Transformation of the Ottoman Empire on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 350px, The Ottoman Empire in 1590, at the peak of its territorial expansion
The Transformation of the Ottoman Empire, also known as the Era of Transformation, constitutes a period in the history of the
350px, The Ottoman Empire in 1590, at the peak of its territorial expansion
The Transformation of the Ottoman Empire, also known as the Era of Transformation, constitutes a period in the history of the

 While in 1550 the Ottoman Empire was a patrimonial state in which all power was held exclusively by the
While in 1550 the Ottoman Empire was a patrimonial state in which all power was held exclusively by the
, or Queen Mother. These two figures were able to sanction the deposition and enthronement of sultans, the former as the empire's highest religious and judicial authority, and the latter as the matriarch of the dynasty. They thus came to wield immense power, as any governmental faction seeking to control the policy of the empire required their support. Two Valide Sultans in particular dominated the seventeenth century:
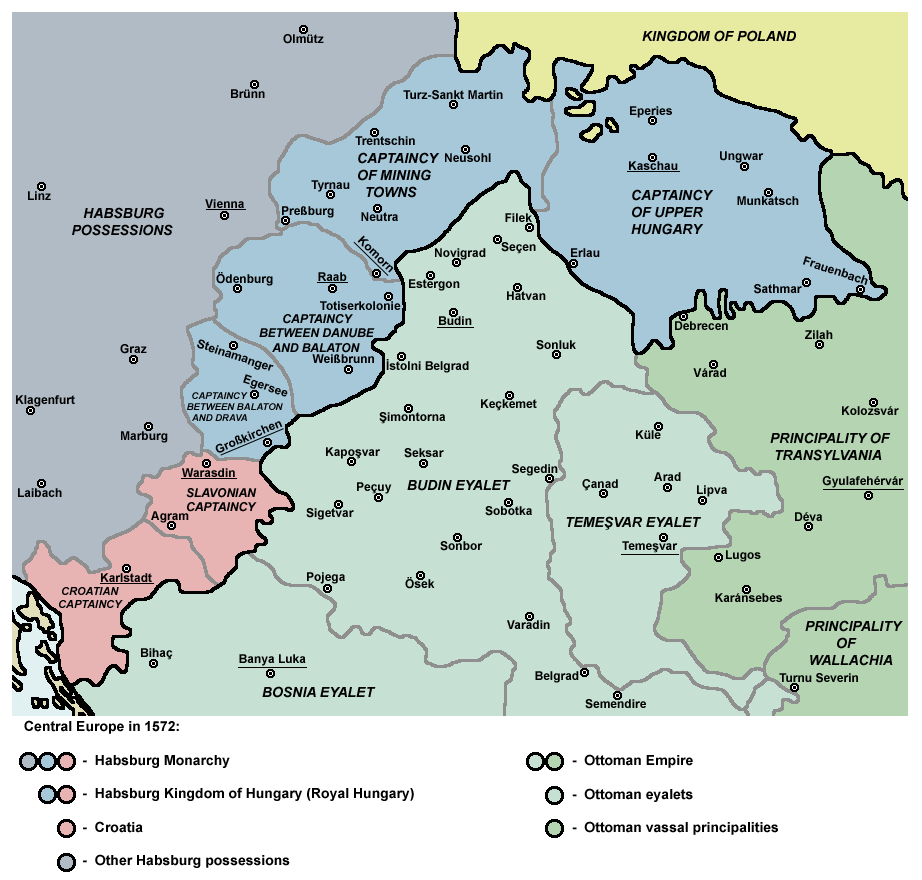 In Hungary the Ottomans were primarily concerned with ensuring the security of
In Hungary the Ottomans were primarily concerned with ensuring the security of
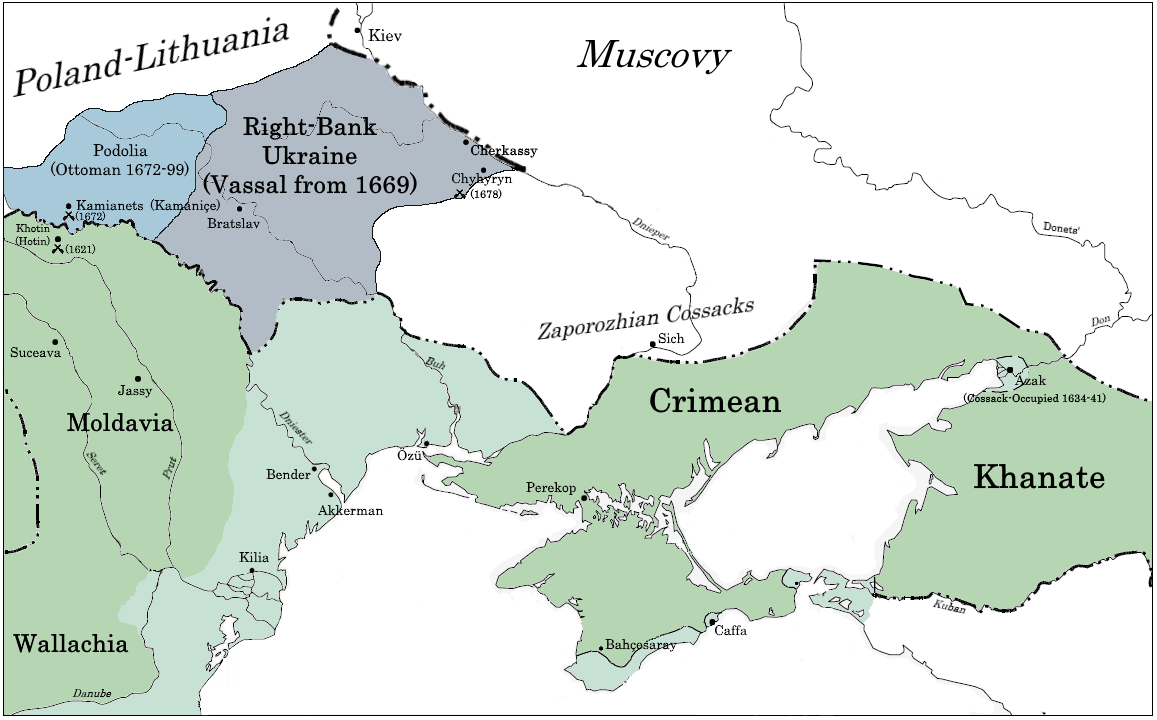 In contrast with their Hungarian and Safavid frontiers, the Ottomans generally did not seek to expand further north from the
In contrast with their Hungarian and Safavid frontiers, the Ottomans generally did not seek to expand further north from the
 The Ottoman Empire of this period was home to a vibrant religious and intellectual life. The legal reforms of Şeyhülislâm
The Ottoman Empire of this period was home to a vibrant religious and intellectual life. The legal reforms of Şeyhülislâm
. This was directly related to the changes taking place in the system of succession, whereby princes no longer traveled to the provinces to take up governorships, but remained in the harem in Istanbul. From the time of Murad III onward, sultans no longer slept in the male segment of  350px, The Ottoman Empire in 1590, at the peak of its territorial expansion
The Transformation of the Ottoman Empire, also known as the Era of Transformation, constitutes a period in the history of the
350px, The Ottoman Empire in 1590, at the peak of its territorial expansion
The Transformation of the Ottoman Empire, also known as the Era of Transformation, constitutes a period in the history of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
from to , spanning roughly from the end of the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I ( ota, سليمان اول, Süleyman-ı Evvel; tr, I. Süleyman; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the West and Suleiman the Lawgiver ( ota, قانونى سلطان سليمان, Ḳ� ...
to the Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed in Karlowitz, Military Frontier of Archduchy of Austria (present-day Sremski Karlovci, Serbia), on 26 January 1699, concluding the Great Turkish War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by the ...
at the conclusion of the War of the Holy League. This period was characterized by numerous dramatic political, social, and economic changes, which resulted in the empire shifting from an expansionist
Expansionism refers to states obtaining greater territory through military empire-building or colonialism.
In the classical age of conquest moral justification for territorial expansion at the direct expense of another established polity (who of ...
, patrimonial state into a bureaucratic
The term bureaucracy () refers to a body of non-elected governing officials as well as to an administrative policy-making group. Historically, a bureaucracy was a government administration managed by departments staffed with non-elected offi ...
empire based on an ideology of upholding justice and acting as the protector of Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagre ...
. These changes were in large part prompted by a series of political and economic crises in the late 16th and early 17th centuries, resulting from inflation, warfare, and political factionalism. Yet despite these crises the empire remained strong both politically and economically, and continued to adapt to the challenges of a changing world. The 17th century was once characterized as a period of decline for the Ottomans, but since the 1980s historians of the Ottoman Empire have increasingly rejected that characterization, identifying it instead as a period of crisis, adaptation, and transformation.
*
*
*
In the second half of the 16th century, the empire came under increasing economic pressure due to rising inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reductio ...
, which was then impacting both Europe and the Middle East. Demographic pressure in Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
contributed to the formation of bandit gangs, which by the 1590s coalesced under local warlords to launch a series of conflicts known as the Celali rebellions
The Celali rebellions ( tr, Celalî ayaklanmaları), were a series of rebellions in Anatolia of irregular troops led by bandit chiefs and provincial officials known as ''celalî'', ''celâli'', or ''jelālī'', against the authority of the Ottoman ...
. Ottoman fiscal insolvency and local rebellion together with the need to compete militarily against their imperial rivals the Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
and Safavids
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often conside ...
created a severe crisis. The Ottomans thus transformed many of the institutions which had previously defined the empire, gradually disestablishing the Timar System
A timar was a land grant by the sultans of the Ottoman Empire between the fourteenth and sixteenth centuries, with an annual tax revenue of less than 20,000 akçes. The revenues produced from the land acted as compensation for military service. A ...
in order to raise modern armies of musketeers
A musketeer (french: mousquetaire) was a type of soldier equipped with a musket. Musketeers were an important part of early modern warfare particularly in Europe as they normally comprised the majority of their infantry. The musketeer was a pre ...
, and quadrupling the size of the bureaucracy in order to facilitate more efficient collection of revenues. In Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
, changes in the nature of dynastic politics led to the abandonment of the Ottoman tradition of royal fratricide
Fratricide (, from the Latin words ' "brother" and the assimilated root of ' "to kill, to cut down") is the act of killing one's own brother.
It can either be done directly or via the use of either a hired or an indoctrinated intermediary (a ...
, and to a governmental system that relied much less upon the personal authority of the sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
. Other figures came to play larger roles in government, particularly the women of the imperial harem
The Imperial Harem ( ota, حرم همايون, ) of the Ottoman Empire was the Ottoman sultan's harem – composed of the wives, servants (both female slaves and eunuchs), female relatives and the sultan's concubines – occupying a secluded po ...
, for which much of this period is often referred to as the Sultanate of Women
The Sultanate of Women ( Turkish: ''Kadınlar saltanatı'') was a period when wives and mothers of the Sultans of the Ottoman Empire exerted extraordinary political influence.
This phenomenon took place from roughly 1528-30 to 1715, beginning in ...
.
The changing nature of sultanic authority led to several political upheavals during the 17th century, as rulers and political factions struggled for control over the imperial government. In 1622 Sultan Osman II
Osman II ( ota, عثمان ثانى ''‘Osmān-i sānī''; tr, II. Osman; 3 November 1604 – 20 May 1622), also known as Osman the Young ( tr, Genç Osman), was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 26 February 1618 until his regicide on 20 May 162 ...
was overthrown in a Janissary
A Janissary ( ota, یڭیچری, yeŋiçeri, , ) was a member of the elite infantry units that formed the Ottoman Sultan's household troops and the first modern standing army in Europe. The corps was most likely established under sultan Orhan ( ...
uprising. His subsequent regicide
Regicide is the purposeful killing of a monarch or sovereign of a polity and is often associated with the usurpation of power. A regicide can also be the person responsible for the killing. The word comes from the Latin roots of ''regis'' ...
was sanctioned by the empire's chief judicial official, demonstrating a reduced importance of the sultan in Ottoman politics. Nevertheless, the primacy of the Ottoman dynasty as a whole was never brought into question. Of seventeenth-century sultans, Mehmed IV
Mehmed IV ( ota, محمد رابع, Meḥmed-i rābi; tr, IV. Mehmed; 2 January 1642 – 6 January 1693) also known as Mehmed the Hunter ( tr, Avcı Mehmed) was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1648 to 1687. He came to the throne at the a ...
was the longest reigning, occupying the throne for 39 years from 1648 to 1687. The empire experienced a long period of stability under his reign, spearheaded by the reform-minded Köprülü family
The Köprülü family ( tr, Köprülü ailesi) was a noble family of Albanian origin in the Ottoman Empire.Ivo Banac''The national question in Yugoslavia: origins, history, politics'' , Cornell University 1988 page 292. The family hailed from th ...
of grand vizier
Grand vizier ( fa, وزيرِ اعظم, vazîr-i aʾzam; ota, صدر اعظم, sadr-ı aʾzam; tr, sadrazam) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. The office of Grand Vizier was first ...
s. This coincided with a period of renewed conquest in Europe, conquests which culminated in the disastrous Siege of Vienna Sieges of Vienna may refer to:
* Siege of Vienna (1239)
* Siege of Vienna (1276)
* Siege of Vienna (1287)
* Siege of Vienna (1477), unsuccessful Hungarian attempt during the Austro–Hungarian War.
