Tunga Penetrans (jigger Flea) (15038071751) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Tunga penetrans'' is a species of flea also known as the jigger, jigger flea, chigoe, chigo, chigoe flea, chigo flea, nigua, sand flea, or burrowing flea. It is a parasitic insect found in most tropical and sub-tropical climates. In its parasitic phase it has significant impact on its hosts, which include humans and certain other mammalian species. A parasitical infestation of ''T. penetrans'' is called tungiasis. Jiggers are often confused with chiggers, a type of mite. Jiggers are native to
Tungiasis and myiasis.
' Clin Dermatol. 2007 Mar-Apr;25(2):158-64. Synonyms for ''Tunga penetrans'' include ''Sarcopsylla penetrans'', ''Pulex penetrates'', and many others.

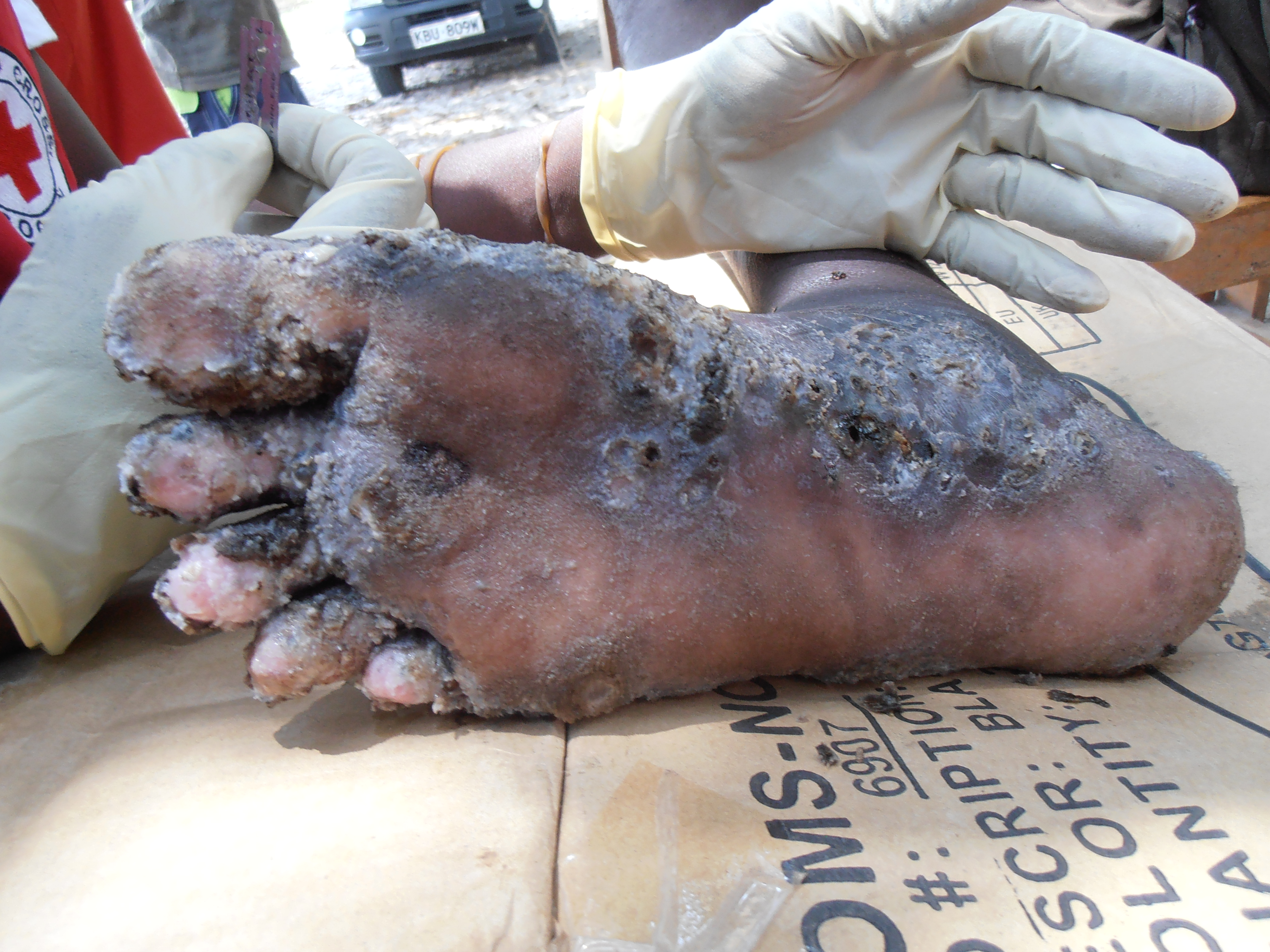 ''T. penetrans'' is the smallest known flea, at only 1 mm. It is most recognizable in its parasite phase. While embedded under the
''T. penetrans'' is the smallest known flea, at only 1 mm. It is most recognizable in its parasite phase. While embedded under the
"Epidermal parasitic skin diseases: a neglected category of poverty-associated plagues"
{{Taxonbar, from=Q133413 Fauna of North America Fauna of South America Fleas Insects described in 1758 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Parasitic arthropods of mammals
Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and South America, and have been introduced by colonialists to sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
.Cestari TF, Pessato S, Ramos-e-Silva M Tungiasis and myiasis.
