Tyumen Airlines on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tyumen ( ; rus, Тюмень, p=tʲʉˈmʲenʲ, a=Ru-Tyumen.ogg) is the

 The
The  At the outbreak of the
At the outbreak of the
 The legislative authority of Tyumen is the City
The legislative authority of Tyumen is the City
 , there are over ten operational Orthodox temples (both newly built and historical), two mosques (both newly built), one synagogue, and one Roman Catholic church in Tyumen ( St. Joseph's Church).
, there are over ten operational Orthodox temples (both newly built and historical), two mosques (both newly built), one synagogue, and one Roman Catholic church in Tyumen ( St. Joseph's Church).
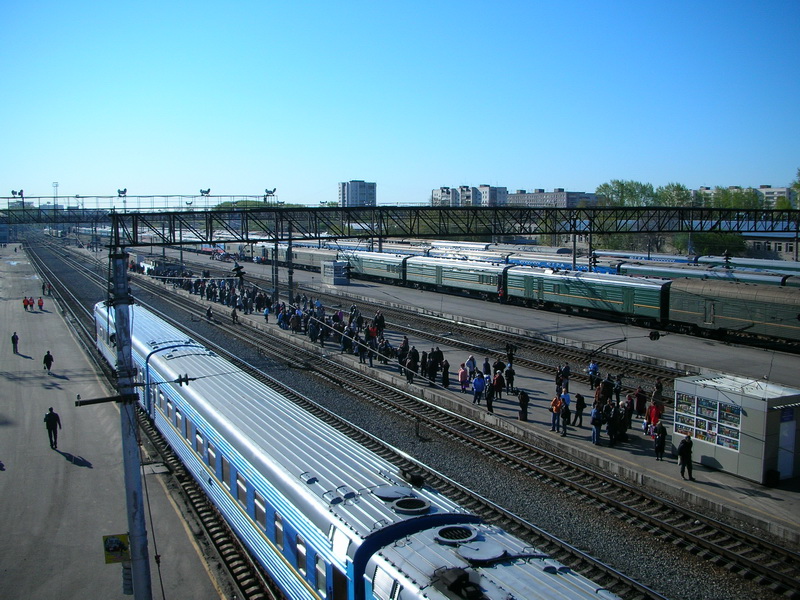

 Tyumen railway station was built in 1885. Currently the station administratively belongs to the Tyumen Division of Sverdlovskaya Rail Road. The station is located in the center of the city. At the regional level, the station services three directions to
Tyumen railway station was built in 1885. Currently the station administratively belongs to the Tyumen Division of Sverdlovskaya Rail Road. The station is located in the center of the city. At the regional level, the station services three directions to
administrative center
An administrative center is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune
A commune is an alternative term for an intentional community. Commune or comună or ...
and largest city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
of Tyumen Oblast
Tyumen Oblast (russian: Тюме́нская о́бласть, ''Tyumenskaya oblast'') is a federal subject (an oblast) of Russia. It is geographically located in the Western Siberia region of Siberia, and is administratively part of the Urals ...
, Russia. It is situated just east of the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
, along the Tura River
The Tura (), also known as Dolgaya (Long River, ) is a historically important Siberian river which flows eastward from the central Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲs ...
. Fueled by the Russian oil and gas industry, Tyumen has experienced rapid population growth in recent years, rising to a population of 847,488 at the 2021 Census. Tyumen is among the largest cities of the Ural
Ural may refer to:
*Ural (region), in Russia and Kazakhstan
*Ural Mountains, in Russia and Kazakhstan
*Ural (river), in Russia and Kazakhstan
* Ual (tool), a mortar tool used by the Bodo people of India
*Ural Federal District, in Russia
*Ural econ ...
region and the Ural Federal District
Ural Federal District (russian: Ура́льский федера́льный о́круг, ''Uralsky federalny okrug'') is one of the eight federal districts of Russia. Its population was 12,080,523 (79.9% urban) according to the 2010 Censu ...
. Tyumen is often regarded as the first Siberian city, from the western direction.
Tyumen was the first Russian settlement in Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
. Founded in 1586 to support Russia's eastward expansion, the city has remained one of the most important industrial and economic centers east of the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
. Located at the junction of several important trade routes and with easy access to navigable waterways, Tyumen rapidly developed from a small military settlement to a large commercial and industrial city. The central part of Old Tyumen retains many historic buildings from throughout the city's history.
Today, Tyumen is an important business center. It is the transport hub
A transport hub is a place where passengers and cargo are exchanged between vehicles and/or between transport modes. Public transport hubs include railway stations, rapid transit stations, bus stops, tram stops, airports and ferry slips. F ...
and industrial center of Tyumen Oblast
Tyumen Oblast (russian: Тюме́нская о́бласть, ''Tyumenskaya oblast'') is a federal subject (an oblast) of Russia. It is geographically located in the Western Siberia region of Siberia, and is administratively part of the Urals ...
– an oil-rich region bordering Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
– as well as the home of many companies active in Russia's oil and gas industry
The petroleum industry, also known as the oil industry or the oil patch, includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transportation (often by oil tankers and pipelines), and marketing of petroleum products. The largest ...
.
Etymology
From the Mongol word, "Tümen/Түмэн" which means a myriad, or ten thousand. Etymologically connected to the Tuman River that delineates sections of the borders between North Korea, Russia, and China.Geography
Tyumen covers an area of . Its primary geographical feature is theTura River
The Tura (), also known as Dolgaya (Long River, ) is a historically important Siberian river which flows eastward from the central Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲs ...
, which crosses the city from northwest to southeast. The river is navigable downstream of the city. The left bank of the Tura is a floodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river which stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls, and which experiences flooding during periods of high discharge.Goudi ...
surrounded by gently rolling hills. The Tura is a shallow river with extensive marshlands.
