Trucking Companies Of The United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Road transport or road transportation is a type of transport using
 Starting in the early 18th century, the
Starting in the early 18th century, the
 By the late 18th and early 19th centuries, new methods of highway construction had been pioneered by the work of three British engineers, John Metcalf,
By the late 18th and early 19th centuries, new methods of highway construction had been pioneered by the work of three British engineers, John Metcalf,
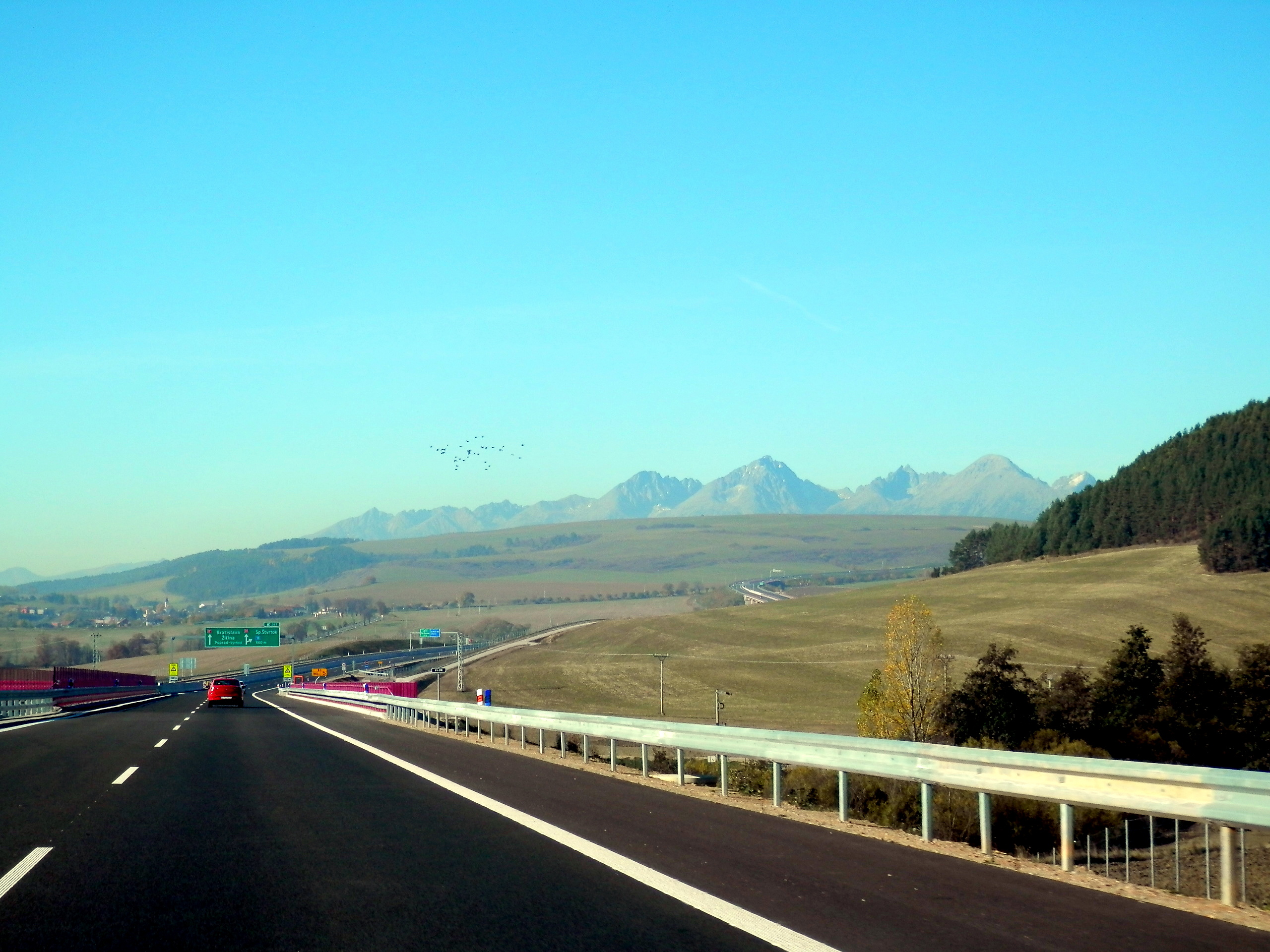 Today, roadways are primarily
Today, roadways are primarily
 Early
Early
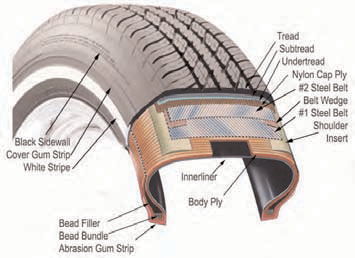 As the horse-drawn
As the horse-drawn
African Civilization Revisited
Africa World Press: 1991 * *
roads
A road is a linear way for the conveyance of traffic that mostly has an improved surface for use by vehicles (motorized and non-motorized) and pedestrians. Unlike streets, the main function of roads is transportation.
There are many types of ...
. Transport on roads can be roughly grouped into the transportation of goods and transportation of people. In many countries licensing requirements and safety regulations ensure a separation of the two industries. Movement along roads may be by bike
A bicycle, also called a pedal cycle, bike or cycle, is a human-powered or motor-powered assisted, pedal-driven, single-track vehicle, having two wheels attached to a frame, one behind the other. A is called a cyclist, or bicyclist.
Bic ...
, automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with Wheel, wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, pe ...
, bus
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for cha ...
, truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame construction ...
, or by animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
such as horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million y ...
or oxen. Standard networks of roads were adopted by Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
, Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those g ...
, and other early empire
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
s, and may be regarded as a feature of empires. Cargo
Cargo consists of bulk goods conveyed by water, air, or land. In economics, freight is cargo that is transported at a freight rate for commercial gain. ''Cargo'' was originally a shipload but now covers all types of freight, including trans ...
may be transported by trucking companies, while passengers may be transported via mass transit
Public transport (also known as public transportation, public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typical ...
