Technology neologisms on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Technology is the application of
Technology is the application of
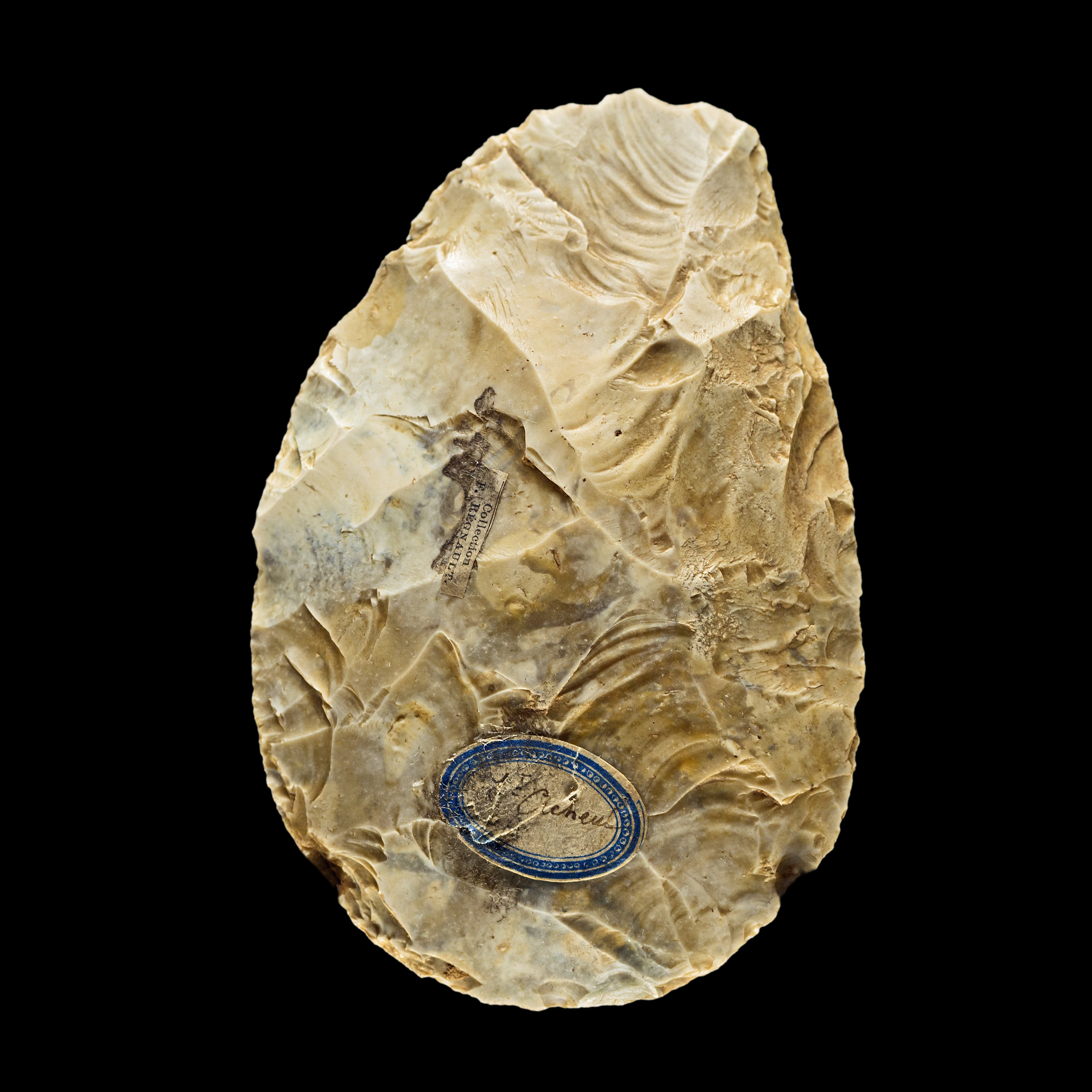 Tools were initially developed by
Tools were initially developed by
 The
The
 After harnessing fire, humans discovered other forms of energy. The earliest known use of wind power is the
After harnessing fire, humans discovered other forms of energy. The earliest known use of wind power is the  Ancient Minoan private homes had
Ancient Minoan private homes had
 Starting in the United Kingdom in the 18th century, the discovery of steam power set off the Industrial Revolution, which saw wide-ranging technological discoveries, particularly in the areas of British Agricultural Revolution, agriculture, manufacturing, mining, metallurgy, and
Starting in the United Kingdom in the 18th century, the discovery of steam power set off the Industrial Revolution, which saw wide-ranging technological discoveries, particularly in the areas of British Agricultural Revolution, agriculture, manufacturing, mining, metallurgy, and
 Since the invention of the wheel, technologies have helped increase humans' economic output. Past automation has both substituted and complemented labor; machines replaced humans at some lower-paying jobs (for example in agriculture), but this was compensated by the creation of new, higher-paying jobs. Studies have found that computers did not create significant net
Since the invention of the wheel, technologies have helped increase humans' economic output. Past automation has both substituted and complemented labor; machines replaced humans at some lower-paying jobs (for example in agriculture), but this was compensated by the creation of new, higher-paying jobs. Studies have found that computers did not create significant net
 Emerging technologies are novel technologies whose development or practical applications are still largely unrealized. They include nanotechnology, biotechnology, robotics, 3D printing, blockchains, and artificial intelligence.
In 2005, futurist Ray Kurzweil claimed the next technological revolution would rest upon advances in genetics, nanotechnology, and robotics, with robotics being the most impactful of the three. Genetic engineering will allow far greater control over human biological nature through a process called Directed evolution (transhumanism), directed evolution. Some thinkers believe that this may shatter our sense of self, and have urged for renewed public debate exploring the issue more thoroughly; others fear that directed evolution could lead to eugenics or extreme social inequality. Nanotechnology will grant us the ability to manipulate matter "at the molecular and atomic scale", which could allow us to reshape ourselves and our environment in fundamental ways. Nanobots could be used within the human body to destroy cancer cells or form new body parts, blurring the line between biology and technology. Autonomous robots have undergone rapid progress, and are expected to replace humans at many dangerous tasks, including search and rescue, bomb disposal, firefighting, and war.
Estimates on the advent of artificial general intelligence vary, but half of machine learning experts surveyed in 2018 believe that AI will "accomplish every task better and more cheaply" than humans by 2063, and automate all human jobs by 2140. This expected technological unemployment has led to calls for increased emphasis on computer science education and debates about UBI. Political science experts predict that this could lead to a rise in extremism, while others see it as an opportunity to usher in a post-scarcity economy.
Emerging technologies are novel technologies whose development or practical applications are still largely unrealized. They include nanotechnology, biotechnology, robotics, 3D printing, blockchains, and artificial intelligence.