The river flood
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrol ...
s during the snow melt
In hydrology, snowmelt is surface runoff produced from melting snow. It can also be used to describe the period or season during which such runoff is produced. Water produced by snowmelt is an important part of the annual water cycle in many part ...
ing season in the spring. The spring flood usually peaks in the second half of May, when the river becomes 8–10 times wider than during the late-summer low water season. The city is protected from flooding by a dike which can withstand floods up to high. The highest ever flood water level in Tyumen was , recorded in 1979. More recently, in 2007, a water level of 7.76 was recorded. In spring 2005, a flood higher than the critical mark was expected, but did not appear.
Climate
Tyumen has ahumid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
''Dfb'') with warm, somewhat humid summers and long, cold winters. The weather in the region is very changeable, and the temperature in town is always higher than in the surrounding area by a few degrees. The town area also attracts more precipitation. The average temperature in January is , with a record low of measured in February 1951. The average temperature in July is , with a record high of .
The average annual precipitation is . The wettest year on record was 1943, with , and the driest was 1917, with only .
History

 The
The Cossack
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
ataman
Ataman (variants: ''otaman'', ''wataman'', ''vataman''; Russian: атаман, uk, отаман) was a title of Cossack and haidamak leaders of various kinds. In the Russian Empire, the term was the official title of the supreme military comman ...
Yermak Timofeyevich
Yermak Timofeyevich ( rus, Ерма́к Тимофе́евич, p=jɪˈrmak tʲɪmɐˈfʲejɪvʲɪtɕ; born between 1532 and 1542 – August 5 or 6, 1585) was a Cossack ataman and is today a hero in Russian folklore and myths. During the reign ...
conquered the Tyumen area, originally part of the Siberia Khanate
The Khanate of Sibir (also Khanate of Turan,
sty, Себер ханлыгы) was a Tatar Khanate located in southwestern Siberia with a Turco-Mongol ruling class. Throughout its history, members of the Shaybanid and Taibugid dynasties often con ...
, to the Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I i ...
in 1585. Both capitals of the Siberia Khanate
The Khanate of Sibir (also Khanate of Turan,
sty, Себер ханлыгы) was a Tatar Khanate located in southwestern Siberia with a Turco-Mongol ruling class. Throughout its history, members of the Shaybanid and Taibugid dynasties often con ...
, Sibir/Qashliq
Qashliq, Isker or Sibir (Siberian Tatar language: ''Qaşlıq'' or ''Iskär'') was a medieval (14th–16th century) Siberian Tatar fortress, in the 16th century the capital of the Khanate of Sibir, located on the right bank of the Irtysh River at it ...
and Tyumen/ Chimgi-Tura (the capital in the 15th century), were completely destroyed. Sibir was never rebuilt, though it gave its name to all concurrent and future lands in North Asia annexed by Russia, but Tyumen was later founded again. On July 29, 1586, Tsar Feodor I
Fyodor I Ivanovich (russian: Фёдор I Иванович) or Feodor I Ioannovich (russian: Феодор I Иоаннович; 31 May 1557 – 17 January (NS) 1598), also known as Feodor the Bellringer (russian: Феодор Звонарь), ...
ordered two regional commanders, Vasily Borisov-Sukin and Ivan Myasnoy, to construct a fortress on the site of the former Siberian Tatar
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
town of Chingi-Tura ("city of Chingis
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; ; xng, Temüjin, script=Latn; ., name=Temujin – August 25, 1227) was the founder and first Great Khan (Emperor) of the Mongol Empire, which became the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in history a ...
"), also known as ''Tyumen'', from the Turkic and Mongol word for "ten thousand" – ''tumen''.
Tyumen stood on the "Tyumen Portage", part of the historical trade route between Central Asia and the Volga region. Various South Siberian nomads had continuously contested control of the portage in the preceding centuries. As a result, Siberian Tatar and Kalmyk raiders often attacked early Russian settlers. The military situation meant that streltsy
, image = 01 106 Book illustrations of Historical description of the clothes and weapons of Russian troops.jpg
, image_size =
, alt =
, caption =
, dates = 1550–1720
, disbanded =
, country = Tsardom of Russia
, allegiance = Streltsy D ...
and Cossack garrisons stationed in the town predominated in the population of Tyumen until the mid-17th century. As the area became less restive, the town began to take on a less military character.
By the beginning of the 18th century Tyumen had developed into an important center of trade between Siberia and China in the east and Central Russia in the west. Tyumen had also become an important industrial center, known for leatherworkers, blacksmiths, and other craftsmen. In 1763, 7,000 people were recorded as living in the town.
In the 19th century the town's development continued. In 1836, the first steam boat
A steamboat is a boat that is propelled primarily by steam power, typically driving propellers or paddlewheels. Steamboats sometimes use the prefix designation SS, S.S. or S/S (for 'Screw Steamer') or PS (for 'Paddle Steamer'); however, thes ...
in Siberia was built in Tyumen. In 1862, the telegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas p ...
came to the town, and in 1864 the first water mains were laid. Further prosperity came to Tyumen after the construction, in 1885, of the Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway (TSR; , , ) connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway line in the world. It runs from the city of Moscow in the west to the city of Vladivostok in the ea ...
. For some years, Tyumen was Russia's easternmost railhead, and the site of transhipment of cargoes between the railway and the cargo boats plying the Tura, Tobol
The Tobol (russian: Тобол, kk, Тобыл ''Tobyl'') is a river in Western Siberia (in Kazakhstan and Russia) and the main (left) tributary of the Irtysh. Its length is , and the area of its drainage basin is .
History
The Tobol River was ...
, Irtysh
The Irtysh ( otk, 𐰼𐱅𐰾:𐰇𐰏𐰕𐰏, Ertis ügüzüg, mn, Эрчис мөрөн, ''Erchis mörön'', "erchleh", "twirl"; russian: Иртыш; kk, Ертіс, Ertis, ; Chinese: 额尔齐斯河, pinyin: ''É'ěrqísī hé'', Xiao'erj ...