. Commonly defined features of modern roads include defined lanes
In road transport, a lane is part of a roadway that is designated to be used by a single line of vehicles to control and guide drivers and reduce traffic conflicts. Most public roads (highways) have at least two lanes, one for traffic in each ...
and signage
Signage is the design or use of signs and symbols to communicate a message. A signage also means signs ''collectively'' or being considered as a group. The term ''signage'' is documented to have been popularized in 1975 to 1980.
Signs are any ...
. Various classes of road exist, from two-lane local roads with at-grade intersection
In mathematics, the intersection of two or more objects is another object consisting of everything that is contained in all of the objects simultaneously. For example, in Euclidean geometry, when two lines in a plane are not parallel, their i ...
s to controlled-access highway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms i ...
s with all cross traffic grade-separated.
The nature of road transportation of goods depends on, apart from the degree of development of the local infrastructure, the distance the goods are transported by road, the weight and volume of an individual shipment, and the type of goods transported. For short distances and light small shipments, a van
A van is a type of road vehicle used for transporting goods or people. Depending on the type of van, it can be bigger or smaller than a pickup truck and SUV, and bigger than a common car. There is some varying in the scope of the word across th ...
or pickup truck
A pickup truck or pickup is a light-duty truck that has an enclosed cabin, and a back end made up of a cargo bed that is enclosed by three low walls with no roof (this cargo bed back end sometimes consists of a tailgate and removable covering) ...
may be used. For large shipments even if less than a full truckload a truck is more appropriate. (Also see Trucking and Hauling below). In some countries cargo
Cargo consists of bulk goods conveyed by water, air, or land. In economics, freight is cargo that is transported at a freight rate for commercial gain. ''Cargo'' was originally a shipload but now covers all types of freight, including trans ...
is transported by road in horse-drawn carriages, donkey cart
A cart or dray (Australia and New Zealand) is a vehicle designed for transport, using two wheels and normally pulled by one or a pair of draught animals. A handcart is pulled or pushed by one or more people.
It is different from the flatbed tr ...
s or other non-motorized mode. Delivery services are sometimes considered a separate category from cargo transport. In many places, fast food is transported on roads by various types of vehicle
A vehicle (from la, vehiculum) is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles (motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters for disabled people), railed vehicles (trains, trams), wa ...
s. For inner city delivery of small packages and documents bike courier
Bicycle messengers (also known as bike or cycle couriers) are people who work for courier companies (also known as messenger companies) carrying and delivering items by bicycle. Bicycle messengers are most often found in the central business dist ...
s are quite common.
People are transported on roads. Special modes of individual transport by road such as cycle rickshaw
The cycle rickshaw is a small-scale local means of transport. It is a type of hatchback tricycle designed to carry passengers on a for-hire basis. It is also known by a variety of other names such as bike taxi, velotaxi, pedicab, bikecab ...
s may also be locally available. There are also specialist modes of road transport for particular situations, such as ambulances.
History
Early roads
The first methods of road transport werehorse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million y ...
s, oxen or even humans carrying goods over dirt tracks that often followed game
A game is a structured form of play (activity), play, usually undertaken for enjoyment, entertainment or fun, and sometimes used as an educational tool. Many games are also considered to be work (such as professional players of spectator s ...
trail
A trail, also known as a path or track, is an unpaved lane or small road usually passing through a natural area. In the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland, a path or footpath is the preferred term for a pedestrian or hiking trail. Th ...
. The Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
later built a network of Royal Road
The Royal Road was an ancient highway reorganized and rebuilt by the Persian king Darius the Great (Darius I) of the first (Achaemenid) Persian Empire in the 5th century BC. Darius built the road to facilitate rapid communication on the western ...
s across their empire.
With the advent of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
, there was a need for armies to be able to travel quickly from one region to another, and the roads that existed were often muddy, which greatly delayed the movement of large masses of troops. To resolve this issue, the Romans built solid and lasting roads. The Roman road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Re ...
s used deep roadbeds of crushed stone as an underlying layer to ensure that they kept dry, as the water would flow out from the crushed stone, instead of becoming mud in clay soils. The Islamic Caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
later built tar-paved roads in Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
.
New road networks
From the 17th century, road transport throughout theAshanti Empire
The Asante Empire (Asante Twi: ), today commonly called the Ashanti Empire, was an Akan state that lasted between 1701 to 1901, in what is now modern-day Ghana. It expanded from the Ashanti Region to include most of Ghana as well as parts of Iv ...
was maintained via a network of well-kept roads that connected the Ashanti mainland with the Niger river
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through ...
and other trade cities.Davidson (1991), p. 240.
After significant road construction undertaken by the kingdom of Dahomey
The Kingdom of Dahomey () was a West African kingdom located within present-day Benin that existed from approximately 1600 until 1904. Dahomey developed on the Abomey Plateau amongst the Fon people in the early 17th century and became a region ...
, toll road
A toll road, also known as a turnpike or tollway, is a public or private road (almost always a controlled-access highway in the present day) for which a fee (or ''toll'') is assessed for passage. It is a form of road pricing typically implemented ...
s were established with the function of collecting yearly taxes based on the goods carried by the people of Dahomey and their occupation.
As states developed and became richer, especially with the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
, new roads and bridges began to be built, often based on Roman designs. Although there were attempts to rediscover Roman methods, there was little useful innovation in road building before the 18th century.
