Tayyibi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tayyibi Isma'ilism is the only surviving sect of the
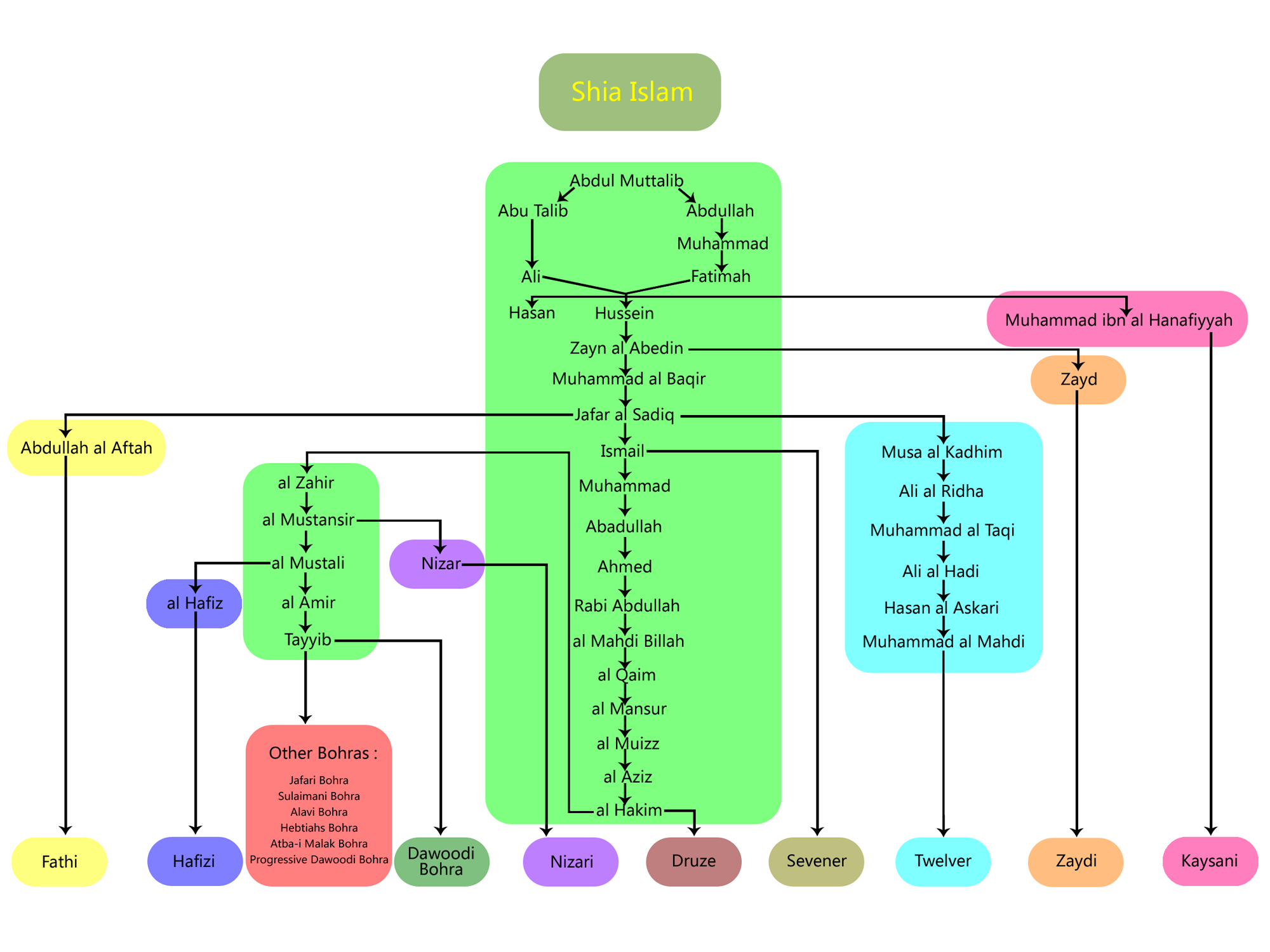
The Hafizids and Tayyibids
* ttps://www.islamawareness.net/Deviant/Ismailis/ismailis.html History of Ismailis
A visual chart of different Shia communities
Doctrine of the Tayyibis
{{Authority control
Musta'li
The Musta‘lī ( ar, مستعلي) are a branch of Isma'ilism named for their acceptance of al-Musta'li as the legitimate nineteenth Fatimid caliph and legitimate successor to his father, al-Mustansir Billah. In contrast, the Nizari—the other ...
