Toxodon Skeleton on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Toxodon'' (meaning "bow tooth" in reference to the curvature of the teeth) is an extinct
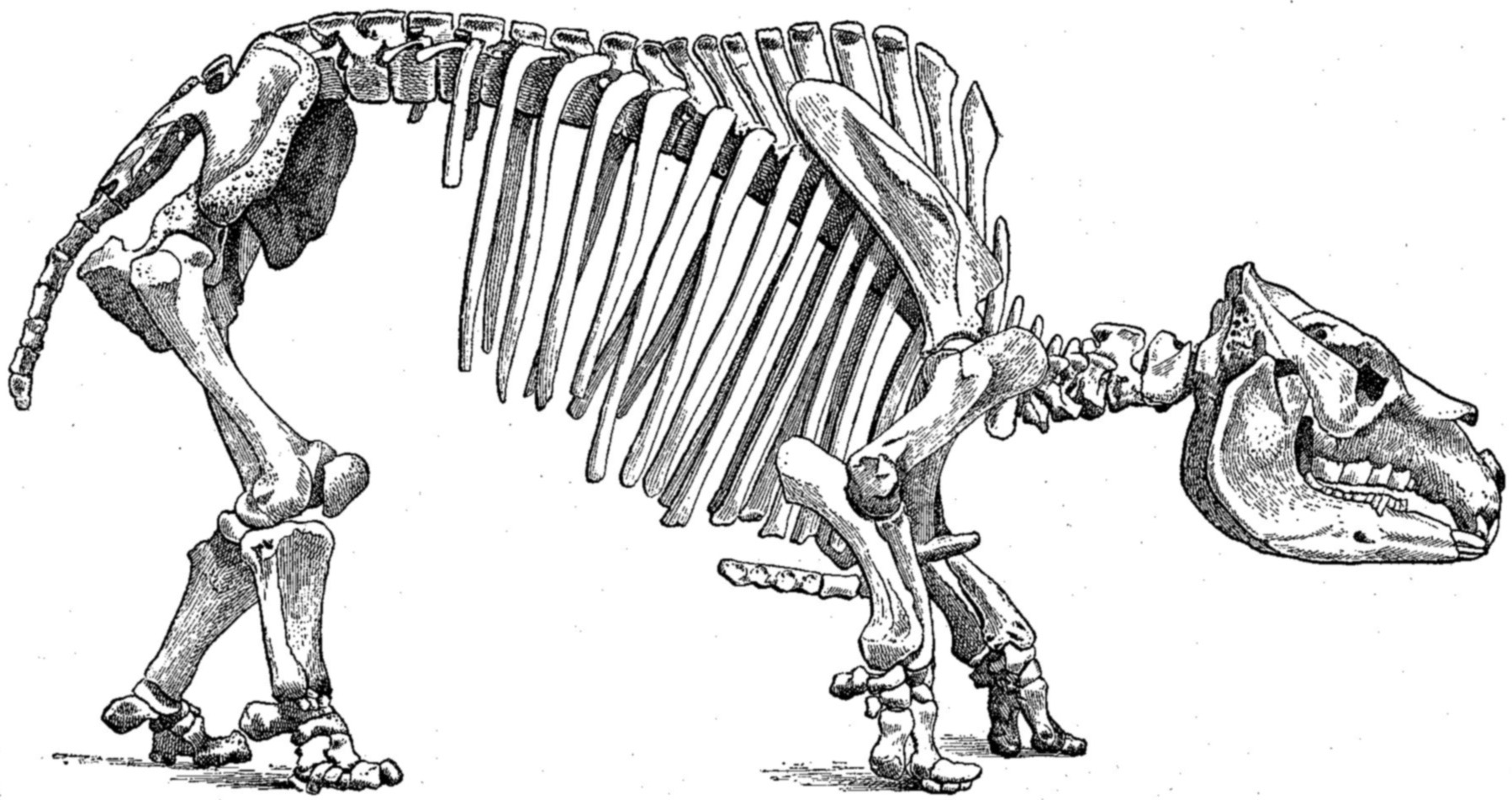 ''Toxodon'' was one of the last members of
''Toxodon'' was one of the last members of
 It was initially believed to have been amphibious, but after examining the proportions of the
It was initially believed to have been amphibious, but after examining the proportions of the


 ''Toxodon'' had a wide distribution in South America during the Late Pleistocene, extending from the
''Toxodon'' had a wide distribution in South America during the Late Pleistocene, extending from the
at Fossilworks.org ;Holocene * Abismo Ponto de Flecha,
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...
n mammals from the Late Miocene to early Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
epochs (Mayoan The Mayoan ( es, Mayoense) age is a period of geologic time from 11.8 to 10 Ma, within the Middle to Late Miocene epoch of the Neogene, used more specifically within the SALMA classification in South America. It follows the Laventan and precedes ...
to Lujanian
The Lujanian age is a South American land mammal age within the Pleistocene and Holocene epochs of the Neogene, from 0.8–0.011 Ma or 800–11 tya. It follows the Ensenadan.