 Starting in the early 18th century, the
Starting in the early 18th century, the British Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative supremacy ...
began to pass a series of acts
The Acts of the Apostles ( grc-koi, Πράξεις Ἀποστόλων, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; la, Actūs Apostolōrum) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of its message ...
that gave the local justices powers to erect toll-gates on the roads, in exchange for professional upkeep.Webb. English Local Government. pp. 157-159 The toll-gate erected at Wade's Mill became the first effective toll-gate in England. The first scheme that had trustees who were not justices was established through a Turnpike Act in 1707, for a section of the London-Chester
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...
road between Foothill and Stony Stafford. The basic principle was that the trustees would manage resources from the several parishes through which the highway passed, augment this with tolls from users from outside the parishes and apply the whole to the maintenance of the main highway. This became the pattern for the turnpiking of a growing number of highways, sought by those who wished to improve flow of commerce through their part of a county.
The quality of early turnpike roads was varied. Although turnpiking did result in some improvement to each highway, the technologies used to deal with geological features, drainage, and the effects of weather were all in their infancy. Road construction
A road is a linear way for the conveyance of traffic that mostly has an improved surface for use by vehicles (motorized and non-motorized) and pedestrians. Unlike streets, the main function of roads is transportation.
There are many types of ...
improved slowly, initially through the efforts of individual surveyors such as John Metcalf in Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a Historic counties of England, historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other Eng ...
in the 1760s. British turnpike builders began to realize the importance of selecting clean stones for surfacing while excluding vegetable material and clay, resulting in more durable roads.
Industrial civil engineering
 By the late 18th and early 19th centuries, new methods of highway construction had been pioneered by the work of three British engineers, John Metcalf,
By the late 18th and early 19th centuries, new methods of highway construction had been pioneered by the work of three British engineers, John Metcalf, Thomas Telford
Thomas Telford FRS, FRSE, (9 August 1757 – 2 September 1834) was a Scottish civil engineer. After establishing himself as an engineer of road and canal projects in Shropshire, he designed numerous infrastructure projects in his native Scotla ...
and John Loudon McAdam
John Loudon McAdam (23 September 1756 – 26 November 1836) was a Scottish civil engineer and road-builder. He invented a new process, "macadamisation", for building roads with a smooth hard surface, using controlled materials of m ...
, and by the French road engineer Pierre-Marie-Jérôme Trésaguet Pierre-Marie-Jérôme Trésaguet (15 January 1716 – 1796) was a French engineer. He is widely credited with establishing the first scientific approach to road building about the year 1764. Among his innovations was the use of a base layer of ...
.
The first professional road builder to emerge during the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
was John Metcalf, who constructed about of turnpike road
A toll road, also known as a turnpike or tollway, is a public or private road (almost always a controlled-access highway in the present day) for which a fee (or ''toll'') is assessed for passage. It is a form of road pricing typically implemented ...
, mainly in the north of England, from 1765. He believed a good road should have good foundations, be well drained and have a smooth convex
Convex or convexity may refer to:
Science and technology
* Convex lens, in optics
Mathematics
* Convex set, containing the whole line segment that joins points
** Convex polygon, a polygon which encloses a convex set of points
** Convex polytope ...
surface to allow rainwater
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water fo ...
to drain quickly into ditches at the side. He understood the importance of good drainage, knowing it was rain that caused most problems on the roads.
Pierre-Marie-Jérôme Trésaguet Pierre-Marie-Jérôme Trésaguet (15 January 1716 – 1796) was a French engineer. He is widely credited with establishing the first scientific approach to road building about the year 1764. Among his innovations was the use of a base layer of ...
established the first scientific approach to road building
A road is a linear way for the conveyance of traffic that mostly has an improved surface for use by vehicles (motorized and non-motorized) and pedestrians. Unlike streets, the main function of roads is transportation.
There are many types of ...
in France at the same time. He wrote a memorandum on his method in 1775, which became general practice in France. It involved a layer of large rocks, covered by a layer of smaller gravel. The lower layer improved on Roman practice in that it was based on the understanding that the purpose of this layer (the sub-base or base course
The base course or basecourse in pavements is a layer of material in an asphalt roadway, race track, riding arena, or sporting field. It is located under the surface layer consisting of the ''wearing course'' and sometimes an extra ''binder cour ...
) is to transfer the weight of the road and its traffic to the ground, while protecting the ground from deformation by spreading the weight evenly. Therefore, the sub-base did not have to be a self-supporting structure. The upper running surface provided a smooth surface for vehicles while protecting the large stones of the sub-base.
The surveyor and engineer Thomas Telford
Thomas Telford FRS, FRSE, (9 August 1757 – 2 September 1834) was a Scottish civil engineer. After establishing himself as an engineer of road and canal projects in Shropshire, he designed numerous infrastructure projects in his native Scotla ...
also made substantial advances in the engineering of new roads and the construction of bridges. His method of road building involved the digging of a large trench in which a foundation of heavy rock was set. He also designed his roads so that they sloped downwards from the centre, allowing drainage to take place, a major improvement on the work of Trésaguet. The surface of his roads consisted of broken stone. He also improved on methods for the building of roads by improving the selection of stone based on thickness, taking into account traffic, alignment and slopes. During his later years, Telford was responsible for rebuilding sections of the London to Holyhead road, a task completed by his assistant of ten years, John MacNeill.
It was another Scottish engineer, John Loudon McAdam
John Loudon McAdam (23 September 1756 – 26 November 1836) was a Scottish civil engineer and road-builder. He invented a new process, "macadamisation", for building roads with a smooth hard surface, using controlled materials of m ...
, who designed the first modern roads. He developed an inexpensive paving material of soil and stone aggregate (known as macadam
Macadam is a type of road construction, pioneered by Scottish engineer John Loudon McAdam around 1820, in which crushed stone is placed in shallow, convex layers and compacted thoroughly. A binding layer of stone dust (crushed stone from the o ...
). His road building method was simpler than Telford's, yet more effective at protecting roadways: he discovered that massive foundations of rock upon rock were unnecessary, and asserted that native soil alone would support the road and traffic upon it, as long as it was covered by a road crust that would protect the soil underneath from water and wear.