branch of Isma'ilism
Isma'ilism ( ar, الإسماعيلية, al-ʾIsmāʿīlīyah) is a branch or sub-sect of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili () get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor ( imām) to Ja'far al ...
, the other being the extinct Hafizi branch. Followers of Tayyibi Isma'ilism are found in various Bohra communities: Dawoodi, Sulaymani
The Sulaymani branch of Tayyibi Isma'ilism is an Islamic community, of which around 70,000 members reside in Yemen, while a few thousand Sulaymani Bohras can be found in India. The Sulaymanis are sometimes headed by a ''Da'i al-Mutlaq'' from ...
, and Alavi.
The Tayyibi originally split from the Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a ...
-supporting Hafizi branch by supporting the right of at-Tayyib Abu'l-Qasim to the Imamate
{{expand Arabic, date=April 2021
The term imamate or ''imamah'' ( ar, إمامة, ''imāmah'') means "leadership" and refers to the office of an ''imam'' or a state ruled by an ''imam''.
Theology
*Imamate, in Sunni doctrine the caliphate
:* Naqshb ...
.
History
Upon the death of the twentieth Imam,al-Amir bi-Ahkam Allah
Abu Ali al-Mansur ibn al-Musta'li ( ar, أبو علي المنصور بن المستعلي, Abū ʿAlī al-Manṣūr ibn al-Mustaʿlī; 31 December 1096 – 7 October 1130), better known by his regnal name al-Amir bi-Ahkam Allah ( ar, الآمر ...
(d. ), his two-year-old child at-Tayyib Abu'l-Qasim (b. ) was appointed the twenty-first Imam. As he was not in a position to run the Dawah
Dawah ( ar, دعوة, lit=invitation, ) is the act of inviting or calling people to embrace Islam. The plural is ''da‘wāt'' (دَعْوات) or ''da‘awāt'' (دَعَوات).
Etymology
The English term ''Dawah'' derives from the Arabic ...
, Queen Arwa al-Sulayhi, the Da'i al-Mutlaq
The term Da'i al-Mutlaq ( ar, الداعي المطلق, al-Dā'ī al-Mutlaq; pl. , ) literally meaning 'the absolute, or unrestricted, missionary', is the most senior spiritual rank and office in Tayyibi Isma'ilism. The Da'i al-Mutlaq has hea ...
, acted as his regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy ...
. The Da'i had now been given absolute authority and made independent from political activity.
Da'i Zoeb bin Moosa
Da'i Zoeb bin Moosa used to live in and died in Hoos, Yemen. His ''ma'zoon'' ("associate") was Khattab bin Hasan. After death of Abdullah, Zoeb bin Moosa appointed Yaqub as thewali
A wali (''wali'' ar, وَلِيّ, '; plural , '), the Arabic word which has been variously translated "master", "authority", "custodian", "protector", is most commonly used by Muslims to indicate an Islamic saint, otherwise referred to by the ...
("representative" or "caretaker") of the Tayyibi organization ("dawah") in India. Yaqub was the first person of Indian origin to receive this honor. He was son of Bharmal, minister of the Chaulukya
The Chaulukya dynasty (), also Solanki dynasty, was a dynasty that ruled parts of what are now Gujarat and Rajasthan in north-western India, between and . Their capital was located at Anahilavada (modern Patan). At times, their rule extende ...
king Jayasimha Siddharaja
Jayasiṃha ( ), who assumed the title Siddharāja (), was an Indian king who ruled western parts of India. He was a member of the Chaulukya (also called Solanki) dynasty.
Jayasimha's capital was located at Anahilapataka (modern Patan) in pres ...