, and Ob River
}
The Ob ( rus, Обь, p=opʲ: Ob') is a major river in Russia. It is in western Siberia; and together with Irtysh forms the world's List of rivers by length, seventh-longest river system, at . It forms at the confluence of the Biya (river), Biya ...
s.
By the end of the 19th century Tyumen's population exceeded 30,000, surpassing that of its northern rival Tobolsk
Tobolsk (russian: Тобо́льск) is a town in Tyumen Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Tobol and Irtysh rivers. Founded in 1590, Tobolsk is the second-oldest Russian settlement east of the Ural Mountains in Asian Russia, and i ...
, and beginning a process whereby Tyumen gradually eclipsed the former regional capital. The growth of Tyumen culminated on August 14, 1944 when the city finally became the administrative center of the extensive Tyumen Oblast
Tyumen Oblast (russian: Тюме́нская о́бласть, ''Tyumenskaya oblast'') is a federal subject (an oblast) of Russia. It is geographically located in the Western Siberia region of Siberia, and is administratively part of the Urals ...
.
 At the outbreak of the
At the outbreak of the Russian Civil War
, date = October Revolution, 7 November 1917 – Yakut revolt, 16 June 1923{{Efn, The main phase ended on 25 October 1922. Revolt against the Bolsheviks continued Basmachi movement, in Central Asia and Tungus Republic, the Far East th ...
in 1917, forces loyal to Admiral Alexander Kolchak
Alexander Vasilyevich Kolchak (russian: link=no, Александр Васильевич Колчак; – 7 February 1920) was an Imperial Russian admiral, military leader and polar explorer who served in the Imperial Russian Navy and fought ...
and his Siberian White Army
The White Army (russian: Белая армия, Belaya armiya) or White Guard (russian: Бѣлая гвардія/Белая гвардия, Belaya gvardiya, label=none), also referred to as the Whites or White Guardsmen (russian: Бѣлогв� ...
controlled Tyumen. However, the city fell to the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
on January 5, 1918.
During the 1930s, Tyumen became a major industrial center of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
. By the onset of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the city had several well-established industries, including shipbuilding, furniture manufacture, and the manufacture of fur and leather goods. World War II saw rapid growth and development in the city. In the winter of 1941, twenty-two major industrial enterprises evacuated to Tyumen from the European part of the Soviet Union. These enterprises went into operation the following spring. Additionally, war-time Tyumen became a "hospital city", where thousands of wounded soldiers were treated. When it seemed that Moscow might fall to German forces during Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after ...
, in 1941 Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 19 ...
's body was secretly moved from his mausoleum in Moscow to a hidden tomb in what is now the Tyumen State Agriculture Academy. Between 1941 and 1945 more than 20,000 Tyumen natives fought at the front, and some 6,000 were killed.
Rich oil- and gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
-fields were discovered in the Tyumen Oblast in the 1960s. While most of these lay hundreds of kilometers away, near the towns of Surgut
Surgut ( rus, Сургу́т, p=sʊrˈgut; Khanty: Сәрханӆ, ''Sərhanł'') is a city in Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug, Russia, located on the Ob River near its junction with the Irtysh River. It is one of the few cities in Russia to be lar ...
and Nizhnevartovsk
Nizhnevartovsk ( rus, Нижневартовск, p=nʲɪʐnʲɪˈvartəfsk) is a city in Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug–Yugra, Russia. Since the 1960s, the Western Siberian oil boom led to Nizhnevartovsk's rapid growth from a small settlement t ...
, Tyumen was the nearest railway junction and so the city became their supply base while the railway was extended northwards. As the result of this economic and population boom, with tens of thousands of skilled workers arriving from across the Soviet Union between 1963 and 1985, the rapid growth of the city also brought a host of problems. Its social infrastructure was limited and the lack of city planning has resulted in uneven development, with which Tyumen has continued to struggle.
Administrative and municipal status
Tyumen is theadministrative center
An administrative center is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune
A commune is an alternative term for an intentional community. Commune or comună or ...
of the oblast
An oblast (; ; Cyrillic (in most languages, including Russian and Ukrainian): , Bulgarian: ) is a type of administrative division of Belarus, Bulgaria, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Ukraine, as well as the Soviet Union and the Kingdom of ...
and, within the framework of administrative divisions, it also serves as the administrative center of Tyumensky District
Tyumensky District (russian: Тюме́нский райо́н) is an administrative district (raion), one of the twenty-two in Tyumen Oblast, Russia.Law #53 Within the framework of municipal divisions, it is incorporated as Tyumensky Municipal ...
, even though it is not a part of it.Law No. 53 As an administrative division, it is incorporated separately as the City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
of Tyumen—an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions o ...
. As a municipal division, the City of Tyumen is incorporated as Tyumen Urban Okrug.Law No. 263
City divisions
Tyumen is divided into four administrative okrugs: Kalininsky, Leninsky, Tsentralny, and Vostochny.Government
City government
 The legislative authority of Tyumen is the City
The legislative authority of Tyumen is the City Duma
A duma (russian: дума) is a Russian assembly with advisory or legislative functions.
The term ''boyar duma'' is used to refer to advisory councils in Russia from the 10th to 17th centuries. Starting in the 18th century, city dumas were for ...
. In addition to legislative activities, the City Duma appoints the Head of the Tyumen City Administration, who is the chief executive officer of the city.
Oblast government
Since Tyumen is the administrative center of the oblast, all the governing bodies of the oblast are located in the city. They include the elected Legislative Assembly (Duma) of Tyumen Oblast, which also confirms the appointment of the Governor of Tyumen Oblast, who is nominated by thePresident of Russia
The president of the Russian Federation ( rus, Президент Российской Федерации, Prezident Rossiyskoy Federatsii) is the head of state of the Russian Federation. The president leads the executive branch of the federal ...
