Temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMD, TMJD) is an umbrella term covering
pain and dysfunction of the
muscles of mastication (the muscles that move the jaw) and the
temporomandibular joint
In anatomy, the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) are the two joints connecting the jawbone to the skull. It is a bilateral synovial articulation between the temporal bone of the skull above and the mandible below; it is from these bones that it ...
s (the joints which connect the
mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
to the
skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
). The most important feature is pain, followed by restricted mandibular movement,
and noises from the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) during jaw movement. Although TMD is not life-threatening, it can be detrimental to
quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
;
[ ] this is because the symptoms can become chronic and difficult to manage.
In this article, the term ''temporomandibular disorder'' is taken to mean any disorder that affects the temporomandibular joint, and ''temporomandibular joint dysfunction'' (here also abbreviated to TMD) is taken to mean symptomatic (e.g. pain, limitation of movement, clicking) dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. However, there is no single, globally accepted term or definition
concerning this topic.
TMDs have a range of causes and often co-occur with a number of overlapping medical conditions, including headaches, fibromyalgia, back pain, and irritable bowel. However, these factors are poorly understood,
and there is disagreement as to their relative importance. There are many treatments available,
although there is a general lack of evidence for any treatment in TMD, and no widely accepted treatment protocol. Common treatments include provision of occlusal splints, psychosocial interventions like
cognitive behavioral therapy, physical therapy, and
pain medication or others. Most sources agree that no irreversible treatment should be carried out for TMD.
About 20% to 30% of the adult population are affected to some degree.
[ ] Usually people affected by TMD are between 20 and 40 years of age,
and it is more common in females than males.
TMD is the second most frequent cause of
orofacial pain after dental pain (i.e.
toothache
Toothache, also known as dental pain,Segen JC. (2002). ''McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine''. The McGraw-Hill Companies. is pain in the teeth or their supporting structures, caused by dental diseases or pain referred to the t ...
).
Classification
TMD is considered by some to be one of the 4 major symptom complexes in chronic orofacial pain, along with
burning mouth syndrome
Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is a burning, tingling or scalding sensation in the mouth, lasting for at least four to six months, with no underlying known dental or medical cause. No related signs of disease are found in the mouth. People with ...
,
atypical facial pain
Atypical facial pain (AFP) is a type of chronic facial pain which does not fulfill any other diagnosis. There is no consensus as to a globally accepted definition, and there is even controversy as to whether the term should be continued to be use ...
and
atypical odontalgia
Atypical facial pain (AFP) is a type of chronic facial pain which does not fulfill any other diagnosis. There is no consensus as to a globally accepted definition, and there is even controversy as to whether the term should be continued to be use ...
.
[ ] TMD has been considered as a type of
musculoskeletal
The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system) is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move using their muscular and skeletal systems. The musculoskeletal system prov ...
,
neuromuscular
A neuromuscular junction (or myoneural junction) is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.
Muscles require innervation ...
,
or
rheumatological
Rheumatism or rheumatic disorders are conditions causing chronic, often intermittent pain affecting the joints or connective tissue. Rheumatism does not designate any specific disorder, but covers at least 200 different conditions, including art ...
disorder.
It has also been called a
functional pain syndrome,
and a
psychogenic
A psychogenic effect is one that originates from the brain instead of other physical organs (i.e. the cause is psychological rather than physiological) and may refer to:
* Psychogenic pain
*Psychogenic disease
* Psychogenic amnesia
*Psychogenic co ...
disorder.
Others consider TMD a "central sensitivity syndrome", in reference to evidence that TMD might be caused by a
centrally mediated sensitivity to pain.
It is hypothesized that there is a great deal of similarity between TMD and other pain syndromes like
fibromyalgia,
irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a "disorder of gut-brain interaction" characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain and or abdominal bloating and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may ...
,
interstitial cystitis
Interstitial cystitis (IC), a type of bladder pain syndrome (BPS), is chronic pain in the bladder and pelvic floor of unknown cause. It is the urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome of women. Symptoms include feeling the need to urinate right aw ...
, headache, chronic lower
back pain
Back pain is pain felt in the back. It may be classified as neck pain (cervical), middle back pain (thoracic), lower back pain (lumbar) or coccydynia (tailbone or sacral pain) based on the segment affected. The lumbar area is the most common ...
and chronic
neck pain
Neck pain, also known as cervicalgia, is a common problem, with two-thirds of the population having neck pain at some point in their lives.
Neck pain, although felt in the neck, can be caused by numerous other spinal problems. Neck pain may arise ...
. These disorders have also been theorized to be caused by centrally mediated sensitivity to pain, and furthermore they often occur together.
Definitions and terminology
Frequently, TMD has been treated as a single
syndrome
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek language, Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a sy ...
, but the prevailing modern view is that TMD is a cluster of related disorders with many common features.
Indeed, some have suggested that, in the future, the term ''TMD'' may be discarded as the different causes are fully identified and separated into different conditions.
Sometimes, "temporomandibular joint dysfunction" is described as the most common form of temporomandibular disorder,
[ ] whereas many other sources use the term ''temporomandibular disorder'' synonymously, or instead of the term ''temporomandibular joint dysfunction''. In turn, the term ''temporomandibular disorder'' is defined as "musculoskeletal disorders affecting the temporomandibular joints and their associated musculature. It is a collective term which represents a diverse group of pathologies involving the temporomandibular joint, the muscles of mastication, or both".
Another definition of temporomandibular disorders is "a group of conditions with similar signs and symptoms that affect the temporomandibular joints, the muscles of mastication, or both."
''Temporomandibular disorder'' is a term that creates confusion since it refers to a group of similarly symptomatic conditions, whilst many sources use the term ''temporomandibular disorders'' as a vague description, rather than a specific syndrome, and refer to any condition which may affect the temporomandibular joints (see table). The temporomandibular joint is susceptible to a huge range of diseases, some rarer than others, and there is no implication that all of these will cause any symptoms or limitation in function at all.
The preferred terms in medical publications is to an extent influenced by geographic location. For example, in the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, the term ''pain dysfunction syndrome'' is in common use.
In the United States, the term ''temporomandibular disorder'' is generally favored. The American Academy of Orofacial Pain uses ''temporomandibular disorder'', whilst the
National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research uses ''temporomandibular joint disorder''.
A more complete list of synonyms for this topic is extensive, with some being more commonly used than others. In addition to those already mentioned, examples include ''temporomandibular joint pain dysfunction syndrome'', ''temporomandibular pain dysfunction syndrome'', ''temporomandibular joint syndrome'', ''temporomandibular dysfunction syndrome'', ''temporomandibular dysfunction'', ''temporomandibular disorder'', ''temporomandibular syndrome'', ''facial arthromyalgia'', ''myofacial pain dysfunction syndrome'', ''craniomandibular dysfunction'' (CMD), ''myofacial pain dysfunction'', ''masticatory myalgia'', ''mandibular dysfunction'', and ''Costen's syndrome''.
The lack of standardization in terms is not restricted to medical papers. Notable internationally recognized sources vary in both their preferred term, and their offered definition. For example:
By cause and symptoms
It has been suggested that TMD may develop following physical trauma, particularly
whiplash
Whiplash may refer to:
* The long flexible part of a whip
* Whiplash (medicine), a neck injury
** Whiplash Injury Protection System (WHIPS), in automobiles
Film and television
* ''Whiplash'' (1948 film), a US film noir about a boxer
* ''Whiplas ...
injury, although the evidence for this is not conclusive. This type of TMD is sometimes termed "posttraumatic TMD" (pTMD) to distinguish it from TMD of unknown cause, sometimes termed "
idiopathic
An idiopathic disease is any disease with an unknown cause or mechanism of apparent spontaneous origin. From Greek ἴδιος ''idios'' "one's own" and πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", ''idiopathy'' means approximately "a disease of its own kin ...
TMD" (iTMD).
