The Constitution of the United Kingdom on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The constitution of the United Kingdom or British constitution comprises the written and unwritten arrangements that establish the
The constitution of the United Kingdom or British constitution comprises the written and unwritten arrangements that establish the
 Although the British constitution is not codified, the Supreme Court recognises constitutional principles, and constitutional statutes, which shape the use of political power. The main sources of constitutional law are Acts of Parliament, court cases, and conventions in the way that government, Parliament and the monarch act. There are at least four main constitutional principles recognised by the courts. First,
Although the British constitution is not codified, the Supreme Court recognises constitutional principles, and constitutional statutes, which shape the use of political power. The main sources of constitutional law are Acts of Parliament, court cases, and conventions in the way that government, Parliament and the monarch act. There are at least four main constitutional principles recognised by the courts. First,
 In recent history, Parliament's sovereignty has evolved in four main ways. First, since 1945 international cooperation meant Parliament augmented its power by working with, not dominating, other sovereign nations. The
In recent history, Parliament's sovereignty has evolved in four main ways. First, since 1945 international cooperation meant Parliament augmented its power by working with, not dominating, other sovereign nations. The  Third, the UK became a member of the
Third, the UK became a member of the
19 September 1946
.e.g. "Speech to the 69th Annual Conservative Party Conference at Llandudno"
9 October 1948
. See J. Danzig, "Winston Churchill: A founder of the European Union" (10 November 2013
EU ROPE
/ref>
 The rule of law requires the law is truly enforced, though enforcement bodies may have room for discretion. In '' R (Corner House Research) v Director of the Serious Fraud Office'', a group campaigning against the arms trade, Corner House Research, claimed the Serious Fraud Office acted unlawfully by dropping an investigation into the UK–Saudi
The rule of law requires the law is truly enforced, though enforcement bodies may have room for discretion. In '' R (Corner House Research) v Director of the Serious Fraud Office'', a group campaigning against the arms trade, Corner House Research, claimed the Serious Fraud Office acted unlawfully by dropping an investigation into the UK–Saudi
 The principle of a "democratic society", with a functioning representative and
The principle of a "democratic society", with a functioning representative and
 Since the World Wars brought an end to the
Since the World Wars brought an end to the
 While principles may be the basis of the UK constitution, the institutions of the state perform its functions in practice. First,
While principles may be the basis of the UK constitution, the institutions of the state perform its functions in practice. First,
 Today, the
Today, the  Along with a hereditary monarch, the
Along with a hereditary monarch, the
 The independence of the judiciary is one of the cornerstones of the constitution, and means in practice that judges cannot be dismissed from office. Since the Act of Settlement 1700, no judge has been removed, as to do so the King must act on address by both Houses of Parliament. It is very likely that a judge would never be dismissed, not merely because of formal rules but a "shared constitutional understanding" of the importance of the integrity of the legal system. This is reflected, for example, in the ''sub judice'' rule that matters awaiting decision in court should not be prejudged in a Parliamentary debate. The
The independence of the judiciary is one of the cornerstones of the constitution, and means in practice that judges cannot be dismissed from office. Since the Act of Settlement 1700, no judge has been removed, as to do so the King must act on address by both Houses of Parliament. It is very likely that a judge would never be dismissed, not merely because of formal rules but a "shared constitutional understanding" of the importance of the integrity of the legal system. This is reflected, for example, in the ''sub judice'' rule that matters awaiting decision in court should not be prejudged in a Parliamentary debate. The
 The executive branch, while subservient to Parliament and judicial oversight, exercises day to day power of the British government. The UK remains a constitutional monarchy. The formal head of state is Majesty, His Majesty Monarchy of the United Kingdom, King Charles III, a Heredity, hereditary monarch since 2022. No Queen or King has withheld assent to any bill passed by Parliament Scottish Militia Bill, since 1708, and all constitutional duties and power are accepted by binding convention to have shifted to the
The executive branch, while subservient to Parliament and judicial oversight, exercises day to day power of the British government. The UK remains a constitutional monarchy. The formal head of state is Majesty, His Majesty Monarchy of the United Kingdom, King Charles III, a Heredity, hereditary monarch since 2022. No Queen or King has withheld assent to any bill passed by Parliament Scottish Militia Bill, since 1708, and all constitutional duties and power are accepted by binding convention to have shifted to the  Although called the Royal prerogative in the United Kingdom, royal prerogative, a series of important powers that were once vested in the king or queen are now exercised by government, and the
Although called the Royal prerogative in the United Kingdom, royal prerogative, a series of important powers that were once vested in the king or queen are now exercised by government, and the
EWHC KB J22
/ref> It is also clear that no exercise of the prerogative can compromise any right contained in an Act of Parliament. So, for instance, in '' R (Miller) v Secretary of State for Exiting the European Union'' the Supreme Court held that the Prime Minister could not notify the Although the Prime Minister is the head of Parliament, His Majesty's Government is formed by a larger group of Members of Parliament, or peers. The "
Although the Prime Minister is the head of Parliament, His Majesty's Government is formed by a larger group of Members of Parliament, or peers. The "
 The constitution of British regional governments is an uncodified patchwork of authorities, mayors, councils and devolved government. In Local government in Wales, Wales, Local government in Scotland, Scotland, Local government in Northern Ireland, Northern Ireland and Greater London Authority, London unified district or borough councils have local government powers, and since 1998 to 2006 new regional assemblies or Parliaments exercise extra powers devolved from Westminster. In Local government in England, England, there are 55 unitary authorities in the larger towns (e.g. Bristol, Brighton, Milton Keynes) and 36 metropolitan boroughs (surrounding Liverpool, Manchester, Leeds, Birmingham, Sheffield, and Newcastle) which function as unitary local authorities.
In other parts of England, local government is split between two tiers of authority: 32 larger County Councils, and within those 192 District Councils, each sharing different functions. Since 1994, England has had Regions of England, eight regions for administrative purposes at Whitehall, yet these have no regional government or democratic assembly (like in London, Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland) after a 2004 referendum on North East Assembly failed. This means that England has among the most centralised, and disunified systems of governance in the Commonwealth and Europe.
Three main issues in local government are the authorities' financing, their powers, and the reform of governance structures. First, councils raise revenue from Council Tax (charged on local residents according to property values in 1993) and business rates charged on businesses with operations in the locality. These powers are, compared to other countries, extreme in limiting local government autonomy, and taxes can be subjected to a local referendum if the Secretary of State determines they are excessive.
In real terms since 2010, central government cut local council funding by nearly 50 per cent, and real spending fell by 21 per cent, as councils failed to make up cuts through business rates. Unitary authorities and district councils are responsible for administering council tax and business rates. The duties of British local governments are also extremely limited compared to other countries, but also uncodified so that in 2011 the Department for Levelling Up, Housing and Communities, Department for Communities and Local Government enumerated Duties of local government in the United Kingdom, 1340 specific duties of local authorities. Generally, the Localism Act 2011 section 1 states local authorities may do anything an individual person may do, unless prohibited by law, but this provision has little effect because human beings or United Kingdom company law, companies cannot tax or regulate other people in the way that governments must.
The
The constitution of British regional governments is an uncodified patchwork of authorities, mayors, councils and devolved government. In Local government in Wales, Wales, Local government in Scotland, Scotland, Local government in Northern Ireland, Northern Ireland and Greater London Authority, London unified district or borough councils have local government powers, and since 1998 to 2006 new regional assemblies or Parliaments exercise extra powers devolved from Westminster. In Local government in England, England, there are 55 unitary authorities in the larger towns (e.g. Bristol, Brighton, Milton Keynes) and 36 metropolitan boroughs (surrounding Liverpool, Manchester, Leeds, Birmingham, Sheffield, and Newcastle) which function as unitary local authorities.
In other parts of England, local government is split between two tiers of authority: 32 larger County Councils, and within those 192 District Councils, each sharing different functions. Since 1994, England has had Regions of England, eight regions for administrative purposes at Whitehall, yet these have no regional government or democratic assembly (like in London, Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland) after a 2004 referendum on North East Assembly failed. This means that England has among the most centralised, and disunified systems of governance in the Commonwealth and Europe.
Three main issues in local government are the authorities' financing, their powers, and the reform of governance structures. First, councils raise revenue from Council Tax (charged on local residents according to property values in 1993) and business rates charged on businesses with operations in the locality. These powers are, compared to other countries, extreme in limiting local government autonomy, and taxes can be subjected to a local referendum if the Secretary of State determines they are excessive.
In real terms since 2010, central government cut local council funding by nearly 50 per cent, and real spending fell by 21 per cent, as councils failed to make up cuts through business rates. Unitary authorities and district councils are responsible for administering council tax and business rates. The duties of British local governments are also extremely limited compared to other countries, but also uncodified so that in 2011 the Department for Levelling Up, Housing and Communities, Department for Communities and Local Government enumerated Duties of local government in the United Kingdom, 1340 specific duties of local authorities. Generally, the Localism Act 2011 section 1 states local authorities may do anything an individual person may do, unless prohibited by law, but this provision has little effect because human beings or United Kingdom company law, companies cannot tax or regulate other people in the way that governments must.
The  In Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland and London there are also regional assemblies and Parliaments, similar to state or provincial governments in other countries. The extent of devolution differs in each place. The
In Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland and London there are also regional assemblies and Parliaments, similar to state or provincial governments in other countries. The extent of devolution differs in each place. The
 Upon the catastrophe of
Upon the catastrophe of
 Administrative law, through
Administrative law, through
 The history of the British constitution, though officially beginning in 1800, traces back to a time long before the four nations of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland, Ireland were fully Formation of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, formed. Before the Norman Conquest, Norman Invasion of 1066, the written history of law was scant. Following the conquest, according to the legal record Leges Edwardi Confessoris, Laws of Edward the Confessor, in 1070 William the Conqueror, on the advice of the King's Council (''Curia Regis''), summoned nobles learned in the law from all parts of the country in order to learn the established laws and customs. After hearing from 12 men from each county on oath, he expressed the wish to establish norse law as the common law in England under one monarch because his ancestors and his Norman barons all came from Norway. He was, however, persuaded by those summoned, that the laws of the Britons, English and Picts should remain in force 'because it was hard to adopt laws and to judge according to those that they did not know'. It is recorded that 'Finally, by the counsel and at the request of his barons, he acquiesced' and authorised and confirmed the laws as they were under Edward the Confessor.
The Domesday Book was compiled in 1086 cataloguing all land and labour to levy History of taxation in the United Kingdom, taxes. Just 12 per cent of people were free, while the feudal system made others serfs, slaves or bordars and cottars.
Henry II of England, Henry II, who became the monarch in 1154, established the
The history of the British constitution, though officially beginning in 1800, traces back to a time long before the four nations of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland, Ireland were fully Formation of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, formed. Before the Norman Conquest, Norman Invasion of 1066, the written history of law was scant. Following the conquest, according to the legal record Leges Edwardi Confessoris, Laws of Edward the Confessor, in 1070 William the Conqueror, on the advice of the King's Council (''Curia Regis''), summoned nobles learned in the law from all parts of the country in order to learn the established laws and customs. After hearing from 12 men from each county on oath, he expressed the wish to establish norse law as the common law in England under one monarch because his ancestors and his Norman barons all came from Norway. He was, however, persuaded by those summoned, that the laws of the Britons, English and Picts should remain in force 'because it was hard to adopt laws and to judge according to those that they did not know'. It is recorded that 'Finally, by the counsel and at the request of his barons, he acquiesced' and authorised and confirmed the laws as they were under Edward the Confessor.
The Domesday Book was compiled in 1086 cataloguing all land and labour to levy History of taxation in the United Kingdom, taxes. Just 12 per cent of people were free, while the feudal system made others serfs, slaves or bordars and cottars.
Henry II of England, Henry II, who became the monarch in 1154, established the  With
