Trabecular Bone Score on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The trabecular bone score is a measure of
 To diagnose
To diagnose
 The trabecular bone score is a textural parameter that can be applied to
The trabecular bone score is a textural parameter that can be applied to
TBS White paper
TBS – main guidelines and fields of usage
bone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provid ...
texture correlated with bone microarchitecture and a marker for the risk of osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone ...
. Introduced in 2008, its main projected use is alongside measures of bone density
Bone density, or bone mineral density, is the amount of bone mineral in bone tissue. The concept is of mass of mineral per volume of bone (relating to density in the physics sense), although clinically it is measured by proxy according to optica ...
in better predicting fracture risk in people with metabolic bone problems.
Need for a marker of microarchitecture
 To diagnose
To diagnose osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone ...
, despite the inclusion of bone mineral density
Bone density, or bone mineral density, is the amount of bone mineral in bone tissue. The concept is of mass of mineral per volume of bone (relating to density in the physics sense), although clinically it is measured by proxy according to optica ...
(BMD), biological markers and clinical factors of fracture risk, many not detected patients are at risk and many fractures are not explained. Bone mineral density
Bone density, or bone mineral density, is the amount of bone mineral in bone tissue. The concept is of mass of mineral per volume of bone (relating to density in the physics sense), although clinically it is measured by proxy according to optica ...
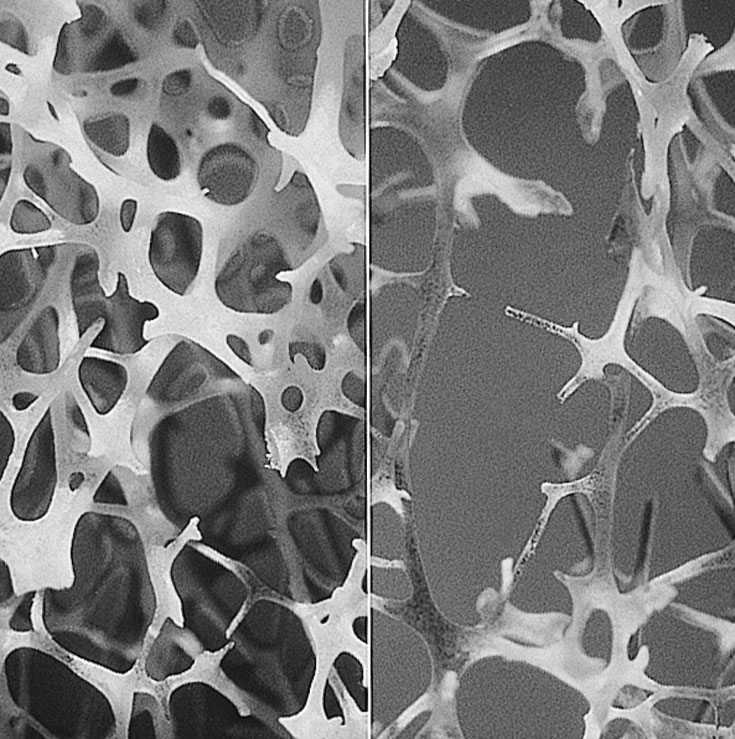
is an assessment of the quantity of bone. It does not provide information on bone quality, another important parameter to describe the bone. In addition, clinical risk factors for fracture are at best an indirect assessment of the bone quality. One way to describe the quality of the bone is to assess its microarchitecture. Bone microarchitecture is related to the mechanical strength of bone and hence its greater or lesser risk of fracture. Indeed, for the same quantity of bone, different mechanically resistant bone structures may exist (few large trabeculae or numerous thin trabeculae that are mechanically stronger). Actually, bone loss is often accompanied by a deterioration of bone architecture, resulted in a decreased number of trabeculae, increased inter-trabecular distances, and a loss connectivity of the trabecular meshwork. Moreover, reduction of cortical bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and ...
thickness and increased porosity accompany trabecular bone loss, and in particular promote the fragility of the femoral neck. Osteoporotic bone is called "porous".
Technical
 The trabecular bone score is a textural parameter that can be applied to
The trabecular bone score is a textural parameter that can be applied to DEXA
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA, or DEXA) is a means of measuring bone mineral density (BMD) using spectral imaging. Two X-ray beams, with different energy levels, are aimed at the patient's bones. When soft tissue absorption is subtracted ...
, which quantifies the local variations in gray level. TBS is derived from the evaluation of the experimental variogram, obtained from the grayscale DEXA
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA, or DEXA) is a means of measuring bone mineral density (BMD) using spectral imaging. Two X-ray beams, with different energy levels, are aimed at the patient's bones. When soft tissue absorption is subtracted ...
.
It was found that TBS is a reflection of the structural condition of the bone microarchitecture. TBS is strongly correlated with the number of trabeculae
A trabecula (plural trabeculae, from Latin for "small beam") is a small, often microscopic, tissue element in the form of a small beam, strut or rod that supports or anchors a framework of parts within a body or organ. A trabecula generally has ...
and their connectivity and negatively with the space between trabeculae. That is to say that a high TBS value means that microarchitecture bone is dense, well connected with little spaces between trabeculaes. Conversely, a low TBS value means that the microarchitecture of bone is incomplete and poorly connected with wide spaces between trabeculae.
Clinical use
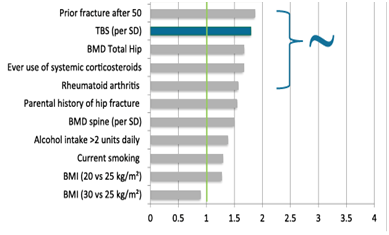
From a clinical standpoint, TBS provides: * assessment the risk of fracture; * in combination with BMD, increase the number of patients at risk (correctly) identified; * improvement the management of patients with secondary osteoporosis; * follow-up of the evolution of microarchitecture of a patient over time; * monitoring of the effect of anti-resorptive or anabolic. All these studies have shown that TBS can be used as a clinical risk factor for osteoporotic fracture since it is reversible (with or without treatment), quantitative and independent of BMD. It should therefore be used as such in the same way that takingcorticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involve ...
, rheumatoid arthritis or prevalent fracture after age 50.
The FRAX
FRAX (Fracture Risk Assessment Tool) is a diagnostic tool used to evaluate the 10-year probability of bone fracture risk. It was developed by the University of Sheffield. FRAX integrates clinical risk factors and bone mineral density at the femora ...
calculator has an option to include TBS for a TBS adjusted FRAX risk score. The calculated probabilities of fracture have been shown to be more accurate when computed including TBS.
As TBS relies on measurement of soft tissue, it is considered unreliable in individuals with a BMI over 37.
Further reading
TBS White paper
TBS – main guidelines and fields of usage
Notes and references
{{Reflist Osteopathies