Transformer Oil Testing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Transformer oil Transformer oil or insulating oil is an oil that is stable at high temperatures and has excellent electrical insulating properties. It is used in oil-filled transformers (wet transformers), some types of high-voltage capacitors, fluorescent lamp b ...
, a type of insulating and cooling oil used in transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...
s and other electrical equipment, needs to be test
Test(s), testing, or TEST may refer to:
* Test (assessment), an educational assessment intended to measure the respondents' knowledge or other abilities
Arts and entertainment
* ''Test'' (2013 film), an American film
* ''Test'' (2014 film), ...
ed periodically to ensure that it is still fit for purpose. This is because it tends to deteriorate over time. Testing sequences and procedures are defined by various international standards, many of them set by ASTM
ASTM International, formerly known as American Society for Testing and Materials, is an international standards organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical standards for a wide range of materials, products, systems, a ...
. Transformer oil testing consists of measuring breakdown voltage
The breakdown voltage of an insulator is the minimum voltage that causes a portion of an insulator to experience electrical breakdown and become electrically conductive.
For diodes, the breakdown voltage is the minimum reverse voltage that ma ...
and other physical
Physical may refer to:
*Physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally cons ...
and chemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wit ...
properties of samples of the oil, either in a laboratory or using portable test equipment on-site.
Motivation for testing
The transformer oil (insulation oil) of voltage transformers and current transformers fulfills the purpose of insulating as well as cooling. Thus, the dielectric quality of transformer oil is essential to secure operation of a transformer. As transformer oil deteriorates through aging and moisture ingress, transformer oil should, depending on economics, transformer duty and other factors, be tested periodically.Electric utility
An electric utility is a company in the electric power industry (often a public utility) that engages in electricity generation and distribution of electricity for sale generally in a regulated market. The electrical utility industry is a majo ...
companies have a vested interest in periodic oil testing because transformers represent a large proportion of their total assets. Through such testing, transformers' life can be substantially increased, thus delaying new investment of replacement transformer assets.

On-site testing
Recently time-consuming testing procedures in test labs have been replaced by on-site oil testing procedures. There are various manufacturers of portable oil testers. With low weight devices in the range of 20 to 40 kg, tests up to 100 kV rms can be performed and reported on-site automatically. Some of them are even battery-powered and come with accessories.Breakdown voltage testing procedure
To assess the insulating property of dielectric transformer oil, a sample of the transformer oil is taken and itsbreakdown voltage
The breakdown voltage of an insulator is the minimum voltage that causes a portion of an insulator to experience electrical breakdown and become electrically conductive.
For diodes, the breakdown voltage is the minimum reverse voltage that ma ...
is measured. The lower the resulting breakdown voltage, the poorer the quality of the transformer oil.
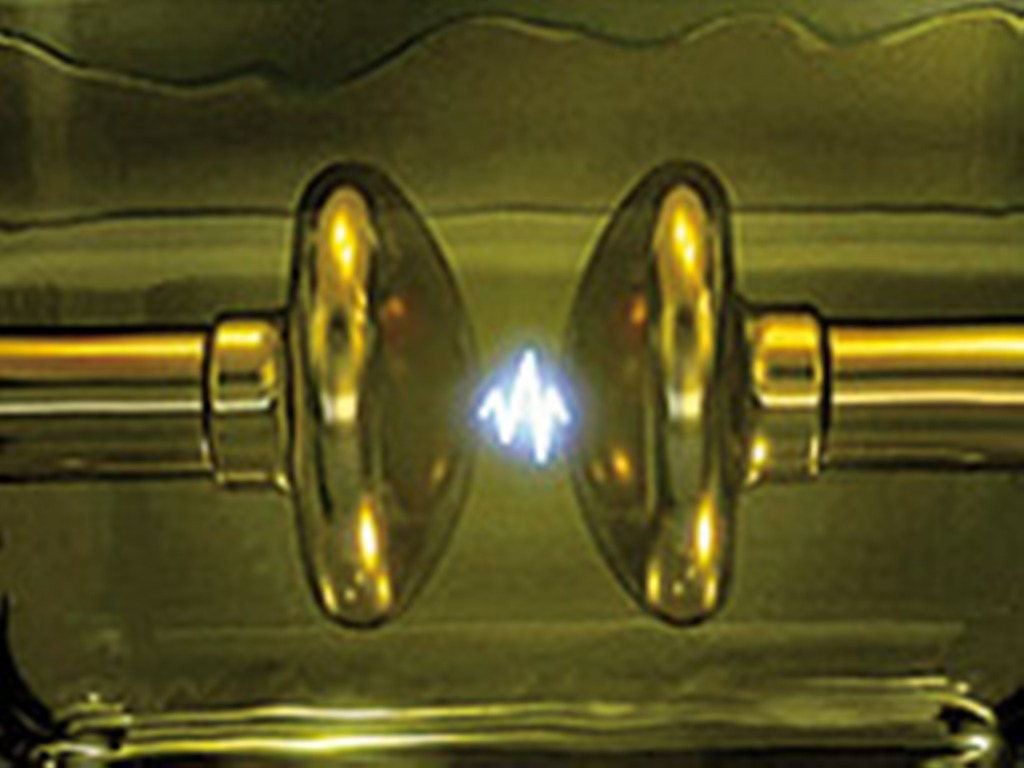
* The transformer oil is filled in the vessel of the testing device. Two standard-compliant test electrodes with a typical clearance of 2.5 mm are surrounded by the dielectric oil.