With 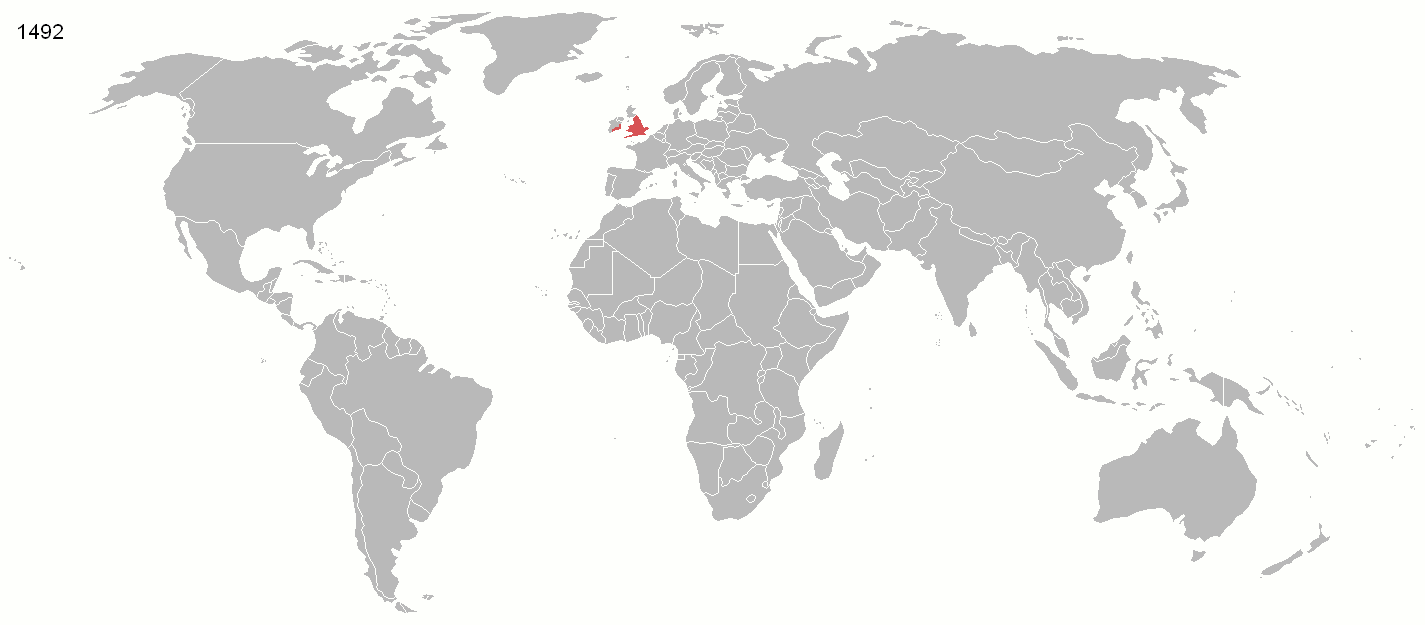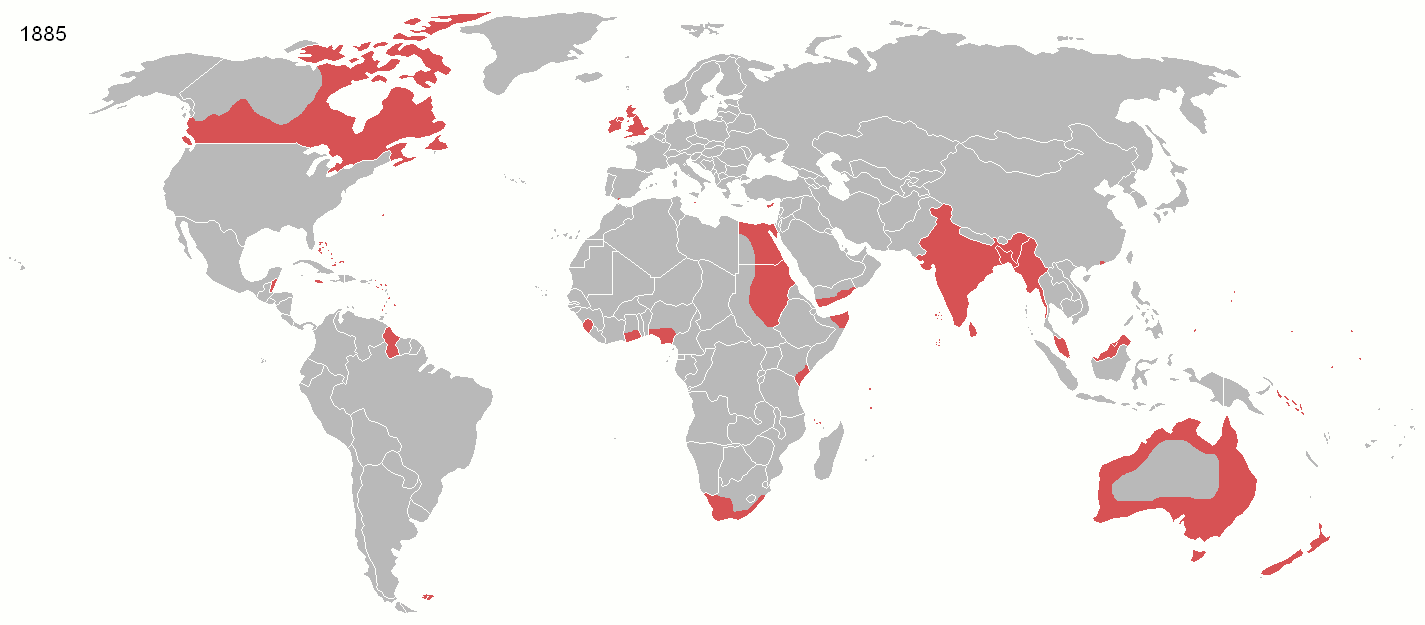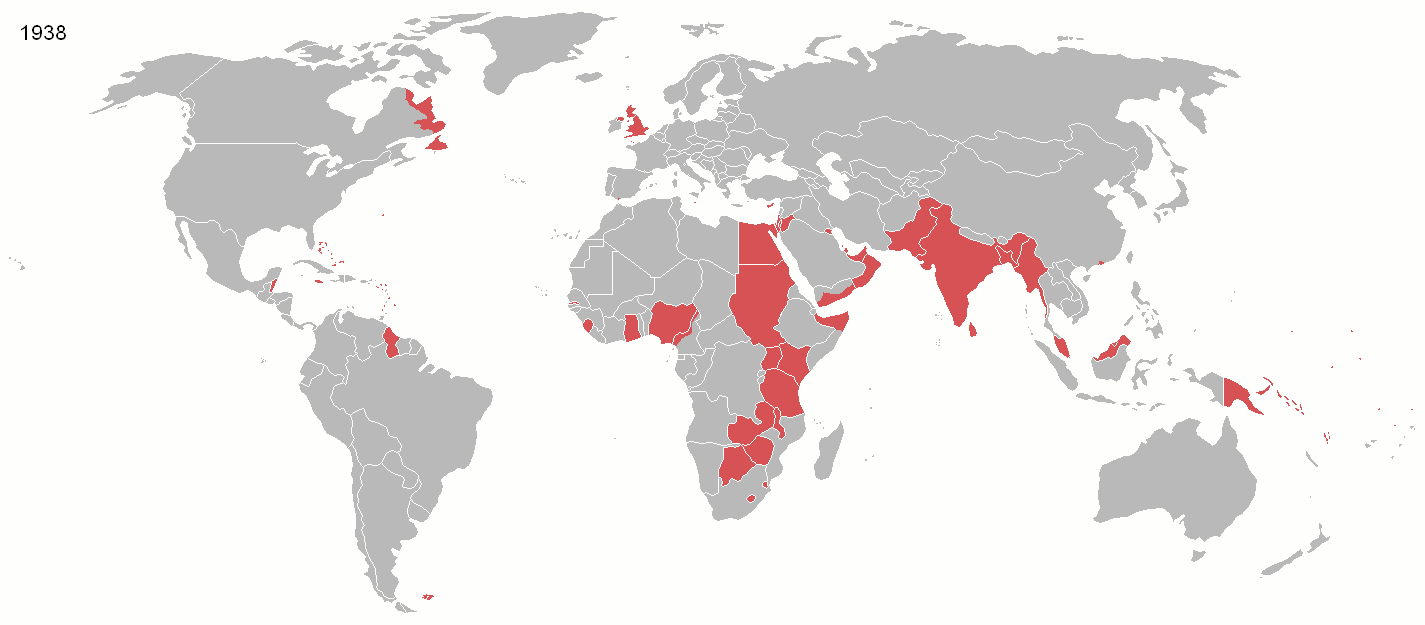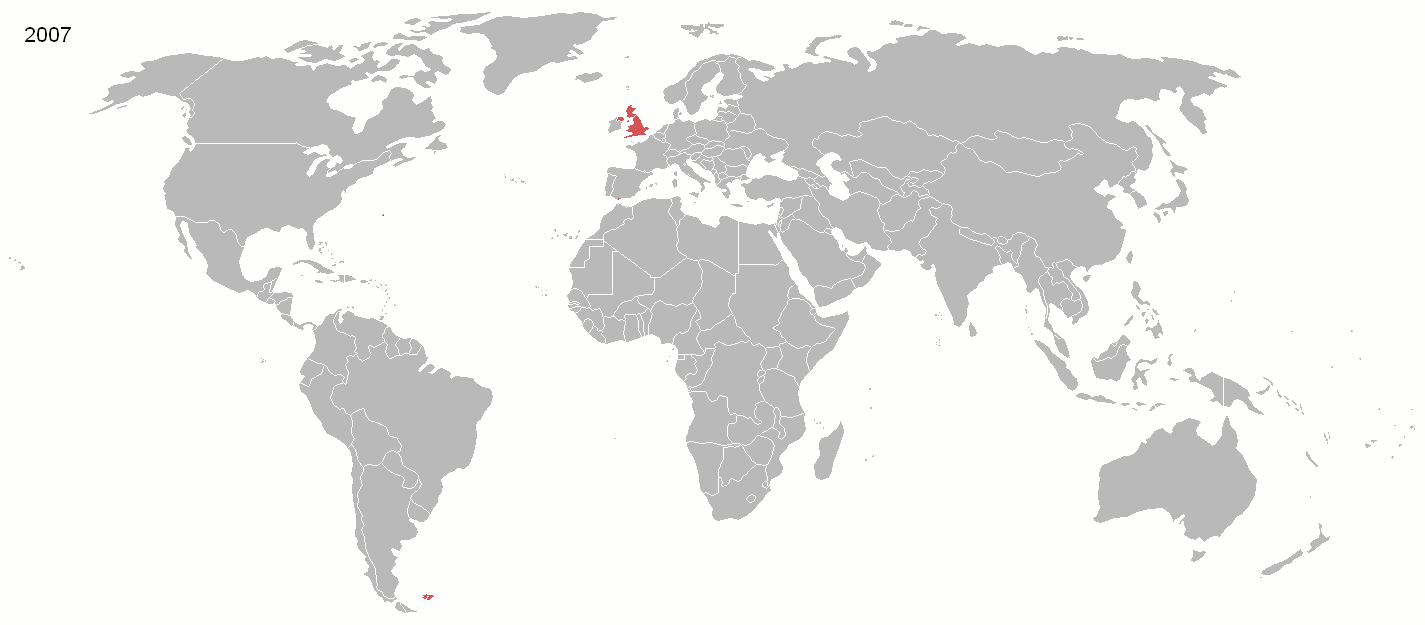 During this time, with the invention of the steam engine the Industrial Revolution had begun. Poverty had also accelerated through the Speenhamland system of English Poor Laws, poor laws by subsidising employers and landowners with parish rates. The Corn Laws from 1815 further impoverished people by fixing prices to maintain landowner profits. While the Reform Act 1832, Great Reform Act 1832 extended the vote slightly, only those with property had any representation in Parliament. The Slavery Abolition Act 1833, 1833 Slavery Abolition Act abolished slavery within the British Empire, compensating slave owners and made ex-slaves in the colonies work for their owners for four to six years as indentured servants without pay; this was abolished in 1838 after public outcry. With the Poor Law Amendment Act 1834, further punishment for poverty was inflicted as people were put into work houses if found to be unemployed. In ''R v Lovelass'' a group of agricultural workers who formed a trade union were prosecuted and sentenced to be transported to Australia under the Unlawful Oaths Act 1797, triggering mass protests.
A movement called Chartism grew demanding the right to vote for everyone in free and fair elections. As the Great Famine (Ireland), great famine hit Ireland and millions migrated to the
During this time, with the invention of the steam engine the Industrial Revolution had begun. Poverty had also accelerated through the Speenhamland system of English Poor Laws, poor laws by subsidising employers and landowners with parish rates. The Corn Laws from 1815 further impoverished people by fixing prices to maintain landowner profits. While the Reform Act 1832, Great Reform Act 1832 extended the vote slightly, only those with property had any representation in Parliament. The Slavery Abolition Act 1833, 1833 Slavery Abolition Act abolished slavery within the British Empire, compensating slave owners and made ex-slaves in the colonies work for their owners for four to six years as indentured servants without pay; this was abolished in 1838 after public outcry. With the Poor Law Amendment Act 1834, further punishment for poverty was inflicted as people were put into work houses if found to be unemployed. In ''R v Lovelass'' a group of agricultural workers who formed a trade union were prosecuted and sentenced to be transported to Australia under the Unlawful Oaths Act 1797, triggering mass protests.
A movement called Chartism grew demanding the right to vote for everyone in free and fair elections. As the Great Famine (Ireland), great famine hit Ireland and millions migrated to the
Magna Carta and contemporary constitutional change
(2015) History and Policy *V Bogdanor, T Khaitan and S Vogenauer, 'Should Britain have a written constitution?' (2007
78(4) Political Quarterly 499
* Briggs, Asa, “Trollope, Bagehot, and the English Constitution,” in Briggs, ''Victorian People'' (1955) pp. 87–115
online
*KD Ewing, 'The Resilience of the Political Constitution' (2013
14(12) German Law Journal 2111
*JAW Griffith, 'The Political Constitution' (1979
42(1) Modern Law Review 1
*F Kessler, 'Natural Law, Justice and Democracy—Some Reflections on Three Types of Thinking About Law and Justice' (1944
19 Tulane Law Review 32
*Lord Hoffmann, (2013
17 Oxford Law News 8-9
from a tribute at St John's Smith Square on 5 June 2013 *O Kahn-Freund, 'Autobiographical Memories of the Weimar Republic: A Conversation with Wolfgang Luthardt' (February 1978
KCL Law School Research Paper No. 2016-34
*J Laws, 'Law and Democracy' [1995] Public Law 72 *S Webb, 'Socialism: true and false. A lecture delivered to the Fabian Society' (21 January 1894) Fabian Tract, 51 *S Webb, 'The reform of the House of Lords' (1917) Fabian Tract, 183 ;Books *W Bagehot, ''The English Constitution'' (1867) *Lord Bingham of Cornhill, ''Rule of Law'' (2010) *AV Dicey, ''Introduction to the Study of the Law of the Constitution''
3rd edn 1889
*H Arendt, ''Eichmann in Jerusalem: A Report on the Banality of Evil'' (1963) *J Froissart, ''Froissart's Chronicles'' (1385) translated by GC Macaulay
1895
*I Jennings, ''A Federation for Western Europe''
1940
*J Locke, ''Two Treatises of Government''
1689Book II, An Essay Concerning the True Origin, Extent, and End of Civil Government
*FW Maitland, ''The Constitutional History of England''
CUP 1919
*JS Mill, ''On Liberty''
1859
*JS Mill, ''Considerations on Representative Government''
1861
*T More, ''Utopia (book), Utopia'' (1516) translated by Gilbert Burnet
1901
*FL Neumann, ''Behemoth: The Structure and Practice of National Socialism, 1933-1944'' (1944) *FL Neumann, ''The Democratic and the Authoritarian State: Essays in Political and Legal Theory'' (1957) *C Turpin and A Tomkins, ''British Government and the Constitution'' (7th edition, CUP) *S Webb and B Webb, ''Industrial Democracy'' (1890) *S Webb, ''English Local Government'' (1906 through 1929) Volumes I–X ;Textbooks *AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, ''Constitutional and Administrative Law'' (2018) *H Kelsen, ''Principles of International Law''
1952
*A Le Sueur, M Sunkin and J Murkens, ''Public Law Text, Cases, and Materials'' (3rd edn 2016) *M Elliott and R Thomas, ''Public Law'' (3rd edn 2017) ;Other papers *C Gearty,
Are judges now out of their depth?
(2007) *D Jenkins,
From Unwritten to Written: Transformation in the British Common-Law Constitution
*J McEldowney
(2003) Written evidence to the Constitution Committee (House of Lords), House of Lords Select Committee on the Constitution. *
The UK constitution - The Constitution Society
consoc.org.uk
What is the UK Constitution? , The Constitution Unit - UCL – University College London
ucl.ac.uk
Britain's unwritten constitution , The British Library
bl.uk *
Cabinet Office - Constitutional Reform
Guardian Special Report – Constitutional Reform
United Kingdom Constitutional Law Association blog on Constitutional Reform
The Constitution Society feature on What is the British Constitution?
LSE - A New UK Constitution
UCL Constitution Unit - About
ESRC Centre on Constitutional Change
Democratic Audit UK
The Parliament and Constitution Centre
Constitutional Law Chronology
Full Constitution of England - Constitute Project
Constitutional Statutes
including discussion of later cases e.g. ''Robinson v Secretary of State for Northern Ireland'' [2002] UKHL 32, ''BH v Lord Advocate'' [2012] UKSC 24, ''R (HS2 Action Alliance Ltd) v Secretary of State for Transport'' [2014] UKSC 3. {{DEFAULTSORT:Constitution of the United Kingdom Constitution of the United Kingdom, Government of the United Kingdom Law of the United Kingdom Politics of the United Kingdom Uncodified constitutions
 The constitution of the United Kingdom or British constitution comprises the written and unwritten arrangements that establish the
The constitution of the United Kingdom or British constitution comprises the written and unwritten arrangements that establish the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and No ...
as a political body. Unlike in most countries, no attempt has been made to codify such arrangements into a single document, thus it is known as an uncodified constitution. This enables the constitution to be easily changed as no provisions are formally entrenched; the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom
The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom ( initialism: UKSC or the acronym: SCOTUK) is the final court of appeal in the United Kingdom for all civil cases, and for criminal cases originating in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. As the Unite ...
recognises that there are constitutional principles, including parliamentary sovereignty
Parliamentary sovereignty, also called parliamentary supremacy or legislative supremacy, is a concept in the constitutional law of some parliamentary democracies. It holds that the legislative body has absolute sovereignty and is supreme over ...
, the rule of law
The rule of law is the political philosophy that all citizens and institutions within a country, state, or community are accountable to the same laws, including lawmakers and leaders. The rule of law is defined in the ''Encyclopedia Britannic ...
, democracy
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation (" direct democracy"), or to choose g ...
, and upholding international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
.
The Supreme Court also recognises that some Acts of Parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation, are texts of law passed by the legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of parliament be ...
have special constitutional status, and are therefore part of the constitution. These include Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by t ...
, which in 1215 required the King to call a "common counsel" (now called Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
) to represent people, to hold courts in a fixed place, to guarantee fair trials, to guarantee free movement of people, to free the church from the state, and to guarantee rights of "common" people to use the land. (Most of Magna Carta is no longer in force; those principles it established that still exist are mostly protected by other enactments.) After the Wars of the Three Kingdoms
The Wars of the Three Kingdoms were a series of related conflicts fought between 1639 and 1653 in the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland, then separate entities united in a personal union under Charles I. They include the 1639 to 1640 Bi ...
and the Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
, the Bill of Rights 1689 and the Claim of Right Act 1689 cemented Parliament's position as the supreme law making body, and said that the "election of members of Parliament ought to be free".
The Treaty of Union between England and Scotland in 1706, followed by two Acts of Union 1707
The Acts of Union ( gd, Achd an Aonaidh) were two Acts of Parliament: the Union with Scotland Act 1706 passed by the Parliament of England, and the Union with England Act 1707 passed by the Parliament of Scotland. They put into effect the t ...
, one in the Scottish, the other in the English parliament, unified England, Wales and Scotland. Ireland joined in a similar way through the Acts of Union 1801. The Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between ...
separated after the 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty
The 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty ( ga , An Conradh Angla-Éireannach), commonly known in Ireland as The Treaty and officially the Articles of Agreement for a Treaty Between Great Britain and Ireland, was an agreement between the government of the ...
took effect in 1922. Northern Ireland remained within the union.
After a slow process of electoral reform, the UK guaranteed every adult citizen (21 years or older) the equal right to vote in the Representation of the People (Equal Franchise) Act 1928. After World War II, the UK became a founding member of the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold human rights, democracy and the rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it has 46 member states, with a p ...
to uphold human rights, and the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
to guarantee international peace and security. The UK was a member of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
, whose predecessor the European Communities
The European Communities (EC) were three international organizations that were governed by the same set of institutions. These were the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or Euratom), and the ...
(the Common Market) it first joined in 1973, but left in 2020. The UK is also a founding member of the International Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is the first and o ...
and the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and ...
to participate in regulating the global economy.
The leading institutions in the United Kingdom's constitution are Parliament, the judiciary, the executive, the and regional and local governments, including the devolved legislatures and executives of Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. Parliament is the supreme law-making body, and represents the people of the United Kingdom. It consists of the monarch and two houses. The House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
is elected by a democratic vote in the country's 650 constituencies. The House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
, historically dominated by hereditary peers, is now (and especially since 2000) mostly appointed by cross-political party groups from the House of Commons; since it lacks democratic legitimacy, it has no power to block legislation introduced in the Commons. To make a new Act of Parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation, are texts of law passed by the legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of parliame ...
, the highest form of law, both Houses must read, amend, or approve proposed legislation three times and the monarch must give their consent. The judiciary interprets the law found in Acts of Parliament and develops the law established by previous cases. The highest court is the twelve-person Supreme Court, as it decides appeals from the Courts of Appeal in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label=Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is #Descriptions, variously described as ...
, or the Court of Session
The Court of Session is the supreme civil court of Scotland and constitutes part of the College of Justice; the supreme criminal court of Scotland is the High Court of Justiciary. The Court of Session sits in Parliament House in Edinburg ...
in Scotland. It does not however hear criminal appeals from Scotland. British courts cannot declare Acts of Parliament to be unconstitutional, but can determine whether the acts of the executive are lawful (and invalidate them with quashing orders if so), or declare any law to be incompatible with the European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by ...
(which does not affect its validity and enforcement). The executive manages the United Kingdom day to day. The executive is led by the prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
who is appointed by the monarch and invited to try to form a government, which by convention must have the support of Parliament. The prime minister appoints the cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filin ...
of other ministers, who lead the executive departments, staffed by civil servants, such as the Department of Health and Social Care
The Department of Health and Social Care (DHSC) is a department of His Majesty's Government responsible for government policy on health and adult social care matters in England, along with a few elements of the same matters which are not otherw ...
which runs the National Health Service
The National Health Service (NHS) is the umbrella term for the publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom (UK). Since 1948, they have been funded out of general taxation. There are three systems which are referred to using the " ...
, or the Department for Education
The Department for Education (DfE) is a department of His Majesty's Government responsible for child protection, child services, education (compulsory, further and higher education), apprenticeships and wider skills in England.
A Departme ...
which funds schools and universities. The monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority ...
in their public capacity, known as the Crown, embodies the state. Laws can only be made by or with the authority of the Crown in Parliament, all judges sit in place of the Crown and all ministers act in the name of the Crown. The monarch is for the most part a ceremonial figurehead. When giving royal assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in oth ...
to new laws, the monarch has not refused to sign any new law since the Scottish Militia Bill in 1708, and it is a constitutional convention that the monarch follows the advice of ministers.
