Tropical Storm Lana (2009) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 2009 Pacific hurricane season was the most active Pacific hurricane season since
 The
The
1994
File:1994 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1994 Winter Olympics are held in Lillehammer, Norway; The Kaiser Permanente building after the 1994 Northridge earthquake; A model of the MS Estonia, which Sinking of the MS Estonia, sank in ...
. The season officially started on May 15 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Pacific basin
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year.
For the first time in ten years, no tropical depressions formed during the month of May. This inactivity continued into the early part of June and was the least active since 1994. The first named storm of the season did not develop until June 21, marking the latest start to a Pacific hurricane season in 40 years. However, according to the NHC's tropical weather summary, August 2009, with seven named storms in their region, was one of the most active Augusts on record for the basin. This level of activity had rarely occurred, if at all, in the past 41 years, since 1968
The year was highlighted by protests and other unrests that occurred worldwide.
Events January–February
* January 5 – "Prague Spring": Alexander Dubček is chosen as leader of the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia.
* Januar ...
, when the most active August on record for the region with eight named storms occurred. When Hurricane Rick reached Category 5 strength on October 17, it became the first Category 5 Pacific hurricane since Ioke in 2006, and the third-strongest Pacific hurricane on record, behind 2015's Patricia
Patricia is a female given name of Latin language, Latin origin. Derived from the Latin word ''Patrician (ancient Rome), patrician'', meaning "noble"; it is the feminine form of the masculine given name Patrick (given name), Patrick. The name Patr ...
and 1997's Linda
Linda may refer to:
As a name
* Linda (given name), a female given name (including a list of people and fictional characters so named)
* Linda (singer) (born 1977), stage name of Svetlana Geiman, a Russian singer
* Anita Linda (born Alice Lake i ...
. The first Central Pacific name to be used was ''Lana'', when it crossed into the region from the Eastern Pacific. With the naming of Tropical Storm Maka on August 11, this season became the first in seven years to use multiple Central Pacific names.
__TOC__
Seasonal forecasts
On May 21, 2009,NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditio ...
released their forecast for the 2009 Eastern Pacific and Central Pacific hurricane seasons. They predicted a below-normal level of activity in the Eastern Pacific, with 13 to 18 named storms, of which 6 to 10 were expected to become hurricanes, and 2 to 5 expected to become major hurricanes. The forecast was based on the dissipation of a La Niña
La Niña (; ) is an oceanic and atmospheric phenomenon that is the colder counterpart of as part of the broader El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) climate pattern. The name ''La Niña'' originates from Spanish for "the girl", by an ...
in April 2009. Sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature (SST), or ocean surface temperature, is the ocean temperature close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the sea surface. Air mass ...
s were near normal around the equator makes the season an ENSO-neutral. Additionally, an El Niño
El Niño (; ; ) is the warm phase of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and is associated with a band of warm ocean water that develops in the central and east-central equatorial Pacific (approximately between the International Date L ...
was forecast to develop during the latter part of the season. Depending on the intensity of the El Niño, forecasters were unsure of whether or not it would have an effect on the overall activity in the basin. However, due to the low-activity cycle that began in 1995, the El Niño only brought the activity to a slightly above normal season.
The Central Pacific basin was also expected to be slightly below average, with three to five tropical cyclones expected to form or cross into the area. However, it was slightly more active than expected, the number of three to five was exceeded, as seven tropical cyclones moved into or formed in the Central Pacific.
Seasonal summary
 The
The accumulated cyclone energy
Accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) is a metric used by various agencies to express the energy released by a tropical cyclone during its lifetime. It is calculating by summing the square of a tropical cyclone's maximum sustained winds, measured ever ...
(ACE) index for the 2009 Pacific hurricane season as calculated by Colorado State University using data from the National Hurricane Center was 126.4 units. Broadly speaking, ACE is a measure of the power of a tropical or subtropical storm multiplied by the length of time it existed. It is only calculated for full advisories on specific tropical and subtropical systems reaching or exceeding wind speeds of .
The season was characterized as "near-normal", featuring 17 named storms 8 hurricanes and 5 major hurricanes. The central Pacific experienced above-average activity with three additional storms forming west of 140°W and three more crossing over from the eastern Pacific. The overall number of storms contrasted to a relative lull in activity experienced over the previous decade. During the course of the year, large-scale factors such as an El Niño and two Madden–Julian oscillation
The Madden–Julian oscillation (MJO) is the largest element of the intraseasonal (30- to 90-day) variability in the tropical atmosphere. It was discovered in 1971 by Roland Madden and Paul Julian of the American National Center for Atmospheric R ...
s greatly contributed to the changed pattern. The season's activity, east of 140°W, was reflected with a near-average cumulative accumulated cyclone energy
Accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) is a metric used by various agencies to express the energy released by a tropical cyclone during its lifetime. It is calculating by summing the square of a tropical cyclone's maximum sustained winds, measured ever ...
(ACE) rating of 100, roughly 94% of the 30-year median. ACE is, broadly speaking, a measure of the power of the hurricane multiplied by the length of time it existed, so storms that last a long time, as well as particularly strong hurricanes, have high ACEs. ACE is only calculated for full advisories on tropical systems at or exceeding or tropical storm strength.
The season started at a below-average pace, with only one named storm forming by the end of June. This marked the first time since 2000
File:2000 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Protests against Bush v. Gore after the 2000 United States presidential election; Heads of state meet for the Millennium Summit; The International Space Station in its infant form as seen from ...
that no tropical storms formed during the month of May; however, on average only one storm develops in the month every other year. The ten-year span of May named storms marked the longest occurrence of this event. The first hurricane of the year, Hurricane Andres The name Andres has been used for eight tropical cyclones in the Eastern Pacific Ocean:
* Hurricane Andres (1979), made landfall in Mexico as a tropical depression.
* Tropical Storm Andres (1985), formed near the Mexican coast but moved out to sea.