The age is usually divided into the middle Pleistocene Bonaerian stag ...
in the SALMA classification) (about 11.6 million to 11,000 years ago). It is a member of Notoungulata
Notoungulata is an extinct order of mammalian ungulates that inhabited South America from the early Paleocene to the Holocene, living from approximately 61 million to 11,000 years ago. Notoungulates were morphologically diverse, with forms resemb ...
, one of several now extinct orders of hoofed mammals indigenous to South America distinct from living perissodactyl
Odd-toed ungulates, mammals which constitute the taxonomic order Perissodactyla (, ), are animals—ungulates—who have reduced the weight-bearing toes to three (rhinoceroses and tapirs, with tapirs still using four toes on the front legs) o ...
s and artiodactyl
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing poster ...
s. It was among the largest and last members of its order, and was probably the most common large hoofed mammal in South America of its time.
Taxonomy
 ''Toxodon'' was one of the last members of
''Toxodon'' was one of the last members of Notoungulata
Notoungulata is an extinct order of mammalian ungulates that inhabited South America from the early Paleocene to the Holocene, living from approximately 61 million to 11,000 years ago. Notoungulates were morphologically diverse, with forms resemb ...
, a group of ungulates that had been part of the fauna of South America since the Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''pal ...
. ''Toxodon'' was a member of Toxodontidae
Toxodontidae is an extinct family of notoungulate mammals, known from the Oligocene to the Holocene (11,000 BP) of South America, with one genus, ''Mixotoxodon'', also known from the Pleistocene of Central America and southwestern North America ...
a large bodied group including similar, vaguely rhinoceros like forms.
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended ...
was one of the first to collect ''Toxodon'' fossils, after paying 18 pence for a ''T. platensis'' skull from a farmer in Uruguay. In ''The Voyage of the Beagle'' Darwin wrote, "November 26th – I set out on my return in a direct line for Montevideo. Having heard of some giant's bones at a neighbouring farm-house on the Sarandis, a small stream entering the Rio Negro, I rode there accompanied by my host, and purchased for the value of eighteen pence the head of the ''Toxodon''." Since Darwin discovered that the fossils of similar mammals of South America were different from those in Europe, he invoked many debates about the evolution and natural selection of animals.
In his own words, Darwin wrote down in his journal,
Analysis of collagen sequences obtained from ''Toxodon'' as well as from '' Macrauchenia'' found that South America's native notoungulates and litopterns form a sister group to perissodactyl
Odd-toed ungulates, mammals which constitute the taxonomic order Perissodactyla (, ), are animals—ungulates—who have reduced the weight-bearing toes to three (rhinoceroses and tapirs, with tapirs still using four toes on the front legs) o ...
s, making them true ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, ...
s. This finding has been corroborated by an analysis of mitochondrial DNA extracted from a ''Macrauchenia'' fossil, which yielded a date of 66 Ma for the time of the split with perissodactyls.
Evolution
In 2014, a study identifying a new species of toxodontid resolved the phylogenetic relations of the toxodontids, including to ''Toxodon''. The below cladogram was found by the study:Description
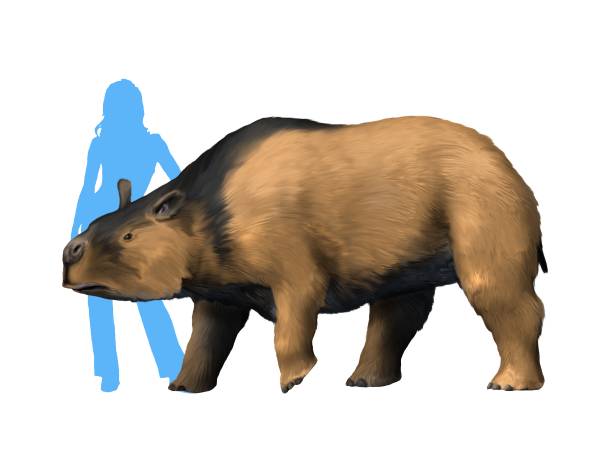
''Toxodon'' was about in body length, with an estimated weight up to and about high at the shoulder and resembled a heavyrhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species ...
, with a short and vaguely hippopotamus
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extan ...
-like head. Because of the position of its nasal openings, it is believed that ''Toxodon'' had a well-developed snout. ''Toxodon'' possessed a large, barrel shaped body. It had short stout legs with plantigrade feet with three functional relatively short toes. The hind limbs are longer and raised higher than the front limbs, giving a sloped appearance to the body. Like horses, it had a stay apparatus allowing the knees to be passively locked while standing.
The vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
e were equipped with high apophyses, which most likely supported the massive weight and muscles as well as its powerful head. ''Toxodon'' had broad jaws which were filled with bow shaped teeth and incisors. The teeth of ''Toxodon'' have no roots and are ever-growing (euhypsodont) like those of rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are n ...
s and lagomorphs, and often exhibit enamel hypoplasia
Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the teeth in which the enamel is deficient in quantity, caused by defective enamel matrix formation during enamel development, as a result of inherited and acquired systemic condition(s). It can be identified as m ...