Most litigation over the British constitution takes place in judicial review
Judicial review is a process under which executive, legislative and administrative actions are subject to review by the judiciary. A court with authority for judicial review may invalidate laws, acts and governmental actions that are incomp ...
applications, to decide whether the decisions or acts of public bodies are lawful. All public authority ultimately derives from the Crown, either under the common law or as granted by Parliament. Every public body can only act in accordance with the law, as declared in Acts of Parliament and the decisions of the courts. Under the Human Rights Act 1998
The Human Rights Act 1998 (c. 42) is an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom which received royal assent on 9 November 1998, and came into force on 2 October 2000. Its aim was to incorporate into UK law the rights contained in the European Con ...
, courts may review government action to decide whether the government has followed the statutory obligation on all public authorities to comply with the European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by ...
. Convention rights include everyone's rights to life, liberty
Liberty is the ability to do as one pleases, or a right or immunity enjoyed by prescription or by grant (i.e. privilege). It is a synonym for the word freedom.
In modern politics, liberty is understood as the state of being free within society fr ...
against arbitrary arrest or detention, torture
Torture is the deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering on a person for reasons such as punishment, extracting a confession, interrogation for information, or intimidating third parties. Some definitions are restricted to acts ...
, and forced labour or slavery, to a fair trial
A fair (archaic: faire or fayre) is a gathering of people for a variety of entertainment or commercial activities. Fairs are typically temporary with scheduled times lasting from an afternoon to several weeks.
Types
Variations of fairs incl ...
, to privacy against unlawful surveillance, to freedom of expression, conscience and religion, to respect for private life, to freedom of association including joining trade union
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits ...
s, and to freedom of assembly and protest.
Principles
 Although the British constitution is not codified, the Supreme Court recognises constitutional principles, and constitutional statutes, which shape the use of political power. The main sources of constitutional law are Acts of Parliament, court cases, and conventions in the way that government, Parliament and the monarch act. There are at least four main constitutional principles recognised by the courts. First,
Although the British constitution is not codified, the Supreme Court recognises constitutional principles, and constitutional statutes, which shape the use of political power. The main sources of constitutional law are Acts of Parliament, court cases, and conventions in the way that government, Parliament and the monarch act. There are at least four main constitutional principles recognised by the courts. First, parliamentary sovereignty
Parliamentary sovereignty, also called parliamentary supremacy or legislative supremacy, is a concept in the constitutional law of some parliamentary democracies. It holds that the legislative body has absolute sovereignty and is supreme over ...
means that Acts of Parliament are the supreme source of law. Through the English Reformation
The English Reformation took place in 16th-century England when the Church of England broke away from the authority of the pope and the Catholic Church. These events were part of the wider European Protestant Reformation, a religious and poli ...
, the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polici ...
, the Glorious Revolution of 1688 and the Acts of Union 1707
The Acts of Union ( gd, Achd an Aonaidh) were two Acts of Parliament: the Union with Scotland Act 1706 passed by the Parliament of England, and the Union with England Act 1707 passed by the Parliament of Scotland. They put into effect the t ...
, Parliament became the dominant branch of the state, above the judiciary, executive, monarchy, and church. Although there are a number of formal limitations on the laws Parliament can make, contained in the 1707 Treaty of Union between England and Scotland, it is sometimes asserted that Parliament can make or unmake any law, a fact that is usually justified by Parliament being democratically elected, and upholding the rule of law
The rule of law is the political philosophy that all citizens and institutions within a country, state, or community are accountable to the same laws, including lawmakers and leaders. The rule of law is defined in the ''Encyclopedia Britannic ...
, including human rights and international law.
Second, the rule of law has run through the constitution as a fundamental principle from the earliest times as "The king must enbsp;... under the law, because the law makes the king" ( Henry de Bracton in the 13th century). This principle was recognised in Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by t ...
and the Petition of Right 1628
The Petition of Right, passed on 7 June 1628, is an English constitutional document setting out specific individual protections against the state, reportedly of equal value to Magna Carta and the Bill of Rights 1689. It was part of a wider c ...
. This means the government may only conduct itself according to legal authority, including respect for human rights. Third, at least since 1928
Events January
* January – British bacteriologist Frederick Griffith reports the results of Griffith's experiment, indirectly proving the existence of DNA.
* January 1 – Eastern Bloc emigration and defection: Boris Bazhano ...
, elections in which all capable adults participate have become a fundamental constitutional principle. Originally only wealthy, property-owning men held rights to vote for the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
, while the monarch, occasionally together with a hereditary House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
, dominated politics. From 1832 onwards adult citizens slowly obtained the right to universal suffrage
Universal suffrage (also called universal franchise, general suffrage, and common suffrage of the common man) gives the right to vote to all adult citizens, regardless of wealth, income, gender, social status, race, ethnicity, or political sta ...
.
Fourth, the British constitution is bound to international law, as Parliament has chosen to increase its practical power in cooperation with other countries in international organisations, such as the International Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is the first and o ...
, the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
, the European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by ...
, the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and ...
, and the International Criminal Court
The International Criminal Court (ICC or ICCt) is an intergovernmental organization and International court, international tribunal seated in The Hague, Netherlands. It is the first and only permanent international court with jurisdiction to pro ...
. However, the UK left membership of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
in 2020 after a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a Representative democr ...
in 2016.
Parliamentary sovereignty
Parliamentary sovereignty is often seen as a central element in the British constitution, although its extent is contested. It means that an Act of Parliament is the highest form of law, but also that "Parliament cannot bind itself". Historically, Parliament became sovereign through a series of power struggles between the monarch, the church, the courts, and the people.Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by t ...
in 1215, which came from the conflict leading to the First Barons' War, granted the right of Parliament to exist for "common counsel" before any tax, against the "divine right of kings
In European Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representin ...
" to rule.
Common land
Common land is land owned by a person or collectively by a number of persons, over which other persons have certain common rights, such as to allow their livestock to graze upon it, to collect wood, or to cut turf for fuel.
A person who has ...
was guaranteed to people to farm, graze, hunt or fish, though aristocrats continued to dominate politics. In the Act of Supremacy 1534, King Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
asserted his divine right over the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
in Rome, declaring himself the supreme leader of the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Brit ...
. Then in the '' Earl of Oxford's case'' in 1615, the Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. Th ...
(both the King's representative and head of the judiciary
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
) asserted the supremacy of the Court of Chancery
The Court of Chancery was a court of equity in England and Wales that followed a set of loose rules to avoid a slow pace of change and possible harshness (or "inequity") of the common law. The Chancery had jurisdiction over all matters of equ ...
over the common law courts, contradicting Sir Edward Coke
Edward is an English given name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortune; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”.
History
The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Sax ...
's assertion that judges could declare statutes void if they went "against common right and reason".
After the Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
of 1688, the Bill of Rights 1689 cemented Parliament's power over the monarch, and therefore over the church and courts. Parliament became "sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
", and supreme. Only 18 years later however, the English Parliament abolished itself in order to create the new "Union" Parliament following on the Treaty of Union between England and Scotland, while the Scottish Parliament did likewise. Power struggles within Parliament continued between the aristocracy and common people. Outside Parliament, people from the Chartists
Chartism was a working-class movement for political reform in the United Kingdom that erupted from 1838 to 1857 and was strongest in 1839, 1842 and 1848. It took its name from the People's Charter of 1838 and was a national protest movement, ...
to the trade unions
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits ( ...
fought for the vote in the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
. The Parliament Act 1911
The Parliament Act 1911 (1 & 2 Geo. 5 c. 13) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It is constitutionally important and partly governs the relationship between the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two Houses of Pa ...
ensured the Commons would prevail in any conflict over the unelected House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
. The Parliament Act 1949
The Parliament Act 1949 (12, 13 & 14 Geo. 6 c. 103) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It reduced the power of the House of Lords to delay certain types of legislation – specifically public bills other than money bills ...
ensured the Lords could only delay legislation by one year, and not delay any budgetary measure over a month.
In a leading case, ''R (Jackson) v Attorney General
''R (Jackson) v Attorney General'' House of Lords case noted for containing obiter">Judicial functions of the House of Lords">House of Lords case noted for containing obiter comments by the Judiciary acting in their official capacity suggestin ...
'', a group of pro-hunting protestors challenged the Hunting Act 2004
The Hunting Act 2004 (c 37) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which bans the hunting of most wild mammals (notably foxes, deer, hares and mink) with dogs in England and Wales, subject to some strictly limited exemptions; ...
's ban on fox hunting, arguing it was not a valid Act because it was passed avoiding the House of Lords, using the Parliament Acts. They argued that the 1949 Act itself was passed using the 1911 Act's power to override the Lords in two years. The claimants argued that this meant the 1949 Act should not be considered a valid law, because the 1911 Act was limited in scope and could not be used to amend its own limitation of the Lords' power. The House of Lords, sitting as the UK's highest court, rejected this argument, holding both the Parliament Act 1949
The Parliament Act 1949 (12, 13 & 14 Geo. 6 c. 103) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It reduced the power of the House of Lords to delay certain types of legislation – specifically public bills other than money bills ...
and the Hunting Act 2004
The Hunting Act 2004 (c 37) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which bans the hunting of most wild mammals (notably foxes, deer, hares and mink) with dogs in England and Wales, subject to some strictly limited exemptions; ...
to be valid. However, in ''obiter dicta
''Obiter dictum'' (usually used in the plural, ''obiter dicta'') is a Latin phrase meaning "other things said",'' Black's Law Dictionary'', p. 967 (5th ed. 1979). that is, a remark in a legal opinion that is "said in passing" by any judge or arbi ...
'' Lord Hope argued that Parliamentary sovereignty "is no longer, if it ever was, absolute", and that the "rule of law enforced by the courts is the ultimate controlling factor on which our constitution is based", and cannot be used to defend unconstitutional Acts (as determined by the courts). There is not yet a consensus on the meaning of "Parliamentary sovereignty", except that its legitimacy depends on the principle of "the democratic process".
 In recent history, Parliament's sovereignty has evolved in four main ways. First, since 1945 international cooperation meant Parliament augmented its power by working with, not dominating, other sovereign nations. The
In recent history, Parliament's sovereignty has evolved in four main ways. First, since 1945 international cooperation meant Parliament augmented its power by working with, not dominating, other sovereign nations. The British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
, which once colonised a quarter of the world's population and a third of its land, declined after World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
and disintegrated after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. While Parliament had nearly uncontested military power before, and so was thought by writers of the Imperial period to be able to "make or unmake any law whatever", the UK chose to join in the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
in 1919, and after its failure, the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
1945 to participate in building a system of international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
in place of Empire.
The Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
in 1919 recalled that "peace can only be established if it is based upon social justice", and the UN Charter, "based on the principle of the sovereign equality of all its Members", said that "to save succeeding generations from the scourge of war, which twice in our lifetime has brought untold sorrow to mankind", the UN would "reaffirm faith in fundamental human rights", and members should "live together in peace with one another as good neighbours". The Bretton Woods Agreements Act 1945, United Nations Act 1946
The United Nations Act 1946 (9 & 10 Geo. 6 c. 45) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which enables His Majesty's Government to implement resolutions under Article 41 of the United Nations Charter as Orders in Council. Thus Parli ...
and International Organisations Act 1968 wrote the UK's funding and membership of the United Nations, the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glo ...
, the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
, and other bodies, into law. For example, the UK bound itself to implement by order UN Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
resolutions, up to the actual use of force, in return for representation in the General Assembly and Security Council.
Although the UK has not always clearly followed international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
, it has accepted as a formal duty that its sovereignty would not be used unlawfully. Second, in 1950 the UK helped to write and joined the European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by ...
. While that convention reflected norms and cases decided under British statutes and the common law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omniprese ...
on civil liberties
Civil liberties are guarantees and freedoms that governments commit not to abridge, either by constitution, legislation, or judicial interpretation, without due process. Though the scope of the term differs between countries, civil liberties ma ...
, the UK accepted that people could appeal to the European Court of Human Rights
The European Court of Human Rights (ECHR or ECtHR), also known as the Strasbourg Court, is an international court of the Council of Europe which interprets the European Convention on Human Rights. The court hears applications alleging that ...
in Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the ...
, if domestic remedies were not enough. In the Human Rights Act 1998
The Human Rights Act 1998 (c. 42) is an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom which received royal assent on 9 November 1998, and came into force on 2 October 2000. Its aim was to incorporate into UK law the rights contained in the European Con ...
, Parliament decided that the British judiciary should be required to apply human rights norms directly in determining British cases, to ensure a more speedy, human rights-based resolution to case law, and effectively influence human rights reasoning more.
 Third, the UK became a member of the
Third, the UK became a member of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
after the European Communities Act 1972 and through its ratification of the Maastricht Treaty
The Treaty on European Union, commonly known as the Maastricht Treaty, is the foundation treaty of the European Union (EU). Concluded in 1992 between the then-twelve member states of the European Communities, it announced "a new stage in the ...
in 1992. The idea of a Union had long been envisaged by European leaders, including Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
, who in 1946 had called for a "United States of Europe
The United States of Europe (USE), the European State, the European Federation and Federal Europe, is the hypothetical scenario of the European integration leading to formation of a sovereign superstate (similar to the United States of Ameri ...
".e.g. "Speech at the University of Zurich"19 September 1946
.e.g. "Speech to the 69th Annual Conservative Party Conference at Llandudno"
9 October 1948
. See J. Danzig, "Winston Churchill: A founder of the European Union" (10 November 2013
EU ROPE
/ref>
EU law
European Union law is a system of rules operating within the member states of the European Union (EU). Since the founding of the European Coal and Steel Community following World War II, the EU has developed the aim to "promote peace, its val ...
has long been held to prevail in any conflict between Acts of Parliament for the limited fields in which it operates, but member states and citizens gain control over the scope of EU law, and so extend their sovereignty in international affairs, through joint representation in the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the Legislature, legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven Institutions of the European Union, institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and in ...
, Council of the European Union
The Council of the European Union, often referred to in the treaties and other official documents simply as the Council, and informally known as the Council of Ministers, is the third of the seven Institutions of the European Union (EU) as ...
, and the Commission. This principle was tested in '' R (Factortame Ltd) v Secretary of State for Transport'', where a fishing business claimed that it should not be required to have 75% of British shareholders, as the Merchant Shipping Act 1988 said.''R v Secretary of State for Transport, ex parte Factortame Ltd'' 990
Year 990 ( CMXC) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place
Europe
* Al-Mansur, ''de facto'' ruler of Al-Andalus, conquers the Castle of Montemor-o-Velho (mode ...
UKHL 7. Under EU law, the principle of freedom of establishment states that nationals of any member state can freely incorporate and run a business across the EU without unjustified interference. The House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
held that, because the EU law conflicted with the sections of the 1988 Act, those sections would not be enforced, and disapplied, because Parliament had not clearly expressed an intention to renounce the 1972 Act. According to Lord Bridge
Lord is an appellation for a person or deity who has authority, control, or power over others, acting as a master, chief, or ruler. The appellation can also denote certain persons who hold a title of the peerage in the United Kingdom, or are ...
"whatever limitation of its sovereignty Parliament accepted when it enacted the 972 Act 97 may refer to:
* 97 (number)
Years
* 97 BC
* AD 97
* 1997
* 2097
Other uses
* Scientific opinion on climate change, 97%, the figure from a seminal study of scientific consensus on climate change (i.e. 97% of surveyed articles on climate change ...
was entirely voluntary". It was, therefore, the duty of the courts to apply EU law.
On the other hand, in '' R (HS2 Action Alliance Ltd) v Secretary of State for Transport'' the Supreme Court held that certain fundamental principles of British constitutional law would not be interpreted by the courts as having been given up by membership of the EU, or probably any international organisation. Here a group protesting against the High Speed 2
High Speed 2 (HS2) is a planned high-speed railway line in England, the first phase of which is under construction in stages and due for completion between 2029 and 2033, depending on approval for later stages. The new line will run from its m ...
rail line from London to Manchester and Leeds claimed that the government had not properly followed an Environmental Impact Assessment Directive by whipping a vote in Parliament to approve the plan. They argued that the Directive required open and free consultation, which was not fulfilled if a party whip
A whip is an official of a political party whose task is to ensure party discipline in a legislature. This means ensuring that members of the party vote according to the party platform, rather than according to their own individual ideolog ...
compelled party members to vote. The Supreme Court unanimously held the Directive did not require that no party whip occurred, but if a conflict had existed a Directive would not be able to compromise the fundamental constitutional principle from the Bill of Rights
A bill of rights, sometimes called a declaration of rights or a charter of rights, is a list of the most important rights to the citizens of a country. The purpose is to protect those rights against infringement from public officials and pr ...
that Parliament is free to organise its affairs.
Fourth, devolution in the United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, devolution is the Parliament of the United Kingdom's statutory granting of a greater level of self-government to the Scottish Parliament, the Senedd (Welsh Parliament), the Northern Ireland Assembly and the London ...
has meant Parliament gave power to legislate on specific topics to nations and regions: the Scotland Act 1998
The Scotland Act 1998 (c. 46) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which legislated for the establishment of the devolved Scottish Parliament with tax varying powers and the Scottish Government (then Scottish Executive). It was o ...
created the Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba ; sco, Scots Pairlament) is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. Located in the Holyrood area of the capital city, Edinburgh, it is frequently referred to by the metonym Holyr ...
, the Government of Wales Act 1998
The Government of Wales Act 1998 (c. 38) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom.
It was passed in 1998 by the Labour government to create a Welsh Assembly, therefore granting Wales a degree of self-government. This legislative ...
created the Welsh Assembly, the Northern Ireland Act 1998
__NOTOC__
The Northern Ireland Act 1998 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which allowed Westminster to devolve power to Northern Ireland, after decades of direct rule.
It renamed the New Northern Ireland Assembly, established by ...
created a Northern Ireland Executive following the historic Good Friday Agreement, to bring peace. In addition, the Local Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 (c. 70) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Gov ...
and the Greater London Authority Act 1999
The Greater London Authority Act 1999 (c. 29) is the Act of Parliament that established the Greater London Authority, the London Assembly and the Mayor of London.