*Siege of Vienna (1485), Hungarian victory during ...
in 1683 and the fall from grace of the Köprülü family. Following the battle a coalition of Christian powers was assembled to combat the Ottomans, bringing about the fall of Ottoman Hungary
Ottoman Hungary ( hu, Török hódoltság) was the southern and central parts of what had been the Kingdom of Hungary in the late medieval period, which were conquered and ruled by the Ottoman Empire from 1541 to 1699. The Ottoman rule covered ...
and its annexation by the Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
during the War of the Holy League (1683–99). The war provoked another political crisis and prompted the Ottomans to carry out additional administrative reforms. These reforms ended the problem of financial insolvency and made the transformation from a patrimonial to a bureaucratic state a permanent one.
Territory
In comparison with earlier periods of Ottoman history, the empire's territory remained relatively stable, stretching fromAlgeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
in the west to Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
in the east, and from Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
in the south to Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
in the north. The pace of expansion slowed during the second half of the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent (1520–66), as the Ottomans sought to consolidate the vast conquests carried out between 1514 and 1541, but did not come to an end. After making peace with Austria in 1568, the Ottomans launched the 1570–73 Ottoman-Venetian War, conquering Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geo ...
and most of Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
. A naval campaign led to the capture of Tunis from the Spanish in 1574, and a truce was signed in 1580.
Subsequently, the Ottomans resumed warfare with the Safavids in the Ottoman–Safavid War of 1578–90, conquering Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
, and western Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. The war resulting in the Ottomans reached its greatest territorial expansion under Murad III
Murad III ( ota, مراد ثالث, Murād-i sālis; tr, III. Murad; 4 July 1546 – 16 January 1595) was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1574 until his death in 1595. His rule saw battles with the Habsburgs and exhausting wars with the Saf ...
. In 1593 a frontier incident led to the renewal of warfare with Habsburg Austria in the Long War (1593–1606), in which neither side was able to achieve decisive victory. The Ottomans briefly held Győr
Győr ( , ; german: Raab, links=no; names of European cities in different languages: E-H#G, names in other languages) is the main city of northwest Hungary, the capital of Győr-Moson-Sopron County and Western Transdanubia, Western Transdanubia ...
(Yanık, 1594–8), but lost control of Novigrad (1594), exposing Buda to attacks from the north. By the end of the war the Ottomans had conquered the strategic fortresses of Eger
Eger ( , ; ; also known by other alternative names) is the county seat of Heves County, and the second largest city in Northern Hungary (after Miskolc). A city with county rights. Eger is best known for its castle, thermal baths, baroque build ...
(Eğri, 1596) and Nagykanizsa
Nagykanizsa (; hr, Velika Kaniža/Velika Kanjiža, or just ''Kaniža/Kanjiža''; german: Großkirchen, Groß-Kanizsa; it, Canissa; sl, Velika Kaniža; tr, Kanije), known colloquially as Kanizsa, is a medium-sized city in Zala County in southw ...
(Kanije, 1600). The Safavids took advantage of Ottoman distraction in the west to reverse all of their recent gains in the east in the Ottoman–Safavid War of 1603–18. After the turmoil of Osman II
Osman II ( ota, عثمان ثانى ''‘Osmān-i sānī''; tr, II. Osman; 3 November 1604 – 20 May 1622), also known as Osman the Young ( tr, Genç Osman), was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 26 February 1618 until his regicide on 20 May 162 ...
's regicide, the Safavids also seized Baghdad and much of Iraq in 1623, holding it until 1638, after which the border of the 1555 Treaty of Amasya
The Peace of Amasya ( fa, پیمان آماسیه ("Peymān-e Amasiyeh"); tr, Amasya Antlaşması) was a treaty agreed to on May 29, 1555, between Shah Tahmasp of Safavid Iran and Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent of the Ottoman Empire at the cit ...
was re-established. While they were occupied with the Safavid wars, an ongoing revolt of the local Zaydi Shi'ites of Yemen finally forced the Ottomans to abandon that province in 1636. The province of Lahsa in eastern Arabia also suffered from perpetual rebellion and tribal resistance to Ottoman rule, and was abandoned in 1670.
From 1645 onward the Ottomans were preoccupied with the difficult conquest of Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and ...
from the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
. The island was quickly overrun, but Venetian naval superiority enabled the fortress of Candia (modern Heraklion) to resist for decades. Sustained expansion in Europe was resumed in the second half of the seventeenth century, under the aegis of the famous Köprülü grand viziers. The rebellious vassal principality of Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
was subdued with the conquests of Ineu
Ineu (; Hungarian: ''Borosjenő''; Serbian: Јенопоље/''Jenopolje''; Turkish: ''Yanova'') is a town in Arad County, western Transylvania, Romania. It is situated at a distance of from the county capital, Arad, it occupies a surface ...
(Yanova, 1658) and Oradea
Oradea (, , ; german: Großwardein ; hu, Nagyvárad ) is a city in Romania, located in Crișana, a sub-region of Transylvania. The county seat, seat of Bihor County, Oradea is one of the most important economic, social and cultural centers in the ...
(Varad, 1660). War with the Habsburgs in 1663-4 led to the recovery of Novigrad and the conquest of Nové Zámky
Nové Zámky (; hu, Érsekújvár; german: Neuhäus ; la, Novum Castrum; tr, Uyvar) is a town in Nové Zámky District in the Nitra Region of southwestern Slovakia.
Geography
The town is located on the Danubian Lowland, on the Nitra River, ...
(Uyvar, 1663). The conquest of Crete was finally completed in 1669 with the fall of Candia. In that same year, the Ottomans accepted the offer of the Cossack state of Right-Bank Ukraine
Right-bank Ukraine ( uk , Правобережна Україна, ''Pravoberezhna Ukrayina''; russian: Правобережная Украина, ''Pravoberezhnaya Ukraina''; pl, Prawobrzeżna Ukraina, sk, Pravobrežná Ukrajina, hu, Jobb p ...
to become an Ottoman vassal in exchange for protection from the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
. This led to war in 1672–76, as the Ottomans conquered Podolia
Podolia or Podilia ( uk, Поділля, Podillia, ; russian: Подолье, Podolye; ro, Podolia; pl, Podole; german: Podolien; be, Падолле, Padollie; lt, Podolė), is a historic region in Eastern Europe, located in the west-central ...
(Kamaniçe) from the Commonwealth, and to war with Russia in 1676–81, in which Russian garrisons were evicted from Cossack lands. Ottoman rule in Europe reached its greatest extent in 1682, when anti-Habsburg Hungarian rebel leader Imre Thököly
Imre is a Hungarian masculine first name, which is also in Estonian use, where the corresponding name day is 10 April. It has been suggested that it relates to the name Emeric, Emmerich or Heinrich. Its English equivalents are Emery and Henry. ...
pledged allegiance to the Ottoman Empire, accepting the title "King of Middle Hungary" ( ota, Orta Macar, script=Latn). Just as the vassalization of Right-Bank Ukraine had led to the Kamaniçe campaign, so too did the vassalization of Imre Thököly lead directly to the 1683 Vienna Campaign.
After the unsuccessful siege of Vienna in 1683, the coalition forces of the Holy League
Commencing in 1332 the numerous Holy Leagues were a new manifestation of the Crusading movement in the form of temporary alliances between interested Christian powers. Successful campaigns included the capture of Smyrna in 1344, at the Battle of ...
began to push the Ottomans out of Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
, with most of the country having fallen by 1688. In the Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed in Karlowitz, Military Frontier of Archduchy of Austria (present-day Sremski Karlovci, Serbia), on 26 January 1699, concluding the Great Turkish War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by the ...
the Ottomans accepted this loss as well as the return of Podolia to the Commonwealth. While Crete remained in Ottoman hands, Morea
The Morea ( el, Μορέας or ) was the name of the Peloponnese peninsula in southern Greece during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The name was used for the Byzantine province known as the Despotate of the Morea, by the Ottoman ...
was ceded to Venice along with most of Dalmatia. This was the first major instance of Ottoman territorial retreat in Europe, and it prompted the adoption of a defensive military policy along the Danube River
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
during the eighteenth century.
Subject states
In addition to territory under direct imperial administration, the Ottoman Empire also possessed varying degrees of sovereignty over its manyvassal states
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to t ...
. Each vassal state's relationship with the empire was unique, but typically involved the payment of tribute, military contribution, or both. Such vassals included the Danubian Principalities
The Danubian Principalities ( ro, Principatele Dunărene, sr, Дунавске кнежевине, translit=Dunavske kneževine) was a conventional name given to the Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia, which emerged in the early 14th ce ...
of Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and so ...
and Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and former principality in Centr ...
, the Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to ...
, the Principality of Transylvania, the Republic of Ragusa
hr, Sloboda se ne prodaje za sve zlato svijeta it, La libertà non si vende nemmeno per tutto l'oro del mondo"Liberty is not sold for all the gold in the world"
, population_estimate = 90 000 in the XVI Century
, currency = ...
, various Georgian
Georgian may refer to:
Common meanings
* Anything related to, or originating from Georgia (country)
** Georgians, an indigenous Caucasian ethnic group
** Georgian language, a Kartvelian language spoken by Georgians
**Georgian scripts, three scrip ...
and Caucasian
Caucasian may refer to:
Anthropology
*Anything from the Caucasus region
**
**
** ''Caucasian Exarchate'' (1917–1920), an ecclesiastical exarchate of the Russian Orthodox Church in the Caucasus region
*
*
*
Languages
* Northwest Caucasian l ...
principalities, and, in the second half of the seventeenth century, the Cossack
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
state of Right-Bank Ukraine
Right-bank Ukraine ( uk , Правобережна Україна, ''Pravoberezhna Ukrayina''; russian: Правобережная Украина, ''Pravoberezhnaya Ukraina''; pl, Prawobrzeżna Ukraina, sk, Pravobrežná Ukrajina, hu, Jobb p ...
and the territory ruled by Imre Thököly
Imre is a Hungarian masculine first name, which is also in Estonian use, where the corresponding name day is 10 April. It has been suggested that it relates to the name Emeric, Emmerich or Heinrich. Its English equivalents are Emery and Henry. ...
, known as Middle Hungary
The Principality of Upper Hungary ( hu, Felső-Magyarországi Fejedelemség; ota, او رتا ماجار, Orta Macâr, lit=Middle Hungary) was a short-lived Ottoman vassal state ruled by Imre Thököly.
Background
After peace treaty of Vasvár ...
. The Sharifs of Mecca
The Sharif of Mecca ( ar, شريف مكة, Sharīf Makkah) or Hejaz ( ar, شريف الحجاز, Sharīf al-Ḥijāz, links=no) was the title of the leader of the Sharifate of Mecca, traditional steward of the holy cities of Mecca and Medina and ...
in western Arabia were also subject to the Ottomans, but neither paid tribute nor offered military forces. At times, the empire also received tribute from Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
, Habsburg Austria The term Habsburg Austria may refer to the lands ruled by the Austrian branch of the Habsburgs, or the historical Austria. Depending on the context, it may be defined as:
* The Duchy of Austria, after 1453 the Archduchy of Austria
* The ''Erbland ...
, Poland–Lithuania, and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, which made them vassals of the Ottoman Empire in theory, if not in practice. The empire's territory also included many smaller and often geographically isolated regions where the state's authority was weak, and local groups could exercise significant degrees of autonomy or even de facto independence. Examples include the highlands of Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
, the area of Mount Lebanon
Mount Lebanon ( ar, جَبَل لُبْنَان, ''jabal lubnān'', ; syr, ܛܘܪ ܠܒ݂ܢܢ, ', , ''ṭūr lewnōn'' french: Mont Liban) is a mountain range in Lebanon. It averages above in elevation, with its peak at .
Geography
The Mount Le ...
, mountainous regions of the Balkans such as Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
, and much of Kurdistan
Kurdistan ( ku, کوردستان ,Kurdistan ; lit. "land of the Kurds") or Greater Kurdistan is a roughly defined geo-cultural territory in Western Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, Kurdish la ...
, where pre-Ottoman dynasties continued to rule under Ottoman authority.