Sometimes muscle-related (myogenous) TMD (also termed myogenous TMD, or TMD secondary to myofascial pain and dysfunction) is distinguished from joint-related TMD (also termed arthogenous TMD, or TMD secondary to true articular disease), based upon whether the muscles of mastication or the TMJs themselves are predominantly involved. This classification, which effectively divides TMD into 2 syndromes, is followed by the American Academy of Orofacial Pain.
However, since most people with TMD could be placed into both of these groups, which makes a single diagnosis difficult when this classification is used. The Research Diagnostic Criteria (RDC/TMD) allows for multiple diagnoses in an attempt to overcome the problems with other classifications. RDC/TMD considers temporomandibular disorders in 2 axes; axis I is the physical aspects, and axis II involves assessment of psychological status, mandibular function and TMD-related psychosocial disability.
Axis I is further divided into 3 general groups. Group I are muscle disorders, group II are disc displacements and group III are joint disorders,
although it is common for people with TMD to fit into more than one of these groups.
By duration
Sometimes distinction is made between acute TMD, where symptoms last for less than 3 months, and chronic TMD, where symptoms last for more than 3 months.
Not much is known about acute TMD since these individuals do not typically attend in
secondary care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
(hospital).
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms of temporomandibular joint disorder vary in their presentation. The symptoms will usually involve more than one of the various components of the masticatory system,
muscles,
nerves
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system.
A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the e ...
,
tendons,
ligaments
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Other ligaments in the body include the:
* Peritoneal l ...
,
bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s,
connective tissue, or the
teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, t ...
.
The three classically described, cardinal signs and symptoms of TMD are:
* Pain and tenderness on
palpation
Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosing a disease or illness. Usually performed by a health care practitioner, it is the process of feeling an object in or on the body to determine ...
in the muscles of mastication, or of the joint itself (preauricular pain – pain felt just in front of the ear). Pain is the defining feature of TMD and is usually aggravated by manipulation or function,
such as when chewing, clenching,
or yawning, and is often worse upon waking. The character of the pain is usually dull or aching, poorly localized,
and intermittent, although it can sometimes be constant. The pain is more usually unilateral (located on one side) rather than bilateral.
It is rarely severe.
* Limited range of mandibular movement,
which may cause difficulty eating or even talking. There may be locking of the jaw, or stiffness in the jaw muscles and the joints, especially present upon waking.
There may also be incoordination, asymmetry or deviation of mandibular movement.
* Noises from the joint during mandibular movement, which may be intermittent.
Joint noises may be described as clicking,
popping,
or crepitus (grating).
TMJ dysfunction is commonly associated with symptoms affecting cervical spine dysfunction and altered head and cervical spine posture.
Other signs and symptoms have also been described, although these are less common and less significant than the cardinal signs and symptoms listed above. Examples include:
* Headache (possibly),
e.g. pain in the
occipital region (the back of the head), or the forehead;
or other types of facial pain including
migraine,
tension headache
Tension headache, also known as stress headache, or tension-type headache (TTH), is the most common type of primary headache. The pain can radiate from the lower back of the head, the neck, eyes or other muscle groups in the body typically affect ...
.
or
myofascial pain.
* Pain elsewhere, such as the teeth
or neck.
*
Diminished auditory acuity (hearing loss).
*
Tinnitus
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no corresponding external sound is present. Nearly everyone experiences a faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely quiet room; but it is of concern only if it is bothersome, interferes with normal hearin ...
(occasionally).
* Dizziness.
* Sensation of malocclusion (feeling that the teeth do not meet together properly).
Causes
TMD is a symptom complex (i.e. a group of symptoms occurring together and characterizing a particular disease), which is thought to be caused by multiple, poorly understood factors,
but the exact etiology is unknown.
There are factors which appear to predispose to TMD (genetic, hormonal, anatomical), factors which may precipitate it (trauma, occlusal changes, parafunction), and also factors which may prolong it (stress and again parafunction).
Overall, two hypotheses have dominated research into the causes of TMD, namely a psychosocial model and a theory of occlusal dysharmony.
Interest in occlusal factors as a causative factor in TMD was especially widespread in the past, and the theory has since fallen out of favor and become controversial due to lack of evidence.
Disc displacement
In people with TMD, it has been shown that the lower head of
lateral pterygoid contracts during mouth closing (when it should relax), and is often tender to palpation. To theorize upon this observation, some have suggested that due to a tear in the back of the joint capsule, the articular disc may be displaced forwards (anterior disc displacement), stopping the upper head of lateral pterygoid from acting to stabilize the disc as it would do normally. As a biologic compensatory mechanism, the lower head tries to fill this role, hence the abnormal muscle activity during mouth closure. There is some evidence that anterior disc displacement is present in a proportion of TMD cases. Anterior disc displacement with reduction refers to abnormal forward movement of the disc during opening which reduces upon closing. Anterior disc displacement without reduction refers to an abnormal forward, bunched-up position of the articular disc which does not reduce. In this latter scenario, the disc is not intermediary between the condyle and the articular fossa as it should be, and hence the articular surfaces of the bones themselves are exposed to a greater degree of wear (which may predispose to osteoarthritis in later life).
Degenerative joint disease
The general term "degenerative joint disease" refers to arthritis (both
osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the w ...
and
rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are invol ...
) and arthrosis. The term arthrosis may cause confusion since in the specialized TMD literature it means something slightly different from in the wider medical literature. In medicine generally, arthrosis can be a nonspecific term for a joint, any disease of a joint (or specifically degenerative joint disease), and is also used as a synonym for osteoarthritis. In the specialized literature that has evolved around TMD research, arthrosis is differentiated from arthritis by the presence of low and no inflammation respectively.
Both are however equally degenerative.
The TMJs are sometimes described as one of the most used joints in the body. Over time, either with normal use or with parafunctional use of the joint, wear and degeneration can occur, termed osteoarthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis, an
autoimmune
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". ...
joint disease, can also affect the TMJs. Degenerative joint diseases may lead to defects in the shape of the tissues of the joint, limitation of function (e.g. restricted mandibular movements), and joint pain.
Psychosocial factors
Emotional stress
In psychology, stress is a feeling of emotional strain and pressure. Stress is a type of psychological pain. Small amounts of stress may be beneficial, as it can improve athletic performance, motivation and reaction to the environment. Excess ...
(anxiety, depression, anger) may increase pain by causing
autonomic,
visceral and skeletal activity and by reduced inhibition via the descending pathways of the
limbic system. The interactions of these biological systems have been described as a vicious "anxiety-pain-tension" cycle which is thought to be frequently involved in TMD. Put simply, stress and anxiety cause grinding of teeth and sustained muscular contraction in the face. This produces pain which causes further anxiety which in turn causes prolonged muscular spasm at trigger points,
vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels resulting from contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, in particular the large arteries and small arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasodilation, the widening of blood vess ...
,
ischemia and release of pain mediators. The pain discourages use of the masticatory system (a similar phenomenon in other chronic pain conditions is termed "fear avoidance" behavior), which leads to reduced muscle flexibility, tone, strength and endurance. This manifests as limited mouth opening and a sensation that the teeth are not fitting properly.
Persons with TMD have a higher prevalence of psychological disorders than people without TMD.
People with TMD have been shown to have higher levels of anxiety,
depression, somatization and
sleep deprivation, and these could be considered important
risk factor
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection.
Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often ...
s for the development of TMD.
In the 6 months before the onset, 50–70% of people with TMD report experiencing stressful life events (e.g. involving work, money, health or relationship loss). It has been postulated that such events induce anxiety and cause increased jaw muscle activity. Muscular hyperactivity has also been shown in people with TMD whilst taking examinations or watching horror films.
Others argue that a link between muscular hyperactivity and TMD has not been convincingly demonstrated, and that emotional distress may be more of a consequence of pain rather than a cause.