Background
The Act was brought in after a referendum was held under the Great ...
give more limited powers to local and London governments. Practically, but also constitutionally, it has become increasingly accepted that decisions should not be taken for the UK which would override, and run counter to, the will of regional governments. However, in '' R (Miller) v Secretary of State for Exiting the European Union'', a group of people who sought to remain in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
contested the government on whether the Prime Minister could trigger Article 50 to notify the European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body ...
of the UK's intention to leave, without an Act of Parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation, are texts of law passed by the legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of parliame ...
. This followed the Brexit poll of 2016 where 51.9% of those voting voted to leave.
The claimants argued that, because Brexit
Brexit (; a portmanteau of "British exit") was the Withdrawal from the European Union, withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU) at 23:00 Greenwich Mean Time, GMT on 31 January 2020 (00:00 1 February 2020 Central Eur ...
would obliterate rights that Parliament had conferred through Acts of Parliament (such as the right of free movement of British citizens in the EU, the right to fair competition through merger control, and the right to vote for EU institutions) only Parliament could consent to notifying the intention to negotiate to leave under Article 50. They also argued that the Sewel Convention
A legislative consent motion (LCM, also known as a Sewel motion in Scotland) is a motion passed by either the Scottish Parliament, Senedd, or Northern Ireland Assembly, in which it consents that the Parliament of the United Kingdom may (or may ...
for devolved assemblies, where the assembly passes a motion that the Westminster Parliament can legislate on a devolved matter before it does so, meant the UK could not negotiate to leave without the Scottish, Welsh or Northern Ireland legislatures' consent. The Supreme Court held that the government could not begin the process of leaving purely through royal prerogative
The royal prerogative is a body of customary authority, privilege and immunity, recognized in common law and, sometimes, in civil law jurisdictions possessing a monarchy, as belonging to the sovereign and which have become widely vested in th ...
; Parliament must pass an Act enabling it to do so. However, the Sewel convention could not be enforced by courts, rather than observed. This led Prime Minister Theresa May
Theresa Mary May, Lady May (; née Brasier; born 1 October 1956) is a British politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and Leader of the Conservative Party from 2016 to 2019. She previously served in David Cameron's cab ...
to procure the European Union (Notification of Withdrawal) Act 2017
The European Union (Notification of Withdrawal) Act 2017 (c. 9) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom to empower the Prime Minister to give to the Council of the European Union the formal notice – required by Article 50 of t ...
, giving her power to notify the intention to leave the EU.
Rule of law
Therule of law
The rule of law is the political philosophy that all citizens and institutions within a country, state, or community are accountable to the same laws, including lawmakers and leaders. The rule of law is defined in the ''Encyclopedia Britannic ...
has been regarded as a fundamental principle of modern legal systems, including the UK. It has been called "as important in a free society as the democratic franchise", and even "the ultimate controlling factor on which our constitution is based". Like parliamentary sovereignty, its meaning and extent is disputed. The most widely accepted meanings speak of several factors: Lord Bingham of Cornhill
Sir Thomas Henry Bingham, Baron Bingham of Cornhill, (13 October 193311 September 2010), was an eminent British judge who was successively Master of the Rolls, Lord Chief Justice and Senior Law Lord. He was described as the greatest lawyer ...
, formerly the highest judge in England and Wales, suggested the rule of law ought to mean that law is clear and predictable, not subject to broad or unreasonable discretion, applies equally to all people, with speedy and fair procedures for enforcement, protects fundamental human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
, and works according to international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
. T Bingham, "The Rule of Law" (2007), 66(1) ''Cambridge Law Journal'' 67, ; and see also T. Bingham, ''Rule of Law'' (2008) 8, "all persons and authorities within the state, whether public or private
Private or privates may refer to:
Music
* " In Private", by Dusty Springfield from the 1990 album ''Reputation''
* Private (band), a Denmark-based band
* "Private" (Ryōko Hirosue song), from the 1999 album ''Private'', written and also recorde ...
should be bound by and entitled to the benefit of laws publicly made, taking effect (generally) in the future and publicly administered in the courts." Lord Bingham, "The Rule of Law and the Sovereignty of Parliament" (31 October 2007), King's College, London
King's College London (informally King's or KCL) is a public university, public research university located in London, England. King's was established by royal charter in 1829 under the patronage of George IV of the United Kingdom, King G ...
, also remarked, "democracy lies at the heart of the concept of the rule of law".
Other definitions seek to exclude human rights and international law as relevant, but largely stem from visions of pre-democratic scholars such as Albert Venn Dicey
Albert Venn Dicey, (4 February 1835 – 7 April 1922), usually cited as A. V. Dicey, was a British Whig jurist and constitutional theorist. He is most widely known as the author of ''Introduction to the Study of the Law of the Constitution ...
. The rule of law was explicitly recognised as a "constitutional principle" in section 1 of the Constitutional Reform Act 2005
The Constitutional Reform Act 2005 (c 4) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, relevant to UK constitutional law. It provides for a Supreme Court of the United Kingdom to take over the previous appellate jurisdiction of the Law L ...
, which limited the judicial role of the Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. Th ...
and recast the judicial appointments system to entrench independence, diversity and merit. As statute gives no further definition, the practical meaning of the "rule of law" develops through case law.
At its core, the rule of law, in English and British law, has traditionally been the principle of "legality
Legality, in respect of an act, agreement, or contract is the state of being consistent with the law or of being lawful or unlawful in a given jurisdiction, and the construct of power.
According to the Merriam-Webster Dictionary, legality is 1 : ...
". This means that the state, government, and any person acting under government authority (including a corporation), may only act according to law. In 1765, in '' Entick v Carrington'' a writer, John Entick
John Entick (c.1703 – May 1773) was an English schoolmaster and author. He was largely a hack writer, working for Edward Dilly, and he padded his credentials with a bogus M.A. and a portrait in clerical dress; some of his works had a more l ...
, claimed that the King's Chief Messenger, Nathan Carrington, had no legal authority to break into and ransack his home, and remove his papers. Carrington claimed he had authority from the Secretary of State, Lord Halifax
Edward Frederick Lindley Wood, 1st Earl of Halifax, (16 April 1881 – 23 December 1959), known as The Lord Irwin from 1925 until 1934 and The Viscount Halifax from 1934 until 1944, was a senior British Conservative politician of the 19 ...
, who issued a search "warrant", but there was no statute that gave Lord Halifax the authority to issue search warrants. Lord Camden CJ held that the "great end, for which men entered into society, was to secure their property", and that without any authority "every invasion of private property, be it ever so minute, is a trespass." Carrington acted unlawfully and had to pay damages.
Today this principle of legality is found throughout the European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by ...
, which enables infringements of rights as a starting point only if "in accordance with the law". In 1979, in '' Malone v Metropolitan Police Commissioner'' a man charged with handling stolen goods claimed the police unlawfully tapped his phone, to get evidence. The only related statute, the Post Office Act 1969 Schedule 5, stated there should be no interference in telecommunications unless the Secretary of State issued a warrant, but said nothing explicit about phone tapping. Megarry VC
Sir Robert Edgar Megarry, Privy Council of the United Kingdom, PC, British Academy, FBA (1 June 1910 – 11 October 2006) was an eminent British lawyer and judge. Originally a solicitor, he requalified as a barrister and also pursued a parallel ...
held there was no wrong at common law, and refused to interpret the statute in light of the right to privacy under the European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by ...
, article 8. On appeal, the European Court of Human Rights concluded the Convention was breached because the statute did not "indicate with reasonable clarity the scope and manner of exercise of the relevant discretion conferred on the public authorities." The judgment, however, was overshadowed by the government swiftly passing a new Act to authorise phone tapping with a warrant. By itself the principle of legality is not enough to alone preserve human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
in the face of ever more intrusive statutory powers of surveillance by corporations or government.
 The rule of law requires the law is truly enforced, though enforcement bodies may have room for discretion. In '' R (Corner House Research) v Director of the Serious Fraud Office'', a group campaigning against the arms trade, Corner House Research, claimed the Serious Fraud Office acted unlawfully by dropping an investigation into the UK–Saudi
The rule of law requires the law is truly enforced, though enforcement bodies may have room for discretion. In '' R (Corner House Research) v Director of the Serious Fraud Office'', a group campaigning against the arms trade, Corner House Research, claimed the Serious Fraud Office acted unlawfully by dropping an investigation into the UK–Saudi Al-Yamamah arms deal
Al Yamamah ( ar, اليمامة, translation=The Dove) is the name of a series of record arms sales by the United Kingdom to Saudi Arabia, paid for by the delivery of up to of crude oil per day to the British government. The prime contract ...
. It was alleged that BAE Systems plc paid bribes to Saudi government figures. The House of Lords held the SFO was entitled to take into account the public interest in not pursuing an investigation, including the security threats that might transpire. Baroness Hale
Brenda Marjorie Hale, Baroness Hale of Richmond, (born 31 January 1945) is a British judge who served as President of the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom from 2017 until her retirement in 2020, and serves as a member of the House of Lords ...
remarked that the SFO had to consider "the principle that no-one, including powerful British companies who do business for powerful foreign countries, is above the law", but the decision reached was not unreasonable. When enforcement or court proceedings do take place, they should proceed swiftly: anyone who is detained must be charged and put on trial or released.
People must also be able to access justice in practice. In '' R (UNISON) v Lord Chancellor'' the Supreme Court held the government's imposition of £1200 in fees to bring an employment tribunal
Employment tribunals are tribunal public bodies in England and Wales and Scotland which have statutory jurisdiction to hear many kinds of disputes between employers and employees. The most common disputes are concerned with unfair dismissal, ...
claim undermined the rule of law
The rule of law is the political philosophy that all citizens and institutions within a country, state, or community are accountable to the same laws, including lawmakers and leaders. The rule of law is defined in the ''Encyclopedia Britannic ...
, and was void. The Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. Th ...
had statutory authority to create fees for court services, but in the case of employment tribunals, his Order led to a 70% drop in claims against employers for breach of labour rights
Labor rights or workers' rights are both legal rights and human rights relating to labor relations between workers and employers. These rights are codified in national and international labor and employment law. In general, these rights influe ...
, such as unfair dismissal, unlawful wage deductions or discrimination. Lord Reed said the "constitutional right of access to the courts is inherent in the rule of law". Without access to courts, "laws are liable to become a dead letter, the work done by Parliament may be rendered nugatory, and the democratic election of Members of Parliament may become a meaningless charade." In principle every person is subject to the law, including government ministers, or corporate executives, who may be held in contempt of court
Contempt of court, often referred to simply as "contempt", is the crime of being disobedient to or disrespectful toward a court of law and its officers in the form of behavior that opposes or defies the authority, justice, and dignity of the cour ...
for violating an order.
In other systems the idea of a separation of powers
Separation of powers refers to the division of a state's government into branches, each with separate, independent powers and responsibilities, so that the powers of one branch are not in conflict with those of the other branches. The typi ...
is seen as an essential part of maintaining the rule of law. In theory, originally advocated by Baron de Montesquieu
Charles Louis de Secondat, Baron de La Brède et de Montesquieu (; ; 18 January 168910 February 1755), generally referred to as simply Montesquieu, was a French judge, man of letters, historian, and political philosopher.
He is the principal ...
, there should be a strict separation of the executive, legislature and judiciary. While other systems, notably the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, attempted to put this into practice (e.g. requiring the executive does not come from the legislature), it is clear that modern political parties may undermine such a separation by capturing all three branches of government, and democracy has been maintained since the 20th century despite the fact that "there is no formal separation of powers in the United Kingdom". The Constitutional Reform Act 2005
The Constitutional Reform Act 2005 (c 4) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, relevant to UK constitutional law. It provides for a Supreme Court of the United Kingdom to take over the previous appellate jurisdiction of the Law L ...
did, however, end the practice of the Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. Th ...
sitting as the head of the judiciary, while also being a Member of Parliament, and sitting in the cabinet. Since the Act of Settlement 1700, there has been only one instance of a judge being removed, and a suspension cannot happen without the Lord Chief Justice and the Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. Th ...
following a judge being subject to criminal proceedings. There is now a duty on all ministers to "uphold the continued independence of the judiciary", including against assault by powerful corporations or the media.
Democracy
 The principle of a "democratic society", with a functioning representative and
The principle of a "democratic society", with a functioning representative and deliberative democracy
Deliberative democracy or discursive democracy is a form of democracy in which deliberation is central to decision-making. It adopts elements of both consensus decision-making and majority rule. Deliberative democracy differs from traditional ...
, that upholds human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
, legitimises the fact of Parliamentary sovereignty, and it is widely considered that "democracy lies at the heart of the concept of the rule of law". The opposite of arbitrary power exercised by one person is "administration is in the hands of the many and not of the few". According to the preamble to the European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by ...
, as drafted by British lawyers following World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, fundamental human rights and freedoms are themselves "best maintained ... by "an effective political democracy". Similarly, this "characteristic principle of democracy" is enshrined by the First Protocol, article 3, which requires the "right to free elections" to "ensure the free expression of the opinion of the people in the choice of the legislature". While there are many conceptions of democracy, such as "direct", "representative" or "deliberative", the dominant view in modern political theory is that democracy requires an active citizenry, not only in electing representatives, but in taking part in political life.
Its essence lies in not simply majority decision-making, nor referendums that can easily be used as a tool of manipulation, "but in the making of politically responsible decisions" and in "large-scale social changes maximising the freedom" of humankind. The legitimacy of law in a democratic society depends upon a constant process of deliberative discussion and public debate, rather than imposition of decisions. It is also generally agreed that basic standards in political, social and economic rights are necessary to ensure everyone can play a meaningful role in political life. For this reason, the rights to free voting in fair elections and "general welfare in a democratic society" have developed hand-in-hand with all human rights, and form a fundamental cornerstone of international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
.
In the UK's "modern democratic constitution", the principle of democracy is manifested through statutes and case law which guarantee the right to vote in fair elections, and through its use as a principle of interpretation by courts. In 1703, in the landmark case of ''Ashby v White
''Ashby v White'' (170392 ER 126 is a foundational case in UK constitutional law and English tort law. It concerns the right to vote and misfeasance of a public officer. Lord Holt laid down the important principle that where there is injury in ...
'', Lord Holt CJ
Sir John Holt (23 December 1642 – 5 March 1710) was an English lawyer who served as Lord Chief Justice of England from 17 April 1689 to his death. He is frequently credited with playing a major role in ending the prosecution of witches in En ...
stated that the right of everyone "to give heir
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Offic ...
vote at the election of a person to represent hemin Parliament, there to concur to the making of laws, which are to bind heir
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Offic ...
liberty and property, is a most transcendent thing, and of an high nature". This has meant that the courts actively ensure that votes cast are counted, and that democratic elections are conducted according to law. In ''Morgan v Simpson
''Morgan v Simpson'' 975QB 151 is a UK constitutional law case, concerning the right to vote and the integrity of votes and elections in the United Kingdom.
Facts
Gladys Morgan and four voters in the 1973 election for the Greater London Council ...
'' the Court of Appeal
A court of appeals, also called a court of appeal, appellate court, appeal court, court of second instance or second instance court, is any court of law that is empowered to hear an appeal of a trial court or other lower tribunal. In much ...
held that if a vote "was conducted so badly that it was not substantially in accordance with the law as" then it would be declared void, and so would even minor irregularities that would affect the result.
A considerable body of regulation, for instance in the Representation of the People Act 1983 or the Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act 2000
The Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act 2000 (c. 41) is an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom that sets out how political parties, elections and referendums are to be regulated in the United Kingdom. It formed an important ...
, restrict spending or any foreign interference because, according to Baroness Hale
Brenda Marjorie Hale, Baroness Hale of Richmond, (born 31 January 1945) is a British judge who served as President of the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom from 2017 until her retirement in 2020, and serves as a member of the House of Lords ...
"each person has equal value" and "we do not want our government or its policies to be decided by the highest spenders". More broadly, the concept of a "democratic society" and what is "necessary" for its functioning underpins the entire scheme of interpretation for the European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by ...
as applied in British law, particularly after the Human Rights Act 1998
The Human Rights Act 1998 (c. 42) is an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom which received royal assent on 9 November 1998, and came into force on 2 October 2000. Its aim was to incorporate into UK law the rights contained in the European Con ...
, because each right can usually only be restricted if "in accordance with law" and as "necessary in a democratic society". The place of the social welfare state that is necessary to support democratic life is also manifested through courts' interpretation. For instance, in ''Gorringe v Calderdale MBC'', Lord Steyn, giving the leading judgement, said it was "necessary" to view the law of negligence in the context of "the contours of our social welfare state". More generally, the common law has been increasingly developed to be harmonious with statutory rights, and also in harmony with rights under international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
.
Internationalism
Like other democratic countries, the principles ofinternational law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
are a basic component of the British constitution, both as a primary tool of interpretation of domestic law, and through the UK's consistent support and membership of major international organisations. As far back as Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by t ...
, English law recognised the right to free movement of people for international trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories because there is a need or want of goods or services. (see: World economy)
In most countries, such trade represents a significa ...
. By 1608, Sir Edward Coke
Edward is an English given name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortune; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”.
History
The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Sax ...
wrote confidently that international commercial law, or the , is part of the laws of the realm, while the constitutional crises of the 17th century centred upon Parliament halting the King's attempting to tax international trade without its consent. Similarly in the 18th century, Lord Holt CJ
Sir John Holt (23 December 1642 – 5 March 1710) was an English lawyer who served as Lord Chief Justice of England from 17 April 1689 to his death. He is frequently credited with playing a major role in ending the prosecution of witches in En ...
viewed international law as a general tool for interpretation of the common law, while Lord Mansfield
William Murray, 1st Earl of Mansfield, PC, SL (2 March 170520 March 1793) was a British barrister, politician and judge noted for his reform of English law. Born to Scottish nobility, he was educated in Perth, Scotland, before moving to Lond ...
in particular did more than any other to affirm that the international "is not the law of a particular country but the law of all nations", and "the law of merchants and the law of the land is the same".