.
Demographics
Tyumen's population grew steadily from the 16th century through the 19th century. However, when the Trans-Siberian Railway arrived at the end of the 19th century, the town's rate of population growth was greatly boosted. Tyumen rapidly became the largest town in the region, with about 30,000 inhabitants by the beginning of the 20th century. Tyumen again experienced rapid population growth with the coming of World War II. The evacuation of workers from factories in central Russia in 1941 more than doubled Tyumen's population to 150,000. In the 1960s, the discovery of the rich oil and gas fields in Western Siberia caused the city's population, which had not been forecast to exceed 250,000 inhabitants that decade, to swell to almost half a million. After the growth of the 1960s, a period of population stability lasted until 1988, when economic depression hit the Soviet Union. The city's population in 1989 was 476,869, according to the census of that year. However, within five or six years Tyumen was again a major economic center with a rising population. By 2002, Tyumen's population had risen to 510,719. Further population growth (mainly due to migration and the incorporation of surrounding settlements) meant that by 2008 regional government statistics put Tyumen's population at 588,600 inhabitants.Ethnic groups
While the population of Tyumen includes people from over a hundred different ethnicities, most belong to one of the following ethnicities: *Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
*Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian. The majority ...
*Siberian Tatars
Siberian Tatars ( sty, , ), the ethnographic and ethnoterritorial group of Tatars of Western Siberia, the indigenous Turkic-speaking population of the forests and steppes of Western Siberia, originate in areas stretching from somewhat east of ...
*Azerbaijanis
Azerbaijanis (; az, Azərbaycanlılar, ), Azeris ( az, Azərilər, ), or Azerbaijani Turks ( az, Azərbaycan Türkləri, ) are a Turkic people living mainly in northwestern Iran and the Republic of Azerbaijan. They are the second-most numer ...
*Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
*Tajiks
Tajiks ( fa, تاجيک، تاجک, ''Tājīk, Tājek''; tg, Тоҷик) are a Persian-speaking Iranian ethnic group native to Central Asia, living primarily in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. Tajiks are the largest ethnicity in Tajik ...
Religion
 , there are over ten operational Orthodox temples (both newly built and historical), two mosques (both newly built), one synagogue, and one Roman Catholic church in Tyumen ( St. Joseph's Church).
, there are over ten operational Orthodox temples (both newly built and historical), two mosques (both newly built), one synagogue, and one Roman Catholic church in Tyumen ( St. Joseph's Church).
Orthodox Christianity
While the state religion of the Russian Empire wasOrthodoxy
Orthodoxy (from Greek: ) is adherence to correct or accepted creeds, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical councils in Antiquity, but different Churc ...
, this religion historically prevailed in Tyumen. In 1616, Trinity Monastery was established in Tyumen by Nifont of Kazan. In 1709–1711, this monastery was rebuilt in stone by the order of Filofey Leshchinsky, the first Metropolitan of Siberia. In 1761, the Tyumen Religious School was established. Overall, from 1708 to 1885, twelve stone Orthodox churches of different size, and two monasteries were constructed in Tyumen.
During Soviet times, two of the churches were completely destroyed, but the rest remained. , most of them are accessible and operating. Some operational churches are also under restoration. Tyumen Religious School was reopened in 1997.
Other religions
Despite the predominance ofOrthodoxy
Orthodoxy (from Greek: ) is adherence to correct or accepted creeds, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical councils in Antiquity, but different Churc ...
, Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
churches as well as mosques and synagogues were also built. However, only one Catholic church remains preserved. The Tyumen Mosque was completely destroyed, but its reconstruction on the same site caused controversy. The Tyumen synagogue collapsed in 2000, but was reconstructed on the same site. At the start of the 20th century, there was a strong Old Believers
Old Believers or Old Ritualists, ''starovery'' or ''staroobryadtsy'' are Eastern Orthodox Christians who maintain the liturgical and ritual practices of the Russian Orthodox Church as they were before the reforms of Patriarch Nikon of Moscow bet ...
community in Tyumen.
All of the aforementioned religions operate cultural centers in Tyumen. There are also several other religious bodies with a few adherents in Tyumen.
Tyumen Trinity Monastery was built with special permission of Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
. At the time, the construction of stone buildings outside Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
was prohibited. The Church of Savior Uncreated was visited by Crown prince
A crown prince or hereditary prince is the heir apparent to the throne in a royal or imperial monarchy. The female form of the title is crown princess, which may refer either to an heiress apparent or, especially in earlier times, to the wif ...
Alexandr (later Alexander II) during his Siberian tour.
Economy
Tyumen is an important service center for the gas and oil industries in Russia. Due to its advantageous location at the crossing of the motor, rail, water and air ways and its moderate climate Tyumen was an ideal base town for servicing the oil and gas industry of the West Siberia. As a result, today Tyumen is a center of industry, science, culture, education and medicine. Many large oil and gas companies such asGazprom
PJSC Gazprom ( rus, Газпром, , ɡɐzˈprom) is a Russian majority state-owned multinational energy corporation headquartered in the Lakhta Center in Saint Petersburg. As of 2019, with sales over $120 billion, it was ranked as the larges ...
, LUKoil
The PJSC Lukoil Oil Company ( stylized as LUKOIL or ЛУКОЙЛ in Cyrillic script) is a Russian multinational energy corporation headquartered in Moscow, specializing in the business of extraction, production, transport, and sale of petrol ...
, Gazpromneft Invest Union (formerly Gazpromneft) is a Russian company based in St. Petersburg and a former subsidiary of Gazprom. It is not to be confused with Gazprom Neft (formerly Sibneft), which is another company.
On 19 December 2004, Gazpromneft (along wi ...
and Shell
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
** Thin-shell structure
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard ou ...
have their representative offices in Tyumen.