In 2005, futurist Ray Kurzweil claimed the next technological revolution would rest upon advances in genetics, nanotechnology, and robotics, with robotics being the most impactful of the three. Genetic engineering will allow far greater control over human biological nature through a process called Directed evolution (transhumanism), directed evolution. Some thinkers believe that this may shatter our sense of self, and have urged for renewed public debate exploring the issue more thoroughly; others fear that directed evolution could lead to eugenics or extreme social inequality. Nanotechnology will grant us the ability to manipulate matter "at the molecular and atomic scale", which could allow us to reshape ourselves and our environment in fundamental ways. Nanobots could be used within the human body to destroy cancer cells or form new body parts, blurring the line between biology and technology. Autonomous robots have undergone rapid progress, and are expected to replace humans at many dangerous tasks, including search and rescue, bomb disposal, firefighting, and war.
Estimates on the advent of artificial general intelligence vary, but half of machine learning experts surveyed in 2018 believe that AI will "accomplish every task better and more cheaply" than humans by 2063, and automate all human jobs by 2140. This expected technological unemployment has led to calls for increased emphasis on computer science education and debates about UBI. Political science experts predict that this could lead to a rise in extremism, while others see it as an opportunity to usher in a post-scarcity economy.
 Technology's central role in our lives has drawn concerns and backlash. The backlash against technology is not a uniform movement and encompasses many heterogeneous ideologies.
The earliest known revolt against technology was Luddite, Luddism, a pushback against early automation in textile production. Automation had resulted in a need for fewer workers, a process known as
Technology's central role in our lives has drawn concerns and backlash. The backlash against technology is not a uniform movement and encompasses many heterogeneous ideologies.
The earliest known revolt against technology was Luddite, Luddism, a pushback against early automation in textile production. Automation had resulted in a need for fewer workers, a process known as
 Engineering is the process by which technology is developed. It often requires problem-solving under strict constraints. Technological development is "action-oriented", while scientific knowledge is fundamentally explanatory. Polish philosopher Henryk Skolimowski framed it like so: "science concerns itself with what , technology with what ."
The direction of causality between scientific discovery and technological innovation has been debated by scientists, philosophers and policymakers. Because innovation is often undertaken at the edge of scientific knowledge, most technologies are not derived from scientific knowledge, but instead from engineering, tinkering and chance. For example, in the 1940s and 1950s, when knowledge of turbulent combustion or fluid dynamics was still crude, jet engines were invented through "running the device to destruction, analyzing what broke [...] and repeating the process". Scientific explanations often follow technological developments rather than preceding them. Many discoveries also arose from pure chance, like the discovery of penicillin as a result of accidental lab contamination. Since the 1960s, the assumption that government funding of basic research would lead to the discovery of marketable technologies has lost credibility. Probabilist Nassim Taleb argues that national research programs that implement the notions of serendipity and Convexity (finance), convexity through frequent trial and error are more likely to lead to useful innovations than research that aims to reach specific outcomes.
Despite this, modern technology is increasingly reliant on deep, domain-specific scientific knowledge. In 1979, an average of one in three patents granted in the U.S. cited the scientific literature; by 1989, this increased to an average of one citation per patent. The average was skewed upwards by patents related to the pharmaceutical industry, chemistry, and electronics. A 2021 analysis shows that patents that are based on scientific discoveries are on average 26% more valuable than equivalent non-science-based patents.
Engineering is the process by which technology is developed. It often requires problem-solving under strict constraints. Technological development is "action-oriented", while scientific knowledge is fundamentally explanatory. Polish philosopher Henryk Skolimowski framed it like so: "science concerns itself with what , technology with what ."
The direction of causality between scientific discovery and technological innovation has been debated by scientists, philosophers and policymakers. Because innovation is often undertaken at the edge of scientific knowledge, most technologies are not derived from scientific knowledge, but instead from engineering, tinkering and chance. For example, in the 1940s and 1950s, when knowledge of turbulent combustion or fluid dynamics was still crude, jet engines were invented through "running the device to destruction, analyzing what broke [...] and repeating the process". Scientific explanations often follow technological developments rather than preceding them. Many discoveries also arose from pure chance, like the discovery of penicillin as a result of accidental lab contamination. Since the 1960s, the assumption that government funding of basic research would lead to the discovery of marketable technologies has lost credibility. Probabilist Nassim Taleb argues that national research programs that implement the notions of serendipity and Convexity (finance), convexity through frequent trial and error are more likely to lead to useful innovations than research that aims to reach specific outcomes.
Despite this, modern technology is increasingly reliant on deep, domain-specific scientific knowledge. In 1979, an average of one in three patents granted in the U.S. cited the scientific literature; by 1989, this increased to an average of one citation per patent. The average was skewed upwards by patents related to the pharmaceutical industry, chemistry, and electronics. A 2021 analysis shows that patents that are based on scientific discoveries are on average 26% more valuable than equivalent non-science-based patents.
 The use of basic technology is also a feature of non-human animal species. Tool use was once considered a defining characteristic of the genus Homo (genus), Homo. This view was supplanted after discovering evidence of tool use among Common chimpanzee, chimpanzees and other primates, dolphins, and crows. For example, researchers have observed wild chimpanzees using basic foraging tools, pestles, levers, using leaves as sponges, and tree bark or vines as probes to fish termites. West African chimpanzees use stone hammers and anvils for cracking nuts, as do capuchin monkeys of Boa Vista, Roraima, Boa Vista, Brazil. Tool use is not the only form of animal technology use; for example, Beaver dam, beaver dams, built with wooden sticks or large stones, are a technology with "dramatic" impacts on river habitats and ecosystems.
The use of basic technology is also a feature of non-human animal species. Tool use was once considered a defining characteristic of the genus Homo (genus), Homo. This view was supplanted after discovering evidence of tool use among Common chimpanzee, chimpanzees and other primates, dolphins, and crows. For example, researchers have observed wild chimpanzees using basic foraging tools, pestles, levers, using leaves as sponges, and tree bark or vines as probes to fish termites. West African chimpanzees use stone hammers and anvils for cracking nuts, as do capuchin monkeys of Boa Vista, Roraima, Boa Vista, Brazil. Tool use is not the only form of animal technology use; for example, Beaver dam, beaver dams, built with wooden sticks or large stones, are a technology with "dramatic" impacts on river habitats and ecosystems.
 Technology is the application of
Technology is the application of knowledge
Knowledge can be defined as awareness of facts or as practical skills, and may also refer to familiarity with objects or situations. Knowledge of facts, also called propositional knowledge, is often defined as true belief that is distinc ...
to reach practical goal
A goal is an idea of the future or desired result that a person or a group of people envision, plan and commit to achieve. People endeavour to reach goals within a finite time by setting deadlines.