In 1774, in '' Somerset v Stewart'', one of the most important cases in legal history, Lord Mansfield
William Murray, 1st Earl of Mansfield, PC, SL (2 March 170520 March 1793) was a British barrister, politician and judge noted for his reform of English law. Born to Scottish nobility, he was educated in Perth, Scotland, before moving to Lond ...
held that slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
was lawful "in no country" and therefore in common law.
In modern case law it has been consistently accepted that it "is a principle of legal policy that ritishlaw should conform to public international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
." The House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
stressed that "there is a strong presumption in favour of interpreting English law (whether common law or statute) in a way which does not place the United Kingdom in breach of an international obligation." For example, in '' Hounga v Allen'' the Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
held that a young lady who had been illegally trafficked to the UK had a right to bring a race discrimination claim against her employers, even though she had herself been in violation of the Immigration Act 1971
The Immigration Act 1971c 77 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom concerning immigration and nearly entirely remaking the field of British immigration law. The Act, as with the Commonwealth Immigrants Act 1962, and that of 1968, res ...
. In doing so, the court unanimously drew upon international treaties signed by the UK, known as the Palermo protocols The Palermo protocols are three protocols that were adopted by the United Nations to supplement the 2000 Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (the Palermo Convention). They are:
*the Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking i ...
, as well as the European Convention on Human Rights, in interpreting the scope of the common law doctrine of illegality
A wrong (from Old English – 'crooked') is an act that is illegal or immoral. Legal wrongs are usually quite clearly defined in the law of a state and/or jurisdiction. They can be divided into civil wrongs and crimes (or ''criminal offenses'') ...
, and held it was no bar for the claimant to assert her legal rights. It has been further debated whether the UK should adopt a theory of that sees international law as part of UK without any further act (a "monist
Monism attributes oneness or singleness (Greek: μόνος) to a concept e.g., existence. Various kinds of monism can be distinguished:
* Priority monism states that all existing things go back to a source that is distinct from them; e.g., i ...
" theory), or whether it should still be required for international law principles to be translated into domestic law (a "dualist" theory). The current position in European Union law
European Union law is a system of rules operating within the member states of the European Union (EU). Since the founding of the European Coal and Steel Community following World War II, the EU has developed the aim to "promote peace, its valu ...
is that while international law binds the EU, it cannot undermine fundamental principles of constitutional law or human rights.
 Since the World Wars brought an end to the
Since the World Wars brought an end to the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
and physically destroyed large parts of the country, the UK has consistently supported organisations formed under international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
. From the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
in 1919, the UK was a founding member of the International Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is the first and o ...
, which sets universal standards for people's rights at work. After the failure of the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
and following World War II, the UK became a founding member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
, recognised by Parliament through the United Nations Act 1946
The United Nations Act 1946 (9 & 10 Geo. 6 c. 45) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which enables His Majesty's Government to implement resolutions under Article 41 of the United Nations Charter as Orders in Council. Thus Parli ...
, enabling any resolution of the Security Council except the use of force to be implemented by an Order in Council. Due the Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN committee chaired by Eleanor Roosevelt ...
in 1948, the continuation of the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
lost substantial legitimacy under international law, and combined with independence movements this led to its rapid dissolution.
Two fundamental treaties, the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights
The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) is a multilateral treaty that commits nations to respect the civil and political rights of individuals, including the right to life, freedom of religion, freedom of speech, fre ...
and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights
The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR) is a multilateral treaty adopted by the United Nations General Assembly (GA) on 16 December 1966 through GA. Resolution 2200A (XXI), and came in force from 3 January 197 ...
in 1966, saw the UK ratify most rights from the Universal Declaration. Codifying the Ponsonby Rule from 1924, the Constitutional Reform and Governance Act 2010
The Constitutional Reform and Governance Act 2010 (c. 25), or CRAG Act, is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom on UK constitutional law which affected the civil service and the ratification of treaties, and made other significant c ...
section 20 stipulates that a treaty is ratified once it is laid before Parliament for 21 days and no adverse resolution is passed against it. Regionally, the UK participated in drafting the 1950 European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by ...
which sought to guarantee basic standards of democracy and human rights to preserve peace in post-war Europe. At the same time, following long-held visions for European integration with the UK "at the centre", democratic European countries sought to integrate their economies both to make war vain, and to advance social progress.
In 1972, the UK joined the European Communities
The European Communities (EC) were three international organizations that were governed by the same set of institutions. These were the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or Euratom), and the ...
(reorganized and renamed the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
in 1992) and committed to implement EU law
European Union law is a system of rules operating within the member states of the European Union (EU). Since the founding of the European Coal and Steel Community following World War II, the EU has developed the aim to "promote peace, its val ...
in which it participated, in the European Communities Act 1972. In 1995, the UK also became a founding member of the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and ...
. To ensure that the European Convention was directly applied by the courts, the Human Rights Act 1998
The Human Rights Act 1998 (c. 42) is an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom which received royal assent on 9 November 1998, and came into force on 2 October 2000. Its aim was to incorporate into UK law the rights contained in the European Con ...
was passed. Parliament also passed the International Criminal Court Act 2001 to enable prosecution of war criminals, and subjected itself to the jurisdiction of the International Criminal Court
The International Criminal Court (ICC or ICCt) is an intergovernmental organization and International court, international tribunal seated in The Hague, Netherlands. It is the first and only permanent international court with jurisdiction to pro ...
. In 2016 the UK voted in a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a Representative democr ...
on whether to leave the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
, resulting—with a 72.2% turnout—in a margin of 51.9% favouring "leave" and 48.1% favouring "remain". Some allegations were made of misconduct taking place in the campaigns in support of both referendum options, whilst authorities found nothing considered serious enough to affect results and little to chastise.
Institutions
 While principles may be the basis of the UK constitution, the institutions of the state perform its functions in practice. First,
While principles may be the basis of the UK constitution, the institutions of the state perform its functions in practice. First, Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
is the sovereign entity. Its two chambers legislate. In the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
each Member of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members o ...
is elected by a simple plurality in a democratic vote, although outcomes do not always accurately match people's preferences overall. Elections must be held within five years after the previous election of a Parliament, though historically they have tended to occur each four years. Election spending is tightly controlled, foreign interference is prohibited, and donations and lobbying are limited in whatever form. The House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
reviews and votes upon legislative proposals by the Commons. It can delay legislation by one year, and cannot delay at all if the proposed Act concerns money.
Most Lords are appointed by the Prime Minister, through the King, on the advice of a Commission which, by convention, offers some balance between political parties. Ninety-two hereditary peers remain. To become law, each Act of Parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation, are texts of law passed by the legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of parliame ...
must be read by both houses three times, and given royal assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in oth ...
by the monarch. The Sovereign does not veto legislation, by convention, since 1708
In the Swedish calendar it was a leap year starting on Wednesday, one day ahead of the Julian and ten days behind the Gregorian calendar.
Events
January–June
* January 1 – Charles XII of Sweden invades Russia, by crossing ...
. Second, the judiciary interprets the law. It can not strike down an Act of Parliament, but the judiciary ensures that any law which may violate fundamental rights has to be clearly expressed, to force politicians to openly confront what they are doing and "accept the political cost".
Under the Constitutional Reform Act 2005
The Constitutional Reform Act 2005 (c 4) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, relevant to UK constitutional law. It provides for a Supreme Court of the United Kingdom to take over the previous appellate jurisdiction of the Law L ...
, the judiciary is appointed by the Judicial Appointments Commission with cross-party and judicial recommendations, to protect judicial independence. Third, the executive branch of government is led by the prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
who must be able to command a majority in the House of Commons. The Cabinet of Ministers is appointed by the Prime Minister to lead the main departments of state, such as the Treasury
A treasury is either
*A government department related to finance and taxation, a finance ministry.
*A place or location where treasure, such as currency or precious items are kept. These can be state or royal property, church treasure or i ...
, the Foreign Office
Foreign may refer to:
Government
* Foreign policy, how a country interacts with other countries
* Ministry of Foreign Affairs, in many countries
** Foreign Office, a department of the UK government
** Foreign office and foreign minister
* Unit ...
, the Department of Health and the Department for Education
The Department for Education (DfE) is a department of His Majesty's Government responsible for child protection, child services, education (compulsory, further and higher education), apprenticeships and wider skills in England.
A Departme ...
. Officially the "head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and ...
" is the monarch, but all prerogative power
The royal prerogative is a body of customary authority, privilege and immunity, recognized in common law and, sometimes, in civil law jurisdictions possessing a monarchy, as belonging to the sovereign and which have become widely vested in th ...
is exercised by the Prime Minister, subject to judicial review
Judicial review is a process under which executive, legislative and administrative actions are subject to review by the judiciary. A court with authority for judicial review may invalidate laws, acts and governmental actions that are incomp ...
. Fourth, as the UK matured as a modern democracy, an extensive system of civil servants, and public service
A public service is any service intended to address specific needs pertaining to the aggregate members of a community. Public services are available to people within a government jurisdiction as provided directly through public sector agencies ...
institutions developed to deliver UK residents economic, social and legal rights. All public bodies, and private bodies that perform public functions, are bound by the rule of law
The rule of law is the political philosophy that all citizens and institutions within a country, state, or community are accountable to the same laws, including lawmakers and leaders. The rule of law is defined in the ''Encyclopedia Britannic ...
.
Parliament
In the British constitution,Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
sits at the apex of power. It emerged through a series of revolutions as the dominant body, over the church
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a building for Christian religious activities
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship
* Chri ...
, courts
A court is any person or institution, often as a government institution, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and carry out the administration of justice in civil, criminal, and administrative matters in accorda ...
, and the monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority ...
, and within Parliament the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
emerged as the dominant chamber, over the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
that traditionally represented the aristocracy
Aristocracy (, ) is a form of government that places strength in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocrats. The term derives from the el, αριστοκρατία (), meaning 'rule of the best'.
At the time of the word' ...
. The central justification for Parliamentary sovereignty
Parliamentary sovereignty, also called parliamentary supremacy or legislative supremacy, is a concept in the constitutional law of some parliamentary democracies. It holds that the legislative body has absolute sovereignty and is supreme over ...
is usually thought to be its democratic nature, although it was only upon the Representation of the People (Equal Franchise) Act 1928 that Parliament could be said to have finally become "democratic" in any modern sense (as property qualifications to vote were abolished for everyone over 21), and not until after the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
that decolonisation, university constituencies and lowering of the voting age took place. Parliament's main functions are to legislate, to allocate money for public spending, and to scrutinise the government.
In practice many MPs are involved in Parliamentary committees of the United Kingdom, Parliamentary committees which investigate spending, policies, laws and their impact, and often report to recommend reform. For instance, the Modernisation Committee of the House of Commons in 2002 recommended publishing draft bills before they became law, and was later found to have been highly successful. There are 650 Member of parliament, Members of Parliament (MPs) in the House of Commons, currently elected for terms of up to five years, and 790 peers in the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
. For a proposed Bill to become an Act, and law, it must be read three times in each chamber, and given royal assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in oth ...
by the monarch.
 Today, the
Today, the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
is the primary organ of representative government. Section 1 of the Representation of the People Act 1983 gives the right to all registered citizens of the United Kingdom, the Republic of Ireland and the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth aged 18 and over to elect Members of Parliament to the House of Commons. Sections 3 and 4 exclude people who are convicted of an offence and in a penal institution, or detained under mental health laws. These restrictions fall below European standards, which require that people who are convicted of very minor crimes (such as petty theft or drug offences) have the right to vote. Since 2013, everyone has to register individually to vote, instead of households being able to register collectively, but an annual household canvass is conducted to increase the number of registered people.
As far back as 1703, ''Ashby v White
''Ashby v White'' (170392 ER 126 is a foundational case in UK constitutional law and English tort law. It concerns the right to vote and misfeasance of a public officer. Lord Holt laid down the important principle that where there is injury in ...
'' recognised the right to "vote at the election of a person to represent him or [her] in Parliament, there to concur to the making of laws, which are to bind his liberty and property" as "a most transcendent thing, and of an high nature". This originally meant that any interference in that right would lead to damages. If the denial of voting would have changed the result, or if a vote was "conducted so badly that it was not substantially in accordance with the law" the vote would have to be run again. So, in ''Morgan v Simpson
''Morgan v Simpson'' 975QB 151 is a UK constitutional law case, concerning the right to vote and the integrity of votes and elections in the United Kingdom.
Facts
Gladys Morgan and four voters in the 1973 election for the Greater London Council ...
'' the Court of Appeal declared that an election for a Greater London Council seat was not valid after it was found that 44 unstamped ballot papers were not counted. These common law principles predate statutory regulation, and therefore appear to apply to any vote, including elections and referendums.
Election spending is tightly controlled today by statute. A maximum of £20 million can be spent by political parties in national campaigns, plus £10,000 in each constituency. Political advertisements on television are prohibited except for those in certain free time slots, although the internet remains largely unregulated. Any spending over £500 by third parties must be disclosed. While these rules are strict, they were held in ''Animal Defenders International v United Kingdom, Animal Defenders International v UK'' to be compatible with the Convention because "each person has equal value" and "we do not want our government or its policies to be decided by the highest spenders." Foreign interference in voting is completely prohibited, including any "broadcasting" (also over the internet) "with intent to influence persons to give or refrain from giving their votes".
Donations by foreign parties can be forfeited in their entirety to the Election commission, Electoral Commission. Domestic donations are limited to registered parties, and must be reported, when they are over £7,500 nationally or £1,500 locally, to the Electoral Commission. The system for electing the Commons is based on constituencies, whose boundaries are Sixth Periodic Review of Westminster constituencies, periodically reviewed to even out populations. There has been considerable debate about the First-past-the-post voting, first-past-the-post system of voting the UK uses, as it tends to exclude minority parties. By contrast, in Australia voters may select preferences for candidates, although this system was rejected in a 2011 United Kingdom Alternative Vote referendum staged by the Cameron-Clegg coalition. In the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the Legislature, legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven Institutions of the European Union, institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and in ...
, voters choose a party from multi-member regional constituencies: this tends to give smaller parties much greater representation. In the Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba ; sco, Scots Pairlament) is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. Located in the Holyrood area of the capital city, Edinburgh, it is frequently referred to by the metonym Holyr ...
, the Senedd, Welsh Parliament and London Assembly, voters have the choice of both constituencies and a party list, which tends to reflect overall preferences best. To be elected as an MP, most people generally become members of Political party, political parties, and must be over 18 on the day of nomination to run for a seat, be a qualifying Commonwealth or Irish citizen, not be bankrupt, found guilty of corrupt practices, or be a Lord, judge or employee of the civil service. To limit the government's practical control over Parliament, the Ministerial and other Salaries Act 1975 restricts higher payment of salaries to a set number of MPs.
 Along with a hereditary monarch, the
Along with a hereditary monarch, the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
remains an historical curiosity in the British constitution. Traditionally it represented the landed aristocracy, and political allies of the monarch or the government, and has only gradually and incompletely been reformed. Today, the House of Lords Act 1999 has abolished all but 92 hereditary peers, leaving most peers to be "life peers" appointed by the government under the Life Peerages Act 1958, law lords appointed under the Appellate Jurisdiction Act 1876, and Lords Spiritual who are senior clergy of the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Brit ...
. Since 2005, senior judges can only sit and vote in the House of Lords after retirement. The government carries out appointment of most peers, but since 2000 has taken advice from a seven-person House of Lords Appointments Commission with representatives from the Labour, Conservatives and Liberal-Democrat parties. A peerage can always be disclaimed, and ex-peers may then run for Parliament. Since 2015, a peer may be suspended or expelled by the House. In practice the Parliament Act 1949
The Parliament Act 1949 (12, 13 & 14 Geo. 6 c. 103) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It reduced the power of the House of Lords to delay certain types of legislation – specifically public bills other than money bills ...
greatly reduced the House of Lords' power, as it can only delay and cannot block legislation by one year, and cannot delay money bills at all.
Several Reform of the House of Lords, options for reform have been debated. A House of Lords Reform Bill 2012 proposed to have 360 directly elected members, 90 appointed members, 12 bishops and an uncertain number of ministerial members. The elected Lords would have been elected by proportional representation for 15-year terms, through 10 regional constituencies on a single transferable vote system. However, the government withdrew support after backlash from Conservative backbenches. It has often been argued that if the Lords were elected by geographic constituencies and a party controlled both sides "there would be little prospect of effective scrutiny or revision of government business." A second option, like in Swedish Riksdag, could simply be to abolish the House of Lords: this was in fact done during the English Civil War in 1649, but restored along with the monarchy in Convention Parliament (1660), 1660. A third proposed option is to elect peers by work and professional groups, so that health care workers elect peers with special health knowledge, people in education elect a fixed number of education experts, legal professionals elect legal representatives, and so on. This is argued to be necessary to improve the quality of legislation.
Judiciary
The judiciary in the United Kingdom has the essential functions of upholding therule of law
The rule of law is the political philosophy that all citizens and institutions within a country, state, or community are accountable to the same laws, including lawmakers and leaders. The rule of law is defined in the ''Encyclopedia Britannic ...
, democracy, and human rights. The highest court of appeal, renamed from the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
officially from 2005, is the Supreme Court. The Lord Chancellor's role changed dramatically on 3 April 2006, as a result of the Constitutional Reform Act 2005. Due to the Constitutional Reform Act of 2005, the make up of the Judiciary is clearly demonstrated for the first time inside the Constitution. This form of enshrined law presents a new branch of government. An independent Supreme Court has been established, separate from the House of Lords and with its own independent appointments system, staff, budget and building.
Further aspects of this explores how independent the Judiciary has become. An Appointments Commission, responsible for selecting candidates to recommend for judicial appointment to the Secretary of State for Justice was established. The Judicial Appointments Commission ensures that merit remains the sole criterion for appointment and the appointments system is modern, open and transparent. In terms of scrutiny, A Judicial Appointment and Conduct Ombudsman, responsible for investigating and making recommendations concerning complaints about the judicial appointments process, and the handling of judicial conduct complaints within the scope of the Constitutional Reform Act, provides checks and balances to the Supreme Court.