Demography
Due to scarcity of records and the tendency to record the number of households rather than individuals in taxation surveys, it is very difficult to determine with accuracy the population level in the Ottoman Empire. Thus rather than definite numbers, historians are more apt to demonstrate trends in population increase and decrease from region to region. It is known that theBalkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
and Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, like Europe, experienced a rapid increase in population over the course of the sixteenth century, increasing by roughly 60% in the period 1520–80. This growth led to population pressure in Anatolia, as the land could no longer adequately support the peasant population. Many landless peasants took up banditry as a way to make a living, or were recruited into the armies of roving Celali rebels. Controlling the bandits' activities became a major policy issue for the Ottomans, as bandit raids only worsened the agricultural situation in Anatolia. One method of control involved their recruitment into the Ottoman army as musketeers, known as sekban and sarıca. Other methods were tried as well, such as the dispatch of an inspection team in 1659, which confiscated 80,000 illegally held firearms. Following the dramatic demographic growth of the sixteenth century, the seventeenth century population was mostly stable and in some regions even declined, again relatively consistent with general European trends.
The empire's premier city was '' Kostantiniyye'' (modern day Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
), with a population of upwards of 250 thousand in the middle of the sixteenth century. Other estimates place it even higher, between 500 thousand and one million inhabitants. Second in size was Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metro ...
, with approximately 400 thousand inhabitants in the year 1660. Most other major urban centers did not even approach this size. Izmir grew from a small town into a major center of international trade, with 90 thousand inhabitants in the mid-seventeenth century, while the Syrian city of Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black".
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_caption =
, image_map1 =
...
also grew from approximately 46 thousand in 1580 to 115 thousand a century later. Bursa
( grc-gre, Προῦσα, Proûsa, Latin: Prusa, ota, بورسه, Arabic:بورصة) is a city in northwestern Turkey and the administrative center of Bursa Province. The fourth-most populous city in Turkey and second-most populous in the ...
, the main city of northwestern Anatolia and a major center for the production of silk textiles, had a population which ranged between 20 and 40 thousand over the course of the seventeenth century. Urban expansion was not universal. In the early seventeenth century, many of the cities and towns of inner Anatolia and the Black Sea coast suffered from the raiding and banditry of the Celali rebellions
The Celali rebellions ( tr, Celalî ayaklanmaları), were a series of rebellions in Anatolia of irregular troops led by bandit chiefs and provincial officials known as ''celalî'', ''celâli'', or ''jelālī'', against the authority of the Ottoman ...
and Cossack
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
raids, such as Ankara
Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the capital of Turkey. Located in the central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5.1 million in its urban center and over 5.7 million in Ankara Province, maki ...
, Tokat
Tokat is the capital city of Tokat Province of Turkey in the mid-Black Sea region of Anatolia. It is located at the confluence of the Tokat River (Tokat Suyu) with the Yeşilırmak. In the 2018 census, the city of Tokat had a population of 155,00 ...
, and Sinop Sinop can refer to:
* Sinop, Turkey, a city on the Black Sea
** Sinop Nuclear Power Plant, was planned in 2013, but cancelled in 2018
** Battle of Sinop, 1853 naval battle in the Sinop port
*** Russian ship ''Sinop'', Russian ships named after the ...
.
In Ottoman Europe this period witnessed a major shift in religious demographics. Many of the cities and towns of the Balkans and Hungary became majority Muslim, including Buda
Buda (; german: Ofen, sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Budim, Будим, Czech and sk, Budín, tr, Budin) was the historic capital of the Kingdom of Hungary and since 1873 has been the western part of the Hungarian capital Budapest, on the ...
, the former capital of the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
. In the Balkan countryside the rate of conversion to Islam gradually increased until reaching a peak in the late seventeenth century, particularly affecting regions such as Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
and eastern Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon ...
.
Economy
Perhaps the most significant economic transformation of this period was the monetization of the economy and subsequent transformation of the feudalTimar System
A timar was a land grant by the sultans of the Ottoman Empire between the fourteenth and sixteenth centuries, with an annual tax revenue of less than 20,000 akçes. The revenues produced from the land acted as compensation for military service. A ...
. Over the course of the sixteenth century, coinage came to play a much larger role in the Ottoman rural economy, with tax payments in cash coming to replace payments in kind. As the Ottoman population expanded, the volume of trade grew and new regional markets appeared across the empire. The Timar System, which had been designed to take advantage of the smaller scale of the economy in previous centuries, was thus rendered obsolete. Timar fiefs, which were once used to support provincial cavalry forces, were increasingly confiscated by the central government to serve other purposes, a process which has been described as "modernization."
Budget
At the end of each year the Ottoman government produced a comprehensive balance-sheet depicting its revenues and expenses, giving historians a window through which to view their finances. Ottoman government income grew from 183 million akçe in 1560 to 581 million in 1660, an increase of 217%. However, this growth did not keep pace with inflation, and consequently the Ottomans experienced budgetary deficits throughout most of the seventeenth century, by an average of 14% but with much wider margins during wartime. The province ofEgypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
played a major role in making up the difference. Each year, after covering local expenses, that province submitted its surplus revenue directly to Istanbul. Egypt was particularly rich, and it provided approximately 72 million akçe annually, allowing the central government to meet its financial obligations. By the end of the seventeenth century, and largely a result of reforms carried out during the War of the Holy League, the central government's income had grown to 1 billion akçe, and continued to grow at an even more dramatic pace during the following period, now far outstripping inflation.
Coinage
Monetization of the economy coincided with thePrice Revolution
The Price Revolution, sometimes known as the Spanish Price Revolution, was a series of economic events that occurred between the second half of the 15th century and the first half of the 17th century, and most specifically linked to the high rate o ...
, a period of inflation affecting both Europe and the Middle East during the sixteenth century. As a result, the value of the main Ottoman silver coin (akçe
The ''akçe'' or ''akça'' (also spelled ''akche'', ''akcheh''; ota, آقچه; ) refers to a silver coin which was the chief monetary unit of the Ottoman Empire. The word itself evolved from the word "silver or silver money", this word is deri ...
) became unstable, particularly after a severe debasement
A debasement of coinage is the practice of lowering the intrinsic value of coins, especially when used in connection with commodity money, such as gold or silver coins. A coin is said to be debased if the quantity of gold, silver, copper or nick ...
in 1585. The currency's instability lasted until the middle of the seventeenth century and led some regions of the empire to import counterfeit European coins for everyday use. This situation was brought under control in the 1690s when the empire carried out far-reaching monetary reforms and issued a new silver and copper currency.
Trade
Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metro ...
, as a major entrepôt for the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
trade, benefited from the emergence of Yemeni coffee as a major trading good. By the end of the sixteenth century coffeehouses
A coffeehouse, coffee shop, or café is an establishment that primarily serves coffee of various types, notably espresso, latte, and cappuccino. Some coffeehouses may serve cold drinks, such as iced coffee and iced tea, as well as other non-caf ...
had emerged in cities and towns across the empire, and the drink became a major item of public consumption. By the end of the seventeenth century approximately 4–5,000 tons of coffee was being imported into Cairo annually, much of it exported to the rest of the empire.
Trade along the maritime routes of the Black Sea was severely disrupted from the late sixteenth century by the extensive raiding activity of the Zaporozhian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporoz ...
, who attacked towns along the Anatolian and Bulgarian coasts, and even established bases in the mouth of the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
in order to plunder its shipping. Likewise, merchant vessels at sea frequently became targets for the Cossacks. After the outbreak of the Khmelnytsky Rebellion
The Khmelnytsky Uprising,; in Ukraine known as Khmelʹnychchyna or uk, повстання Богдана Хмельницького; lt, Chmelnickio sukilimas; Belarusian: Паўстанне Багдана Хмяльніцкага; russian: � ...
in 1648 Cossack activity reduced in intensity, but remained an issue of critical importance for the Ottoman government.

European merchants
European merchants active in the Ottoman Empire are by far the most highly studied aspect of Ottoman commerce, a fact which has frequently caused their importance to be exaggerated. European merchants were by no means dominant in the empire during this period, and far from imposing their will upon the Ottomans, they were required to accommodate themselves to the terms which the Ottomans set for them. These terms were defined in a series of trade agreements known as the "capitulations" ( ota, ʿahdnāme, script=Latn), which granted Europeans the right to establish mercantile communities in specified Ottoman ports and to pay a lower rate of tariff on their goods. European communities were exempt from regular taxation and were given judicial autonomy with regard to personal and family issues. All commercial disputes were to be settled in the empire's Sharia courts, until the 1670s when they were granted the right to appeal major cases directly to Istanbul, where they could be argued by their resident ambassadors. Capitulations were granted first to the French (1569), then the English (1580), and finally to the Dutch (1612). The arrival of Western European traders in the Levant, dubbed the "Northern Invasion", did not result in their takeover or domination of Mediterranean commerce, but it did usher in certain changes. Venice in particular suffered from heavy competition, and its commercial presence declined significantly, particularly after 1645, when the Ottomans and Venetians went to war over Crete. The English were by far the most successful European merchants in the empire during the seventeenth century, and they benefited from friendly relations between the two states. The Ottomans exported raw silk and imported cheap woolen cloth, as well as tin necessary for the production of military armaments.Government
 While in 1550 the Ottoman Empire was a patrimonial state in which all power was held exclusively by the
While in 1550 the Ottoman Empire was a patrimonial state in which all power was held exclusively by the sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
, by 1700 it had experienced a political transformation whereby the sultan's monopoly on power was replaced with a multi-polar system in which political power was informally shared among many different individuals and factions. This process came about gradually, and was not unopposed. Certain rulers, such as Osman II
Osman II ( ota, عثمان ثانى ''‘Osmān-i sānī''; tr, II. Osman; 3 November 1604 – 20 May 1622), also known as Osman the Young ( tr, Genç Osman), was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 26 February 1618 until his regicide on 20 May 162 ...
and Murad IV
Murad IV ( ota, مراد رابع, ''Murād-ı Rābiʿ''; tr, IV. Murad, was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1623 to 1640, known both for restoring the authority of the state and for the brutality of his methods. Murad IV was born in Cons ...
, sought to reverse this trend and reestablish absolute power for themselves. For his efforts, Osman II became the victim of regicide in 1622, the significance of which one historian has compared to the 1649 regicide of Charles I of England
Charles I (19 November 1600 – 30 January 1649) was King of England, Scotland, and Ireland from 27 March 1625 until Execution of Charles I, his execution in 1649. He was born into the House of Stuart as the second son of King James VI of ...
.
Significant in this process of transformation were several changes in the nature of succession to the throne. At the outset of this period, Ottoman princes took up posts in the Anatolian provincial government upon reaching the age of maturity. However, Mehmed III
Mehmed III (, ''Meḥmed-i sālis''; tr, III. Mehmed; 26 May 1566 – 22 December 1603) was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1595 until his death in 1603. Mehmed was known for ordering the execution of his brothers and leading the army in the L ...
(r. 1595–1603) died before any of his sons came of age. Ahmed I
Ahmed I ( ota, احمد اول '; tr, I. Ahmed; 18 April 1590 – 22 November 1617) was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1603 until his death in 1617. Ahmed's reign is noteworthy for marking the first breach in the Ottoman tradition of royal f ...
was thus enthroned as a minor, and subsequently princes were no longer sent to the provinces to govern. While the motivation behind this change cannot be known for certain, it may have been a method of preventing the type of fratricidal civil war experienced in the last years of the reign of Suleiman I. Just as princely government was abandoned, so too did the practice of royal fratricide, which had been enforced since the time of Mehmed II
Mehmed II ( ota, محمد ثانى, translit=Meḥmed-i s̱ānī; tr, II. Mehmed, ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror ( ota, ابو الفتح, Ebū'l-fetḥ, lit=the Father of Conquest, links=no; tr, Fâtih Su ...
, fall out of use. This seems to have been a reaction to the unusually gruesome fratricides occasioned by the enthronements of Murad III and Mehmed III, in which dozens of infants and young boys were killed. The result was that the whole imperial family collectively remained in Istanbul, and sultans allowed their brothers to live in the harem undisturbed. The ultimate consequence of this was a change in the order of succession; upon his death in 1617 Ahmed I was succeeded not by one of his sons, but by his brother Mustafa I
Mustafa I (; ; 1600, Constantinople – 20 January 1639, Constantinople), called Mustafa the Saint (Veli Mustafa) during his second reign, and often called Mustafa the Mad (Deli Mustafa) by historians, was the son of Sultan Mehmed III and H ...
. Henceforth the general principle of Ottoman succession would be that of seniority
Seniority is the state of being older or placed in a higher position of status relative to another individual, group, or organization. For example, one employee may be senior to another either by role or rank (such as a CEO vice a manager), or by ...
rather than patrilineality. However, in practice this meant that sovereignty came to be viewed as something vested in the Ottoman dynasty as a whole rather than in a particular member, making the individual sultan replaceable.
