ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Ody ...
'' as well.
John Gould argues that Herodotus should be understood as falling in a long line of story-tellers, rather than thinking of his means of explanation as a "philosophy of history" or "simple causality." Thus, according to Gould, Herodotus's means of explanation is a mode of story-telling and narration that has been passed down from generations prior:
Reliability
 The accuracy of the works of Herodotus has been controversial since his own era. Kenton L. Sparks writes, "In antiquity, Herodotus had acquired the reputation of being unreliable, biased, parsimonious in his praise of heroes, and mendacious". The historian
The accuracy of the works of Herodotus has been controversial since his own era. Kenton L. Sparks writes, "In antiquity, Herodotus had acquired the reputation of being unreliable, biased, parsimonious in his praise of heroes, and mendacious". The historian Duris of Samos
Duris of Samos (or Douris) ( grc-gre, Δοῦρις ὁ Σάμιος; BCafter 281BC) was a Greek historian and was at some period tyrant of Samos. Duris was the author of a narrative history of events in Greece and Macedonia from 371BC to 281BC ...
called Herodotus a "myth-monger". Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
(''On the Laws'' I.5) said that his works were full of legends or "fables". The controversy was also commented on by Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ...
, Flavius Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
and Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for hi ...
. The Alexandrian grammarian Harpocration
__NOTOC__
Valerius Harpocration ( grc-gre, Οὐαλέριος or , ''gen''. Ἁρποκρατίωνος) was a Greek grammarian of Alexandria, probably working in the 2nd century AD. He is possibly the Harpocration mentioned by Julius Capitolinus ...
wrote a whole book on "the lies of Herodotus". Lucian
Lucian of Samosata, '; la, Lucianus Samosatensis ( 125 – after 180) was a Hellenized Syrian satirist, rhetorician and pamphleteer who is best known for his characteristic tongue-in-cheek style, with which he frequently ridiculed supersti ...
of Samosata went as far as to deny the "father of history" a place among the famous on the Island of the Blessed in his ''Verae Historiae''.
The works of Thucydides
Thucydides (; grc, , }; BC) was an Athenian historian and general. His '' History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of " scienti ...
were often given preference for their "truthfulness and reliability", even if Thucydides basically continued on foundations laid by Herodotus, as in his treatment of the Persian Wars. In spite of these lines of criticism, Herodotus' works were in general kept in high esteem and regarded as reliable by many. Many scholars, ancient and modern (such as Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
, A. H. L. Heeren
Arnold Hermann Ludwig Heeren (25 October 1760, Arbergen6 March 1842, Göttingen) was a German historian. He was a member of the Göttingen School of History.
Biography
Heeren was born on 25 October 1760 in Arbergen near Bremen, a small village ...
, etc.), routinely cited Herodotus.
To this day, some scholars regard his works as being at least partly unreliable. Detlev Fehling writes of "a problem recognized by everybody", namely that Herodotus frequently cannot be taken at face value. Fehling argues that Herodotus exaggerated the extent of his travels and invented his sources. For Fehling, the sources of many stories, as reported by Herodotus, do not appear credible in themselves. Persian and Egyptian informants tell stories that dovetail neatly into Greek myths and literature, yet show no signs of knowing their own traditions. For Fehling, the only credible explanation is that Herodotus invented these sources, and that the stories themselves were concocted by Herodotus himself.
Like many ancient historians, Herodotus preferred an element of show to purely analytic history, aiming to give pleasure with "exciting events, great dramas, bizarre exotica." As such, certain passages have been the subject of controversy and even some doubt, both in antiquity and today.
Despite the controversy, Herodotus has long served and still serves as the primary, often only, source for events in the Greek world, Persian Empire, and the broader region in the two centuries leading up to his own days. So even if the ''Histories'' were criticized in some regards since antiquity, modern historians and philosophers generally take a more positive view as to their source and epistemologic
Epistemology (; ), or the theory of knowledge, is the branch of philosophy concerned with knowledge. Epistemology is considered a major subfield of philosophy, along with other major subfields such as ethics, logic, and metaphysics.
Episte ...
value. Herodotus is variously considered "father of comparative anthropology," "the father of ethnography," and "more modern than any other ancient historian in his approach to the ideal of total history."
Discoveries made since the end of the 19th century have generally added to Herodotus' credibility. He described Gelonus, located in Scythia
Scythia ( Scythian: ; Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) or Scythica (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Pontic Scythia, was a kingdom created by the Scythians during the 6th to 3rd centuries BC in the Pontic–Caspian steppe.