...
, also became the first June hurricane since Hurricane Carlotta in 2000. Below-average activity continued into July with four named storms forming. By the end of the month, season to date ACE values were roughly 37% of the long-term mean, the sixth lowest since reliable records began in 1971.
An abrupt shift in activity took place during August as seven named storms formed, three of which became major hurricanes. This marked the most storms to form in a single month since 1985
The year 1985 was designated as the International Youth Year by the United Nations.
Events January
* January 1
** The Internet's Domain Name System is created.
** Greenland withdraws from the European Economic Community as a result of a ...
and the most in August since 1968
The year was highlighted by protests and other unrests that occurred worldwide.
Events January–February
* January 5 – "Prague Spring": Alexander Dubček is chosen as leader of the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia.
* Januar ...
. Of these storms, Hurricane Jimena became the first cyclone of the season to make landfall
Landfall is the event of a storm moving over land after being over water. More broadly, and in relation to human travel, it refers to 'the first land that is reached or seen at the end of a journey across the sea or through the air, or the fact ...
, as well as the strongest storm to strike the west coast Baja California Sur
Baja California Sur (; 'South Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California Sur ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California Sur), is the least populated state and the 31st admitted state of the 32 federal ent ...
, alongside Hurricane Norbert The name Norbert has been used for five tropical cyclones in the Eastern Pacific Ocean:
* Hurricane Norbert (1984) – took an erratic track several hundred miles south of Baja California, making landfall there
* Hurricane Norbert (1990) – stayed ...
in 2008
File:2008 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Lehman Brothers went bankrupt following the Subprime mortgage crisis; Cyclone Nargis killed more than 138,000 in Myanmar; A scene from the opening ceremony of the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing; ...
. Following the well-above average August, September experienced below-average activity with ACE reaching 70% of the long-term mean. The final month of activity featured the third-strongest storm on record in the eastern Pacific: Hurricane Rick The name Rick has been used for six tropical cyclones worldwide.
In the Eastern Pacific:
* Hurricane Rick (1985), strong Category 4 hurricane, never a threat to land
* Hurricane Rick (1997), weak Category 2 hurricane, made landfall near Puerto Esco ...
. A Category 5 storm, Rick attained winds of off the coast of Mexico on October 18 before succumbing to increased wind shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal ...
and dry air. ACE for the month was 59% above average, mostly attributed to Rick.
Systems
Tropical Depression One-E
The first system of the season, One-E formed out of atropical wave
A tropical wave (also called easterly wave, tropical easterly wave, and African easterly wave), in and around the Atlantic Ocean, is a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which ...
on June 18 roughly south-southwest of Mazatlán
Mazatlán () is a city in the Mexican state of Sinaloa. The city serves as the municipal seat for the surrounding ''municipio'', known as the Mazatlán Municipality. It is located at on the Pacific coast, across from the southernmost tip of ...
and initially tracked slowly northwards. Throughout the day, convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convec ...
developed around the center of circulation and the system was anticipated to become a tropical storm. Late on June 18, the National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 3 ...
noted that the system was on the verge of becoming a tropical storm. However, the following day, strong wind shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal ...
caused the depression to rapidly degenerate into a trough
Trough may refer to:
In science
* Trough (geology), a long depression less steep than a trench
* Trough (meteorology), an elongated region of low atmospheric pressure
* Trough (physics), the lowest point on a wave
* Trough level (medicine), the l ...
of low pressure before dissipating off the coast of Sinaloa
Sinaloa (), officially the Estado Libre y Soberano de Sinaloa ( en, Free and Sovereign State of Sinaloa), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is d ...
.
Although no longer a tropical cyclone, the remnants of the depression brought moderate rainfall to parts of Sinaloa, Nayarit
Nayarit (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Nayarit ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Nayarit), is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 20 municipalities and its ...
and Jalisco
Jalisco (, , ; Nahuatl: Xalixco), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Jalisco ; Nahuatl: Tlahtohcayotl Xalixco), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal En ...
. High winds accompanied the rainfall and left about 50,000 residences without power. Several trees were downed and some structures sustained damage from fresh water flooding. Landslides occurred along major highways and significant structural damage was reported around Mazatlán. However, there was no loss of life or reports of injuries.
Hurricane Andres
Hurricane Andres formed on June 21 out of an area of disturbed weather associated with a shower and thunder storm that crossed Central America a few days earlier. Andres gradually intensified as it tracked along the Mexican coastline. Deepconvection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convec ...
developed around the center of circulation and by June 23, the storm attained hurricane-status, peaking with winds of . Upon attaining this intensity, the storm featured a developing eyewall
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather at the center of tropical cyclones. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area, typically in diameter. It is surrounded by the ''eyewall'', a ring of towering thunderstorms where the most severe weat ...
within a central dense overcast
The central dense overcast, or CDO, of a tropical cyclone or strong subtropical cyclone is the large central area of thunderstorms surrounding its circulation center, caused by the formation of its eyewall. It can be round, angular, oval, or irr ...
. Within 36 hours, the storm rapidly degenerated, having most of the convection being displaced by high wind shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal ...
, becoming a non-tropical trough
Trough may refer to:
In science
* Trough (geology), a long depression less steep than a trench
* Trough (meteorology), an elongated region of low atmospheric pressure
* Trough (physics), the lowest point on a wave
* Trough level (medicine), the l ...
during the afternoon of June 24.
Prior to becoming a tropical depression, Andres produced heavy rainfall Oaxaca
Oaxaca ( , also , , from nci, Huāxyacac ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca), is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of Mexico. It is ...
and Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Oce ...
, resulting in two deaths. Rough seas off the coast of Guerrero
Guerrero is one of the 32 states that comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 81 municipalities and its capital city is Chilpancingo and its largest city is Acapulcocopied from article, GuerreroAs of 2020, Guerrero the pop ...
resulted in one fatality. Inland, flooding caused by heavy rains killed two people and injured twenty. Several dozen structures were damaged and a few were destroyed. Following the storm, roughly 350 people were left homeless.