The existence of multiple adult males of the Ottoman dynasty facilitated the emergence of other centers of power within the government. Two figures of particular importance were the Şeyhülislâm, or chief of the Islamic religious hierarchy, and the Valide Sultan #REDIRECT Valide sultan #REDIRECT Valide sultan
{{redirect category shell, {{R from move{{R from miscapitalization{{R unprintworthy ...
{{redirect category shell, {{R from move{{R from miscapitalization{{R unprintworthy ...Kösem Sultan
Kösem Sultan ( ota, كوسم سلطان, translit=;, 1589Baysun, M. Cavid, s.v. "Kösem Walide or Kösem Sultan" in ''The Encyclopaedia of Islam'' vol. V (1986), Brill, p. 272 " – 2 September 1651), also known as Mahpeyker SultanDouglas Arth ...
, mother of Murad IV
Murad IV ( ota, مراد رابع, ''Murād-ı Rābiʿ''; tr, IV. Murad, was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1623 to 1640, known both for restoring the authority of the state and for the brutality of his methods. Murad IV was born in Cons ...
and Ibrahim I, and Turhan Hatice
Turhan Hatice Sultan ( ota, تورخان سلطان, "''nobility of the Khan''" or ''mercy of the Khan'' " and "''respecful lady''"; 1627 – 4 August 1683) was the first Haseki Sultan of the Ottoman Sultan Ibrahim (reign 1640–48) and V ...
, mother of Mehmed IV
Mehmed IV ( ota, محمد رابع, Meḥmed-i rābi; tr, IV. Mehmed; 2 January 1642 – 6 January 1693) also known as Mehmed the Hunter ( tr, Avcı Mehmed) was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1648 to 1687. He came to the throne at the a ...
. Several sultans during this period occupied the throne while still children, and it was in their roles as regents that the Valide Sultans could become the most powerful figures in the empire.
Another locus of power was the ever-expanding imperial army, consisting of the Janissaries
A Janissary ( ota, یڭیچری, yeŋiçeri, , ) was a member of the elite infantry units that formed the Ottoman Sultan's household troops and the first modern standing army in Europe. The corps was most likely established under sultan Orhan ( ...
and Imperial Cavalry. The size of these organizations increased dramatically in the second half of the sixteenth century, with the number of janissaries increasing from 7,886 in 1527 to 39,282 in 1609. While many of these men went on to serve in the empire's foreign wars, others were janissaries only on paper, benefiting from the status they received as members of the corps but otherwise avoiding the obligation to serve in war. Such men connected the Janissary Corps with the common people, giving them a voice in politics. Protests, mutinies, and rebellions allowed the Janissaries to express their disapproval of imperial policy, and they frequently played a role in forming political coalitions within the Ottoman government. The Janissaries thus transformed from an elite fighting force into a complex hybrid organization, part military and part sociopolitical association, maintaining an important influence over Ottoman government in spite of attempts by heavy-handed rulers to suppress them over the course of the seventeenth century.
Political households
Another major development was the proliferation of so-called "vizier and pasha households" (''kapı'') among the political elite of the empire. The premier household in the empire was the sultan's imperial household in Istanbul, which the elite sought to emulate. Wealthy governors assembled large retinues of servants as well as private armies, forming connections of politicalpatronage
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows on another. In the history of art, arts patronage refers to the support that kings, popes, and the wealthy have provided to artists su ...
with one another. The formation of households coincided with a general increase in the wealth and power of the empire's highest-ranking provincial officials, which proved to be a mixed blessing for the central government: while the governors used their power to centralize imperial control and assemble larger armies to combat the Ottoman Empire's enemies, they also constituted more formidable foes in times of rebellion. The most successful elite household was established by the grand vizier Köprülü Mehmed Pasha
Köprülü Mehmed Pasha ( ota, كپرولی محمد پاشا, tr, Köprülü Mehmet Paşa; or ''Qyprilliu'', also called ''Mehmed Pashá Rojniku''; 1575, Roshnik,– 31 October 1661, Edirne) was the founder of the Köprülü political dynas ...
(1656–1661), who used it to dominate the empire during his tenure in office, placing loyal men from his household in positions of power and authority. Men raised in the Köprülü household continued to occupy important positions in the Ottoman government well into the early eighteenth century.
Bureaucracy
The Ottoman bureaucracy (''mālīye'') expanded dramatically both with regard to size and range of activity. While only 38 salaried scribes were serving in 1549, by 1593 this number had increased to 183. As theTimar System
A timar was a land grant by the sultans of the Ottoman Empire between the fourteenth and sixteenth centuries, with an annual tax revenue of less than 20,000 akçes. The revenues produced from the land acted as compensation for military service. A ...
was phased out of use, tax revenues which had once been distributed locally to the empire's army of feudal cavalry were now remitted to Istanbul, either through direct collection (''emānet'') or through tax farming
Farming or tax-farming is a technique of financial management in which the management of a variable revenue stream is assigned by legal contract to a third party and the holder of the revenue stream receives fixed periodic rents from the contract ...
(''iltizām''). A larger bureaucracy was thus needed in order to cope with the empire's increasingly centralized fiscal system. Bureaucratic organization was diversified, with new branches being formed and scribal duties increasingly specialized. The high quality of the Ottoman bureaucracy was underpinned by stringent standards of scribal recruitment. By the early seventeenth century the bureaucracy was moved out of its original location in Topkapı Palace
The Topkapı Palace ( tr, Topkapı Sarayı; ota, طوپقپو سرايى, ṭopḳapu sarāyı, lit=cannon gate palace), or the Seraglio
A seraglio, serail, seray or saray (from fa, سرای, sarāy, palace, via Turkish and Italian) i ...
, indicating that it was becoming independent of the sultan's household. It thus became a stabilizing influence for the empire; while sultans and viziers rose and fell, the bureaucracy remained in place, providing cohesion and continuity to imperial administration.
Military
The nature of the Ottoman military shifted dramatically during this period. From its inception the Ottoman army was dominated by cavalry forces, with cavalry outnumbering infantry in the sixteenth century on a 3:1 or 4:1 basis. As a result of the empire's rapid expansion and the stabilization of its borders in the preceding period, as well as the increasing importance of gunpowder technology to military success, the empire adapted by widening the range of its recruitment in order to raise much larger numbers of infantry troops. By the 1690s, the infantry proportion of the field army had increased to 50–60 percent, equivalent to that of the neighboringHabsburg Empire
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
. Calculations of total strength during this period remain unreliable, but it has been estimated that the average Ottoman army consisted of a core force of approximately 65,000–70,000 men from the timariot
Timariot (or ''tımar'' holder; ''tımarlı'' in Turkish) was the name given to a Sipahi cavalryman in the Ottoman army. In return for service, each timariot received a parcel of revenue called a timar, a fief, which were usually recently conquer ...
s and standing army, joined also by irregular militias and the armies of the empire's vassals, with a particularly significant contribution coming from the Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to ...
. In general, the Ottoman army remained at least as effective as those of its European rivals throughout this period. In contrast with older historical views, which posited a failure to keep pace with European military developments, the Ottomans in fact demonstrated a significant degree of dynamism and a continued capacity and willingness to innovate and improve their military forces. Although the empire experienced significant defeats and territorial loss in the 1683–99 War of the Holy League, this was caused not by military inferiority, but by the size and effective coordination of the Christian coalition, as well as the logistical challenges of warfare on multiple fronts.
Standing army
The Ottoman standing army (''ḳapukulu''), also referred to as the "central army", consisted of three main divisions: the infantry, known as theJanissary
A Janissary ( ota, یڭیچری, yeŋiçeri, , ) was a member of the elite infantry units that formed the Ottoman Sultan's household troops and the first modern standing army in Europe. The corps was most likely established under sultan Orhan ( ...
corps, the cavalry (sipahi
''Sipahi'' ( ota, سپاهی, translit=sipâhi, label=Persian, ) were professional cavalrymen deployed by the Seljuk dynasty, Seljuks, and later the Ottoman Empire, including the land grant-holding (''timar'') provincial ''Timariots, timarli s ...
) corps, known as the Six Regiments ( Altı Bölük), and the Artillery corps. Unlike the provincial army, the standing army was based in Istanbul and was subject to regular training and discipline, and was paid quarterly in cash salaries. The size of the army expanded dramatically beginning from the second half of the sixteenth century, more than doubling from 29,175 men in 1574 to 75,868 in 1609. Following this growth its numbers remained relatively stable for the rest of the century. The payment of salaries to the standing army was by far the largest single expense in the imperial budget, and this growth in size was paired with a proportional growth in expenditures. By the seventeenth century the cost of the standing army could at times absorb more than half of the empire's entire central budget. As the army grew the nature of its relationship with the government began to shift, as the janissaries and cavalry increasingly became involved in imperial politics and administration.
Logistics
The Ottomans possessed a distinct superiority in logistical organization over their European rivals, who were typically forced to resort to ''ad hoc'' solutions or even outright plunder in order to keep their armies in good supply. State centralization allowed the Ottomans to maintain a sophisticated system of waystations ( ota, menzil, script=Latn) across the empire, stocked with provisions for the army along their route of march. Border fortresses contained depots which could supply the army once it arrived at the frontier. This enabled the Ottoman army to largely, though not entirely, avoid having to live off the land through plunder.Border defense
Hungary
 In Hungary the Ottomans were primarily concerned with ensuring the security of
In Hungary the Ottomans were primarily concerned with ensuring the security of Buda
Buda (; german: Ofen, sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Budim, Будим, Czech and sk, Budín, tr, Budin) was the historic capital of the Kingdom of Hungary and since 1873 has been the western part of the Hungarian capital Budapest, on the ...
and the Danube River
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
, which served as a critical transport route for munitions and provisions. For this purpose they constructed several fortresses along the route of the river and surrounded Buda with a ring of protective fortresses, the most significant of which was Esztergom
Esztergom ( ; german: Gran; la, Solva or ; sk, Ostrihom, known by alternative names) is a city with county rights in northern Hungary, northwest of the capital Budapest. It lies in Komárom-Esztergom County, on the right bank of the river Danu ...
(Estergon), which was significantly enlarged and fortified subsequent to its capture in 1543. Buda's protective ring was completed in 1596 with the conquest of Eger
Eger ( , ; ; also known by other alternative names) is the county seat of Heves County, and the second largest city in Northern Hungary (after Miskolc). A city with county rights. Eger is best known for its castle, thermal baths, baroque build ...
(Eğri) to the northeast. Subsequent to the Peace of Zsitvatorok
The Peace of Zsitvatorok (or Treaty of Sitvatorok) was a peace treaty which ended the 15-year Long Turkish War between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburg monarchy on 11 November 1606. The treaty was part of a system of peace treaties which put an ...
in 1606 the pace of Ottoman fortress construction slowed as the military threat of the Habsburgs receded.
By the mid-seventeenth century Ottoman Hungary contained approximately 130 fortresses of varying size and strength, ranging from small castles of less than a hundred men to major strongholds with garrisons in the thousands. The most heavily manned were those on the border, while interior forts often contained no more than a token garrison. During the seventeenth century, Buda's garrison ranged from a low of 2,361 in the peaceful years after Zsitvatorok to a high of 5,697 during the third quarter of the century when war with the Habsburgs again resumed. By the 1660s, the total number of men serving in Hungarian garrisons reached as high as 24,000, split between some 17,450 local troops and 6,500 janissaries
A Janissary ( ota, یڭیچری, yeŋiçeri, , ) was a member of the elite infantry units that formed the Ottoman Sultan's household troops and the first modern standing army in Europe. The corps was most likely established under sultan Orhan ( ...
. These forces were supplemented by local timariots
Timariot (or ''tımar'' holder; ''tımarlı'' in Turkish language, Turkish) was the name given to a Sipahi cavalryman in the Ottoman army. In return for service, each timariot received a parcel of revenue called a timar, a fief, which were usuall ...
as well as the private armies of Ottoman governors. These numbers, however, constitute wartime levels. During peacetime the garrison sizes would frequently be reduced in order to cut costs. While in the second half of the sixteenth century the Hungarian fortress network was financially self-sufficient, and the local governors were even able to remit surplus revenue to Istanbul, this had deteriorated by the seventeenth century such that the administrative border of the province of Buda needed to be extended south of the Danube in order to increase its available revenue. Nevertheless, the Ottoman financial system was in better shape than that of the Habsburgs, who continually struggled to raise the revenue needed to maintain their own defense network.
