Trabzon Akçaabat F.K. on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Trabzon, historically known as Trebizond, is a city on the
 The Turkish name of the city is Trabzon. The first recorded name of the city is the Greek (), referencing the table-like central hill between the Zağnos (İskeleboz) and Kuzgun streams on which it was founded (' meant "table" in
The Turkish name of the city is Trabzon. The first recorded name of the city is the Greek (), referencing the table-like central hill between the Zağnos (İskeleboz) and Kuzgun streams on which it was founded (' meant "table" in
 Trebizond's trade partners included the
Trebizond's trade partners included the
File:Ivan Aivazovsky Trebizond 1865.jpg, Trebizond from the sea by Ivan Aivazovsky
File:Harbour Trebizond C. Lapante HQ.jpg, Engraving of the port at Çömlekçi by C. Lapante
File:Durand-Brager 3.jpg, Trebizond by Jean-Baptiste Henri Durand-Brager
File:Port of Trebizond Y.M. Tadevossian.jpg, Trebizond from the sea by Yeghishe Tadevosyan
File:Trebizond Godfrey Thomas Vigne (1833).jpg, Trebizond from the south by Godfrey Vigne
File:Quarantine station at Trebizond by Jules Laurens.jpg, The quarantine station by Jules Laurens
File:Trebizond 'East town' 1922.jpg, Street view by Nikolay Lanceray

 As of 1920, the port at Trabzon was considered "the most important of the Turkish Black Sea ports" by the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, British. It traded as far as Tabriz and Mosul. As of 1911, the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey signed an agreement to develop a harbor at the port. When the Russians occupied Trabzon, a Mole (architecture), mole was built. They built a Breakwater (structure), breakwater and were responsible for creating an extended pier, making loading and unloading easier. In 1920, Trabzon produced linen cloth, silver filagree, Tanning (leather), tanning and small amounts of cotton, silk and wool. Tobacco and hazelnuts were exported. The tobacco produced in Trabzon was called ''Trebizond-Platana''. It was described as having "large leaves and a bright colour." Trabzon was known for producing poor quality cereals, mostly for local use.
Trabzon produced a white green bean, which was sold in Europe. It was, as of 1920, the only vegetable exported out of the province. Poultry farming was also popular in Trabzon. Sericulture was seen in the area before 1914. The area produced copper, silver, zinc, iron and manganese. Copper was kept for local use by coppersmiths. During the Balkan Wars production ceased due to poor exportation and fuel supplies.
Trabzon Airport opened in 1957.
As of 1920, the port at Trabzon was considered "the most important of the Turkish Black Sea ports" by the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, British. It traded as far as Tabriz and Mosul. As of 1911, the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey signed an agreement to develop a harbor at the port. When the Russians occupied Trabzon, a Mole (architecture), mole was built. They built a Breakwater (structure), breakwater and were responsible for creating an extended pier, making loading and unloading easier. In 1920, Trabzon produced linen cloth, silver filagree, Tanning (leather), tanning and small amounts of cotton, silk and wool. Tobacco and hazelnuts were exported. The tobacco produced in Trabzon was called ''Trebizond-Platana''. It was described as having "large leaves and a bright colour." Trabzon was known for producing poor quality cereals, mostly for local use.
Trabzon produced a white green bean, which was sold in Europe. It was, as of 1920, the only vegetable exported out of the province. Poultry farming was also popular in Trabzon. Sericulture was seen in the area before 1914. The area produced copper, silver, zinc, iron and manganese. Copper was kept for local use by coppersmiths. During the Balkan Wars production ceased due to poor exportation and fuel supplies.
Trabzon Airport opened in 1957.
 Laz people also live in Trabzon. Numerous villages inside and out of Trabzon of the Laz date back as early as the period of Tamar of Georgia, Queen Tamar's rule (Georgian: თამარი, also transliterated as T'amar or Thamar; c. 1160 – 18 January 1213) in the newly unified Kingdom of Georgia. During the Queen's rule, sizeable groups of immigrating Georgians moved to Trabzon where they continue to preserve their native tongue. There was an Armenian community in Trebizond as early as the 7th century.
During the 13th and 14th centuries, numerous Armenians, Armenian families migrated there from Ani. Robert W. Edwards published part of an early 15th-century diary from the Castilian ambassador who visited Trabzon and compared the churches of the Greek and Armenian communities. It was stated by the ambassador that the Armenians, who were not well-liked by the Greeks, had a population large enough to support a resident bishop. According to Ronald C. Jennings, in the early 16th century, Armenians made up approximately 13 percent of the city's population. At present, Trabzon does not have an Armenian-speaking community.
The Chepni people, a tribe of Oghuz Turks who played an important role in the history of the eastern Black Sea area in the 13th and 14th centuries, live in the Şalpazarı (Ağasar valley) region of the Trabzon Province. Very little has been written on the Turkification of the area. There are no historical records of any considerable Turkish-speaking groups in the Trabzon area until the late 15th century, with the exception of the Chepnis. The original Pontic Greek, Greek (and in some regions
Laz people also live in Trabzon. Numerous villages inside and out of Trabzon of the Laz date back as early as the period of Tamar of Georgia, Queen Tamar's rule (Georgian: თამარი, also transliterated as T'amar or Thamar; c. 1160 – 18 January 1213) in the newly unified Kingdom of Georgia. During the Queen's rule, sizeable groups of immigrating Georgians moved to Trabzon where they continue to preserve their native tongue. There was an Armenian community in Trebizond as early as the 7th century.
During the 13th and 14th centuries, numerous Armenians, Armenian families migrated there from Ani. Robert W. Edwards published part of an early 15th-century diary from the Castilian ambassador who visited Trabzon and compared the churches of the Greek and Armenian communities. It was stated by the ambassador that the Armenians, who were not well-liked by the Greeks, had a population large enough to support a resident bishop. According to Ronald C. Jennings, in the early 16th century, Armenians made up approximately 13 percent of the city's population. At present, Trabzon does not have an Armenian-speaking community.
The Chepni people, a tribe of Oghuz Turks who played an important role in the history of the eastern Black Sea area in the 13th and 14th centuries, live in the Şalpazarı (Ağasar valley) region of the Trabzon Province. Very little has been written on the Turkification of the area. There are no historical records of any considerable Turkish-speaking groups in the Trabzon area until the late 15th century, with the exception of the Chepnis. The original Pontic Greek, Greek (and in some regions
 Folk dancing is still very much in evidence in the Black Sea Region. The "Horon (dance), Horon" is a famous dance that is indigenous to the city and its surrounding area. It is performed by men, women, the young and elderly alike; in festivities, local weddings and harvest times. While similar to Russian Cossacks, Cossack dances in terms of vividness, the Trabzon folk dance is probably indigenous to the eastern Black Sea region, which has an impressive variety of folk music.
The people of Trabzon have a reputation for being religiously conservative and nationalist. Many Trabzonites generally show a strong sense of loyalty to their family, friends, religion and country. Atatürk selected his presidential guards from Trabzon and the neighbouring city of Giresun because of their fierce fighting ability and their loyalty.
Outside of the relatively urban space of Trabzon proper, and within parts of it as well, rural traditions from the Black Sea village life are still thriving. These include traditional gender roles, social conservatism, hospitality, and a willingness to help strangers; and all aspects, both positive and negative, of an agrarian lifestyle, such as hard work, poverty, strong family ties, and a closeness to nature.
The people of the eastern Black Sea region are also known for their wit and sense of humour; many jokes in Turkey are told about the natives of the Black Sea region ''Karadeniz fıkraları'' (Black Sea jokes). The character ''Temel'', a universal buffoon figure found in many cultures, forms an important part of the Turkish oral tradition.
The city's profile was raised somewhat in the English-speaking world by Rose Macaulay, Dame Rose Macaulay's last novel, ''The Towers of Trebizond'' (1956), which is still in print.
Folk dancing is still very much in evidence in the Black Sea Region. The "Horon (dance), Horon" is a famous dance that is indigenous to the city and its surrounding area. It is performed by men, women, the young and elderly alike; in festivities, local weddings and harvest times. While similar to Russian Cossacks, Cossack dances in terms of vividness, the Trabzon folk dance is probably indigenous to the eastern Black Sea region, which has an impressive variety of folk music.
The people of Trabzon have a reputation for being religiously conservative and nationalist. Many Trabzonites generally show a strong sense of loyalty to their family, friends, religion and country. Atatürk selected his presidential guards from Trabzon and the neighbouring city of Giresun because of their fierce fighting ability and their loyalty.
Outside of the relatively urban space of Trabzon proper, and within parts of it as well, rural traditions from the Black Sea village life are still thriving. These include traditional gender roles, social conservatism, hospitality, and a willingness to help strangers; and all aspects, both positive and negative, of an agrarian lifestyle, such as hard work, poverty, strong family ties, and a closeness to nature.
The people of the eastern Black Sea region are also known for their wit and sense of humour; many jokes in Turkey are told about the natives of the Black Sea region ''Karadeniz fıkraları'' (Black Sea jokes). The character ''Temel'', a universal buffoon figure found in many cultures, forms an important part of the Turkish oral tradition.
The city's profile was raised somewhat in the English-speaking world by Rose Macaulay, Dame Rose Macaulay's last novel, ''The Towers of Trebizond'' (1956), which is still in print.