A goal is roughly similar to a purpose or ai ...
s in a specifiable and reproducible
Reproducibility, also known as replicability and repeatability, is a major principle underpinning the scientific method. For the findings of a study to be reproducible means that results obtained by an experiment or an observational study or in a ...
way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
, science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
, industry
Industry may refer to:
Economics
* Industry (economics), a generally categorized branch of economic activity
* Industry (manufacturing), a specific branch of economic activity, typically in factories with machinery
* The wider industrial sector ...
, communication
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inquir ...
, transport
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipelin ...
ation, and daily life. Technologies include physical objects like utensils or machine
A machine is a physical system using Power (physics), power to apply Force, forces and control Motion, movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to na ...
s and intangible tools such as software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
At the lowest programming level, executable code consists ...
.
Many technological advancements have led to societal changes. The earliest known technology is the stone tool, used in the prehistoric era
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of ...
, followed by fire use, which contributed to the growth
Growth may refer to:
Biology
* Auxology, the study of all aspects of human physical growth
* Bacterial growth
* Cell growth
* Growth hormone, a peptide hormone that stimulates growth
* Human development (biology)
* Plant growth
* Secondary growth ...
of the human brain and the development of language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
in the Ice Age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
. The invention of the wheel
A wheel is a circular component that is intended to rotate on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machines. Wheels, in conjunction wi ...
in the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
enabled wider travel and the creation of more complex machine
A machine is a physical system using Power (physics), power to apply Force, forces and control Motion, movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to na ...
s. Recent technological developments, including the printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in wh ...
, the telephone
A telephone is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into e ...
, and the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
have lowered communication
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inquir ...
barriers and ushered in the knowledge economy.
While technology contributes to economic development
In the economics study of the public sector, economic and social development is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals and o ...
and human prosperity
Prosperity is the flourishing, thriving, good fortune and successful social status. Prosperity often produces profuse wealth including other factors which can be profusely wealthy in all degrees, such as happiness and health.
Competing notion ...
, it can also have negative impacts like pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the ...
or resource depletion
Resource depletion is the consumption of a resource faster than it can be replenished. Natural resources are commonly divided between renewable resources and non-renewable resources (see also mineral resource classification). Use of either ...
, or cause social harms like technological unemployment
Technological unemployment is the loss of jobs caused by technological change. It is a key type of structural unemployment.
Technological change typically includes the introduction of labour-saving "mechanical-muscle" machines or more efficie ...
caused by automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, namely by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines ...
. As a result, philosophical and political debates have arisen over the role and use of technology, the ethics of technology
The ethics of technology is a sub-field of ethics addressing the ethical questions specific to the Technology Age, the transitional shift in society wherein personal computers and subsequent devices provide for the quick and easy transfer of info ...
, and the mitigation of technology's potential downsides. Historical and contemporary movements like neo-Luddism
Neo-Luddism or new Luddism is a philosophy opposing many forms of modern technology. The term Luddite is generally used as a pejorative applied to people showing technophobic leanings. The name is based on the historical legacy of the English Lud ...
and anarcho-primitivism
Anarcho-primitivism is an anarchist critique of civilization (anti-civ) that advocates a return to non-civilized ways of life through deindustrialization, abolition of the division of labor or specialization, and abandonment of large-scale organ ...
criticize technology's pervasiveness, while adherents to transhumanism
Transhumanism is a philosophical and intellectual movement which advocates the enhancement of the human condition by developing and making widely available sophisticated technologies that can greatly enhance longevity and cognition.
Transhuma ...
and techno-progressivism
Techno-progressivism or tech-progressivism is a stance of active support for the wikt:convergence, convergence of technological change and social change. Techno-progressives argue that technological developments can be profoundly empowerment, e ...
actively support technological change, viewing it as emancipatory. Many negative impacts of technology can be mitigated through technological innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entit ...
s like renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
in transportation and industry, genetically modified crops to address soil depletion
Soil fertility refers to the ability of soil to sustain agricultural plant growth, i.e. to provide plant habitat and result in sustained and consistent Crop yield, yields of high quality.
, and space exploration
Space exploration is the use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space. While the exploration of space is carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration though is conducted both by robotic spacec ...
to mitigate global catastrophic risk
A global catastrophic risk or a doomsday scenario is a hypothetical future event that could damage human well-being on a global scale, even endangering or destroying modern civilization. An event that could cause human extinction or permanen ...
s.
Etymology
''Technology'' is a term dating back to the early 17th century that meant 'systematic treatment' (fromGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, ''from τέχνη'' 'art, craft' and , 'study, knowledge').'''' It is predated in use by the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
''τέχνη'', used to mean 'knowledge of how to make things', which encompassed activities like architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
.
Starting in the 19th century, continental Europeans started using the terms ''Technik'' (German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
) or ''technique'' ( French) to refer to a 'way of doing', which included all technical arts, such as dancing, navigation, or printing, whether or not they required tools or instruments. At the time, ''Technologie'' (German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
and French) referred either to the academic discipline studying the "methods of arts and crafts", or to the political discipline "intended to legislate on the functions of the arts and crafts." Since the distinction between ''Technik'' and ''Technologie'' is absent in English, both were translated as ''technology''. The term was previously uncommon in English and mostly referred to the academic discipline, as in the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the ...
.
In the 20th century, as a result of scientific progress
Progress is the movement towards a refined, improved, or otherwise desired state. In the context of progressivism, it refers to the proposition that advancements in technology, science, and social organization have resulted, and by extension wi ...
and the Second Industrial Revolution
The Second Industrial Revolution, also known as the Technological Revolution, was a phase of rapid scientific discovery, standardization, mass production and industrialization from the late 19th century into the early 20th century. The Fi ...
, ''technology'' stopped being considered a distinct academic discipline and took on its current-day meaning: the systemic use of knowledge to practical ends.
History
Prehistoric
 Tools were initially developed by
Tools were initially developed by hominids
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); ''Gorilla'' (the ...
through observation and trial and error
Trial and error is a fundamental method of problem-solving characterized by repeated, varied attempts which are continued until success, or until the practicer stops trying.
According to W.H. Thorpe, the term was devised by C. Lloyd Morgan (18 ...
. Around 2 Mya (million years ago), they learned to make the first stone tools by hammering flakes off a pebble, forming a sharp hand axe
A hand axe (or handaxe or Acheulean hand axe) is a prehistoric stone tool with two faces that is the longest-used tool in human history, yet there is no academic consensus on what they were used for. It is made from stone, usually flint or ch ...
. This practice was refined 75 kya (thousand years ago) into pressure flaking
In archaeology, in particular of the Stone Age, lithic reduction is the process of fashioning stones or rocks from their natural state into tools or weapons by removing some parts. It has been intensely studied and many archaeological industrie ...
, enabling much finer work.