Aside from periods of open warfare (1541–68, 1593–1606, 1660–4, 1683–99), the Ottoman-Habsburg frontier in Hungary was characterized by local skirmishes and small-scale conflict known as the "little war" ( ger, Kleinkrieg). In the absence of the imperial army, command was entrusted to the governor of Buda, who could wield significant provincial forces in the defense of the frontier. Local military ventures could occasionally lead to escalation, as in 1592-3 when the Long War was provoked by the Ottoman governor of Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and He ...
's conquest of Bihać
Bihać ( cyrl, Бихаћ) is a city and the administrative centre of Una-Sana Canton of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, an entity of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is situated on the banks of river Una in northwestern Bosnia and Herzegovina ...
.
Northern frontier
 In contrast with their Hungarian and Safavid frontiers, the Ottomans generally did not seek to expand further north from the
In contrast with their Hungarian and Safavid frontiers, the Ottomans generally did not seek to expand further north from the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
, being concerned primarily with its defense and the security of its sea lanes. The Ottomans maintained a series of fortresses along the Black Sea's northern shore, in the territory of modern Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
. Major sites were located in Akkerman
Bilhorod-Dnistrovskyi ( uk, Бі́лгород-Дністро́вський, Bílhorod-Dnistróvskyy, ; ro, Cetatea Albă), historically known as Akkerman ( tr, Akkerman) or under different names, is a city, municipality and port situated on ...
, Özü, and Azak
Azov (russian: Азов), previously known as Azak,
is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town in Rostov Oblast, Russia, situated on the Don River (Russia), Don River just from the Sea of Azov, which derives its name from the town. Popu ...
. Also of critical importance for the northern frontier was the Ottoman vassal state of the Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to ...
, a major power in its own right, which frequently engaged in raiding activity against the Ottomans' northern neighbors the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
. Crimean raiding created a flourishing slave trade through the port of Caffa
uk, Феодосія, Теодосія crh, Kefe
, official_name = ()
, settlement_type=
, image_skyline = THEODOSIA 01.jpg
, imagesize = 250px
, image_caption = Genoese fortress of Caffa
, image_shield = Fe ...
, directly administered by the Ottomans, but also created perpetual tension between the Ottomans and their neighbors.
The security of the Ottomans' northern frontier was first threatened at the end of the sixteenth century with the emergence of the Zaporozhian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporoz ...
as a military and political force on the Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and B ...
River. Theoretically under the sovereignty of the Commonwealth, the Cossacks used riverboats to enter the Black Sea and launch raids on the Ottoman coastline, becoming marauders and slavers in a manner roughly analogous to the raids of the Crimean Tatars. The Ottomans had long since suppressed all piracy in the Black Sea, the ports of which they entirely controlled, and were thus completely unprepared for the irruption of the Cossacks. By 1614 they were targeting the northern shore of Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, where major towns were sacked and burned, including Sinop Sinop can refer to:
* Sinop, Turkey, a city on the Black Sea
** Sinop Nuclear Power Plant, was planned in 2013, but cancelled in 2018
** Battle of Sinop, 1853 naval battle in the Sinop port
*** Russian ship ''Sinop'', Russian ships named after the ...
, Samsun
Samsun, historically known as Sampsounta ( gr, Σαμψούντα) and Amisos (Ancient Greek: Αμισός), is a List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, city on the north coast of Turkey and is a major Black Sea port. In 2021, Samsun reco ...
, and Trabzon
Trabzon (; Ancient Greek: Tραπεζοῦς (''Trapezous''), Ophitic Pontic Greek: Τραπεζούντα (''Trapezounta''); Georgian: ტრაპიზონი (''Trapizoni'')), historically known as Trebizond in English, is a city on the Bl ...
. Ottoman exasperation over the Cossack problem resulted in worsening relations with the Commonwealth, and the two countries went to war in 1621 and very nearly again in 1634 and 1646. Countermeasures were developed in order to limit the damage the Cossacks could cause; by the 1620s the Ottomans had established tighter control over the mouth of the Dnieper, preventing large flotillas from passing into the sea, and naval squadrons were established to patrol for raiders.
The Commonwealth had little ability to control the activities of the Cossacks, and in 1648 Ukraine descended into chaos with the Khmelnytsky Uprising
The Khmelnytsky Uprising,; in Ukraine known as Khmelʹnychchyna or uk, повстання Богдана Хмельницького; lt, Chmelnickio sukilimas; Belarusian language, Belarusian: Паўстанне Багдана Хмяльніц ...
, whereby the Cossacks sought to overthrow the control of the Commonwealth and establish an independent state. War continued for nearly twenty years, leading to the intervention of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
and Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
, among others. In 1669 Cossack Hetman
( uk, гетьман, translit=het'man) is a political title from Central and Eastern Europe, historically assigned to military commanders.
Used by the Czechs in Bohemia since the 15th century. It was the title of the second-highest military co ...
Petro Doroshenko
Petro Doroshenko ( uk, Петро Дорофійович Дорошенко, russian: Пётр Дорофе́евич Дороше́нко, pl, Piotr Doroszenko; 1627–1698) was a Cossack political and military leader, Hetman of Right-bank Ukr ...
turned to the Ottomans, offering his state of Right-Bank Ukraine
Right-bank Ukraine ( uk , Правобережна Україна, ''Pravoberezhna Ukrayina''; russian: Правобережная Украина, ''Pravoberezhnaya Ukraina''; pl, Prawobrzeżna Ukraina, sk, Pravobrežná Ukrajina, hu, Jobb p ...
as a vassal in exchange for protection from the Commonwealth and Russia. The Ottomans accepted his offer, seeing this as an opportunity to bring an end to perennial Cossack raiding and to shore up the defenses of the northern frontier. Following a Commonwealth attack on the Cossacks, the Ottomans went to war and in 1672 conquered the fortress of Kamianets-Podilskyi
Kamianets-Podilskyi ( uk, Ка́м'яне́ць-Поді́льський, russian: Каменец-Подольский, Kamenets-Podolskiy, pl, Kamieniec Podolski, ro, Camenița, yi, קאַמענעץ־פּאָדאָלסק / קאַמעניץ, ...
, known to the Ottomans as Kamaniçe. Peace was signed in 1676, whereby the Ottomans annexed the province of Podolia
Podolia or Podilia ( uk, Поділля, Podillia, ; russian: Подолье, Podolye; ro, Podolia; pl, Podole; german: Podolien; be, Падолле, Padollie; lt, Podolė), is a historic region in Eastern Europe, located in the west-central ...
. The Ottomans thus acquired a strong foothold from which to increase their control over the Cossack state, and shortly thereafter established garrisons in the major towns of Ukraine, clashing with the Russians and expelling them from the traditional Cossack capital of Chyhyryn
Chyhyryn ( uk, Чигирин, ) is a city and historic site located in Cherkasy Raion of Cherkasy Oblast of central Ukraine. From 1648 to 1669 the city was a Hetman residence. After a forced relocation of the Ruthenian Orthodox metropolitan see ...
in 1678. Kamaniçe remained the bulwark of the Ottoman northern frontier throughout the War of the Holy League. With a garrison of over 6,000 men and 200 cannons, it was one of the most heavily defended fortresses in the Ottoman Empire. Despite continuous attempts by the Commonwealth to blockade and besiege the city, Kamaniçe managed to hold out throughout the war, and in accordance with the Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed in Karlowitz, Military Frontier of Archduchy of Austria (present-day Sremski Karlovci, Serbia), on 26 January 1699, concluding the Great Turkish War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by the ...
was returned to the Commonwealth in 1699 without having been conquered.
Navy
Although the Ottoman army remained effective throughout this period, the same cannot be said of the navy. While dominant in the Mediterranean in 1550, theBattle of Lepanto
The Battle of Lepanto was a naval engagement that took place on 7 October 1571 when a fleet of the Holy League, a coalition of Catholic states (comprising Spain and its Italian territories, several independent Italian states, and the Soverei ...
in 1571 resulted in a significant loss of skilled manpower and experienced commanders. The Ottoman navy went on to conquer Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
in 1574, but subsequent events shifted imperial attention away from the Mediterranean. The resumption of the Ottoman-Safavid Wars in 1578 and the death of Grand Vizier Sokollu Mehmed Pasha
Sokollu Mehmed Pasha ( ota, صوقوللى محمد پاشا, Ṣoḳollu Meḥmed Pașa, tr, Sokollu Mehmet Paşa; ; ; 1506 – 11 October 1579) was an Ottoman statesman most notable for being the Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Empire. Born in ...
the following year paved the way for a truce with Habsburg Spain in 1580, bringing to an end the imperial wars in the Mediterranean which had characterized the middle of the sixteenth century. The Ottoman navy subsequently fought no maritime war until the outbreak of the Cretan War with Venice in 1645, nearly seventy years later. This period of inaction played a role in weakening the effectiveness of the Ottoman navy, such that the Venetians were able to blockade the Dardanelles
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; ...
and inflict several defeats upon the Ottomans, most significantly in the 1656 Battle of the Dardanelles, described as the worst Ottoman defeat since Lepanto. Although these defeats have often been ascribed to an Ottoman failure to modernize their navy through the replacement of oar-propelled galley
A galley is a type of ship that is propelled mainly by oars. The galley is characterized by its long, slender hull, shallow draft, and low freeboard (clearance between sea and gunwale). Virtually all types of galleys had sails that could be used ...
s with sail-driven galleon
Galleons were large, multi-decked sailing ships first used as armed cargo carriers by European states from the 16th to 18th centuries during the age of sail and were the principal vessels drafted for use as warships until the Anglo-Dutch War ...
s, in fact the Ottoman navy contained just as many galleons as that of the Venetians. Rather than innovation or technical ability, what the Ottomans lacked was skilled mariners to crew and command their vessels, whereas the Venetians could draw upon their extensive merchant marine for manpower. In contrast with the sixteenth century, the skilled mariners of the Barbary Coast were less willing to commit themselves to the Ottoman cause. Whereas sixteenth-century Ottoman admirals frequently began their careers as corsairs in North Africa, in the middle of the seventeenth century the admiralty was merely a prestigious office to be held by various statesmen who did not necessarily have any naval experience. Despite these difficulties, the Ottomans were ultimately able to overcome the Venetians, breaking the blockade of the Dardanelles in 1657 and completing the conquest of Crete with the fall of Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
in 1669.
Subsequent to the Cretan War, the Ottomans sought to improve the quality of their navy, and particularly its galleons. Investments were made toward improving their technical design, such that by 1675 an English captain could write home with suggestions for altering the design of English ships on the Ottoman model. In 1682 a dedicated squadron of galleons was created, organizationally separate from the fleet's remaining galleys, and in that year alone ten new galleons were commissioned to be built. The Ottomans' next major naval conflict began in 1684, when Venice aligned with Habsburg Austria The term Habsburg Austria may refer to the lands ruled by the Austrian branch of the Habsburgs, or the historical Austria. Depending on the context, it may be defined as:
* The Duchy of Austria, after 1453 the Archduchy of Austria
* The ''Erbland ...
, Poland–Lithuania, and the Papacy to combat the Ottomans in the War of the Holy League. The Venetians opened a front in the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek language, Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish language, Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It ...
and Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic regions of Greece, geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmu ...
, but failed in an attempt to reconquer Crete in 1692. From 1695 to 1701 the Ottoman navy was placed under the command of Mezemorta Hüseyin Pasha, an experienced corsair from Algiers, who defeated the Venetian fleet in battle on 9 February 1695 and demonstrated the success of the previous decades' reforms.
Religious and intellectual life
 The Ottoman Empire of this period was home to a vibrant religious and intellectual life. The legal reforms of Şeyhülislâm
The Ottoman Empire of this period was home to a vibrant religious and intellectual life. The legal reforms of Şeyhülislâm Ebussuud Efendi
Ebussuud Efendi ( tr, Mehmed Ebüssuûd Efendi, 30 December 1490 – 23 August 1574)İsmail Hâmi Danişmend, ''Osmanlı Devlet Erkânı'', Türkiye Yayınevi, İstanbul, 1971, p. 114. was a Hanafi Maturidi Ottoman jurist and Qur'an exegete, w ...
(1545–74) stimulated Ottoman intellectuals to vigorously debate many of society's issues. Ottomans were conflicted over the religious and moral qualities of newly available consumer goods, such as coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulant, stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
S ...
and tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, which were sometimes banned and sometimes permitted. Equally divisive was the legality of several religious practices associated with Sufism
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, r ...
, which were most staunchly opposed by the fiercely conservative Kadızadelis, a movement which began in the early seventeenth century but traced its origins to the sixteenth century preacher Birgili Mehmed Efendi (d. 1573). Kazıdadeli ideology centered on the Islamic invocation to " enjoin good and forbid wrong," leading them to oppose practices they perceived as "innovation" (''bid'ah
In Islam, bid'ah ( ar, بدعة; en, innovation) refers to innovation in religious matters. Linguistically, the term means "innovation, novelty, heretical doctrine, heresy".