 Association football, Football is the most popular sport in Trabzon. The city's top sports club, Trabzonspor, was until 2009–10 Süper Lig, 2010 the only Turkish football club outside İstanbul to win the Süper Lig (six times), which was previously (until Trabzonspor's first championship title in the 1975–76 1.Lig, 1975–76 season) won only by the "Big Three" clubs of
Association football, Football is the most popular sport in Trabzon. The city's top sports club, Trabzonspor, was until 2009–10 Süper Lig, 2010 the only Turkish football club outside İstanbul to win the Süper Lig (six times), which was previously (until Trabzonspor's first championship title in the 1975–76 1.Lig, 1975–76 season) won only by the "Big Three" clubs of
Trabzon Travel Guide
Governorship of Trabzon
Photos of Trabzon city
{{Authority control Trabzon, Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Turkey Black Sea port cities and towns in Turkey Capitals of former nations Empire of Trebizond Fishing communities in Turkey Greek colonies in Pontus Populated coastal places in Turkey Roman towns and cities in Turkey Roman harbors in Turkey Milesian Pontic colonies Populated places established in the 8th century BC
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
coast of northeastern Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
and the capital of Trabzon Province
Trabzon Province () is a Provinces of Turkey, province and Metropolitan municipalities in Turkey, metropolitan municipality of Turkey on the Black Sea coast. Its area is 4,628 km2, and its population is 818,023 (2022). Located in a strategic ...
. The city was founded in 756 BC as "Trapezous" by colonists from Miletus
Miletus (Ancient Greek: Μίλητος, Mílētos) was an influential ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in present day Turkey. Renowned in antiquity for its wealth, maritime power, and ex ...
. It was added into the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
by Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia ( ; 530 BC), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire. Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Hailing from Persis, he brought the Achaemenid dynasty to power by defeating the Media ...
and was later part of the independent Kingdom of Pontus
Pontus ( ) was a Hellenistic kingdom centered in the historical region of Pontus in modern-day Turkey, and ruled by the Mithridatic dynasty of Persian origin, which may have been directly related to Darius the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty. ...
that challenged Rome until 68 BC. Thenceforth part of the Roman and later Byzantine Empire, the city was the capital of the Empire of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond or the Trapezuntine Empire was one of the three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire that existed during the 13th through to the 15th century. The empire consisted of the Pontus, or far northeastern corner of A ...
, one of the successor states of the Byzantine Empire after the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
in 1204. In 1461 it came under Ottoman rule. During the early modern period, Trabzon, because of the importance of its port, again became a focal point of trade to Persia and the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
. Today Trabzon is the second largest city and port on the Black Sea coast of Turkey with a population of almost 300,000. The urban population of the city is 330,836 (Ortahisar), with a metropolitan population of 822,270.
Name
 The Turkish name of the city is Trabzon. The first recorded name of the city is the Greek (), referencing the table-like central hill between the Zağnos (İskeleboz) and Kuzgun streams on which it was founded (' meant "table" in
The Turkish name of the city is Trabzon. The first recorded name of the city is the Greek (), referencing the table-like central hill between the Zağnos (İskeleboz) and Kuzgun streams on which it was founded (' meant "table" in Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
; note the table on the coin in the figure). In Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
, Trabzon is called ', which is a latinization of its ancient Greek name. Both in Pontic Greek
Pontic Greek (, ; or ''Romeika'') is a variety of Modern Greek indigenous to the Pontus region on the southern shores of the Black Sea, northeastern Anatolia, and the Eastern Turkish and Caucasus region. An endangered Greek language variety ...
and Modern Greek
Modern Greek (, or , ), generally referred to by speakers simply as Greek (, ), refers collectively to the dialects of the Greek language spoken in the modern era, including the official standardized form of the language sometimes referred to ...
, it is called (). In Ottoman Turkish
Ottoman Turkish (, ; ) was the standardized register of the Turkish language in the Ottoman Empire (14th to 20th centuries CE). It borrowed extensively, in all aspects, from Arabic and Persian. It was written in the Ottoman Turkish alphabet. ...
and Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
, it is written as . During Ottoman times, ''Tara Bozan'' was also used. In Laz it is known as (''T'amt'ra'') or ''T'rap'uzani'', in Georgian it is (''T'rap'izoni'') and in Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
it is (''Trapizon''). The 19th-century Armenian travelling priest Byjiskian called the city by other, native names, including ''Hurşidabat'' and ''Ozinis''. Western geographers and writers used many spelling variations of the name throughout the Middle Ages. These versions of the name, which have incidentally been used in English literature as well, include: ''Trebizonde'' ( Fr.), ''Trapezunt'' (German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
), ''Trebisonda'' ( Sp.), ''Trapesunta'' ( It.), ''Trapisonda'', ''Tribisonde'', ''Terabesoun'', ''Trabesun'', ''Trabuzan'', ''Trabizond'' and ''Tarabossan''.
In Spanish the name was known from chivalric romance
As a literary genre, the chivalric romance is a type of prose and verse narrative that was popular in the noble courts of high medieval and early modern Europe. They were fantastic stories about marvel-filled adventures, often of a chivalri ...
s and ''Don Quixote
, the full title being ''The Ingenious Gentleman Don Quixote of La Mancha'', is a Spanish novel by Miguel de Cervantes. Originally published in two parts in 1605 and 1615, the novel is considered a founding work of Western literature and is of ...
''.
Because of its similarity to and , acquired the meaning "hullabaloo, imbroglio".
History
Iron Age and Classical Antiquity
Before the city was founded as a Greek colony the area was dominated byColchians
In classical antiquity and Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the ...
(west Georgian) and Chaldian (Anatolian) tribes. The Hayasa
Hayasa-Azzi or Azzi-Hayasa (, ) was a Late Bronze Age confederation in the Armenian Highlands and/or Pontic region of Asia Minor. The Hayasa-Azzi confederation was in conflict with the Hittite Empire in the 14th century BC, leading up to the ...
, who had been in conflict with the Central-Anatolian Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in mo ...
in the 14th century BC, are believed to have lived in the area south of Trabzon. Later Greek authors mentioned the Macrones
The Macrones ( ka, მაკრონები, ; , ''Makrōnes'') were an ancient Colchian tribe in the east of Pontus, about the Moschici Mountains (modern Yalnizçam Dağlari, Turkey). The name is allegedly derived from the name of Kromni ...
and the Chalybes
The Chalybes (; ; ka, ხალიბები, Khalibebi) and Chaldoi (; ) were peoples mentioned by classical authors as living in Pontus and Cappadocia in northern Anatolia during Classical Antiquity. Their territory was known as Chaldia, e ...
as native peoples. One of the dominant Caucasian groups to the east were the Laz, who were part of the monarchy of the Colchis
In classical antiquity and Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the ...
, together with other related Georgian peoples.
The city was founded in classical antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the inter ...
in 756 BC as Tραπεζούς (''Trapezous''), by Milesian traders from Sinope
Sinope may refer to:
*Sinop, Turkey, a city on the Black Sea, historically known as Sinope
** Battle of Sinop, 1853 naval battle in the Sinop port
*Sinop Province
* Sinope, Leicestershire, a hamlet in the Midlands of England
* Sinope (mythology), i ...
. It was one of a number (about ten) of Milesian ''emporia'' or trading colonies along the shores of the Black Sea. Others included Abydos and Cyzicus
Cyzicus ( ; ; ) was an ancient Greek town in Mysia in Anatolia in the current Balıkesir Province of Turkey. It was located on the shoreward side of the present Kapıdağ Peninsula (the classical Arctonnesus), a tombolo which is said to have or ...
in the Dardanelles
The Dardanelles ( ; ; ), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli (after the Gallipoli peninsula) and in classical antiquity as the Hellespont ( ; ), is a narrow, natural strait and internationally significant waterway in northwestern Turkey th ...
, and nearby Kerasous. Like most Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
colonies, the city was a small enclave of Greek life, and not an empire unto its own, in the later European sense of the word. As a colony, Trapezous initially paid tribute to Sinope, but early banking (money-changing) activity is suggested to have occurred in the city already in the 4th century BC, according to a silver drachma
Drachma may refer to:
* Ancient drachma, an ancient Greek currency
* Modern drachma
The drachma ( ) was the official currency of modern Greece from 1832 until the launch of the euro in 2001.
First modern drachma
The drachma was reintroduce ...
coin from Trapezus in the British Museum
The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is the largest in the world. It documents the story of human cu ...
, London. Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia ( ; 530 BC), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire. Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Hailing from Persis, he brought the Achaemenid dynasty to power by defeating the Media ...
added the city to the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
, and was possibly the first ruler to consolidate the eastern Black Sea region into a single political entity (a satrapy
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Persian (Achaemenid) Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires. A satrapy is the territory governed by a satrap.
...
).
 Trebizond's trade partners included the
Trebizond's trade partners included the Mossynoeci
Mossynoeci ( ka, მოსინიკები, , , modern Greek ', "dwellers in wooden towers") is a name that the Greeks of the Euxine Sea (Black Sea) applied to the peoples of Pontus, the northern Anatolian coast west of Trebizond. The Moss ...
. When Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; ; 355/354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian. At the age of 30, he was elected as one of the leaders of the retreating Ancient Greek mercenaries, Greek mercenaries, the Ten Thousand, who had been ...
and the Ten Thousand
The Ten Thousand (, ''hoi Myrioi'') were a force of mercenary units, mainly Greeks, employed by Cyrus the Younger to attempt to wrest the throne of the Persian Empire from his brother, Artaxerxes II. Their march to the Battle of Cunaxa and bac ...
mercenaries were fighting their way out of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, the first Greek city they reached was Trebizond (Xenophon, ''Anabasis'', 5.5.10). The city and the local Mossynoeci had become estranged from the Mossynoecian capital, to the point of civil war. Xenophon's force resolved this in the rebels' favor, and so in Trebizond's interest.