...
, as a city thousands of times larger than Troy
Troy ( el, Τροία and Latin: Troia, Hittite: 𒋫𒊒𒄿𒊭 ''Truwiša'') or Ilion ( el, Ίλιον and Latin: Ilium, Hittite: 𒃾𒇻𒊭 ''Wiluša'') was an ancient city located at Hisarlik in present-day Turkey, south-west of Ç ...
; this was widely disbelieved until it was rediscovered in 1975. The archaeological study of the now-submerged ancient Egyptian city of Heracleion
Heracleion (Ancient Greek: ), also known by its Egyptian name Thonis ( Ancient Egyptian: ; cop, Ⲧϩⲱⲛⲓ , ; Ancient Greek: ) and sometimes called Thonis-Heracleion, was an ancient Egyptian port city located near the Canopic Mouth o ...
and the recovery of the so-called "Naucratis stela" give credibility to Herodotus's previously unsupported claim that Heracleion was founded during the Egyptian New Kingdom
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator ...
.
Babylon
Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
. The absence of any mention of the Hanging Gardens of Babylon
The Hanging Gardens of Babylon were one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World listed by Hellenic culture. They were described as a remarkable feat of engineering with an ascending series of tiered gardens containing a wide variety of tre ...
in his work has attracted further attacks on his credibility. In response, Dalley has proposed that the Hanging Gardens may have been in Nineveh
Nineveh (; akk, ; Biblical Hebrew: '; ar, نَيْنَوَىٰ '; syr, ܢܝܼܢܘܹܐ, Nīnwē) was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul in northern Iraq. It is located on the eastern ba ...
rather than in Babylon.
Egypt
The reliability of Herodotus's writing about Egypt is sometimes questioned. Alan B. Lloyd argues that, as a historical document, the writings of Herodotus are seriously defective, and that he was working from "inadequate sources." Nielsen writes: "Though we cannot entirely rule out the possibility of Herodotus having been in Egypt, it must be said that his narrative bears little witness to it." German historian Detlev Fehling questions whether Herodotus ever traveled up the Nile River, and considers doubtful almost everything that he says about Egypt and Ethiopia. Fehling states that "there is not the slightest bit of history behind the whole story" about the claim of Herodotus that Pharaoh Sesostris campaigned in Europe, and that he left a colony in Colchia. Fehling concludes that the works of Herodotus are intended as fiction. Boedeker concurs that much of the content of the works of Herodotus are literary devices. However, a recent discovery of a baris (described in ''The Histories'') during an excavation of the sunken Egyptian port city of Thonis-Heracleion lends credence to Herodotus's travels and storytelling. Herodotus' contribution to the history and ethnography of ancient Egypt and Africa was especially valued by various historians of the field (such asConstantin François de Chassebœuf, comte de Volney
Constantin François de Chassebœuf, comte de Volney (3 February 175725 April 1820) was a French philosopher, abolitionist, writer, orientalist, and politician. He was at first surnamed ''Boisgirais'' after his father's estate, but afterwards a ...
, W. E. B. Du Bois
William Edward Burghardt Du Bois ( ; February 23, 1868 – August 27, 1963) was an American-Ghanaian sociologist, socialist, historian, and Pan-Africanist civil rights activist. Born in Great Barrington, Massachusetts, Du Bois grew up i ...
, Pierre Montet
Jean Pierre Marie Montet (27 June 1885 – 19 June 1966) was a French Egyptologist.
Biography
Montet was born in Villefranche-sur-Saône, Rhône, and began his studies under Victor Loret at the University of Lyon.
He excavated at Byblos ...
, Martin Bernal
Martin Gardiner Bernal (; 10 March 1937 – 9 June 2013)
was a British scholar of modern Chinese political history. He was a Professor of Government and Near Eastern Studies at Cornell University. He is best known for his work '' Black Athena'', ...
, Basil Davidson
Basil Risbridger Davidson (9 November 1914 – 9 July 2010) was a British journalist and historian who wrote more than 30 books on African history and politics. According to two modern writers, "Davidson, a campaigning journalist whose fi ...