Also unlike Telford and other road builders, McAdam laid his roads as level as possible. His road required only a rise of three inches from the edges to the center. Cambering and elevation of the road above the water table enabled rainwater to run off into ditches on either side.McAdam (1824), p.38 Size of stones was central to the McAdam's road building theory. The lower road thickness was restricted to stones no larger than . The upper layer of stones was limited to size and stones were checked by supervisors who carried scales. A workman could check the stone size himself by seeing if the stone would fit into his mouth. The importance of the 20 mm stone size was that the stones needed to be much smaller than the 100 mm width of the iron carriage
A carriage is a private four-wheeled vehicle for people and is most commonly horse-drawn. Second-hand private carriages were common public transport, the equivalent of modern cars used as taxis. Carriage suspensions are by leather strapping an ...
tyres
A tire (American English) or tyre (British English) is a ring-shaped component that surrounds a Rim (wheel), wheel's rim to transfer a vehicle's load from the axle through the wheel to the ground and to provide Traction (engineering), t ...
that traveled on the road. Macadam roads were being built widely in the United States and Australia in the 1820s and in Europe in the 1830s and 1840s.
20th century
Macadam roads were adequate for use by horses and carriages or coaches, but they were very dusty and subject to erosion with heavy rain. TheGood Roads Movement
The Good Roads Movement occurred in the United States between the late 1870s and the 1920s. It was the rural dimension of the Progressive movement. A key player was the United States Post Office Department. Once a commitment was made for Rural Fre ...
occurred in the United States between the late 1870s and the 1920s. Advocates for improved roads led by bicyclists turned local agitation into a national political movement.
Outside cities, roads were dirt or gravel; mud in the winter and dust in the summer. Early organizers cited Europe where road construction
A road is a linear way for the conveyance of traffic that mostly has an improved surface for use by vehicles (motorized and non-motorized) and pedestrians. Unlike streets, the main function of roads is transportation.
There are many types of ...
and maintenance was supported by national and local governments. In its early years, the main goal of the movement was education for road building in rural areas
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry typically are describ ...
between cities and to help rural populations gain the social and economic benefits enjoyed by cities where citizens benefited from railroads, trolleys and paved streets. Even more than traditional vehicles, the newly invented bicycles could benefit from good country roads. Later on, they did not hold up to higher-speed motor vehicle use. Methods to stabilise macadam roads with tar date back to at least 1834 when John Henry Cassell, operating from ''Cassell's Patent Lava Stone Works'' in Millwall
Millwall is a district on the western and southern side of the Isle of Dogs, in east London, England, in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. It lies to the immediate south of Canary Wharf and Limehouse, north of Greenwich and Deptford, east ...
, patented "Pitch Macadam".
This method involved spreading tar on the subgrade
In transport engineering, subgrade is the native material underneath a constructed road,http://www.highwaysmaintenance.com/drainage.htm The Idiots' Guide to Highways Maintenance ''highwaysmaintenence.com'' pavement or railway track (US: railroad ...
, placing a typical macadam layer, and finally sealing the macadam with a mixture of tar and sand. Tar-grouted macadam was in use well before 1900 and involved scarifying the surface of an existing macadam pavement, spreading tar, and re-compacting. Although the use of tar in road construction was known in the 19th century, it was little used and was not introduced on a large scale until the motorcar arrived on the scene in the early 20th century.
Modern tarmac was patented by British civil engineer Edgar Purnell Hooley
Edgar Purnell Hooley (5 June 1860 – 26 January 1942) was a Welsh inventor. After inventing Tarmacadam, tarmac in 1902, he founded Tarmac Group, Tar Macadam Syndicate Ltd the following year and registered tarmac as a trademark. Following a merger ...
, who noticed that spilled tar on the roadway kept the dust down and created a smooth surface.. (Details of this story vary a bit, but the essence of is the same, as are the basic facts). He took out a patent in 1901 for tarmac.
Trucking and haulage
Trucking companies (inAmerican English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the Languages of the United States, most widely spoken lan ...
terminology) or haulage companies / hauliers (in British English) accept cargo
Cargo consists of bulk goods conveyed by water, air, or land. In economics, freight is cargo that is transported at a freight rate for commercial gain. ''Cargo'' was originally a shipload but now covers all types of freight, including trans ...
for road transport. Truck driver
A truck driver (commonly referred to as a trucker, teamster, or driver in the United States and Canada; a truckie in Australia and New Zealand; a HGV driver in the United Kingdom, Ireland and the European Union, a lorry driver, or driver in ...
s operate either independently – working directly for the client – or through freight carriers or shipping agents. Some big companies (e.g. grocery store chains) operate their own internal trucking operations. The market size for general freight trucking was nearly $125 billion in 2010.
In the U.S. many truckers own their truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame construction ...
(rig), and are known as owner-operator
An owner-operator is a small business or microbusiness owner who also runs the day-to-day operations of the company. Owner-operators are found in many business models and franchising companies in many different industries like restaurant chains, ...
s. Some road transportation is done on regular routes or for only one consignee
{{Admiralty law
In a contract of carriage, the consignee is the Party (law), entity who is financially responsible (the buyer) for the receipt of a shipment. Generally, but not always, the consignee is the same as the receiver.
If a sender dis ...
per run, while others transport goods from many different loading stations/shippers to various consignees. On some long runs only cargo for one leg of the route (to) is known when the cargo is loaded. Truckers may have to wait at the destination for a backhaul.
A bill of lading
A bill of lading () (sometimes abbreviated as B/L or BOL) is a document issued by a carrier (or their agent) to acknowledge receipt of cargo for shipment. Although the term historically related only to carriage by sea, a bill of lading may toda ...
issued by the shipper provides the basic document for road freight. On cross-border
Borders are usually defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political borders c ...
transportation the trucker will present the cargo and documentation provided by the shipper to customs
Customs is an authority or agency in a country responsible for collecting tariffs and for controlling the flow of goods, including animals, transports, personal effects, and hazardous items, into and out of a country. Traditionally, customs ...
for inspection (for EC see also Schengen Agreement
The Schengen Agreement ( , ) is a treaty which led to the creation of Europe's Schengen Area, in which internal border checks have largely been abolished. It was signed on 14 June 1985, near the town of Schengen, Luxembourg, by five of the t ...