Up until the conquests of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
the city remained under the dominion of the Achaemenids. While the Pontus was not directly affected by the war, its cities gained independence as a result of it. Local ruling families continued to claim partial Persian heritage, and Persian culture had some lasting influence on the city; the holy springs of Mt. Minthrion to the east of the old town were devoted to the Persian-Anatolian Greek god Mithra
Mithra ( ; ) is an ancient Iranian deity ('' yazata'') of covenants, light, oaths, justice, the Sun, contracts, and friendship. In addition to being the divinity of contracts, Mithra is also a judicial figure, an all-seeing protector of Truth ( ...
. In the 2nd century BC, the city with its natural harbours was added to the Kingdom of Pontus
Pontus ( ) was a Hellenistic kingdom centered in the historical region of Pontus in modern-day Turkey, and ruled by the Mithridatic dynasty of Persian origin, which may have been directly related to Darius the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty. ...
by Pharnaces I. Mithridates VI Eupator
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator (; 135–63 BC) was the ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an effective, ambitious, and ...
made it the home port of the Pontic fleet, in his quest to remove the Romans from Anatolia.
After the defeat of Mithridates in 66 BC, the city was first handed to the Galatians Galatians may refer to:
* Galatians (people)
* Epistle to the Galatians, a book of the New Testament
* English translation of the Greek ''Galatai'' or Latin ''Galatae'', ''Galli,'' or ''Gallograeci'' to refer to either the Galatians or the Gauls in ...
, but it was soon returned to the grandson of Mithradates, and subsequently became part of the new client Kingdom of Pontus. When the kingdom was finally annexed to the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
province of Galatia
Galatia (; , ''Galatía'') was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace (cf. Tylis), who settled here ...
two centuries later, the fleet passed to new commanders, becoming the ''Classis Pontica
The Classis Pontica was a '' provincialis'' fleet, established initially by Augustus and then by Nero on a permanent basis (around 57). It was tasked with guarding the southern ''Pontus Euxinus'', coordinating with the neighboring fleet of Mesia ...
''. The city received the status of civitas libera, extending its judicial autonomy and the right to mint its own coin. Trebizond gained importance for its access to roads leading over the Zigana Pass to the Armenian frontier or the upper Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
valley. New roads were constructed from Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
under the rule of Vespasian
Vespasian (; ; 17 November AD 9 – 23 June 79) was Roman emperor from 69 to 79. The last emperor to reign in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty, which ruled the Empire for 27 years. His fiscal reforms and consolida ...
. In the next century, the emperor Hadrian
Hadrian ( ; ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic peoples, Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, Aelia '' ...
commissioned improvements to give the city a more structured harbor. William Miller, ''Trebizond: The Last Greek Empire'', 1926, (Chicago: Argonaut Publishers, 1968), p. 9 The emperor visited the city in the year 129 as part of his inspection of the eastern border (limes
Limes may refer to:
* ''Limes'' (Roman Empire), a border marker and defense system of the Roman Empire
* ''Limes'' (Italian magazine), an Italian geopolitical magazine
* ''Limes'' (Romanian magazine), a Romanian literary and political quarterly ma ...
). A mithraeum
A Mithraeum , sometimes spelled Mithreum and Mithraion (), is a Roman temple, temple erected in classical antiquity by the Mithraism, worshippers of Mithras. Most Mithraea can be dated between 100 BC and 300 AD, mostly in the Roman ...
now serves as a crypt for the church and monastery of Panagia Theoskepastos (''Kızlar Manastırı'') in nearby Kizlara, east of the citadel and south of the modern harbor.
Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; ; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through cursus honorum, the ...
punished Trebizond for having supported his rival Pescennius Niger
Gaius Pescennius Niger (c. 135 – 194) was a Roman usurper from 193 to 194 during the Year of the Five Emperors. He claimed the imperial throne in response to the murder of Pertinax and the elevation of Didius Julianus, but was defeated by a ...
during the Year of the Five Emperors
The Year of the Five Emperors was AD 193, in which five men claimed the title of Roman emperor: Pertinax, Didius Julianus, Pescennius Niger, Clodius Albinus, and Septimius Severus. This year started a period of civil war when multiple rulers vie ...
. In 257 the city was pillaged by the Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is ...
, despite reportedly being defended by "10,000 above its usual garrison" and two bands of walls. Trebizond was subsequently rebuilt, pillaged again, by the Persians
Persians ( ), or the Persian people (), are an Iranian ethnic group from West Asia that came from an earlier group called the Proto-Iranians, which likely split from the Indo-Iranians in 1800 BCE from either Afghanistan or Central Asia. They ...
, in 258, and then rebuilt once more. It did not soon recover. Only in the reign of Diocletian
Diocletian ( ; ; ; 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed Jovius, was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Diocles to a family of low status in the Roman province of Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia. As with other Illyri ...
does an inscription allude to the restoration of the city; Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus, occasionally anglicized as Ammian ( Greek: Αμμιανός Μαρκελλίνος; born , died 400), was a Greek and Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from antiquit ...
had nothing to say of Trebizond except that it was "not an obscure town."
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
had reached Trebizond by the third century, for during the reign of Diocletian occurred the martyrdom of Eugenius
Eugenius (died 6 September 394) was a Western Roman emperor from 392 to 394, unrecognized by the Eastern Roman emperor Theodosius I. While Christian himself, Eugenius capitalized on the discontent in the West caused by Theodosius' religious p ...
and his associates Candidius, Valerian, and Aquila. Eugenius had destroyed the statue of Mithras
Mithraism, also known as the Mithraic mysteries or the Cult of Mithras, was a Roman Empire, Roman mystery religion focused on the god Mithras. Although inspired by Iranian peoples, Iranian worship of the Zoroastrian divinity (''yazata'') Mit ...
which overlooked the city from Mount Minthrion (Boztepe), and became the patron saint of the city after his death. Early Christians sought refuge in the Pontic Mountains south of the city, where they established Vazelon Monastery
Vazelon Monastery () is a ruin located in the Black Sea region of Turkey. It was built in 270 and is south of Trabzon. Justinian I, a ruler of the Byzantine Empire, ordered the monastery to be repaired in 565, and it was renovated multiple time ...
in 270 AD and Sumela Monastery
Sumela Monastery (, ''Moní Panagías Soumelá''; ) is a museum and former Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, Greek Orthodox monastery in the Pontic Mountains, in the Maçka district of Trabzon Province in modern Turkey.
Nestled in a ...
in 386 AD. As early as the First Council of Nicea
The First Council of Nicaea ( ; ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I. The Council of Nicaea met from May until the end of July 325.
This ecume ...
, Trebizond had its own bishop.Hewsen, 46 Subsequently, the Bishop of Trebizond was subordinated to the Metropolitan Bishop
In Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, churches with episcopal polity, the rank of metropolitan bishop, or simply metropolitan (alternative obsolete form: metropolite), is held by the diocesan bishop or archbishop of a Metropolis (reli ...
of Poti
Poti ( ka, ფოთი ; Mingrelian language, Mingrelian: ფუთი; Laz language, Laz: ჶაში/Faşi or ფაში/Paşi) is a port city in Georgia (country), Georgia, located on the eastern Black Sea coast in the mkhare, region of ...
. Then during the 9th century, Trebizond itself became the seat of the Metropolitan Bishop of Lazica
The Kingdom of Lazica (; ; ), sometimes called Lazian Empire, was a state in the territory of west Georgia in the Roman era, Georgia in the Roman period, from about the 1st century BC. Created as a result of the collapse of the kingdom of Colc ...
.
Byzantine period
By the time ofJustinian
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
, the city served as an important base in his Persian Wars, and Miller notes that a portrait of the general Belisarius
BelisariusSometimes called Flavia gens#Later use, Flavius Belisarius. The name became a courtesy title by the late 4th century, see (; ; The exact date of his birth is unknown. March 565) was a military commander of the Byzantine Empire under ...
"long adorned the church of St. Basil."Miller, ''Trebizond'', p. 11 An inscription above the eastern gate of the city, commemorated the reconstruction of the civic walls at Justinian's expense following an earthquake. At some point before the 7th century the university (Pandidakterion) of the city was reestablished with a quadrivium
From the time of Plato through the Middle Ages, the ''quadrivium'' (plural: quadrivia) was a grouping of four subjects or arts—arithmetic, geometry, music, and astronomy—that formed a second curricular stage following preparatory work in th ...
curriculum. The university drew students not just from the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
, but from Armenia as well.
The city regained importance when it became the seat of the theme of Chaldia
Chaldia (, ''Khaldia'') was a historical region located in the mountainous interior of the eastern Black Sea, northeast Anatolia (modern Turkey). Its name was derived from a people called the ''Chaldoi'' (or '' Chalybes'') that inhabited the reg ...
. Trebizond also benefited when the trade route regained importance in the 8th to 10th centuries; 10th-century Muslim authors note that Trebizond was frequented by Muslim merchants, as the main source transshipping Byzantine silk
Byzantine silk is silk woven in the Byzantine Empire (Byzantium) from about the fourth century until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453.
The Byzantine capital of Constantinople was the first significant silk-weaving center in Europe. Silk was one ...
s into eastern Muslim countries. According to the 10th century Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
geographer Abul Feda it was regarded as being largely a Lazian port. The Italian maritime republics such as the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
and in particular the Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
were active in the Black Sea trade for centuries, using Trebizond as an important seaport for trading goods between Europe and Asia. Some of the Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
caravans carrying goods from Asia stopped at the port of Trebizond, where the European merchants purchased these goods and carried them to the port cities of Europe with ships. This trade provided a source of revenue to the state in the form of custom duties, or ''kommerkiaroi'', levied on the goods sold in Trebizond. The Greeks protected the coastal and inland trade routes with a vast network of garrison forts.