Tropical Storm Blanca
A tropical wave exited the western coast of Africa on June 19, which moved westward across the Atlantic without development. By June 29, the wave crossed Central America into the eastern Pacific. Thunderstorms increased over the next several days, which organized into curved rainbands around a developing low-pressure area on July 4. Following further organization, the system developed into a tropical depression on July 6, located roughly 435 miles (700 kilometres) south ofCabo San Lucas, Mexico
Cabo San Lucas (, "Saint Luke Cape"), or simply just Cabo, is a resort city at the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula, in the Mexican state of Baja California Sur. As at the 2020 Census, the population of the city was 202,694 inhabitan ...
. Soon after, it strengthened into Tropical Storm Blanca. Operationally, the NHC classified the system immediately as a tropical storm. At that time, Blanca developed an eye-feature, though it was not expected to develop into a hurricane. Steered by a ridge to the north, the storm moved west-northwestward throughout its existence. Early on July 7, Blanca attained peak winds of and a barometric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 7 ...
of 998 mbar (hPa; ). The storm's convection developed into a central dense overcast
The central dense overcast, or CDO, of a tropical cyclone or strong subtropical cyclone is the large central area of thunderstorms surrounding its circulation center, caused by the formation of its eyewall. It can be round, angular, oval, or irr ...
over the center, which soon began deteriorating, with cloud tops warming and convection shrinking. By late on July 7, the center became devoid of shower and thunderstorm activity, with only intermittent convection. On July 8, Blanca weakened into a tropical depression, and the next day it degenerated into a remnant low. Although no longer a tropical cyclone, the remnants of Blanca maintained a well-defined low pressure center as it continued its northwesterly movement. Early on July 11, the system turned northward and gradually weakened. By the following day, Blanca had dissipated over open waters.
Due to the developing storm, Mexican officials posted high seas advisories for Michoacán
Michoacán, formally Michoacán de Ocampo (; Purépecha: ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Michoacán de Ocampo ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Michoacán de Ocampo), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of ...
, Jalisco
Jalisco (, , ; Nahuatl: Xalixco), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Jalisco ; Nahuatl: Tlahtohcayotl Xalixco), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal En ...
, Nayarit
Nayarit (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Nayarit ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Nayarit), is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 20 municipalities and its ...
, Baja California Sur
Baja California Sur (; 'South Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California Sur ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California Sur), is the least populated state and the 31st admitted state of the 32 federal ent ...
and Colima
Colima (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Colima ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Colima), is one of the 31 states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It shares its name with its capital and ...
, and advised ships to remain at port in July 6. These advisories were discontinued the following day as Blanca moved out to sea. Moisture from the system enhanced a frontal system
A weather front is a boundary separating air masses for which several characteristics differ, such as air density, wind, temperature, and humidity. Disturbed and unstable weather due to these differences often arises along the boundary. For ins ...
over Coahuila
Coahuila (), formally Coahuila de Zaragoza (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Coahuila de Zaragoza ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Coahuila de Zaragoza), is one of the 32 states of Mexico.
Coahuila borders the Mexican states of N ...
. The system produced upwards of in the span of a few hours, triggering flooding throughout the state. Numerous streets were closed due to flooding and local fire departments were deployed to assist in draining the water. No injuries or structural damage resulted from the flooding. The remnants of the storm also brought unseasonable rainfall, although negligible, to parts of southern and central California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
on July 11. The moisture reached the region after being pulled northward by an upper-level low off the coast of Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
.
Hurricane Carlos
A tropical wave departed the west coast of Africa on June 25, which moved across the Atlantic without development. The wave entered the eastern Pacific on July 4, later developing more convection on July 8 to the south of Mexico. Early on July 10, convective banding features developed along the periphery of the system and anarea of low pressure
In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather (such as cloudy, windy, with possible ...
developed within the wave. On July 10, the NHC designated the system as Tropical Depression Four-E about 900 mi (1,450 km) south of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula. Soon after, it strengthened into Tropical Storm Carlos while moving westward through an area of warm waters and light wind shear. On July 11, Carlos intensified further into a minimal hurricane. At that time, the small storm developed a small eye-like feature, which had disappeared the next day, causing Carlos to weaken back into a tropical storm. The eye feature redeveloped, signaling that Carlos reintensified into a hurricane on July 14, reaching peak winds of early the next day. Located at 10.1ºN, this made Carlos the southernmost Category 2 hurricane in the eastern Pacific proper. Late on July 15, the hurricane encountered strong wind shear, resulting in rapid weakening. About 24 hours after its peak intensity, Carlos deteriorated into a tropical depression, and dissipated early on July 17 well to the southeast of Hawaii.
Tropical Storm Dolores
On July 11, a broad area of low pressure developed within atropical wave
A tropical wave (also called easterly wave, tropical easterly wave, and African easterly wave), in and around the Atlantic Ocean, is a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which ...
several hundred miles south of Acapulco, Mexico
Acapulco de Juárez (), commonly called Acapulco ( , also , nah, Acapolco), is a city and major seaport in the state of Guerrero on the Pacific Coast of Mexico, south of Mexico City. Acapulco is located on a deep, semicircular bay and has bee ...
. Shower and thunderstorm activity associated with the system gradually increased over the next several days as it tracked west-northwestward. By July 15, the low became sufficiently organized and was declared a tropical depression roughly of Manzanillo, Colima
Manzanillo () is a city and seat of Manzanillo Municipality, in the Mexican state of Colima. The city, located on the Pacific Ocean, contains Mexico's busiest port, responsible for handling Pacific cargo for the Mexico City area. It is the larges ...