There are numerous factories, engineering companies, oil industry service companies ( KCA DEUTAG and Schlumberger
Schlumberger Limited (), doing business as SLB, is an oilfield services company. Schlumberger has four principal executive offices located in Paris, Houston, London, and The Hague.
Schlumberger is the world's largest offshore drilling compa ...
), design institutes, shipyard and other oil servicing companies located in Tyumen. Schwank, market leader for industrial heaters, has its subsidiary, SibSchwank, in Tyumen, holding market shares of about 25%. UTair
Utair (russian: ОАО «Авиакомпания «ЮТэйр») () is a Russian airline with its head office at Khanty-Mansiysk Airport while its hubs are at Surgut International Airport and Vnukovo International Airport. It operates scheduled ...
is also based in Tyumen.
Transportation
Railway

 Tyumen railway station was built in 1885. Currently the station administratively belongs to the Tyumen Division of Sverdlovskaya Rail Road. The station is located in the center of the city. At the regional level, the station services three directions to
Tyumen railway station was built in 1885. Currently the station administratively belongs to the Tyumen Division of Sverdlovskaya Rail Road. The station is located in the center of the city. At the regional level, the station services three directions to Yekaterinburg
Yekaterinburg ( ; rus, Екатеринбург, p=jɪkətʲɪrʲɪnˈburk), alternatively romanized as Ekaterinburg and formerly known as Sverdlovsk ( rus, Свердло́вск, , svʲɪrˈdlofsk, 1924–1991), is a city and the administra ...
, Omsk
Omsk (; rus, Омск, p=omsk) is the administrative center and largest city of Omsk Oblast, Russia. It is situated in southwestern Siberia, and has a population of over 1.1 million. Omsk is the third largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk ...
, and Tobolsk
Tobolsk (russian: Тобо́льск) is a town in Tyumen Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Tobol and Irtysh rivers. Founded in 1590, Tobolsk is the second-oldest Russian settlement east of the Ural Mountains in Asian Russia, and i ...
. The railroad to Yekaterinburg has been electrified since 1980. At the international level, the station services passage to (Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway (TSR; , , ) connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway line in the world. It runs from the city of Moscow in the west to the city of Vladivostok in the ea ...
): Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
, Germany, China, Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
, and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
.
Additional stations within the city territory include: Tyumen North, Tyumen yard, Voynovka yard.
Public transportation
Public transportation in Tyumen is dominated by both municipal bus services and by numerous private operators (marshrutka
''Marshrutka''
Tyumen is served by the international
total in Tyumen Oblast (), previous count 151,000 (Jan. 2008)
 Historically, Tyumen occupied a small area on the high bank of the
Historically, Tyumen occupied a small area on the high bank of the  Bukharskaya Sloboda is a historic residential area on the low bank of the Tura river. This area is mostly made up of very old one and two-storey wooden buildings. The area is part of the Historical Centre on the city and has a mostly Muslim population. Low bank Dormitories is a cluster of standard 9-storey buildings was built on reclaimed land east of Bukharskaya Sloboda – Zareka and Vatutina.
Bukharskaya Sloboda is a historic residential area on the low bank of the Tura river. This area is mostly made up of very old one and two-storey wooden buildings. The area is part of the Historical Centre on the city and has a mostly Muslim population. Low bank Dormitories is a cluster of standard 9-storey buildings was built on reclaimed land east of Bukharskaya Sloboda – Zareka and Vatutina.
 The area to the east of the historical town centre built between 1948 and 1978 and is mostly 4 and 5-storey buildings. Earlier buildings in this area have individual designs, but the later buildings have a rectangular style. This area contains most of the political and business activities of the town.
The area to the east of the historical town centre built between 1948 and 1978 and is mostly 4 and 5-storey buildings. Earlier buildings in this area have individual designs, but the later buildings have a rectangular style. This area contains most of the political and business activities of the town.

 The Old Dormitories area features standard 5-storey blocks of flats constructed in the 1960s and 1970s at the west and east extremities of the city. However, today this area is actually in the town centre. While there are almost no variety in the area's architecture, this area has the most greenery in the city and the best social infrastructure.
The Old Dormitories area features standard 5-storey blocks of flats constructed in the 1960s and 1970s at the west and east extremities of the city. However, today this area is actually in the town centre. While there are almost no variety in the area's architecture, this area has the most greenery in the city and the best social infrastructure.
 The New dormitories area features clusters of standard tall buildings constructed after 1980 at the south and south-east edges of Tyumen. This area is considered to be the worst place to live in the city. The area is remote, badly planned, and has very poor social infrastructure.
The New dormitories area features clusters of standard tall buildings constructed after 1980 at the south and south-east edges of Tyumen. This area is considered to be the worst place to live in the city. The area is remote, badly planned, and has very poor social infrastructure.
File:Tyumen_Historic_Brick_Building_04.JPG,
File:Lernejo N 30 (Tjumeno).jpg,
File:Tyumen_Later_Soviet Buildings_01.JPG,
File:Tyumne_Old_Style_Imitation_02.JPG,
File:Tyumen_Moder_building_01.JPG
 Tyumen has many cinemas and clubs.
Tyumen has many cinemas and clubs.
 Museums and art galleries in Tyumen include the Tyumen Museum of Local Lore, the Tyumen Museum of the Fine Arts, Museum of Kolokolnikov estate and the Medical History Museum.
Museums and art galleries in Tyumen include the Tyumen Museum of Local Lore, the Tyumen Museum of the Fine Arts, Museum of Kolokolnikov estate and the Medical History Museum.
 The town has its own philharmonic orchestra and the Tyumen Music hall hosts performances.
The town has its own philharmonic orchestra and the Tyumen Music hall hosts performances.
 There are about fifty public libraries in Tyumen.
