Tenterfield Oration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
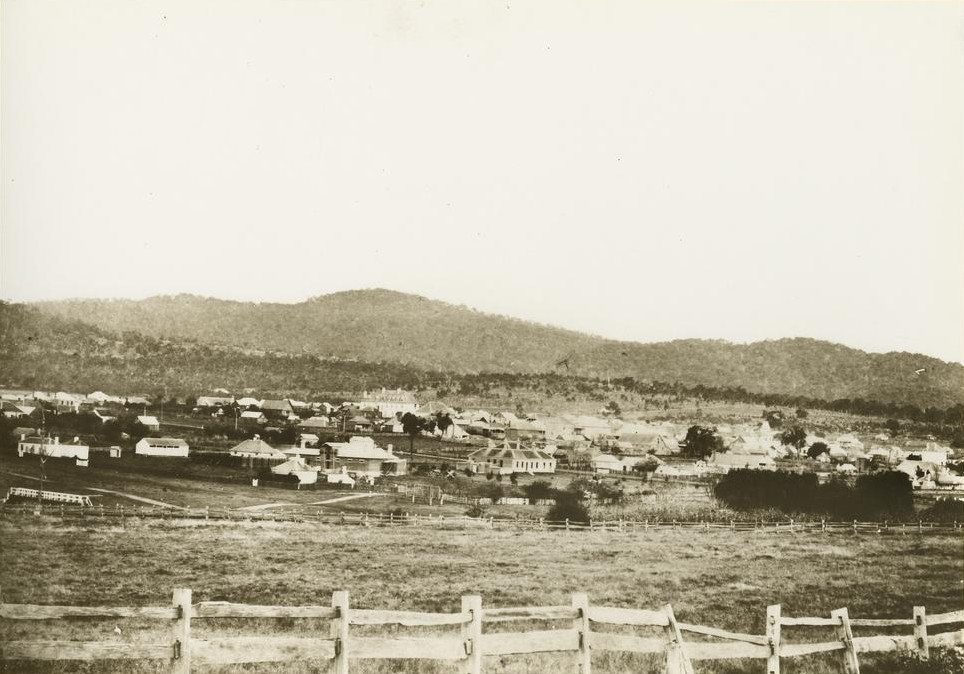 The Tenterfield Oration was a
The Tenterfield Oration was a
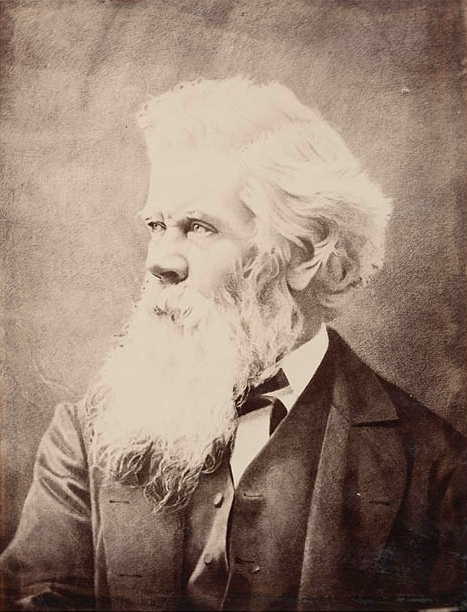 The speech referred to the
The speech referred to the
 The Tenterfield Oration was a
The Tenterfield Oration was a speech
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are ...
given by Sir Henry Parkes
Sir Henry Parkes, (27 May 1815 – 27 April 1896) was a colonial Australian politician and longest non-consecutive Premier of the Colony of New South Wales, the present-day state of New South Wales in the Commonwealth of Australia. He has b ...
, Premier of the Colony of New South Wales at the Tenterfield School of Arts in Tenterfield, in rural
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry typically are describ ...
New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, e ...
, Australia, on 24 October 1889. In the Oration, Parkes called for the Federation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governing ...
of the six Australian colonies, which were at the time self-governing but under the distant central authority of the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
Colonial Secretary. The speech is considered to be the start of the federation process in Australia, which led to the foundation of the Commonwealth of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
12 years later.
Background
The north ofNew South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, e ...
suffered from the disunited administration, as it was distant from the colony's capital of Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountains ...
but closer to commercial areas across the border, in Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, established_ ...