Bruxism
Bruxism is an oral
parafunctional activity A para-functional habit or parafunctional habit is the habitual exercise of a body part in a way that is other than the most common use of that body part. In dentistry, orthodontics, and oral and maxillofacial pathology, the body part in question i ...
where there is excessive clenching and grinding of the teeth. It can occur during sleep or whilst awake. The cause of bruxism itself is not completely understood, but psychosocial factors appear to be implicated in awake bruxism and
dopaminergic dysfunction and other
central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
mechanisms may be involved in sleep bruxism. If TMD pain and limitation of mandibular movement are greatest upon waking, and then slowly resolve throughout the day, this may indicate sleep bruxism. Conversely, awake bruxism tends to cause symptoms that slowly get worse throughout the day, and there may be no pain at all upon waking.
The relationship of bruxism with TMD is debated. Many suggest that sleep bruxism can be a causative or contributory factor to pain symptoms in TMD.
Indeed, the symptoms of TMD overlap with those of bruxism.
Others suggest that there is no strong association between TMD and bruxism.
A systematic review investigating the possible relationship concluded that when self-reported bruxism is used to diagnose bruxism, there is a positive association with TMD pain, and when more strict diagnostic criteria for bruxism are used, the association with TMD symptoms is much lower.
Self-reported bruxism is probably a poor method of identifying bruxism.
There are also very many people who grind their teeth and who do not develop TMD.
Bruxism and other parafunctional activities may play a role in perpetuating symptoms in some cases.
Other parafunctional habits such as pen chewing, lip and cheek biting (which may manifest as
morsicatio buccarum
Morsicatio buccarum is a condition characterized by chronic irritation or injury to the buccal mucosa (the lining of the inside of the cheek within the mouth), caused by repetitive chewing, biting or nibbling.
Signs and symptoms
The lesions are ...
or
linea alba), are also suggested to contribute to the development of TMD.
Other parafunctional activities might include jaw thrusting, excessive gum chewing,
nail biting
Nail biting, also known as onychophagy or onychophagia (or even erroneously onyhophagia), is an oral compulsive habit of biting one's fingernails. It is sometimes described as a parafunctional activity, the common use of the mouth for an activit ...
and eating very hard foods.
Trauma
Trauma, both micro and macrotrauma, is sometimes identified as a possible cause of TMD; however, the evidence for this is not strong.
Prolonged mouth opening (hyper-extension) is also suggested as a possible cause. It is thought that this leads to microtrauma and subsequent muscular hyperactivity. This may occur during dental treatment, with oral
intubation
Intubation (sometimes entubation) is a medical procedure involving the insertion of a tube into the body. Patients are generally anesthetized beforehand. Examples include tracheal intubation, and the balloon tamponade with a Sengstaken-Blake ...
whilst under a
general anesthetic, during singing or wind instrument practice (really these can be thought of as parafunctional activities).
Damage may be incurred during violent yawning, laughing,
road traffic accidents, sports injuries, interpersonal violence, or during dental treatment,
(such as
tooth extraction
A dental extraction (also referred to as tooth extraction, exodontia, exodontics, or informally, tooth pulling) is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reason ...
).
It has been proposed that a link exists between
whiplash
Whiplash may refer to:
* The long flexible part of a whip
* Whiplash (medicine), a neck injury
** Whiplash Injury Protection System (WHIPS), in automobiles
Film and television
* ''Whiplash'' (1948 film), a US film noir about a boxer
* ''Whiplas ...
injuries (sudden neck hyper-extension usually occurring in road traffic accidents), and the development of TMD. This has been termed "post-traumatic TMD", to separate it from "
idiopathic
An idiopathic disease is any disease with an unknown cause or mechanism of apparent spontaneous origin. From Greek ἴδιος ''idios'' "one's own" and πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", ''idiopathy'' means approximately "a disease of its own kin ...
TMD".
Despite multiple studies having been performed over the years, the cumulative evidence has been described as conflicting, with moderate evidence that TMD can occasionally follow whiplash injury.
The research that suggests a link appears to demonstrate a low to moderate
incidence of TMD following whiplash injury, and that pTMD has a poorer response to treatment than TMD which has not developed in relation to trauma.
Occlusal factors
Occlusal factors as an etiologic factor in TMD is a controversial topic.
Abnormalities of occlusion (problems with the bite) are often blamed for TMD but there is no evidence that these factors are involved.
Occlusal abnormalities are incredibly common, and most people with occlusal abnormalities do not have TMD.
Although occlusal features may affect observed electrical activity in masticatory muscles,
there are no
statistically significant differences in the number of occlusal abnormalities in people with TMD and in people without TMD.
There is also no evidence for a causal link between orthodontic treatment and TMD.
The modern, mainstream view is that the vast majority of people with TMD, occlusal factors are not related.
Theories of occlusal factors in TMD are largely of historical interest. A causal relationship between occlusal factors and TMD was championed by Ramfjord in the 1960s.
[ ] A small minority of dentists continue to prescribe occlusal adjustments in the belief that this will prevent or treat TMD despite the existence of systematic reviews of the subject which state that there is no evidence for such practices,
and the vast majority of opinion being that no irreversible treatment should be carried out in TMD (see
Occlusal adjustment).
Genetic factors
TMD does not obviously run in families like a genetic disease. It has been suggested that a genetic predisposition for developing TMD (and chronic pain syndromes generally) could exist. This has been postulated to be explained by variations of the gene which codes for the enzyme
catechol-O-methyl transferase
Catechol-''O''-methyltransferase (COMT; ) is one of several enzymes that degrade catecholamines (neurotransmitters such as dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine), catecholestrogens, and various drugs and substances having a catechol struct ...
(COMT) which may produce 3 different
phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological pr ...
s with regards pain sensitivity. COMT (together with
monoamine oxidase) is involved in breaking down
catecholamine
A catecholamine (; abbreviated CA) is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol (benzene with two hydroxyl side groups next to each other) and a side-chain amine.
Catechol can be either a free molecule or a su ...
s (e.g.
dopamine,
epinephrine, and
norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as both a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline" (from Latin '' ad' ...
). The variation of the COMT gene which produces less of this enzyme is associated with a high sensitivity to pain. Females with this variation, are at 2–3 times greater risk of developing TMD than females without this variant. However this theory is controversial since there is conflicting evidence.
Hormonal factors
Since females are more often affected by TMD than males, the
female sex hormone estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
has been suggested to be involved.
The results of one study suggested that the periods of highest pain in TMD can be correlated with rapid periods of change in the circulating estrogen level. Low estrogen was also correlated to higher pain.
In the
menstrual cycle, estrogen levels fluctuate rapidly during
ovulation
Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries. In women, this event occurs when the ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilize ...
, and also rapidly increases just before menstruation and rapidly decreases during menstruation.
Post-menopausal females who are treated with
hormone replacement therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), also known as menopausal hormone therapy or postmenopausal hormone therapy, is a form of hormone therapy used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause. These symptoms can include hot flashes, vaginal ...
are more likely to develop TMD, or may experience an exacerbation if they already had TMD. Several possible mechanisms by which estrogen might be involved in TMD symptoms have been proposed. Estrogen may play a role in modulating joint inflammation,
nociceptive neurons in the trigeminal nerve, muscle reflexes to pain and
μ-opioid receptors.
Possible associations
TMD has been suggested to be associated with other conditions or factors, with varying degrees of evidence and some more commonly than others. E.g. It has been shown that 75% of people with TMD could also be diagnosed with fibromyalgia, since they met the diagnostic criteria, and that conversely, 18% of people with fibromyalgia met diagnostic criteria for TMD.
A possible link between many of these chronic pain conditions has been hypothesized to be due to shared pathophysiological mechanisms, and they have been collectively termed "central sensitivity syndromes",
although other apparent associations cannot be explained in this manner. Recently a plethora of research has substantiated a causal relationship between TMD and Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA). Severe TMD restricts oral airway opening, and can result in a retrognathic posture that results in glossal blockage of the oropharynx as the tongue relaxes in sleep. This mechanism is exacerbated by alcohol consumption, as well as other chemicals that result in reduced myotonic status of the oropharynx.