). This also applies to shipments that are transported out of a free port
Free economic zones (FEZ), free economic territories (FETs) or free zones (FZ) are a class of special economic zone (SEZ) designated by the trade and commerce administrations of various countries. The term is used to designate areas in which com ...
.
Hours of service
To avoid accidents caused by fatigue, truckers have to adhere to strict rules for drive time and required rest periods. In the United States and Canada, these regulations are known ashours of service
Hours of Service (HOS) regulations are issued by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) and govern the working hours of anyone operating a commercial motor vehicle (CMV) in the United States. These regulations apply to truck dr ...
, and in the European Union as drivers working hours
Drivers' working hours is the commonly used term for regulations that govern the activities of the drivers of commercial goods vehicles and passenger carrying vehicles. In the United States, they are known as hours of service.
Within the Europea ...
. One such regulation is the Hours of Work and Rest Periods (Road Transport) Convention, 1979
Hours of Work and Rest Periods (Road Transport) Convention, 1979 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
It was established in 1979, with the preamble stating:
Having decided upon the adoption of certain proposals with regard to ho ...
. Tachograph
A tachograph is a device fitted to a vehicle that automatically records its speed and distance, together with the driver's activity selected from a choice of modes. The drive mode is activated automatically when the vehicle is in motion, and ...
s or Electronic on-board recorder
An electronic on-board recorder (EOBR) is an electronic device attached to a commercial motor vehicle, which is used to record the amount of time a vehicle is being driven. This is similar to the tachograph, and is the American equivalent of the ...
s record the times the vehicle is in motion and stopped. Some companies use two drivers per truck to ensure uninterrupted transportation; with one driver resting or sleeping in a bunk in the back of the cab while the other is driving.
Licenses
Truck drivers often need special licenses to drive, known in the U.S. as acommercial driver's license
A commercial driver's license (CDL) is a driver's license required in the United States to operate large and heavy vehicles (including trucks, buses, and trailers) or a vehicle of any size that transports hazardous materials or more than 15 p ...
. In the U.K. a large goods vehicle licence is required. For transport of hazardous materials (see dangerous goods
Dangerous goods, abbreviated DG, are substances that when transported are a risk to health, safety, property or the environment. Certain dangerous goods that pose risks even when not being transported are known as hazardous materials ( syllabi ...
) truckers need a licence, which usually requires them to pass an exam (e.g. in the EU). They have to make sure they affix proper labels for the respective hazard(s) to their vehicle. Liquid goods are transported by road in tank truck
A tank truck, gas truck, fuel truck, or tanker truck (American English) or tanker (British English) is a motor vehicle designed to carry liquids or gases on roads. The largest such vehicles are similar to railroad tank cars, which are also design ...
s (in American English) or tanker lorries (in British English) (also road-tankers) or special tank containers for intermodal transport
Intermodal transport (or intermodal transportation) involves the use of more than one mode of transport for a journey. It may refer to:
* Intermodal passenger transport
* Intermodal freight transport
See also
* Intermodal transportation center
...
. For transportation of live animals special requirements have to be met in many countries to prevent cruelty to animals (see animal rights
Animal rights is the philosophy according to which many or all sentient animals have moral worth that is independent of their utility for humans, and that their most basic interests—such as avoiding suffering—should be afforded the sa ...
). For fresh and frozen goods refrigerator truck
A refrigerator truck or chiller lorry (also called a Reefer), is a van or truck designed to carry perishable freight at low temperatures. Most long-distance refrigerated transport by truck is done in articulated trucks pulling refrigerated sem ...
s or reefers are used.
Weights
Some loads are weighed at the point of origin and the driver is responsible for ensuring weights conform to maximum allowed standards. This may involve using on-board weight gauges (load pressure gauges), knowing the empty weight of the transport vehicle and the weight of the load, or using a commercial weight scale. In routeweigh station
A weigh station is a checkpoint along a highway to inspect vehicular weights and safety compliance criteria. Usually, trucks and commercial vehicles are subject to the inspection.
Weigh stations are equipped with truck scales, some of which are ...
s check that gross vehicle weights do not exceed the maximum weight for that particular jurisdiction and will include individual axle weights. This varies by country, states within a country, and may include federal standards. The United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
uses FMCSA federal standards that include bridge law
Bridge law is the body of laws which apply to bridges in a particular jurisdiction.
United States
In the United States, legislative authority to erect a bridge is necessary in three cases: first, when toll is demanded for its use—the right to ...
formulas
In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''chemical formula''. The informal use of the term ''formula'' in science refers to the general construct of a relationship betwee ...
. Many states, not on the national road system, use their own road and bridge standards. Enforcement scales may include portable scales, scale houses with low speed scales or weigh-in-motion (WIM) scales.
The European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
uses the ''International Recommendation'', OIML R 134-2 (2009). The process may involve a scale house and low-speed scales or higher-speed WIM road or bridge scales with the goal of public safety, as well as road and bridge safety, according to the Bridges Act
Bridges Act is a stock short title used in the United Kingdom for legislation relating to bridges.
List
Acts of the Parliament of England
*The Bridges Act 1530 (22 Hen 8 c 5)
*The Bridges Act 1670 (22 Car 2 c 12)
*The Bridges Act 1702 (1 Anne ...
.
Modern roads
asphalt
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term a ...
or concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wi ...