' Clin Dermatol. 2007 Mar-Apr;25(2):158-64. Synonyms for ''Tunga penetrans'' include ''Sarcopsylla penetrans'', ''Pulex penetrates'', and many others.
Identification
 ''T. penetrans'' is the smallest known flea, at only 1 mm. It is most recognizable in its parasite phase. While embedded under the
''T. penetrans'' is the smallest known flea, at only 1 mm. It is most recognizable in its parasite phase. While embedded under the stratum corneum
The stratum corneum (Latin for 'horny layer') is the outermost layer of the epidermis. The human stratum corneum comprises several levels of flattened corneocytes that are divided into two layers: the ''stratum disjunctum'' and ''stratum compact ...
layer of the skin, it may reach up to 1 cm across. During the first day or two of infestation, the host may feel an itching or irritation which then passes as the area around the flea calluses and becomes insensitive. As the flea's abdomen swells with eggs later in the cycle, the pressure from the swelling may press neighbouring nerves or blood vessels. Depending on the exact site, this can cause sensations ranging from mild irritation to serious discomfort.
Local terms for ''T. penetrans''
Distinction
The colloquial name jigger may be confused withchigger
''Trombicula'', known as chiggers, red bugs, scrub-itch mites, or berry bugs, are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) in the Trombiculidae family. In their larval stage, they attach to various animals, including humans, and feed on skin, ...
, a parasitical mite. However, the jigger is of the order Siphonaptera as it is a flea. The chigger is a minute arachnid. Mites penetrate the skin and feed on skin cells that are broken down through an enzyme they secrete from their mouth, but they will then leave the host. The adult and the larval forms both feed on other animals. This is not the case with ''T. penetrans'', as only the adults feed on mammals, and the mature female remains in the host for the rest of her life.
Genus and hosts
''T. penetrans'' is unusual for the 13 known species of the genus ''Tunga''. First, it has a wide distribution: some 88 countries, in the Caribbean, Central and South America, tropical (sub-Saharan) Africa, and India. Second, It can infest a wide variety of hosts: at least 26 different species in over 5 different orders of mammals. In contrast, most of the 13 species of ''Tungidae'' are only in the Western hemisphere, and each only targets 1-2 specific warm-blooded hosts. Seven Tunga species infest only rodents. Two dedicate themselves to armadillos, one to sloths, and another prefers only cattle. Only one, ''Tunga trimamillata'', has also been found infesting humans as well as cows, but only in Ecuador and Peru. Host species for ''T. penetrans * Artiodactyla: '' Bos taurus'' (cow), ''Sus domesticus
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus ''Sus (genus), Sus'', is an Omnivore, omnivorous, Domestication, domesticated, even-toed ungulate, even-toed, hoofed ma ...
'' (pig), '' Capra hircus'' (goat), '' Ovis aries'' (sheep), '' Dicotyles tajacu'' (peccary), '' Lama glama'' (llama), '' Lama vicugna'' (vicuña), ''Potamochoerus porcus
The red river hog (''Potamochoerus porcus'') or bushpig (a named also used for the '' Potamochoerus larvatus''), is a wild member of the pig family living in Africa, with most of its distribution in the Guinean and Congolian forests. It is rarel ...
'' (red river hog)
*Carnivora
Carnivora is a Clade, monophyletic order of Placentalia, placental mammals consisting of the most recent common ancestor of all felidae, cat-like and canidae, dog-like animals, and all descendants of that ancestor. Members of this group are f ...
: '' Canis familiaris'' (dog), '' Felis catus'' (cat), '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar)
* Cingulata (armadillos): ''Dasypus novemcinctus
The nine-banded armadillo (''Dasypus novemcinctus''), also known as the nine-banded long-nosed armadillo or common long-nosed armadillo, is a mammal found in North, Central, and South America, making it the most widespread of the armadillos. It ...