Following the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
defeat at the Battle of Manzikert
The Battle of Manzikert or Malazgirt was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, Iberia (theme), Iberia (modern Malazgirt in Muş Province, Turkey). The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army ...
in 1071, Trebizond came under Seljuk Seljuk (, ''Selcuk'') or Saljuq (, ''Saljūq'') may refer to:
* Seljuk Empire (1051–1153), a medieval empire in the Middle East and central Asia
* Seljuk dynasty (c. 950–1307), the ruling dynasty of the Seljuk Empire and subsequent polities
* S ...
rule. This rule proved transient when an expert soldier and local aristocrat, Theodore Gabras
Theodore Gabras () was a Byzantine Empire, Byzantine governor in the Pontus (region), Pontus who was involved in a minor unsuccessful rebellion against the Byzantine Emperor, Emperor Alexios I Komnenos around the year 1091. He is an Eastern Orthodo ...
took control of the city from the Turkish invaders, and regarded Trebizond, in the words of Anna Comnena
Anna Komnene (; 1 December 1083 – 1153), commonly Latinized as Anna Comnena, was a Byzantine Greek historian. She is the author of the '' Alexiad'', an account of the reign of her father, Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos. Her work constit ...
, "as a prize which had fallen to his own lot" and ruled it as his own kingdom. Supporting Comnena's assertion, Simon Bendall has identified a group of rare coins he believes was minted by Gabras and his successors. Although he was killed by the Turks in 1098, other members of his family continued his de facto independent rule into the next century.
Empire of Trebizond
TheEmpire of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond or the Trapezuntine Empire was one of the three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire that existed during the 13th through to the 15th century. The empire consisted of the Pontus, or far northeastern corner of A ...
was formed after a Georgian expedition in Chaldia, commanded by Alexios
Alexius is the Latinization (literature), Latinized form of the given name Alexios (, polytonic , "defender", cf. Alexander), especially common in the Byzantine Empire. The female form is Alexia (given name), Alexia () and its variants such as Ales ...
Komnenos
The House of Komnenos ( Komnenoi; , , ), Latinized as Comnenus ( Comneni), was a Byzantine Greek noble family who ruled the Byzantine Empire in the 11th and 12th centuries. The first reigning member, Isaac I Komnenos, ruled from 1057 to 1059. ...
a few weeks before the sack of Constantinople
The sack of Constantinople occurred in April 1204 and marked the culmination of the Fourth Crusade. Crusaders sacked and destroyed most of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire. After the capture of the city, the Latin Empire ( ...
in 1204. Located at the far northeastern corner of Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, it was the longest surviving of the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
successor states. Byzantine authors, such as Pachymeres, and to some extent Trapezuntines such as Lazaropoulos and Bessarion
Bessarion (; 2 January 1403 – 18 November 1472) was a Byzantine Greek Renaissance humanist, theologian, Catholic cardinal and one of the famed Greek scholars who contributed to the revival of letters in the 15th century. He was educated ...
, regarded the Trebizond Empire as being no more than a Lazian border state. Thus, from the point of view of the Byzantine writers connected with the Lascaris and later with the Palaiologos
The House of Palaiologos ( Palaiologoi; , ; female version Palaiologina; ), also found in English-language literature as Palaeologus or Palaeologue, was a Byzantine Greeks, Byzantine Greek Nobility, noble family that rose to power and produced th ...
, the rulers of Trebizond were not emperors.Finlay, George. The History Of Greece From Its Conquest By The Crusaders To Its Conquest By The Turks And Of The Empire Of Trebizond, 1204–1461, By George Finlay. 1st ed. Edinburgh: W. Blackwood and sons, 1851. Print.Vasilev, A. A. The Foundation Of The Empire Of Trebizond 1204–1222. 1st ed. Cambridge, Mass.: Medieval Academy of America, 1936. Print.
Geographically, the Empire of Trebizond consisted of little more than a narrow strip along the southern coast of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
, and not much further inland than the Pontic Mountains
The Pontic Mountains or Pontic Alps (, meaning 'North Anatolian Mountains'), form a mountain range in northern Anatolia, Turkey. They are also known as the "Parhar Mountains" in the local Turkish and Pontic Greek languages. The term ''Parhar'' ...
. However, the city gained great wealth from the taxes it levied on the goods traded between Persia and Europe via the Black Sea. The Mongol siege of Baghdad
The siege of Baghdad took place in early 1258. A large army commanded by Hulegu, a prince of the Mongol Empire, attacked the historic capital of the Abbasid Caliphate after a series of provocations from its ruler, caliph al-Musta'sim. Within ...
in 1258 diverted more trade caravans towards the city. Genoese and to a lesser extent Venetian traders regularly came to Trebizond. To secure their part of the Black Sea trade, the Genoese bought the coastal fortification "Leonkastron", just west of the winter harbour, in the year 1306. The Venetians likewise built a trading outpost in the city, a few hundred meters to the west of the Genoese. In between these two Italian colonies settled many other European traders, and it thus became known as the "European Quarter". Small groups of Italians continued to live in the city until the early decades of the 20th century. One of the most famous persons to have visited the city in this period was Marco Polo
Marco Polo (; ; ; 8 January 1324) was a Republic of Venice, Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known a ...
, who ended his overland return journey at the port of Trebizond, and sailed to his hometown Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
with a ship; passing by Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
(Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ...
) on the way, which was retaken by the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
s in 1261.
Together with Persian goods, Italian traders brought stories about the city to Western Europe. Trebizond played a mythical role in European literature of the late Middle Ages and the Renaissance. Miguel de Cervantes
Miguel de Cervantes Saavedra ( ; ; 29 September 1547 (assumed) – 22 April 1616 Old Style and New Style dates, NS) was a Spanish writer widely regarded as the greatest writer in the Spanish language and one of the world's pre-eminent novelist ...
and François Rabelais
François Rabelais ( , ; ; born between 1483 and 1494; died 1553) was a French writer who has been called the first great French prose author. A Renaissance humanism, humanist of the French Renaissance and Greek scholars in the Renaissance, Gr ...
gave their protagonists the desire to possess the city. Next to literature, the legendary history of the city – and that of the Pontus in general – also influenced the creation of paintings
Painting is a visual art, which is characterized by the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called "matrix" or " support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush. Other implements, ...
, theatre plays and operas
Opera is a form of Western theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a li ...
in Western Europe throughout the following centuries.
The city also played a role in the early Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
; the western takeover of Constantinople, which formalized Trebizond's political independence, also led Byzantine intellectuals to seek refuge in the city. Especially Alexios II of Trebizond
Alexios II Megas Komnenos (; Sept./Dec. 1282 – 3 May 1330) was Emperor of Trebizond from 1297 to 1330. He was the elder son of John II and Eudokia Palaiologina.
Alexios proved to be a skillful and energetic ruler, under whose rule the Empire ...
and his grandson Alexios III were patrons of the arts and sciences. After the great city fire of 1310, the ruined university was reestablished. As part of the university Gregory Choniades opened a new academy of astronomy, which housed the best observatory outside Persia. Choniades brought with him the works of Shams al-Din al-Bukhari, Nasir al-Din al-Tusi
Muḥammad ibn Muḥammad ibn al-Ḥasan al-Ṭūsī (1201 – 1274), also known as Naṣīr al-Dīn al-Ṭūsī (; ) or simply as (al-)Tusi, was a Persians, Persian polymath, architect, Early Islamic philosophy, philosopher, Islamic medicine, phy ...
and Abd al-Rahman al-Khazini from Tabriz, which he translated into Greek. These works later found their way to western Europe, together with the astrolabe
An astrolabe (; ; ) is an astronomy, astronomical list of astronomical instruments, instrument dating to ancient times. It serves as a star chart and Model#Physical model, physical model of the visible celestial sphere, half-dome of the sky. It ...
. The observatory Choniades built would become known for its accurate solar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six months, during the eclipse season i ...
predictions, but was probably used mostly for astrological
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions of celesti ...
purposes for the emperor and/or the church. Scientists and philosophers of Trebizond were among the first western thinkers to compare contemporaneous theories with classical Greek texts. Basilios Bessarion
Bessarion (; 2 January 1403 – 18 November 1472) was a Byzantine Greeks, Byzantine Greek Renaissance humanist, theologian, Catholic Church, Catholic Cardinal (Catholic Church), cardinal and one of the famed Greek scholars who contributed ...
and George of Trebizond
George of Trebizond (; 1395–1486) was a Byzantine Greek philosopher, scholar, and humanist.
Life
He was born on the Greek island of Crete (then a Venetian colony known as the Kingdom of Candia), and derived his surname Trapezuntius (Τραπ ...
travelled to Italy and taught and published works on Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the writte ...
and Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
, starting a fierce debate and literary tradition that continues to this day on the topic of national identity and global citizenship
Global citizenship is a form of transnationality, specifically the idea that one's identity transcends geography or political borders and that responsibilities or rights are derived from membership in a broader global class of "humanity". This do ...
. They were so influential that Bessarion was considered for the position of Pope
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
, and George could survive as an academic even after being defamed for his heavy criticism of Plato.
The Black Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. ...
arrived at the city in September 1347, probably via Kaffa. At that time the local aristocracy was engaged in the Trapezuntine Civil War.
In 1340, Tur Ali Beg, an early ancestor of the Aq Qoyunlu, raided Trebizond. In 1348, he besieged Trebizond, however he failed and lifted the siege. Later on, Alexios III of Trebizond gave his sister to Qutlugh bin Tur Ali, Kutlu Beg son of Tur Ali Beg, and established a kinship with them.
Constantinople remained the Byzantine capital until it was Fall of Constantinople, conquered by the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Sultan Mehmed II in 1453, who also Siege of Trebizond (1461), conquered Trebizond eight years later, in 1461.