The discovery of fire was described by Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended fr ...
as "possibly the greatest ever made by man". Archeological, dietary, and social evidence point to "continuous uman
Uman ( uk, Умань, ; pl, Humań; yi, אומאַן) is a city located in Cherkasy Oblast in central Ukraine, to the east of Vinnytsia. Located in the historical region of the eastern Podolia, the city rests on the banks of the Umanka River ...
fire-use" at least 1.5 Mya. Fire, fueled with wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin th ...
and charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, cal ...
, allowed early humans to cook their food to increase its digestibility, improving its nutrient value and broadening the number of foods that could be eaten. The '' cooking hypothesis'' proposes that the ability to cook promoted an increase in hominid brain size
The size of the brain is a frequent topic of study within the fields of anatomy, biological anthropology, animal science and evolution. Brain size is sometimes measured by weight and sometimes by volume (via MRI scans or by skull volume). Neur ...
, though some researchers find the evidence inconclusive. Archeological evidence of hearth
A hearth () is the place in a home where a fire is or was traditionally kept for home heating and for cooking, usually constituted by at least a horizontal hearthstone and often enclosed to varying degrees by any combination of reredos (a lo ...
s was dated to 790 kya; researchers believe this is likely to have intensified human socialization
In sociology, socialization or socialisation (see spelling differences) is the process of internalizing the norms and ideologies of society. Socialization encompasses both learning and teaching and is thus "the means by which social and cultur ...
and may have contributed to the emergence of language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
.
Other technological advances made during the Paleolithic era include clothing
Clothing (also known as clothes, apparel, and attire) are items worn on the body. Typically, clothing is made of fabrics or textiles, but over time it has included garments made from animal skin and other thin sheets of materials and natural ...
and shelter. No consensus exists on the approximate time of adoption of either technology, but archeologists have found archeological evidence of clothing 90-120 kya and shelter 450 kya. As the Paleolithic era progressed, dwellings became more sophisticated and more elaborate; as early as 380 kya, humans were constructing temporary wood huts. Clothing, adapted from the fur and hides of hunted animals, helped humanity expand into colder regions; humans began to migrate out of Africa around 200 kya, initially moving to Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
.
Neolithic
 The
The Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an incre ...
(or ''First Agricultural Revolution'') brought about an acceleration of technological innovation, and a consequent increase in social complexity. The invention of the polished stone axe
A hand axe (or handaxe or Acheulean hand axe) is a prehistoric stone tool with two faces that is the longest-used tool in human history, yet there is no academic consensus on what they were used for. It is made from stone, usually flint or che ...
was a major advance that allowed large-scale forest clearance
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated d ...
and farming. This use of polished stone axes increased greatly in the Neolithic but was originally used in the preceding Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
in some areas such as Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
. Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
fed larger populations, and the transition to sedentism
In cultural anthropology, sedentism (sometimes called sedentariness; compare sedentarism) is the practice of living in one place for a long time. , the large majority of people belong to sedentary cultures. In evolutionary anthropology and a ...
allowed for the simultaneous raising of more children, as infants no longer needed to be carried around by nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the popu ...
s. Additionally, children could contribute labor to the raising of crops more readily than they could participate in hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
activities.
With this increase in population and availability of labor came an increase in labor specialization
The division of labour is the separation of the tasks in any economic system or organisation so that participants may specialise (specialisation). Individuals, organizations, and nations are endowed with, or acquire specialised capabilities, and ...
. What triggered the progression from early Neolithic villages to the first cities, such as Uruk
Uruk, also known as Warka or Warkah, was an ancient city of Sumer (and later of Babylonia) situated east of the present bed of the Euphrates River on the dried-up ancient channel of the Euphrates east of modern Samawah, Al-Muthannā, Iraq.Harm ...
, and the first civilizations, such as Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of c ...
, is not specifically known; however, the emergence of increasingly hierarchical
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important ...
social structures and specialized labor, of trade and war amongst adjacent cultures, and the need for collective action to overcome environmental challenges such as irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow Crop, crops, Landscape plant, landscape plants, and Lawn, lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,00 ...
, are all thought to have played a role.
Continuing improvements led to the furnace
A furnace is a structure in which heat is produced with the help of combustion.
Furnace may also refer to:
Appliances Buildings
* Furnace (central heating): a furnace , or a heater or boiler , used to generate heat for buildings
* Boiler, used t ...
and bellows
A bellows or pair of bellows is a device constructed to furnish a strong blast of air. The simplest type consists of a flexible bag comprising a pair of rigid boards with handles joined by flexible leather sides enclosing an approximately airtigh ...
and provided, for the first time, the ability to smelt
Smelt may refer to:
* Smelting, chemical process
* The common name of various fish:
** Smelt (fish), a family of small fish, Osmeridae
** Australian smelt in the family Retropinnidae and species ''Retropinna semoni''
** Big-scale sand smelt ''Ath ...
and forge
A forge is a type of hearth used for heating metals, or the workplace (smithy) where such a hearth is located. The forge is used by the smith to heat a piece of metal to a temperature at which it becomes easier to shape by forging, or to th ...
gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
, and lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
native metals found in relatively pure form in nature. The advantages of copper tools over stone, bone and wooden tools were quickly apparent to early humans, and native copper was probably used from near the beginning of Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
times (about 10 ka). Native copper does not naturally occur in large amounts, but copper ores are quite common and some of them produce metal easily when burned in wood or charcoal fires. Eventually, the working of metals led to the discovery of alloys
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility ...
such as bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
and brass
Brass is an alloy of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn), in proportions which can be varied to achieve different mechanical, electrical, and chemical properties. It is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two constituents may replace each other wit ...
(about 4,000 BCE). The first use of iron alloys such as steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
dates to around 1,800 BCE.
Ancient
 After harnessing fire, humans discovered other forms of energy. The earliest known use of wind power is the
After harnessing fire, humans discovered other forms of energy. The earliest known use of wind power is the sailing ship
A sailing ship is a sea-going vessel that uses sails mounted on masts to harness the power of wind and propel the vessel. There is a variety of sail plans that propel sailing ships, employing square-rigged or fore-and-aft sails. Some ships c ...
; the earliest record of a ship under sail is that of a Nile boat dating to around 7,000 BCE. From prehistoric times, Egyptians likely used the power of the annual flooding of the Nile
The flooding of the Nile has been an important natural cycle in Egypt since ancient times. It is celebrated by Egyptians as an annual holiday for two weeks starting August 15, known as ''Wafaa El-Nil''. It is also celebrated in the Coptic Church ...
to irrigate their lands, gradually learning to regulate much of it through purposely built irrigation channels and "catch" basins. The ancient Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of c ...
ians in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
used a complex system of canals and levees to divert water from the Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the ...
and Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
rivers for irrigation.