, Derek A. Welsby, Henry T. Aubin). Many scholars explicitly mention the reliability of Herodotus's work (such as on the Nile Valley
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
) and demonstrate corroboration of Herodotus' writings by modern scholars. A. H. L. Heeren quoted Herodotus throughout his work and provided corroboration by scholars regarding several passages (source of the Nile, location of Meroë
Meroë (; also spelled ''Meroe''; Meroitic: or ; ar, مرواه, translit=Meruwah and ar, مروي, translit=Meruwi, label=none; grc, Μερόη, translit=Meróē) was an ancient city on the east bank of the Nile about 6 km north-east ...
, etc.).
Cheikh Anta Diop provides several examples (like the inundations of the Nile) which, he argues, support his view that Herodotus was "quite scrupulous, objective, scientific for his time." Diop argues that Herodotus "always distinguishes carefully between what he has seen and what he has been told." Diop also notes that Strabo corroborated Herodotus' ideas about the Black Egyptians, Ethiopians, and Colchians. Martin Bernal
Martin Gardiner Bernal (; 10 March 1937 – 9 June 2013)
was a British scholar of modern Chinese political history. He was a Professor of Government and Near Eastern Studies at Cornell University. He is best known for his work '' Black Athena'', ...
has relied on Herodotus "to an extraordinary degree" in his controversial book ''Black Athena
''Black Athena: The Afroasiatic Roots of Classical Civilization'', its three volumes first published in 1987, 1991, and 2006 respectively, is a controversial book by Martin Bernal proposing an alternative hypothesis on the origins of ancient Gre ...
''.
British egyptologist Derek A. Welsby said that "archaeology graphically confirms Herodotus's observations." To further his work on the Egyptians and Assyrians, historian and fiction writer Henry T. Aubin used Herodotus' accounts in various passages. For Aubin, Herodotus was "the author of the first important narrative history of the world."
Scientific reasoning
; On geography Herodotus provides much information about the nature of the world and the status of science during his lifetime, often engaging in private speculation likewise. For example, he reports that the annual flooding of theNile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
was said to be the result of melting snows far to the south, and he comments that he cannot understand how there can be snow in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, the hottest part of the known world, offering an elaborate explanation based on the way that desert winds affect the passage of the Sun over this part of the world (2:18ff). He also passes on reports from Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their his ...
n sailors that, while circumnavigating Africa, they "saw the sun on the right side while sailing westwards", although, being unaware of the existence of the southern hemisphere, he says that he does not believe the claim. Owing to this brief mention, which is included almost as an afterthought, it has been argued that Africa was circumnavigated by ancient seafarers, for this is precisely where the sun ought to have been. His accounts of India are among the oldest records of Indian civilization by an outsider.
; On biology
 After journeys to India and Pakistan, French ethnologist
After journeys to India and Pakistan, French ethnologist Michel Peissel
Michel Georges Francois Peissel (February 11, 1937 – October 7, 2011) was a French ethnologist, explorer and author. He wrote twenty books mostly on his Himalayan and Tibetan expeditions. Peissel was an emeritus member of the Explorers Club a ...
claimed to have discovered an animal species that may illuminate one of the most bizarre passages in the ''Histories''. In Book 3, passages 102 to 105, Herodotus reports that a species of fox-sized, furry "ant
Ants are eusocial insects of the family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cretaceous period. More than 13,800 of an estimated total of ...
s" lives in one of the far eastern, Indian provinces of the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
. This region, he reports, is a sandy desert, and the sand there contains a wealth of fine gold dust. These giant ants, according to Herodotus, would often unearth the gold dust when digging their mounds and tunnels, and the people living in this province would then collect the precious dust. Later Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
would mention this story in the gold mining
Gold mining is the extraction of gold resources by mining. Historically, mining gold from alluvial deposits used manual separation processes, such as gold panning. However, with the expansion of gold mining to ores that are not on the surface, ...
section of his ''Naturalis Historia
The ''Natural History'' ( la, Naturalis historia) is a work by Pliny the Elder. The largest single work to have survived from the Roman Empire to the modern day, the ''Natural History'' compiles information gleaned from other ancient authors. ...
''.
 Peissel reports that, in an isolated region of northern Pakistan on the Deosai Plateau in
Peissel reports that, in an isolated region of northern Pakistan on the Deosai Plateau in Gilgit–Baltistan
Gilgit-Baltistan (; ), formerly known as the Northern Areas, is a region administered by Pakistan as an administrative territory, and constituting the northern portion of the larger Kashmir region which has been the subject of a dispute bet ...
province, there is a species of marmot
Marmots are large ground squirrels in the genus ''Marmota'', with 15 species living in Asia, Europe, and North America. These herbivores are active during the summer, when they can often be found in groups, but are not seen during the winter, ...
