tunable laser on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A tunable laser is a
A tunable laser is a
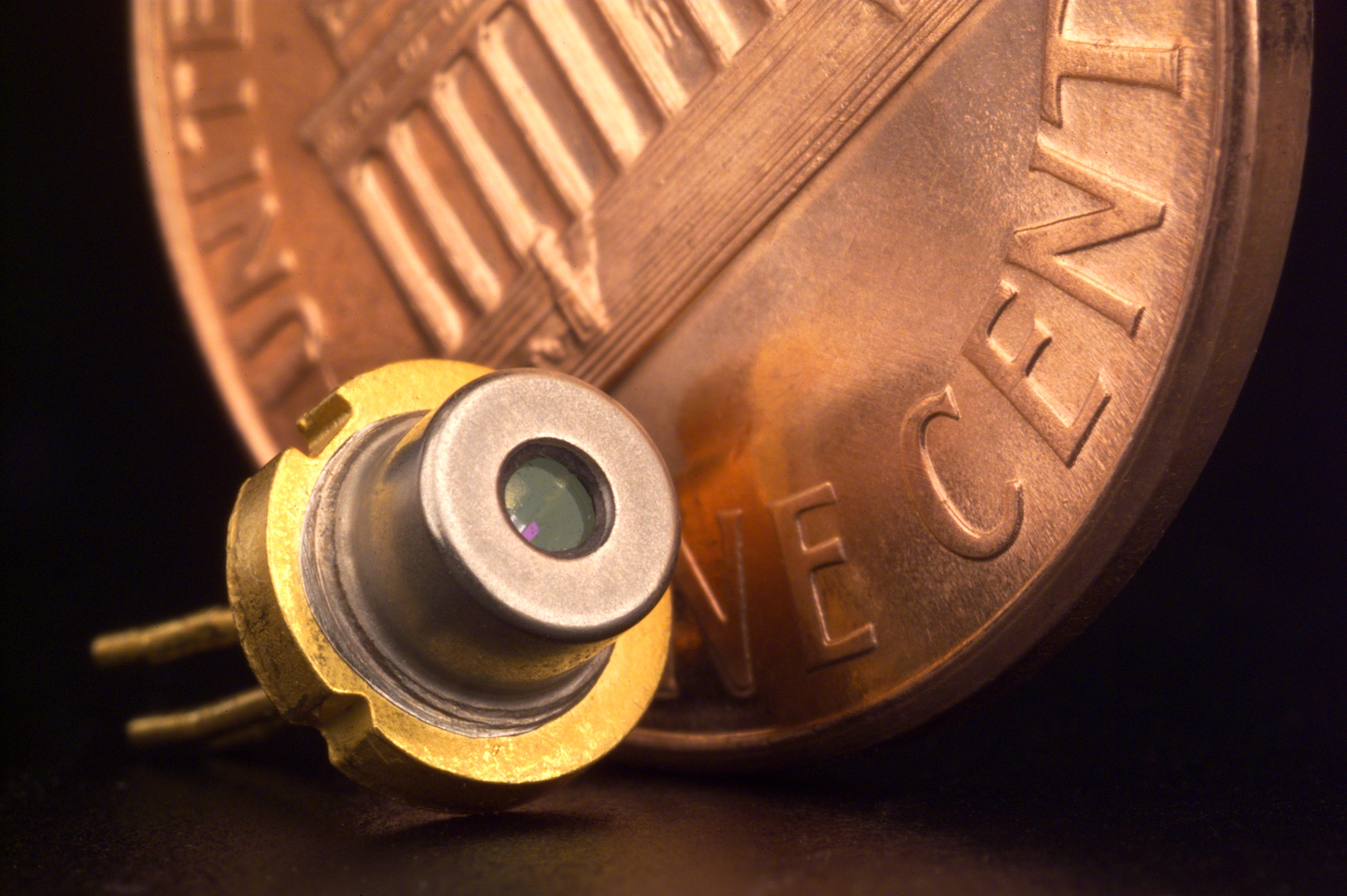 Sample Grating Distributed Bragg Reflector lasers (SG-DBR) have a much larger tunable range; by the use of vernier-tunable Bragg mirrors and a phase section, a single-mode output range of > 50 nm can be selected. Other technologies to achieve wide tuning ranges for DWDM-systems are:
*External cavity lasers using a MEMS structure for tuning the cavity length, such as devices commercialized by Iolon.