Archaeologists estimate that the wheel
A wheel is a circular component that is intended to rotate on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machines. Wheels, in conjunction wi ...
was invented independently and concurrently in Mesopotamia (in present-day Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
), the Northern Caucasus (Maykop culture
The Maykop culture (, , scientific transliteration: ''Majkop,''), c. 3700 BC– 3000 BC, was a major Bronze Age archaeological culture in the western Caucasus region.
It extends along the area from the Taman Peninsula at the Kerch Strait to ...
), and Central Europe. Time estimates range from 5,500 to 3,000 BCE with most experts putting it closer to 4,000 BCE. The oldest artifacts with drawings depicting wheeled carts date from about 3,500 BCE. More recently, the oldest-known wooden wheel in the world was found in the Ljubljana Marsh
The Ljubljana Marsh ( sl, Ljubljansko barje), located south of Ljubljana, the capital of Slovenia, is the largest marsh in the country. It covers or 0.8% of the Slovene territory. It is administered by the municipalities of Borovnica, Brezovica ...
of Slovenia.
The invention of the wheel revolutionized trade and war. It did not take long to discover that wheeled wagons could be used to carry heavy loads. The ancient Sumerians used a potter's wheel
In pottery, a potter's wheel is a machine used in the shaping (known as throwing) of clay into round ceramic ware. The wheel may also be used during the process of trimming excess clay from leather-hard dried ware that is stiff but malleable, a ...
and may have invented it. A stone pottery wheel found in the city-state of Ur dates to around 3,429 BCE, and even older fragments of wheel-thrown pottery have been found in the same area. Fast (rotary) potters' wheels enabled early mass production
Mass production, also known as flow production or continuous production, is the production of substantial amounts of standardized products in a constant flow, including and especially on assembly lines. Together with job production and batch ...
of pottery, but it was the use of the wheel as a transformer of energy (through water wheel
A water wheel is a machine for converting the energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power, often in a watermill. A water wheel consists of a wheel (usually constructed from wood or metal), with a number of blades or buckets ...
s, windmills, and even treadmills) that revolutionized the application of nonhuman power sources. The first two-wheeled carts were derived from travois
A travois (; Canadian French, from French , a frame for restraining horses; also obsolete travoy or travoise) is a historical frame structure that was used by indigenous peoples, notably the Plains Aboriginals of North America, to drag loads ov ...
and were first used in Mesopotamia and Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
in around 3,000 BCE.
The oldest known constructed roadways are the stone-paved streets of the city-state of Ur, dating to circa 4,000 BCE, and timber roads leading through the swamps of Glastonbury, England
Glastonbury (, ) is a town and civil parish in Somerset, England, situated at a dry point on the low-lying Somerset Levels, south of Bristol. The town, which is in the Mendip District, Mendip district, had a population of 8,932 in the 2011 cens ...
, dating to around the same period. The first long-distance road, which came into use around 3,500 BCE, spanned 2,400 km from the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Persis, Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a Mediterranean sea (oceanography), me ...
to the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
, but was not paved and was only partially maintained. In around 2,000 BCE, the Minoans on the Greek island of Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and ...
built a 50 km road leading from the palace of Gortyn
Gortyn, Gortys or Gortyna ( el, Γόρτυν, , or , ) is a municipality, and an archaeological site, on the Mediterranean island of Crete away from the island's capital, Heraklion. The seat of the municipality is the village Agioi Deka. Gorty ...
on the south side of the island, through the mountains, to the palace of Knossos
Knossos (also Cnossos, both pronounced ; grc, Κνωσός, Knōsós, ; Linear B: ''Ko-no-so'') is the largest Bronze Age archaeological site on Crete and has been called Europe's oldest city.
Settled as early as the Neolithic period, the na ...
on the north side of the island. Unlike the earlier road, the Minoan road was completely paved. Ancient Minoan private homes had
Ancient Minoan private homes had running water
Tap water (also known as faucet water, running water, or municipal water) is water supplied through a tap, a water dispenser valve. In many countries, tap water usually has the quality of drinking water. Tap water is commonly used for drinkin ...
. A bathtub virtually identical to modern ones was unearthed at the Palace of Knossos. Several Minoan private homes also had toilet
A toilet is a piece of sanitary hardware that collects human urine and feces, and sometimes toilet paper, usually for disposal. Flush toilets use water, while dry or non-flush toilets do not. They can be designed for a sitting position popu ...
s, which could be flushed by pouring water down the drain. The ancient Romans had many public flush toilets, which emptied into an extensive sewage system
Sewerage (or sewage system) is the infrastructure that conveys sewage or surface runoff (stormwater, meltwater, rainwater) using sewers. It encompasses components such as receiving drains, manholes, pumping stations, storm overflows, and scree ...
. The primary sewer in Rome was the Cloaca Maxima
The Cloaca Maxima ( lat, Cloāca Maxima, lit. ''Greatest Sewer'') was one of the world's earliest sewage systems. Its name derives from Cloacina, a Roman goddess. Built during either the Roman Kingdom or early Roman Republic, it was constructed ...
; construction began on it in the sixth century BCE and it is still in use today.
The ancient Romans also had a complex system of aqueducts
Aqueduct may refer to:
Structures
*Aqueduct (bridge), a bridge to convey water over an obstacle, such as a ravine or valley
*Navigable aqueduct, or water bridge, a structure to carry navigable waterway canals over other rivers, valleys, railw ...
, which were used to transport water across long distances. The first Roman aqueduct
The Romans constructed aqueducts throughout their Republic and later Empire, to bring water from outside sources into cities and towns. Aqueduct water supplied public baths, latrines, fountains, and private households; it also supported mining o ...
was built in 312 BCE. The eleventh and final ancient Roman aqueduct was built in 226 CE. Put together, the Roman aqueducts extended over 450 km, but less than 70 km of this was above ground and supported by arches.
Pre-modern
Innovations continued through theMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
with the introduction of silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the coc ...
production (in Asia and later Europe), the horse collar
A horse collar is a part of a horse harness that is used to distribute the load around a horse's neck and shoulders when pulling a wagon or plough. The collar often supports and pads a pair of curved metal or wooden pieces, called hames, to whi ...
, and horseshoes. Simple machine
A simple machine is a mechanical device that changes the direction or magnitude of a force. In general, they can be defined as the simplest mechanisms that use mechanical advantage (also called leverage) to multiply force. Usually the term refer ...
s (such as the lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or '' fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is d ...
, the screw, and the pulley) were combined into more complicated tools, such as the wheelbarrow, windmills, and clocks. A system of University, universities developed and spread scientific ideas and practices, including University of Oxford, Oxford and University of Cambridge, Cambridge.
The Renaissance technology, Renaissance era produced many innovations, including the introduction of the movable type printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in wh ...
to Europe, which facilitated the communication of knowledge. Technology became increasingly influenced by science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
, beginning a cycle of mutual advancement.