. Both are based on McAdam's concept of stone aggregate in a binder, asphalt cement or Portland cement
Portland cement is the most common type of cement in general use around the world as a basic ingredient of concrete, mortar, stucco, and non-specialty grout. It was developed from other types of hydraulic lime in England in the early 19th c ...
respectively. Asphalt is known as a flexible pavement, one which slowly will "flow" under the pounding of traffic. Concrete is a rigid pavement, which can take heavier loads but is more expensive and requires more carefully prepared subbase. So, generally, major roads are concrete and local roads are asphalt. Concrete roads are often covered with a thin layer of asphalt to create a wearing surface.
Modern pavements are designed for heavier vehicle loads and faster speeds, requiring thicker slabs and deeper subbase. Subbase is the layer or successive layers of stone, gravel and sand supporting the pavement. It is needed to spread out the slab load bearing on the underlying soil and to conduct away any water getting under the slabs. Water will undermine a pavement over time, so much of pavement and pavement joint design are meant to minimize the amount of water getting and staying under the slabs.
Shoulders are also an integral part of highway design. They are multipurpose; they can provide a margin of side clearance, a refuge for incapacitated vehicles, an emergency lane, and parking space. They also serve a design purpose, and that is to prevent water from percolating into the soil near the main pavement's edge. Shoulder pavement is designed to a lower standard than the pavement in the traveled way and won't hold up as well to traffic, so driving on the shoulder is generally prohibited.
Pavement technology is still evolving, albeit in not easily noticed increments. For instance, chemical additives in the pavement mix make the pavement more weather resistant, grooving and other surface treatments improve resistance to skidding and hydroplaning
Aquaplaning or hydroplaning by the tires of a road vehicle, aircraft or other wheeled vehicle occurs when a layer of water builds between the wheels of the vehicle and the road surface, leading to a loss of traction that prevents the vehicle fr ...
, and joint seals which were once tar are now made of low maintenance neoprene.
Traffic control
Nearly all roadways are built with devices meant to controltraffic
Traffic comprises pedestrians, vehicles, ridden or herded animals, trains, and other conveyances that use public ways (roads) for travel and transportation.
Traffic laws govern and regulate traffic, while rules of the road include traffic ...
. Most notable to the motorist are those meant to communicate directly with the driver. Broadly, these fall into three categories: signs, signals or pavement markings. They help the driver navigate; they assign the right-of-way at intersections; they indicate laws such as speed limit
Speed limits on road traffic, as used in most countries, set the legal maximum speed at which vehicles may travel on a given stretch of road. Speed limits are generally indicated on a traffic sign reflecting the maximum permitted speed - expres ...
s and parking regulations; they advise of potential hazards; they indicate passing and no passing zones; and otherwise deliver information and to assure traffic is orderly and safe.
Two hundred years ago these devices were signs, nearly all informal. In the late 19th century signals began to appear in the biggest cities at a few highly congested intersections. They were manually operated, and consisted of semaphores, flags or paddle
A paddle is a handheld tool with an elongated handle and a flat, widened distal end (i.e. the ''blade''), used as a lever to apply force onto the bladed end. It most commonly describes a completely handheld tool used to propel a human-powered wa ...
s, or in some cases colored electric lights, all modeled on railroad signals. In the 20th century signals were automated, at first with electromechanical devices and later with computers. Signals can be quite sophisticated: with vehicle sensors embedded in the pavement, the signal can control and choreograph the turning movements of heavy traffic in the most complex of intersections. In the 1920s traffic engineers
Traffic engineering is a branch of civil engineering that uses engineering techniques to achieve the safe and efficient movement of people and goods on roadways. It focuses mainly on research for safe and efficient traffic flow, such as road geo ...
learned how to coordinate signals along a thoroughfare to increase its speeds and volumes. In the 1980s, with computers, similar coordination of whole networks became possible.
In the 1920s pavement markings were introduced. Initially they were used to indicate the road's centerline. Soon after they were coded with information to aid motorists in passing safely. Later, with multi-lane roads they were used to define lanes
In road transport, a lane is part of a roadway that is designated to be used by a single line of vehicles to control and guide drivers and reduce traffic conflicts. Most public roads (highways) have at least two lanes, one for traffic in each ...
. Other uses, such as indicating permitted turning movements and pedestrian crossings soon followed.
In the 20th century traffic control devices were standardized. Before then every locality decided on what its devices would look like and where they would be applied. This could be confusing, especially to traffic from outside the locality. In the United States standardization was first taken at the state level, and late in the century at the federal level. Each country has a Manual of Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD) and there are efforts to blend them into a worldwide standard.
Besides signals, signs, and markings, other forms of traffic control are designed and built into the roadway. For instance, curbs and rumble strips can be used to keep traffic in a given lane and median barriers can prevent left turns and even U-turns.
Toll roads
toll road
A toll road, also known as a turnpike or tollway, is a public or private road (almost always a controlled-access highway in the present day) for which a fee (or ''toll'') is assessed for passage. It is a form of road pricing typically implemented ...
s were usually built by private companies under a government franchise. They typically paralleled or replaced routes already with some volume of commerce, hoping the improved road would divert enough traffic to make the enterprise profitable. Plank roads were particularly attractive as they greatly reduced rolling resistance and mitigated the problem of getting mired in mud. Another improvement, better grading to lessen the steepness of the worst stretches, allowed draft animals to haul heavier loads.
A ''toll road'' in the United States is often called a ''turnpike''. The term ''turnpike'' probably originated from the gate, often a simple pike, which blocked passage until the fare was paid at a ''toll house'' (or ''toll booth'' in current terminology). When the toll was paid the pike, which was mounted on a swivel, was turned to allow the vehicle to pass. Tolls were usually based on the type of cargo being transported, not the type of vehicle. The practice of selecting routes so as to avoid tolls is called shunpiking
Shunpiking is the act of deliberately avoiding roads that require payment of a fee or toll to travel on them, usually by traveling on alternative "free" roads which bypass the toll road. The term comes from the word ''shun'', meaning "to avoid", an ...