Its demographic legacy endured for several centuries after the Ottoman conquest in 1461, as a substantial number of Greek Orthodox inhabitants, usually referred to as Pontic Greeks, continued to live in the area during Ottoman rule, up until 1923, when they were deported to Greece. A few thousand Greek Muslims still live in the area, mostly in the Çaykara-Of, Turkey, Of dialectical region to the southeast of Trabzon. Most are Sunni Muslim, while there are some recent converts in the city and possibly a few Crypto-Christians in the Tonya, Turkey, Tonya/Gümüşhane area to the southwest of the city. Compared to most previously Greek cities in Turkey, a large amount of its Greek Byzantine architectural heritage survives as well.
Ottoman era
The last Emperor of Trebizond, David of Trebizond, David, surrendered the city to Sultan Mehmed II of the Ottoman Empire in 1461. Following this takeover, Mehmed II sent many Turkish settlers into the area, but the old ethnic Greeks, Greek, Laz and Armenians, Armenian communities remained. According to the Ottoman tax books (''tahrir defterleri''), the total population of taxable adult males (only those with a household) in the city was 1,473 in the year 1523.''The Armenian People from Ancient to Modern Times'', Richard G. Hovannisian, page 27/28, 2004 The total population of the city was much higher. Approximately 85% of the population was Christian, and 15% Muslim. Thirteen percent of the adult males belonged to the Armenian community, while the vast majority of Christians were Greeks. However, a significant portion of the local Christians were Islamization, Islamized by the end of the 17th century - especially those outside the city - according to a research by Prof. Halil İnalcık on the Ottoman tax books (''tahrir defterleri''). Between 1461 and 1598 Trabzon remained the administrative center of the wider region; first as 'sanjac center' of Rum Eyalet, later of Erzincan-Bayburt eyalet, Anadolu Eyalet, and Erzurum Eyalet. In 1598 it became the capital of its own province - the Trebizond Eyalet, Eyalet of Trebizond - which in 1867 became the Trebizond Vilayet, Vilayet of Trebizond. During the reign of Sultan Bayezid II, his son Selim I, Prince Selim (later Sultan Selim I) was the Sanjak-bey of Trabzon, and Selim I's son Suleiman the Magnificent was born in Trabzon in 1494. The Ottoman government often appointed local Chepni people, Chepni Turks and Laz beys as the regional beylerbey. It is also recorded that some Bosniaks were appointed by the Sublime Porte as the regional beylerbeys in Trabzon. The Eyalet of Trabzon had always sent troops for the Ottoman wars in Europe, Ottoman campaigns in Europe during the 16th and 17th centuries. Trebizond had a wealthy merchant class during the late Ottoman period, and the local Christian minority had a substantial influence in terms of culture, economy and politics. A number of European consulates were opened in the city due to its importance in regional trade and commerce. In the first half of the 19th century, Trebizond even became the main port for Persian exports. The opening of the Suez Canal greatly diminished the international trading position of the city, but did not halt the economic development of the region. In the last decades of the 19th century, the city saw some demographic changes. As the population of the province greatly expanded due to increased living standards, many families and young men - mostly Christians, but also some Jews and Greek or Turkish speaking Muslims - chose to migrate to the Crimea and southern Ukraine, in search for farmland or employment in one of the cities which had been newly established there. Among these migrants were the grandparents of Bob Dylan and Greek politicians and artists. Many Christian and Muslim families from Trabzon also moved to Constantinople, where they established businesses or sought employment - such as the grandfather of Ahmet Ertegün. These migrants were active in a wide range of trades including baking, confection, tailoring, carpentry, education, advocacy, politics and administration. The influence of this diaspora has since continued, and can still be seen in the many restaurants and shops in cities around the Black Sea in the 21st century such as in Istanbul, Odesa and Mariupol. At the same time, thousands of Muslim refugees from the Caucasus arrived in the city, especially after 1864, in what is known as the Circassian genocide. Next to Constantinople, Smyrna (now İzmir) and Salonika (now Thessaloniki), Trebizond was one of the cities where western cultural and technological innovations were first introduced to the Ottoman Empire. In 1835, the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions opened the Trebizond Mission station that it occupied from 1835 to 1859 and from 1882 to at least 1892. Hundreds of schools were constructed in the province during the first half of the 19th century, giving the region one of the highest literacy rates of the empire. First, the Greek community set up their schools, but soon the Muslim and Armenian communities followed. International schools were also established in the city; An American school, five French schools, a Persian school and a number of Italian schools were opened in the second half of the 19th century. The city got a post office in 1845. New churches and mosques were built in the second half of the 19th century, as well as the first theater, public and private printing houses, multiple photo studios and banks. The oldest known photographs of the city center date from the 1860s and depict one of the last camel trains from Persia. Between one and two thousand Armenians are believed to have been killed in the Trebizond vilayet during the Hamidian massacres of 1895. While this number was low in comparison to other Ottoman provinces, its impact on the Armenian community in the city was large. Many prominent Armenian residents, among them scholars, musicians, photographers and painters, decided to migrate towards the Russian Empire or France. The large Greek population of the city was not affected by the massacre. Ivan Aivazovsky made the painting ''Massacre of the Armenians in Trebizond 1895'' based on the events. Due to the high number of Western Europeans in the city, news from the region was being reported on in many European newspapers. These western newspapers were in turn also very popular among the residents of the city. Ottoman era paintings and drawings of TrebizondModern era
In 1901 the harbour was equipped with cranes by Stothert & Pitt of Bath, Somerset, Bath in England. In 1912 the Sümer Opera House was opened on the central Meydan square, being one of the first in the empire. The start of the First World War brought an abrupt end to the relatively peaceful and prosperous period the city had seen during the previous century. First Trebizond would lose many of its young male citizens at the Battle of Sarikamish in the winter of 1914–15, while during those same months the Russian navy bombarded the city a total of five times, taking 1300 lives. Especially the port quarter Çömlekçi and surrounding neighborhoods were targeted. In July 1915 most of the adult male Armenians of the city were marched off south in five convoys, towards the mines of Gümüşhane, never to be seen again. Other victims of the Armenian genocide were reportedly taken out to sea in boats which were then capsized. In some areas of Trebizond province - such as the Karadere river valley in modern-day Araklı, 25 kilometers east of the city - the local Muslim population tried to protect the Christian Armenians. The coastal region between the city and the Russian frontier became the site of key battles between the Ottoman and Russian Empire, Russian armies during the Trebizond Campaign, as part of the Caucasus Campaign of World War I. The Russian army landed at Pazar, Rize, Atina, east of Rize on March 4, 1916. Lazistan Sanjak fell within two days. However, due to heavy guerrilla resistance around Of and Çaykara some 50 km to the east of Trabzon, it took a further 40 days for the Russian army to advance west. The Ottoman administration of Trabzon foresaw the fall of the city and called for a meeting with community leaders, where they handed control of the city to Greek metropolitan bishop Archbishop Chrysanthus of Athens, Chrysantos Philippidis. Chrysantos promised to protect the Muslim population of the city. Ottoman forces retreated from Trabzon, and on April 15 the city was taken without a fight by the Russian Caucasus Army (World War I), Russian Caucasus Army under command of Grand Duke Nikolai Nikolaevich of Russia (1856–1929), Grand Duke Nicholas and Nikolai Nikolaevich Yudenich, Nikolai Yudenich. There was also a massacre of Armenians and Greeks in Trabzon just before the Russian takeover of the city. In early 1917 Chrysantos tried to broker a peace between the Russians and the Ottomans, to no avail. During the Russian Revolution of 1917 Russian soldiers in the city turned to rioting and looting, with officers commandeering Trebizonian ships to flee the scene. Governor Chrysantos was able to calm the Russian soldiers down, and the Russian Army ultimately retreated from the city and the rest of eastern and northeasternAnatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
. In March and April of 1918 the city hosted the Trebizond Peace Conference, where the Ottomans agreed to give up their military gains in the Caucasus in return for recognition of the eastern borders of the empire in Anatolia by the Transcaucasian Seim (a short-lived transcaucasian government).
In December 1918 Trabzon deputy governor Hafız Mehmet gave a speech at the Ottoman parliament in which he blamed the former governor of Trebizond Vilayet, Trebizond province Cemal Azmi – a non-native appointee who had fled to Germany after the Russian invasion – for orchestrating the Armenian genocide in the city in 1915, by means of drowning. Subsequently, a series of war crimes trials were held in Trebizond in early 1919 (see Trebizond during the Armenian genocide). Among others, Cemal Azmi was sentenced to death in absentia.
During the Turkish War of Independence several Christian Pontic Greeks, Pontic Greek communities in the Trebizond province rebelled against the new army of Mustafa Kemal (notably in Bafra and Dumanlı, Santa), but when nationalist Greeks came to Trabzon to proclaim revolution, they were not received with open arms by the local Pontic Greek population of the city. At the same time the Muslim population of the city, remembering their protection under Greek governor Chrysantos, protested the arrest of prominent Christians. Liberal delegates of Trebizond opposed the election of Mustafa Kemal as the leader of the Turkish revolution at the Erzurum Congress.