* A test voltage is applied to the electrodes and is continuously increased up to the breakdown voltage with a constant, standard-compliant slew rate
In electronics, slew rate is defined as the change of voltage or current, or any other electrical quantity, per unit of time. Expressed in SI units, the unit of measurement is volts/ second or amperes/second, but is usually expressed in terms of ...
of e.g. 2 kV/s.
* At a certain voltage level breakdown occurs in an electric arc
An electric arc, or arc discharge, is an electrical breakdown of a gas that produces a prolonged electrical discharge. The electric current, current through a normally Electrical conductance, nonconductive medium such as air produces a plasma (p ...
, leading to a collapse of the test voltage.
* An instant after ignition of the arc, the test voltage is switched off automatically by the testing device. Ultra fast switch off is highly desirable, as the carbonisation due to the electric arc must be limited to keep the additional pollution as low as possible.
* The transformer oil testing device measures and reports the root mean square
In mathematics and its applications, the root mean square of a set of numbers x_i (abbreviated as RMS, or rms and denoted in formulas as either x_\mathrm or \mathrm_x) is defined as the square root of the mean square (the arithmetic mean of th ...
value of the breakdown voltage.
* After the transformer oil test is completed, the insulation oil is stirred automatically and the test sequence is performed repeatedly: typically 5 repetitions, depending on the standard.
* As a result the breakdown voltage is calculated as mean value of the individual measurements.
Types of test
*Color; e.g., ASTM D1500. *Dielectric breakdown voltage; e.g., D 877, ASTM D1816 * Dissolved gas analysis; e.g., ASTM D3612 *Dissolved metals; e.g., ASTM D7151 *Flash point
The flash point of a material is the "lowest liquid temperature at which, under certain standardized conditions, a liquid gives off vapours in a quantity such as to be capable of forming an ignitable vapour/air mixture". (EN 60079-10-1)
The fl ...
, fire point
The fire point of a fuel is the lowest temperature at which the vapour of that fuel will continue to burn for at least five seconds after ignition by an open flame of standard dimension. At the flash point, a lower temperature, a substance will ig ...
; e.g., ASTM D92
*Interfacial tension; e.g. D 971
*Furan
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.
Furan is a colorless, flammable, highly ...
ic compounds; e.g., ASTM D5837
* Karl Fischer moisture; e.g., ASTM D1533
*Liquid power factor; e.g., ASTM D924
* Neutralization number; e.g., ASTM D974
* Oxidation inhibitor content; e.g., ASTM D2668
*Polychlorinated biphenyl
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are highly carcinogenic chemical compounds, formerly used in industrial and consumer products, whose production was banned in the United States by the Toxic Substances Control Act in 1979 and internationally by ...
s content; e.g., ASTM D4059
*Relative density
Relative density, or specific gravity, is the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water at its densest ...
(specific gravity
Relative density, or specific gravity, is the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water (molecule), wa ...
); e.g., D 1298, ASTM D1524
*Resistivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows ...
; e.g., ASTM D1169
*Visual examination; e.g., D1524
International transformer oil testing standards
* VDE370-5/96 * OVE EN60156 * IEC 60156/97, * ASTM1816-04-1 * ASTM1816-04-2 * ASTM877-02 * ASTM877-02B * AS1767.2.1 * BS EN60156 * NEN 10 156 * NF EN60156 * PA SEV EN60156 * SABS EN60156 * UNE EN60156 * IS:6792 * IS 335See also
*Electrical measurements
Electrical measurements are the methods, devices and calculations used to measure electrical quantities. Measurement of electrical quantities may be done to measure electrical parameters of a system. Using transducers, physical properties such as t ...
* Severity factor
References
{{Electric transformers Electric transformers Electrical tests