* Obstructive sleep apnea.
* Headache.
* Chronic neck pain.
* Chronic back pain.
* Systemic joint laxity.
*
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are invol ...
.
* Irritable bowel syndrome.
* Interstitial cystitis.
* Regular
scuba diving
Scuba diving is a mode of underwater diving whereby divers use breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface air supply. The name "scuba", an acronym for " Self-Contained Underwater Breathing Apparatus", was coined by Chr ...
.
Pathophysiology
Anatomy and physiology
Temporomandibular joints
The temporomandibular joints are the dual articulation of the mandible with the skull. Each TMJ is classed as a "ginglymoarthrodial" joint since it is both a
ginglymus
A hinge joint (ginglymus or ginglymoid) is a bone joint in which the articular surfaces are molded to each other in such a manner as to permit motion only in one plane. According to one classification system they are said to be uniaxial (having ...
(hinging joint) and an
arthrodial
A plane joint (arthrodial joint, gliding joint, plane articulation) is a synovial joint which, under physiological conditions, allows only gliding movement.
Plane joints permit sliding movements in the plane of articular surfaces. The opposed sur ...
(sliding) joint,
and involves the condylar process of the mandible below, and the articular fossa (or glenoid fossa) of the
temporal bone
The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex.
The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples, and house the structures of the ears. ...
above. Between these articular surfaces is the articular disc (or meniscus), which is a biconcave, transversely oval disc composed of dense fibrous connective tissue. Each TMJ is covered by a fibrous capsule. There are tight fibers connecting the mandible to the disc, and loose fibers which connect the disc to the temporal bone, meaning there are in effect 2 joint capsules, creating an upper joint space and a lower joint space, with the articular disc in between. The
synovial membrane of the TMJ lines the inside of the fibrous capsule apart from the articular surfaces and the disc. This membrane secretes
synovial fluid, which is both a lubricant to fill the joint spaces, and a means to convey nutrients to the tissues inside the joint. Behind the disc is loose vascular tissue termed the "bilaminar region" which serves as a posterior attachment for the disc and also fills with blood to fill the space created when the head of the condyle translates down the articular eminence.
Due to its concave shape, sometimes the articular disc is described as having an anterior band, intermediate zone and a posterior band.
When the mouth is opened, the initial movement of the mandibular condyle is rotational, and this involves mainly the lower joint space, and when the mouth is opened further, the movement of the condyle is translational, involving mainly the upper joint space.
This translation movement is achieved by the condylar head sliding down the articular eminence, which constitutes the front border of the articular fossa.
The function of the articular eminence is to limit the forwards movement of the condyle.
The ligament directly associated with the TMJ is the
temporomandibular ligament, also termed the lateral ligament, which really is a thickening of the lateral aspect of the fibrous capsule.
The
stylomandibular ligament and the
sphenomandibular ligament are not directly associated with the joint capsule. Together, these ligaments act to restrict the extreme movements of the joint.
Muscles of mastication
The muscles of mastication are paired on each side and work together to produce the movements of the mandible. The main muscles involved are the masseter, temporalis and medial and lateral pterygoid muscles.
File:Gray383.png, Left medial and lateral pterygoid muscles
File:Gray382.png, Left temporalis muscle
File:Gray378 (masseter highlight).png, Left masseter muscle (red highlight)
They can be thought of in terms of the directions they move the mandible, with most being involved in more than one type of movement due to the variation in the orientation of muscle fibers within some of these muscles.
* Protrusion – Lateral and medial pterygoid.
* Retraction – Posterior fibers of temporalis (and the digastric and geniohyoid muscles to a lesser extent).
* Elevation – Anterior and middle fibers of temporalis, the superficial and deep fibers of masseter and the medial pterygoid.
* Lateral movements – Medial and lateral pterygoid (the ipsilateral temporalis and the pterygoid muscles of the contralateral side pull the mandible to the ipsilateral side).
Each lateral pterygoid muscle is composed of 2 heads, the upper or superior head and the lower or inferior head. The lower head
originates from the lateral surface of the
lateral pterygoid plate
The pterygoid processes of the sphenoid (from Greek ''pteryx'', ''pterygos'', "wing"), one on either side, descend perpendicularly from the regions where the body and the greater wings of the sphenoid bone unite.
Each process consists of a me ...
and
inserts at a depression on the neck of mandibular condyle, just below the articular surface, termed the
pterygoid fovea. The upper head originates from the infratemporal surface and the infratemporal crest of the greater wing of the
sphenoid bone. The upper head also inserts at the fovea, but a part may be attached directly to the joint capsule and to the anterior and medial borders of the articular disc.
The 2 parts of lateral pterygoid have different actions. The lower head contracts during mouth opening, and the upper head contracts during mouth closing. The function of the lower head is to steady the articular disc as it moves back with the condyle into the articular fossa. It is relaxed during mouth closure.
Mechanisms of symptoms
Joint noises
Noises from the TMJs are a symptom of dysfunction of these joints. The sounds commonly produced by TMD are usually described as a "click" or a "pop" when a single sound is heard and as "crepitation" or "crepitus" when there are multiple, grating, rough sounds. Most joint sounds are due to internal derangement of the joint, which is instability or abnormal position of the articular disc.
Clicking often accompanies either jaw opening or closing, and usually occurs towards the end of the movement. The noise indicates that the articular disc has suddenly moved to and from a temporarily displaced position (disk displacement with reduction) to allow completion of a phase of movement of the mandible.
If the disc displaces and does not reduce (move back into position) this may be associated with locking. Clicking alone is not diagnostic of TMD since it is present in high proportion of the general population, mostly in people who have no pain.
Crepitus often indicates arthritic changes in the joint, and may occur at any time during mandibular movement, especially lateral movements.
Perforation of the disc may also cause crepitus.
Due to the proximity of the TMJ to the
ear canal, joint noises are perceived to be much louder to the individual than to others. Often people with TMD are surprised that what sounds to them like very loud noises cannot be heard at all by others next to them. However, it is occasionally possible for loud joint noises to be easily heard by others in some cases and this can be a source of embarrassment e.g. when eating in company.
Pain
Pain symptoms in TMD can be thought of as originating from the joint (arthralgia), or from the muscles (myofascial), or both. There is a poor correlation between TMD pain severity and evidence of tissue pathology.
Generally, degenerative joint changes are associated with greater pain.
=Myofascial pain
=
Pain originating from the muscles of mastication as a result of abnormal muscular function or hyperactivity. The muscular pain is frequently, but not always, associated with daytime clenching or nocturnal bruxism.
Limitation of mandibular movement
The jaw deviates to the affected side during opening,
and restricted mouth opening usually signifies that both TMJs are involved, but severe
trismus
Trismus, commonly called ''lockjaw'' as associated with tetanus, is a condition of limited jaw mobility. It may be caused by spasm of the muscles of mastication or a variety of other causes. Temporary trismus occurs much more frequently than perma ...
rarely occurs. If the greatest reduction in movement occurs upon waking then this may indicate that there is concomitant sleep bruxism. In other cases the limitation in movement gets worse throughout the day.
The jaw may lock entirely.
Limitation of mandibular movement itself may lead to further problems involving the TMJs and the muscles of mastication. Changes in the synovial membrane may lead to a reduction in lubrication of the joint and contribute to degenerative joint changes.
The muscles become weak, and
fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of perma ...
may occur. All these factors may lead to a further limitation of jaw movement and increase in pain.
Degenerative joint disease, such as osteoarthritis or organic degeneration of the articular surfaces, recurrent fibrous or bony ankylosis, developmental abnormality, or pathologic lesions within the TMJ.
Myofascial pain syndrome.
=Referred TMD pain
=
Sometimes TMD pain can radiate or be referred from its cause (i.e. the TMJ or the muscles of mastication) and be felt as headaches, earache or toothache.
Due to the proximity of the ear to the temporomandibular joint, TMJ pain can often be confused with ear pain.
