taeniae coli on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The taeniae coli (also teniae coli or tenia coli) are three separate longitudinal ribbons (''taeniae'' meaning ribbon in Latin) of 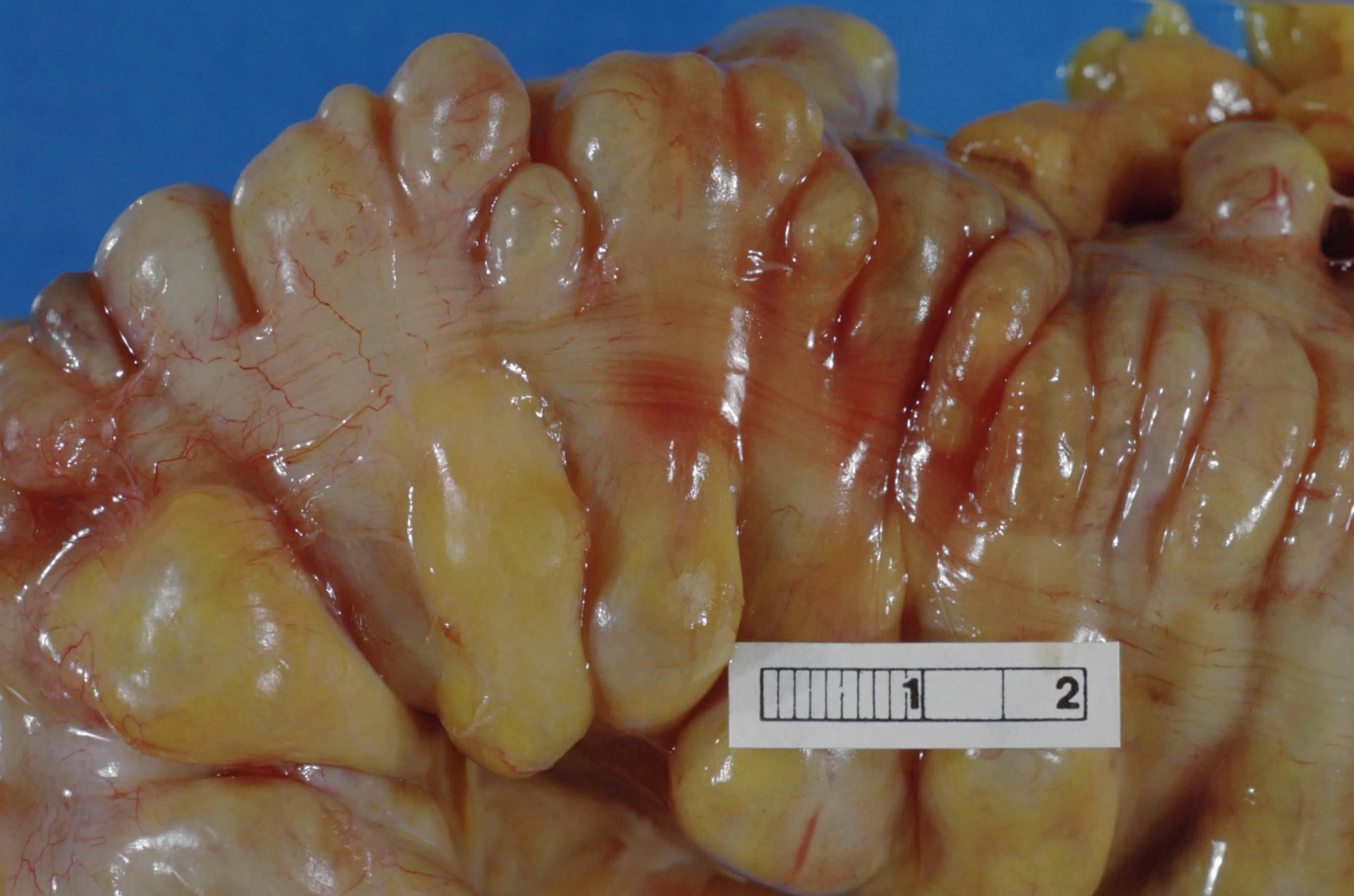 The bands converge at the root of the
The bands converge at the root of the
smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non- striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit ...
on the outside of the ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid colons. They are visible and can be seen just below the serosa or fibrosa. There are three teniae coli: mesocolic, free and omental taeniae coli. The teniae coli contract lengthwise to produce the haustra
The haustra (singular haustrum) of the colon are the small pouches caused by sacculation (sac formation), which give the colon its segmented appearance. The teniae coli run the length of the colon. Because the taenia coli are shorter than the co ...
, the bulges in the colon. The bands converge at the root of the
The bands converge at the root of the vermiform appendix
The appendix (or vermiform appendix; also cecal r caecalappendix; vermix; or vermiform process) is a finger-like, blind-ended tube connected to the cecum, from which it develops in the embryo. The cecum is a pouch-like structure of the large ...
. At the rectosigmoid junction, the taeniae spread out and unite to form the longitudinal muscle layer. In the caecum, the ascending colon, the descending colon and sigmoid colon the positions of these bands are fixed. The taenia libera, is placed anteriorly in the caecum, ascending, descending and sigmoid colon, but is placed inferiorly in the transverse colon. The taenia mesocolica is present on the posteromedial surface of caecum, ascending, descending and sigmoid colon, but is placed posteriorly on transverse colon at the site of attachment of transverse mesocolon. The taenia omentalis is situated posterolaterally in caecum, ascending, descending and sigmoid colon, but is situated on the anterosuperior surface of transverse colon where layers three and four of the greater omentum
The greater omentum (also the great omentum, omentum majus, gastrocolic omentum, epiploon, or, especially in animals, caul) is a large apron-like fold of visceral peritoneum that hangs down from the stomach. It extends from the greater curvature ...
meet the transverse colon. This change in position is due to the twist in transverse colon. These bands correspond to the outer layer of the muscularis externa
The muscular layer (muscular coat, muscular fibers, muscularis propria, muscularis externa) is a region of muscle in many organs in the vertebrate body, adjacent to the submucosa. It is responsible for gut movement such as peristalsis. The Latin, ...
, in other portions of the digestive tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and ...
.
The teniae coli are regulated by the sacral nerves of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
, which are under control of the parasympathetic nervous system
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part o ...
.
Diverticulosis
Spaces between the circular bands of taeniae are weak points in the bowel, and are the sites of diverticulosis. Most diverticulosis occur in thesigmoid colon
The sigmoid colon (or pelvic colon) is the part of the large intestine that is closest to the rectum and anus. It forms a loop that averages about in length. The loop is typically shaped like a Greek letter sigma (ς) or Latin letter S (thus ' ...
as it is the segment with the highest intraluminal pressure. Diverticulosis does not occur in the rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the sigmoid colon) at the l ...
as the tenia coli become a continuous muscular layer. Diverticulosis can then become diverticulitis
Diverticulitis, specifically colonic diverticulitis, is a gastrointestinal disease characterized by inflammation of abnormal pouches— diverticula—which can develop in the wall of the large intestine. Symptoms typically include lower abdomi ...
if the patient develops inflammation of the diverticulosis, this whole spectrum of disease is called diverticular disease
Diverticular disease is when problems occur due to diverticulosis, a condition defined by the presence of pouches in the wall of the large intestine (diverticula). This includes diverticula becoming inflamed (diverticulitis) or bleeding. Colonic p ...
.
References
External links
* - "Digestive System: Alimentary Canal: colon, taeniae coli" * * - "Intestines and Pancreas: Large Intestine" * {{Authority control Large intestine