.
Palaeobiology
femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates wit ...
and tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
, as well as the position of its head, below the top of the spinal column, palaeontologists realized that it had features similar to terrestrial animals such as elephants or rhinoceroses. The fossils are also usually found in arid and semi-arid areas, typically an indication of a primarily terrestrial life.
''Toxodon'' would have had a very unusual gait, due to its peculiar proportions. It may have galloped to escape predators, but like a rhino, it probably relied more on its size as protection.
''Toxodon'' is believed to have been ecologically plastic, with its diet varying according to local conditions, with an almost totally C3 browsing
Browsing is a kind of orienting strategy. It is supposed to identify something of relevance for the browsing organism. When used about human beings it is a metaphor taken from the animal kingdom. It is used, for example, about people browsing o ...
diet in the Amazon rainforest, mixed feeding C3 in Bahia
Bahia ( , , ; meaning "bay") is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region of the country. It is the fourth-largest Brazilian state by population (after São Paulo, Minas Gerais, and Rio de Janeiro) and the 5th-largest b ...
and the Pampas
The Pampas (from the qu, pampa, meaning "plain") are fertile South American low grasslands that cover more than and include the Argentine provinces of Buenos Aires, La Pampa, Santa Fe, Entre Ríos, and Córdoba; all of Uruguay; and Brazi ...
to almost completely C4 dominated grazing
In agriculture, grazing is a method of animal husbandry whereby domestic livestock are allowed outdoors to roam around and consume wild vegetations in order to convert the otherwise indigestible (by human gut) cellulose within grass and other ...
diet in the Chaco.
Extinction
''Toxodon'' became extinct at the beginning of the Holocene as part of theQuaternary extinction event
The Quaternary period (from 2.588 ± 0.005 million years ago to the present) has seen the extinctions of numerous predominantly megafaunal species, which have resulted in a collapse in faunal density and diversity and the extinction of key ecolog ...
, alongside almost all other large animals in South America. Previous mid-Holocene dates are now thought to be in error. Remains from the Arroyo Seco 2 site in the Pampas have been interpreted to be the result of butchery, suggesting that human hunting was a contributing factor to extinction.


Distribution
 ''Toxodon'' had a wide distribution in South America during the Late Pleistocene, extending from the
''Toxodon'' had a wide distribution in South America during the Late Pleistocene, extending from the Pampas
The Pampas (from the qu, pampa, meaning "plain") are fertile South American low grasslands that cover more than and include the Argentine provinces of Buenos Aires, La Pampa, Santa Fe, Entre Ríos, and Córdoba; all of Uruguay; and Brazi ...
into the Amazon rainforest.
Fossils of ''Toxodon'' have been found in:''Toxodon''at Fossilworks.org ;Holocene * Abismo Ponto de Flecha,
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
;Pleistocene
* San José, Fortin Tres Pozos, Chaco and Luján Formations, Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
* Tarija
Tarija or San Bernardo de la Frontera de Tarixa is a city in southern Bolivia. Founded in 1574, Tarija is the largest city and capital and municipality within the Tarija Department, with an airport ( Capitán Oriel Lea Plaza Airport, (TJA)) off ...
and Ñuapua Formations, Bolivia
* Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
* Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to th ...
* Sopas
''Sopas'' is a Philippine cuisine, Filipino macaroni soup made with elbow macaroni, various vegetables, and meat (usually chicken as food, chicken), in a creamy broth with evaporated milk. It is regarded as a comfort food in the Philippines and ...
and Dolores Formations, Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
;Miocene-Pliocene (Montehermosan
The Montehermosan age is a period of geologic time (6.8–4.0 Ma) within the Miocene and Pliocene epochs of the Neogene used more specifically with South American Land Mammal Ages. It follows the Huayquerian and precedes the Chapadmalalan
The C ...
)
* Monte Hermoso Formation, Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
;Miocene
* Ituzaingó Formation
The Ituzaingó Formation ( es, Formación Ituzaingó), in older literature also described as Entre Ríos or Entrerriana Formation, is an extensive geological formation of Late Miocene (Tortonian, or Huayquerian in the SALMA classification) age i ...
, then described as Entrerriana Formation, Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
References
Further reading
* {{Taxonbar, from=Q131467 Toxodonts Miocene genus first appearances Holocene extinctions Miocene mammals of South America Pliocene mammals of South America Pleistocene mammals of South America Lujanian Ensenadan Uquian Chapadmalalan Montehermosan Huayquerian Chasicoan Mayoan Neogene Argentina Ituzaingó Formation Pleistocene Argentina Pleistocene Bolivia Pleistocene Brazil Pleistocene Paraguay Pleistocene Uruguay Fossils of Argentina Fossils of Bolivia Fossils of Brazil Fossils of Paraguay Fossils of Uruguay Fossil taxa described in 1837 Taxa named by Richard Owen Prehistoric placental genera