'' (nine-banded armadillo), '' D. hybridus'' (southern long-nosed armadillo), ''Chaetophractus villosus
The big (or large) hairy armadillo (''Chaetophractus villosus'') is one of the largest and most numerous armadillos in South America. It lives from sea level to altitudes of up to 1,300 meters across the southern portion of South America, and c ...
'' (big hairy armadillo)
* Primate: '' Homo sapiens'' (human), ''Papio
Baboons are primates comprising the genus ''Papio'', one of the 23 genera of Old World monkeys. There are six species of baboon: the hamadryas baboon, the Guinea baboon, the olive baboon, the yellow baboon, the Kinda baboon and the chacma ba ...
'' sp. (baboon)
* Rodentia: '' Cuniculus paca'' (lowland paca), ''Dasyprocta punctata
The Central American agouti (''Dasyprocta punctata'') is a species of agouti from the family Dasyproctidae. The main portion of its range is from Chiapas and the Yucatan Peninsula (southern Mexico), through Central America, to northwestern Ecuad ...
'' (Central American agouti), '' Mus musculus'' (house mouse), ''Mus musculoides
Temminck's mouse (''Mus musculoides'') is a species of the genus ''Mus'' and of the subgenus ''Nannomys''. It is found throughout West Africa, Central Africa, and East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern s ...
'' (Temminck's mouse), '' Rattus rattus'' (black rat), '' Rattus norvegicus'' (brown rat), '' Cavia porcellus'' (guinea pig), '' Cavia aperea'' (Brazilian guinea pig), '' Myoprocta acouchy'' (red acouchi), Hystrix (porcupine)
Environment
For the most part, the chigoe flea lives 2–5 cm below sand, an observation which helps explain its overall distribution. The temperature is generally too hot for the larvae to develop on the surface of the sand and the deeper sand does not have enough oxygen. In a study of off-host stages, samples were taken from the top of the soil (to a maximum depth of 1 cm). The presence of ''T. penetrans'' in a soil sample was unaffected by soil temperature, air temperature or air humidity. No life stages of ''T. penetrans'' were found in any outdoor sample. There is an observable drop in infestations during the wet season.Life cycle
''T. penetrans'' eggs, on average, are 0.6 mm long, The larva will hatch from the egg within one to six days, assuming the environmental conditions (e.g., moisture, humidity, etc.) are favorable. After hatching, the flea will progress through two instar phases. This is unique in that most fleas go through three. Over the course of that development, the flea will first decrease in size from its just-hatched size of 1.5 mm to 1.15 mm (first instar) before growing to 2.9 mm (second instar). About six to eight days after hatching, the larva pupates and builds a cocoon around itself. Because it lives mostly on and below the surface of sand, sand is used to stabilize the cocoon and help to promote its development. An environmental disturbance such as rain or a lack of sand have been shown to decrease incidence, most likely due to decreasing the environmental factors (i.e., sand) on which the flea depends for overall growth. Barring any disturbances to the cocoon, an adult flea will emerge from the puparium after 9–15 days. Males are still mobile after ablood meal
Blood meal is a dry, inert powder made from blood, used as a high-nitrogen organic fertilizer and a high protein animal feed. N = 13.25%, P = 1.0%, K = 0.6%. It is one of the highest non-synthetic sources of nitrogen. It usually comes from cattle ...
like other fleas, but the female flea burrows head-first into the host's skin, leaving the caudal tip of its abdomen visible through an orifice in a skin lesion. This orifice allows the flea to breathe, defecate, mate and expel eggs while feeding from blood vessels. It lives in the cutaneous and subcutaneous Subcutaneous may refer to:
* Subcutaneous injection
* Subcutaneous tissue
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The ...
dermal layer
Cutis is the combined term for the epidermis (skin), epidermis and the dermis, the two outer layers of the skin. The subcutis is the layer below the cutis. Sweat pores are contained in the cutis, along with other organs, while hair follicles are c ...
.
Tungiasis lesions almost always occur on the feet (97%), but may occur on any part of the body. The toes are afflicted over 70% of the time, with periungual folds (around the toenail) a preferred site.
Only once the female burrows into the skin can reproduction occur, as the male and female show no interest in each other in the wild. The male flea dies after copulation. The female flea continues ''in vivo'' development, described in stages by the Fortaleza classification of tungiasis.