In classical Arabic literature ('' adab''), it has been used as a fo ...
''), in a manner roughly analogous to modern Wahhabism
Wahhabism ( ar, ٱلْوَهَّابِيَةُ, translit=al-Wahhābiyyah) is a Sunni Islamic revivalist and fundamentalist movement associated with the reformist doctrines of the 18th-century Arabian Islamic scholar, theologian, preacher, an ...
. The Kadızadelis spread their ideology by serving as preachers in Istanbul's major mosques, and twice won the support of the imperial government, first under Murad IV
Murad IV ( ota, مراد رابع, ''Murād-ı Rābiʿ''; tr, IV. Murad, was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1623 to 1640, known both for restoring the authority of the state and for the brutality of his methods. Murad IV was born in Cons ...
and later under Mehmed IV
Mehmed IV ( ota, محمد رابع, Meḥmed-i rābi; tr, IV. Mehmed; 2 January 1642 – 6 January 1693) also known as Mehmed the Hunter ( tr, Avcı Mehmed) was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1648 to 1687. He came to the throne at the a ...
. Despite this, the Kadızadelis were looked upon with scorn by many of Istanbul's scholars and intellectuals, who ridiculed them for their zealous conservatism. The Kadızadeli preacher Vani Mehmed Efendi acted as a personal spiritual advisor to Mehmed IV, but fell from grace and was banished from court following the unsuccessful Siege of Vienna Sieges of Vienna may refer to:
* Siege of Vienna (1239)
* Siege of Vienna (1276)
* Siege of Vienna (1287)
* Siege of Vienna (1477), unsuccessful Hungarian attempt during the Austro–Hungarian War.
*Siege of Vienna (1485), Hungarian victory during ...
in 1683. The Kadızadelis henceforth received no direct imperial support.
In the early seventeenth century, Ottoman intellectual life was further influenced by an influx of scholars from Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and Kurdistan
Kurdistan ( ku, کوردستان ,Kurdistan ; lit. "land of the Kurds") or Greater Kurdistan is a roughly defined geo-cultural territory in Western Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, Kurdish la ...
. These scholars encouraged a revival of the rational sciences through emphasis on 'verification' (Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
: ''taḥqīq'', as opposed to ''taqlīd'', "imitation") of the scientific discoveries of previous generations. The result was a burst of new written works on rationalist topics, such as mathematics, logic, and dialectics, with many scholars tracing their intellectual lineage back to these Iranian and Kurdish immigrants.
Nasihatname
This period also witnessed the flowering of the literary genre known as "Advice for Kings" ('' nasihatname''). Literary works of this nature were written to address the struggles which the state was experiencing, and to advise the ruler on how to properly solve them. Advice writers frequently alluded to the reign of Sultan Suleiman I (1520–1566) as the ideal model which contemporary rulers should seek to emulate. Writers who portrayed the empire as being in decline from a previous golden age were often motivated to do so by class or factional interests, as they often came from or were influenced by groups who had been disenfranchised by the empire's reforms, such as thetimariots
Timariot (or ''tımar'' holder; ''tımarlı'' in Turkish language, Turkish) was the name given to a Sipahi cavalryman in the Ottoman army. In return for service, each timariot received a parcel of revenue called a timar, a fief, which were usuall ...
, or otherwise felt personal indignation toward the state as a result of failing to achieve career advancement, indicating a clear bias in their writings. Historians had once accepted these writers' description of Ottoman decline as fact, and thus portrayed the Ottoman Empire as entering a period of decline after the death of Suleiman the Magnificent, a view which has come to be known as the Ottoman Decline Thesis
The Ottoman decline thesis or Ottoman decline paradigm ( tr, Osmanlı Gerileme Tezi) is an obsolete
*
*
*
*
* Leslie Peirce, "Changing Perceptions of the Ottoman Empire: the Early Centuries," ''Mediterranean Historical Review'' 19/1 (20 ...
. However, since the 1980s, due to a reexamination of the ''nasihatname'' literature as well as countless other facets of Ottoman civilization, historians have achieved a consensus that in fact no such decline occurred, and thus the notion of the "Decline of the Ottoman Empire" was a myth.
Historiography
Ottoman historical writing underwent major changes during this period. Particularly after 1600, Ottoman writers shifted away from the Persianate style of previous generations, writing in a form ofTurkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
prose which was much less ornate in comparison with works produced in the sixteenth century. Ottoman historians came to see themselves as problem-solvers, using their historical knowledge to offer solutions to contemporary issues, and for this they chose to write in a straightforward, easily understood vernacular form of Turkish. Rather than writing solely to buttress the prestige of the Ottoman dynasty, Ottoman historians of the seventeenth century believed in the importance of reporting events in as honest and accurate a manner as was possible. Major historians of this period include Mustafa Âlî
Gelibolulu Mustafa Âlî bin Ahmed bin Abdülmevlâ Çelebi (b. 28 April 1541 – d. 1600) was an Ottoman historian, bureaucrat and major literary figure.
Life and work
Mustafa Ali was born on 28 April, 1541 in Gelibolu, a provincial town on the ...
, Katib Çelebi, and Mustafa Naima
Mustafa Naima ( ota, مصطفى نعيما; ''Muṣṭafā Na'īmā''; Aleppo, Ottoman Syria 1655 – 1716) was an Ottoman bureaucrat and historian who wrote the chronicle known as the ''Tārīḫ-i Na'īmā'' (''Naima's History''). He is ofte ...
.
Political narrative
Suleiman's successors
upright=1.35, The Ottoman Empire in 1590, following the signing of the Treaty of Constantinople (1590), Treaty of Constantinople with theSafavids
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often conside ...
.
Sultan Suleiman I (r. 1520–1566) was the longest-reigning sultan in Ottoman history, but the last years of his reign were characterized by uncertainty over who would be his successor. Suleiman had three sons who could hope to succeed, Mustafa
Mustafa ( ar, مصطفى
, Muṣṭafā) is one of the names of Prophet Muhammad, and the name means "chosen, selected, appointed, preferred", used as an Arabic given name and surname. Mustafa is a common name in the Muslim world.
Given name Mou ...
, Bayezid, and Selim
Salim, Saleem or Selim may refer to:
People
*Salim (name), or Saleem or Salem or Selim, a name of Arabic origin
*Salim (poet) (1800–1866)
*Saleem (playwright) (fl. 1996)
*Selim I, Selim II and Selim III, Ottoman Sultans
* Selim people, an eth ...
. While the latter two were the children of Suleiman's wife Hurrem Sultan
Hurrem Sultan (, ota, خُرّم سلطان, translit=Ḫurrem Sulṭān, tr, Hürrem Sultan, label=Modern Turkish; 1500 – 15 April 1558), also known as Roxelana ( uk, Роксолана}; ), was the chief consort and legal wife of the Ottom ...
, the first was the son of Mahidevran Sultan
Mahidevran Hatun ( ota, ماه دوران "''lucky's moon''", 1500 – 3 February 1581; also known as Gülbahar Hatun) was a concubine of Suleiman the Magnificent of the Ottoman Empire and the mother of Şehzade Mustafa. After Suleiman ascended ...
. Mustafa may have felt that his half-brothers possessed an unfair advantage over him, and thus worked to secure the favor of the military. Perhaps suspecting that Mustafa planned to dethrone him just as his own father had done to his grandfather
Grandparents, individually known as grandmother and grandfather, are the parents of a person's father or mother – paternal or maternal. Every sexually-reproducing living organism who is not a genetic chimera has a maximum of four genetic ...
, Suleiman acted first and in 1553 ordered that Mustafa be executed. The death of Hurrem Sultan in 1558 triggered open conflict between the two remaining candidates, and Selim ultimately emerged victorious. Suleiman further strengthened his son's position by arranging a marriage between Selim's daughter and the influential Sokollu Mehmed Pasha
Sokollu Mehmed Pasha ( ota, صوقوللى محمد پاشا, Ṣoḳollu Meḥmed Pașa, tr, Sokollu Mehmet Paşa; ; ; 1506 – 11 October 1579) was an Ottoman statesman most notable for being the Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Empire. Born in ...
(Grand Vizier
Grand vizier ( fa, وزيرِ اعظم, vazîr-i aʾzam; ota, صدر اعظم, sadr-ı aʾzam; tr, sadrazam) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. The office of Grand Vizier was first ...
1565–1579). Suleiman died in 1566, while besieging the fortress of Szigetvar in Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
, bringing Selim to the throne.
Selim II
Selim II ( Ottoman Turkish: سليم ثانى ''Selīm-i sānī'', tr, II. Selim; 28 May 1524 – 15 December 1574), also known as Selim the Blond ( tr, Sarı Selim) or Selim the Drunk ( tr, Sarhoş Selim), was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire ...
was a relatively inactive ruler who was content to allow the highly competent Sokollu Mehmed to run the empire on his behalf. Sokollu carried out a far-reaching foreign policy, dispatching armies to territories as distant as Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
in the south and Astrakhan
Astrakhan ( rus, Астрахань, p=ˈastrəxənʲ) is the largest city and administrative centre of Astrakhan Oblast in Southern Russia. The city lies on two banks of the Volga, in the upper part of the Volga Delta, on eleven islands of the ...
in the north. Most significant, however, was the conquest of Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geo ...
in 1570 and subsequent Ottoman defeat in the Battle of Lepanto
The Battle of Lepanto was a naval engagement that took place on 7 October 1571 when a fleet of the Holy League, a coalition of Catholic states (comprising Spain and its Italian territories, several independent Italian states, and the Soverei ...
, which paved the way for a Spanish-Ottoman truce in 1580 and continual détente in the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
. This allowed the Ottomans to focus their expansion to the east against Safavid Iran
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often conside ...
, where a long and devastating war was fought from 1578 to 1590, from which the Ottomans emerged with significant, if short-lived, conquests.
Selim died in 1574 and was succeeded by his son Murad III
Murad III ( ota, مراد ثالث, Murād-i sālis; tr, III. Murad; 4 July 1546 – 16 January 1595) was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1574 until his death in 1595. His rule saw battles with the Habsburgs and exhausting wars with the Saf ...
(r. 1574–95). This ruler, like his two successors Mehmed III
Mehmed III (, ''Meḥmed-i sālis''; tr, III. Mehmed; 26 May 1566 – 22 December 1603) was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1595 until his death in 1603. Mehmed was known for ordering the execution of his brothers and leading the army in the L ...
(r. 1595–1603) and Ahmed I
Ahmed I ( ota, احمد اول '; tr, I. Ahmed; 18 April 1590 – 22 November 1617) was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1603 until his death in 1617. Ahmed's reign is noteworthy for marking the first breach in the Ottoman tradition of royal f ...
(r. 1603–1617), was highly influenced by the changing scene of palace politics. Most significant was the rise in importance of the harem
Harem (Persian: حرمسرا ''haramsarā'', ar, حَرِيمٌ ''ḥarīm'', "a sacred inviolable place; harem; female members of the family") refers to domestic spaces that are reserved for the women of the house in a Muslim family. A hare ...
. Whereas Hurrem Sultan's power was based on her personal relationship with Suleiman, the imperial women of this period derived their power from the institutional structure of the harem, which placed immense power into the hands of the sultan's mother, the Valide Sultan #REDIRECT Valide sultan #REDIRECT Valide sultan
{{redirect category shell, {{R from move{{R from miscapitalization{{R unprintworthy ...
{{redirect category shell, {{R from move{{R from miscapitalization{{R unprintworthy ...Topkapı Palace
The Topkapı Palace ( tr, Topkapı Sarayı; ota, طوپقپو سرايى, ṭopḳapu sarāyı, lit=cannon gate palace), or the Seraglio
A seraglio, serail, seray or saray (from fa, سرای, sarāy, palace, via Turkish and Italian) i ...
, but resided in a new bedchamber within the harem. Due to the increasing role of imperial women in political life, this period is sometimes referred to as the Sultanate of Women
The Sultanate of Women ( Turkish: ''Kadınlar saltanatı'') was a period when wives and mothers of the Sultans of the Ottoman Empire exerted extraordinary political influence.
This phenomenon took place from roughly 1528-30 to 1715, beginning in ...
.
Crisis and adaptation
 The Ottoman government at the turn of the century was presented with a severe military and economic crisis. War erupted with the
The Ottoman government at the turn of the century was presented with a severe military and economic crisis. War erupted with the Austrian Habsburgs The term Habsburg Austria may refer to the lands ruled by the Austrian branch of the Habsburgs, or the historical Austria. Depending on the context, it may be defined as:
* The Duchy of Austria, after 1453 the Archduchy of Austria
* The ''Erbland ...
in 1593 just as Anatolia experienced the first of several Celali Rebellions
The Celali rebellions ( tr, Celalî ayaklanmaları), were a series of rebellions in Anatolia of irregular troops led by bandit chiefs and provincial officials known as ''celalî'', ''celâli'', or ''jelālī'', against the authority of the Ottoman ...