– the Himalayan marmot, a type of burrowing squirrel
Squirrels are members of the family Sciuridae, a family that includes small or medium-size rodents. The squirrel family includes tree squirrels, ground squirrels (including chipmunks and prairie dogs, among others), and flying squirrels. ...
– that may have been what Herodotus called giant ants. The ground of the Deosai Plateau is rich in gold dust, much like the province that Herodotus describes. According to Peissel, he interviewed the Minaro tribal people who live in the Deosai Plateau, and they have confirmed that they have, for generations, been collecting the gold dust that the marmots bring to the surface when they are digging their burrows.
Peissel offers the theory that Herodotus may have confused the old Persian word for "marmot" with the word for "mountain ant." Research suggests that Herodotus probably did not know any Persian (or any other language except his native Greek) and was forced to rely on many local translators when travelling in the vast multilingual Persian Empire. Herodotus did not claim to have personally seen the creatures which he described. Herodotus did, though, follow up in passage 105 of Book 3 with the claim that the "ants" are said to chase and devour full-grown camels.
Accusations of bias
Some "calumnious fictions" were written about Herodotus in a work titled ''On the Malice of Herodotus
"On the Malice of Herodotus" or "On the Malignity of Herodotus" ( grc-gre, Περὶ τῆς Ἡροδότου κακοηθείας) is an essay by Plutarch criticizing the historian Herodotus for all manner of prejudice and misrepresentation in ...
'' by Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for hi ...
, a Chaeronea
Chaeronea (English: or ; el, Χαιρώνεια , ) is a village and a former municipality in Boeotia, Greece, located about 35 kilometers east of Delphi. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Livadeia, of which ...
n by birth, (or it might have been a Pseudo-Plutarch Pseudo-Plutarch is the conventional name given to the actual, but unknown, authors of a number of pseudepigrapha (falsely attributed works) attributed to Plutarch but now known to have not been written by him.
Some of these works were included in s ...
, in this case "a great collector of slanders"), including the allegation that the historian was prejudiced against Thebes because the authorities there had denied him permission to set up a school. Similarly, in a ''Corinthian Oration'', Dio Chrysostom
Dio Chrysostom (; el, Δίων Χρυσόστομος ''Dion Chrysostomos''), Dion of Prusa or Cocceianus Dio (c. 40 – c. 115 AD), was a Greek orator, writer, philosopher and historian of the Roman Empire in the 1st century AD. Eighty of hi ...
(or yet another pseudonymous author) accused the historian of prejudice against Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part ...
, sourcing it in personal bitterness over financial disappointments – an account also given by Marcellinus in his ''Life of Thucydides''. In fact, Herodotus was in the habit of seeking out information from empowered sources within communities, such as aristocrats and priests, and this also occurred at an international level, with Periclean Athens becoming his principal source of information about events in Greece. As a result, his reports about Greek events are often coloured by Athenian bias against rival states – Thebes and Corinth in particular.
Use of sources and sense of authority
 It is clear from the beginning of Book 1 of the ''Histories'' that Herodotus utilizes (or at least claims to utilize) various sources in his narrative. K. H. Waters relates that "Herodotos did not work from a purely Hellenic standpoint; he was accused by the patriotic but somewhat imperceptive Plutarch of being ''philobarbaros'', a pro-barbarian or pro-foreigner."
Herodotus at times relates various accounts of the same story. For example, in Book 1 he mentions both the Phoenician and the Persian accounts of Io. However, Herodotus at times arbitrates between varying accounts: "I am not going to say that these events happened one way or the other. Rather, I will point out the man ''who I know for a fact'' began the wrong-doing against the Greeks." Again, later, Herodotus claims himself as an authority: "I know this is how it happened because I heard it from the Delphians myself."
Throughout his work, Herodotus attempts to explain the actions of people. Speaking about Solon the Athenian, Herodotus states " olonsailed away on the pretext of seeing the world, ''but it was really so that he could not be compelled to repeal any of the laws he had laid down''." Again, in the story about Croesus and his son's death, when speaking of Adrastus (the man who accidentally killed Croesus' son), Herodotus states: "Adrastus ... ''believing himself to be the most ill-fated man he had ever known'', cut his own throat over the grave."