The pain may be
referred in around half of all patients and experienced as
otalgia
Ear pain, also known as earache or otalgia, is pain in the ear. Primary ear pain is pain that originates from the ear. Secondary ear pain is a type of referred pain, meaning that the source of the pain differs from the location where the pain ...
(earache).
Conversely, TMD is an important possible cause of
secondary otalgia. Treatment of TMD may then significantly reduce symptoms of otalgia and
tinnitus
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no corresponding external sound is present. Nearly everyone experiences a faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely quiet room; but it is of concern only if it is bothersome, interferes with normal hearin ...
, as well as
atypical facial pain
Atypical facial pain (AFP) is a type of chronic facial pain which does not fulfill any other diagnosis. There is no consensus as to a globally accepted definition, and there is even controversy as to whether the term should be continued to be use ...
.
Despite some of these findings, some researchers question whether TMJD therapy can reduce symptoms in the ear, and there is currently an ongoing debate to settle the controversy.
Diagnosis
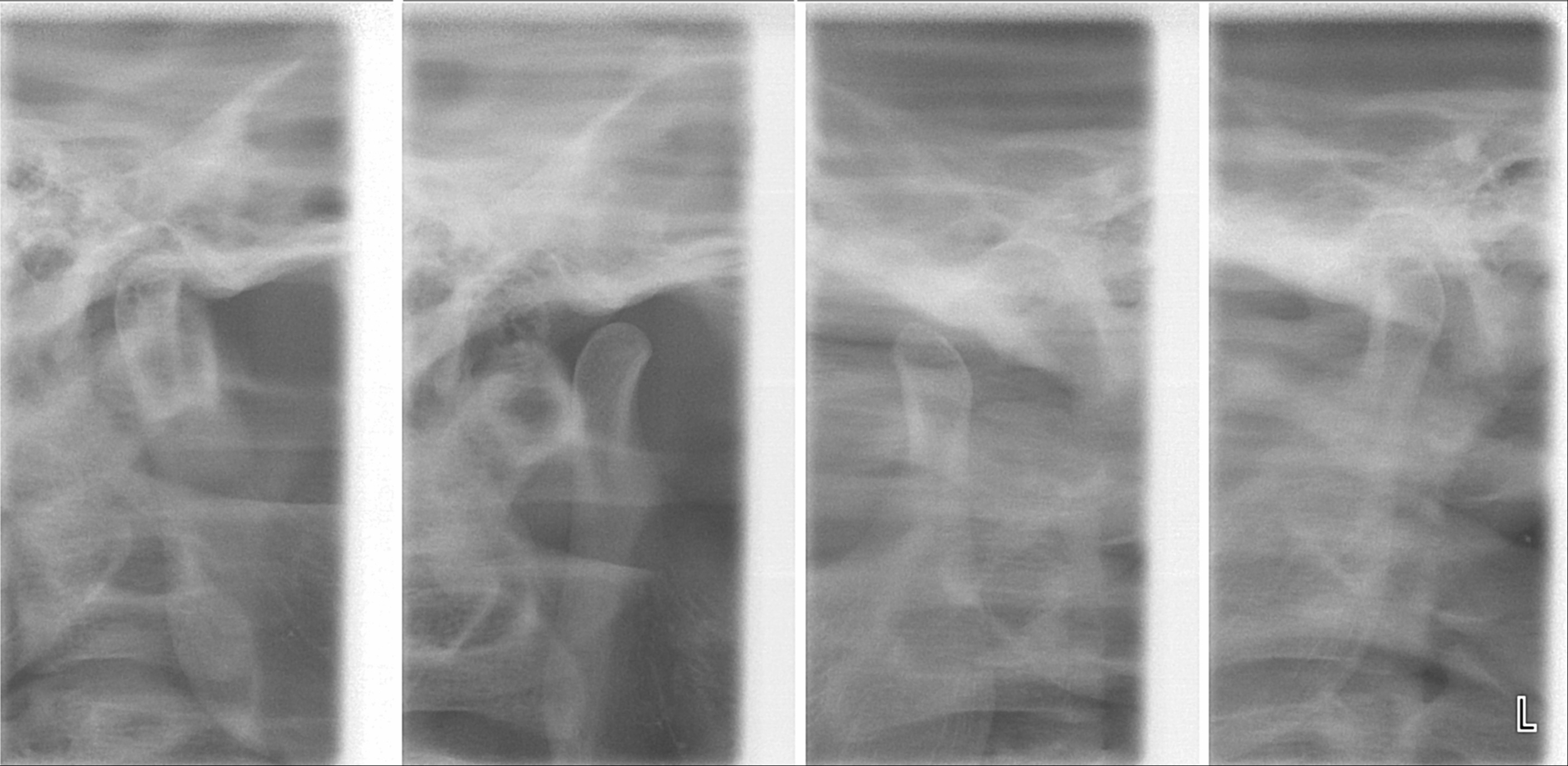
Pain is the most common reason for people with TMD to seek medical advice.
Joint noises may require
auscultation with a
stethoscope to detect.
Clicks of the joint may also be palpated, over the joint itself in the preauricular region, or via a finger inserted in the external acoustic meatus,
which lies directly behind the TMJ.
The
differential diagnosis is with degenerative joint disease (e.g. osteoarthritis),
rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are invol ...
,
temporal arteritis
Temporal may refer to:
Entertainment
* Temporal (band), an Australian metal band
* ''Temporal'' (Radio Tarifa album), 1997
* ''Temporal'' (Love Spirals Downwards album), 2000
* ''Temporal'' (Isis album), 2012
* ''Temporal'' (video game), a 200 ...
,
otitis media,
parotitis
Parotitis is an inflammation of one or both parotid glands, the major salivary glands located on either side of the face, in humans. The parotid gland is the salivary gland most commonly affected by inflammation.
Etymology
From Greek παρωτῖ ...
, mandibular
osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the ...
,
Eagle syndrome
Eagle syndrome (also termed stylohyoid syndrome, styloid syndrome, styloid-stylohyoid syndrome, or styloid–carotid artery syndrome) is a rare condition commonly characterized but not limited to sudden, sharp nerve-like pain in the jaw bone and ...
,
trigeminal neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN or TGN), also called Fothergill disease, tic douloureux, or trifacial neuralgia is a long-term pain disorder that affects the trigeminal nerve, the nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as ...
,
oromandibular dystonia, deafferentation pains, and
psychogenic pain
Psychogenic pain is physical pain that is caused, increased, or prolonged by mental, emotional, or behavioral factors.
Headache, back pain, or stomach pain are some of the most common types of psychogenic pain. Commonly it accompanies or is indu ...
.
Diagnostic criteria
Various diagnostic systems have been described. Some consider the Research Diagnostic Criteria method the gold standard.
Abbreviated to "RDC/TMD", this was first introduced in 1992 by Dworkin and LeResche in an attempt to classify temporomandibular disorders by etiology and apply universal standards for research into TMD.
This method involves 2 diagnostic axes, namely axis I, the physical diagnosis, and axis II, the psychologic diagnosis.
Axis I contains 3 different groups which can occur in combinations of 2 or all 3 groups,
(see table).
McNeill 1997 described TMD diagnostic criteria as follows:
* Pain in muscles of mastication, the TMJ, or the periauricular area (around the ear), which is usually made worse by manipulation or function.
* Asymmetric mandibular movement with or without clicking.
* Limitation of mandibular movements.
* Pain present for a minimum of 3 months.