, in which rural bandit gangs grouped together under provincial warlords to wreak havoc on the countryside. In 1603 Shah Abbas of the Safavids launched a new war against the Ottomans, reversing all of the gains that had made in the previous decades. Thus the Ottomans found themselves fighting on three fronts at once, at a time when the economy was still recovering from the currency debasement of 1585. To overcome this challenge, they adopted an innovative strategy of co-opting the rebel forces into the structure of the empire. The Celali armies were manned by Anatolian bandits known as sekban
The Sekban were mercenaries of peasant background in the Ottoman Empire. The term ''sekban'' initially referred to irregular military units, particularly those without guns, but ultimately it came to refer to any army outside the regular military ...
, former peasants who sought an alternate livelihood in the harsh economic climate of the turn of the century. When given the opportunity, these men were eager to earn pay and status by serving in the Ottoman army as mercenaries. By recruiting such men into the Ottoman army as musketeers their energies were redirected from banditry and put to use against the empire's external enemies. The Celali leaders, as well, were at times granted positions within the provincial administration in order to pacify them. This did not bring the anarchy in Anatolia to an end, but it did make it easier to manage. In 1609 the grand vizier Kuyucu Murad Pasha
Kuyucu Murad Pasha (Ottoman Turkish for "Murad Pasha the Well-digger", i.e. "Gravedigger"; sh, Murat-paša Kujudžić; 1535 – 1611) was an Ottoman statesman who served as Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Empire during the reign of Ahmed I bet ...
traversed Anatolia with an army, clearing away the Celalis wherever he found them and bringing an end to the greater part of Celali activity.
The wars with the Habsburgs and Safavids eventually devolved into stalemates. Mehmed III personally led the Ottoman army to victory over the Habsburgs in the Battle of Mezőkeresztes
), Hungary
, result = Ottoman victory,
, combatant1 = Ottoman Empire
, combatant2 = Principality of Transylvania (1571–1711), Transylvania Kingdom of HungaryWalloons, Walloon and French mercenariesSerbian hajduksC ...
in 1596, and the Ottomans went on to seize the Hungarian fortresses of Eger
Eger ( , ; ; also known by other alternative names) is the county seat of Heves County, and the second largest city in Northern Hungary (after Miskolc). A city with county rights. Eger is best known for its castle, thermal baths, baroque build ...
and Nagykanizsa
Nagykanizsa (; hr, Velika Kaniža/Velika Kanjiža, or just ''Kaniža/Kanjiža''; german: Großkirchen, Groß-Kanizsa; it, Canissa; sl, Velika Kaniža; tr, Kanije), known colloquially as Kanizsa, is a medium-sized city in Zala County in southw ...
, but ultimately neither side was able to achieve a decisive victory and the war was brought to an end in 1606 with the Treaty of Zsitvatorok. The war with the Safavids continued to drag on until 1618.
The recruitment of sekban
The Sekban were mercenaries of peasant background in the Ottoman Empire. The term ''sekban'' initially referred to irregular military units, particularly those without guns, but ultimately it came to refer to any army outside the regular military ...
as musketeers was part of a larger process of military and fiscal reform which was carried out during this period. The cavalry army which had been supported by the Timar System
A timar was a land grant by the sultans of the Ottoman Empire between the fourteenth and sixteenth centuries, with an annual tax revenue of less than 20,000 akçes. The revenues produced from the land acted as compensation for military service. A ...
during the sixteenth century was becoming obsolete as a result of the increasing importance of musket-wielding infantry, and the Ottomans sought to adapt to the changing times. The central army was greatly expanded, particularly the Janissary Corps
A Janissary ( ota, یڭیچری, yeŋiçeri, , ) was a member of the elite infantry units that formed the Ottoman Sultan's household troops and the first modern standing army in Europe. The corps was most likely established under sultan Orhan ...
, the empire's premier infantry force. The Janissaries began to experiment with new battlefield tactics, becoming one of the first armies in Europe to utilize volley fire
Volley fire, as a military tactic, is (in its simplest form) the concept of having soldiers shoot in the same direction en masse. In practice, it often consists of having a line of soldiers all discharge their weapons simultaneously at the enemy ...
. To pay for the newly expanded army, the Ottomans expanded the practice of tax farming
Farming or tax-farming is a technique of financial management in which the management of a variable revenue stream is assigned by legal contract to a third party and the holder of the revenue stream receives fixed periodic rents from the contract ...
, formerly used primarily in the Arab provinces. Taxation rights which were formerly given to cavalrymen were now sold to the highest bidder, a practice which was in use in much of Europe as well. Other taxes were also reformed, with the wartime tax known as ''avarız'' becoming permanent and providing for 20% of the empire's annual revenue. These reforms greatly increased the revenue available to the central government and played a major role in the empire's continued strength throughout the century. To accommodate these changes, the bureaucracy was expanded and diversified, coming to play a much larger role in the empire's administration.

Regicide and war
Ahmed I's death in 1617 brought his brother to the throne asMustafa I
Mustafa I (; ; 1600, Constantinople – 20 January 1639, Constantinople), called Mustafa the Saint (Veli Mustafa) during his second reign, and often called Mustafa the Mad (Deli Mustafa) by historians, was the son of Sultan Mehmed III and H ...
, the first instance of a sultan succeeding through seniority. However, before long it became apparent that Mustafa was not mentally sound, and he was deposed the following year in favor of Sultan Ahmed's son Osman II
Osman II ( ota, عثمان ثانى ''‘Osmān-i sānī''; tr, II. Osman; 3 November 1604 – 20 May 1622), also known as Osman the Young ( tr, Genç Osman), was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 26 February 1618 until his regicide on 20 May 162 ...
, then aged 13. Osman II was an exceptionally energetic ruler, and sought to restore the authority of the Ottoman sultanate over the other factional groups within the empire. This aroused the anger of both the religious establishment as well as the Janissaries
A Janissary ( ota, یڭیچری, yeŋiçeri, , ) was a member of the elite infantry units that formed the Ottoman Sultan's household troops and the first modern standing army in Europe. The corps was most likely established under sultan Orhan ( ...
and Imperial Cavalry, and relations became particularly strained after the sultan's failed Polish campaign
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week afte ...
, in which the army felt it had been mistreated. After their return to Istanbul, Osman II announced his desire to perform the pilgrimage to Mecca
The Hajj (; ar, حَجّ '; sometimes also spelled Hadj, Hadji or Haj in English) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for Muslims that must be carried o ...
; in fact this was a plan to recruit a new and more loyal army in Anatolia, out of the bandit-mercenary forces which had taken part in the Celali Rebellions and the Ottomans' wars with the Habsburgs and Safavids. To prevent him from carrying out this plan, the imperial army launched a revolt on May 18, 1622, and two days later, with the approval of the Şeyhülislâm, executed Sultan Osman II. This event, the legally approved regicide of a reigning Ottoman monarch, cemented the empire's transformation from a patrimonial empire into one in which power was shared between various loci of authority.
The regicide was followed by the revolt of Abaza Mehmed Pasha
Abaza Mehmed Pasha ( tr, Abaza Mehmed Paşa, ab, Меҳмеҭ Росҭом-иԥа Лакырба, ма Кыржәаа); 1576 – August 23, 1634) was a statesman and military commander of the Ottoman Empire, the namesake of the Abaza rebellion. ...
, then governor of Erzurum
Erzurum (; ) is a city in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. It is the largest city and capital of Erzurum Province and is 1,900 meters (6,233 feet) above sea level. Erzurum had a population of 367,250 in 2010.
The city uses the double-headed eagle as ...
, who vowed to take revenge upon the sultan's killers and massacred the janissaries wherever he found them. Mustafa I, who had been enthroned for the second time, was soon deposed yet again and replaced by Ahmed I's son Murad IV
Murad IV ( ota, مراد رابع, ''Murād-ı Rābiʿ''; tr, IV. Murad, was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1623 to 1640, known both for restoring the authority of the state and for the brutality of his methods. Murad IV was born in Cons ...
, still a child. Thus with a child on the throne, Istanbul under the control of a Janissary clique, and Abaza Mehmed running rampant in the east, the Safavids
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often conside ...
saw another opportunity to attack and seized control of Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
in January 1624, but were unable to advance to Diyarbakır
Diyarbakır (; ; ; ) is the largest Kurdish-majority city in Turkey. It is the administrative center of Diyarbakır Province.
Situated around a high plateau by the banks of the Tigris river on which stands the historic Diyarbakır Fortress, ...
. In 1628 Abaza Mehmed's revolt was suppressed by the grand vizier Husrev Pasha, whose dismissal from office in 1632 triggered a Janissary revolt. This event fueled Murad IV's desire to regain control over the state, and he henceforth began to exercise power in his own right. He carried out a reform of military land tenure in an effort to strengthen the army, encouraged peasant resettlement of abandoned fields, and enforced moral reform in Istanbul in conjunction with the religious movement of the Kadızadelis. First achieving military success in 1635 with the conquest of Yerevan
Yerevan ( , , hy, Երևան , sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia and one of the world's List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Y ...
, he was ultimately able to lead the empire to victory by reconquering Baghdad in 1638 and establishing a long-lasting peace with the Safavids the following year.
Murad IV died in 1640, only 29 years old. He was succeeded by his brother Ibrahim
Ibrahim ( ar, إبراهيم, links=no ') is the Arabic name for Abraham, a Biblical patriarch and prophet in Islam.
For the Islamic view of Ibrahim, see Abraham in Islam.
Ibrahim may also refer to:
* Ibrahim (name), a name (and list of people ...
, the only remaining male member of the Ottoman dynasty. Like Mustafa I before him, Ibrahim was mentally unstable, and was initially content to leave the government in the hands of Murad IV's last grand vizier, Kemankeş Mustafa Pasha. This lasted only until 1644, when Ibrahim had him executed and replaced by a rival. The following year war between the Ottoman Empire and Venice was sparked by an incident in which Maltese pirates docked on Venetian Crete
The Realm or Kingdom of Candia ( Venetian: ''Regno de Càndia'') or Duchy of Candia ( Venetian: ''Dogado de Càndia'' ) was the official name of Crete during the island's period as an overseas colony of the Republic of Venice, from the initial V ...
after attacking an Ottoman ship carrying pilgrims, including the Chief Black Eunuch
The kizlar agha ( ota, قيزلر اغاسی, tr, kızlar ağası, ), formally the agha of the House of Felicity ( ota, links=no, دار السعاده اغاسي, tr, links=no, Darüssaade Ağası), was the head of the eunuchs who guarded the i ...
, to Mecca. The Ottomans quickly overran most of Crete, but were unable to evict the Venetians from the fortress of Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
. At sea, the Venetians managed to achieve the upper hand and blockade the Dardanelles
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; ...
, strangling Istanbul's trade and food supply. The subsequent disorder in the capital prompted Ibrahim's deposition in 1648, which was sanctioned by the Janissaries, the ''şeyhülislâm,'' and even Kösem Sultan
Kösem Sultan ( ota, كوسم سلطان, translit=;, 1589Baysun, M. Cavid, s.v. "Kösem Walide or Kösem Sultan" in ''The Encyclopaedia of Islam'' vol. V (1986), Brill, p. 272 " – 2 September 1651), also known as Mahpeyker SultanDouglas Arth ...
, his mother. Ibrahim's replacement was his seven-year-old son, who was enthroned as Mehmed IV
Mehmed IV ( ota, محمد رابع, Meḥmed-i rābi; tr, IV. Mehmed; 2 January 1642 – 6 January 1693) also known as Mehmed the Hunter ( tr, Avcı Mehmed) was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1648 to 1687. He came to the throne at the a ...
. The new government in Istanbul thus consisted of the young ruler's grandmother and regent Kösem Sultan and her allies in the Janissary Corps, one of whom was made grand vizier. Despite continued unrest both in Istanbul and the provinces, the blockade of the Dardanelles was successfully broken the following year. Kösem's position was nevertheless under threat from Mehmed IV's mother Turhan Sultan
Turhan Hatice Sultan ( ota, تورخان سلطان, "''nobility of the Khan''" or ''mercy of the Khan'' " and "''respecful lady''"; 1627 – 4 August 1683) was the first Haseki Sultan of the Ottoman Sultan Ibrahim (reign 1640–48) and Val ...
. Upon learning of a plot by Kösem to poison Mehmed IV, Turhan's faction leapt into action and assassinated her in 1651.