. Fakhruddin, son of Tarmal, was sent to western Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern ...
. One Da'i after another continued until the twenty-fourth Da'i, Yusuf Najmuddin ibn Sulaiman
Syedna Yusuf Najmuddin bin Sulaiman () (died on 23 June 1567 CE or 16 Dhu al-Hijjah 974 AH, Taiba, Yemen) was the 24th Da'i al-Mutlaq (Absolute Missionary) of the Taiyabi Ismailis. He succeeded Mohammad Ezzuddin to the religious post.
Fam ...
, in Yemen. Due to prosecution by a local ruler, the dawah then shifted to India under the twenty-fifth Da'i, Jalal bin Hasan.
Sulaymani-Dawoodi-Alavi split
In 1592, the Tayyibi broke into two factions in a dispute over who should become the twenty-seventh Da'i:Dawood Bin Qutubshah
Syedna Dawood Bin Qutubshah (born 23 Rabi-Ul-Awwal 946 AH/8 August 1539; died 15 Jumadil Akhir 1021 AH/1612 AD, Ahmedabad, India) was the 27th ''Da'i al-Mutlaq'' (Absolute Missionary) of the Dawoodi Bohra sect of Musta‘lī Islam. He succeed ...
or Sulayman bin Hassan
The 27th Da'i al-Mutlaq of Ismailism according to the Sulaymanis. His becoming a Dai' as per Nass-e-Shareef of Sayyidna, Dawood Bin Ajabshah led to a schism with a group who did not accept him primarily in India and elsewhere in Arab lands. Tho ...
. The followers of the former, primarily in India, became the Dawoodi Bohra
The Dawoodi Bohras are a religious denomination within the Ismā'īlī branch of Shia Islam. Their largest numbers reside in India, Pakistan, Yemen, East Africa, and the Middle East, with a growing presence across Europe, North America, South ...
, the latter the Sulaymani
The Sulaymani branch of Tayyibi Isma'ilism is an Islamic community, of which around 70,000 members reside in Yemen, while a few thousand Sulaymani Bohras can be found in India. The Sulaymanis are sometimes headed by a ''Da'i al-Mutlaq'' from ...
of Yemen. In 1621, the Alavi Bohra split from the Dawoodi bohra community.
There is also a community of Sunni Bohra
Sunni Vahoras or Sunni Bohras ( ar, سنی بوہرہ; also Jafari Bohras or Patani Bohras), are a community from the state of Gujarat in India. Sharing many cultural similarities with the Dawoodi Bohras, they are often confused with that commu ...
in India. In the fifteenth century, there was schism in the Bohra community of Patan in Gujarat as a large number converted from Mustaali Ismaili Shia Islam to mainstream Hanafi Sunni Islam. The leader of this conversion movement to Sunni was Syed Jafar Ahmad Shirazi who also had the support of Mughal governor of Gujarat. Thus this new group is known as Jafari Bohras, Patani Bohras or Sunni Bohra
Sunni Vahoras or Sunni Bohras ( ar, سنی بوہرہ; also Jafari Bohras or Patani Bohras), are a community from the state of Gujarat in India. Sharing many cultural similarities with the Dawoodi Bohras, they are often confused with that commu ...
. In 1538, Syed Jafar Ahmad Shirazi convinced the Patani Bohras to cease social relations with Ismaili Bohras. The cumulative results of these pressures resulted in large number of Bohras converting from Ismaili Shia fiqh to Sunni Hanafi fiqh.