Modern
 Starting in the United Kingdom in the 18th century, the discovery of steam power set off the Industrial Revolution, which saw wide-ranging technological discoveries, particularly in the areas of British Agricultural Revolution, agriculture, manufacturing, mining, metallurgy, and
Starting in the United Kingdom in the 18th century, the discovery of steam power set off the Industrial Revolution, which saw wide-ranging technological discoveries, particularly in the areas of British Agricultural Revolution, agriculture, manufacturing, mining, metallurgy, and transport
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipelin ...
, and the widespread application of the factory system. This was followed a century later by the Second Industrial Revolution
The Second Industrial Revolution, also known as the Technological Revolution, was a phase of rapid scientific discovery, standardization, mass production and industrialization from the late 19th century into the early 20th century. The Fi ...
which led to rapid scientific discovery, standardization, and mass production. New technologies were developed, including Sewage treatment, sewage systems, electricity, Electric light, light bulbs, electric motors, Rail transport, railroads, Car, automobiles, and airplanes. These technological advances led to significant developments in medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
, chemistry, physics, and engineering. They were accompanied by consequential social change, with the introduction of skyscrapers accompanied by rapid urban area, urbanization. Communication improved with the invention of the telegraph, the telephone
A telephone is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into e ...
, the radio, and television.
The 20th century brought a host of innovations. In physics, the discovery of nuclear fission in the Atomic Age led to both nuclear weapons and nuclear power. Computers were invented and later shifted from Analog computer, analog to digital in the Digital Revolution. Information technology, particularly optical fiber and optical amplifiers led to the birth of the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
, which ushered in the Information Age. The Space Age began with the launch of Sputnik 1 in 1957, and later the launch of Human spaceflight, crewed missions to the moon in the 1960s. Organized efforts to search for extraterrestrial intelligence have used radio telescopes to detect signs of technology use, or ''technosignatures'', given off by alien civilizations. In medicine, new technologies were developed for diagnosis (CT scan, CT, Positron emission tomography, PET, and MRI scanning), treatment (like the dialysis machine, defibrillator, Artificial cardiac pacemaker, pacemaker, and a wide array of new pharmaceutical drugs), and research (like interferon cloning and DNA microarrays).
Complex manufacturing and construction techniques and organizations are needed to make and maintain more modern technologies, and entire Industry (economics), industries have arisen to develop succeeding generations of increasingly more complex tools. Modern technology increasingly relies on training and education – their designers, builders, maintainers, and users often require sophisticated general and specific training. Moreover, these technologies have become so complex that entire fields have developed to support them, including engineering, medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
, and computer science; and other fields have become more complex, such as construction, transportation, and architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
.
Impact
Many new technologies have had deep societal ramifications. Technologies have contributed to human welfare through increased prosperity, improved comfort and quality of life, and Health technology, medical progress, but they can also disrupt existing social hierarchies, causepollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the ...
, and harm individuals or groups.
Recent years have brought about a rise in social media's cultural prominence, with potential repercussions on democracy, and economic and social life. Early on, the internet was seen as a "liberation technology" that would democratize knowledge, improve access to education, and promote democracy. Modern research has turned to investigate the internet's downsides, including disinformation, polarization, hate speech, and propaganda.
Since the 1970s, technology's impact on the environment has been criticized, leading to a surge in investment in Solar power, solar, Wind power, wind, and other forms of Sustainable energy, clean energy.
 Since the invention of the wheel, technologies have helped increase humans' economic output. Past automation has both substituted and complemented labor; machines replaced humans at some lower-paying jobs (for example in agriculture), but this was compensated by the creation of new, higher-paying jobs. Studies have found that computers did not create significant net
Since the invention of the wheel, technologies have helped increase humans' economic output. Past automation has both substituted and complemented labor; machines replaced humans at some lower-paying jobs (for example in agriculture), but this was compensated by the creation of new, higher-paying jobs. Studies have found that computers did not create significant net technological unemployment
Technological unemployment is the loss of jobs caused by technological change. It is a key type of structural unemployment.
Technological change typically includes the introduction of labour-saving "mechanical-muscle" machines or more efficie ...
. Due to artificial intelligence being far more capable than computers, and still being in its infancy, it is not known whether it will follow the same trend; the question has been debated at length among economists and policymakers. A 2017 survey found no clear consensus among economists on whether AI would increase long-term unemployment.
Philosophy
Philosophy of technology is a branch of philosophy that studies the "practice of designing and creating artifacts", and the "nature of the things so created." It emerged as a discipline over the past two centuries, and has grown "considerably" since the 1970s. The ''humanities philosophy of technology'' is concerned with the "meaning of technology for, and its impact on, society and culture". Initially, technology was seen as an extension of the human organism that replicated or amplified bodily and mental faculties. Marx framed it as a tool used by capitalists to oppress the proletariat, but believe technology would be a fundamentally liberating force once it was "freed from societal deformations". Second-wave philosophers like Ortega later shifted their focus from economics and politics to "daily life and living in a techno-material culture," arguing that technology could oppress "even the members of the bourgeoisie who were its ostensible masters and possessors." Third-stage philosophers like Don Ihde and Albert Borgmann represent a turn toward de-generalization and empiricism, and considered how humans can learn to live with technology. Early scholarship on technology was split between two arguments: technological determinism, and Social construction of technology, social construction. Technological determinism is the idea that technologies cause unavoidable social changes. It usually encompasses a related argument, technological autonomy, which asserts that technological progress follows a natural progression and cannot be prevented. Social constructivists argue that technologies follow no natural progression, and are shaped by cultural values, laws, politics, and economic incentives. Modern scholarship has shifted towards an analysis of Sociotechnical system, sociotechnical systems, "assemblages of things, people, practices, and meanings", looking at the value judgments that shape technology. Cultural critic Neil Postman distinguished tool-using societies from technological societies and from what he called "technopolies," societies that are dominated by an ideology of technological and scientific progress to the detriment of other cultural practices, values, and world views. Herbert Marcuse and John Zerzan suggest that technological society will inevitably deprive us of our freedom and psychological health.Ethics
