Treaty Of St. Petersburg, 1825 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
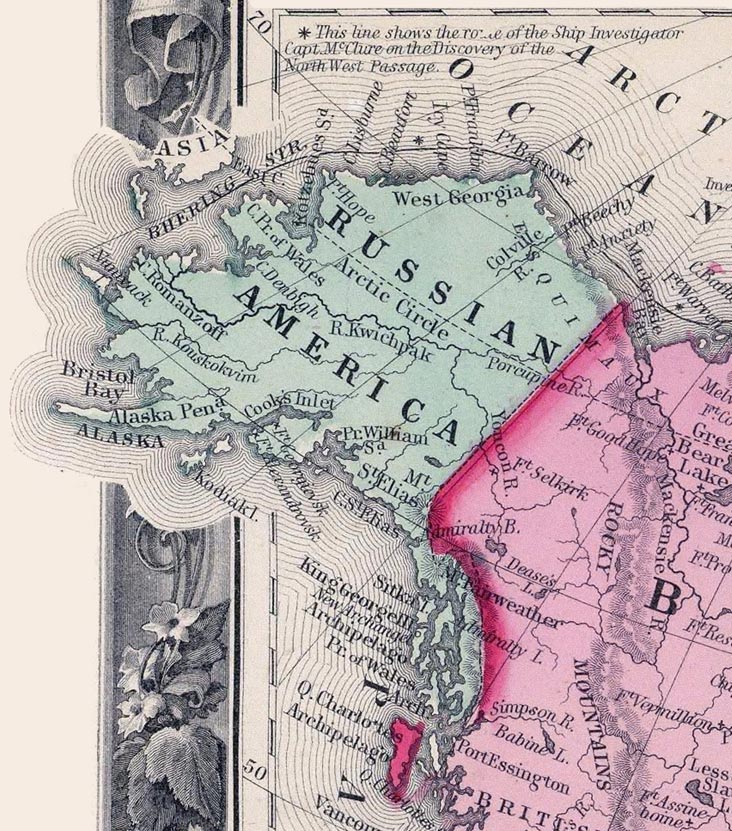 The Treaty of Saint Petersburg of 1825 or the Anglo-Russian Convention of 1825, officially the Convention Concerning the Limits of Their Respective Possessions on the Northwest Coast of America and the Navigation of the Pacific Ocean, defined the boundaries between
The Treaty of Saint Petersburg of 1825 or the Anglo-Russian Convention of 1825, officially the Convention Concerning the Limits of Their Respective Possessions on the Northwest Coast of America and the Navigation of the Pacific Ocean, defined the boundaries between ''The Hudson's Bay Company'', page 154
/ref> The same clauses enabled British access to the
online
(Treaty of St. Petersburg)
 The Treaty of Saint Petersburg of 1825 or the Anglo-Russian Convention of 1825, officially the Convention Concerning the Limits of Their Respective Possessions on the Northwest Coast of America and the Navigation of the Pacific Ocean, defined the boundaries between
The Treaty of Saint Petersburg of 1825 or the Anglo-Russian Convention of 1825, officially the Convention Concerning the Limits of Their Respective Possessions on the Northwest Coast of America and the Navigation of the Pacific Ocean, defined the boundaries between Russian America
Russian America (russian: Русская Америка, Russkaya Amerika) was the name for the Russian Empire's colonial possessions in North America from 1799 to 1867. It consisted mostly of present-day Alaska in the United States, but a ...
and British claims and possessions of the Pacific Coast
Pacific coast may be used to reference any coastline that borders the Pacific Ocean.
Geography Americas
Countries on the western side of the Americas have a Pacific coast as their western or southwestern border, except for Panama, where the Pac ...
, and the later Yukon
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
and Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenla ...
regions of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
. It was agreed that along the coast at the southern tip of Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales ( cy, Tywysog Cymru, ; la, Princeps Cambriae/Walliae) is a title traditionally given to the heir apparent to the English and later British throne. Prior to the conquest by Edward I in the 13th century, it was used by the rulers ...
island (now known as parallel 54°40′ north
The Oregon boundary dispute or the Oregon Question was a 19th-century territorial dispute over the political division of the Pacific Northwest of North America between several nations that had competing territorial and commercial aspirations in t ...
) northward to the 56 parallel, with the island wholly belonging to Russia, then to 10 marine leagues () inland going north and west to the 141st meridian west
The meridian 141° west of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, North America, the Pacific Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole.