It is clear from the beginning of Book 1 of the ''Histories'' that Herodotus utilizes (or at least claims to utilize) various sources in his narrative. K. H. Waters relates that "Herodotos did not work from a purely Hellenic standpoint; he was accused by the patriotic but somewhat imperceptive Plutarch of being ''philobarbaros'', a pro-barbarian or pro-foreigner."
Herodotus at times relates various accounts of the same story. For example, in Book 1 he mentions both the Phoenician and the Persian accounts of Io. However, Herodotus at times arbitrates between varying accounts: "I am not going to say that these events happened one way or the other. Rather, I will point out the man ''who I know for a fact'' began the wrong-doing against the Greeks." Again, later, Herodotus claims himself as an authority: "I know this is how it happened because I heard it from the Delphians myself."
Throughout his work, Herodotus attempts to explain the actions of people. Speaking about Solon the Athenian, Herodotus states " olonsailed away on the pretext of seeing the world, ''but it was really so that he could not be compelled to repeal any of the laws he had laid down''." Again, in the story about Croesus and his son's death, when speaking of Adrastus (the man who accidentally killed Croesus' son), Herodotus states: "Adrastus ... ''believing himself to be the most ill-fated man he had ever known'', cut his own throat over the grave."
Herodotus and myth
Although Herodotus considered his "inquiries" a serious pursuit of knowledge, he was not above relating entertaining tales derived from the collective body of myth, but he did so judiciously with regard for hishistorical method
Historical method is the collection of techniques and guidelines that historians use to research and write histories of the past. Secondary sources, primary sources and material evidence such as that derived from archaeology may all be draw ...
, by corroborating the stories through enquiry and testing their probability. While the gods never make personal appearances in his account of human events, Herodotus states emphatically that "many things prove to me that the gods take part in the affairs of man" (IX, 100).
In Book One, passages 23 and 24, Herodotus relates the story of Arion
Arion (; grc-gre, Ἀρίων; fl. c. 700 BC) was a kitharode in ancient Greece, a Dionysiac poet credited with inventing the dithyramb. The islanders of Lesbos claimed him as their native son, but Arion found a patron in Periander, tyrant ...
, the renowned harp player, "second to no man living at that time," who was saved by a dolphin. Herodotus prefaces the story by noting that "a very wonderful thing is said to have happened," and alleges its veracity by adding that the "Corinthians and the Lesbians agree in their account of the matter." Having become very rich while at the court of Periander, Arion conceived a desire to sail to Italy and Sicily. He hired a vessel crewed by Corinthians, whom he felt he could trust, but the sailors plotted to throw him overboard and seize his wealth. Arion discovered the plot and begged for his life, but the crew gave him two options: that either he kill himself on the spot or jump ship and fend for himself in the sea. Arion flung himself into the water, and a dolphin carried him to shore.
Herodotus clearly writes as both historian and teller of tales. Herodotus takes a fluid position between the artistic story-weaving of Homer and the rational data-accounting of later historians. John Herington has developed a helpful metaphor for describing Herodotus's dynamic position in the history of Western art and thought – Herodotus as centaur:
Herodotus is neither a mere gatherer of data nor a simple teller of tales – he is both. While Herodotus is certainly concerned with giving accurate accounts of events, this does not preclude for him the insertion of powerful mythological elements into his narrative, elements which will aid him in expressing the truth of matters under his study. Thus to understand what Herodotus is doing in the ''Histories'', we must not impose strict demarcations between the man as mythologist and the man as historian, or between the work as myth and the work as history. As James Romm has written, Herodotus worked under a common ancient Greek cultural assumption that the way events are remembered and retold (e.g. in myths or legends) produces a valid kind of understanding, even when this retelling is not entirely factual. For Herodotus, then, it takes both myth and history to produce truthful understanding.
Legacy
On the legacy of ''The Histories'' ofHerodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
, historian Barry S. Strauss writes:
In popular culture
Historical novels sourcing material from HerodotusCritical editions
Translations
Manuscripts
* Papyrus Oxyrhynchus 18 * Papyrus Oxyrhynchus 19 * Papyrus Oxyrhynchus 2099, early 2nd century CE – fragment of Book VIIISee also
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* — Complete online text * — Searchable textfile * — Complete online text * * * * *Direct link to PDF
{{DEFAULTSORT:Histories Of Herodotus, The 5th-century BC history books Books about civilizations Herodotus, Greco-Roman ethnography Texts in Ionic Greek History books about the Greco-Persian Wars