. Turning towards the northwest in response to a ridge
A ridge or a mountain ridge is a geographical feature consisting of a chain of mountains or hills that form a continuous elevated crest for an extended distance. The sides of the ridge slope away from the narrow top on either side. The line ...
over Mexico, the depression intensified into Tropical Storm Dolores later that day. Despite southwesterly wind shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal ...
displacing the center of Dolores from the deepest convection, the system continued to strengthen, attaining peak winds of on July 16. Shortly thereafter, convection associated with the storm dissipated, possibly due to entrainment of dry air. Later that day the system degenerated into a remnant low and gradually weakened. The remnants of Dolores eventually dissipated on July 19, roughly west-southwest of Los Angeles.
Tropical Storm Lana
On July 30, the NHC began issuing advisories on Tropical Depression Six-E near theCentral Pacific Hurricane Center
The Central Pacific Hurricane Center (CPHC) of the United States National Weather Service is the official body responsible for tracking and issuing tropical cyclone warnings, watches, advisories, discussions, and statements for the Central Pacifi ...
's area of responsibility. Later that day, it moved into the Central Pacific as a tropical depression, quickly strengthening into Tropical Storm Lana, the first Central Pacific storm since Kika (2008). Lana is one of six central Pacific tropical cyclones to form as a depression in the eastern Pacific but be named in the Central; the others were Lala
Lala may refer to:
Geography
* Lala language (disambiguation) Places
* Lala (Naples Metro), an underground metro station in Naples, Italy
* Lala, Assam, a town in Assam, India
* Lala, Ilam, a village in Ilam Province, Iran
* Lala, Lanao del No ...
, Iniki, Li, Ela
Ela or ELA may refer to:
Companies and organizations
* Basque Workers' Solidarity (Basque: '), a trade union
* Earth Liberation Army
* ELA Aviación, a Spanish aircraft manufacturer
* English Lacrosse Association
* Equatorial Launch Australia, ...
and Ulika. Lana was also the first tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
to cross from the eastern north to central north Pacific since Flossie (2007). It also started to develop an eye feature, based on satellite imagery. But, southerly shear, introduced by a large upper-level trough, caused Lana to become slightly disorganized on July 31. Despite this, Lana reached its peak intensity of early on August 1, and slowly weakened to become a very disorganized, yet still fairly strong tropical storm, maintaining maximum winds of for the next couple of days. However, Lana weakened to a tropical depression late on August 2, while continuing to quickly become disorganized. Lana degenerated to a remnant low on 00:00 UTC of August 3, roughly southwest of Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the island ...
, and east of Johnston Island
Johnston Atoll is an unincorporated territory of the United States, currently administered by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS). Johnston Atoll is a National Wildlife Refuge and part of the Pacific Remote Islands Marine Nation ...
, with the CPHC issuing their last advisory at the same time. Lana's remnants lingered for six hours before dissipating by 06:00 UTC.
Tropical Storm Enrique
Tropical Storm Enrique developed out of a broad area of low pressure several hundred miles south-southwest ofBaja California Sur
Baja California Sur (; 'South Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California Sur ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California Sur), is the least populated state and the 31st admitted state of the 32 federal ent ...
. The center of circulation was embedded within a central dense overcast and located within an area favoring further development. The depression tracked just north of due west in response to a mid-tropospheric ridge north of the system. Upon becoming a tropical cyclone, a second area of low pressure, that would later become Hurricane Felicia located nine degrees of longitude to the west, had the possibility to develop into a tropical depression and possibly influence the system. Late on August 3, the depression intensified to a tropical storm and was given the name ''Enrique''. Enrique strengthened to reach a peak intensity of on August 4. However, interaction with Hurricane Felicia weakened the system late that evening, with maximum winds decreasing to 50 mph. Enrique maintained winds of for the next day or so, until early on August 6, when the NHC downgraded Enrique to depression status. On August 7, the NHC issued their final advisory on Enrique as the system degenerated into a remnant low.