The Judiciary hears appeals from the whole UK in civil law matters, and for criminal law in England and Wales, and Northern Ireland. It cannot hear criminal appeals from Scotland, as that was precluded by the 1707 Treaty of Union, and it is outside the formal competence of the British Parliament to alter that position. The Supreme Court does however consider "devolution issues" where these may affect Scottish criminal law. Since the 1966 Practice Statement, the judiciary has acknowledged that while a system of precedent, that binds lower courts, is necessary to provide "at least some degree of certainty", the courts should update their jurisprudence and "depart from a previous decision when it appears right to do so."
Litigation usually begins in a County Court (England and Wales), County Court or the High Court of Justice, High Court for civil law issues, or a magistrates' court (England and Wales), magistrates' court or the Crown Court for English criminal law, criminal law issues. There are also employment tribunal
Employment tribunals are tribunal public bodies in England and Wales and Scotland which have statutory jurisdiction to hear many kinds of disputes between employers and employees. The most common disputes are concerned with unfair dismissal, ...
s for United Kingdom labour law, labour law disputes, and the First-tier Tribunal for public or regulatory disputes, ranging from immigration, to social security, to tax. After the High Court, Crown Court, or appeal tribunals, cases generally may appeal to the Court of Appeal
A court of appeals, also called a court of appeal, appellate court, appeal court, court of second instance or second instance court, is any court of law that is empowered to hear an appeal of a trial court or other lower tribunal. In much ...
in England and Wales. In Scotland, the Court of Session
The Court of Session is the supreme civil court of Scotland and constitutes part of the College of Justice; the supreme criminal court of Scotland is the High Court of Justiciary. The Court of Session sits in Parliament House in Edinburg ...
has an Outer (first instance) and Inner (appeal) House. Appeals then go to the Supreme Court, although at any time a court may make a "Preliminary ruling, preliminary reference" to the Court of Justice of the European Union to clarify the meaning of EU law
European Union law is a system of rules operating within the member states of the European Union (EU). Since the founding of the European Coal and Steel Community following World War II, the EU has developed the aim to "promote peace, its val ...
. Since the Human Rights Act 1998
The Human Rights Act 1998 (c. 42) is an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom which received royal assent on 9 November 1998, and came into force on 2 October 2000. Its aim was to incorporate into UK law the rights contained in the European Con ...
, courts have been expressly required to interpret law to be compatible with the European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by ...
. This follows a longer tradition of courts interpreting the law to be compatible with international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
obligations.
It is generally accepted that the British courts do not merely apply but also create new law through their interpretative function: this is obvious in the common law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omniprese ...
and Equity (law), equity, where there is no codified statutory basis for large parts of the law, such as English contract law, contracts, English tort law, torts or English trust law, trusts. This also means an element of retroactivity, since an application of developing rules may differ from at least one party's understanding of the law in any conflict. Although formally the British judiciary may not declare an Act of Parliament "unconstitutional", in practice the judiciary's power to interpret the law so as to be compatible with human rights can render a statute inoperative, much like in other countries. The courts do so sparingly because they recognise the importance of the democratic process. Judges may also sit from time to time on public inquiries.
Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. Th ...
, once head of the judiciary but now simply a government minister, also has a statutory duty to uphold the independence of the judiciary, for instance, against attacks upon their integrity by media, corporations, or the government itself.
Members of the judiciary can be appointed from among any member of the legal profession who has over 10 years of experience having rights of audience before a court: this usually includes barristers, but can also mean solicitors or academics. Appointments should be made "solely on merit" but regard may be had to the need for diversity when two candidates have equal qualifications. For appointments to the Supreme Court, a five-member Judicial Appointments Committee is formed including one Supreme Court judge, three members from the Judicial Appointments Commission, and one lay person. For other senior judges such as those on the Court of Appeal, or for the Lord Chief Justice, Master of the Rolls, or the heads of the High Court divisions, a similar five member panel with two judges is formed. Gender and ethnic diversity is lacking in the British judiciary compared to other developed countries, and potentially compromises the expertise and administration of justice.
Backing up the judiciary is a considerable body of administrative law. The Contempt of Court Act 1981 enables a court to hold anyone in contempt, and commit the person to imprisonment, for violating a court order, or behaviour that could compromise a fair judicial process. In practice this is enforced by the executive. The Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. Th ...
heads the Ministry of Justice, which performs various functions including administering the Legal Aid Agency for people who cannot afford access to the courts. In '' R (UNISON) v Lord Chancellor'' the government suffered scathing criticism for creating high fees that cut the number of applicants to employment tribunals by 70 per cent. The Attorney General of England and Wales, and in Scottish matters, the Advocate General for Scotland, and the Solicitor General for England and Wales represent the Crown in litigation. The Attorney General also appoints the Director of Public Prosecutions who heads the Crown Prosecution Service, which reviews cases submitted by the police for prosecution, and conducts them on behalf of the Crown.
Executive
 The executive branch, while subservient to Parliament and judicial oversight, exercises day to day power of the British government. The UK remains a constitutional monarchy. The formal head of state is Majesty, His Majesty Monarchy of the United Kingdom, King Charles III, a Heredity, hereditary monarch since 2022. No Queen or King has withheld assent to any bill passed by Parliament Scottish Militia Bill, since 1708, and all constitutional duties and power are accepted by binding convention to have shifted to the
The executive branch, while subservient to Parliament and judicial oversight, exercises day to day power of the British government. The UK remains a constitutional monarchy. The formal head of state is Majesty, His Majesty Monarchy of the United Kingdom, King Charles III, a Heredity, hereditary monarch since 2022. No Queen or King has withheld assent to any bill passed by Parliament Scottish Militia Bill, since 1708, and all constitutional duties and power are accepted by binding convention to have shifted to the prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
, Parliament or the courts. Over the 17th century, the Petition of Right was asserted by Parliament to prevent any taxation by the monarch without Parliament's consent, and the Habeas Corpus Act 1640 denied the monarch any power to arrest people for failing to pay taxes.
The monarch's continued assertion of the Divine right of kings, divine right to rule led to Charles I of England, Charles I being executed in the English Civil War, and finally the settlement of power in the Bill of Rights 1689, Bill of Rights of 1689. Following the Acts of Union 1707, Act of Union 1707 and an early financial crisis as South Sea Company shares crashed, Robert Walpole emerged as a dominant political figure. Leading the House of Commons from 1721 to 1742, Walpole is generally acknowledged to be the first prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
(''Primus inter pares''). The PM's modern functions include leading the dominant political party, setting policy priorities, creating Ministries and appointing ministers, judges, peers, and civil servants. The PM also has considerable control through the convention of collective responsibility (that ministers must publicly support the government even when they privately disagree, or resign), and control over the government's communications to the public.
By contrast in law, as is necessary in a democratic society, the monarch is a figurehead with no political power, but a series of ceremonial duties, and considerable funding. Aside from Finances of the British royal family, private wealth and finance, the monarchy is funded under the Sovereign Grant Act 2011, which reserves 25 per cent of the net revenue from the Crown Estate. The Crown Estate is a public, government corporation, which in 2015 held £12 billion in investments, mostly land and property, and therefore generates income by charging English land law, rent to businesses or people for homes. The monarch's major ceremonial duties are to appoint the prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
who can command the majority of the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
, to give royal assent to Acts of Parliament, and to dissolve Parliament upon the calling of an election.
Minor ceremonial duties include giving an audience to the Prime Minister, as well as visiting ministers or diplomats from the Commonwealth, and acting on state occasions, such as delivering the "Speech from the throne, King's speech" (written by the government, outlining its political platform) at the opening of Parliament. Public support for the monarchy remains high, with only 21% of the population preferring a republic instead. However, on the other hand, it has been argued that the UK should Abolition of monarchy, abolish the monarchy, on the ground that hereditary inheritance of political office has no place in a modern democracy. A referendum was held in Australia, in 1999 on 1999 Australian republic referendum, becoming a Republic, but failed to get a majority.
 Although called the Royal prerogative in the United Kingdom, royal prerogative, a series of important powers that were once vested in the king or queen are now exercised by government, and the
Although called the Royal prerogative in the United Kingdom, royal prerogative, a series of important powers that were once vested in the king or queen are now exercised by government, and the prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
in particular. These are powers of day-to-day management, but tightly constrained to ensure that executive power cannot usurp Parliament or the courts. In the ''Case of Prohibitions'' in 1607, it was held that the royal prerogative could not be used to determine court cases, and in the ''Case of Proclamations'' in 1610 it was held new prerogative powers could not be created by the executive.''Case of Proclamations'' [1610EWHC KB J22
/ref> It is also clear that no exercise of the prerogative can compromise any right contained in an Act of Parliament. So, for instance, in '' R (Miller) v Secretary of State for Exiting the European Union'' the Supreme Court held that the Prime Minister could not notify the
European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body ...
of an intention to leave under Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union without an Act of Parliament, because it could result in rights being withdrawn that were granted under the European Communities Act 1972, such as the right to work in other EU member states or vote in European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the Legislature, legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven Institutions of the European Union, institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and in ...
elections.
Though royal prerogative powers can be categorised in different ways, there are around 15. First, the executive may create hereditary titles, confer honours and create peers. Second, the executive can legislate by an Order in Council, though this has been called an 'anachronistic survival'. Third, the executive can create and administer financial benefits schemes. Fourth, through the Attorney General the executive can stop prosecutions or pardon convicted offenders after taking advice. Fifth, the executive may acquire more territory or alter limits of British territorial waters. Sixth, the executive may expel aliens and theoretically restrain people from leaving the UK. Seventh, the executive can sign treaties, although before it is considered ratified the treaty must be laid before Parliament for 21 days and there must be no resolution against it. Eighth, the executive governs the armed forces and can do "all those things in an emergency which are necessary for the conduct of war".
The executive cannot declare war without Parliament by convention, and in any case has no hope in funding war without Parliament. Ninth, the Prime Minister can appoint ministers, judges, public officials or royal commissioners. Tenth, the monarch needs to pay no tax, unless statute states it expressly. Eleventh, the executive may by royal charter create corporations, such as the BBC, and franchises for markets, ferries and fisheries. Twelfth, the executive has the right to mine precious metals, and to take treasure troves. Thirteenth, it may make coins. Fourteenth, it can print or license the authorised version of the Bible, Book of Common Prayer and state papers. And fifteenth, subject to modern English family law, family law, it may take guardianship of infants.
In addition to these royal prerogative powers, there are innumerable powers explicitly laid down in statutes enabling the executive to make legal changes. This includes a growing number of Henry VIII clauses, which enable a Secretary of State to alter provisions of primary legislation. For this reason it has often been argued that executive authority should be reduced, written into statute, and never used to deprive people of rights without Parliament. All uses of the prerogative, however, are subject to judicial review: in the ''Council of Civil Service Unions v Minister for the Civil Service, GCHQ case'' the House of Lords held that no person could be deprived of legitimate expectations by use of the royal prerogative.
cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filin ...
" is a still smaller group of 22 or 23 people, though only twenty ministers may be paid. Each minister typically heads a Department or Ministry, which can be created or renamed by prerogative. Cabinet committees are usually organised by the Prime Minister. Every minister is expected to follow collective responsibility, and the Ministerial Code, Ministerial Code 2010. This includes rules that Ministers are "expected to behave in a way that upholds the highest standards of propriety", "give accurate and truthful information to Parliament", resign if they "knowingly mislead Parliament", to be "as open as possible", have no possible conflicts of interest and give a full list of interests to a permanent secretary, and only "remain in office for so long as they retain the confidence of the Prime Minister".Constitutional Reform and Governance Act 2010
The Constitutional Reform and Governance Act 2010 (c. 25), or CRAG Act, is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom on UK constitutional law which affected the civil service and the ratification of treaties, and made other significant c ...
s 3, putting management of the civil service into statute. Civil Service Management Code s 11.1.1, civil servants employed at pleasure of the Crown, theoretically lacking a wrongful dismissal remedy according to somewhat outdated case law: ''Dunn v R'' [1896] 1 QB 116 and ''Riordan v War Office'' [1959] 1 WLR 1046, but under the Employment Rights Act 1996 s 191, civil servants expressly have the right to claim unfair dismissal.
Assisting ministers is a modern Civil Service (United Kingdom), civil service and network of government bodies, who are employed at the pleasure of the Crown. The Civil Service Code requires civil servants to show "high standards of behaviour", uphold core values of "integrity, honesty, objectivity and impartiality", and never put themselves in a position that "might reasonably be seen to compromise their personal judgment or integrity". Since the Freedom of Information Act 2000, it has been expected that government should be open about information, and should disclose it upon a request unless disclosure would compromise personal data, security or may run against the public interest. In this way the trend has been to more open, transparent and accountable governance.
Regional government
 The constitution of British regional governments is an uncodified patchwork of authorities, mayors, councils and devolved government. In Local government in Wales, Wales, Local government in Scotland, Scotland, Local government in Northern Ireland, Northern Ireland and Greater London Authority, London unified district or borough councils have local government powers, and since 1998 to 2006 new regional assemblies or Parliaments exercise extra powers devolved from Westminster. In Local government in England, England, there are 55 unitary authorities in the larger towns (e.g. Bristol, Brighton, Milton Keynes) and 36 metropolitan boroughs (surrounding Liverpool, Manchester, Leeds, Birmingham, Sheffield, and Newcastle) which function as unitary local authorities.
In other parts of England, local government is split between two tiers of authority: 32 larger County Councils, and within those 192 District Councils, each sharing different functions. Since 1994, England has had Regions of England, eight regions for administrative purposes at Whitehall, yet these have no regional government or democratic assembly (like in London, Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland) after a 2004 referendum on North East Assembly failed. This means that England has among the most centralised, and disunified systems of governance in the Commonwealth and Europe.
Three main issues in local government are the authorities' financing, their powers, and the reform of governance structures. First, councils raise revenue from Council Tax (charged on local residents according to property values in 1993) and business rates charged on businesses with operations in the locality. These powers are, compared to other countries, extreme in limiting local government autonomy, and taxes can be subjected to a local referendum if the Secretary of State determines they are excessive.
In real terms since 2010, central government cut local council funding by nearly 50 per cent, and real spending fell by 21 per cent, as councils failed to make up cuts through business rates. Unitary authorities and district councils are responsible for administering council tax and business rates. The duties of British local governments are also extremely limited compared to other countries, but also uncodified so that in 2011 the Department for Levelling Up, Housing and Communities, Department for Communities and Local Government enumerated Duties of local government in the United Kingdom, 1340 specific duties of local authorities. Generally, the Localism Act 2011 section 1 states local authorities may do anything an individual person may do, unless prohibited by law, but this provision has little effect because human beings or United Kingdom company law, companies cannot tax or regulate other people in the way that governments must.
The
The constitution of British regional governments is an uncodified patchwork of authorities, mayors, councils and devolved government. In Local government in Wales, Wales, Local government in Scotland, Scotland, Local government in Northern Ireland, Northern Ireland and Greater London Authority, London unified district or borough councils have local government powers, and since 1998 to 2006 new regional assemblies or Parliaments exercise extra powers devolved from Westminster. In Local government in England, England, there are 55 unitary authorities in the larger towns (e.g. Bristol, Brighton, Milton Keynes) and 36 metropolitan boroughs (surrounding Liverpool, Manchester, Leeds, Birmingham, Sheffield, and Newcastle) which function as unitary local authorities.
In other parts of England, local government is split between two tiers of authority: 32 larger County Councils, and within those 192 District Councils, each sharing different functions. Since 1994, England has had Regions of England, eight regions for administrative purposes at Whitehall, yet these have no regional government or democratic assembly (like in London, Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland) after a 2004 referendum on North East Assembly failed. This means that England has among the most centralised, and disunified systems of governance in the Commonwealth and Europe.
Three main issues in local government are the authorities' financing, their powers, and the reform of governance structures. First, councils raise revenue from Council Tax (charged on local residents according to property values in 1993) and business rates charged on businesses with operations in the locality. These powers are, compared to other countries, extreme in limiting local government autonomy, and taxes can be subjected to a local referendum if the Secretary of State determines they are excessive.
In real terms since 2010, central government cut local council funding by nearly 50 per cent, and real spending fell by 21 per cent, as councils failed to make up cuts through business rates. Unitary authorities and district councils are responsible for administering council tax and business rates. The duties of British local governments are also extremely limited compared to other countries, but also uncodified so that in 2011 the Department for Levelling Up, Housing and Communities, Department for Communities and Local Government enumerated Duties of local government in the United Kingdom, 1340 specific duties of local authorities. Generally, the Localism Act 2011 section 1 states local authorities may do anything an individual person may do, unless prohibited by law, but this provision has little effect because human beings or United Kingdom company law, companies cannot tax or regulate other people in the way that governments must.
The Local Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 (c. 70) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Gov ...
section 101 says that a local authority can discharge its functions through a committee or any officer, and can transfer functions to another authority, while section 111 gives authorities the power to do any thing including spending or borrowing 'which is calculated to facilitate, or is conducive or incidental to, the discharge of any of their functions'. However the real duties of local council are found in hundreds of scattered Acts and statutory instruments. These include duties to administer Planning permission, planning consent, to carry out compulsory purchasing according to law, to administer school education, libraries, care for children, roads or highway maintenance and local buses, provide care for the elderly and disabled, prevent pollution and ensure clean air, ensure collection, recycling and disposal of waste, regulate building standards, provide social and affordable housing, and shelters for the homeless.
Local authorities do not yet have powers common in other countries, such as setting minimum wages, regulating rents, or borrowing and taxing as is necessary in the public interest, which frustrates objectives of pluralism, localism and autonomy. Since 2009, authorities have been empowered to merge into 'combined authorities' and to have an Directly elected mayors in England and Wales, elected mayor. This has been done around Manchester, Sheffield, Liverpool, Newcastle, Leeds, Birmingham, the Tees Valley, Bristol and Peterborough. The functions of an elected mayor are not substantial, but can include those of Police and Crime Commissioners.