. This may be simply to avoid the expense, as a form of economic protest (or boycott
A boycott is an act of nonviolent, voluntary abstention from a product, person, organization, or country as an expression of protest. It is usually for moral, social, political, or environmental reasons. The purpose of a boycott is to inflict som ...
), or simply to seek a road less traveled as a bucolic interlude.
Companies were formed to build, improve, and maintain a particular section of roadway, and tolls were collected from users to finance the enterprise. The enterprise was usually named to indicate the locale of its roadway, often including the name of one of both of the termini. The word ''turnpike'' came into common use in the names of these roadways and companies, and is essentially used interchangeably with ''toll road'' in current terminology.
In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, toll roads began with the Lancaster Turnpike
The Philadelphia and Lancaster Turnpike, first used in 1795, is the first long-distance paved road built in the United States, according to engineered plans and specifications. It links Lancaster, Pennsylvania, and Philadelphia at 34th Street, s ...
in the 1790s, within Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, connecting Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
and Lancaster. In the state of New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
, the Great Western Turnpike The Great Western Turnpike was a series of east–west toll roads that crossed part of New York in the United States. The toll roads that carried this name were:
*The First Great Western Turnpike, extending from Albany to Cherry Valley over a path s ...
was started in Albany in 1799 and eventually extended, by several alternate routes, to near what is now Syracuse, New York
Syracuse ( ) is a City (New York), city in and the county seat of Onondaga County, New York, Onondaga County, New York, United States. It is the fifth-most populous city in the state of New York following New York City, Buffalo, New York, Buffa ...
.
Toll roads peaked in the mid 19th century, and by the turn of the twentieth century most toll roads were taken over by state highway departments. The demise of this early toll road era was due to the rise of canals and railroads, which were more efficient (and thus cheaper) in moving freight over long distances. Roads wouldn't again be competitive with rails and barges until the first half of the 20th century when the internal combustion engine replaces draft animals as the source of motive power.
With the development, mass production, and popular embrace of the automobile, faster and higher capacity roads were needed. In the 1920s limited access highways appeared. Their main characteristics were dual roadways with access points limited to (but not always) grade-separated interchanges. Their dual roadways allowed high volumes of traffic
Traffic comprises pedestrians, vehicles, ridden or herded animals, trains, and other conveyances that use public ways (roads) for travel and transportation.
Traffic laws govern and regulate traffic, while rules of the road include traffic ...
, the need for no or few traffic light
Traffic lights, traffic signals, or stoplights – known also as robots in South Africa are signalling devices positioned at intersection (road), road intersections, pedestrian crossings, and other locations in order to control flows of traf ...
s along with relatively gentle grades and curves allowed higher speeds.
The first limited access highways were ''Parkways'', so called because of their often park-like landscaping
Landscaping refers to any activity that modifies the visible features of an area of land, including the following:
# Living elements, such as flora or fauna; or what is commonly called gardening, the art and craft of growing plants with a goal o ...
and, in the metropolitan New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
area, they connected the region's system of parks. When the German autobahns
The (; German plural ) is the federal controlled-access highway system in Germany. The official German term is (abbreviated ''BAB''), which translates as 'federal motorway'. The literal meaning of the word is 'Federal Auto(mobile) Track'. ...
built in the 1930s introduced higher design standards and speeds, road planners and road-builders in the United States started developing and building toll roads to similar high standards. The Pennsylvania Turnpike
The Pennsylvania Turnpike (Penna Turnpike or PA Turnpike) is a toll highway operated by the Pennsylvania Turnpike Commission (PTC) in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. A controlled-access highway, it runs for across the state. The turnpike's we ...
, which largely followed the path of a partially built railroad, was the first, opening in 1940.
After 1940 with the Pennsylvania Turnpike
The Pennsylvania Turnpike (Penna Turnpike or PA Turnpike) is a toll highway operated by the Pennsylvania Turnpike Commission (PTC) in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. A controlled-access highway, it runs for across the state. The turnpike's we ...
, toll roads saw a resurgence, this time to fund limited access highways. In the late 1940s and early 1950s, after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
interrupted the evolution of the highway, the US resumed building toll roads. They were to still higher standards and one road, the New York State Thruway
{{Infobox road
, state = NY
, type = NYST
, alternate_name = Governor Thomas E. Dewey Thruway
, maint = NYSTA
, map = {{maplink, frame=yes, plain=yes, frame-align=center, frame-width=290, type=line, stroke-width=2, type2=line, from2=New Yor ...
, had standards that became the prototype for the U.S. Interstate Highway System
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. T ...
. Several other major toll-roads which connected with the Pennsylvania Turnpike were established before the creation of the Interstate Highway System. These were the Indiana Toll Road
The Indiana Toll Road, officially the Indiana East–West Toll Road, is a tolled freeway that runs for east–west across northern Indiana from the Illinois state line to the Ohio state line. It has been advertised as the "Main Street of the ...
, Ohio Turnpike
The Ohio Turnpike, officially the James W. Shocknessy Ohio Turnpike, is a limited-access toll highway in the U.S. state of Ohio, serving as a primary corridor between Chicago and Pittsburgh. The road runs east–west in the northern section of ...
, and New Jersey Turnpike
The New Jersey Turnpike (NJTP) is a system of controlled-access highways in the U.S. state of New Jersey. The turnpike is maintained by the New Jersey Turnpike Authority (NJTA).The Garden State Parkway, although maintained by NJTA, is not consi ...
.
Interstate Highway System
In the United States, beginning in 1956, Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly called theInterstate Highway System
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. Th ...
was built. It uses 12 foot (3.65m) lanes, wide medians
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, th ...
, a maximum of 4% grade
Grade most commonly refers to:
* Grade (education), a measurement of a student's performance
* Grade, the number of the year a student has reached in a given educational stage
* Grade (slope), the steepness of a slope
Grade or grading may also ref ...
, and full access control, though many sections don't meet these standards due to older construction or constraints. This system created a continental-sized network meant to connect every population center of 50,000 people or more.