There are about fifty public libraries in Tyumen.
Тюменьстат
Official website of Tyumen
{{Use mdy dates, date=April 2016 Ski areas and resorts in Russia Tyumensky Uyezd
Roschino Airport
Roshchino International Airport is an airport in Tyumen Oblast, Russia located 13 km west of the city of Tyumen.
History
The need for a new airport in the region was growing as oil industry was developing fast. There was a need for airp ...
located west of the city. In addition Plekhanovo Airport is in the area. The Roschino airport has permits to handle the following types of aircraft: Tu-154
The Tupolev Tu-154 (russian: Tyполев Ту-154; NATO reporting name: "Careless") is a three-engined, medium-range, narrow-body airliner designed in the mid-1960s and manufactured by Tupolev. A workhorse of Soviet and (subsequently) Russian ...
, Tu-134
The Tupolev Tu-134 (NATO reporting name: Crusty) is a twin-engined, narrow-body jet airliner built in the Soviet Union for short and medium-haul routes from 1966 to 1989. The original version featured a glazed-nose design and, like certain ot ...
, An-12
The Antonov An-12 ( Russian: Антонов Ан-12; NATO reporting name: Cub) is a four-engined turboprop transport aircraft designed in the Soviet Union. It is the military version of the Antonov An-10 and has many variants. For more than th ...
, An-24
The Antonov An-24 (Russian/Ukrainian: Антонов Ан-24) ( NATO reporting name: Coke) is a 44-seat twin turboprop transport/passenger aircraft designed in 1957 in the Soviet Union by the Antonov Design Bureau and manufactured by Kyiv, Irk ...
, An-26
The Antonov An-26 (NATO reporting name: Curl) is a twin-engined turboprop civilian and military transport aircraft, designed and produced in the Soviet Union from 1969 to 1986.Gordon, Yefim. Komissarov, Dmitry & Sergey. "Antonov's Turboprop Twins ...
, Yak-40
The Yakovlev Yak-40 (russian: Яковлев Як-40; NATO reporting name: Codling) is a regional jet designed by Yakovlev. The trijet's maiden flight was in 1966, and it was in production from 1967 to 1981. Introduced in September 1968, the Yak ...
, Yak-42
The Yakovlev Yak-42 (russian: Яковлев Як-42; NATO reporting name: "Clobber") is a 100/120-seat three-engined mid-range passenger jet developed in the mid 1970s to replace the technically obsolete Tupolev Tu-134. It was the first airli ...
, IL-18, L-410
The Let L-410 Turbolet is a twin-engine short-range transport aircraft, manufactured by the Czech Republic, Czech aircraft manufacturer Let Kunovice (named Aircraft Industries since 2005), often used as an airliner. The aircraft is capable of lan ...
, B-737, B-767, B-757, IL-86
The Ilyushin Il-86 (russian: Илью́шин Ил-86; NATO reporting name: Camber) is a short- to medium-range wide-body jet airliner that served as the USSR's first wide-bodied aircraft. Designed and tested by the Ilyushin design bureau in th ...
, IL-76
The Ilyushin Il-76 (russian: Илью́шин Ил-76; NATO reporting name: Candid) is a multi-purpose, fixed-wing, four-engine turbofan strategic airlifter designed by the Soviet Union's Ilyushin design bureau. It was first planned as a commer ...
, ATR-42
The ATR 42 is a regional airliner produced by Franco-Italian manufacturer ATR, with final assembly in Toulouse, France.
On 4 November 1981, the aircraft was launched with ATR, as a joint venture between French Aérospatiale (now Airbus) and ...
, ATR-72
The ATR 72 is a twin-engine turboprop, short-haul regional airliner developed and produced in France and Italy by aircraft manufacturer ATR (french: Avions de transport régional or it, Aerei da Trasporto Regionale), a joint venture formed by ...
, HS-125. The airport also has a permit to handle all types of helicopters. The airstrip is capable of handling large freight aircraft such as the An-22 Antaeus.
The city has a regular service to a large number of Russian towns, including, Moscow (9 flights a day), St. Petersburg, and Samara
Samara ( rus, Сама́ра, p=sɐˈmarə), known from 1935 to 1991 as Kuybyshev (; ), is the largest city and administrative centre of Samara Oblast. The city is located at the confluence of the Volga and the Samara (Volga), Samara rivers, with ...
. There are also weekly or biweekly flights to the following international locations: Baku
Baku (, ; az, Bakı ) is the capital and largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region. Baku is located below sea level, which makes it the lowest lying national capital in the world a ...
, Erevan
Yerevan ( , , hy, Երևան , sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia and one of the world's oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerevan is the administrative, cultural, and i ...
, Khujand
Khujand ( tg, Хуҷанд, Khujand; Uzbek: Хўжанд, romanized: Хo'jand; fa, خجند, Khojand), sometimes spelled Khodjent and known as Leninabad (russian: Ленинабад, Leninabad; tg, Ленинобод, Leninobod; fa, لن� ...
, and Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of ...
.
Road
Tyumen is divided by theTura River
The Tura (), also known as Dolgaya (Long River, ) is a historically important Siberian river which flows eastward from the central Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲs ...
, the Tyumneka River, and the Trans-Siberian Railroad
The Trans-Siberian Railway (TSR; , , ) connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway line in the world. It runs from the city of Moscow in the west to the city of Vladivostok in the eas ...
, creating several isolated zones. Ten bridges, one footbridge, seven flyovers, and five foot crossings connect these zones.
In addition, the road network was planned before the fall of the Soviet Union, and in its current state, it can operate normally only in the scheme which includes public transportation only. Compact planning of the city center prevents expansion of main roads; congestion coming from the city periphery moves slower and slower as it approaches the town center. To date, the road network serves about 200% above planned capacity, which leads to numerous traffic jams and high accident rates.