. Border importation tariff
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government of a country or by a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and po ...
s were imposed by Queensland, and people in neighbouring districts were strongly in favour of free trade
Free trade is a trade policy that does not restrict imports or exports. It can also be understood as the free market idea applied to international trade. In government, free trade is predominantly advocated by political parties that hold eco ...
.
The primary reason given by Premier Parkes for federation in the Tenterfield Oration was the united defence
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense industr ...
of the Australian continent. In a 1999 address, Bob Carr
Robert John Carr (born 28 September 1947) is an Australian retired politician and journalist who served as the 39th Premier of New South Wales from 1995 to 2005, as the leader of the NSW Branch of the Australian Labor Party (ALP). He later en ...
(premier of NSW 1995–2005) compared the Tenterfield Oration's significance for Australia with that of Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation throu ...
's Gettysburg Address
The Gettysburg Address is a speech that U.S. President Abraham Lincoln delivered during the American Civil War at the dedication of the Soldiers' National Cemetery, now known as Gettysburg National Cemetery, in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania on the ...
in America.
At Tenterfield, Parkes urged the seven colonies (the seventh being the Colony of New Zealand
The Colony of New Zealand was a Crown colony of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland that encompassed the islands of New Zealand from 1841 to 1907. The power of the British government was vested in the Governor of New Zealand, as th ...
) to 'unite and create a great national government for all Australia'. He explicitly stated the inspiration that the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territo ...
should hold for Australians in terms of its gaining any independence from the British. This sentiment struck a chord with colonials. Due to the widespread publication of this speech in Australian newspapers, and due also to Parkes' subsequent roles in petitioning the Queen and in drafting the constitution, he is regarded as the "father of federation". The site of the Tenterfield Oration was commemorated by the Commonwealth Governor General in 1946.
Prompted by Parkes' Tenterfield Oration, the colonies agreed to send delegates to Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a metrop ...
in 1890 for a Constitutional Conference. That set in motion the process of writing and adopting the Commonwealth Constitution over the course of the 1890s, resulting in the union of the colonies and the establishment of a system of federalism in Australia
Federalism was adopted, as a constitutional principle, in Australia on 1 January 1901 – the date upon which the six self-governing Australian Colonies of New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria, and Western Australia ...
.
The Speech
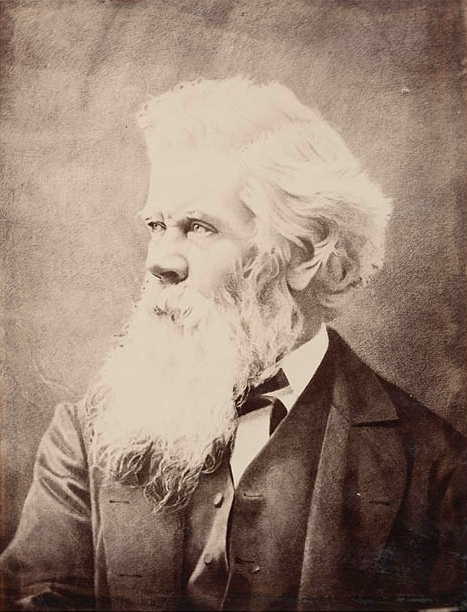 The speech referred to the
The speech referred to the Parliament of New South Wales
The Parliament of New South Wales is a bicameral legislature in the Australian state of New South Wales (NSW), consisting of the New South Wales Legislative Assembly (lower house) and the New South Wales Legislative Council (upper house). Eac ...
and the Parliament of Queensland
The Parliament of Queensland is the legislature of Queensland, Australia. As provided under the Constitution of Queensland, the Parliament consists of the Monarch of Australia and the Legislative Assembly. It has been the only unicameral s ...
, and quoted the poem ''The Dominion'' by James Brunton Stephens
James Brunton Stephens (17 June 1835 – 29 June 1902) was a Scottish-born Australian poet, and author of ''Convict Once''.
Early life
Stephens was born in Bo'ness, on the Firth of Forth, Scotland; the son of John Stephens, the parish scho ...
:
See also
*Canadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation (french: Confédération canadienne, link=no) was the process by which three British North American provinces, the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick, were united into one federation called the Dominion ...
* Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union was an agreement among the 13 Colonies of the United States of America that served as its first frame of government. It was approved after much debate (between July 1776 and November 1777) by ...
(United States)
References
{{Reflist, 30em 1889 in Australia 1880s speeches