*External cavity lasers using multiple-prism grating arrangements for wide-range tunability.
*DFB laser arrays based on several thermal tuned DFB lasers, in which coarse tuning is achieved by selecting the correct laser bar. Fine tuning is then done thermally, such as in devices commercialized by Santur Corporation.
*Tunable VCSELs, in which one of the two mirror stacks is movable. To achieve sufficient output power out of a VCSEL structure, lasers in the nm domain are usually either optically pumped or have an additional optical amplifier built into the device.
Rather than placing the resonator mirrors at the edges of the device, the mirrors in a VCSEL are located on the top and bottom of the semiconductor material. Somewhat confusingly, these mirrors are typically DBR devices. This arrangement causes light to "bounce" vertically in a laser chip, so that the light emerges through the top of the device, rather than through the edge. As a result, VCSELs produce beams of a more circular nature than their cousins and beams that do not diverge as rapidly.
, there is no widely tunable VCSEL commercially available any more for DWDM-system application.
It is claimed that the first infrared laser with a tunability of more than one octave was a germanium crystal laser.
Sample Grating Distributed Bragg Reflector lasers (SG-DBR) have a much larger tunable range; by the use of vernier-tunable Bragg mirrors and a phase section, a single-mode output range of > 50 nm can be selected. Other technologies to achieve wide tuning ranges for DWDM-systems are:
*External cavity lasers using a MEMS structure for tuning the cavity length, such as devices commercialized by Iolon.
*External cavity lasers using multiple-prism grating arrangements for wide-range tunability.
*DFB laser arrays based on several thermal tuned DFB lasers, in which coarse tuning is achieved by selecting the correct laser bar. Fine tuning is then done thermally, such as in devices commercialized by Santur Corporation.
*Tunable VCSELs, in which one of the two mirror stacks is movable. To achieve sufficient output power out of a VCSEL structure, lasers in the nm domain are usually either optically pumped or have an additional optical amplifier built into the device.
Rather than placing the resonator mirrors at the edges of the device, the mirrors in a VCSEL are located on the top and bottom of the semiconductor material. Somewhat confusingly, these mirrors are typically DBR devices. This arrangement causes light to "bounce" vertically in a laser chip, so that the light emerges through the top of the device, rather than through the edge. As a result, VCSELs produce beams of a more circular nature than their cousins and beams that do not diverge as rapidly.
, there is no widely tunable VCSEL commercially available any more for DWDM-system application.
It is claimed that the first infrared laser with a tunability of more than one octave was a germanium crystal laser.
/ref>
 A tunable laser is a
A tunable laser is a laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
whose wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of operation can be altered in a controlled manner. While all laser gain media allow small shifts in output wavelength, only a few types of lasers allow continuous tuning over a significant wavelength range.
There are many types and categories of tunable lasers. They exist in the gas, liquid, and solid states. Among the types of tunable lasers are excimer lasers, gas lasers (such as CO2 and He-Ne lasers), dye lasers (liquid and solid state), transition-metal solid-state lasers, semiconductor crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
and diode lasers, and free-electron laser
A free-electron laser (FEL) is a fourth generation light source producing extremely brilliant and short pulses of radiation. An FEL functions much as a laser but employs relativistic electrons as a active laser medium, gain medium instead of using ...
s. Tunable lasers find applications in spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spectro ...
, photochemistry, atomic vapor laser isotope separation, and optical communications.
Types of tunability
Single line tuning
No real laser is trulymonochromatic
A monochrome or monochromatic image, object or palette is composed of one color (or values of one color). Images using only shades of grey are called grayscale (typically digital) or black-and-white (typically analog). In physics, mon ...