By 1956, most limited access highways in the eastern United States were toll roads. In that year, the Federal Aid Highway Act of 1956
The Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1956, also known as the National Interstate and Defense Highways Act, was enacted on June 29, 1956, when President Dwight D. Eisenhower signed the bill into law. With an original authorization of $25 billion for t ...
was passed, funding non-toll roads with 90% federal dollars and 10% state match, giving little incentive for states to expand their turnpike system. Funding rules initially restricted collections of tolls on newly funded roadways, bridges, and tunnels. In some situations, expansion or rebuilding of a toll facility using Interstate Highway Program funding resulted in the removal of existing tolls. This occurred in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
on Interstate 64
Interstate 64 (I-64) is an east–west Interstate Highway in the Eastern United States. Its western terminus is at I-70, U.S. Route 40 (US 40), and US 61 in Wentzville, Missouri. Its eastern terminus is at an interchange w ...
at the Hampton Roads Bridge-Tunnel
Hampton may refer to:
Places Australia
*Hampton bioregion, an IBRA biogeographic region in Western Australia
*Hampton, New South Wales
* Hampton, Queensland, a town in the Toowoomba Region
*Hampton, Victoria
Canada
*Hampton, New Brunswick
*Ham ...
when a second parallel roadway to the regional 1958 bridge-tunnel was completed in 1976.
Since the completion of the initial portion of the Interstate Highway System, regulations were changed, and portions of toll facilities have been added to the system. Some states are again looking at toll financing for new roads and maintenance, to supplement limited federal funding. In some areas, new road projects have been completed with public-private partnerships funded by tolls, such as the Pocahontas Parkway
State Route 895 (SR 895), also known as the Pocahontas Parkway and Pocahontas 895, is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. It connects the junction of Interstate 95 and State Route 150 in Chesterfield County with Interstat ...
(I-895) near Richmond, Virginia
(Thus do we reach the stars)
, image_map =
, mapsize = 250 px
, map_caption = Location within Virginia
, pushpin_map = Virginia#USA
, pushpin_label = Richmond
, pushpin_m ...
.
The newest policy passed by Congress and the Obama Administration regarding highways is the Surface and Air Transportation Programs Extension Act of 2011 The Surface and Air Transportation Program Extension Act of 2011 became a United States law when President Barack Obama signed the Act on September 16, 2011 (Public Law No. 112-30). The law extends taxes which fund federal highway expenditures throu ...
.
Pneumatic tyres
 As the horse-drawn
As the horse-drawn carriage
A carriage is a private four-wheeled vehicle for people and is most commonly horse-drawn. Second-hand private carriages were common public transport, the equivalent of modern cars used as taxis. Carriage suspensions are by leather strapping an ...
was replaced by the car
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarded as ...
, bus
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for cha ...
and lorry or truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame construction ...
, and speeds increased, the need for smoother roads and less vertical displacement became more apparent, and pneumatic tyres were developed to decrease the apparent roughness. Wagon
A wagon or waggon is a heavy four-wheeled vehicle pulled by draught animals or on occasion by humans, used for transporting goods, commodities, agricultural materials, supplies and sometimes people.
Wagons are immediately distinguished from ...
and carriage wheel
A wheel is a circular component that is intended to rotate on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machines. Wheels, in conjunction wi ...
s, made of wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin th ...
, had a tyre in the form of an iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
strip that kept the wheel from wearing out quickly. Pneumatic tyres, which had a larger footprint than iron tyres, also were less likely to get bogged down in the mud
A MUD (; originally multi-user dungeon, with later variants multi-user dimension and multi-user domain) is a Multiplayer video game, multiplayer Time-keeping systems in games#Real-time, real-time virtual world, usually Text-based game, text-bas ...
on unpaved roads.
See also
* National Highway System (USA) * Passenger vehicles in the USA *Transportation in the United States
Transportation in the United States is facilitated by road, air, rail, and waterways. The vast majority of passenger travel occurs by automobile for shorter distances, and airplane (or railroad, in some regions) for longer distances. In desc ...
* National Transportation Safety Board
The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) is an independent U.S. government investigative agency responsible for civil transportation accident investigation. In this role, the NTSB investigates and reports on aviation accidents and incid ...
* German autobahns
The (; German plural ) is the federal controlled-access highway system in Germany. The official German term is (abbreviated ''BAB''), which translates as 'federal motorway'. The literal meaning of the word is 'Federal Auto(mobile) Track'. ...
* Glossary of road transport terms
Terminology related to road transport—the transport of passengers or goods on paved (or otherwise improved) routes between places—is diverse, with variation between dialects of English. There may also be regional differences within a single co ...
* Neo-bulk cargo In the ocean shipping trade, neo-bulk cargo is a type of cargo that is a subcategory of general / break-bulk cargo, that exists alongside the other main categories of bulk cargo and containerized cargo. Gerhardt Muller, erstwhile professor at the ...
* Public transport
Public transport (also known as public transportation, public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typical ...
* Traffic congestion
Traffic congestion is a condition in transport that is characterized by slower speeds, longer trip times, and increased vehicular queueing. Traffic congestion on urban road networks has increased substantially since the 1950s. When traffic de ...
* Transportation forecasting
Transportation forecasting is the attempt of estimating the number of vehicles or people that will use a specific transportation facility in the future. For instance, a forecast may estimate the number of vehicles on a planned road or bridge, the r ...
* Transport engineering
Transportation engineering or transport engineering is the application of technology and scientific principles to the planning, functional design, operation and management of facilities for any mode of transportation in order to provide for th ...
* List of roads and highways
List of articles related to roads and highways around the world.
International/World
* Asian Highway Network
* Arab Mashreq International Road Network
* Alaska Highway
* International E-road network
* Pan-American Highway
* Trans-African Highwa ...
Bibliography
*Basil, DavidsonAfrican Civilization Revisited
Africa World Press: 1991 * *
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Road Transport