 In Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland and London there are also regional assemblies and Parliaments, similar to state or provincial governments in other countries. The extent of devolution differs in each place. The
In Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland and London there are also regional assemblies and Parliaments, similar to state or provincial governments in other countries. The extent of devolution differs in each place. The Scotland Act 1998
The Scotland Act 1998 (c. 46) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which legislated for the establishment of the devolved Scottish Parliament with tax varying powers and the Scottish Government (then Scottish Executive). It was o ...
created a unicameral Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba ; sco, Scots Pairlament) is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. Located in the Holyrood area of the capital city, Edinburgh, it is frequently referred to by the metonym Holyr ...
with 129 elected members each four years: 73 from single member constituencies with simple majority vote, and 56 from additional member systems of proportional representation. Under section 28, the Scottish Parliament can make any laws except for on 'reserved matters' listed in Schedule 5. These powers, reserved for the British Parliament, include foreign affairs, defence, finance, economic planning, home affairs, trade and industry, social security, employment, broadcasting, and equal opportunities.
By Legislative consent motion, convention, members of the British Parliament from Scottish constituencies do not vote on issues that the Scottish Parliament has exercised power over. This is the most powerful regional government so far. The Northern Ireland Act 1998
__NOTOC__
The Northern Ireland Act 1998 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which allowed Westminster to devolve power to Northern Ireland, after decades of direct rule.
It renamed the New Northern Ireland Assembly, established by ...
lists which matters are transferred to the Northern Ireland Assembly. The Government of Wales Act 1998
The Government of Wales Act 1998 (c. 38) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom.
It was passed in 1998 by the Labour government to create a Welsh Assembly, therefore granting Wales a degree of self-government. This legislative ...
created a 60-member national assembly with elections every four years, and set out twenty fields of government competence, with some exceptions. The fields include agriculture, fisheries, forestry and rural development, economic development, education, environmental policy, health, highways and transport, housing, planning, and some aspects of social welfare. The Supreme Court has tended to interpret these powers in favour of devolution.
Human rights
Codification ofhuman rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
is recent, but before the Human Rights Act 1998
The Human Rights Act 1998 (c. 42) is an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom which received royal assent on 9 November 1998, and came into force on 2 October 2000. Its aim was to incorporate into UK law the rights contained in the European Con ...
and the European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by ...
, British law had one of the world's longest human rights traditions. Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by t ...
bound the King to require Parliament's consent before any tax, respect the right to a trial "by lawful judgment of his Peers, or by the Law of the Land", stated that "We will sell to no man, we will not deny or defer to any man either Justice or Right", guaranteed Freedom of movement, free movement for people, and preserved common land for everyone. After the English Civil War the Claim of Right 1689, Bill of Rights 1689 in England and Wales, and the Claim of Rights Act 1689 in Scotland, enshrined principles of representative democracy, no tax without Parliament, freedom of speech in Parliament, and no "cruel and unusual punishment". By 1789, these ideas evolved and inspired both the United States Bill of Rights, US Bill of Rights, and the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen after the American Revolution, American and French Revolutions. Although some labelled natural rights as "nonsense upon stilts", more legal rights were slowly developed by Parliament and the courts. In 1792, Mary Wollstonecraft began the British movement for women's rights and equality, while movements behind the Tolpuddle Martyrs and the Chartists
Chartism was a working-class movement for political reform in the United Kingdom that erupted from 1838 to 1857 and was strongest in 1839, 1842 and 1848. It took its name from the People's Charter of 1838 and was a national protest movement, ...
drove reform for labour and democratic freedom.
 Upon the catastrophe of
Upon the catastrophe of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
and The Holocaust, the new international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
order put the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, Universal Declaration of Human Rights 1948 at its centre, enshrining civil, political, economic, social and cultural rights. In 1950, the UK co-authored the European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by ...
, enabling people to appeal to the European Court of Human Rights
The European Court of Human Rights (ECHR or ECtHR), also known as the Strasbourg Court, is an international court of the Council of Europe which interprets the European Convention on Human Rights. The court hears applications alleging that ...
in Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the ...
even against Acts of Parliament: Parliament has always undertaken to comply with basic principles of international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
. Because this appeals process was long, Parliament legislated to "bring rights home" with the Human Rights Act 1998
The Human Rights Act 1998 (c. 42) is an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom which received royal assent on 9 November 1998, and came into force on 2 October 2000. Its aim was to incorporate into UK law the rights contained in the European Con ...
, so that people can raise human rights claims in British courts based on the European Convention on Human Rights, Convention directly. The European Convention on Human Rights, Convention contains the rights to life, rights against torture, against forced labour, to marry, to an effective remedy, and the right to suffer no discrimination in those rights. Most case law concerns the rights to liberty
Liberty is the ability to do as one pleases, or a right or immunity enjoyed by prescription or by grant (i.e. privilege). It is a synonym for the word freedom.
In modern politics, liberty is understood as the state of being free within society fr ...
, privacy, Freedom of thought, freedom of conscience and Freedom of speech, freedom of expression, and to freedom of association and assembly. The UK also enshrines rights to fair labour standards, social security, and a multitude of Economic, social and cultural rights, social and economic rights through its legislation.
Administrative law
 Administrative law, through
Administrative law, through judicial review
Judicial review is a process under which executive, legislative and administrative actions are subject to review by the judiciary. A court with authority for judicial review may invalidate laws, acts and governmental actions that are incomp ...
, is essential to hold executive power and public bodies accountable under the law. In practice, constitutional principles emerge through cases of judicial review, because every public body, whose decisions affect people's lives, is created and bound by law. A person can apply to the High Court to challenge a public body's decision if they have a "sufficient interest", within three months of the grounds of the cause of action becoming known. By contrast, claims against public bodies in English tort law, tort or English contract law, contract, where the Limitation Act 1980 usually sets the period as 6 years. Almost any public body, or private bodies exercising public functions, can be the target of judicial review, including a government department, a local council, any Minister, the Prime Minister, or any other body that is created by law. The only public body whose decisions cannot be reviewed is Parliament, when it passes an Act. Otherwise, a claimant can argue that a public body's decision was unlawful in five main types of case: (1) it exceeded the lawful power of the body, used its power for an improper purpose, or acted unreasonably, (2) it violated a legitimate expectation, (3) failed to exercise relevant and independent judgement, (4) exhibited bias or a conflict of interest, or failed to give a fair hearing, and (5) violated a human right. As a remedy, a claimant can ask for the public body's decisions to be declared void and quashed (or ''certiorari''), or it could ask for an order to make the body do something (or ''mandamus''), or prevent the body from acting unlawfully (or Writ of prohibition, prohibition). A court may also declare the parties' rights and duties, give an injunction, or compensation could also be payable in English tort law, tort or English contract law, contract.
History
 The history of the British constitution, though officially beginning in 1800, traces back to a time long before the four nations of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland, Ireland were fully Formation of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, formed. Before the Norman Conquest, Norman Invasion of 1066, the written history of law was scant. Following the conquest, according to the legal record Leges Edwardi Confessoris, Laws of Edward the Confessor, in 1070 William the Conqueror, on the advice of the King's Council (''Curia Regis''), summoned nobles learned in the law from all parts of the country in order to learn the established laws and customs. After hearing from 12 men from each county on oath, he expressed the wish to establish norse law as the common law in England under one monarch because his ancestors and his Norman barons all came from Norway. He was, however, persuaded by those summoned, that the laws of the Britons, English and Picts should remain in force 'because it was hard to adopt laws and to judge according to those that they did not know'. It is recorded that 'Finally, by the counsel and at the request of his barons, he acquiesced' and authorised and confirmed the laws as they were under Edward the Confessor.
The Domesday Book was compiled in 1086 cataloguing all land and labour to levy History of taxation in the United Kingdom, taxes. Just 12 per cent of people were free, while the feudal system made others serfs, slaves or bordars and cottars.
Henry II of England, Henry II, who became the monarch in 1154, established the
The history of the British constitution, though officially beginning in 1800, traces back to a time long before the four nations of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland, Ireland were fully Formation of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, formed. Before the Norman Conquest, Norman Invasion of 1066, the written history of law was scant. Following the conquest, according to the legal record Leges Edwardi Confessoris, Laws of Edward the Confessor, in 1070 William the Conqueror, on the advice of the King's Council (''Curia Regis''), summoned nobles learned in the law from all parts of the country in order to learn the established laws and customs. After hearing from 12 men from each county on oath, he expressed the wish to establish norse law as the common law in England under one monarch because his ancestors and his Norman barons all came from Norway. He was, however, persuaded by those summoned, that the laws of the Britons, English and Picts should remain in force 'because it was hard to adopt laws and to judge according to those that they did not know'. It is recorded that 'Finally, by the counsel and at the request of his barons, he acquiesced' and authorised and confirmed the laws as they were under Edward the Confessor.
The Domesday Book was compiled in 1086 cataloguing all land and labour to levy History of taxation in the United Kingdom, taxes. Just 12 per cent of people were free, while the feudal system made others serfs, slaves or bordars and cottars.
Henry II of England, Henry II, who became the monarch in 1154, established the common law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omniprese ...
by creating a unified system of law "common" to the country.
In 1190 Richard I of England, Richard the Lionheart, more closely tied with List of popes, the Pope in Rome, joined the Third Crusade to invade the Holy Land, but at great cost. Taxes levied by Richard I, and his successor John, King of England, King John to pay for the wars led to intense discontent, and the aristocracy forcing the King to sign the Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by t ...
1215. This was a commitment to hold 'common counsel' before any taxation, hold courts at a fixed place, hold trials according to law or before an accused's peers, guarantee free movement of people for trade, and give back common land.
Failure to abide by Magna Carta led to the First Barons' War, and the popular legend of Robin Hood emerged: a returned crusader who robbed from the rich to give to the poor. The commitments on common land were soon recast in the Charter of the Forest 1217, signed at St Paul's by Henry III of England, Henry III. These documents established that the monarch, even with apparent authority from God, was bound by law, and it remains 'the nearest approach to an irrepealable "fundamental statute" that England has ever had.'
Throughout the England in the Middle Ages, Middle Ages, common land was a source of welfare for common people, peasant labourers bound by a feudal system of control. In 1348, the Black Death struck England, and killed around a third of the population. As peasants lost their lords, and there was a shortage of workers, wages rose. The King and Parliament responded with the Statute of Labourers 1351 to freeze wage rises. This led to the Peasants' Revolt, Peasants' Revolt of 1381, where leaders demanded an end to feudalism, and for everything to be held in common. Despite the revolt's violent repression, slavery and serfdom broke down, yet most people remained without any substantial liberty, in political or economic rights. As sheep farming became more profitable than agricultural work, enclosures of common land dispossessed more people, who turned into paupers and were punished.
Under Henry VIII, to seal a divorce from Catherine of Aragon and marry Anne Boleyn (who he soon beheaded for supposed infidelity), the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Brit ...
was declared separate from Rome in the Act of Supremacy 1534, with the King as the head. The Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542, Law in Wales Act 1535 united Wales and England in one administrative system, while the King became ever more despotic, executing the Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. Th ...
, Sir Thomas More in 1535, and Dissolution of the monasteries and murdering those who resisted. After Henry VIII died, and power struggles following the death of his boy Edward VI at age 15, Elizabeth I, the daughter of Henry VIII and Anne Boleyn, took the throne in 1558. Half a century of prosperity followed as Elizabeth I avoided wars, but founded United Kingdom company law, corporations including the East India Company to monopolise trade routes. Under her successor, James I, further companies were created to colonise North America, including the London Company and the Virginia Company in 1606, and the Massachusetts Bay Colony, Massachusetts Bay Company in 1628. Many religious dissidents left England to settle the new world.
While Elizabeth I maintained a Protestant church, under her successor James VI and I, who unified the Scottish and English Crowns, religious and political tensions grew as he asserted a Divine right of kings, divine right of Kings. This prompted a series of cases from Sir Edward Coke
Edward is an English given name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortune; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”.
History
The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Sax ...
, the Chief Justice of the Court of Common Pleas, Common Pleas and then Court of King's Bench (England), King's Bench courts, which denied that the King could pass judgment in legal proceedings, and held that the royal prerogative
The royal prerogative is a body of customary authority, privilege and immunity, recognized in common law and, sometimes, in civil law jurisdictions possessing a monarchy, as belonging to the sovereign and which have become widely vested in th ...
was subject to the law and cannot be expanded. Coke CJ went even further in ''Dr. Bonham's Case, Dr Bonham's case'', holding that even that "the common law will control Acts of Parliament". Though supported by some judges, the idea that common law courts could nullify Acts of Parliament was rejected, and the common law was formally placed under the King's control in the '' Earl of Oxford's case'', establishing that equity (law), equity (then administered by the Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. Th ...
in the House of Lords) was above common law.
Coke fell from favour, and was removed from judicial office. When Charles I of England, Charles I succeeded to the throne in 1625, and more fervently asserted a divine right, including the ability to levy tax without Parliament, Coke and others presented the Petition of Right 1628
The Petition of Right, passed on 7 June 1628, is an English constitutional document setting out specific individual protections against the state, reportedly of equal value to Magna Carta and the Bill of Rights 1689. It was part of a wider c ...
. This demanded the King to abide by Magna Carta, levy no tax without Parliament, not arbitrarily commit people to prison, not have martial law in times of peace, and not billet soldiers in private homes. Charles I responded by shutting down or Prorogation in the United Kingdom, proroguing Parliament and taxing trade (or "ship money") without authority. The country descended into the English Civil War in 1642 culminating in the capture and execution of Charles I of England, King Charles I on Whitehall in 1649 by the New Model Army led by Oliver Cromwell.
Cromwell, not wishing to become a King, became a ''de facto'' dictator. After his death, the monarchy was restored with Charles II of England, Charles II in 1660, but his successor James II of England, James VII and II again attempted to assert divine right to rule. In 1688, Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
'invited' a replacement King and Queen, William III of England, William and Mary of Orange, and after a brief conflict forced James II out. Known as the Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
, Parliament proclaimed a new Bill of Rights 1689, with a Claim of Right Act 1689 in Scotland, that cemented Parliamentary sovereignty
Parliamentary sovereignty, also called parliamentary supremacy or legislative supremacy, is a concept in the constitutional law of some parliamentary democracies. It holds that the legislative body has absolute sovereignty and is supreme over ...
. As well as reaffirming Magna Carta, it says the 'pretended power of suspending laws or the execution of laws by regal authority without consent of Parliament is illegal', that 'election of members of Parliament ought to be free', and that 'Parliament ought to be held frequently'. The justification for government itself, encapsulated by John Locke in his ''Two Treatises of Government, Second Treatise on Government'' was the protection of people's rights: "lives, liberties and estates."
 With
With Parliamentary sovereignty
Parliamentary sovereignty, also called parliamentary supremacy or legislative supremacy, is a concept in the constitutional law of some parliamentary democracies. It holds that the legislative body has absolute sovereignty and is supreme over ...
as the cornerstone of the new constitution, Parliament proceeded to set up a system of finance in the Bank of England Act 1694 and the Act of Settlement 1700 created an independent system of justice: judges were salaried and could not be removed except by both Houses of Parliament, no member of the House of Commons could be paid by the Crown, and the Crown had to be Anglican. In 1703, ''Ashby v White
''Ashby v White'' (170392 ER 126 is a foundational case in UK constitutional law and English tort law. It concerns the right to vote and misfeasance of a public officer. Lord Holt laid down the important principle that where there is injury in ...
'' established that the Suffrage, right to vote was a constitutional right. The Treaty of Union of 1707, between the then independent states of Scotland and England resulted in them both merging their states to create a new international state, the Kingdom of Great Britain, and their parliaments to create a new Union Parliament, which continued to sit at Westminster. The Treaty also stipulated that Scottish private law would continue under a Scottish court system.
The new union was soon faced with disaster as in the Peace of Utrecht, Treaty of Utrecht, History of Spain (1700–1808), Spain granted the ''Asiento de Negros'' to Britain, allowing British merchants to sell slaves in Spanish America. The South Sea Company, incorporated to monopolise the ''asiento'' license, became the object of mass financial speculation, provoked by government ministers interested in its rising share price. When it transpired, contrary to promoters' stories, that no trade was done because the Spanish had revoked their promise the South Sea Bubble, stock market crashed, driving economic chaos. This was made worse by the decision of conservative politicians to endorse the company to take over the Government debt, national debt as an alternative financier to the government over the Whigs (British political party), Whig dominated Bank of England. The result of the crash was that the Chancellor of the Exchequer was imprisoned in the Tower of London for his corruption, the Postmaster General committed suicide, and the disgraced Lord Chancellor was replaced with Peter King, 1st Baron King, Lord King LC who promptly ruled that people in a position of trust must avoid any possibility of a conflict of interest. Out of the chaos, Robert Walpole emerged as a stable political figure who for 21 years held a majority of the House of Commons, and is now considered the first "Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Prime Minister".
In 1765, '' Entick v Carrington'' established that the government could do nothing but that which was empowered by law, while the first teacher of English law, William Blackstone represented the standard view in his ''Commentaries on the Laws of England'' that Slavery at common law, slavery was unlawful and that "the spirit of liberty is so deeply ingrained in our constitution" any person enslaved in England must be freed. However, the Atlantic slave trade had accelerated to the Thirteen Colonies, North American colonies. In 1772, when Lord Mansfield
William Murray, 1st Earl of Mansfield, PC, SL (2 March 170520 March 1793) was a British barrister, politician and judge noted for his reform of English law. Born to Scottish nobility, he was educated in Perth, Scotland, before moving to Lond ...
ruled in '' Somerset v Stewart'' that slavery was unlawful at common law, this set off a wave of outrage in southern, enslavement colonies of America. Together with northern colonies grievances over taxation without representation, this led to the American Revolution and United States Declaration of Independence, declaration of independence in 1776. The British military failed to hold control. Instead, it began settling Australia from 1788.