The International Headache Society's diagnostic criteria for "headache or facial pain attributed to temporomandibular joint disorder" is similar to the above:
* A. Recurrent pain in one or more regions of the head or face fulfilling criteria C and D
* B. X-ray, MRI or bone scintigraphy demonstrate TMJ disorder
* C. Evidence that pain can be attributed to the TMJ disorder, based on at least one of the following:
** pain is precipitated by jaw movements or chewing of hard or tough food
** reduced range of or irregular jaw opening
** noise from one or both TMJs during jaw movements
** tenderness of the joint capsule(s) of one or both TMJs
* D. Headache resolves within 3 months, and does not recur, after successful treatment of the TMJ disorder
Medical imaging
The advantages brought about by diagnostic imaging mainly lie within diagnosing TMD of articular origin. Additional benefits of imaging the TMJ are as follows:
* Assess the integrity of anatomical structures in suspicion of disorders
* Staging the extent of any pathology
* Monitoring and staging the progress of disease
* Determining the effects of treatment
When clinical examination alone is unable to bring sufficient detail to ascertain the state of the TMJ, imaging methods can act as an adjuvant to clinical examination in the diagnosis of TMD.
Plain radiography
This method of imaging allows the visualisation of the joint's mineralised areas, therefore excluding the cartilage and soft tissues.
A disadvantage of plain radiography is that images are prone to superimposition from surrounding anatomical structures, thereby complicating radiographic interpretation.
It was concluded that there is no evidence to support the use of plain radiography in the diagnosis of joint erosions and osteophytes.
It is reasonable to conclude that plain film can only be used to diagnose extensive lesions.
Panoramic tomography
The distortion brought about by panoramic imaging decreases its overall reliability. Data concluded from a systematic review showed that only extensive erosions and large osteophytes can be detected by panoramic imaging.
Computerised tomography (CT)
Studies have shown that tomography of the TMJ provided supplementary information that supersedes what is obtainable from clinical examination alone. However, the issues lies in the fact that it is impossible to determine whether certain patient groups would benefit more or less from a radiographic examination.
The main indications of
CT and CBCT examinations are to assess the bony components of the TMJ, specifically the location and extent of any abnormalities present.
The introduction of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) imaging allowed a lower radiation dose to patients, in comparison to conventional CT. Hintze et al. compared CBCT and CT techniques and their ability to detect morphological TMJ changes. No significant difference was concluded in terms of their diagnostic accuracy.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
is the optimal choice for the imaging of soft tissues surrounding the TMJ.
It allows three-dimensional evaluation of the axial, coronal and sagittal plane.
It is the gold standard method for assessing disc position and is sensitive for intra-articular degenerative alterations.
Indications for MRI are pre-auricular pain, detection of joint clicking and crepitus, frequent incidents of subluxation and jaw dislocation, limited mouth opening with terminal stiffness, suspicion of neoplastic growth, and osteoarthritic symptoms.
It is also useful for assessing the integrity of neural tissues, which may produce orofacial pain when compressed.
MRI provides evaluation of pathology such as necrosis and oedema all without any exposure to
ionizing radiation.
However, there is a high cost associated with this method of imaging, due to the need for sophisticated facilities.
Caution should be taken in patient selection, as MRI is contraindicated in those with claustrophobic tendencies,
pacemakers
An artificial cardiac pacemaker (or artificial pacemaker, so as not to be confused with the natural cardiac pacemaker) or pacemaker is a medical device that generates electrical impulses delivered by electrodes to the chambers of the heart eit ...
and metallic heart valves,
ferromagnetic foreign bodies and pregnant women.
Ultrasound
Where internal TMJ disorders are concerned,
ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
(US) imaging can be a useful alternative in assessing the position of the disc
While having significant diagnostic
sensitivity, US has inadequate
specificity when identifying
osteoarthrosis. Moreover, it is not accurate enough for the diagnosis of cortical and
articular disc
The articular disk (or disc) is a thin, oval plate of fibrocartilage present in several joints which separates synovial cavities. This separation of the cavity space allows for separate movements to occur in each space.
The presence of an articula ...
morphology based on the findings done related to morphological alterations.
However, with US, identification of
effusion in individuals with inflammatory conditions associated with pain is possible and confirmed by MRI
US can be a useful alternative in initial investigation of internal TMJ dysfunctions especially in MRI contraindicated individuals
despite its limitations.
in addition to being less costly,
US provides a quick and comfortable real-time imaging without exposing the individual to ionizing radiation
US is commonly assessed in the differential diagnosis of alterations of glandular and neighbouring structures, such as the TMJ and the
masseter muscle
In human anatomy, the masseter is one of the muscles of mastication. Found only in mammals, it is particularly powerful in herbivores to facilitate chewing of plant matter. The most obvious muscle of mastication is the masseter muscle, since it ...
. Symptoms of sialendenitis and sialothiasis cases can be confused with
Eagle syndrome
Eagle syndrome (also termed stylohyoid syndrome, styloid syndrome, styloid-stylohyoid syndrome, or styloid–carotid artery syndrome) is a rare condition commonly characterized but not limited to sudden, sharp nerve-like pain in the jaw bone and ...
, TMD, myofascial and nerve pain, and other pain of the orofacial region.
US assessment is also indicated where there is need to identify the correct position of the joint spaces for infiltrative procedures,
arthrocentesis
Arthrocentesis, or joint aspiration, is the clinical procedure performed to diagnose and, in some cases, treat musculoskeletal conditions. The procedure entails using a syringe to collect synovial fluid from or inject medication into the joint caps ...
, and
viscosupplementation. This is due to the fact that US provides a dynamic and real-time location of the component of the joints, while providing adequate lubrication and washing, which can be confirmed by the joint space increase post-treatment.
Management
TMD can be difficult to manage, and since the disorder transcends the boundaries between several health-care disciplines – in particular,
dentistry and
neurology
Neurology (from el, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal ...
, the treatment may often involve multiple approaches and be multidisciplinary.
Most who are involved in treating and researching TMD now agree that any treatment carried out should not permanently alter the jaw or teeth, and should be reversible.
To avoid permanent change,
over-the-counter
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are medicines sold directly to a consumer without a requirement for a prescription from a healthcare professional, as opposed to prescription drugs, which may be supplied only to consumers possessing a valid prescr ...
or
prescription pain medications may be prescribed.
Psychosocial and behavioral interventions
Given the important role that psychosocial factors appear to play in TMD, psychosocial interventions could be viewed to be central to management of the condition.
There is a suggestion that treatment of factors that modulate pain sensitivity such as
mood disorder
A mood disorder, also known as an affective disorder, is any of a group of conditions of mental and behavioral disorder where a disturbance in the person's mood is the main underlying feature. The classification is in the '' Diagnostic and St ...
s, anxiety and
fatigue, may be important in the treatment of TMD, which often tends to attempt to address the pain directly.
(CBT) has been used in TMD and has been shown to be efficacious by meta analyses.
Hypnosis
Hypnosis is a human condition involving focused attention (the selective attention/selective inattention hypothesis, SASI), reduced peripheral awareness, and an enhanced capacity to respond to suggestion.In 2015, the American Psychologica ...
is suggested by some to be appropriate for TMD. Studies have suggested that it may even be more beneficial than occlusal splint therapy, and has comparable effects to relaxation techniques.
include
progressive muscle relaxation,
yoga
Yoga (; sa, योग, lit=yoke' or 'union ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines which originated in ancient India and aim to control (yoke) and still the mind, recognizing a detached witness-consci ...
, and
meditation
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique – such as mindfulness, or focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity – to train attention and awareness, and achieve a mentally clear and emotionally calm ...
.
It has been suggested that TMD involves increased sensitivity to external stimuli leading to an increased
sympathetic ("fight or flight") response with cardiovascular and respiratory alterations.
Relaxation techniques cause reduced sympathetic activity, including muscle relaxation and reducing sensitivity to external stimuli, and provoke a general sense of well-being and reduced anxiety.
Devices

 Occlusal splint
Occlusal splints (also termed bite plates or intra-oral appliances) are often used by dentists to treat TMD. They are usually made of
acrylic and can be hard or soft. They can be designed to fit onto the upper teeth or the lower teeth. They may cover all the teeth in one arch (full coverage splint) or only some (partial coverage splint). Splints are also termed according to their intended mechanism, such as the anterior positioning splint or the stabilization splint.
