trichilemmal cyst on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A trichilemmal cyst (or pilar cyst) is a common
A trichilemmal cyst (or pilar cyst) is a common
 Trichilemmal cysts are derived from the outer root sheath of the hair follicle. Their origin is currently unknown, but they may be produced by budding from the external root sheath as a
Trichilemmal cysts are derived from the outer root sheath of the hair follicle. Their origin is currently unknown, but they may be produced by budding from the external root sheath as a
 A trichilemmal cyst (or pilar cyst) is a common
A trichilemmal cyst (or pilar cyst) is a common cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and cell division, division compared with the nearby Biological tissue, tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of Cell (biology), cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which ...
that forms from a hair follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction between h ...
, most often on the scalp
The scalp is the anatomical area bordered by the human face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back.
Structure
The scalp is usually described as having five layers, which can conveniently be remembered as a mnemonic:
* S: The ski ...
, and is smooth, mobile, and filled with keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ...
, a protein component found in hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals.
The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and f ...
, nail
Nail or Nails may refer to:
In biology
* Nail (anatomy), toughened protective protein-keratin (known as alpha-keratin, also found in hair) at the end of an animal digit, such as fingernail
* Nail (beak), a plate of hard horny tissue at the tip ...
s, skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have diffe ...
, and horns Horns or The Horns may refer to:
* Plural of Horn (instrument), a group of musical instruments all with a horn-shaped bells
* The Horns (Colorado), a summit on Cheyenne Mountain
* ''Horns'' (novel), a dark fantasy novel written in 2010 by Joe Hill ...
. Trichilemmal cysts are clinically and histologically distinct from trichilemmal horns, hard tissue that is much rarer and not limited to the scalp. Rarely, these cysts may grow more extensively and form rapidly multiplying trichilemmal tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s, also called proliferating trichilemmal cysts, which are benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not s ...
, but may grow aggressively at the cyst site. Very rarely, trichilemmal cysts can become cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
ous.
Classification
Trichilemmal cysts may be classified assebaceous cyst
A sebaceous cyst is a term commonly used to refer to either:
* Epidermoid cysts (also termed epidermal cysts, infundibular cyst)
* Pilar cysts (also termed trichelemmal cysts, isthmus-catagen cysts)
Both of the above types of cysts contain ker ...
s, although technically speaking are not sebaceous. "True" sebaceous cysts, which originate from sebaceous gland
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest nu ...
s and which contain sebum, are relatively rare and are known as steatocystoma simplex or, if multiple, as steatocystoma multiplex
Steatocystoma multiplex, is a benign, autosomal dominant congenital condition resulting in multiple cysts on a person's body. Steatocystoma simplex is the solitary counterpart to steatocystoma multiplex.
In steatocystoma multiplex, the tendency to ...
. Medical professionals have suggested that the term "sebaceous cyst" be avoided since it can be misleading. In practice, however, the term is still often used for epidermoid and pilar cysts.
Pathogenesis
 Trichilemmal cysts are derived from the outer root sheath of the hair follicle. Their origin is currently unknown, but they may be produced by budding from the external root sheath as a
Trichilemmal cysts are derived from the outer root sheath of the hair follicle. Their origin is currently unknown, but they may be produced by budding from the external root sheath as a genetically
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar working i ...