The Hebtiahs Bohra
The Hebtiahs Bohra are a branch of Mustaali Ismaili Shi'a Islam that broke off from the mainstream Dawoodi Bohra after the death of the 39th Da'i al-Mutlaq in 1754. They are mostly concentrated in Ujjain in India with a few families who are Heb ...
are a branch of Mustaali Ismaili Shi'a Islam that broke off from the mainstream Dawoodi Bohra after the death of the 39th Da'i al-Mutlaq in 1754. The Atba-e-Malak
The Atba-e-Malak community are a branch of Musta'ali Isma'ili Shi'a Islam that broke off from the mainstream Dawoodi Bohra after the death of the 46th Da'i al-Mutlaq, under the leadership of Moulana Abdul Hussain Jivaji Saheb in 1890. They are bas ...
community are a branch of Mustaali Ismaili Shi'a Islam that broke off from the mainstream Dawoodi Bohra after the death of the 46th Da'i al-Mutlaq, under the leadership of Abdul Hussain Jivaji in 1840. They have further split into two more branches, the Atba-e-Malak Badar
The Atba-i-Malak Badar are a branch of Atba-i-Malak Mustaali Ismaili Shi'a Islam. They follow the preachings of both Abdul Hussain Jivaji and Badruddin Ghulam Hussain Miya Khan Saheb. The current leader or Dai al Mutlaq is Maulana Amiruddin Malak ...
and Atba-e-Malak Vakil
The Atba-e-Malak community are a branch of Musta'ali Isma'ili Shi'a Islam that broke off from the mainstream Dawoodi Bohra after the death of the 46th Da'i al-Mutlaq, under the leadership of Moulana Abdul Hussain Jivaji Saheb in 1890. They are bas ...
. The Progressive Dawoodi Bohra
Progressive Dawoodi Bohra also known as ''Bohra Youth'' is a reform movement within the Dawoodi Bohra subsect of Mustaali Ismai'li Shi'a Islam. They disagree with mainstream Dawoodi Bohra, as led by the incumbent Da'i al-Mutlaq, on doctrinal, ...
is a reformist sect within Mustaali Ismai'li Shi'a Islam that broke off circa 1977. They disagree with mainstream Dawoodi Bohra, as led by the Da'i al-Mutlaq, on doctrinal, economic and social issues.
At present, the largest Tayyibi faction/sub-sect is the Dawoodi Bohra
The Dawoodi Bohras are a religious denomination within the Ismā'īlī branch of Shia Islam. Their largest numbers reside in India, Pakistan, Yemen, East Africa, and the Middle East, with a growing presence across Europe, North America, South ...
, whose current leader is Syedna Mufaddal Saifuddin
Mufaddal Saifuddin () is the spiritual leader and 53rd Da'i al-Mutlaq of one million Dawoodi Bohras, a subgroup of the Tayyibi, Mustaali, Ismaili Shia branch of Islam. He is the second son of the 52nd Da'i al-Mutlaq, Mohammed Burhanuddin, wh ...
. Taher Fakhruddin
Taher Fakhruddin is the 54th Da'i al-Mutlaq of the Qutbi Bohras, a sect within Shia Islam. He is the son of Khuzaima Qutbuddin, the 53rd Syedna succession controversy (Dawoodi Bohra). After the death of the 52nd Da'i al-Mutlaq, Mohammed Burh ...
is also a claimant to the title of Dai al Mutlaq since 2016, although it is widely accepted that Syedna Mufaddal Saifuddin is the leader of the Dawoodi Bohras, in all aspects and administration.

References
*''The Ismaili, their history and doctrine'' by Farhad Daftary *''Religion, learning and science'' by Lathan Young *''Medieval Islamic Civilisation'' by Joseph W. Meri, Bacharach *''Sayyida Hurra: The Isma‘ili Sulayhid Queen of Yemen''by Farhad Daftary *The ''Uyun al-akhbar'' is the most complete text written by an Ismaili/Tayyibi/Dawoodi 19th Dai Sayyedna Idris bin Hasan on the history of the Ismaili community from its origins up to the 12th century CE. period of the Fatimid caliphs al-Mustansir (d. 487 AH / 1094 AD), the time of Musta‘lian rulers including al-Musta‘li (d. 495 AH / 1102 AD) and al-Amir (d. 526 AH / 1132 AD), and then the Tayyibi Ismaili community in Yemen.External links
The Hafizids and Tayyibids
* ttps://www.islamawareness.net/Deviant/Ismailis/ismailis.html History of Ismailis
A visual chart of different Shia communities
Doctrine of the Tayyibis
{{Authority control