The governor and mayor of Trebizond were appalled by the violence against Ottoman Greek subjects, and the government of Trabzon thus refused arms to Mustafa Kemal's henchman Topal Osman, who was responsible for mass murders in the western Pontus which were part of the Greek genocide. Osman was forced out of the city by armed Turkish port-workers. Governor Chrysantos travelled to the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace Conference, where he proposed the establishment of the Republic of Pontus, which would protect its different ethnic groups. For this he was condemned to death by the Turkish Nationalist forces, and he could not return to his post in Trebizond. Instead, the city was to be handed to 'Wilsonian Armenia', which likewise never materialized. Following the war, the Treaty of Sèvres was annulled and replaced with the Treaty of Lausanne (1923). As part of this new treaty, Trebizond became part of the new Turkey, Turkish Republic. The efforts of the pro-Ottoman Empire, Ottoman, anti-nationalist population of Trebizond only postponed the inevitable, because the national governments of Turkey and Greece agreed to a mutual Population exchange between Greece and Turkey, forced population exchange. This exchange included well over 100,000 Pontic Greeks, Greeks from Trebizond and the vicinity, who moved to Greece (founding the new towns of Nea Trapezounta, Pieria and Nea Trapezounta, Grevena amongst others).
During the war Trebizond parliamentarian Ali Şükrü Bey had been one of the leading figures of the Second Group (Turkey), first Turkish opposition party. In his newspaper ''Tan'', Şükrü and colleagues publicized critiques of the Kemalist government, such as towards the violence perpetrated against Greeks during the population exchange. Şükrü argued that recognition of ethnic diversity was not a threat to the Turkish nation.
Topal Osman's men would eventually murder parliamentarian Şükrü for his criticism of the nationalist government of Mustafa Kemal in March 1923. Topal Osman was later sentenced to death and killed while resisting arrest. After pressure from the opposition, his headless body was hanged by his foot in front of the Turkish parliament. Ali Şükrü Bey, who had studied in Deniz Harp Okulu (Turkish Naval Academy) and worked as a journalist in the United Kingdom, is seen as a hero by the people of Trabzon, while in neighboring Giresun there is a statue of his murderer Topal Osman. Three years later Trabzon deputy Hafız Mehmet – who had testified to his knowledge of, and opposition to, the Armenian Ggenocide – was also executed, for his alleged involvement in the İzmir plot to assassinate Mustafa Kemal. The literal decapitation of the Turkish political opposition – which was in large part based in the Trabzon region – decreased the city's national influence, and led to a long-standing animosity between the Kemalists and the population of Trabzon. A political and cultural divide between the Eastern Black Sea Region and the rest of Anatolia continued to exist throughout the 20th century, and still influences Turkish politics today. Even in the 21st century, politicians who hail from Trabzon are often faced with xenophobic attacks from both nationalist and conservative circles.
During World War II shipping activity was limited because the Black Sea had again become a war zone. Hence, the most important export products, tobacco and hazelnuts, could not be sold and living standards degraded.
As a result of the general development of the country, Trabzon has developed its economic and commercial life. The coastal highway and a new harbour have increased commercial relations with central Anatolia, which has led to some growth. However, progress has been slow in comparison to the western and the southwestern parts of Turkey.
Trabzon is famous throughout Turkey for its anchovies called ''hamsi'', which are the main meal in many restaurants in the city. Major exports from Trabzon include hazelnuts and tea.
The city still has a sizable community of Greek Muslims#Greek Muslims of Pontus and the Caucasus, Greek-speaking Muslims, most of whom are originally from the vicinities of Tonya, Turkey, Tonya, Sürmene and Çaykara. However, the variety of the Pontic Greek, Pontic Greek language - known as "''Romeika''" in the local vernacular, ''Pontiaka'' in Greek, and ''Rumca'' in Turkish - is spoken mostly by the older generations.
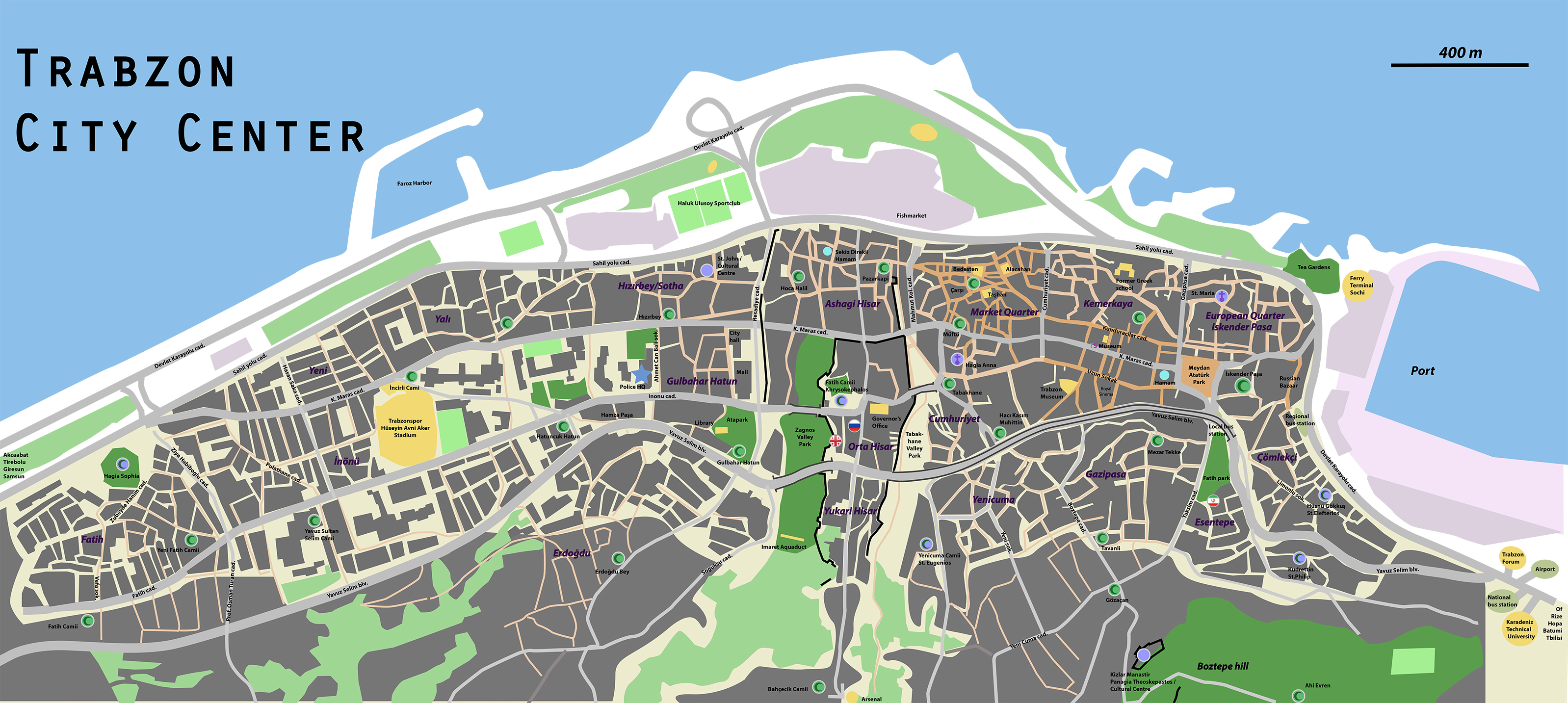
Geography

Trabzon Province
Trabzon Province () is a Provinces of Turkey, province and Metropolitan municipalities in Turkey, metropolitan municipality of Turkey on the Black Sea coast. Its area is 4,628 km2, and its population is 818,023 (2022). Located in a strategic ...
has a total area of and is bordered by the provinces of Rize Province, Rize, Giresun Province, Giresun, and Gümüşhane Province, Gümüşhane. The total area is 22.4% plateau and 77.6% hills. The Pontic Mountains
The Pontic Mountains or Pontic Alps (, meaning 'North Anatolian Mountains'), form a mountain range in northern Anatolia, Turkey. They are also known as the "Parhar Mountains" in the local Turkish and Pontic Greek languages. The term ''Parhar'' ...
pass through the Trabzon Province.
Trabzon used to be an important pilotage, reference point for navigation, navigators in the Black Sea during harsh weather conditions. The popular expression "perdere la Trebisonda" (losing Trebizond) is still commonly used in the Italian language to describe situations in which the sense of direction is lost. The Italian maritime republics such as Republic of Venice, Venice and in particular Republic of Genoa, Genoa were active in the Black Sea trade for centuries.
Trabzon has four lakes: Uzungöl, Çakırgöl, Sera, and Haldizen Lakes. There are several streams, but no rivers in Trabzon.
Climate
Trabzon has a climate typical of the eastern Black Sea region, a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification, Köppen: ''Cfa,'' Trewartha climate classification, Trewartha'': Cf'') near the coast. A very small percentage of the province can be classified as subtropical, however, as slightly elevated rural areas near the coast are oceanic climate, oceanic (''Cfb/Do''), the mountainous offshores are humid continental climate, humid continental (''Dfb/Dc'') and subarctic climate, subarctic (''Dfc/Eo''); and tundra (''ET/Ft'') can be found in the peaks of the Pontic Alps. Furthermore, during the time the Köppen climate classification was created, the city center had a borderline oceanic-humid subtropical climate, falling just under the threshold for the hottest month of the year, yet climate change and the city's urban heat island contributed to its reclassification as humid subtropical in recent decades. This and the fact that the subtropical microclimate zone along the shore occupies a very narrow band due to the continuous parallel mountain range starting right at the coast is why local authorities still classify the city as oceanic, as this climate subtype is better representative of the entire coastal region of the province. Summers are warm, the average maximum temperature is around in August, while winters are generally cool, the lowest average minimum temperature is almost in February. Precipitation is heaviest in autumn and winter, with a marked reduction in the summer months, a microclimate, microclimatic condition of the city center compared to the rest of the region. Snowfall is somewhat common between the months of December and March, snowing for a week or two, and it can be heavy once it snows (this is due to the "lake-effect snow"). The water temperature, like in the rest of the Black Sea coast of Turkey, is generally mild, and fluctuates between and throughout the year.Economy
 As of 1920, the port at Trabzon was considered "the most important of the Turkish Black Sea ports" by the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, British. It traded as far as Tabriz and Mosul. As of 1911, the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey signed an agreement to develop a harbor at the port. When the Russians occupied Trabzon, a Mole (architecture), mole was built. They built a Breakwater (structure), breakwater and were responsible for creating an extended pier, making loading and unloading easier. In 1920, Trabzon produced linen cloth, silver filagree, Tanning (leather), tanning and small amounts of cotton, silk and wool. Tobacco and hazelnuts were exported. The tobacco produced in Trabzon was called ''Trebizond-Platana''. It was described as having "large leaves and a bright colour." Trabzon was known for producing poor quality cereals, mostly for local use.