Turhan Sultan was henceforth in a secure position of power, but was unable to find an effective grand vizier, leaving the empire without a coherent policy with regard to the war with Venice. The result was another revolt of the imperial troops in March 1656, which demanded the lives of several government officials, blamed for neglecting to properly pay the troops who had been struggling to conquer Crete for so long.
Köprülü era
 In 1656 the Venetians seized control over the islands of
In 1656 the Venetians seized control over the islands of Lemnos
Lemnos or Limnos ( el, Λήμνος; grc, Λῆμνος) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within the Lemnos regional unit, which is part of the North Aegean region. The p ...
and Tenedos
Tenedos (, ''Tenedhos'', ), or Bozcaada in Turkish language, Turkish, is an island of Turkey in the northeastern part of the Aegean Sea. Administratively, the island constitutes the Bozcaada, Çanakkale, Bozcaada district of Çanakkale Provinc ...
, and established another blockade of the Dardanelles. This action led to panic in Istanbul and prompted a renewed political crisis. In need of a change of policy, Turhan Hatice appointed the highly experienced Köprülü Mehmed Pasha
Köprülü Mehmed Pasha ( ota, كپرولی محمد پاشا, tr, Köprülü Mehmet Paşa; or ''Qyprilliu'', also called ''Mehmed Pashá Rojniku''; 1575, Roshnik,– 31 October 1661, Edirne) was the founder of the Köprülü political dynas ...
as grand vizier, who immediately set forth on a drastic process of reform. This involved the dismissal or execution of all officials deemed corrupt, and their replacement with men loyal to the vizier. While wintering in Edirne
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis (Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, ...
after leading a successful campaign to reconquer the islands, Köprülü extended his purge to the imperial cavalry, executing thousands of soldiers who showed any sign of disloyalty. This move prompted a serious reaction, and as Köprülü led the army in a campaign against Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
, many of the empire's eastern governors first refused to join him, then launched an open revolt under the leadership of Abaza Hasan Pasha
Abaza Hasan Pasha, also called Kara Hasan Pasha or Celali Hasan Pasha; ( ota, ابازه حسن پاشا, ''Abāza Ḥasan Paşa''), was an Ottoman provincial governor and celali rebel of the mid-seventeenth century. He launched two rebellions a ...
, demanding from the sultan that Köprülü be executed. Mehmed IV, now no longer a minor, chose to side with his vizier and dispatched an army to defeat the rebels. Despite initial rebel victories, the revolt was suddenly brought to an end in February 1659 with the assassination of Abaza Hasan.
Köprülü Mehmed died in 1661, leaving the empire in a much better military and financial position than he had found it. He was succeeded in office by his son Fazıl Ahmed Pasha :
Fazıl (also, Fazil and Fazyl) is a village and municipality in the Shaki Rayon of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transc ...
(1661–1676), the first time in history that a grand vizier passed on the office to his son. Fazıl Ahmed was himself succeeded by his adopted brother Merzifonlu Kara Mustafa Pasha
Merzifonlu Kara Mustafa Pasha ( ota, مرزيفونلى قره مصطفى پاشا, tr, Merzifonlu Kara Mustafa Paşa; "Mustafa Pasha the Courageous of Merzifon"; 1634/1635 – 25 December 1683) was an Ottoman nobleman, military figure and Gr ...
(1676–1683), and it is due to this unbroken control of the Köprülü family
The Köprülü family ( tr, Köprülü ailesi) was a noble family of Albanian origin in the Ottoman Empire.Ivo Banac''The national question in Yugoslavia: origins, history, politics'' , Cornell University 1988 page 292. The family hailed from th ...
over the office of grand vizier that this period is referred to as the Köprülü era.
Köprülü Mehmed's two successors were highly competent administrators, and the empire enjoyed a remarkable degree of stability under their tutelage. Mehmed IV was content to allow them to manage the political affairs of the empire, but was nevertheless not an inactive ruler. He played a major role in imperial symbolism and legitimation, traveling with the army on campaign before handing supreme command over to the grand vizier. Thus while not directly leading the army, he still participated in the imperial campaigns, for which he was referred to as gazi
A ''ghazi'' ( ar, غازي, , plural ''ġuzāt'') is an individual who participated in ''ghazw'' (, '' ''), meaning military expeditions or raiding. The latter term was applied in early Islamic literature to expeditions led by the Islamic prophe ...
, or "holy warrior," by contemporaries. Under the Köprülüs the empire revived its expansion into Europe, conquering territory from the Habsburgs, Poland–Lithuania, and Russia, as well as bringing the war with Venice to an end with the conquest of Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban A ...
in 1669. The push for territorial expansion under the Köprülüs reached its apex in 1683 with the Siege of Vienna Sieges of Vienna may refer to:
* Siege of Vienna (1239)
* Siege of Vienna (1276)
* Siege of Vienna (1287)
* Siege of Vienna (1477), unsuccessful Hungarian attempt during the Austro–Hungarian War.
*Siege of Vienna (1485), Hungarian victory during ...
, which ended in Ottoman defeat.
The defeat at Vienna ushered in a major political shift in the empire. As punishment for his failure, Mehmed IV ordered that Merzifonlu Kara Mustafa be executed, bringing an end to the undisputed Köprülü hold over the empire. The result was a period of political confusion at a time when the Ottoman Empire's European enemies were rallying together. In 1684 the Habsburgs, Poland–Lithuania, Venice, and the Papacy forged an alliance known as the Holy League
Commencing in 1332 the numerous Holy Leagues were a new manifestation of the Crusading movement in the form of temporary alliances between interested Christian powers. Successful campaigns included the capture of Smyrna in 1344, at the Battle of ...
to oppose the Ottomans, launching a period of warfare which would last for sixteen years.
War of the Holy League
 Conflict on multiple fronts placed great strain on the Ottoman ability to wage war. The empire was attacked simultaneously in Hungary, Podolia, and the Mediterranean region, while after 1686 their
Conflict on multiple fronts placed great strain on the Ottoman ability to wage war. The empire was attacked simultaneously in Hungary, Podolia, and the Mediterranean region, while after 1686 their Crimean
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
vassals, who under normal circumstances supported the Ottoman army with tens of thousands of cavalry, were continually distracted by the need to fend off Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
invasion. Istanbul's food supply was again threatened by Venetian naval activity in the Aegean, contributing to instability in the capital. In Hungary, the Habsburgs first reconquered Nové Zámky in 1684, before moving on to Buda. Despite resisting a siege in 1685, it was unable to hold out against a second the following year, and capitulated to the Habsburgs, leading to much of the country falling under Habsburg control. The Ottomans were able to rescue Osijek
Osijek () is the fourth-largest city in Croatia, with a population of 96,848 in 2021. It is the largest city and the economic and cultural centre of the eastern Croatian region of Slavonia, as well as the administrative centre of Osijek-Baranja ...
from capture, but were defeated in the Second Battle of Mohács in 1687. The army subsequently mutinied and marched on Istanbul, deposing Mehmed IV in favor of his brother Suleiman II. In the chaos the Habsburgs were able to make rapid inroads into Ottoman territory, seizing strongholds such as Eger and Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
, reaching as far south as Niš
Niš (; sr-Cyrl, Ниш, ; names in other languages) is the third largest city in Serbia and the administrative center of the Nišava District. It is located in southern part of Serbia. , the city proper has a population of 183,164, while ...
. However, in 1689 the tide turned back in the Ottomans' favor. In 1688 Louis XIV of France
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Versa ...
had launched the Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg monarch ...
, distracting Habsburg attention from the Ottoman front. Fazıl Mustafa Pasha, a younger son of Köprülü Mehmed, was appointed grand vizier and led the army to successfully recover both Niš and Belgrade. What followed was a long period of stalemate, with the Habsburgs having lost their bridgehead south of the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
and the Ottomans unable to achieve any lasting success north of it. The Habsburgs concerned themselves with the conquest of the Principality of Transylvania, an Ottoman vassal state, the loss of which the Ottomans were forced to accept after the disastrous defeat of an army personally led by Sultan Mustafa II
Mustafa II (; ota, مصطفى ثانى ''Muṣṭafā-yi sānī''; 6 February 1664 – 29 December 1703) was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1695 to 1703.
Early life
He was born at Edirne Palace on 6 February 1664. He was the son of Sult ...
in the 1697 Battle of Zenta
The Battle of Zenta, also known as the Battle of Senta, was fought on 11 September 1697, near Zenta, Ottoman Empire (modern-day Senta, Serbia), between Ottoman and Holy League armies during the Great Turkish War. The battle was the most decis ...
. This defeat prompted the Ottomans to sue for peace.
While territorial losses to the Habsburgs have at times been cited as evidence of military weakness, more recently historians have challenged this notion, arguing that Ottoman defeats were primarily a result of the sheer size of the coalition arrayed against them, and the logistical burden of fighting a war on multiple fronts. To this may be added political instability, for the empire's greatest losses took place from 1684 to 1688, when its political leadership was paralyzed first by the execution of Kara Mustafa Pasha and then the deposition of Mehmed IV. Subsequently, the Ottomans were able to stabilize their position and reverse Habsburg gains south of the Danube.
The pressure of sustained warfare had prompted the Ottomans to carry out extensive fiscal reform. The sale of tobacco was legalized and taxed, previously tax-immune waqf
A waqf ( ar, وَقْف; ), also known as hubous () or '' mortmain'' property is an inalienable charitable endowment under Islamic law. It typically involves donating a building, plot of land or other assets for Muslim religious or charitabl ...
finances were reformed, and the janissary
A Janissary ( ota, یڭیچری, yeŋiçeri, , ) was a member of the elite infantry units that formed the Ottoman Sultan's household troops and the first modern standing army in Europe. The corps was most likely established under sultan Orhan ( ...
payrolls were examined and updated. Most significantly, in 1691 the standard unit of cizye
Jizya ( ar, جِزْيَة / ) is a per capita yearly taxation historically levied in the form of financial charge on dhimmis, that is, permanent non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Islamic law. The jizya tax has been understood in Isl ...
assessment was shifted from the household to the individual, and in 1695 the sale of life-term tax farms
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, or n ...
known as malikâne
Malikâne was a form of tax farming introduced in the Ottoman empire in 1695. It was intended as an improvement on the Iltizam system, in which a tax-farmer was responsible for a single year. Malikâne contracts were for life; this provided more se ...
was implemented, vastly increasing the empire's revenue. These measures enabled the Ottoman Empire to maintain fiscal solvency during the war, and to enjoy significant budget surpluses by the beginning of the eighteenth century.
The war was brought to an end in 1699 with the Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed in Karlowitz, Military Frontier of Archduchy of Austria (present-day Sremski Karlovci, Serbia), on 26 January 1699, concluding the Great Turkish War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by the ...
. On the general principle of ''uti possidetis
''Uti possidetis'' is an expression that originated in Roman private law, where it was the name of a procedure used in litigation about land. It came from a praetorial edict that could be abbreviated "As you possess, so shall you possess". La ...
'', the Ottomans agreed to permanently cede all of Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
and Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
to the Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
, with the exception of the Banat
Banat (, ; hu, Bánság; sr, Банат, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of T ...
region. Morea
The Morea ( el, Μορέας or ) was the name of the Peloponnese peninsula in southern Greece during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The name was used for the Byzantine province known as the Despotate of the Morea, by the Ottoman ...
was annexed by Venice, while Podolia
Podolia or Podilia ( uk, Поділля, Podillia, ; russian: Подолье, Podolye; ro, Podolia; pl, Podole; german: Podolien; be, Падолле, Padollie; lt, Podolė), is a historic region in Eastern Europe, located in the west-central ...
was returned to Poland–Lithuania. Karlowitz was highly significant for both Ottoman and Eastern European history in general, for it marked the definitive end of Ottoman imperial expansion. Ottoman foreign policy in Europe during the subsequent eighteenth century was generally peaceful and defensive, focused on the maintenance of a secure network of fortresses along the Danube frontier. Sultan Mustafa II was overthrown in the 1703 Edirne incident, bringing an end to the rule of the final Ottoman warrior-sultan, cementing the empire's transformation into a bureaucratic empire.
See also
*The General Crisis
The General Crisis is a term used by some historians to describe an alleged period of widespread global conflict and instability that occurred from the early 17th century to the early 18th century in Europe, and in more recent historiography in ...
*Great power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power inf ...
*Superpower
A superpower is a state with a dominant position characterized by its extensive ability to exert influence or project power on a global scale. This is done through the combined means of economic, military, technological, political and cultural s ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *n German
N, or n, is the fourteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''en'' (pronounced ), plural ''ens''.
History
...
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
General surveys
* * * *Significant works
* * * * * * * * * * * {{Turkey topics 16th century in the Ottoman Empire 17th century in the Ottoman Empire