Although occlusal splints are generally considered a reversible treatment,
sometimes partial coverage splints lead to pathologic tooth migration (changes in the position of teeth). Normally splints are only worn during sleep, and therefore probably do nothing for people who engage in parafunctional activities during wakefulness rather than during sleep. There is slightly more evidence for the use of occlusal splints in sleep bruxism than in TMD. A splint can also have a diagnostic role if it demonstrates excessive occlusal wear after a period of wearing it each night. This may confirm the presence of sleep bruxism if it was in doubt. Soft splints are occasionally reported to worsen discomfort related to TMD.
Specific types of occlusal splint are discussed below.
A stabilization splint is a hard acrylic splint that forces the teeth to meet in an "ideal" relationship for the muscles of mastication and the TMJs. It is claimed that this technique reduces abnormal muscular activity and promotes "neuromuscular balance". A stabilization splint is only intended to be used for about 2–3 months.
It is more complicated to construct than other types of splint since a
face bow record is required and significantly more skill on the part of the
dental technician
A dental technologist (dental laboratory technician) is a member of the dental team who, upon prescription from a dental clinician, constructs custom-made restorative and dental appliances.
There are four major disciplines within dental technol ...
. This kind of splint should be properly fitted to avoid exacerbating the problem and used for brief periods of time. The use of the splint should be discontinued if it is painful or increases existing pain.
[ A systematic review of all the scientific studies investigating the efficacy of stabilization splints concluded the following:
Partial coverage splints are recommended by some experts, but they have the potential to cause unwanted tooth movements, which can occasionally be severe. The mechanism of this tooth movement is that the splint effectively holds some teeth out of contact and puts all the force of the bite onto the teeth which the splint covers. This can cause the covered teeth to be intruded, and those that are not covered to over-erupted. I.e. a partial coverage splint can act as a Dahl appliance. Examples of partial coverage splints include the NTI-TSS ("nociceptive trigeminal inhibitor tension suppression system"), which covers the upper front teeth only. Due to the risks involved with long term use, some discourage the use of any type of partial coverage splint.]
Medication
Medication is the main method of managing pain in TMD, mostly because there is little if any evidence of the effectiveness of surgical or dental interventions. Many drugs have been used to treat TMD pain, such as analgesics (pain killers), benzodiazepines (e.g. clonazepam
Clonazepam, sold under the brand names Klonopin and Rivotril, is a medication used to prevent and treat seizures, panic disorder, anxiety disorders, and the movement disorder known as akathisia. It is a tranquilizer of the benzodiazepine class ...
, prazepam
Prazepam is a benzodiazepine derivative drug developed by Warner-Lambert in the 1960s. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Prazepam is a prodrug for desmethyldiazepam which is responsible fo ...
, diazepam
Diazepam, first marketed as Valium, is a medicine of the benzodiazepine family that acts as an anxiolytic. It is commonly used to treat a range of conditions, including anxiety, seizures, alcohol withdrawal syndrome, muscle spasms, insomnia, ...
), anticonvulsants (e.g. gabapentin
Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat partial seizures and neuropathic pain. It is a first-line medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabeti ...
), muscle relaxant
A muscle relaxant is a drug that affects skeletal muscle function and decreases the muscle tone. It may be used to alleviate symptoms such as muscle spasms, pain, and hyperreflexia. The term "muscle relaxant" is used to refer to two major therap ...
s (e.g. cyclobenzaprine), and others. Analgesics that have been studied in TMD include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
s (e.g. piroxicam
Piroxicam is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the oxicam class used to relieve the symptoms of painful inflammatory conditions like arthritis. Piroxicam works by preventing the production of endogenous prostaglandins which are in ...
, diclofenac
Diclofenac, sold under the brand name Voltaren, among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain and inflammatory diseases such as gout. It is taken by mouth or rectally in a suppository, used by injection, or ...
, naproxen
Naproxen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain, menstrual cramps, inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout and fever. It is taken orally. It is available in immediate and delayed release formulat ...
) and cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitors (e.g. celecoxib
Celecoxib, sold under the brand name Celebrex among others, is a COX-2 inhibitor and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is used to treat the pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis, acute pain in adults, rheumatoid arthritis, ankyl ...
).
Topical
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
methyl salicylate
Methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen or wintergreen oil) is an organic compound with the formula C8H8O3. It is the methyl ester of salicylic acid. It is a colorless, viscous liquid with a sweet, fruity odor reminiscent of root beer, but often a ...
and topical capsaicin
Capsaicin (8-methyl-''N''-vanillyl-6-nonenamide) ( or ) is an active component of chili peppers, which are plants belonging to the genus ''Capsicum''. It is a chemical irritant for mammals, including humans, and produces a sensation of burnin ...
have also been used.
Other drugs that have been described for use in TMD include glucosamine hydrochloride/ chondroitin sulphate and propranolol
Propranolol, sold under the brand name Inderal among others, is a medication of the beta blocker class. It is used to treat high blood pressure, a number of types of irregular heart rate, thyrotoxicosis, capillary hemangiomas, performance an ...
. Low-doses of anti-muscarinic tricyclic antidepressants such as amitriptyline
Amitriptyline, sold under the brand name Elavil among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant primarily used to treat cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS), major depressive disorder and a variety of pain syndromes from neuropathic pain to fibromyalgi ...
,randomized control trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical t ...
s being conducted on these commonly used medications for TMD a systematic review carried out in 2010 concluded that there was insufficient evidence to support or not to support the use of these drugs in TMD.morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. T ...
, fentanyl
Fentanyl, also spelled fentanil, is a very potent synthetic opioid used as a pain medication. Together with other drugs, fentanyl is used for anesthesia. It is also used illicitly as a recreational drug, sometimes mixed with heroin, cocain ...
, oxycodone
Oxycodone, sold under various brand names such as Roxicodone and OxyContin (which is the extended release form), is a strong, semi-synthetic opioid used medically for treatment of moderate to severe pain. It is highly addictive and a commonly ...
, tramadol, hydrocodone
Hydrocodone, also known as dihydrocodeinone, is an opioid used to treat pain and as a cough suppressant. It is taken by mouth. Typically it is dispensed as the combination acetaminophen/hydrocodone or ibuprofen/hydrocodone for pain severe eno ...
, and methadone
Methadone, sold under the brand names Dolophine and Methadose among others, is a synthetic opioid agonist used for chronic pain and also for opioid dependence. It is used to treat chronic pain, and it is also used to treat addiction to heroi ...
.local anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of pain sensation. In the context of surgery, a local anesthetic creates an absence of pain in a specific location of the body without a loss of consciousness, as opposed to a general a ...
, sometimes combined with steroids, into the muscles (e.g. the temoralis muscle or its tendon) are also sometimes used. Local anesthetics may provide temporary pain relief, and steroids inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
s.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy (physical therapy) is sometimes used as an adjuvant to other methods of treatment in TMD.hyperemia
Hyperaemia (also hyperemia) is the increase of blood flow to different tissues in the body. It can have medical implications but is also a regulatory response, allowing change in blood supply to different tissues through vasodilation. Clinically, ...
in the muscles, and this is hypothesized to inactivate trigger points and disrupt small fibrous adhesions within the muscle that have formed following surgery or muscular shortening due to restricted movement.transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS or TNS) is the use of electric current produced by a device to stimulate the nerves for therapeutic purposes. TENS, by definition, covers the complete range of transcutaneously applied currents ...
(TENS), which may override pain by stimulation of superficial nerve fibers and lead to pain reduction which extends after the time where the TENS is being actually being applied, possibly due to release of endorphins. Others recommend the use of ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
, theorized to produce tissue heating, alter blood flow and metabolic activity at a level that is deeper than possible with surface heat applications.proprioception
Proprioception ( ), also referred to as kinaesthesia (or kinesthesia), is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position. It is sometimes described as the "sixth sense".
Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, mechanosensory neurons ...