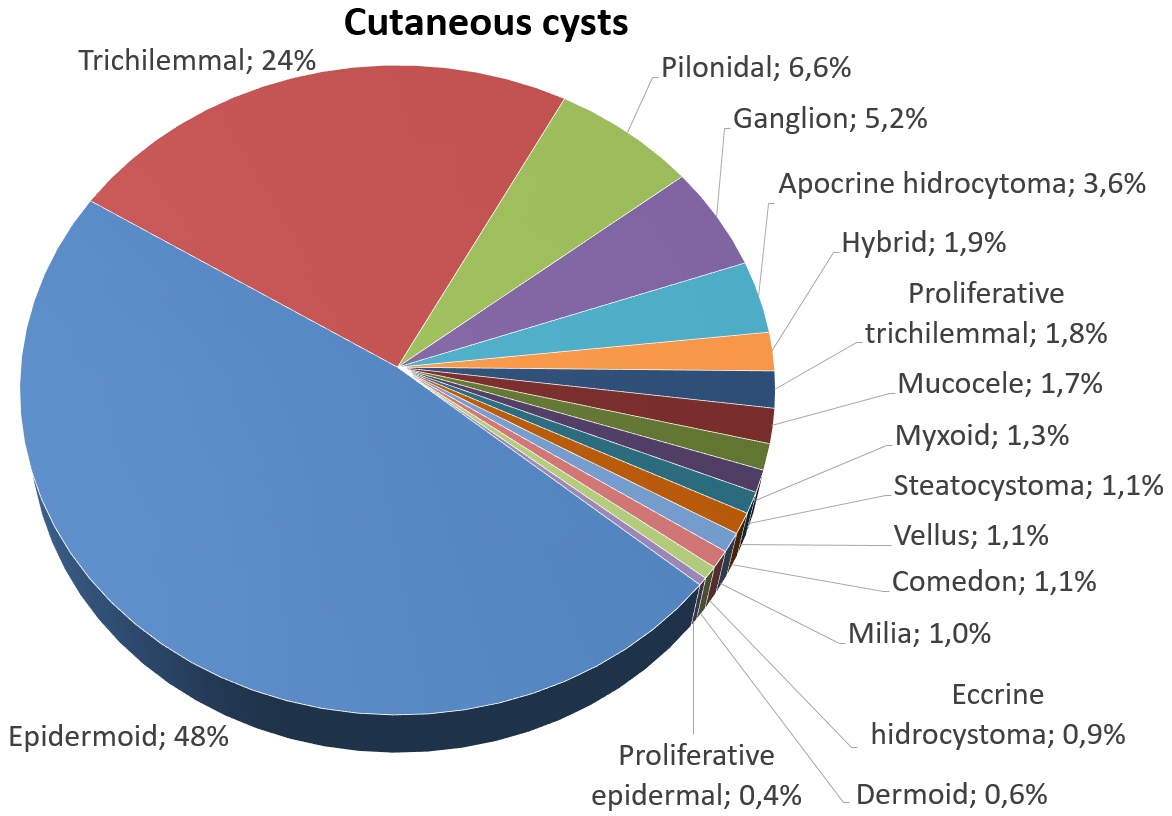
determined structural aberration. They arise preferentially in areas of high hair follicle concentrations, so 90% of cases occur on the scalp. They are solitary in 30% and multiple in 70% of cases.
Histologically
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures vis ...
, they are lined by stratified squamous epithelium that lacks a granular cell layer and are filled with compact "wet" keratin. Areas consistent with proliferation can be found in some cysts. In rare cases, this leads to formation of a tumor, known as a proliferating trichilemmal cyst. The tumor is clinically benign, although it may display nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
* Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
atypia
Atypia (from Greek, ''a'' + ''typos'', without type; a condition of being irregular or nonstandard) is a histopathologic term for a structural abnormality in a cell, i.e. it is used to describe atypical cells.
Atypia can be caused by an infection ...
, dyskeratotic cells, and mitotic
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintai ...
figures. These features can be misleading, and a diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma may be mistakenly rendered.
Treatment
Surgical excision
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ...
is required to treat a trichilemmal cyst. The method of treatment varies depending on the physician's training. Most physicians perform the procedure under local anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of pain sensation. In the context of surgery, a local anesthetic creates an absence of pain in a specific location of the body without a loss of consciousness, as opposed to a general a ...
. Others prefer a more conservative approach. This involves the use of a small punch biopsy about one-fourth the diameter of the cyst. The punch biopsy is used to enter the cyst cavity. The contents of the cyst are emptied, leaving an empty sac. As the pilar cyst wall is the thickest and most durable of the many varieties of cysts, it can be grabbed with forceps
Forceps (plural forceps or considered a plural noun without a singular, often a pair of forceps; the Latin plural ''forcipes'' is no longer recorded in most dictionaries) are a handheld, hinged instrument used for grasping and holding objects. Fo ...
and pulled out of the small incision. This method is best performed on cysts larger than a pea that have formed a thick enough wall to be easily identified after the sac is emptied. Small cysts have thin walls, so are easily fragmented on traction. This increases the likelihood of cyst recurrence. This method often results in only a small scar, and very little if any bleeding.
See also
* Proliferating epidermoid cyst * List of cutaneous conditionsReferences
External links
{{Tumors of skin appendages Cysts