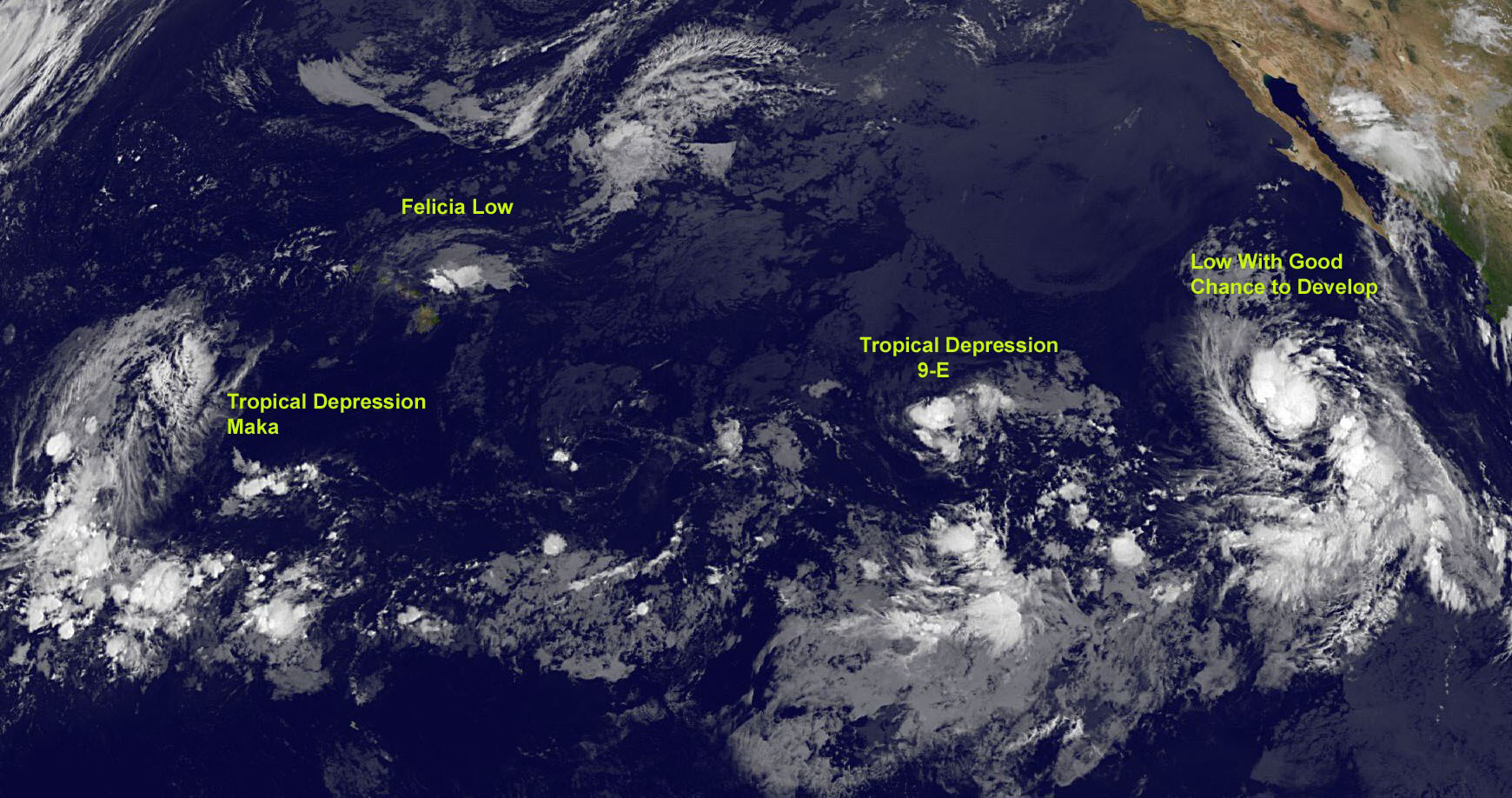
Hurricane Felicia
Hurricane Felicia developed out of a broad area of low pressure that formed several hundred miles southwest ofBaja California Sur
Baja California Sur (; 'South Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California Sur ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California Sur), is the least populated state and the 31st admitted state of the 32 federal ent ...
on August 3, developing into Tropical Depression Eight-E the next day, shortly after Tropical Depression Seven-E formed directly to the east. It strengthened into a tropical storm and was named Felicia early on August 4. It rapidly strengthened that morning as an eyewall quickly developed, the rapid intensification being attributed to warm water along the forecast track, which allowed for more rapid intensification. Felicia continued to intensify and became a hurricane that afternoon. Rapid intensification continued into that evening, and the NHC upgraded Felicia to a Category 2 hurricane. It continued to rapidly strengthen, becoming the first major hurricane of the season on the morning of August 5, when the NHC upgraded it to a Category 3 hurricane. Later that day, Felicia rapidly intensified to a Category 4 hurricane, with maximum winds increasing to , making it the strongest storm in the Eastern Pacific since Daniel
Daniel is a masculine given name and a surname of Hebrew origin. It means "God is my judge"Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 68. (cf. Gabriel—"God is my strength" ...
in 2006
File:2006 Events Collage V1.png, From top left, clockwise: The 2006 Winter Olympics open in Turin; Twitter is founded and launched by Jack Dorsey; The Nintendo Wii is released; Montenegro 2006 Montenegrin independence referendum, votes to declare ...
. The NHC predicted that Felicia would rapidly weaken during the next couple of days starting on August 6, but it was also noted by the NHC that Felicia was displaying annular hurricane characteristics, which would allow for it to maintain intensity for longer than expected over marginal SSTS.
On August 8 it crossed into the Central Pacific basin, gradually weakening to a tropical storm and then a tropical depression as it approached the Hawaiian Islands. Tropical storm and flash flood watches were issued on August 7 for the Big Island of Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii ) is the List of islands of the United States by area, largest island in the United States, located in the U.S. state, state of Hawaii. It is the southeasternmost of the Hawaiian Islands, a chain of High island, volcanic ...
and Maui County
Maui County, officially the County of Maui, is a county in the U.S. state of Hawaii. It consists of the islands of Maui, Lānai, Molokai (except for a portion of Molokai that comprises Kalawao County), Kahoolawe, and Molokini. The latter two ar ...
, and were extended to include Oahu
Oahu () (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Oʻahu'' ()), also known as "The Gathering place#Island of Oʻahu as The Gathering Place, Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million people—over t ...
on August 9. The watches for the Big Island were later canceled as the track for Felicia appeared to turn toward the north. All watches were canceled at 11 a.m. HST August 11 as Felicia dissipated to a remnant low.
Tropical Depression Nine-E
Tropical Depression Nine-E developed out of a small area of low pressure west-southwest of Baja California on August 9. Nine-E initially formed as a tropical wave that had entered the eastern Pacific on August 1, but was ill-defined, and difficult to trace. The NHC had initially forecast Nine-E to strengthen to a tropical storm by August 10, but moderate shear inhibited development, and the depression was no longer forecast to strengthen to a tropical storm, as the shear inhibited deep convection within the depression's circulation. Shear continually inhibited development until the end, when Nine-E degenerated to a remnant low on August 12. The next day, the NHC noted the possibility for regeneration of the system, although, by late on the 14th, the disturbance had weakened, and was becoming embedded in theITCZ
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal e ...
, as a result, the probability for regeneration was low. Nine-E's remnants dissipated on August 15, while located just within the central Pacific.
Tropical Storm Maka
Tropical Storm Maka was first identified on August 8, 2009 by theCentral Pacific Hurricane Center
The Central Pacific Hurricane Center (CPHC) of the United States National Weather Service is the official body responsible for tracking and issuing tropical cyclone warnings, watches, advisories, discussions, and statements for the Central Pacifi ...