The ''ethics of technology'' is an interdisciplinary subfield of ethics that analyzes technology's ethical implications and explores ways to mitigate the potential negative impacts of new technologies. There is a broad range of ethical issues revolving around technology, from specific areas of focus affecting professionals working with technology to broader social, ethical, and legal issues concerning the role of technology in society and everyday life. Prominent debates have surrounded genetically modified organisms, the use of robotic soldiers, algorithmic bias, and the issue of AI alignment, aligning AI behavior with human values Technology ethics encompasses several key fields. Bioethics looks at ethical issues surrounding biotechnologies and modern medicine, including cloning, human genetic engineering, and stem cell research. Computer ethics focuses on issues related to computing. Cyberethics explores internet-related issues like Intellectual property, intellectual property rights, Internet privacy, privacy, and Internet censorship, censorship. Ethics of nanotechnologies, Nanoethics examines issues surrounding the alteration of matter at the atomic and molecular level in various disciplines including computer science, engineering, and biology. And engineering ethics deals with the professional standards of engineers, including Software engineering, software engineers and their moral responsibilities to the public. A wide branch of technology ethics is concerned with the ethics of artificial intelligence: it includes robot ethics, which deals with ethical issues involved in the design, construction, use, and treatment of robots, as well as machine ethics, which is concerned with ensuring the ethical behavior of Intelligent agent, artificial intelligent agents. Within the field of AI ethics, significant yet-unsolved research problems include AI alignment (ensuring that AI behaviors are aligned with their creators' intended goals and interests) and the reduction of algorithmic bias. Some researchers have warned against the hypothetical risk of an AI takeover, and have advocated for the use of AI capability control in addition to AI alignment methods. Other fields of ethics have had to contend with technology-related issues, including military ethics, media ethics, and Philosophy of education, educational ethics.Futures studies
''Futures studies'' is the systematic and interdisciplinary study of social and technological progress. It aims to quantitatively and qualitatively explore the range of plausible futures and to incorporate human values in the development of new technologies. More generally, futures researchers are interested in improving "the freedom and welfare of humankind". It relies on a thorough quantitative and qualitative analysis of past and present technological trends, and attempts to rigorously extrapolate them into the future. Science fiction is often used as a source of ideas. Futures research methodologies include Survey (human research), survey research, modeling, Statistical inference, statistical analysis, and Simulation, computer simulations.Existential risk
Existential risk researchers analyze risks that could lead to human extinction or civilizational collapse, and look for ways to build resilience against them. Relevant research centers include the Centre for the Study of Existential Risk, Cambridge Center for the Study of Existential Risk, and the Stanford Existential Risk Initiative. Future technologies may contribute to the risks of artificial general intelligence, biological warfare, nuclear warfare, nanotechnology, Climate change, anthropogenic climate change, global warming, or stable global totalitarianism, though technologies may also help us mitigate Impact event, asteroid impacts and gamma-ray bursts. In 2019 philosopher Nick Bostrom introduced the notion of a ''vulnerable world'', "one in which there is some level of technological development at which civilization almost certainly gets devastated by default", citing the risks of a pandemic caused by Bioterrorism, bioterrorists, or an arms race triggered by the development of novel armaments and the loss of mutual assured destruction. He invites policymakers to question the assumptions that technological progress is always beneficial, that scientific openness is always preferable, or that they can afford to wait until a dangerous technology has been invented before they prepare mitigations.Emerging technologies
 Emerging technologies are novel technologies whose development or practical applications are still largely unrealized. They include nanotechnology, biotechnology, robotics, 3D printing, blockchains, and artificial intelligence.
In 2005, futurist Ray Kurzweil claimed the next technological revolution would rest upon advances in genetics, nanotechnology, and robotics, with robotics being the most impactful of the three. Genetic engineering will allow far greater control over human biological nature through a process called Directed evolution (transhumanism), directed evolution. Some thinkers believe that this may shatter our sense of self, and have urged for renewed public debate exploring the issue more thoroughly; others fear that directed evolution could lead to eugenics or extreme social inequality. Nanotechnology will grant us the ability to manipulate matter "at the molecular and atomic scale", which could allow us to reshape ourselves and our environment in fundamental ways. Nanobots could be used within the human body to destroy cancer cells or form new body parts, blurring the line between biology and technology. Autonomous robots have undergone rapid progress, and are expected to replace humans at many dangerous tasks, including search and rescue, bomb disposal, firefighting, and war.
Estimates on the advent of artificial general intelligence vary, but half of machine learning experts surveyed in 2018 believe that AI will "accomplish every task better and more cheaply" than humans by 2063, and automate all human jobs by 2140. This expected technological unemployment has led to calls for increased emphasis on computer science education and debates about UBI. Political science experts predict that this could lead to a rise in extremism, while others see it as an opportunity to usher in a post-scarcity economy.
Emerging technologies are novel technologies whose development or practical applications are still largely unrealized. They include nanotechnology, biotechnology, robotics, 3D printing, blockchains, and artificial intelligence.
In 2005, futurist Ray Kurzweil claimed the next technological revolution would rest upon advances in genetics, nanotechnology, and robotics, with robotics being the most impactful of the three. Genetic engineering will allow far greater control over human biological nature through a process called Directed evolution (transhumanism), directed evolution. Some thinkers believe that this may shatter our sense of self, and have urged for renewed public debate exploring the issue more thoroughly; others fear that directed evolution could lead to eugenics or extreme social inequality. Nanotechnology will grant us the ability to manipulate matter "at the molecular and atomic scale", which could allow us to reshape ourselves and our environment in fundamental ways. Nanobots could be used within the human body to destroy cancer cells or form new body parts, blurring the line between biology and technology. Autonomous robots have undergone rapid progress, and are expected to replace humans at many dangerous tasks, including search and rescue, bomb disposal, firefighting, and war.
Estimates on the advent of artificial general intelligence vary, but half of machine learning experts surveyed in 2018 believe that AI will "accomplish every task better and more cheaply" than humans by 2063, and automate all human jobs by 2140. This expected technological unemployment has led to calls for increased emphasis on computer science education and debates about UBI. Political science experts predict that this could lead to a rise in extremism, while others see it as an opportunity to usher in a post-scarcity economy.
Movements
Appropriate technology
Some segments of the Counterculture of the 1960s, 1960s hippie counterculture grew to dislike urban living and developed a preference for Localism (politics), locally autonomous, Sustainability, sustainable, and Decentralization, decentralized technology, termed ''appropriate technology''. This later influenced hacker culture and technopaganism.Technological utopianism
Technological utopianism refers to the belief that technological development is a Good, moral good, which can and should bring about a utopia, that is, a society in which laws, governments, and social conditions serve the needs of all its citizens. Examples of techno-utopian goals include Post-scarcity economy, post-scarcity economics, life extension, mind uploading, cryonics, and the creation of artificial superintelligence. Major techno-utopian movements includetranshumanism
Transhumanism is a philosophical and intellectual movement which advocates the enhancement of the human condition by developing and making widely available sophisticated technologies that can greatly enhance longevity and cognition.
Transhuma ...
and singularitarianism.
The transhumanism movement is founded upon the "continued evolution of human life beyond its current human form" through science and technology, informed by "life-promoting principles and values." The movement gained wider popularity in the early 21st century.
Singularitarians believe that machine superintelligence will "accelerate technological progress" by orders of magnitude and "create even more intelligent entities ever faster", which may lead to a pace of societal and technological change that is "incomprehensible" to us. This ''event horizon'' is known as the technological singularity.