Over the next two weeks, its abdomen swells with up to several hundred to a thousand egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the a ...
s, which it releases through the caudal orifice to fall to the ground when ready to hatch. The flea then dies and is often the cause of infection as the body rots under the thick scales its body chemistry created to protect it. The eggs mature into adult fleas within three to four weeks and the process begins anew.
''In vivo'' development
In a seminal paper on the biology and pathology of ''Tunga penetrans'', Eisele ''et al.'' (2003) provided and detailed the five stages of tungiasis, thereby detailing the ''in vivo'' development of the female chigoe flea for the first time. In dividing the natural history of the disease, the Fortaleza Classification formally describes the last part of the female flea's life cycle where it burrows into its host's skin, expels eggs, and dies. Stage 1 is characterized by the penetration of the skin by the female chigoe flea. Running along the body, the female uses its posterior legs to push its body upward by an angle between 45 and 90 degrees. Penetration then starts, beginning with the proboscis going through the epidermis. By stage 2 (days 1–2), penetration is complete and the flea has burrowed most of its body into the skin. Only the anus, the copulatory organs, and four rear air holes in fleas called stigmata remain on the outside of the epidermis. The anus will excrete feces that is thought to attract male fleas for mating, described in a later section. The hypertrophic zone between tergites 2 and 3 in the abdominal region begins to expand a day or two after penetration and takes the appearance of a life belt. During this time, the flea begins to feed on the host's blood. Stage 3 is divided into two substages, the first of which being 2–3 days after penetration is complete. In 3a, maximum hypertrophy is achieved and the flea's midsection swells to the size of a pea. Due to the expanding flea, the outer layer of the skin is stretched thin, resulting in the appearance of a white halo around the black dot (rear end of the flea) at the center of the lesion. The black dot is the flea's exposed hind legs, respiratory spiracles andreproductive organ
A sex organ (or reproductive organ) is any part of an animal or plant that is involved in sexual reproduction. The reproductive organs together constitute the reproductive system. In animals, the testis in the male, and the ovary in the female, a ...
s.
In 3b, the chitin exoskeleton of tergites 2 and 3 increase in thickness and gives the structure the look of a mini caldera. Egg release is common in substage 3b, as are fecal coils. The eggs tend to stick to the skin.
At about the 3rd week after penetration, stage 4 begins, which is also divided into two substages. In 4a, the flea loses its signs of vitality and appears near death. As a result, the lesion shrinks in size, turns brown, and appears wrinkled. The death of the flea marks the beginning of substage 4b (around day 25 post-penetration) as the body begins to eliminate the parasite through skin repair mechanisms (e.g. shedding and subsequent skin repair). At this phase, the lesion is seen as brown or black.
If the flea is left within the skin, dangerous complications can occur including secondary infections from trapped bacteria such as ''Staphylococcus
''Staphylococcus'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultative ...
'', '' Streptococcus'', enterobacteriaceae
Enterobacteriaceae is a large family (biology), family of Gram-negative bacteria. It was first proposed by Rahn in 1936, and now includes over 30 genera and more than 100 species. Its classification above the level of family is still a subject ...
, and '' Clostridium tetani''. Lingering effects may include loss of toenails and toe deformation. These seem to be commonplace especially where heavy infestations combine with unsanitary conditions and poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in ...
.
History
Tungiasis was endemic in pre-Columbian Andean society for centuries before discovery of ''T. penetrans'' as native to the West Indies. The first European description was published in 1526 by Gonzalo Fernández de Oviedo y Valdés, where he discussed the skin infection and its symptoms on crew members from Columbus's ''Santa Maria'' after they were shipwrecked on Haiti. Through ship routes and further expeditions, the chigoe flea was spread to the rest of the world, particularly to the rest of Latin America and Africa. The spread to greater Africa occurred throughout the 17th and 19th centuries, specifically in 1873 when the infected crewmen of the Thomas Mitchell's ship introduced it into Angola, having sailed from Brazil.Treatment
There are no drugs currently available with proven effectiveness. Clinical trials performed in the last few years did not show promising results. Thus, surgical extraction still remains the treatment of choice in patients with a low parasite load, such as tourists returning from endemic areas. The only approach to reduce tungiasis-associated morbidity in heavily affected individuals is the application of a repellent to prevent the penetration of sand fleas.See also
* TungiasisReferences
External links
* The World Health Organization issued a bulletin, published online 28 November 2008, entitle"Epidermal parasitic skin diseases: a neglected category of poverty-associated plagues"
{{Taxonbar, from=Q133413 Fauna of North America Fauna of South America Fleas Insects described in 1758 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Parasitic arthropods of mammals