; all lasers can emit light over some range of frequencies, known as the linewidth
A spectral line is a weaker or stronger region in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum. It may result from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used ...
of the laser transition. In most lasers, this linewidth is quite narrow (for example, the nm wavelength transition of a Nd:YAG laser has a linewidth of approximately 120 GHz, or 0.45 nm). Tuning of the laser output across this range can be achieved by placing wavelength-selective optical elements (such as an etalon) into the laser's optical cavity
An optical cavity, resonating cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors or other optical elements that confines light waves similarly to how a cavity resonator confines microwaves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, ...
, to provide selection of a particular longitudinal mode of the cavity.
Multi-line tuning
Most laser gain media have a number of transition wavelengths on which laser operation can be achieved. For example, as well as the principal nm output line, Nd:YAG has weaker transitions at wavelengths of nm, nm, nm, nm, and a number of other lines. Usually, these lines do not operate unless the gain of the strongest transition is suppressed, such as by use of wavelength-selectivedielectric mirror
A dielectric mirror, also known as a Bragg mirror, is a type of mirror composed of multiple thin film, thin layers of dielectric material, typically deposited on a substrate of glass or some other optical material. By careful choice of the type a ...
s. If a dispersive element, such as a prism, is introduced into the optical cavity, tilting the cavity's mirrors can cause tuning of the laser as it "hops" between different laser lines. Such schemes are common in argon
Argon is a chemical element; it has symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abu ...
- ion lasers, allowing tuning of the laser to a number of lines from the ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
and blue
Blue is one of the three primary colours in the RYB color model, RYB colour model (traditional colour theory), as well as in the RGB color model, RGB (additive) colour model. It lies between Violet (color), violet and cyan on the optical spe ...
through to green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a com ...
wavelengths.
Narrowband tuning
For some types of lasers, the laser's cavity length can be modified, and thus they can be continuously tuned over a significant wavelength range. Distributed feedback (DFB) semiconductor lasers and vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) use periodic distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) structures to form the mirrors of the optical cavity. If thetemperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
of the laser is changed, then the index change of the DBR structure causes a shift in its peak reflective wavelength and thus the wavelength of the laser. The tuning range of such lasers is typically a few nanometres, up to a maximum of approximately 6 nm, as the laser temperature is changed over ~50 K. As a rule of thumb, the wavelength is tuned by 0.08 nm/K for DFB lasers operating in the 1,550 nm wavelength regime. Such lasers are commonly used in optical communications applications, such as DWDM-systems, to allow adjustment of the signal wavelength. To get wideband tuning using this technique, some such as Santur Corporation or Nippon Telegraph and Telephone (NTT Corporation) contain an array of such lasers on a single chip and concatenate the tuning ranges.
Widely tunable lasers
 Sample Grating Distributed Bragg Reflector lasers (SG-DBR) have a much larger tunable range; by the use of vernier-tunable Bragg mirrors and a phase section, a single-mode output range of > 50 nm can be selected. Other technologies to achieve wide tuning ranges for DWDM-systems are:
*External cavity lasers using a MEMS structure for tuning the cavity length, such as devices commercialized by Iolon.
*External cavity lasers using multiple-prism grating arrangements for wide-range tunability.
*DFB laser arrays based on several thermal tuned DFB lasers, in which coarse tuning is achieved by selecting the correct laser bar. Fine tuning is then done thermally, such as in devices commercialized by Santur Corporation.
*Tunable VCSELs, in which one of the two mirror stacks is movable. To achieve sufficient output power out of a VCSEL structure, lasers in the nm domain are usually either optically pumped or have an additional optical amplifier built into the device.
Rather than placing the resonator mirrors at the edges of the device, the mirrors in a VCSEL are located on the top and bottom of the semiconductor material. Somewhat confusingly, these mirrors are typically DBR devices. This arrangement causes light to "bounce" vertically in a laser chip, so that the light emerges through the top of the device, rather than through the edge. As a result, VCSELs produce beams of a more circular nature than their cousins and beams that do not diverge as rapidly.
, there is no widely tunable VCSEL commercially available any more for DWDM-system application.
It is claimed that the first infrared laser with a tunability of more than one octave was a germanium crystal laser.