Trabzon produced a white green bean, which was sold in Europe. It was, as of 1920, the only vegetable exported out of the province. Poultry farming was also popular in Trabzon. Sericulture was seen in the area before 1914. The area produced copper, silver, zinc, iron and manganese. Copper was kept for local use by coppersmiths. During the Balkan Wars production ceased due to poor exportation and fuel supplies.
Trabzon Airport opened in 1957.
As of 1920, the port at Trabzon was considered "the most important of the Turkish Black Sea ports" by the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, British. It traded as far as Tabriz and Mosul. As of 1911, the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey signed an agreement to develop a harbor at the port. When the Russians occupied Trabzon, a Mole (architecture), mole was built. They built a Breakwater (structure), breakwater and were responsible for creating an extended pier, making loading and unloading easier. In 1920, Trabzon produced linen cloth, silver filagree, Tanning (leather), tanning and small amounts of cotton, silk and wool. Tobacco and hazelnuts were exported. The tobacco produced in Trabzon was called ''Trebizond-Platana''. It was described as having "large leaves and a bright colour." Trabzon was known for producing poor quality cereals, mostly for local use.
Trabzon produced a white green bean, which was sold in Europe. It was, as of 1920, the only vegetable exported out of the province. Poultry farming was also popular in Trabzon. Sericulture was seen in the area before 1914. The area produced copper, silver, zinc, iron and manganese. Copper was kept for local use by coppersmiths. During the Balkan Wars production ceased due to poor exportation and fuel supplies.
Trabzon Airport opened in 1957.
People
History
Trebizond was an overwhelmingly Christianity, Christian and Greeks, Greek city at the time of its fall to the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans in 1461. The Greek Christians slowly lost their majority through the end of that century. Initially, the Muslims were mainly immigrants fromAnatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
with a minority of local converts, but this quickly changed with the emergence of an active missionary spirit in the 16th century, as mosques and dervish lodges were built in predominantly Christian neighborhoods. Laz people also live in Trabzon. Numerous villages inside and out of Trabzon of the Laz date back as early as the period of Tamar of Georgia, Queen Tamar's rule (Georgian: თამარი, also transliterated as T'amar or Thamar; c. 1160 – 18 January 1213) in the newly unified Kingdom of Georgia. During the Queen's rule, sizeable groups of immigrating Georgians moved to Trabzon where they continue to preserve their native tongue. There was an Armenian community in Trebizond as early as the 7th century.
During the 13th and 14th centuries, numerous Armenians, Armenian families migrated there from Ani. Robert W. Edwards published part of an early 15th-century diary from the Castilian ambassador who visited Trabzon and compared the churches of the Greek and Armenian communities. It was stated by the ambassador that the Armenians, who were not well-liked by the Greeks, had a population large enough to support a resident bishop. According to Ronald C. Jennings, in the early 16th century, Armenians made up approximately 13 percent of the city's population. At present, Trabzon does not have an Armenian-speaking community.
The Chepni people, a tribe of Oghuz Turks who played an important role in the history of the eastern Black Sea area in the 13th and 14th centuries, live in the Şalpazarı (Ağasar valley) region of the Trabzon Province. Very little has been written on the Turkification of the area. There are no historical records of any considerable Turkish-speaking groups in the Trabzon area until the late 15th century, with the exception of the Chepnis. The original Pontic Greek, Greek (and in some regions
Laz people also live in Trabzon. Numerous villages inside and out of Trabzon of the Laz date back as early as the period of Tamar of Georgia, Queen Tamar's rule (Georgian: თამარი, also transliterated as T'amar or Thamar; c. 1160 – 18 January 1213) in the newly unified Kingdom of Georgia. During the Queen's rule, sizeable groups of immigrating Georgians moved to Trabzon where they continue to preserve their native tongue. There was an Armenian community in Trebizond as early as the 7th century.
During the 13th and 14th centuries, numerous Armenians, Armenian families migrated there from Ani. Robert W. Edwards published part of an early 15th-century diary from the Castilian ambassador who visited Trabzon and compared the churches of the Greek and Armenian communities. It was stated by the ambassador that the Armenians, who were not well-liked by the Greeks, had a population large enough to support a resident bishop. According to Ronald C. Jennings, in the early 16th century, Armenians made up approximately 13 percent of the city's population. At present, Trabzon does not have an Armenian-speaking community.
The Chepni people, a tribe of Oghuz Turks who played an important role in the history of the eastern Black Sea area in the 13th and 14th centuries, live in the Şalpazarı (Ağasar valley) region of the Trabzon Province. Very little has been written on the Turkification of the area. There are no historical records of any considerable Turkish-speaking groups in the Trabzon area until the late 15th century, with the exception of the Chepnis. The original Pontic Greek, Greek (and in some regions Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
) speakers imposed features from their mother language into the Turkish spoken in the region. Heath W. Lowry's work with Halil İnalcık on Ottoman tax books (''Tahrir Defteri'') provides detailed demographic statistics for the city of Trabzon and its surrounding areas during the Ottoman period.
It is possible that the majority of the population of Trabzon and Rize (another ancient Greek colony in the Pontus region) — except up to the time of the Chepni Turk immigration waves — consisted of indigenous Caucasian tribes (the Colchians and the Laz) who had been partly Hellenization, Hellenized religiously and linguistically. Michael Meeker stresses the cultural resemblances (e.g. in village structure, house types, and pastoral techniques) between the Eastern Black Sea coast and the areas in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
proper.
Urbanization
Main sights
Trabzon has a number of tourist attractions, some of them dating back to the times of the ancient empires that once existed in the region. In the city itself, one can find a hub of shops, stalls and restaurants surrounding the ''Meydan (park), Meydan'', a square in the center of the city, which includes a tea garden. * The Hagia Sophia, Trabzon, Hagia Sophia (formerly , now a mosque), a stunning Byzantine church, is probably the town's most important tourist attraction. * Trabzon Castle ruins are visible in the town but cannot be visited as they fall in a military zone. The outside wall of the castle now serves as the back wall of a military building. * The "Atatürk Köşkü" is a villa built in 1890 by a local Greek merchant. In 1924 Mustafa Kemal Atatürk stayed in the villa during his visit to Trabzon. He stayed there again in 1937. It houses period rooms and serves as a monument to the memory of the founder and first president of the Republic of Turkey. * Boztepe hill, Trabzon, Boztepe Park is a small park and tea garden on the hills above Trabzon that has a panoramic view of nearly the entire city. The terrain in Trabzon is ascending in such a way that although the view is far above that of the buildings below, it is still close enough to be able to observe the flow of traffic and the people moving about in the city. * Uzun Sokak is one of the most crowded streets of Trabzon. * Trabzon Museum is located in the town centre and offers interesting exhibits on the history of the region, including an impressive collection of Byzantine artifacts. * Trabzon's Bazaar District offers interesting shopping opportunities on ancient narrow streets, continuing from Kunduracılar Street from the Meydan (town square). * Saint Anne Church, Trabzon, is located in the city centre of Trabzon, and one of the oldest in the city. * Kostaki Mansion is located to the north of Zeytinlik, Artvin, Zeytinlik, near Uzun Sokak. * Uzungöl Dursun Ali İnan Museum An ethnographic museum in Uzungol that tells the history of Trabzon and the region. Other sites of the city include: Fatih Mosque of Trabzon, Fatih Mosque (originally the Panagia Khrysokephalos Church), Yeni Cuma Mosque (originally the Agios Eugenios Church), Nakip Mosque (originally the Agios Andreas Church), Hüsnü Köktuğ Mosque (originally the Agios Elevtherios Church), İskender Pasha Mosque, Trabzon, İskender Pasha Mosque, Semerciler Mosque, Çarşı Mosque, Gülbahar Hatun Mosque and Türbe (commissioned by Sultan Selim I), and Kalepark (originally Leonkastron). WithinTrabzon Province
Trabzon Province () is a Provinces of Turkey, province and Metropolitan municipalities in Turkey, metropolitan municipality of Turkey on the Black Sea coast. Its area is 4,628 km2, and its population is 818,023 (2022). Located in a strategic ...
, the main attractions are the Sümela Monastery (i. e. the Monastery of the Panagia Soumelá) and the Uzungöl lake. The monastery is built on the side of a very steep mountain overlooking the green forests below and is about south of the city. Uzungöl is known for its natural environment and scenery. Other sites of interest in the broader region include:
* Kaymaklı Monastery, a formerly Armenian Monastery of the All-Saviour (arm. Ամենափրկիչ Վանք, Amenaprgič Vank);
* Kızlar Monastery of Panagia Theoskepastos (the God-veiled Virgin);
* Kuştul Monastery of Gregorios Peristereotas (gr. Ιερά Μονή του Αγίου Γεωργίου Περιστερεώτα, Ierá Moní tou Agíou Georgíou Peristereóta);
* Vazelon Monastery
Vazelon Monastery () is a ruin located in the Black Sea region of Turkey. It was built in 270 and is south of Trabzon. Justinian I, a ruler of the Byzantine Empire, ordered the monastery to be repaired in 565, and it was renovated multiple time ...
of Agios Savvas (Maşatlık);
* Cave churches of Agia Anna (Little Ayvasıl), Sotha (St. John), Agios Theodoros, Agios Konstantinos, Agios Christophoros, Agia Kyriakí, Agios Michail, and Panagia Tzita churches.