Since 2002, city and regional authorities have undertaken numerous initiatives to improve Tyumen's road network, but due to the continued growth of private automobile ownership rates, these efforts have only had short term positive effects. To date, a complex transport infrastructure reconstruction project is being directed by Regional Administration. In January 2015, a paid parking program and prohibition of vehicle access for non-residents began.
*Total length of the city roads: (Jan 2009).
*Total number of cars: 380,000 of 1,176,441ТОП-10 регионов России по количеству легковых автомобилей, поставленных на госучет - Колеса.руtotal in Tyumen Oblast (), previous count 151,000 (Jan. 2008)
Cityscape
 Historically, Tyumen occupied a small area on the high bank of the
Historically, Tyumen occupied a small area on the high bank of the Tura River
The Tura (), also known as Dolgaya (Long River, ) is a historically important Siberian river which flows eastward from the central Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲs ...
around the foundation site of the city. The city consisted of one and two-storey wooden buildings, surrounded by a number of villages. With time, the territory of the city was developed and extended by including the surrounding villages.
When viewed from above, present-day Tyumen appears to be a collection of low-rise towns with occasional clusters of tall buildings. Two areas of the city, Yamskaya Sloboda and Republic Street are noted for their historic character. These areas are dominated by old brick and wooden merchant houses and buildings, with the occasional intrusion of mid-century Soviet low-rise buildings.
 Bukharskaya Sloboda is a historic residential area on the low bank of the Tura river. This area is mostly made up of very old one and two-storey wooden buildings. The area is part of the Historical Centre on the city and has a mostly Muslim population. Low bank Dormitories is a cluster of standard 9-storey buildings was built on reclaimed land east of Bukharskaya Sloboda – Zareka and Vatutina.
Bukharskaya Sloboda is a historic residential area on the low bank of the Tura river. This area is mostly made up of very old one and two-storey wooden buildings. The area is part of the Historical Centre on the city and has a mostly Muslim population. Low bank Dormitories is a cluster of standard 9-storey buildings was built on reclaimed land east of Bukharskaya Sloboda – Zareka and Vatutina.

 The Old Dormitories area features standard 5-storey blocks of flats constructed in the 1960s and 1970s at the west and east extremities of the city. However, today this area is actually in the town centre. While there are almost no variety in the area's architecture, this area has the most greenery in the city and the best social infrastructure.
The Old Dormitories area features standard 5-storey blocks of flats constructed in the 1960s and 1970s at the west and east extremities of the city. However, today this area is actually in the town centre. While there are almost no variety in the area's architecture, this area has the most greenery in the city and the best social infrastructure.
 The New dormitories area features clusters of standard tall buildings constructed after 1980 at the south and south-east edges of Tyumen. This area is considered to be the worst place to live in the city. The area is remote, badly planned, and has very poor social infrastructure.
The New dormitories area features clusters of standard tall buildings constructed after 1980 at the south and south-east edges of Tyumen. This area is considered to be the worst place to live in the city. The area is remote, badly planned, and has very poor social infrastructure.
Architecture
Tyumen is not characterized by any particular architectural style. The town was built without planning for decades and because of that its architecture is an eclectic mix of buildings of different styles and eras. Tyumen's nickname is the Capital of Villages because the most of its territory is built up by lumber houses. Many of the wooden buildings located in the historical part of the city are considered culturally valuable.Society and culture
Leisure and entertainment
 Tyumen has many cinemas and clubs.
Tyumen has many cinemas and clubs.
Literature and film
A writer closely associated with the city is the children's writerVladislav Krapivin
Vladislav Petrovich Krapivin (russian: Владислав Петрович Крапивин; 14 October 1938 – 1 September 2020) was a Russian children's books writer.
Biography
Vladislav Petrovich Krapivin was born in the city of Tyumen on ...
.
Museums and art galleries
 Museums and art galleries in Tyumen include the Tyumen Museum of Local Lore, the Tyumen Museum of the Fine Arts, Museum of Kolokolnikov estate and the Medical History Museum.
Museums and art galleries in Tyumen include the Tyumen Museum of Local Lore, the Tyumen Museum of the Fine Arts, Museum of Kolokolnikov estate and the Medical History Museum.
Music
 The town has its own philharmonic orchestra and the Tyumen Music hall hosts performances.
The town has its own philharmonic orchestra and the Tyumen Music hall hosts performances.
Sports
Many Soviet and Russian sportsmen started their careers in Tyumen youth sport, including Soviet cyclists Sergey Uslamin, Yury Korotkikh, and Oleg Polovnikov Tyumen has a national levelice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice hock ...
team, soccer team and futsal Futsal is a football-based game played on a hardcourt, hard court smaller than a football pitch, and mainly indoors. It has similarities to five-a-side football and Indoor soccer, indoor football.
Futsal is played between two teams of five players ...
team.
Important ice hockey and soccer teams are:
*Rubin Tyumen
Rubin Tyumen is an ice hockey team in Tyumen, Russia. They play in the VHL, the second level of Russian ice hockey.
History
The club's direct predecessor was a team called Vodnik Tyumen. It participated in lower levels of the Soviet hockey champi ...
* Tyumensky Legion
*FC Tyumen
FC Tyumen is a Russian football club based in Tyumen. The former member of the Russian Premier League now plays in the third-tier FNL 2.
The club was previously known as ''Geolog'' (in 1961–1963 and 1983–1991, meaning Geologist), ''Priboy'' ...
Education
Higher education
In 1964, Tyumen Industrial Institute was founded to supply the oil industry with a qualified local workforce. Most students are not counted in the city population since they are non-residents of the Tyumen city according to Russian law.Libraries
 There are about fifty public libraries in Tyumen.
There are about fifty public libraries in Tyumen.