Sample Grating Distributed Bragg Reflector lasers (SG-DBR) have a much larger tunable range; by the use of vernier-tunable Bragg mirrors and a phase section, a single-mode output range of > 50 nm can be selected. Other technologies to achieve wide tuning ranges for DWDM-systems are:
*External cavity lasers using a MEMS structure for tuning the cavity length, such as devices commercialized by Iolon.
*External cavity lasers using multiple-prism grating arrangements for wide-range tunability.
*DFB laser arrays based on several thermal tuned DFB lasers, in which coarse tuning is achieved by selecting the correct laser bar. Fine tuning is then done thermally, such as in devices commercialized by Santur Corporation.
*Tunable VCSELs, in which one of the two mirror stacks is movable. To achieve sufficient output power out of a VCSEL structure, lasers in the nm domain are usually either optically pumped or have an additional optical amplifier built into the device.
Rather than placing the resonator mirrors at the edges of the device, the mirrors in a VCSEL are located on the top and bottom of the semiconductor material. Somewhat confusingly, these mirrors are typically DBR devices. This arrangement causes light to "bounce" vertically in a laser chip, so that the light emerges through the top of the device, rather than through the edge. As a result, VCSELs produce beams of a more circular nature than their cousins and beams that do not diverge as rapidly.
, there is no widely tunable VCSEL commercially available any more for DWDM-system application.
It is claimed that the first infrared laser with a tunability of more than one octave was a germanium crystal laser.
Applications
The range of applications of tunable lasers is extremely wide. When coupled to the right filter, a tunable source can be tuned over a few hundreds of nanometers with a spectral resolution that can go from 4 nm to 0.3 nm, depending on thewavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
range. With a good enough isolation (>OD4), tunable sources can be used for basic absorption and photoluminescence studies. They can be used for solar cells characterisation in a light-beam-induced current (LBIC) experiment, from which the external quantum efficiency (EQE) of a device can be mapped. They can also be used for the characterisation of gold nanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is a particle of matter 1 to 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At ...
s and single-walled carbon nanotube
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with a diameter in the nanometre range ( nanoscale). They are one of the allotropes of carbon. Two broad classes of carbon nanotubes are recognized:
* ''Single-walled carbon nanotubes'' (''S ...
thermopiles, where a wide tunable range from 400 nm to nm is essential. Tunable sources were recently used for the development of hyperspectral imaging
Hyperspectral imaging collects and processes information from across the electromagnetic spectrum. The goal of hyperspectral imaging is to obtain the spectrum for each pixel in the image of a scene, with the purpose of finding objects, identifyi ...
for early detection of retinal diseases where a wide range of wavelengths, a small bandwidth, and outstanding isolation is needed to achieve efficient illumination of the entire retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
. Tunable sources can be a powerful tool for reflection and transmission spectroscopy, photobiology
Photobiology is the scientific study of the beneficial and harmful interactions of light (technically, non-ionizing radiation) in living organisms. The field includes the study of photophysics, photochemistry, photosynthesis, photomorphogenesis, ...
, detector calibration, hyperspectral imaging, and steady-state pump probe experiments, to name only a few.
History
The first true broadly tunable laser was the dye laser in 1966. F. P. Schäfer (ed.), ''Dye Lasers'' (Springer, 1990) Hänsch introduced the first narrow-linewidth tunable laser in 1972. Dye lasers and some vibronic solid-state lasers have extremely large bandwidths, allowing tuning over a range of tens to hundreds of nanometres.Koechner, §2.5, pp66–78. Titanium-doped sapphire is the most common tunable solid-state laser, capable of laser operation from 670 nm to nm wavelengths. Typically these laser systems incorporate a Lyot filter into the laser cavity, which is rotated to tune the laser. Other tuning techniques involve diffraction gratings, prisms, etalons, and combinations of these.F. J. Duarte and L. W. Hillman (eds.), ''Dye Laser Principles'' (Academic, 1990) Chapter 4 Multiple-prism grating arrangements, in several configurations, as described by Duarte, are used in diode, dye, gas, and other tunable lasers.F. J. Duarte, ''Tunable Laser Optics'', 2nd Ed. (CRC, New York, 2015) Chapter 7./ref>
See also
References
Further reading
* {{Authority control Laser types