In 1789, the French Revolution broke out, and the French King was deposed with demands for "liberty, equality and fraternity". The British aristocracy reacted with repression on free speech and association to forestall any similar movement. While figures like Jeremy Bentham called natural rights "nonsense upon stilts", Mary Wollstonecraft called for ''A Vindication of the Rights of Woman'' as well as men, arguing that unjust gender and class oppression flowed from "the respect paid to property... as from a poisoned fountain". While successful in the Napoleonic Wars in defeating France, and cementing union with Ireland in the Acts of Union 1800, Act of Union 1800, liberty, freedom and democracy were scarcely protected in the new "United Kingdom".
 During this time, with the invention of the steam engine the Industrial Revolution had begun. Poverty had also accelerated through the Speenhamland system of English Poor Laws, poor laws by subsidising employers and landowners with parish rates. The Corn Laws from 1815 further impoverished people by fixing prices to maintain landowner profits. While the Reform Act 1832, Great Reform Act 1832 extended the vote slightly, only those with property had any representation in Parliament. The Slavery Abolition Act 1833, 1833 Slavery Abolition Act abolished slavery within the British Empire, compensating slave owners and made ex-slaves in the colonies work for their owners for four to six years as indentured servants without pay; this was abolished in 1838 after public outcry. With the Poor Law Amendment Act 1834, further punishment for poverty was inflicted as people were put into work houses if found to be unemployed. In ''R v Lovelass'' a group of agricultural workers who formed a trade union were prosecuted and sentenced to be transported to Australia under the Unlawful Oaths Act 1797, triggering mass protests.
A movement called Chartism grew demanding the right to vote for everyone in free and fair elections. As the Great Famine (Ireland), great famine hit Ireland and millions migrated to the
During this time, with the invention of the steam engine the Industrial Revolution had begun. Poverty had also accelerated through the Speenhamland system of English Poor Laws, poor laws by subsidising employers and landowners with parish rates. The Corn Laws from 1815 further impoverished people by fixing prices to maintain landowner profits. While the Reform Act 1832, Great Reform Act 1832 extended the vote slightly, only those with property had any representation in Parliament. The Slavery Abolition Act 1833, 1833 Slavery Abolition Act abolished slavery within the British Empire, compensating slave owners and made ex-slaves in the colonies work for their owners for four to six years as indentured servants without pay; this was abolished in 1838 after public outcry. With the Poor Law Amendment Act 1834, further punishment for poverty was inflicted as people were put into work houses if found to be unemployed. In ''R v Lovelass'' a group of agricultural workers who formed a trade union were prosecuted and sentenced to be transported to Australia under the Unlawful Oaths Act 1797, triggering mass protests.
A movement called Chartism grew demanding the right to vote for everyone in free and fair elections. As the Great Famine (Ireland), great famine hit Ireland and millions migrated to the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, Chartists staged a mass march from Kennington Common to Parliament in 1848 as Revolutions of 1848, revolutions broke out across Europe, and the ''Communist Manifesto'' was drafted by German revolutionary Karl Marx and Manchester factory owner Friedrich Engels. While the Crimean War distracted from social reform and Viscount Palmerston opposed anything, the American Civil War of 1860 to 1865 ended Slavery in the United States, slavery in the US, and the UK gradually enabled greater political freedom. In the Second Reform Act 1867 more middle class property owners were enfranchised, the Elementary Education Act 1870 provided free primary school, and the Trade Union Act 1871 enabled free association without criminal penalty. The Representation of the People Act 1884 reduced the property qualification further, so that around one third of men in Britain could vote. However, the act did not establish universal suffrage; 40% of men and all women could not vote.
From the start of the 20th century, Britain underwent vast social and constitutional change, beginning with an attempt by the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
to suppress British trade unions. In response, the labour movement organised to support representatives in Parliament, and in the 1906 United Kingdom general election, 1906 general election won 29 seats and supported the Liberal Party's programme of reform. This included a legal guarantee of the right of unions to collectively bargain and strike for fair wages, an old age pension, a system of minimum wages, a People's Budget with higher taxes on the wealthy to fund spending. After a January 1910 United Kingdom general election, further election brought by the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
blocking reform, Parliament pass a National Insurance system for welfare, and the Parliament Act 1911
The Parliament Act 1911 (1 & 2 Geo. 5 c. 13) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It is constitutionally important and partly governs the relationship between the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two Houses of Pa ...
prevented the House of Lords blocking legislation for more than two years, and removed the right to delay any money bills. Despite this, the Liberal government, against the opposition of Labour, armed for and entered the World War I, First World War. At the end of the War, with millions dead, Parliament passed the Representation of the People Act 1918 which enabled every adult male the vote, although it was only after the mass protest of the Suffragettes that the Representation of the People (Equal Franchise) Act 1928 enabled all women to vote, and that the UK became democratic. The War also triggered uprising in Ireland, and an Irish War of Independence leading to the partition of the island between the Republic of Ireland in the south and Northern Ireland in the Government of Ireland Act 1920.
The Treaty of Versailles, Versailles Treaty at the end of the War demanded German reparations, beggaring the country through the 1920s and upon the Great Depression leading to a fascist collapse under Adolf Hitler, Hitler. The failed international law system, was replaced following the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
with the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
where the UK held a permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council, UN Security Council. However the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
began to crumble as decolonization occurred Decolonization of Asia, in Asia, Decolonisation of Africa, Africa and Decolonization of the Americas, the Americas. To prevent any recurrence of the Holocaust and war, the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold human rights, democracy and the rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it has 46 member states, with a p ...
was established to draft the European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by ...
in 1950. Further it was seen that the only way to prevent conflict was through economic integration. The European Economic Community, which became the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
in 1992, was supported by Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
with the UK to be "at the centre", although it did not enter until the European Communities Act 1972.
Under Margaret Thatcher, significant cuts were made to public services, labour rights, and the powers of local government, including abolishing the Greater London Council. However some powers were restored with extensive devolution of power in the Scotland Act 1998
The Scotland Act 1998 (c. 46) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which legislated for the establishment of the devolved Scottish Parliament with tax varying powers and the Scottish Government (then Scottish Executive). It was o ...
, Northern Ireland Act 1998
__NOTOC__
The Northern Ireland Act 1998 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which allowed Westminster to devolve power to Northern Ireland, after decades of direct rule.
It renamed the New Northern Ireland Assembly, established by ...
, Greater London Authority Act 1999
The Greater London Authority Act 1999 (c. 29) is the Act of Parliament that established the Greater London Authority, the London Assembly and the Mayor of London.
Background
The Act was brought in after a referendum was held under the Great ...
and the Government of Wales Act 2006. After many years of War, armed conflict in Northern Ireland, the Good Friday Agreement of 1998 brought peace. The Human Rights Act 1998
The Human Rights Act 1998 (c. 42) is an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom which received royal assent on 9 November 1998, and came into force on 2 October 2000. Its aim was to incorporate into UK law the rights contained in the European Con ...
empowered courts to apply European Convention on Human Rights, Convention rights without the need for claimants to take cases to the European Court of Human Rights, Strasbourg court. The House of Lords Act 1999 reduced but did not fully eliminate hereditary peers. Since a financial crisis of 2007–2008, a Conservative and Liberal Democrat coalition launched a programme of "austerity" cuts, and cemented their term in the Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011. After 2015, however, early elections were held anyway in 2017, following a 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, referendum on EU membership that resulted in 51.89 per cent of people favouring to leave, and 48.11 per cent of voters favouring to remain.
Theory and reform
The legal scholar Eric Barendt argues that the uncodified nature of the United Kingdom constitution does not mean it should not be characterised as a "constitution", but also claims that the lack of an effectiveseparation of powers
Separation of powers refers to the division of a state's government into branches, each with separate, independent powers and responsibilities, so that the powers of one branch are not in conflict with those of the other branches. The typi ...
, and the fact that parliamentary sovereignty
Parliamentary sovereignty, also called parliamentary supremacy or legislative supremacy, is a concept in the constitutional law of some parliamentary democracies. It holds that the legislative body has absolute sovereignty and is supreme over ...
allows Parliament to overrule fundamental rights, makes it to some extent a "facade" constitution. Leslie Scarman, Baron Scarman, Lord Scarman presents a spirited argument for a written constitution for the UK, but still refers to the Bill of Rights 1689, 1688 compromise and resulting Acts of Parliament as a constitution.
A. V. Dicey identified that ultimately "the electorate are politically sovereign," and Parliament is legally sovereign. Barendt argues that the greater political party discipline in the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
that has evolved since Dicey's era, and the reduction in checks on governmental power, has led to an excessively powerful government that is not legally constrained by the observance of fundamental rights. A Constitution would impose limits on what Parliament could do. To date, the Parliament of the UK has no limit on its power other than the possibility of extra-parliamentary action (by the people) and of other sovereign states (pursuant to treaties made by Parliament and otherwise). It has been commented by Dicey that formally, the British Parliament was limited by the terms of the international treaties that created it in the first place. His comment that it would be imprudent for the British Parliament to try and abolish Scots Law for example, has been criticised judicially as "cynical" but was written in the high Victorian era when Parliament was grappling with the concept of Irish Home Rule, strongly opposed by many politicians at the time.
Proponents of a codified constitution argue it would strengthen the legal protection of democracy and freedom. As a strong advocate of the "unwritten constitution", Dicey highlighted that English rights were embedded in the general English common law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omniprese ...
of personal liberty, and "the institutions and manners of the nation". Opponents of a codified constitution argue that the country is not based on a founding document that tells its citizens who they are and what they can do. There is also a belief that any unwarranted encroachment on the spirit of constitutional authority would be stiffly resisted by the British people, a perception expounded by the 19th century American judge Joseph P. Bradley, Justice Bradley in the course of delivering his opinion in a case heard in Louisiana in 1873: "England has no written constitution, it is true; but it has an unwritten one, resting in the acknowledged, and frequently declared, privileges of Parliament and the people, to violate which in any material respect would produce a revolution in an hour."
The Labour Party (UK), Labour government under prime minister Tony Blair instituted constitutional reforms in the late 1990s and early-to-mid 2000s. The effective incorporation of the European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by ...
into British law through the Human Rights Act 1998
The Human Rights Act 1998 (c. 42) is an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom which received royal assent on 9 November 1998, and came into force on 2 October 2000. Its aim was to incorporate into UK law the rights contained in the European Con ...
has granted citizens specific Negative and positive rights, positive rights and given the judiciary some power to enforce them. The courts can advise Parliament of Primary and secondary legislation, primary legislation that conflicts with the Act by means of "Declaration of incompatibility, Declarations of Incompatibility" – however Parliament is not bound to amend the law nor can the judiciary void any statute – and it can refuse to enforce, or "strike down", any incompatible Primary and secondary legislation, secondary legislation. Any actions of government authorities that violate Convention rights are illegal except if mandated by an Act of Parliament.
Changes also include the Constitutional Reform Act 2005
The Constitutional Reform Act 2005 (c 4) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, relevant to UK constitutional law. It provides for a Supreme Court of the United Kingdom to take over the previous appellate jurisdiction of the Law L ...
which alters the structure of the House of Lords to separate its judicial and legislative functions. For example, the legislative, judicial and executive functions of the Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. Th ...
are now shared between the Lord Chancellor (executive), Lord Chief Justice of England and Wales, Lord Chief Justice (judicial) and the newly created post of Lord Speaker (legislative). The role of Lords of Appeal in Ordinary, Law Lord (a member of the judiciary in the House of Lords) was abolished by transferring them to the new Supreme Court of the United Kingdom
The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom ( initialism: UKSC or the acronym: SCOTUK) is the final court of appeal in the United Kingdom for all civil cases, and for criminal cases originating in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. As the Unite ...
in October 2009.
Gordon Brown launched a "The Governance of Britain, Governance of Britain" process when he took over as PM in 2007. This was an ongoing process of constitutional reform with the Ministry of Justice (United Kingdom), Ministry of Justice as lead ministry. The Constitutional Reform and Governance Act 2010 is a piece of constitutional legislation. It enshrines in statute the impartiality and integrity of the British Civil Service and the principle of open and fair recruitment. It enshrines in law the Ponsonby Rule which requires that treaties are laid before Parliament before they can be ratified.
The Coalition Government formed in May 2010 proposed a series of further constitutional reforms in their coalition agreement. Consequently, the Parliamentary Voting System and Constituencies Act 2011 and the Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011 were passed, though the government of Boris Johnson subsequently Dissolution and Calling of Parliament Act 2022, repealed the latter in 2022. The Acts were intended to reduce the number of MPs in the House of Commons from 650 to 600, change the way the UK is divided into parliamentary constituencies, introduce 2011 United Kingdom Alternative Vote referendum, a referendum on changing the system used to elect MPs and take the power to dissolve Parliament away from the monarch. The Coalition also promised to introduce law on the reform of the House of Lords. In the referendum, the Alternative Vote system was rejected by 67% to 33%, and therefore all reforms regarding the voting system were dropped. Conservatives forced the government to drop House of Lords reforms, and the Liberal Democrats (UK), Liberal Democrats said they would refuse to support changes to the boundaries of constituencies, as they believed such changes favoured the Conservatives.
See also
*UK human rights law, British human rights law *UK administrative law, British administrative law *UK labour law, British labour law *English land law *Constitutional government *Constitution Committee, House of Lords Constitution Committee *Political and Constitutional Reform Select Committee *Parliament in the Making *Royal Commission on the Constitution (United Kingdom) *Power Inquiry *Ancient constitution of EnglandNotes
References
;Articles *A Blick,Magna Carta and contemporary constitutional change
(2015) History and Policy *V Bogdanor, T Khaitan and S Vogenauer, 'Should Britain have a written constitution?' (2007
78(4) Political Quarterly 499
* Briggs, Asa, “Trollope, Bagehot, and the English Constitution,” in Briggs, ''Victorian People'' (1955) pp. 87–115
online
*KD Ewing, 'The Resilience of the Political Constitution' (2013
14(12) German Law Journal 2111
*JAW Griffith, 'The Political Constitution' (1979
42(1) Modern Law Review 1
*F Kessler, 'Natural Law, Justice and Democracy—Some Reflections on Three Types of Thinking About Law and Justice' (1944
19 Tulane Law Review 32
*Lord Hoffmann, (2013
17 Oxford Law News 8-9
from a tribute at St John's Smith Square on 5 June 2013 *O Kahn-Freund, 'Autobiographical Memories of the Weimar Republic: A Conversation with Wolfgang Luthardt' (February 1978
KCL Law School Research Paper No. 2016-34
*J Laws, 'Law and Democracy' [1995] Public Law 72 *S Webb, 'Socialism: true and false. A lecture delivered to the Fabian Society' (21 January 1894) Fabian Tract, 51 *S Webb, 'The reform of the House of Lords' (1917) Fabian Tract, 183 ;Books *W Bagehot, ''The English Constitution'' (1867) *Lord Bingham of Cornhill, ''Rule of Law'' (2010) *AV Dicey, ''Introduction to the Study of the Law of the Constitution''
3rd edn 1889
*H Arendt, ''Eichmann in Jerusalem: A Report on the Banality of Evil'' (1963) *J Froissart, ''Froissart's Chronicles'' (1385) translated by GC Macaulay
1895
*I Jennings, ''A Federation for Western Europe''
1940
*J Locke, ''Two Treatises of Government''
1689
*FW Maitland, ''The Constitutional History of England''
CUP 1919
*JS Mill, ''On Liberty''
1859
*JS Mill, ''Considerations on Representative Government''
1861
*T More, ''Utopia (book), Utopia'' (1516) translated by Gilbert Burnet
1901
*FL Neumann, ''Behemoth: The Structure and Practice of National Socialism, 1933-1944'' (1944) *FL Neumann, ''The Democratic and the Authoritarian State: Essays in Political and Legal Theory'' (1957) *C Turpin and A Tomkins, ''British Government and the Constitution'' (7th edition, CUP) *S Webb and B Webb, ''Industrial Democracy'' (1890) *S Webb, ''English Local Government'' (1906 through 1929) Volumes I–X ;Textbooks *AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, ''Constitutional and Administrative Law'' (2018) *H Kelsen, ''Principles of International Law''
1952
*A Le Sueur, M Sunkin and J Murkens, ''Public Law Text, Cases, and Materials'' (3rd edn 2016) *M Elliott and R Thomas, ''Public Law'' (3rd edn 2017) ;Other papers *C Gearty,
Are judges now out of their depth?
(2007) *D Jenkins,
From Unwritten to Written: Transformation in the British Common-Law Constitution
*J McEldowney
(2003) Written evidence to the Constitution Committee (House of Lords), House of Lords Select Committee on the Constitution. *
External links
The UK constitution - The Constitution Society
consoc.org.uk
What is the UK Constitution? , The Constitution Unit - UCL – University College London
ucl.ac.uk
Britain's unwritten constitution , The British Library
bl.uk *
Cabinet Office - Constitutional Reform
Guardian Special Report – Constitutional Reform
United Kingdom Constitutional Law Association blog on Constitutional Reform
The Constitution Society feature on What is the British Constitution?
LSE - A New UK Constitution
UCL Constitution Unit - About
ESRC Centre on Constitutional Change
Democratic Audit UK
The Parliament and Constitution Centre
Constitutional Law Chronology
Full Constitution of England - Constitute Project
Constitutional Statutes
including discussion of later cases e.g. ''Robinson v Secretary of State for Northern Ireland'' [2002] UKHL 32, ''BH v Lord Advocate'' [2012] UKSC 24, ''R (HS2 Action Alliance Ltd) v Secretary of State for Transport'' [2014] UKSC 3. {{DEFAULTSORT:Constitution of the United Kingdom Constitution of the United Kingdom, Government of the United Kingdom Law of the United Kingdom Politics of the United Kingdom Uncodified constitutions