The 141st meridian west forms a grea ...
and then north to the "Frozen Ocean", the current Alaska/Canadian Yukon boundary, would be the boundary. The coastal limit had, the year before, been established as the limit of overlapping American claims in the parallel Russo-American Treaty of 1824
The Russo-American Treaty of 1824 (also known as the Convention of 1824) was signed in St. Petersburg between representatives of Russia and the United States on April 17, 1824, ratified by both nations on January 11, 1825 and went into effect on Ja ...
. The Russian sphere in the region was later sold
Sold may refer to:
* ''Sold'' (Boy George album), 1987
* ''Sold'' (Died Pretty album), 1996
* ''Sold'' (TV series), a British comedy drama television series
* ''Sold'' (McCormick novel), a 2006 novel by Patricia McCormick and Illustrated by Br ...
to the United States, eventually becoming the State of Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
, while the British claim, along the coast to the south of parallel 54°40′ is now the coast of the Canadian province of British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
, and for inland regions it defined the western limit of what became the modern day Canadian territory of Yukon. It also defined associated rights and obligations concerning waters and ports in the region. The treaty, in establishing a vague division of coastal Russian interests and inland British interests between 56 and 60 degrees north latitude, led to conflicting interpretations of the meaning of the treaty's wording which later manifested in the Alaska Boundary Dispute
The Alaska boundary dispute was a territorial dispute between the United States and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, which then controlled Canada's foreign relations. It was resolved by arbitration in 1903. The dispute had existed ...
between the United States on the one hand, and Canada (with Britain acting, in foreign affairs, on behalf of Canada) on the other.
Other terms of the treaty, including the right to navigation by British vessels to both commerce in the region affected, and also access to rivers crossing the designated coastal boundary, were exercised by the Hudson's Bay Company in 1834 but were met with opposition by then Russian-American Company
The Russian-American Company Under the High Patronage of His Imperial Majesty (russian: Под высочайшим Его Императорского Величества покровительством Российская-Американс� ...
Governor Wrangel in the form of warships and a blockade. This conflict, known as the ''Dryad'' affair, led to the RAC-HBC Agreement, in which the RAC agreed to lease the mainland coastal portion of the region south of Cape Spencer at the entrance to Cross Sound
Cross Sound is a passage in the Alexander Archipelago in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of Alaska, located between Chichagof Island to its south and the mainland to its north. It is long and extends from the Gulf of Alaska to Icy Strai ...
and the HBC promised to supply Russian America settlements with foodstuffs and manufactured goods. In addition the HBC waived its demand for payments for damages incurred during the ''Dryad'' affair./ref> The same clauses enabled British access to the
Stikine River
The Stikine River is a major river in northern British Columbia (BC), Canada and southeastern Alaska in the United States. It drains a large, remote upland area known as the Stikine Country east of the Coast Mountains. Flowing west and south f ...
goldfields in 1862 but were not assumed by the Americans upon their purchase of Russian interests in 1867, resulting in further conflict over British rights of access to the inland regions. The treaty's terms pertaining to the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
(referred to as the "Frozen Ocean" in the treaty) also played a part in the terms of the Bering Sea Arbitration The Bering Sea Arbitration of 1893 arose out of a fishery dispute between the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and the United States in the 1880s. The United States Revenue Cutter Service, today known as the United States Coast Guard, cap ...
and other decisions in Alaskan/US courts over marine and offshore interests.
See also
*Stikine Territory
The Stickeen Territories , also colloquially rendered as Stickeen Territory, Stikine Territory, and Stikeen Territory, was a territory of British North America whose brief existence began July 19, 1862, and concluded July of the following year. ...
*North-Western Territory
The North-Western Territory was a region of British North America extant until 1870 and named for where it lay in relation to Rupert's Land.
Due to the lack of development, exploration, and cartographic limits of the time, the exact boundarie ...
*Atlin District The Atlin District, also known as the Atlin Country, is a historical region located in the far northwestern corner of the Canadian province of British Columbia, centred on Atlin Lake and the gold-rush capital of the region, the town of Atlin. The ...
*Maritime fur trade
The maritime fur trade was a ship-based fur trade system that focused on acquiring furs of sea otters and other animals from the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast and natives of Alaska. The furs were mostly sold in China in ex ...
References
{{reflistFurther reading
* Hodgins, Thomas. ''The Alaska-Canada Boundary Dispute: Under the Anglo-Russian Treaty of 1825; the Russian-American Alaska Treaty of 1867; and the Anglo-American Conventions of 1892, 1894 and 1897. An Historical and Legal Review'' (W. Tyrrell and Company, 1903)online
External links
(Treaty of St. Petersburg)
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
History of the Pacific Northwest
Boundary treaties
1825 treaties
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
Russia–United Kingdom relations
Canada–United States border
Bilateral treaties of Russia
Bilateral treaties of the United Kingdom