(CPHC) as an area of disturbed weather roughly south of Lihue, Hawaii
Lihue or Līhue is an unincorporated community, census-designated place (CDP) and the county seat of Kauai County, Hawaii, United States. Lihue (pronounced ) is the second largest town on the Hawaiian island of Kauai after Kapaa. As of the 2010 ...
. Situated over warm waters, estimated at and within an area of low wind shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal ...
, the system gradually intensified as it tracked northwestward in response to a subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Geographical z ...
ridge
A ridge or a mountain ridge is a geographical feature consisting of a chain of mountains or hills that form a continuous elevated crest for an extended distance. The sides of the ridge slope away from the narrow top on either side. The line ...
to the north. By August 11, convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convec ...
had consolidated around an area of low pressure
In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather (such as cloudy, windy, with possible ...
that formed within the system. Since further development was expected, a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert
A Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (TCFA) is a bulletin released by the U.S. Navy-operated Joint Typhoon Warning Center in Honolulu, Hawaii or the Fleet Weather Center in Norfolk, Virginia, warning of the possibility of a tropical cyclone forming ...
was issued. Shortly thereafter, the CPHC upgraded the low to a tropical depression, assigning it with the identifier One-C. Over the following 12 hours, further development took place, and the depression intensified into a tropical storm. Upon attaining this intensity, the storm was given the name ''Maka'' from the list of names for the Central Pacific basin. The next afternoon, the final advisory on Maka was issued as it degenerates into a remnant low. The remnants of Tropical Storm Maka crossed the International Date Line and moved into the Western Pacific, regenerating into a tropical depression.
Hurricane Guillermo
Hurricane Guillermo formed on August 12 from a broad area of low pressure nearly SW ofBaja California
Baja California (; 'Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California), is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mex ...
. The system developed a good series of banding features and convection, and as a result, in the afternoon later that day, it strengthened into a tropical storm, the seventh in the eastern Pacific that year. On August 14, it strengthened to become the fourth hurricane of the season, concurrent to the development of a good, banding type eye. That afternoon, Guillermo strengthened to a Category 2 hurricane with maximum winds increasing to . Early on August 15, Guillermo intensified to become the second major hurricane of the season, as it was upgraded by the NHC to a Category 3 hurricane, with maximum winds increasing to . On August 16 it crossed into the Central Pacific basin as a Category 1 hurricane, and then quickly weakened to a tropical storm thereafter due to very high wind shear. Despite over very strong as high as of shear, Guillermo survived as a weak tropical storm for a further 3 days before weakening to a depression and degenerating to a remnant low on August 19, near the West Coast. However, the remnants continued to curve towards the northeast for the next several days, before finally dissipating on August 23.
Although Guillermo remained well away from land, large swells produced by the system resulted in surf along the eastern coasts of the Hawaiian Islands between August 18 and 19.
Tropical Storm Hilda
Tropical Depression Eleven-E formed toward the western edge of the eastern Pacific basin on August 22, and soon strengthened to become Tropical Storm Hilda. The next day it crossed the 140°W meridian and passed into the CPHC's area of responsibility. On August 26, Hilda quickly weakened to a depression after several small pulses of brief convection in the disorganized center, but these waned quickly when it weakened to depression status. Hilda also attempted, but failed, to reorganize its overall structure throughout the late 25th and most of the 26th. The system's structure continued to degrade, and finally, on August 28, the CPHC issued their final advisory on Hilda, as it had degenerated into a remnant low. The remnants of Hilda lingered for several days, until finally dissipating on August 31.Tropical Storm Ignacio
Ignacio formed as a portion of the same tropical wave that caused the formation of Tropical Storm Ana in the Atlantic. The portion of the wave that would become Ignacio crossed Central America on August 16. While the wave axis was located over the eastern Pacific on August 20, shower and thunderstorm activity began to increase, but associated convection remained minimal. Two days later, on August 22, the wave transformed into a broad area of low pressure, with convective activity organizing enough over the next couple of days to be classified as Tropical Depression Twelve-E on August 24 about SW of the southern tip of the Baja California peninsula. Thoughconvection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convec ...
within the rainband
A rainband is a cloud and precipitation structure associated with an area of rainfall which is significantly elongated. Rainbands can be stratiform or convective, and are generated by differences in temperature. When noted on weather radar ima ...
located along the western semicircle of the system diminished somewhat, the system continued to become better organized, and became a tropical storm that evening, receiving the name ''Ignacio''. Despite the upgrade, the storm was not well organized, with several smaller circulations rotating around the center of circulation. Ignacio weakened to a tropical depression on the morning of August 27, as it moved over sub-26 °C SSTs, the lowest temperature needed to support a tropical cyclone, and entered an environment of stable air. The system continued to weaken, and Ignacio degenerated into an area of low pressure later on that day.
Hurricane Jimena
Originating from a tropical wave that moved off the western coast of Africa on August 15, an area of disturbed weather associated with the tropical wave had formed in the westernCaribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
. Moving across Central America earlier in the week, and slowly developed off the west coast of Mexico, about south of Acapulco
Acapulco de Juárez (), commonly called Acapulco ( , also , nah, Acapolco), is a city and major seaport in the state of Guerrero on the Pacific Coast of Mexico, south of Mexico City. Acapulco is located on a deep, semicircular bay and has bee ...
, until it organized into a tropical depression early in the morning of August 29. It soon strengthened to become Tropical Storm Jimena, and intensified rapidly to become a Category 2 hurricane later the same day as a pinhole eye developed. The next day it strengthened into a Category 3 hurricane, becoming the third major hurricane of season. Later that day, it continued to intensify and became a Category 4 hurricane. However, by the morning of August 31, the eye had become less defined, likely because of an eyewall replacement cycle. As Jimena moved over cooler waters, and shear began to increase, it began to weaken starting on September 1, weakening below major hurricane status later that day. The storm soon made first landfall of the season as a weak Category 2 early the next day near Cabo San Lazaro Cabo is Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for cape. It may refer to:
* Cabo San Lucas, a resort city in Baja California Sur, Mexico
* Cabó, a municipality in Alt Urgell, Lleida, Catalonia, Spain
Other places
* Cabo Blanco, Costa Rica
* Cabo Corr ...