Culture
 Folk dancing is still very much in evidence in the Black Sea Region. The "Horon (dance), Horon" is a famous dance that is indigenous to the city and its surrounding area. It is performed by men, women, the young and elderly alike; in festivities, local weddings and harvest times. While similar to Russian Cossacks, Cossack dances in terms of vividness, the Trabzon folk dance is probably indigenous to the eastern Black Sea region, which has an impressive variety of folk music.
The people of Trabzon have a reputation for being religiously conservative and nationalist. Many Trabzonites generally show a strong sense of loyalty to their family, friends, religion and country. Atatürk selected his presidential guards from Trabzon and the neighbouring city of Giresun because of their fierce fighting ability and their loyalty.
Outside of the relatively urban space of Trabzon proper, and within parts of it as well, rural traditions from the Black Sea village life are still thriving. These include traditional gender roles, social conservatism, hospitality, and a willingness to help strangers; and all aspects, both positive and negative, of an agrarian lifestyle, such as hard work, poverty, strong family ties, and a closeness to nature.
The people of the eastern Black Sea region are also known for their wit and sense of humour; many jokes in Turkey are told about the natives of the Black Sea region ''Karadeniz fıkraları'' (Black Sea jokes). The character ''Temel'', a universal buffoon figure found in many cultures, forms an important part of the Turkish oral tradition.
The city's profile was raised somewhat in the English-speaking world by Rose Macaulay, Dame Rose Macaulay's last novel, ''The Towers of Trebizond'' (1956), which is still in print.
Folk dancing is still very much in evidence in the Black Sea Region. The "Horon (dance), Horon" is a famous dance that is indigenous to the city and its surrounding area. It is performed by men, women, the young and elderly alike; in festivities, local weddings and harvest times. While similar to Russian Cossacks, Cossack dances in terms of vividness, the Trabzon folk dance is probably indigenous to the eastern Black Sea region, which has an impressive variety of folk music.
The people of Trabzon have a reputation for being religiously conservative and nationalist. Many Trabzonites generally show a strong sense of loyalty to their family, friends, religion and country. Atatürk selected his presidential guards from Trabzon and the neighbouring city of Giresun because of their fierce fighting ability and their loyalty.
Outside of the relatively urban space of Trabzon proper, and within parts of it as well, rural traditions from the Black Sea village life are still thriving. These include traditional gender roles, social conservatism, hospitality, and a willingness to help strangers; and all aspects, both positive and negative, of an agrarian lifestyle, such as hard work, poverty, strong family ties, and a closeness to nature.
The people of the eastern Black Sea region are also known for their wit and sense of humour; many jokes in Turkey are told about the natives of the Black Sea region ''Karadeniz fıkraları'' (Black Sea jokes). The character ''Temel'', a universal buffoon figure found in many cultures, forms an important part of the Turkish oral tradition.
The city's profile was raised somewhat in the English-speaking world by Rose Macaulay, Dame Rose Macaulay's last novel, ''The Towers of Trebizond'' (1956), which is still in print.
Education
Karadeniz Technical University in Trabzon hosts students from all over Turkey, especially from the Black Sea Region, Black Sea and East Anatolia Region, Turkey, East Anatolian regions, as well as students from the Turkic states in Central Asia. Historically the city was a center of Greek culture and education and from 1683 to 1921, a teachers' college operated known as Phrontisterion of Trapezous, which provided a major impetus for the rapid expansion of Greek education throughout the region. The building of this institution (built in 1902) still remains the most impressive Pontic Greeks, Pontic Greek monument in the city and today hosts the Turkish school ''Anadolu Lisesi''.Cuisine
Trabzon's regional cuisine is traditionally reliant on fish, especially ''hamsi'' (fresh European Anchovy similar to the British Sprat or American Smelt). Trabzon meets 20% of the total fish production in Turkey. Regional dishes include the ''Akçaabat köfte'' (spicy lamb meatball from the Akçaabat district), ''Karadeniz pidesi'' (canoe shaped pita bread, often filled with ground beef, cheese and eggs), ''kuymak'' (a Turkish fondue made with cornmeal, fresh butter and cheese), ''Vakfıkebir ekmeği'' (large country-style bread), ''Tonya tereyağı'' (Tonya butter), ''tava mısır ekmeği'' (deep-dish corn bread) and ''kara lahana çorbası'' (bean and cabbage soup). ''Taflan kavurması'' is a Prunus laurocerasus, cherry laurel dish served with onions and olive oil. Trabzon is also famous for its hazelnuts. The Black Sea region of Turkey is the world's largest producer of cherry and hazelnut; and a large production area of tea; all of which play an important role in the local cuisine.Sports
 Association football, Football is the most popular sport in Trabzon. The city's top sports club, Trabzonspor, was until 2009–10 Süper Lig, 2010 the only Turkish football club outside İstanbul to win the Süper Lig (six times), which was previously (until Trabzonspor's first championship title in the 1975–76 1.Lig, 1975–76 season) won only by the "Big Three" clubs of
Association football, Football is the most popular sport in Trabzon. The city's top sports club, Trabzonspor, was until 2009–10 Süper Lig, 2010 the only Turkish football club outside İstanbul to win the Süper Lig (six times), which was previously (until Trabzonspor's first championship title in the 1975–76 1.Lig, 1975–76 season) won only by the "Big Three" clubs of Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ...
, namely Galatasaray S.K. (football), Galatasaray, Fenerbahçe S.K. (football), Fenerbahçe, and Beşiktaş J.K., Beşiktaş. Due to Trabzonspor's success, the decades-old term "Big Three" which defined the most successful football clubs in Turkey had to be modified into the "Big Four".
Trabzonspor is also one of the most successful Turkish clubs in the UEFA, European Cups, managing to beat numerous prominent teams such as FC Barcelona, Barcelona, Inter Milan, Inter, Liverpool F.C., Liverpool, Aston Villa F.C., Aston Villa and Olympique Lyonnais, Lyon. Renowned former players of Trabzonspor include Şenol Güneş, Lars Olsen and Shota Arveladze. In the 2021–2022 season, Trabzonspor left their Istanbul competition far behind, securing an early championship and ending a 38-year dry streak. Hundreds of thousands Trabzonite expatriates and fans from around the globe made their way to the city to participate in one of the first mass gatherings in the country for nearly two years, marking the end of the Corona pandemic. Officially the pandemic-measures had not been fully lifted, which led to some criticism towards the city's municipal government for allowing the festivities to continue for hours into the night, long past curfew.
Trabzon hosted the first edition of the Black Sea Games in July 2007 and the 2011 European Youth Summer Olympic Festival.
Built in 2017, a two-lane Trabzon Curling Hall is situated ubder stadium of the Şenol Güneş Sports Complex.
Mayors of Trabzon Metropolitan Municipality
* 1984 Turkish local elections, 1984-1989 Turkish local elections, 1989 Orhan Karakullukçu Anavatan Partisi * 1989 Turkish local elections, 1989-1994 Turkish local elections, 1994 Atay Aktuğ Social Democratic Populist Party (Turkey), SHP, Republican People's Party, CHP * 1994 Turkish local elections, 1994-2002 Turkish general election, 2002 :tr:Asım Aykan, Asım Aykan Refah Party, Fazilet Partisi, AK Party * 2002 Turkish general election, 2002-2004 Turkish local elections, 2004 :tr:Niyazi Sürmen, Niyazi Sürmen AK Party * 2004 Turkish local elections, 2004-2009 Turkish local elections, 2009 Volkan Canalioğlu Republican People's Party, CHP * 2009 Turkish local elections, 2009-2019 Turkish local elections, 2019 :tr:Orhan Fevzi Gümrükçüoğlu, Orhan Fevzi Gümrükçüoğlu AK Party * 2019 Turkish local elections, 2019-2024 Turkish local elections, 2024 :tr:Murat Zorluoğlu, Murat Zorluoğlu AK Party * 2024 Turkish local elections, 2024-present :tr:Ahmet Metin Genç AK PartyNotable residents
International relations
Twin towns - sister cities
Trabzon is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned with: * Batumi, Georgia, since 2000 * Dortmund, Germany, since 2013 * Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan, since 2014 * Gabès, Tunisia, since 2013 * Rasht, Iran, since 2000 * Rizhao, China, since 1997 * Sochi, Russia, since 1993 * Szigetvár, Hungary, since 1998 * Zanjan, Iran, Zanjan, Iran, since 2001 Drohgheda, IrelandSee also
* Amasya (ancient Amaseia, capital of the Pontic Greeks during classical antiquity) * Anatolian Tigers * Black Sea Region, Turkey, Black Sea Region * Kemençe of the Black Sea * Kolbastı * World Trade Center Trabzon * Capture of Trabzon (1918), Capture of TrabzonNotes and references
Further reading
* * * * * Özhan Öztürk (2005). Karadeniz (Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
): Ansiklopedik Sözlük. 2 Cilt. Heyamola Yayıncılık. Istanbul.
*
External links
Trabzon Travel Guide
Governorship of Trabzon
Photos of Trabzon city
{{Authority control Trabzon, Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Turkey Black Sea port cities and towns in Turkey Capitals of former nations Empire of Trebizond Fishing communities in Turkey Greek colonies in Pontus Populated coastal places in Turkey Roman towns and cities in Turkey Roman harbors in Turkey Milesian Pontic colonies Populated places established in the 8th century BC