Major figures of techno-utopianism include Ray Kurzweil and Nick Bostrom. Techno-utopianism has attracted both praise and criticism from progressive, religious, and conservative thinkers.
Anti-technology backlash
 Technology's central role in our lives has drawn concerns and backlash. The backlash against technology is not a uniform movement and encompasses many heterogeneous ideologies.
The earliest known revolt against technology was Luddite, Luddism, a pushback against early automation in textile production. Automation had resulted in a need for fewer workers, a process known as
Technology's central role in our lives has drawn concerns and backlash. The backlash against technology is not a uniform movement and encompasses many heterogeneous ideologies.
The earliest known revolt against technology was Luddite, Luddism, a pushback against early automation in textile production. Automation had resulted in a need for fewer workers, a process known as technological unemployment
Technological unemployment is the loss of jobs caused by technological change. It is a key type of structural unemployment.
Technological change typically includes the introduction of labour-saving "mechanical-muscle" machines or more efficie ...
.
Between the 1970s and 1990s, American terrorist Ted Kaczynski carried out a series of bombings across America and published the Unabomber Manifesto denouncing technology's negative impacts on nature and human freedom. The essay resonated with a large part of the American public. It was partly inspired by Jacques Ellul's ''The Technological Society''.
Some subcultures, like the off-the-grid movement, advocate a withdrawal from technology and a return to nature. The ecovillage movement seeks to reestablish harmony between technology and nature.
Relation to science and engineering
 Engineering is the process by which technology is developed. It often requires problem-solving under strict constraints. Technological development is "action-oriented", while scientific knowledge is fundamentally explanatory. Polish philosopher Henryk Skolimowski framed it like so: "science concerns itself with what , technology with what ."
The direction of causality between scientific discovery and technological innovation has been debated by scientists, philosophers and policymakers. Because innovation is often undertaken at the edge of scientific knowledge, most technologies are not derived from scientific knowledge, but instead from engineering, tinkering and chance. For example, in the 1940s and 1950s, when knowledge of turbulent combustion or fluid dynamics was still crude, jet engines were invented through "running the device to destruction, analyzing what broke [...] and repeating the process". Scientific explanations often follow technological developments rather than preceding them. Many discoveries also arose from pure chance, like the discovery of penicillin as a result of accidental lab contamination. Since the 1960s, the assumption that government funding of basic research would lead to the discovery of marketable technologies has lost credibility. Probabilist Nassim Taleb argues that national research programs that implement the notions of serendipity and Convexity (finance), convexity through frequent trial and error are more likely to lead to useful innovations than research that aims to reach specific outcomes.
Despite this, modern technology is increasingly reliant on deep, domain-specific scientific knowledge. In 1979, an average of one in three patents granted in the U.S. cited the scientific literature; by 1989, this increased to an average of one citation per patent. The average was skewed upwards by patents related to the pharmaceutical industry, chemistry, and electronics. A 2021 analysis shows that patents that are based on scientific discoveries are on average 26% more valuable than equivalent non-science-based patents.
Engineering is the process by which technology is developed. It often requires problem-solving under strict constraints. Technological development is "action-oriented", while scientific knowledge is fundamentally explanatory. Polish philosopher Henryk Skolimowski framed it like so: "science concerns itself with what , technology with what ."
The direction of causality between scientific discovery and technological innovation has been debated by scientists, philosophers and policymakers. Because innovation is often undertaken at the edge of scientific knowledge, most technologies are not derived from scientific knowledge, but instead from engineering, tinkering and chance. For example, in the 1940s and 1950s, when knowledge of turbulent combustion or fluid dynamics was still crude, jet engines were invented through "running the device to destruction, analyzing what broke [...] and repeating the process". Scientific explanations often follow technological developments rather than preceding them. Many discoveries also arose from pure chance, like the discovery of penicillin as a result of accidental lab contamination. Since the 1960s, the assumption that government funding of basic research would lead to the discovery of marketable technologies has lost credibility. Probabilist Nassim Taleb argues that national research programs that implement the notions of serendipity and Convexity (finance), convexity through frequent trial and error are more likely to lead to useful innovations than research that aims to reach specific outcomes.
Despite this, modern technology is increasingly reliant on deep, domain-specific scientific knowledge. In 1979, an average of one in three patents granted in the U.S. cited the scientific literature; by 1989, this increased to an average of one citation per patent. The average was skewed upwards by patents related to the pharmaceutical industry, chemistry, and electronics. A 2021 analysis shows that patents that are based on scientific discoveries are on average 26% more valuable than equivalent non-science-based patents.
Other animal species
 The use of basic technology is also a feature of non-human animal species. Tool use was once considered a defining characteristic of the genus Homo (genus), Homo. This view was supplanted after discovering evidence of tool use among Common chimpanzee, chimpanzees and other primates, dolphins, and crows. For example, researchers have observed wild chimpanzees using basic foraging tools, pestles, levers, using leaves as sponges, and tree bark or vines as probes to fish termites. West African chimpanzees use stone hammers and anvils for cracking nuts, as do capuchin monkeys of Boa Vista, Roraima, Boa Vista, Brazil. Tool use is not the only form of animal technology use; for example, Beaver dam, beaver dams, built with wooden sticks or large stones, are a technology with "dramatic" impacts on river habitats and ecosystems.
The use of basic technology is also a feature of non-human animal species. Tool use was once considered a defining characteristic of the genus Homo (genus), Homo. This view was supplanted after discovering evidence of tool use among Common chimpanzee, chimpanzees and other primates, dolphins, and crows. For example, researchers have observed wild chimpanzees using basic foraging tools, pestles, levers, using leaves as sponges, and tree bark or vines as probes to fish termites. West African chimpanzees use stone hammers and anvils for cracking nuts, as do capuchin monkeys of Boa Vista, Roraima, Boa Vista, Brazil. Tool use is not the only form of animal technology use; for example, Beaver dam, beaver dams, built with wooden sticks or large stones, are a technology with "dramatic" impacts on river habitats and ecosystems.
Popular culture
Man's relationship with technology has been explored in science-fiction literature, for example in ''Brave New World'', ''A Clockwork Orange (novel), A Clockwork Orange'', ''Nineteen Eighty-Four'', Isaac Asimov's essays, and movies like ''Minority Report (film), Minority Report'', ''Total Recall (1990 film), Total Recall'', ''Gattaca'', and ''Inception''. It has spawned the dystopian and futuristic cyberpunk genre, which juxtaposes futuristic technology with societal collapse, dystopia or decay. See pp. 75–76. Notable cyberpunk works include William Gibson's ''Neuromancer'' novel, and movies like ''Blade Runner'', and ''The Matrix''.See also
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Authority control Technology, Technology systems, Main topic articles