, break fibrous adhesions, stimulate synovial fluid production and reduce pain. Exercises and MT are safe and simple interventions that could potentially be beneficial for patients with TMD. No adverse events regarding exercise therapy and manual therapy have been reported.
Occlusal adjustment
This is the adjustment or reorganizing of the existing occlusion, carried out in the belief that this will redistribute forces evenly across the dental arches or achieve a more favorable position of the condyles in the fossae, which is purported to lessen tooth wear, bruxism and TMD, but this is controversial. These techniques are sometimes termed "occlusal rehabilitation" or "occlusal equilibration".orthodontic
Orthodontics is a dentistry specialty that addresses the diagnosis, prevention, management, and correction of mal-positioned teeth and jaws, and misaligned bite patterns. It may also address the modification of facial growth, known as dentofacial ...
s, restorative dentistry
Restorative dentistry is the study, diagnosis and integrated management of diseases of the teeth and their supporting structures and the rehabilitation of the dentition to functional and aesthetic requirements of the individual. Restorative dentis ...
or even orthognathic surgery
Orthognathic surgery (), also known as corrective jaw surgery or simply jaw surgery, is surgery designed to correct conditions of the jaw and lower face related to structure, growth, airway issues including sleep apnea, TMJ disorders, malocclusi ...
. Some have criticized these occlusal reorganizations as having no evidence base, and irreversibly damaging the dentition on top of the damage already caused by bruxism.placebo
A placebo ( ) is a substance or treatment which is designed to have no therapeutic value. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
In general, placebos can af ...
. The reviewers also stated that there are ethical implications if occlusal adjustment was found to be ineffective in preventing TMD.
Surgery
Attempts in the last decade to develop surgical treatments based on MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
and CAT
The cat (''Felis catus'') is a domestic species of small carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species in the family Felidae and is commonly referred to as the domestic cat or house cat to distinguish it from the wild members of ...
scans now receive less attention. These techniques are reserved for the most difficult cases where other therapeutic modalities have failed. The American Society of Maxillofacial Surgeons recommends a conservative/non-surgical approach first. Only 20% of patients need to proceed to surgery.
Examples of surgical procedures that are used in TMD, some more commonly than others, include arthrocentesis
Arthrocentesis, or joint aspiration, is the clinical procedure performed to diagnose and, in some cases, treat musculoskeletal conditions. The procedure entails using a syringe to collect synovial fluid from or inject medication into the joint caps ...
arthroscopy
Arthroscopy (also called arthroscopic or keyhole surgery) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure on a joint in which an examination and sometimes treatment of damage is performed using an arthroscope, an endoscope that is inserted into the ...
, meniscectomy, disc repositioning, condylotomy or joint replacement
Replacement arthroplasty (from Greek ''arthron'', joint, limb, articulate, + ''plassein'', to form, mould, forge, feign, make an image of), or joint replacement surgery, is a procedure of orthopedic surgery in which an arthritic or dysfunctional ...
. Invasive surgical procedures in TMD may cause symptoms to worsen.
Alternative medicine
Acupuncture
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientif ...
is sometimes used for TMD.placebo
A placebo ( ) is a substance or treatment which is designed to have no therapeutic value. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
In general, placebos can af ...
.
Chiropractic
Chiropractic adjustments (also termed manipulations or mobilizations) are sometimes used in the belief that this will treat TMD.case series
A case series (also known as a clinical series) is a type of medical research study that tracks subjects with a known exposure, such as patients who have received a similar treatment, or examines their medical records for exposure and outcome. Cas ...
of only 9 participants. One review concluded "inconclusive evidence in a favorable direction regarding mobilization and massage for TMD".
Prognosis
It has been suggested that the natural history of TMD is benign and self-limiting,quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
.
Epidemiology
TMD mostly affects people in the 20 – 40 age group,nulliparous
In biology and human medicine, gravidity and parity are the number of times a woman is or has been pregnant (gravidity) and carried the pregnancies to a viable gestational age (parity). These terms are usually coupled, sometimes with additional te ...
than females without TMD.African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
s.
History
Temporomandibular disorders were described as early as ancient Egypt.otolaryngologist
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical a ...
,malocclusion
In orthodontics, a malocclusion is a misalignment or incorrect relation between the teeth of the upper and lower dental arches when they approach each other as the jaws close. The English-language term dates from 1864; Edward Angle (1855-19 ...
caused TMD, and placed emphasis on ear symptoms, such as tinnitus, otaglia, impaired hearing, and even dizziness.
References
{{Authority control
Musculoskeletal disorders
Articles containing video clips
Pathology of temporomandibular joints, muscles of mastication and associated structures
Ailments of unknown cause
 Pain is the most common reason for people with TMD to seek medical advice.
Joint noises may require auscultation with a stethoscope to detect. Clicks of the joint may also be palpated, over the joint itself in the preauricular region, or via a finger inserted in the external acoustic meatus, which lies directly behind the TMJ.
The differential diagnosis is with degenerative joint disease (e.g. osteoarthritis),
Pain is the most common reason for people with TMD to seek medical advice.
Joint noises may require auscultation with a stethoscope to detect. Clicks of the joint may also be palpated, over the joint itself in the preauricular region, or via a finger inserted in the external acoustic meatus, which lies directly behind the TMJ.
The differential diagnosis is with degenerative joint disease (e.g. osteoarthritis), 
 Occlusal splints (also termed bite plates or intra-oral appliances) are often used by dentists to treat TMD. They are usually made of acrylic and can be hard or soft. They can be designed to fit onto the upper teeth or the lower teeth. They may cover all the teeth in one arch (full coverage splint) or only some (partial coverage splint). Splints are also termed according to their intended mechanism, such as the anterior positioning splint or the stabilization splint. Although occlusal splints are generally considered a reversible treatment, sometimes partial coverage splints lead to pathologic tooth migration (changes in the position of teeth). Normally splints are only worn during sleep, and therefore probably do nothing for people who engage in parafunctional activities during wakefulness rather than during sleep. There is slightly more evidence for the use of occlusal splints in sleep bruxism than in TMD. A splint can also have a diagnostic role if it demonstrates excessive occlusal wear after a period of wearing it each night. This may confirm the presence of sleep bruxism if it was in doubt. Soft splints are occasionally reported to worsen discomfort related to TMD. Specific types of occlusal splint are discussed below.
A stabilization splint is a hard acrylic splint that forces the teeth to meet in an "ideal" relationship for the muscles of mastication and the TMJs. It is claimed that this technique reduces abnormal muscular activity and promotes "neuromuscular balance". A stabilization splint is only intended to be used for about 2–3 months. It is more complicated to construct than other types of splint since a face bow record is required and significantly more skill on the part of the
Occlusal splints (also termed bite plates or intra-oral appliances) are often used by dentists to treat TMD. They are usually made of acrylic and can be hard or soft. They can be designed to fit onto the upper teeth or the lower teeth. They may cover all the teeth in one arch (full coverage splint) or only some (partial coverage splint). Splints are also termed according to their intended mechanism, such as the anterior positioning splint or the stabilization splint. Although occlusal splints are generally considered a reversible treatment, sometimes partial coverage splints lead to pathologic tooth migration (changes in the position of teeth). Normally splints are only worn during sleep, and therefore probably do nothing for people who engage in parafunctional activities during wakefulness rather than during sleep. There is slightly more evidence for the use of occlusal splints in sleep bruxism than in TMD. A splint can also have a diagnostic role if it demonstrates excessive occlusal wear after a period of wearing it each night. This may confirm the presence of sleep bruxism if it was in doubt. Soft splints are occasionally reported to worsen discomfort related to TMD. Specific types of occlusal splint are discussed below.
A stabilization splint is a hard acrylic splint that forces the teeth to meet in an "ideal" relationship for the muscles of mastication and the TMJs. It is claimed that this technique reduces abnormal muscular activity and promotes "neuromuscular balance". A stabilization splint is only intended to be used for about 2–3 months. It is more complicated to construct than other types of splint since a face bow record is required and significantly more skill on the part of the