, Mexico. Jimena then made second landfall near Cabo San Lázaro
Cabo San Lázaro is a cape in the municipality of Comondú, in the Mexican state of Baja California Sur.
Geography
The headland lies on a sand bar separating the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's f ...
at the same intensity just after re-entering Pacific. Moving over land, Jimena weakened into a Category 1 later that day, only to move back offshore as a Category 1 hurricane. The hurricane made a third landfall near San Junacio with winds. Finally, around 03:00 UTC of September 3, Jimena weakened to a tropical storm, but despite reemerging in the Gulf of California, Jimena continued to weaken due to increased wind shear. On September 4, the storm weakened into a tropical depression and made a fourth and final landfall near Santa Rosalía, Baja California Sur
Santa Rosalía is a city and municipal seat of Mulegé Municipality, in Baja California Sur, situated along the Gulf of California. Located on the east coast of the Baja Peninsula, the town had a population of 14,160 inhabitants in 2015. The ci ...
. Five hours after Jimena made the final landfall, Jimena degenerated into a remnant low and dissipated by September 5.
Owing to the storm's slow movement, torrential rains fell over much of Baja California Sur and Sinaloa, resulting in widespread flooding. In Guaymas
Guaymas () is a city in Guaymas Municipality, in the southwest part of the state of Sonora, in northwestern Mexico. The city is south of the state capital of Hermosillo, and from the U.S. border. The municipality is located on the Gulf of Califo ...
, a record of rain fell in association with Jimena. According to a report by Mexico's Centro Nacional de Prevención de Desastres, the magnitude of the event was analyzed to be a once in 2000 year occurrence. Thousands of homes were damaged or destroyed across Baja California and much of Puerto Lopez Mateos was leveled. Significant damage to infrastructure not only left people without water and power, it hampered relief efforts as many towns were isolated from surrounding areas. At least six people were killed and an estimated 72,000 were affected across the region. Total losses related to Hurricane Jimena reached 2.3 billion pesos
The peso is the monetary unit of several countries in the Americas, and the Philippines. Originating in the Spanish Empire, the word translates to "weight". In most countries the peso uses the same sign, "$", as many currencies named "dollar" ...
($173.9 million).
Tropical Depression Two-C
A small area of disturbed weather developed into Tropical Depression Two-C to the southwest ofKauai
Kauai, () anglicized as Kauai ( ), is geologically the second-oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands (after Niʻihau). With an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), it is the fourth-largest of these islands and the 21st largest island ...
at 1200 UTC on August 28. Despite favorable conditions, sustained winds did not exceed . Early the next day, the depression crossed the International Date Line
The International Date Line (IDL) is an internationally accepted demarcation on the surface of Earth, running between the South and North Poles and serving as the boundary between one calendar day and the next. It passes through the Pacific O ...
and warning responsibility of the system was passed on to the Japan Meteorological Agency
The , abbreviated JMA, is an agency of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. It is charged with gathering and providing results for the public in Japan that are obtained from data based on daily scientific observation an ...
. By August 30, the depression began weakening and degenerated back into an area of disturbed weather. The remnants tracked further west-northwestward into the West Pacific for the next few days, before dissipating early on September 2.
Tropical Storm Kevin
Kevin formed from Tropical Depression Fourteen-E on August 29 from an area of disturbed weather southwest ofBaja California
Baja California (; 'Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California), is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mex ...
. The system strengthened to Tropical Storm Kevin later that day. Kevin began to weaken early on August 30, and this trend continued for the next day or so, until early on the 31st, when Kevin weakened to a tropical depression. Kevin continued to degrade, and the NHC declared it dissipated on September 1, as it had weakened to a remnant low. It finally was absorbed into the ITCZ in the area of Central Pacific on September 8, seven days after it had weakened into a remnant low.
Hurricane Linda
Atropical wave
A tropical wave (also called easterly wave, tropical easterly wave, and African easterly wave), in and around the Atlantic Ocean, is a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which ...
exited Africa into the Atlantic Ocean on August 18, and the northern portion split to become Tropical Storm Danny. The wave continued westward without development, crossing Central America into the Pacific Ocean on August 28. Convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convec ...
remained minimal until September 3, when the system became better organized. A Low-pressure area
In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather (such as cloudy, windy, with possible ...
developed on September 6, and deep convection consolidated around the circulation. Early on September 7, the National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 3 ...
(NHC) designated the low as Tropical Depression Fifteen-E about west-southwest of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula. Moving over warm water temperatures and modest wind shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal ...
, gradual intensification was anticipated. The depression moved slowly to the west due to a weakening subtropical ridge
The horse latitudes are the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. They are characterized by sunny skies, calm winds, and very little precipitation. They are also known as Subtropics, subtropical ridges, or highs. It is a h ...
to its north. Shortly after developing, the depression intensified into Tropical Storm Linda. By September 9, a new ridge developed east of Linda, causing the storm to turn northwestward. Despite intensifying into a strong tropical storm, Linda's low-level circulation was misaligned from its upper circulations, although the system developed expansive outflow
Outflow may refer to:
*Capital outflow, the capital leaving a particular economy
*Bipolar outflow, in astronomy, two continuous flows of gas from the poles of a star
*Outflow (hydrology), the discharge of a lake or other reservoir system
* Outflow ...
to the south and east.