Twin towns - sister cities
Tyumen is twinned with: *Brest
Brest may refer to:
Places
*Brest, Belarus
**Brest Region
**Brest Airport
**Brest Fortress
*Brest, Kyustendil Province, Bulgaria
*Břest, Czech Republic
*Brest, France
**Arrondissement of Brest
**Brest Bretagne Airport
** Château de Brest
*Brest, ...
, Belarus (1999)
* Celle
Celle () is a town and capital of the district of Celle, in Lower Saxony, Germany. The town is situated on the banks of the river Aller, a tributary of the Weser, and has a population of about 71,000. Celle is the southern gateway to the Lü ...
, Germany (1994)
* Daqing
Daqing (; alternately romanized as Taching) is a prefecture-level city in the west of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China. The name literally means "Great Celebration". Daqing is known as the "Oil Capital of China" and has experi ...
, China (1993)
* Houston
Houston (; ) is the most populous city in Texas, the most populous city in the Southern United States, the fourth-most populous city in the United States, and the sixth-most populous city in North America, with a population of 2,304,580 in ...
, United States (1995)
Notable people
Natives of Tyumen
*Yevgeni Bushmanov
Yevgeni Aleksandrovich Bushmanov (russian: Евгений Александрович Бушманов; born 2 November 1971) is a Russian football coach and a former player.
Playing career
He played for Shinnik Yaroslavl, Spartak Moscow, CSKA ...
, association football player and coach
* Yuri Aleksandrovich Gulyayev, opera singer
*Vladislav Krapivin
Vladislav Petrovich Krapivin (russian: Владислав Петрович Крапивин; 14 October 1938 – 1 September 2020) was a Russian children's books writer.
Biography
Vladislav Petrovich Krapivin was born in the city of Tyumen on ...
, children's books writer
*Boris Krasin
Boris Borisovich Krasin (3 (15) April 1884, Tyumen–21 June 1936) was a Russian musician who was politically active in Proletkult and the Russian Association of Proletarian Musicians.
Early life
Boris was the fifth and youngest son of Boris Iv ...
, composer
*Tamara Toumanova
Tamara Toumanova ( ka, თამარა თუმანოვა; 2 March 1919 – 29 May 1996) was a Georgian-American prima ballerina and actress. A child of exiles in Paris after the Russian Revolution of 1917, she made her debut at the ag ...
, ballerina and actress
*Anastasiya Kuzmina
Anastasiya Vladimirovna Kuzmina ( sk, Anastasia Kuzminová, russian: Анастасия Владимировна Кузьмина; née Shipulina; born 28 August 1984) is a retired Russian-born Slovak biathlete.
Career
Kuzmina represented Slova ...
, Olympic biathlete
*Viktor Leonenko
Viktor Yevhenovych Leonenko ( ua, Ві́ктор Євге́нович Лео́ненко; russian: Виктор Евгеньевич Леоненко; born 5 October 1969) is a former footballer and Ukraine international who played as a forward. ...
, association football player
*Alexander Zhuravlyov
Colonel General Alexander Alexandrovich Zhuravlyov (russian: Александр Александрович Журавлёв; born 5 December 1965) is a Russian Ground Forces officer who has commanded the military force in Syria during the Russ ...
, Russian general
* Vladilen Mashkovtsev, writer
* Irina Mataeva, soprano
* Nikolay Pereverzev, futsal player
*Abraham Walkowitz
Abraham Walkowitz (March 28, 1878, Tyumen, Russia - January 27, 1965, New York City, EUA) was a Russian-American painter grouped in with early American Modernists working in the Modernist style. While never attaining the same level of fame as h ...
, painter
*Ksenia Sukhinova
Ksenia Vladimirovna Sukhinova (russian: Ксе́ния Влади́мировна Сухи́нова; born 26 August 1987) is a Russian model, television host and beauty queen who was crowned Miss World 2008. She was the second Russian woman to ...
, Miss World 2008
*Andrei Vasilevskiy
Andrei Andreyevich Vasilevskiy (russian: Андрей Андреевич Василевский; born 25 July 1994) is a Russian professional ice hockey goaltender for the Tampa Bay Lightning of the National Hockey League (NHL). He was drafted i ...
, professional hockey player
*Anton Shipulin
Anton Vladimirovich Shipulin (russian: Антон Владимирович Шипулин; born 21 August 1987) is a retired Russian biathlete and politician serving as the member of the State Duma since 2019.
Sport career
Absolute champion of E ...
, Olympic biathlete
*Alena Shishkova
Alena Shishkova (russian: Алёна Шишкова, ; born 12 November 1992) is a Russian glamour model and beauty queen. She has modeled for glamour photo shoots with Russian men's magazine Maxim, commercial advertising campaigns and walked a ...
, Russian model
Other
*Irving Berlin
Irving Berlin (born Israel Beilin; yi, ישראל ביילין; May 11, 1888 – September 22, 1989) was a Russian-American composer, songwriter and lyricist. His music forms a large part of the Great American Songbook.
Born in Imperial Russi ...
, composer whose family was from Tolochin
Talachyn ( be, Талачы́н, Łacinka: ''Tałačyn'', ) or Tolochin (russian: Толо́чин; pl, Tołoczyn, yi, Tolotshin טאָלאָטשין, lt, Talačynas) is a city in the Vitebsk Region of Belarus, an administrative center of the ...
, born in Tyumen
* Nikolai Chukmaldin, merchant and enlightener
*Georg Wilhelm Steller
Georg Wilhelm Steller (10 March 1709 – 14 November 1746) was a German botanist, zoologist, physician and explorer, who worked in Russia and is considered a pioneer of Alaskan natural history.Evans, Howard Ensign. Edward Osborne Wilson (col.) ...
, German scientist
See also
* Chimgi-TuraReferences
Notes
*30Тюменьстат
Sources
* *External links
Official website of Tyumen
{{Use mdy dates, date=April 2016 Ski areas and resorts in Russia Tyumensky Uyezd