Late on September 9, Linda attained hurricane status, and although an eye
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and conv ...
developed, it was not over the center due to increasing wind shear. Early on September 10, Linda attained peak winds of and a pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and e ...
of . Operationally, the NHC assessed Linda to have been slightly stronger with peak winds of . Persistent wind shear eroded the eyewall and led to weakening. Compounded with decreasing water temperatures, Linda deteriorated to tropical storm status early on September 11. At that time, the center became exposed and lacked deep convection. After the intrusion of dry air, the convection dissipated, and late on September 11, the NHC issued their final advisory on Linda after it degenerated into a remnant low. At this time, the system weakened below tropical storm intensity. The remnants of Linda persisted for several more days, initially tracking southwest before turning due west. The system eventually dissipated on September 15 roughly east of the Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kur ...
.
Tropical Storm Marty
Tropical Storm Marty can be track back from an area of thunderstorm activity associated with atropical wave
A tropical wave (also called easterly wave, tropical easterly wave, and African easterly wave), in and around the Atlantic Ocean, is a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which ...
that were off the south coast of Mexican state of Guerrero
Guerrero is one of the 32 states that comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 81 municipalities and its capital city is Chilpancingo and its largest city is Acapulcocopied from article, GuerreroAs of 2020, Guerrero the pop ...
on September 11. A weak mid-level cyclonic circulation was also find near that wave. Clusters of scattered convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convec ...
developed south of the circulation despite strong easterly wind shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal ...
. Then the National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 3 ...
(NHC) began to issue Tropical Weather Outlooks for that wave around 11 am EDT (1900 UTC on September 13). The wave was part of a large area of disorganized multilayered clouds which is basically tied into a large monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
al circulation. It became better organized on the afternoon of September 14 with scattered convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convec ...
occurring and also developing a 1008 milibar (29.77 inHg) surface low. The NHC upgraded it to a tropical depression
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
, around 4 am PDT (1200 UTC on September 16) while it was located about south-southwest of Cabo San Lucas
Cabo San Lucas (, "Saint Luke Cape"), or simply just Cabo, is a resort city at the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula, in the Mexican state of Baja California Sur. As at the 2020 Census, the population of the city was 202,694 inhabitan ...
, Mexico. As it was numbered, the circulation of Sixteen-E finally began to separate from the northeast end of the elongated monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
al like circulation. It was named Marty six hours later as it became a tropical storm
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
with winds of and a barometric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 7 ...
of 1003 mbar (hPa; ). Despite becoming a tropical storm
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
, the low level circulation center of Marty was located on the eastern edge of its deep convection
Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air masses lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the ...
, possibly due to the influence of a ridge of high pressure locating inland Mexico. Marty moved slowly, and did not become significantly better organized although associating with deep convective activity. It began to slowly weaken after reaching a peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of and a barometric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 7 ...
of 1001 mbar (hPa; ). Despite this, and reaching sub-26.5 °C water temperatures, Marty managed to remain at tropical storm strength until 1800 UTC on the 18th, when it finally weakened back to depression strength. With all environmental factors against it, and almost completely devoid of any convection, on September 19, the NHC issued their last advisory on Marty as it had weakened into a remnant low. The remnants lingered until eventual complete dissipation on September 23.
Tropical Storm Nora
On September 21, a broad area of low pressure formed about 900 miwest-southwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
of the southern tip of Baja California
Baja California (; 'Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California), is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mex ...
. The disturbance slowly started to organize, strengthening into a tropical depression late on September 22 (September 23 in UTC time). On the early morning of September 23, the depression strengthened into a tropical storm and received the name Nora. On September 23, Tropical Storm Nora reached a peak intensity of before starting to weaken back into a depression on September 24. Early on September 25, the NHC issued their last advisory on Nora, as it weakened into a remnant low. However, the remnant low of Nora continued to drift westward for the next 4 days, before dissipating on September 29.
Tropical Storm Olaf
Tropical Depression Eighteen-E formed from a broad area of low pressure on October 1, and quickly strengthened to become Tropical Storm Olaf. However, as it moved north or northeast towards the Baja California Peninsula, cooler waters and shearing winds caused it to weaken to a tropical depression on October 3. Later that day, the NHC issued their last advisory on Olaf, as it weakened into a remnant low. The remnant low of Olaf continued to drift eastward for the next day, before dissipating overBaja California Sur
Baja California Sur (; 'South Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California Sur ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California Sur), is the least populated state and the 31st admitted state of the 32 federal ent ...
on October 4.
In Baja California Sur, heavy rains from the remnants of Olaf resulted in flooding of low-lying areas in several municipalities, notably near the city of La Paz
La Paz (), officially known as Nuestra Señora de La Paz (Spanish pronunciation: ), is the seat of government of the Bolivia, Plurinational State of Bolivia. With an estimated 816,044 residents as of 2020, La Paz is the List of Bolivian cities ...
. Officials in the affected regions also opened shelters if residents wanted to seek refuge away from their home. Heavy rains, amounting to , fell across portions of Sonora hit hard by Hurricane Jimena a month earlier; however, no damage resulted from Olaf.
Tropical Storm Patricia
Patricia developed from atropical wave
A tropical wave (also called easterly wave, tropical easterly wave, and African easterly wave), in and around the Atlantic Ocean, is a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which ...
that traversed the Atlantic Ocean during September and was first classified as a tropical depression on October 11 several hundred miles south of the Baja California Peninsula. The system quickly intensified into a tropical storm as it tracked in a general northward direction. By October 12, Patricia attained its peak intensity with winds of and a minimum barometric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 7 ...
of . The following day, increasing wind shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal ...
and unfavorable conditions caused the storm to rapidly weaken. By the morning of October 14, Patricia had degenerated into a remnant low near the southern coastline of Baja California Sur
Baja California Sur (; 'South Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California Sur ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California Sur), is the least populated state and the 31st admitted state of the 32 federal ent ...
. The remnants of the storm persisted until October 15, at which time they dissipated over open waters.
Although the center
Center or centre may refer to:
Mathematics
*Center (geometry), the middle of an object
* Center (algebra), used in various contexts
** Center (group theory)
** Center (ring theory)
* Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentricity ...
of Patricia did not impact land, the outer bands
{{Short pages monitor